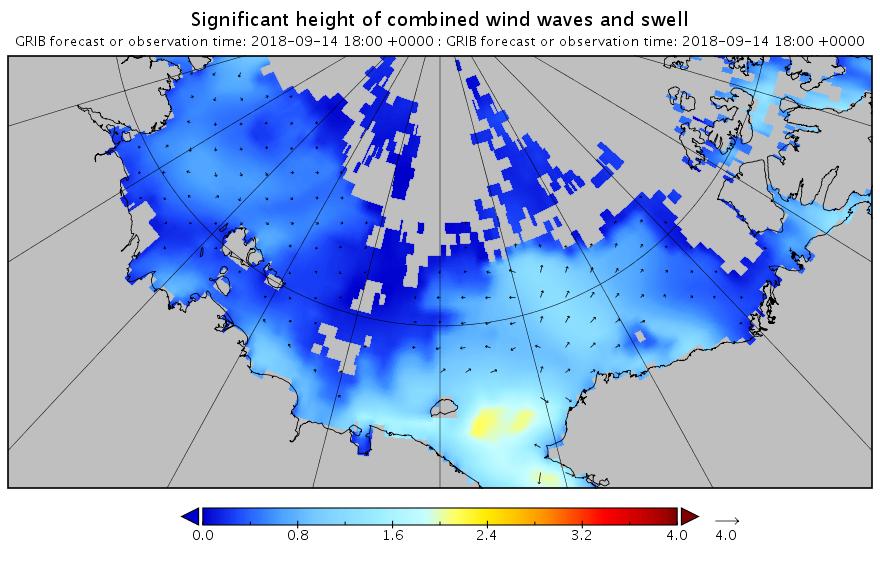
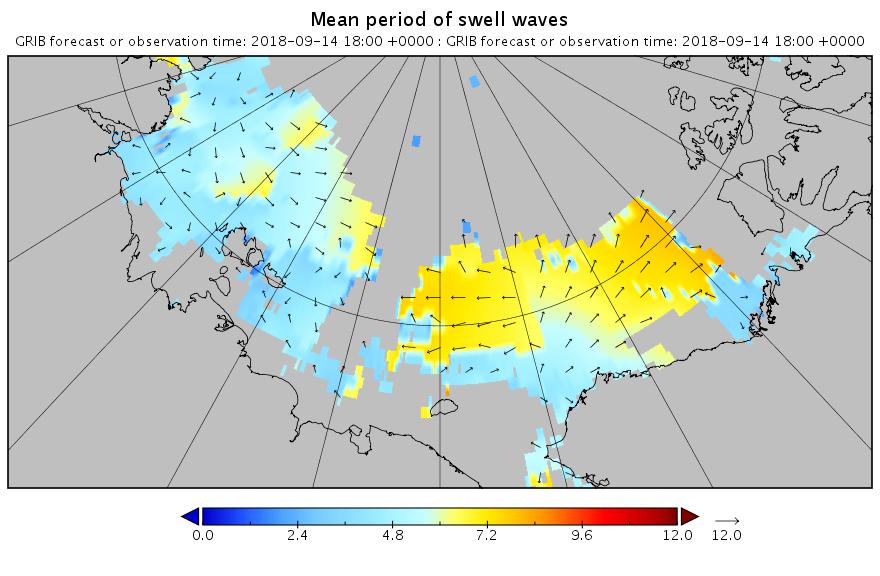
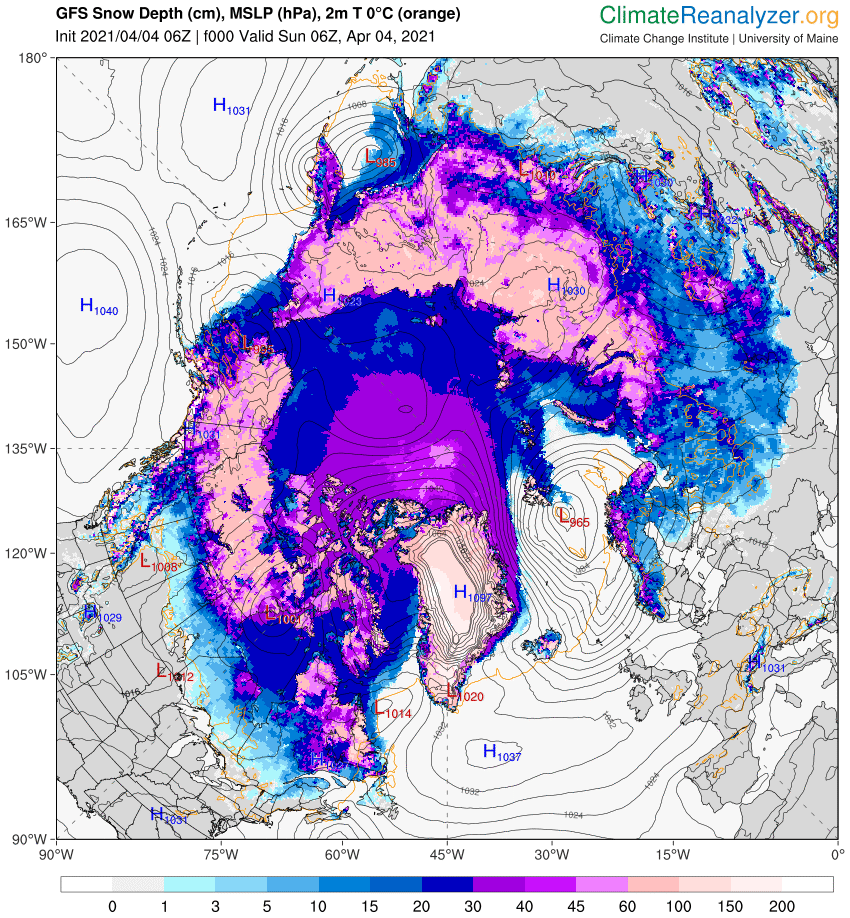
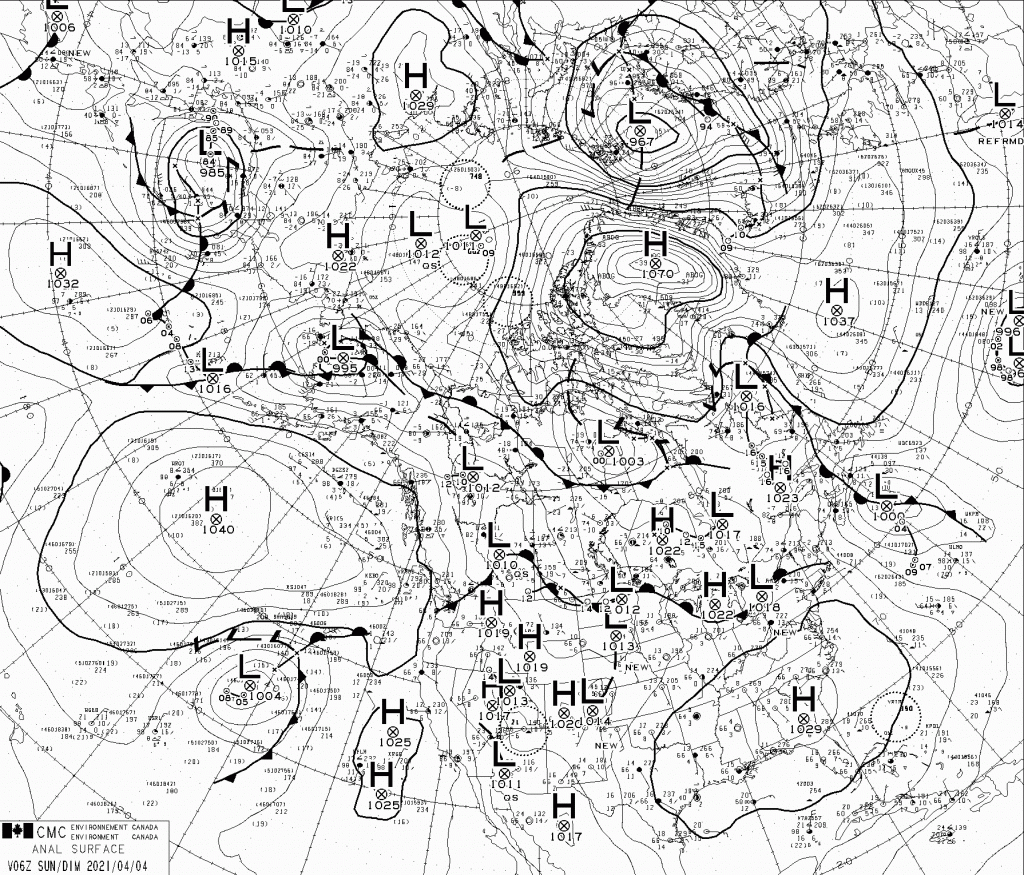
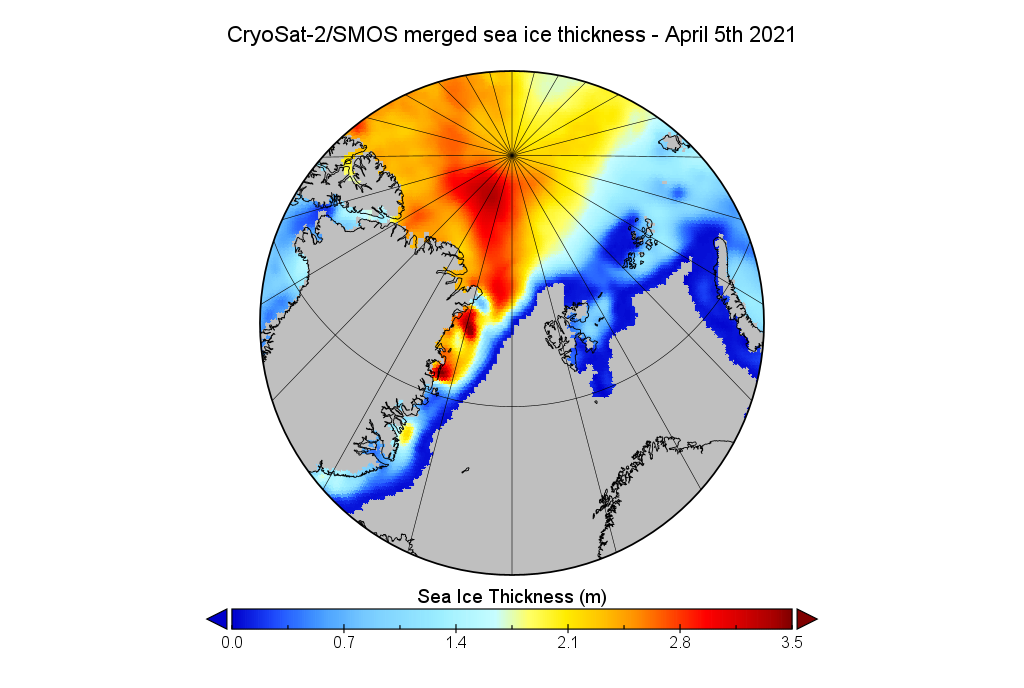
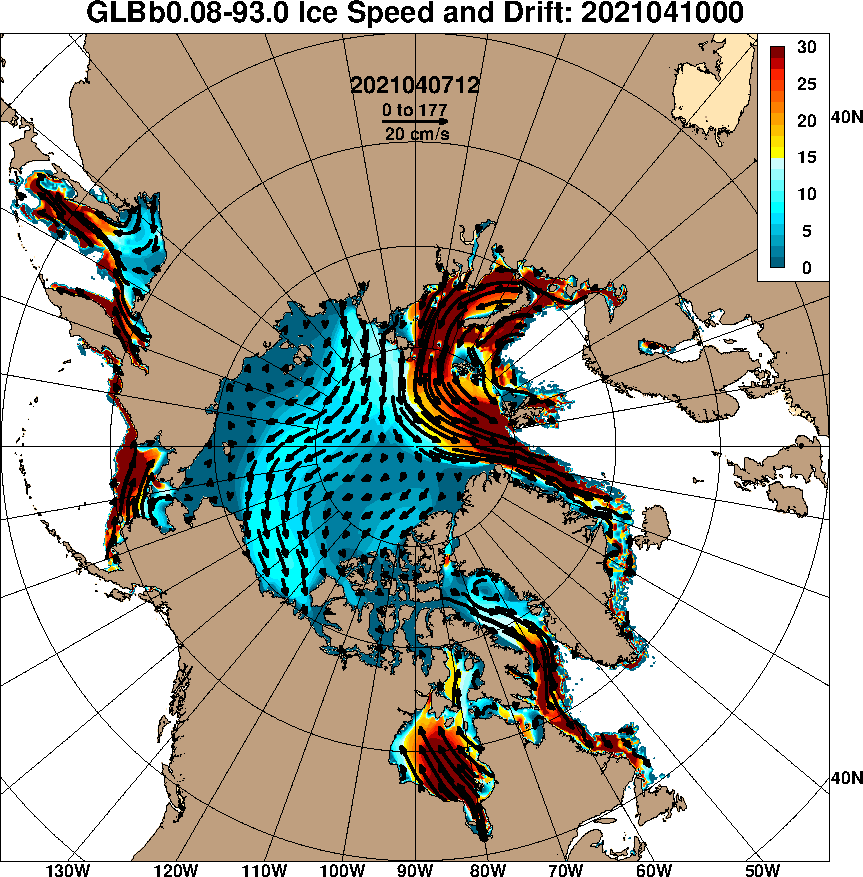
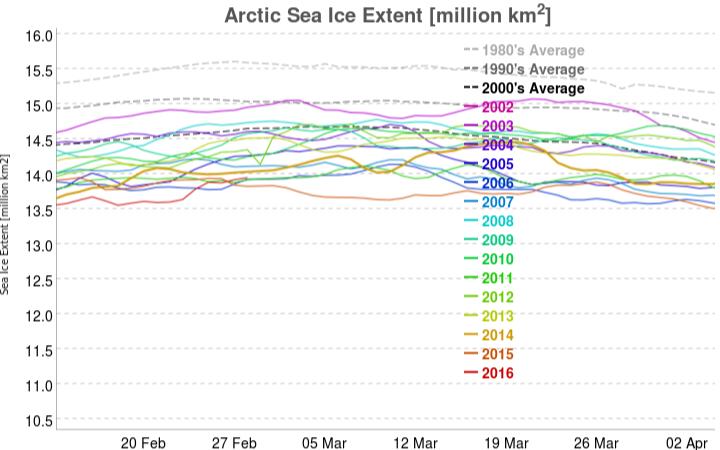
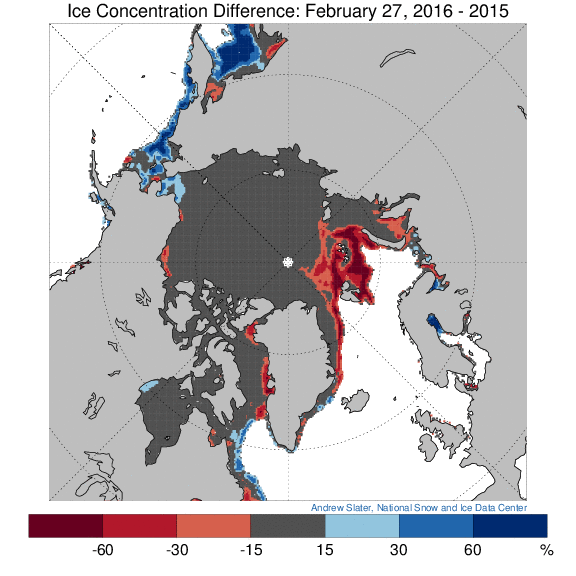
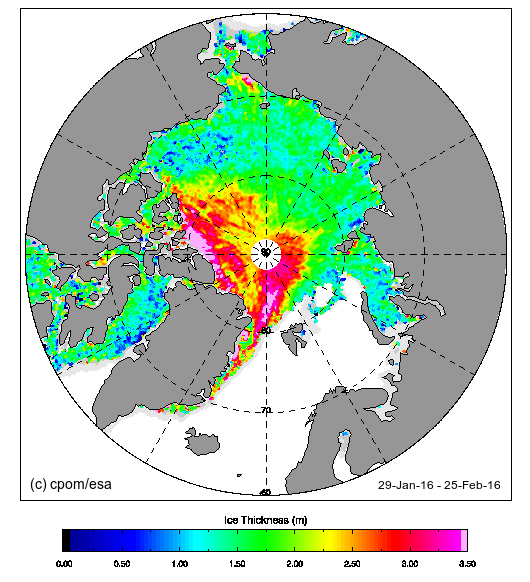
