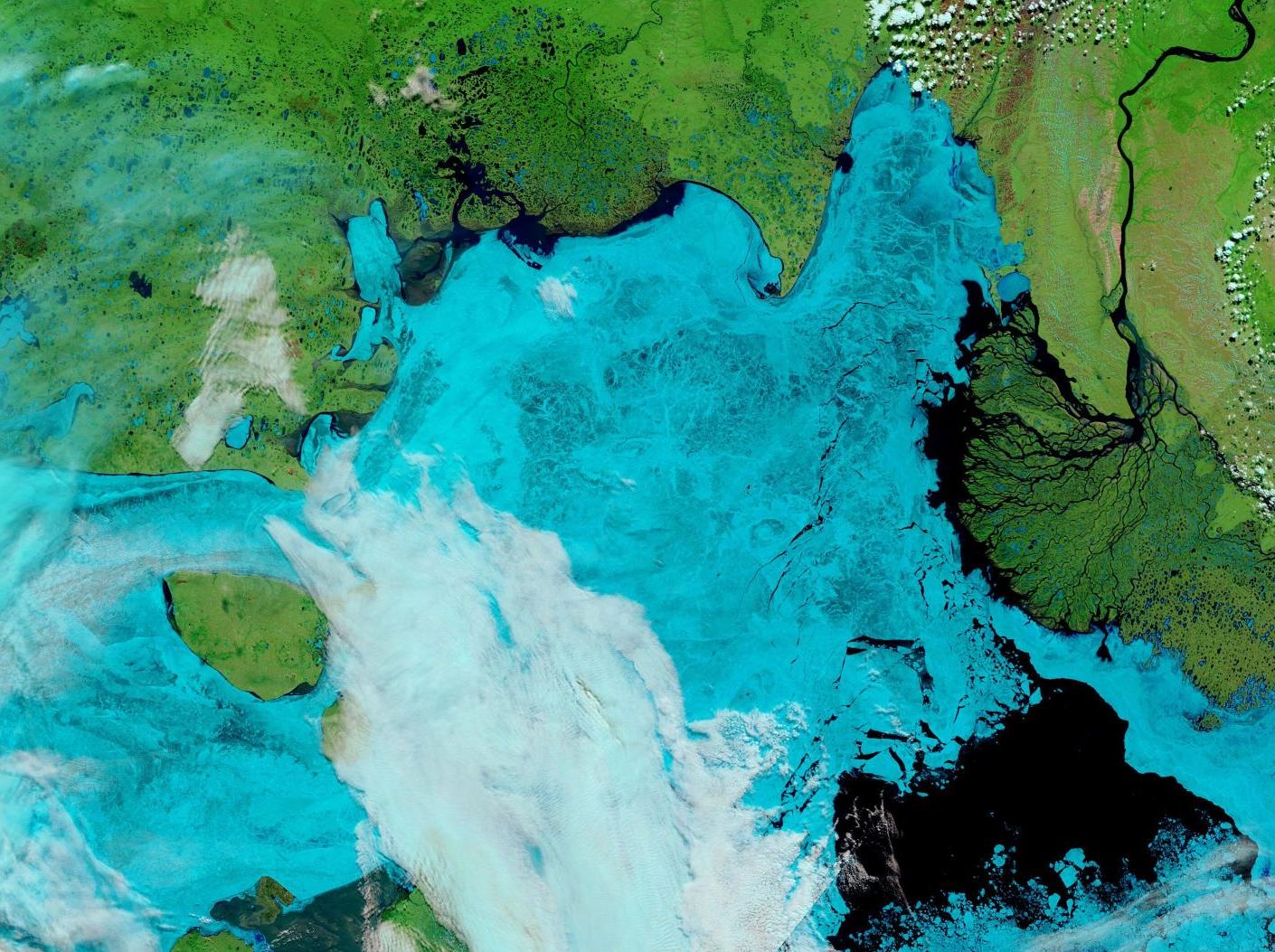
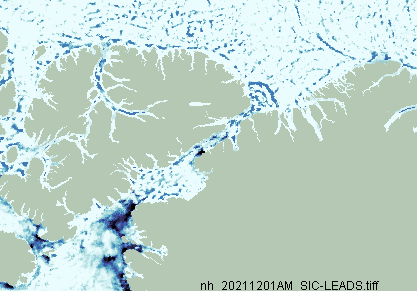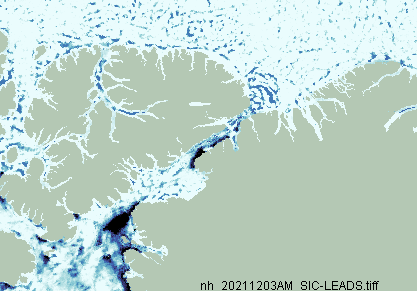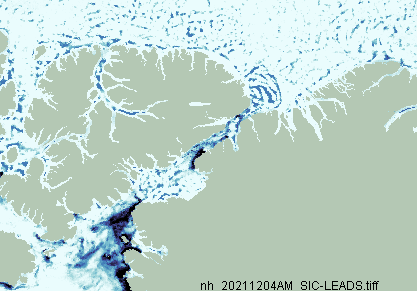