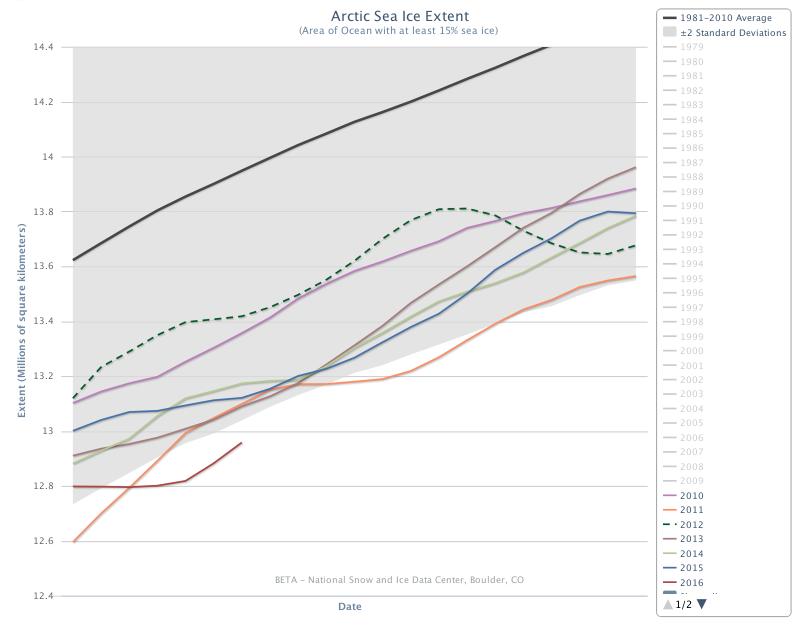
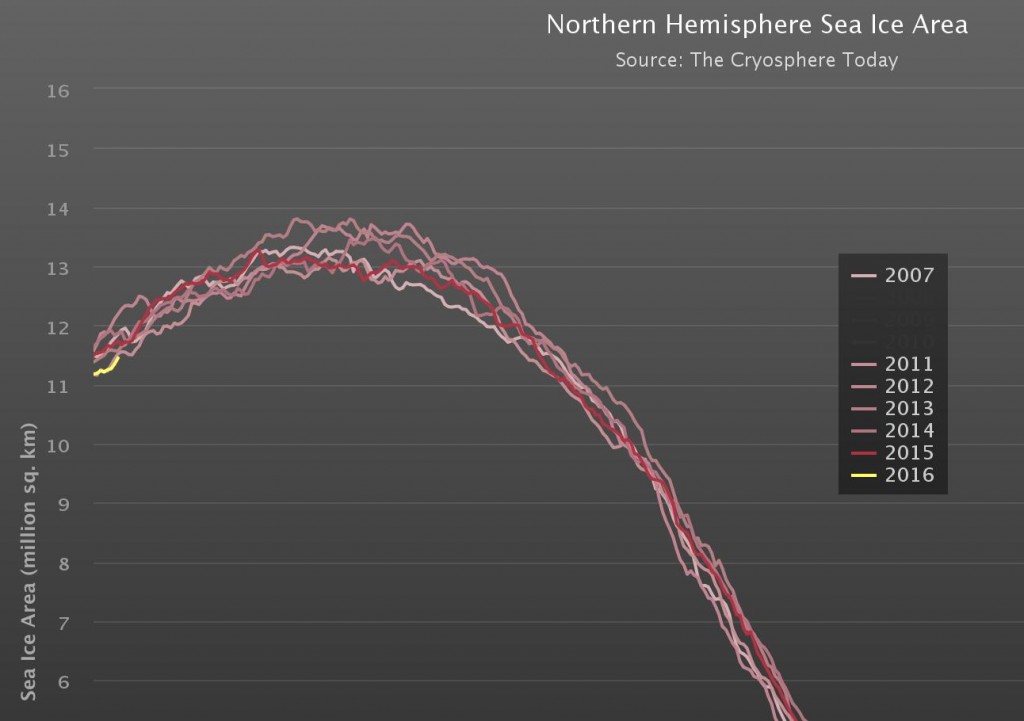
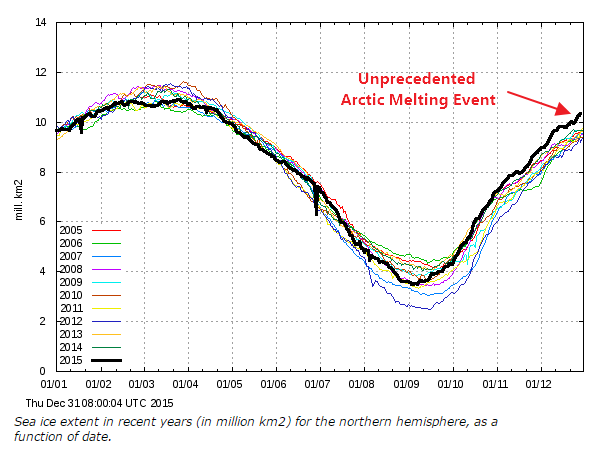
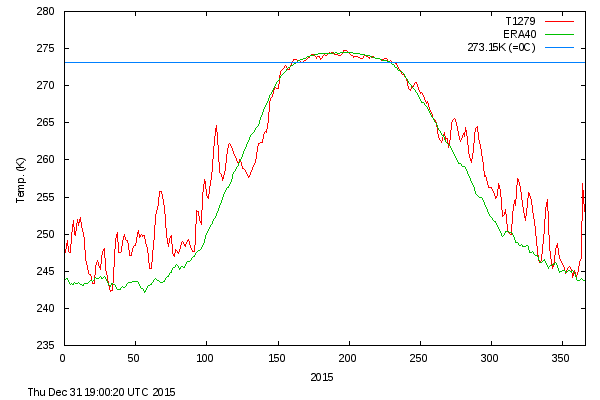
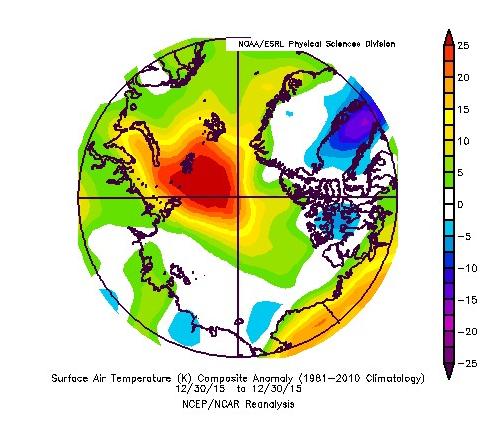
Our title for today refers back to the Great Arctic Cyclone of August 2012. There has been some speculation over on the Arctic Sea Ice Blog about whether a similar event is about to occur this year.
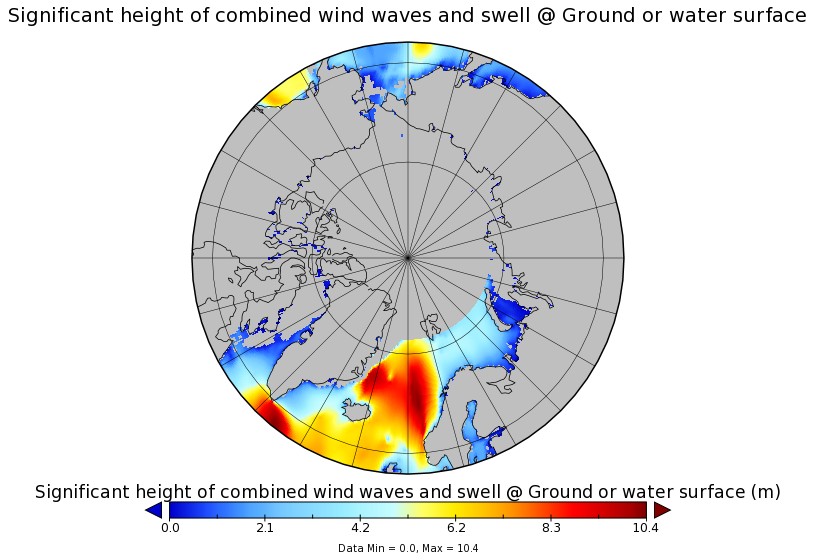
It’s later in the season of course, but as is our wont we always look at the waves first. Here is the current WaveWatch III forecast for the evening of August 31st UTC:
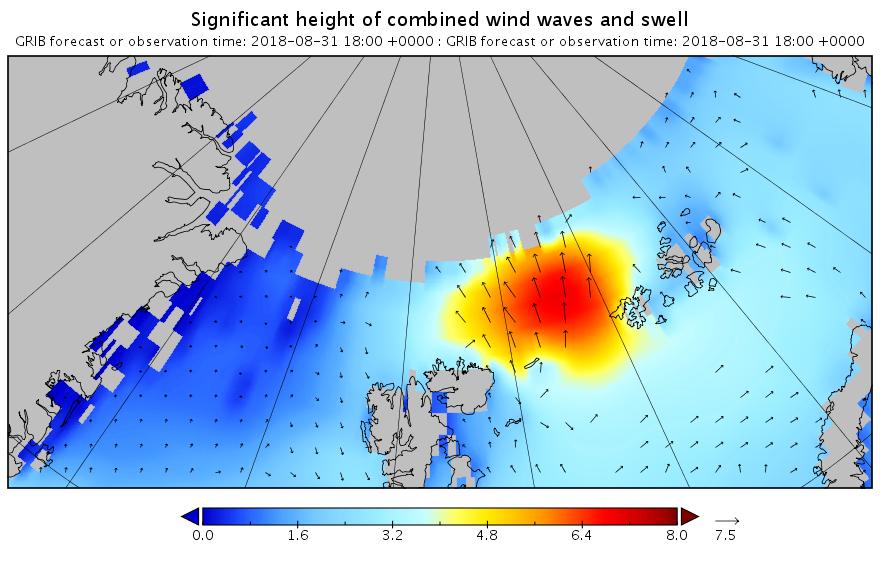
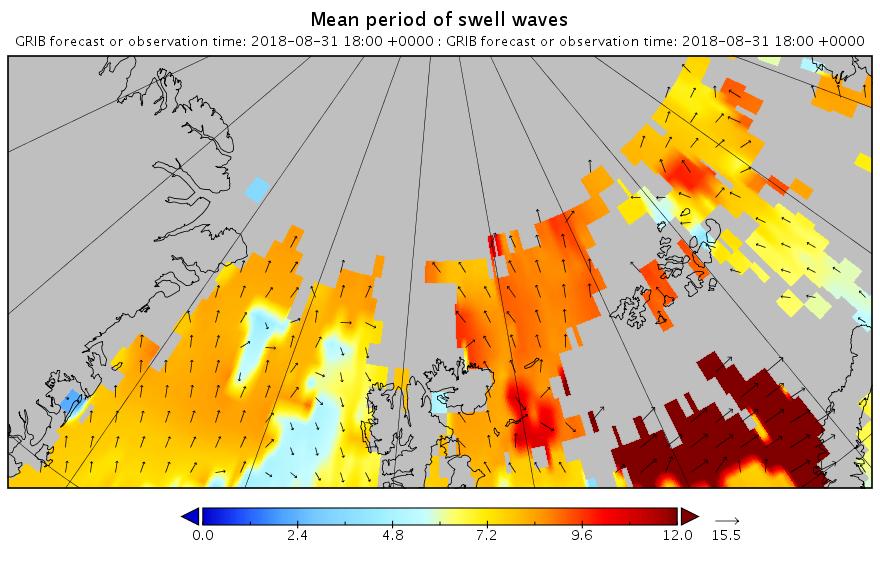
In summary the forecast shows some very large waves with a substantial period for inside the Arctic Circle directed straight at the ice edge. Let’s follow the forecast over the next few days carefully shall we?
[Edit – August 30th]
The latest wave forecast for tomorrow evening isn’t as extreme as 3 days ago. Note the change in the significant height scale:
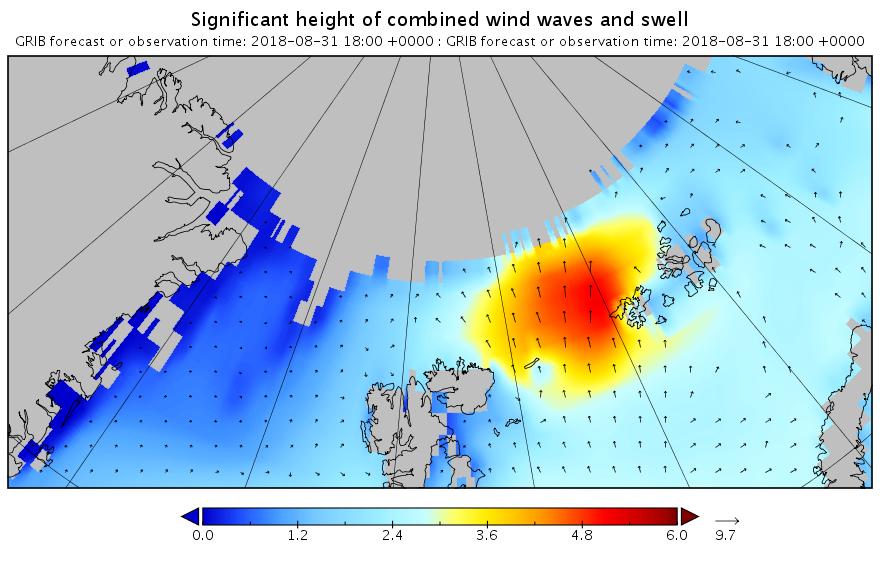
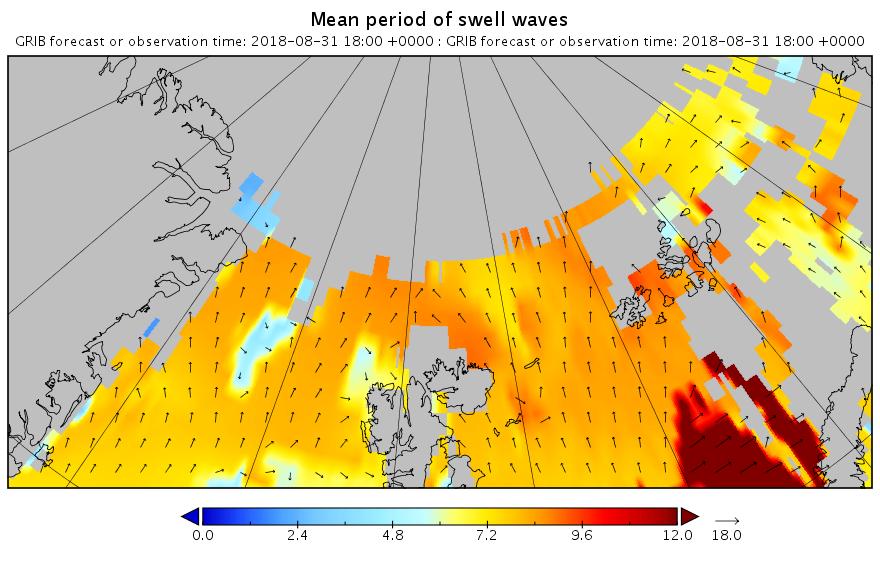
Nonetheless the height and period are still very significant!
[Edit – August 31st]
Here’s the latest forecast for 6 PM this evening (UTC):
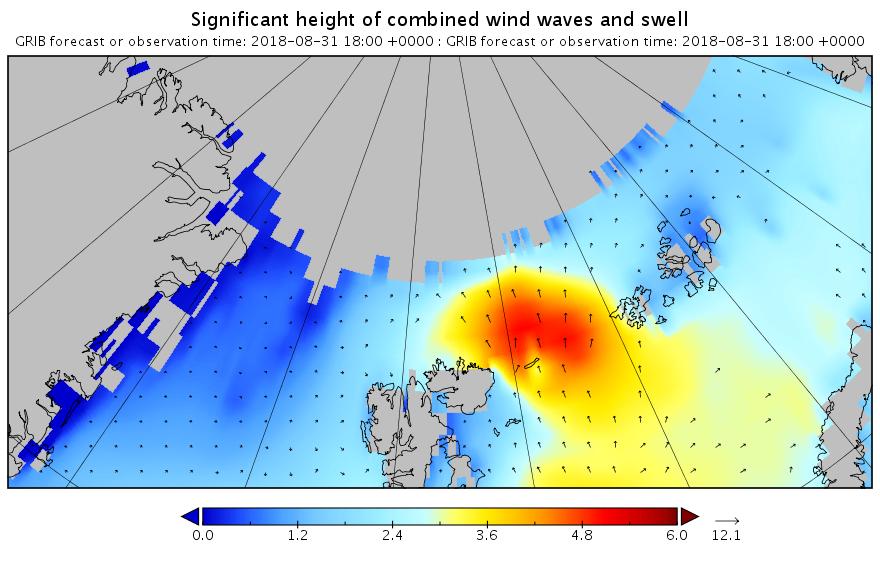
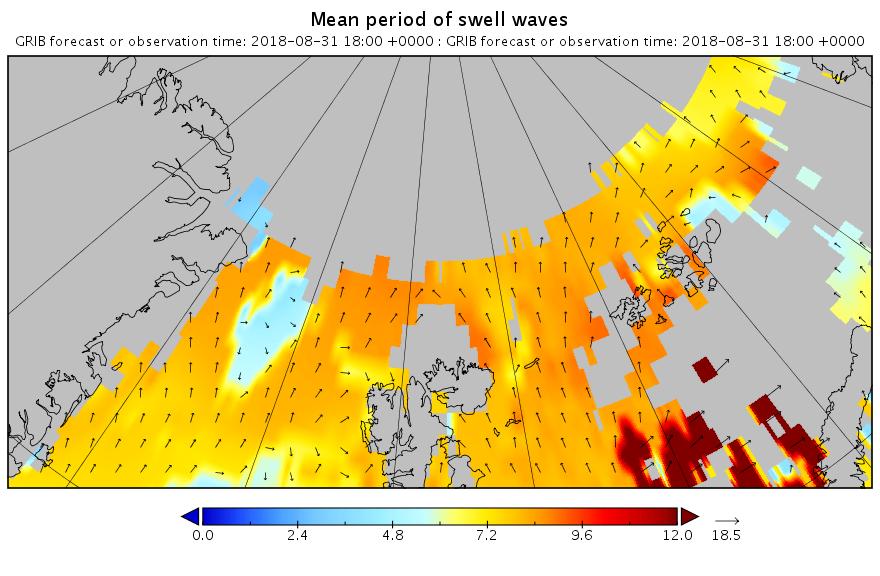
Note how the open water across almost the entire map is full of what in the Arctic counts as a long period swell. That means that the forecast for 2 days later looks like this:
Less height but with a longer period. All of which means that the sea ice north of the Atlantic Ocean isn’t about to receive a short sharp shock. It has a sustained battering lasting several days to look forward to.