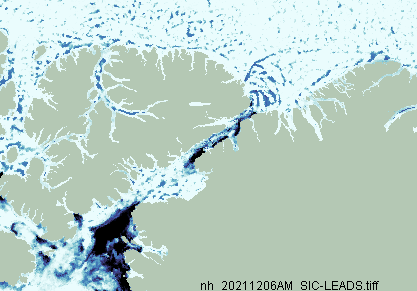
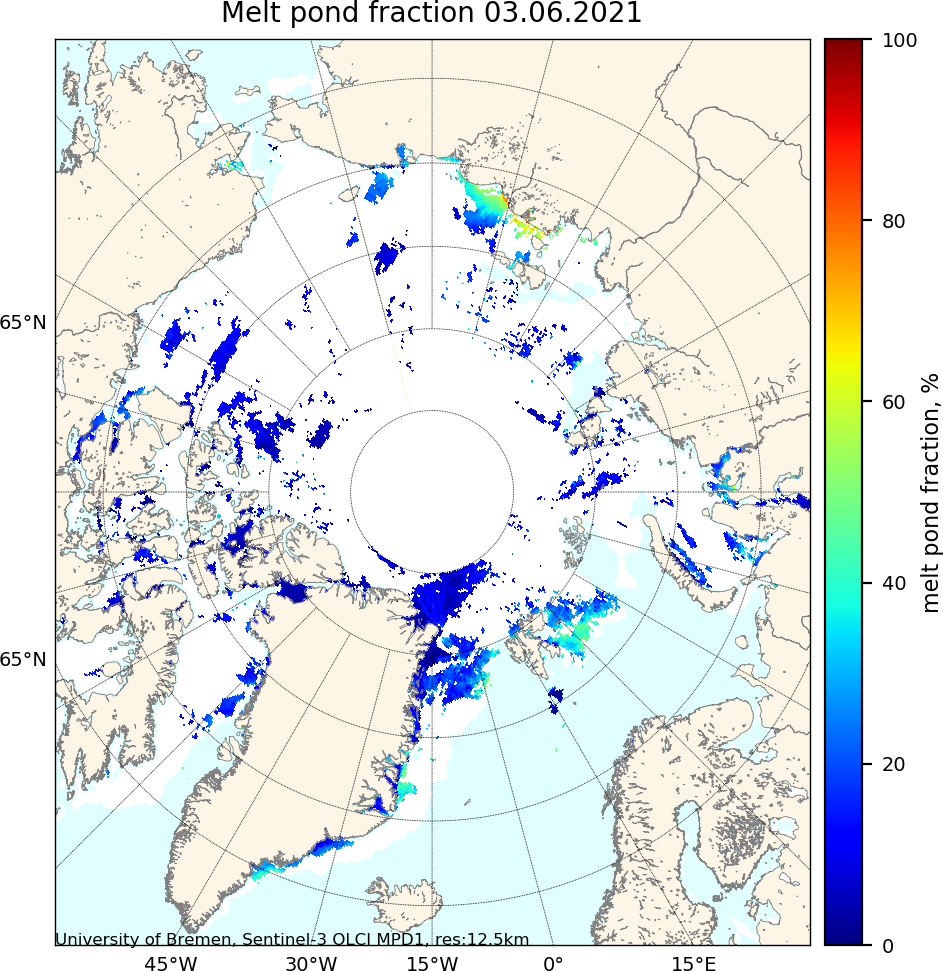
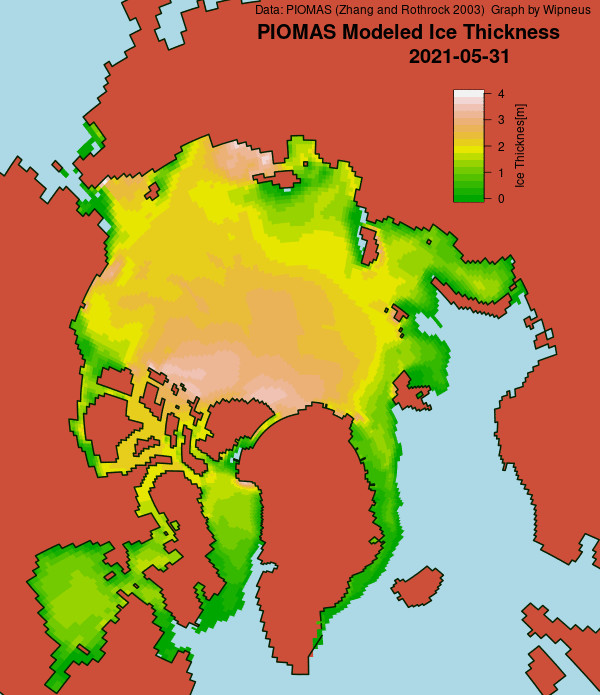