[Edit – September 1st]
The barrage of assorted swells has begun. Here’s the “hindcast” from midnight last night UTC:
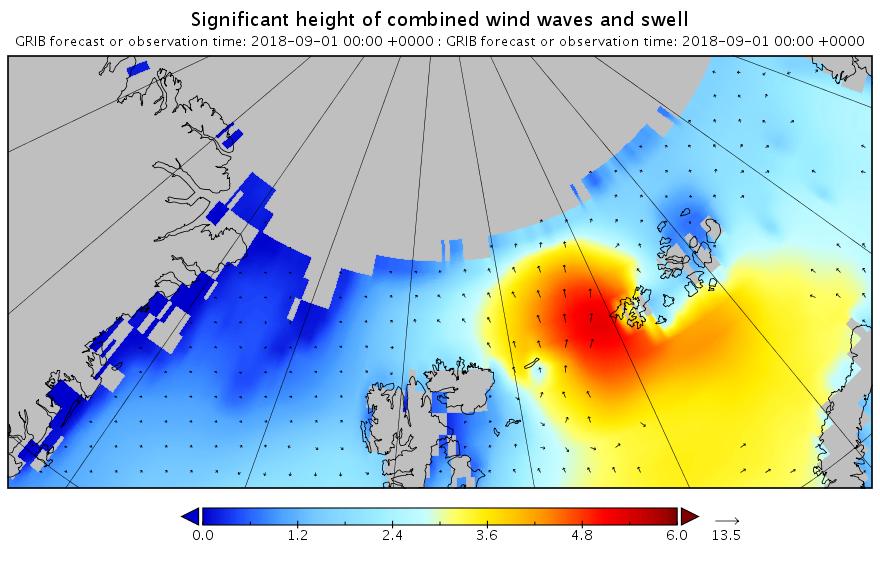
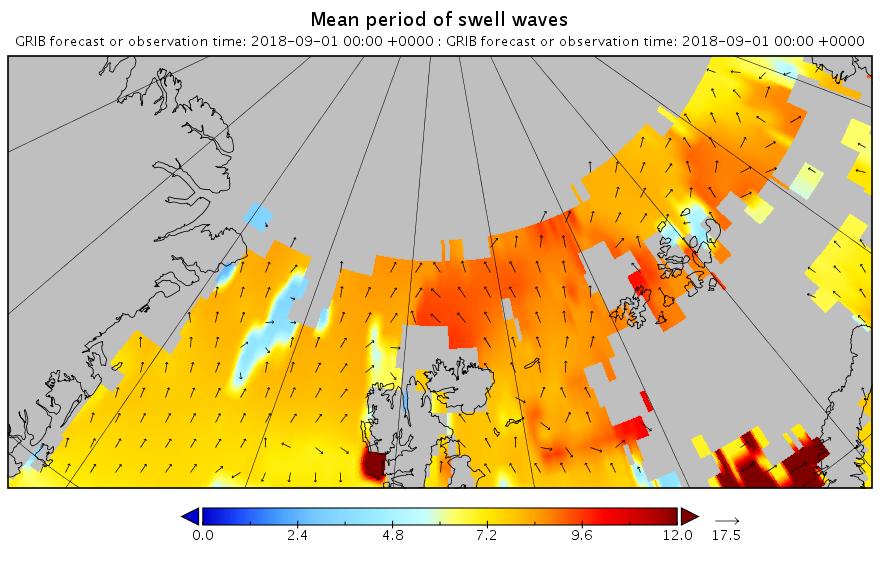
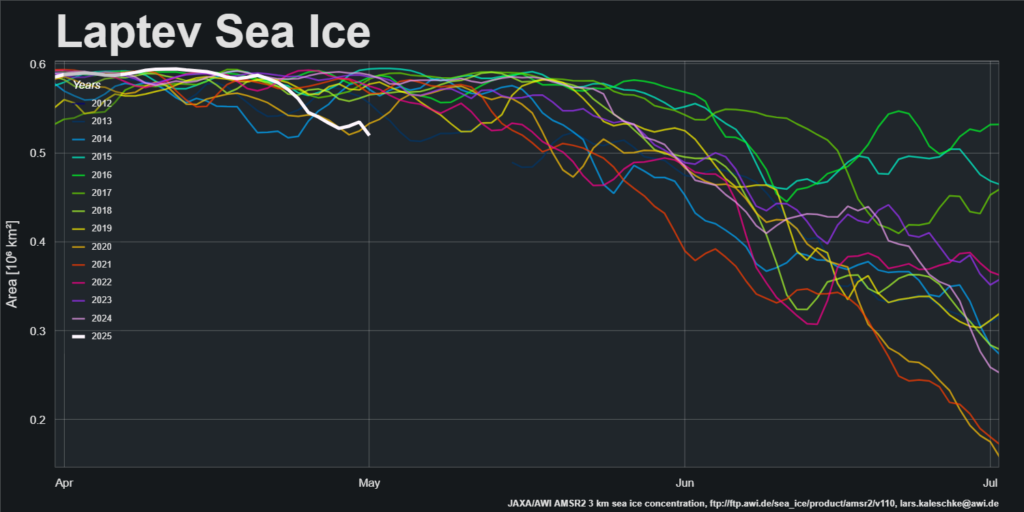
Now lets take a look at tomorrow’s forecast for the Laptev Sea. This is for 09:00 UTC:
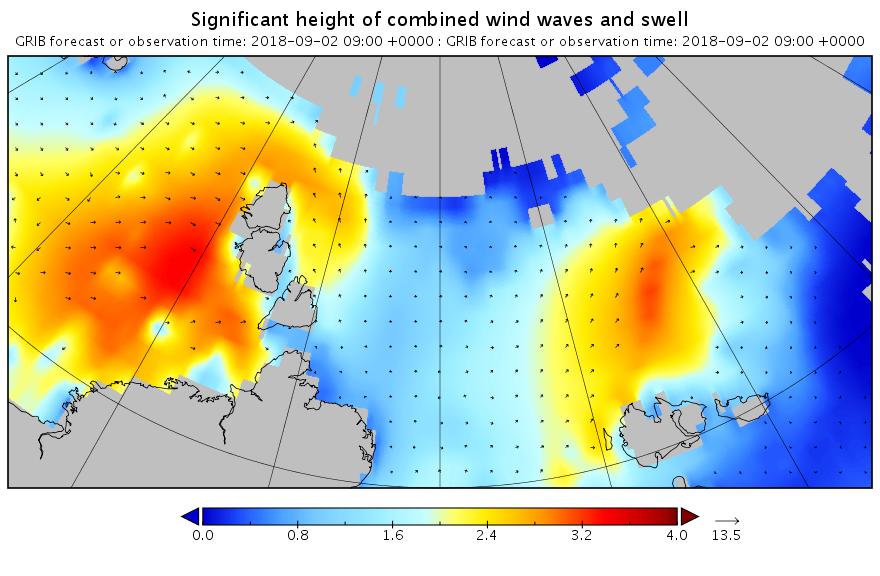
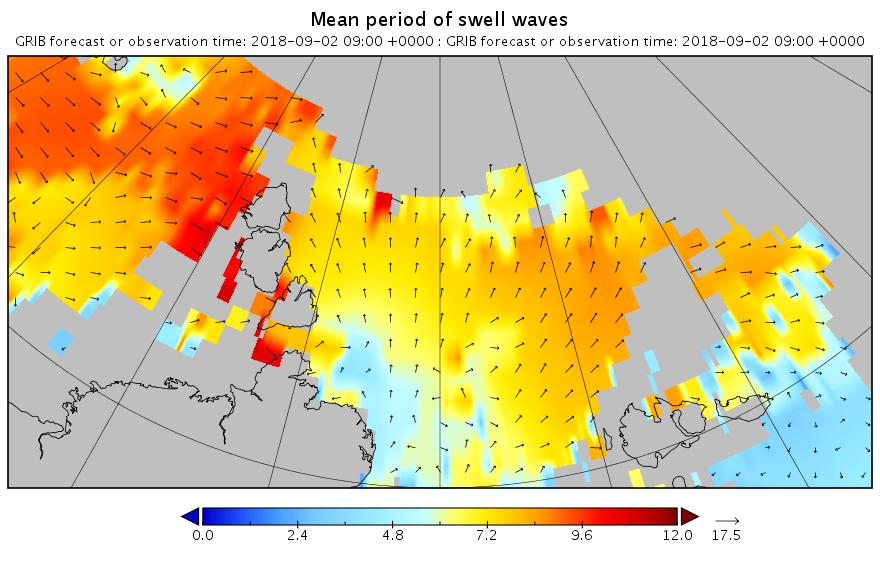
Note once again the change of scale on the wave/swell height map. Nevertheless a 3+ meter swell heading over into the East Siberian Sea isn’t something you see every day.
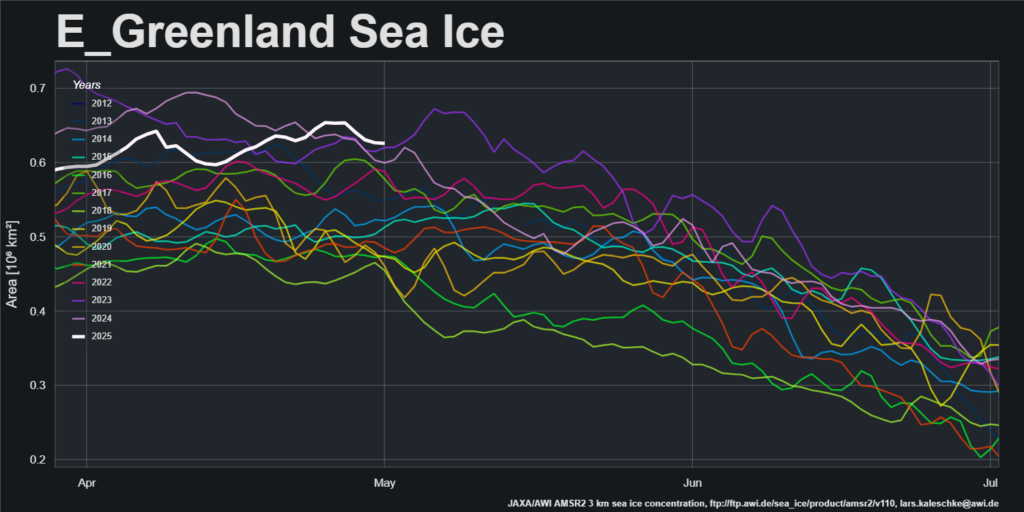
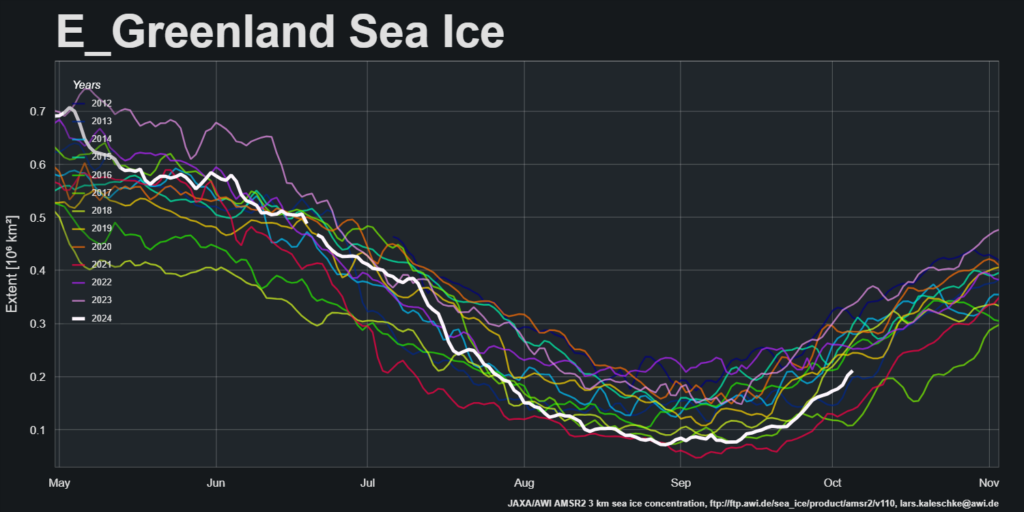
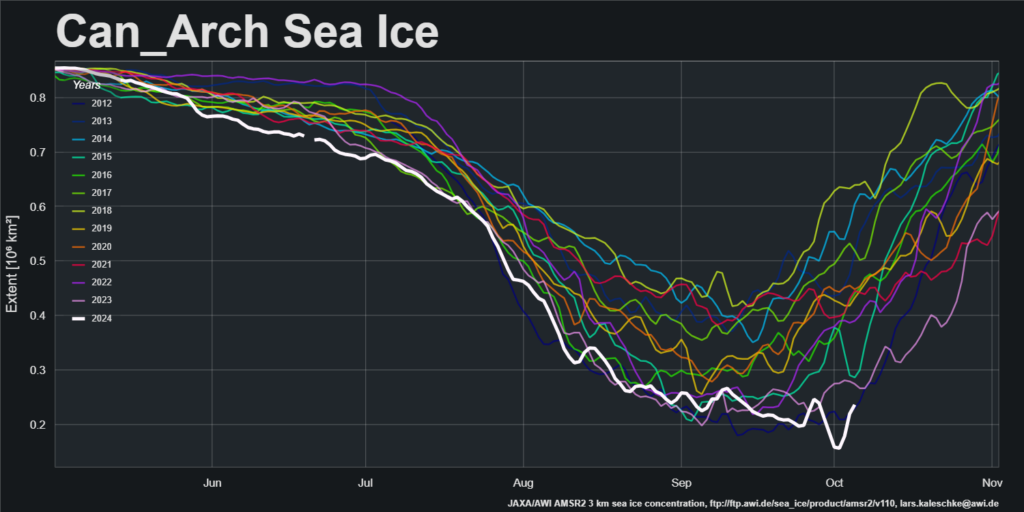
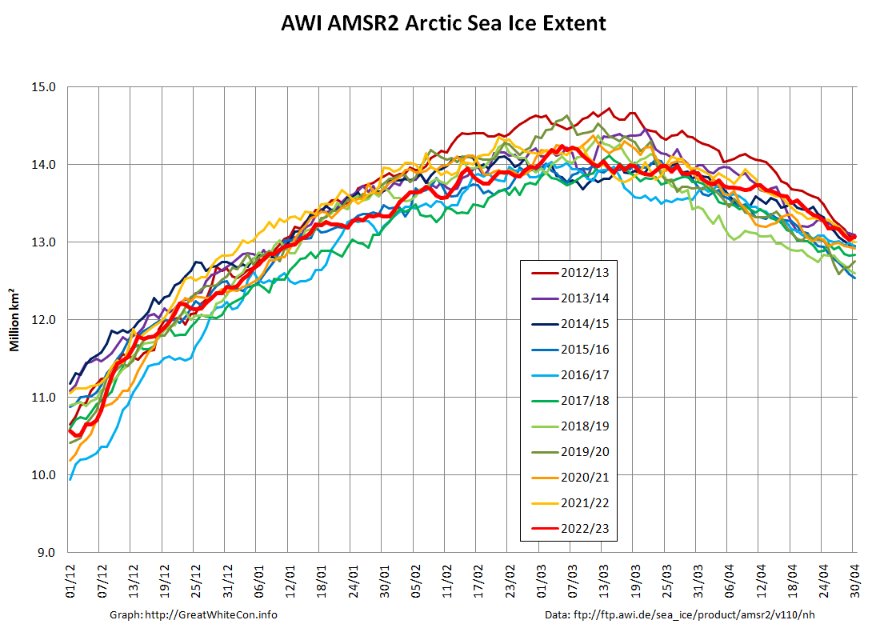
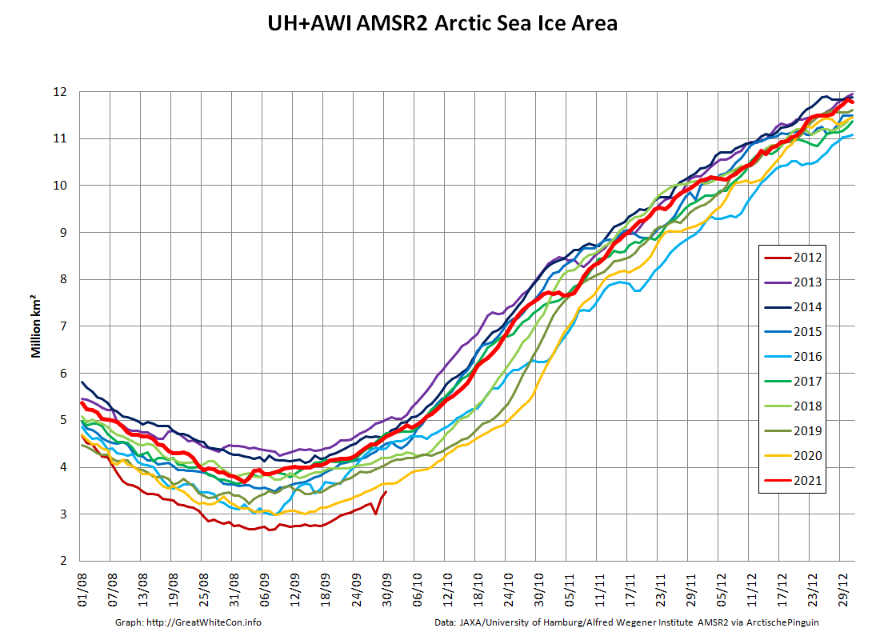
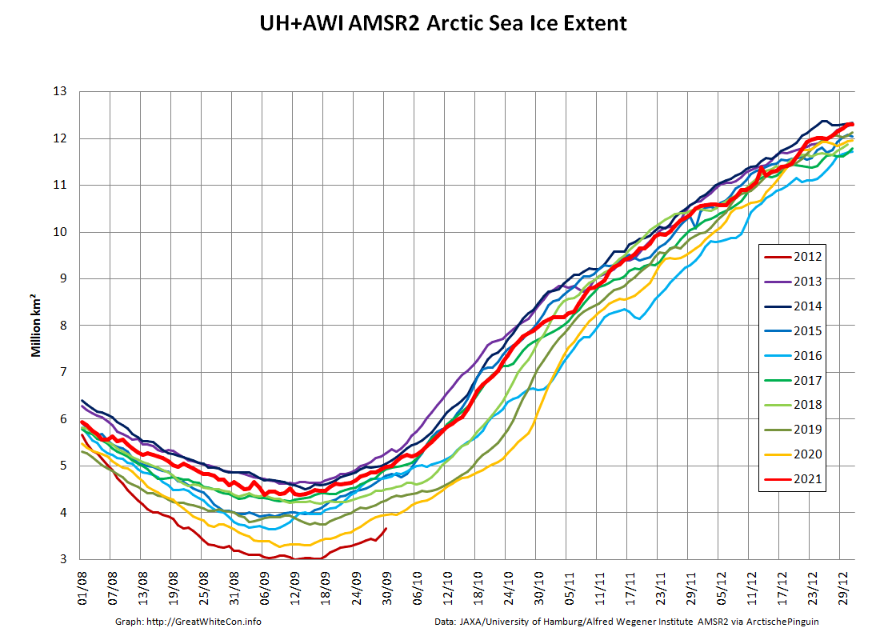
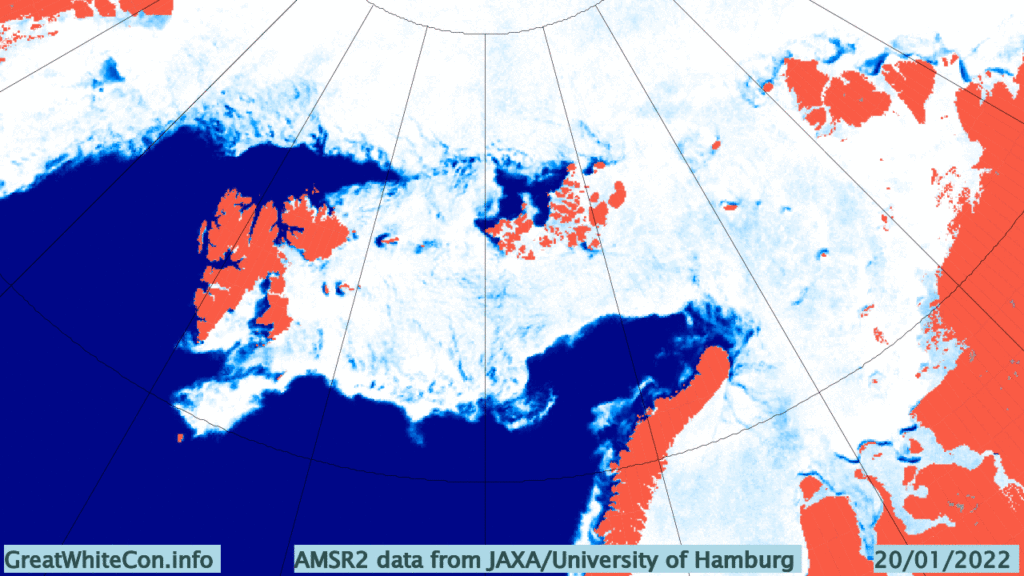
Now were into September the 2018 annual minimum extent can’t be too far away. Extent decline appears to have stalled. However “high res” AMSR2 area is currently falling fast, for the time of year at least:
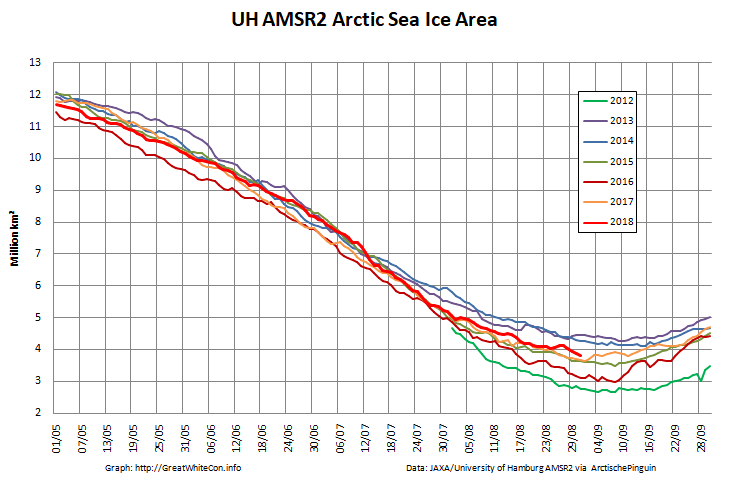
[Edit – September 2nd]
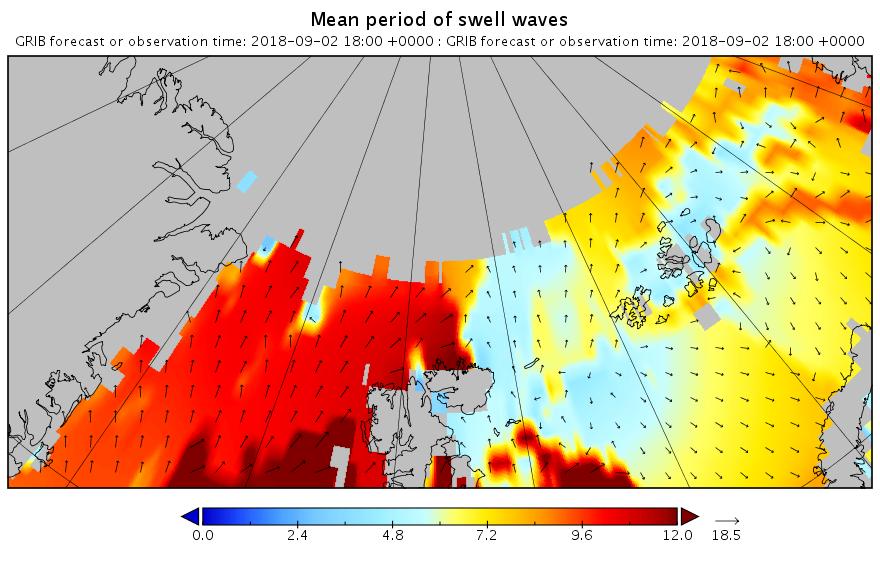
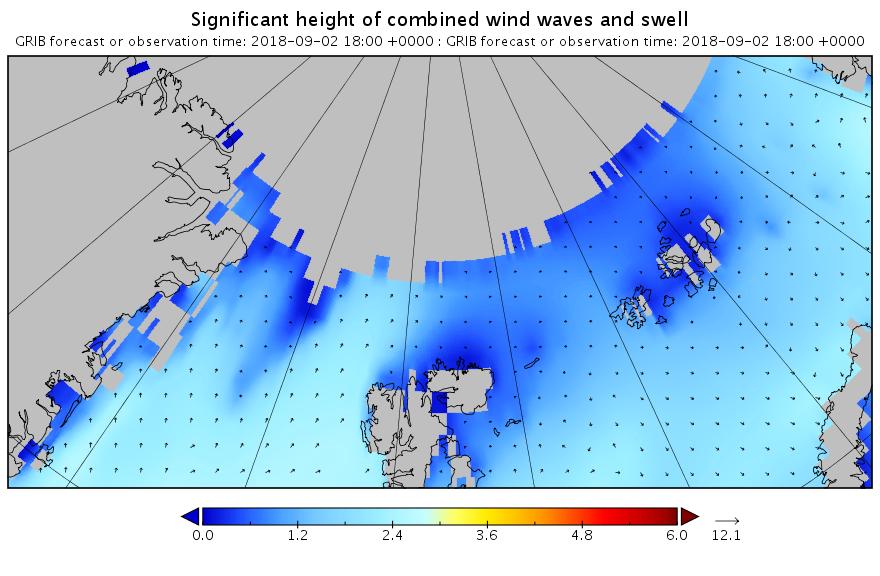
Here are the swell and period forecasts at midnight for round about now, 09:00 UTC:
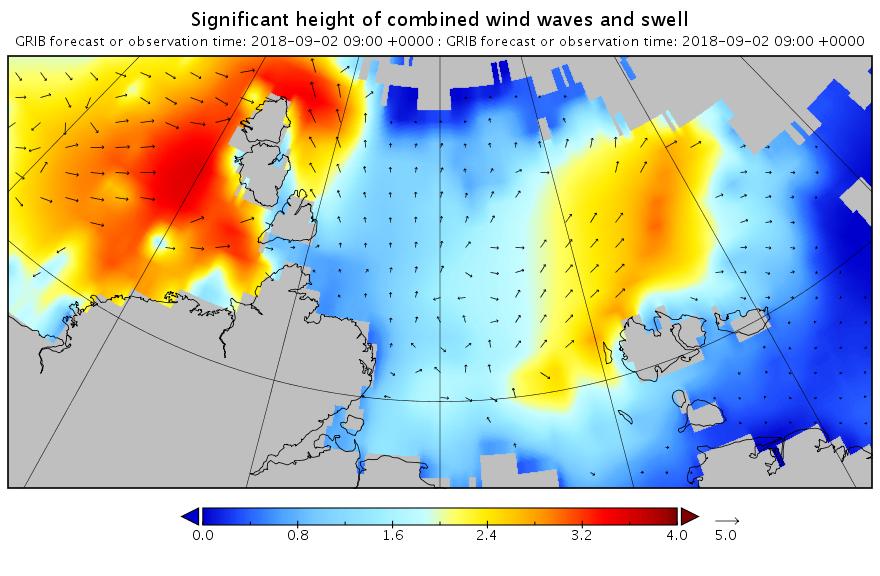
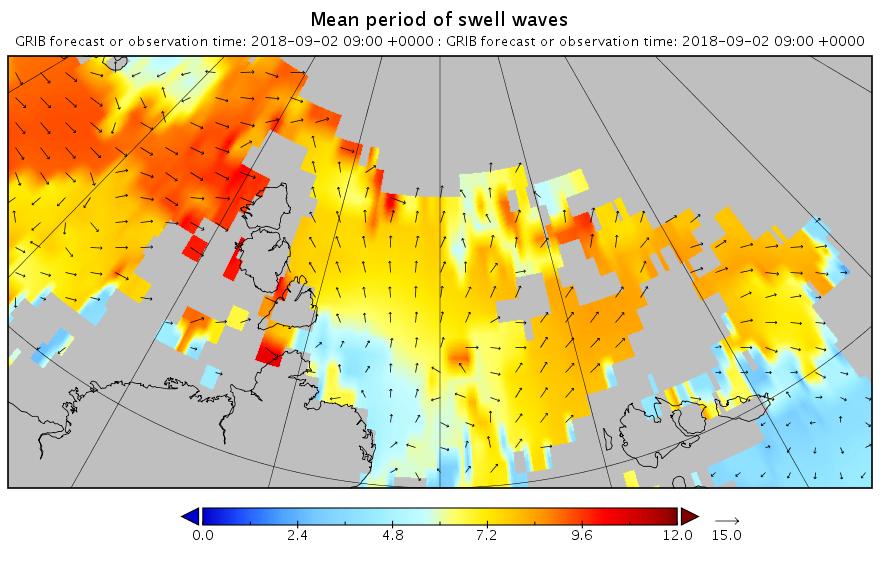
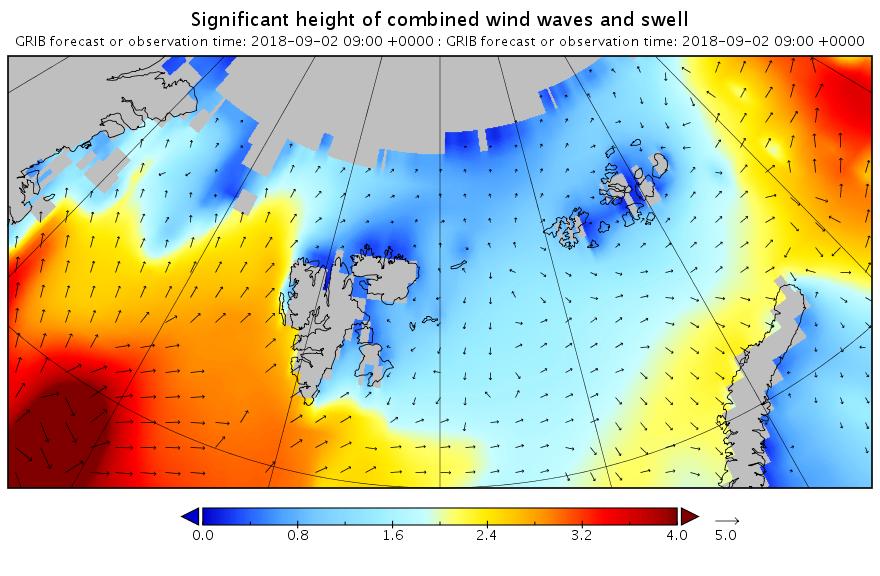
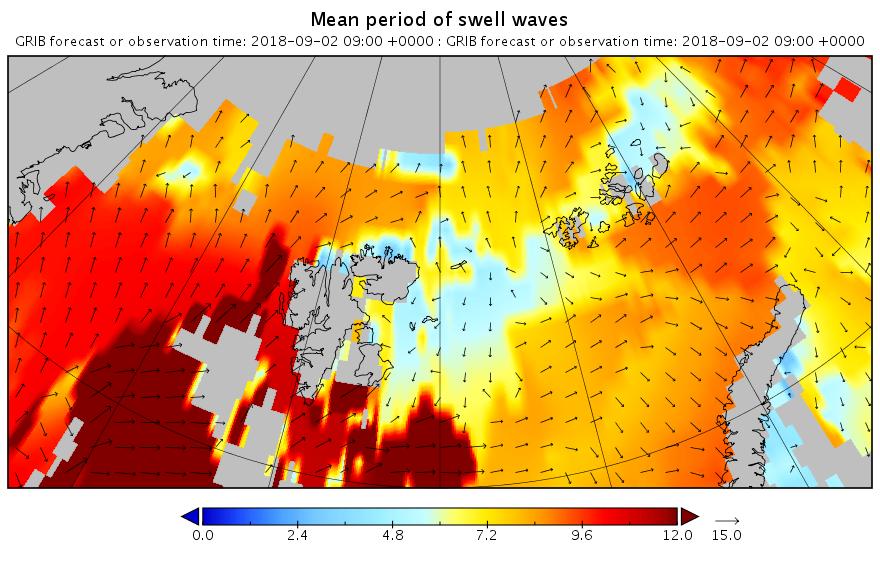
All the seas between Greenland and the New Siberian Islands are awash with swells with a period of 8 second or greater. This is most unusual, to put it mildly!
[Edit – September 3rd]
Here’s the WaveWatch III “hindcast” from midnight last night UTC for the Russian side of the Arctic Ocean:
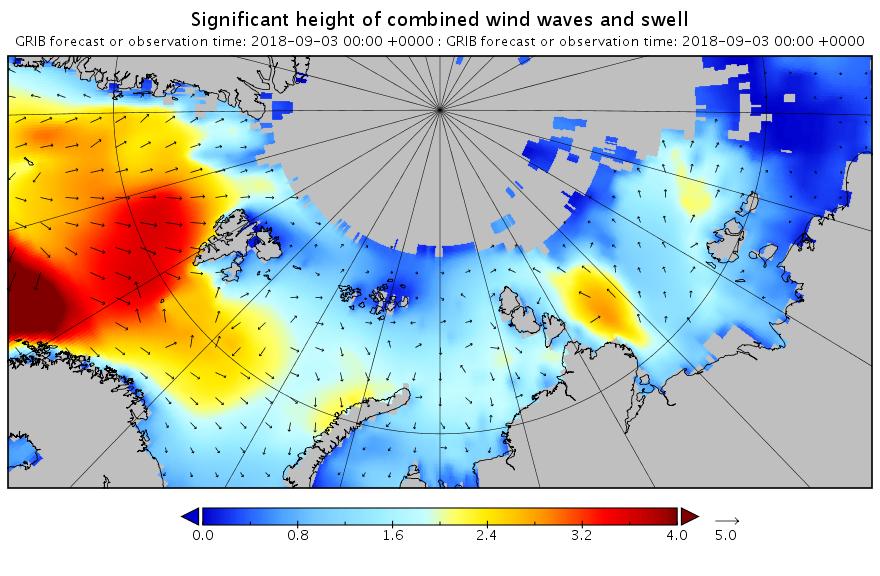
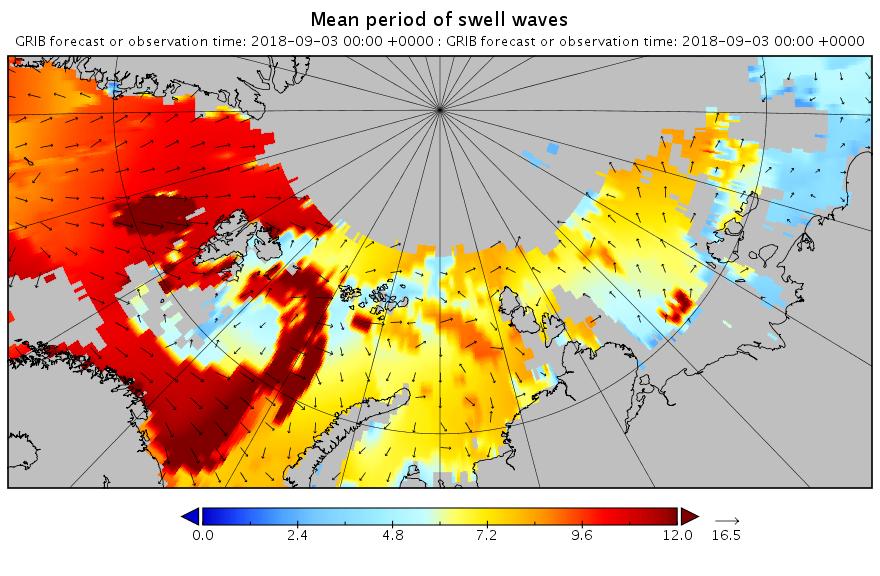
There are still significant swells almost everywhere you look.
[Edit – September 4th]
Using the same scales as yesterday, here’s today’s hindcast from midnight:
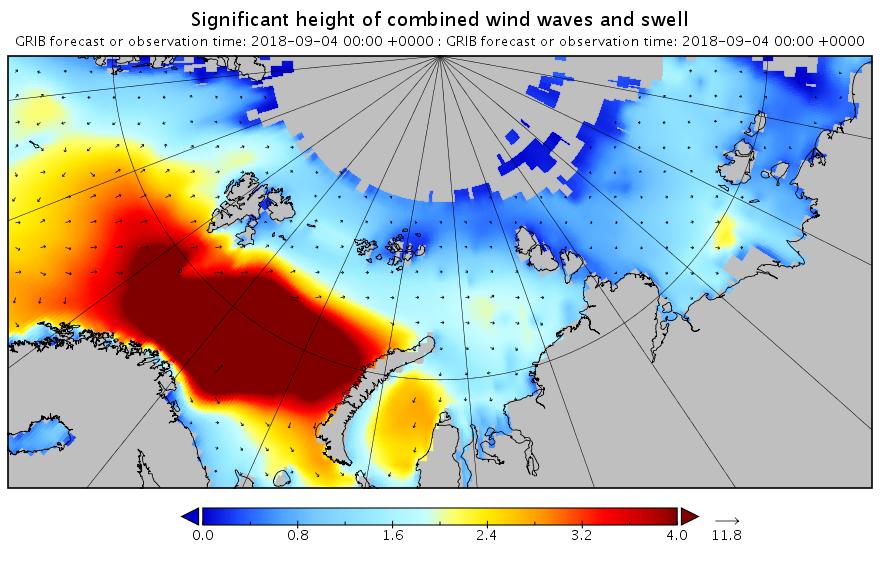
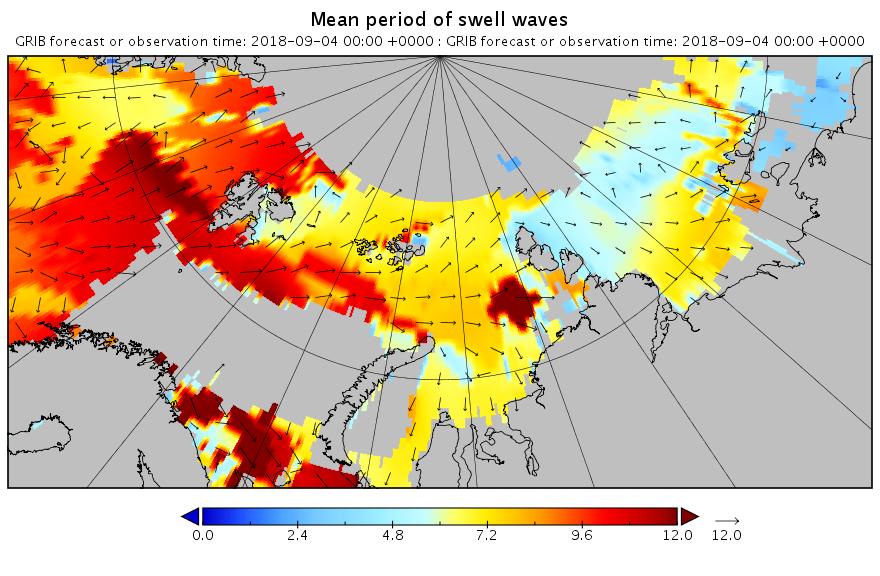
There’s still plenty of action in the Arctic Ocean!
[Edit – September 5th]
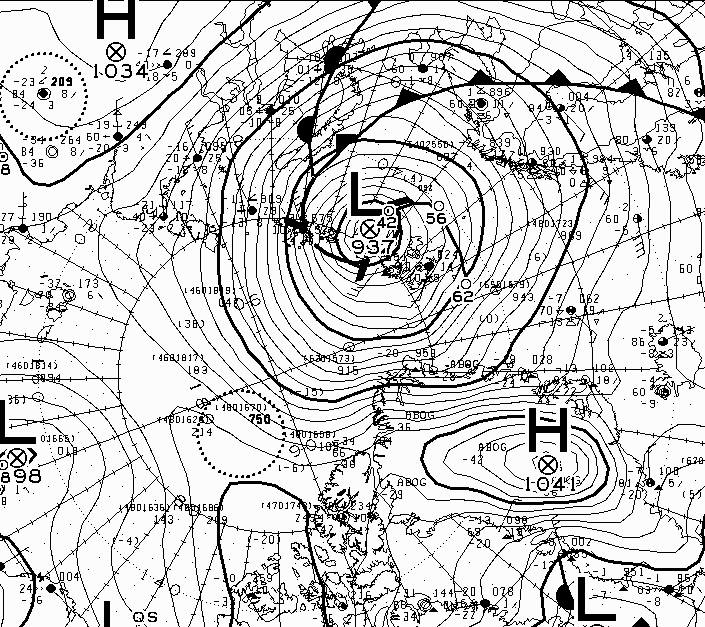
Feel free to debate whether it merits the “Great” prefix, but this is how the early September 2018 Arctic cyclone has panned out. According to this morning’s Environment Canada synopsis the cyclone is centred near the coast of the Laptev Sea and is down to a MSLP of 977 hPa:
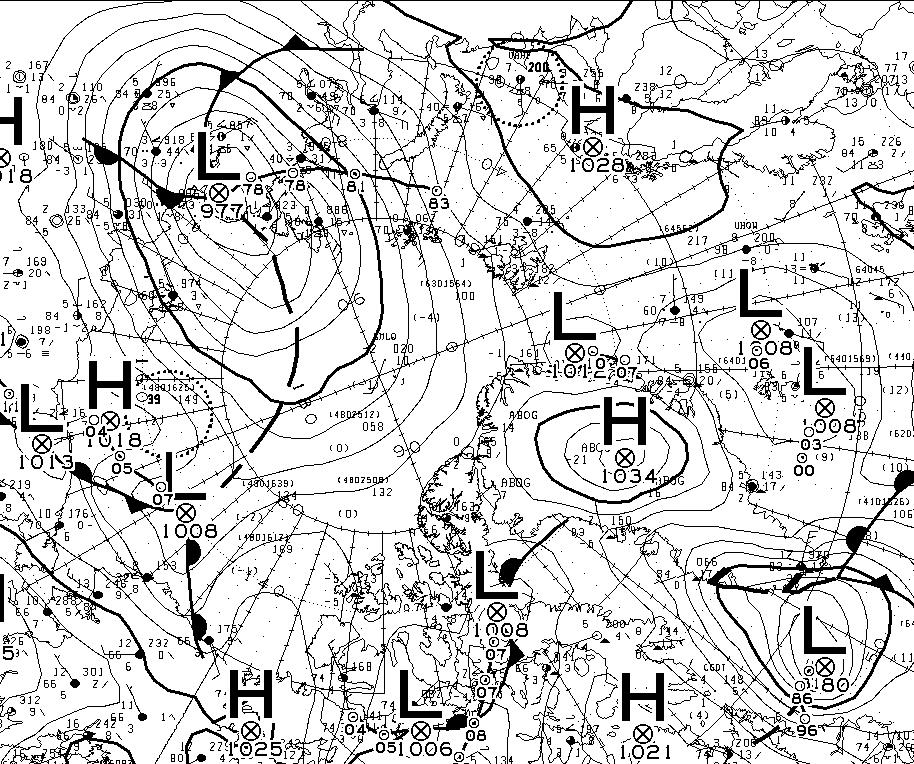
Here’s another WaveWatch III hindcast from midnight UTC:
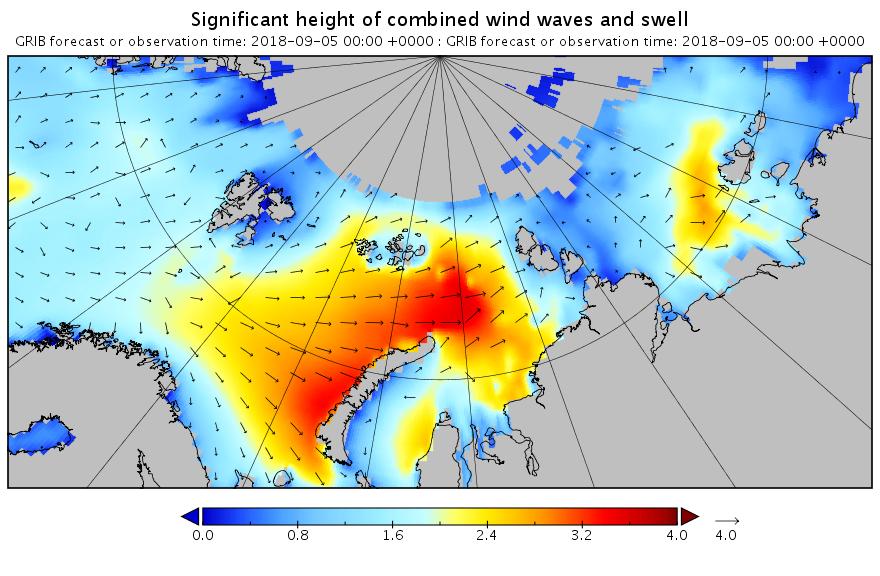
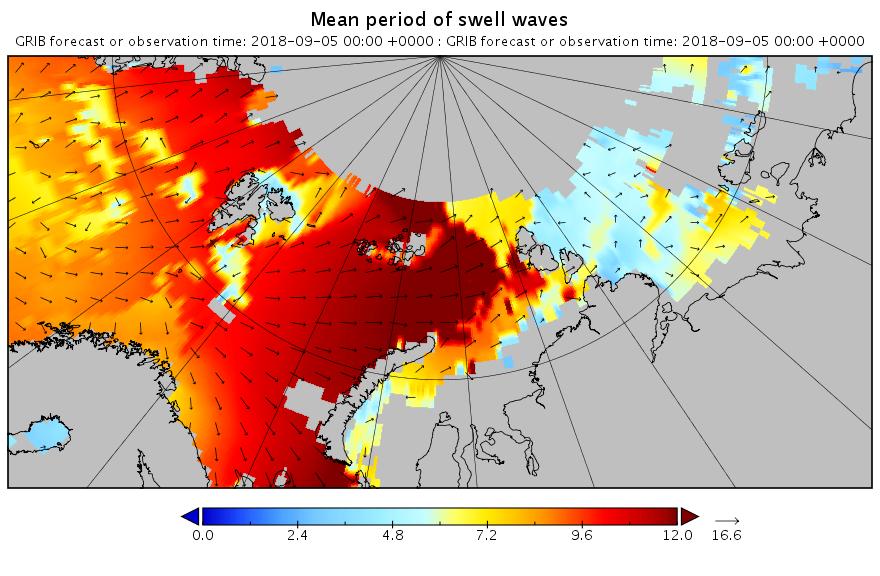
[Edit – September 6th]
Need I say more?
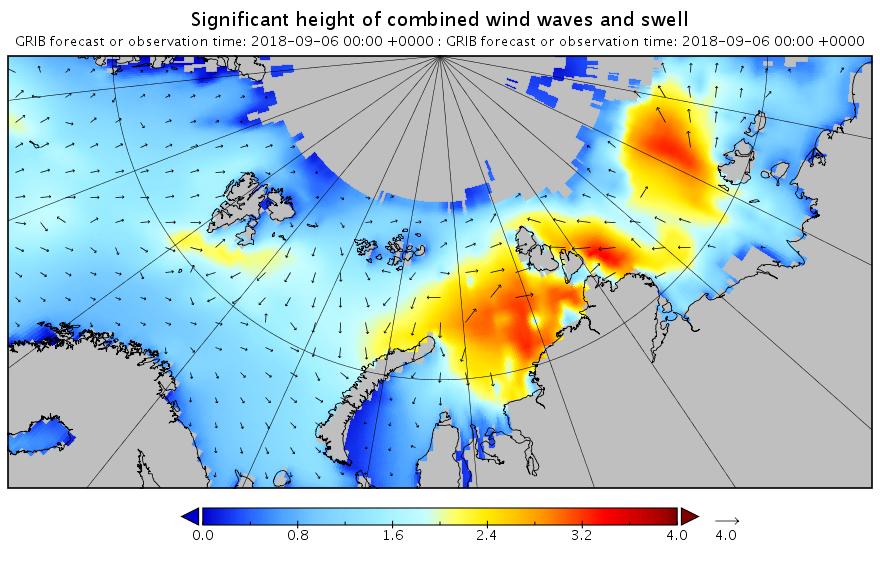
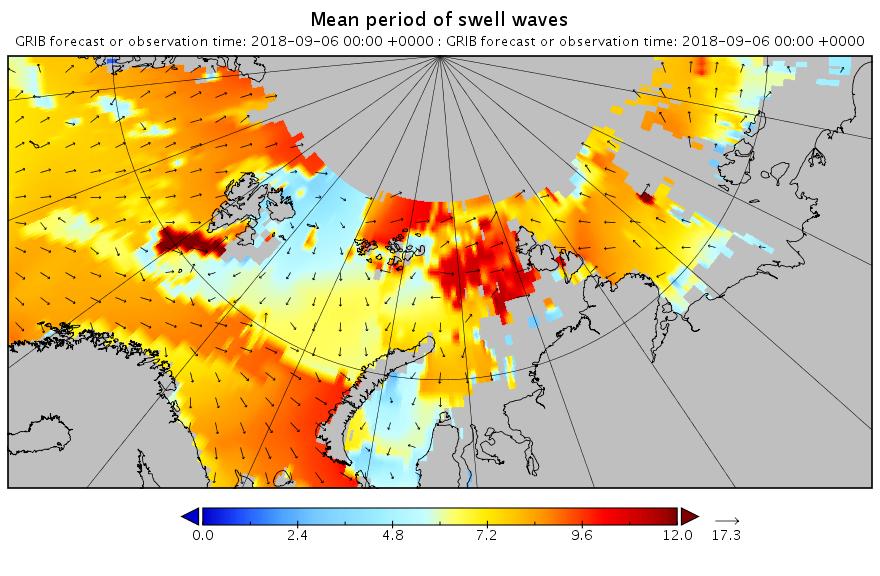
[Edit – September 7th]
The swell in the Fram Strait an Barents Sea is diminishing, but the period in the Laptev Sea is increasing now:
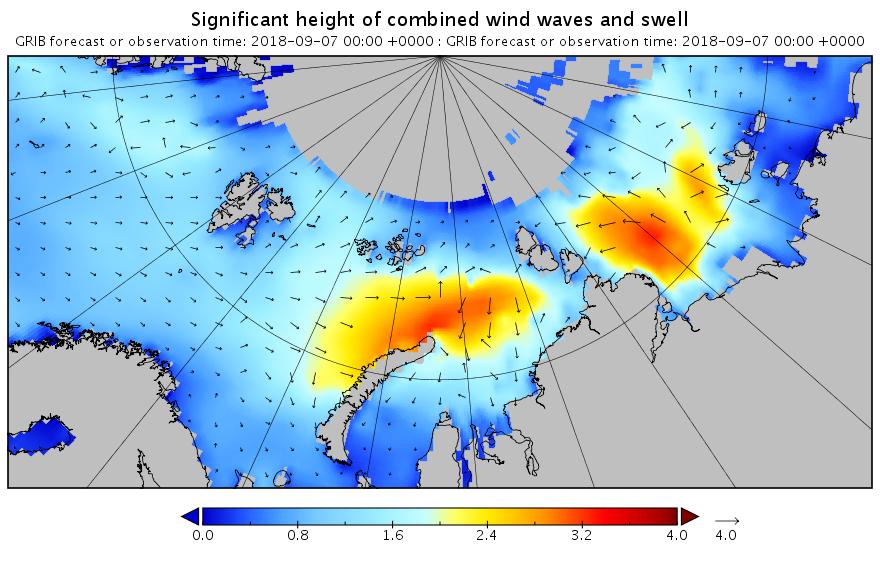
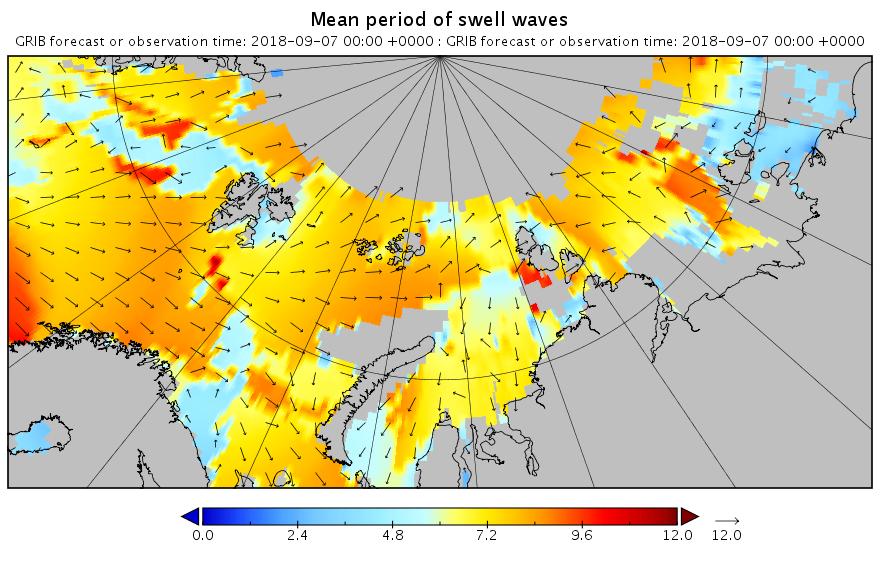
[Edit – September 8th]
All the wave activity in the Laptev Sea is diminishing. Here’s the hindcast from midnight:
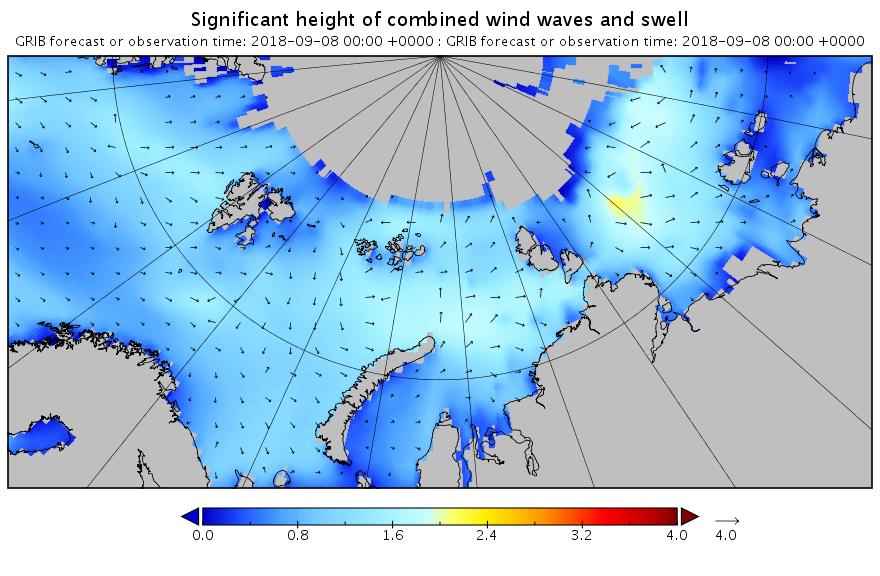
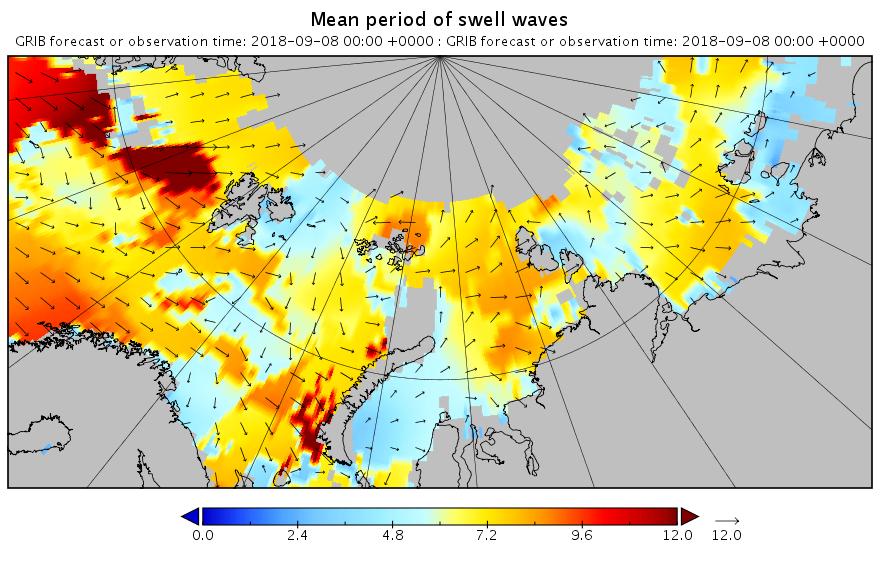
Meanwhile things are warming up in the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas. Here’s the forecast for midnight tonight:
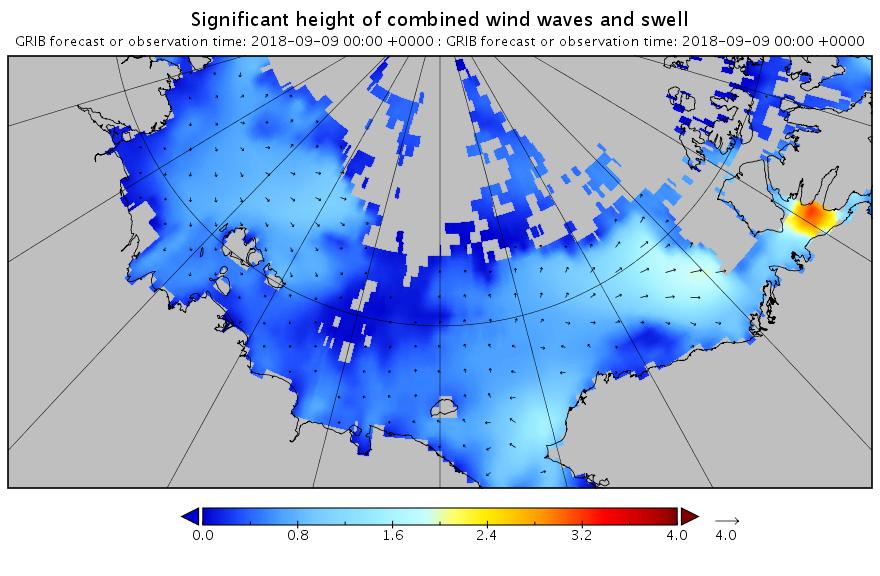
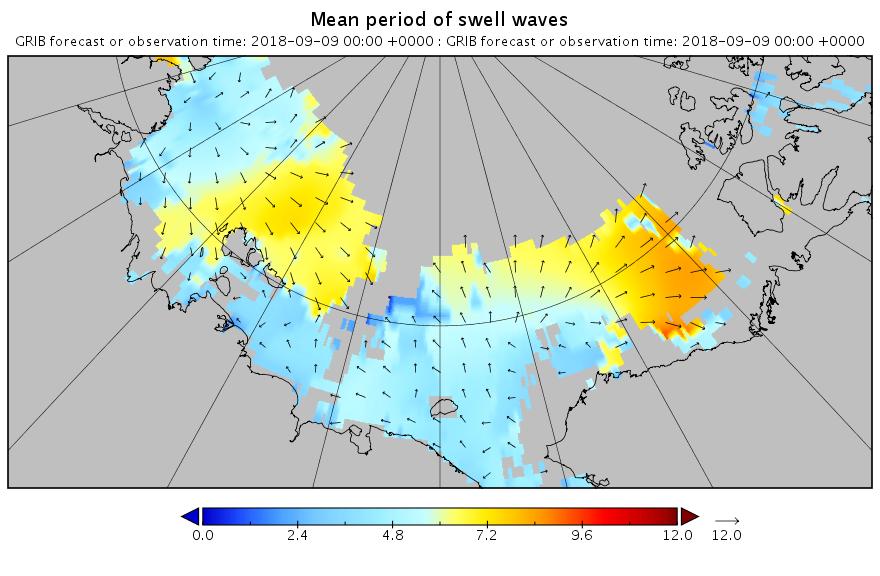
[Edit – September 9th]
Here’s the hindcast for this morning’s swell in the Beaufort Sea:
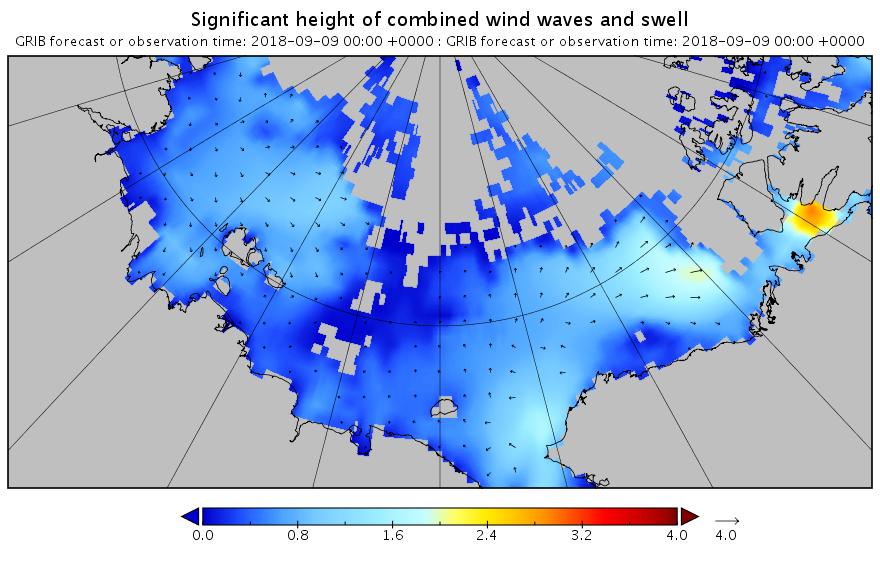
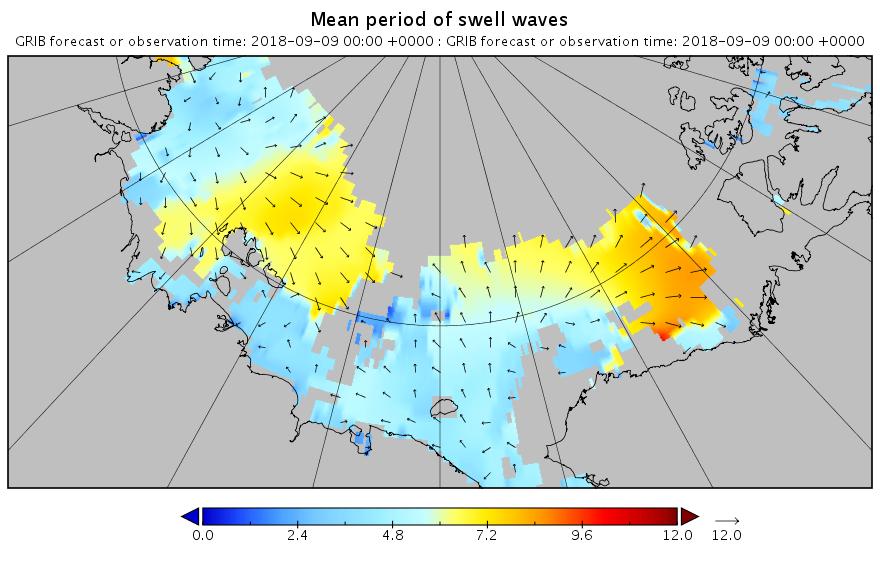
This is currently a long way into the future and hence may not verify in practice. However any pulse of swell is currently forecast for September 13th: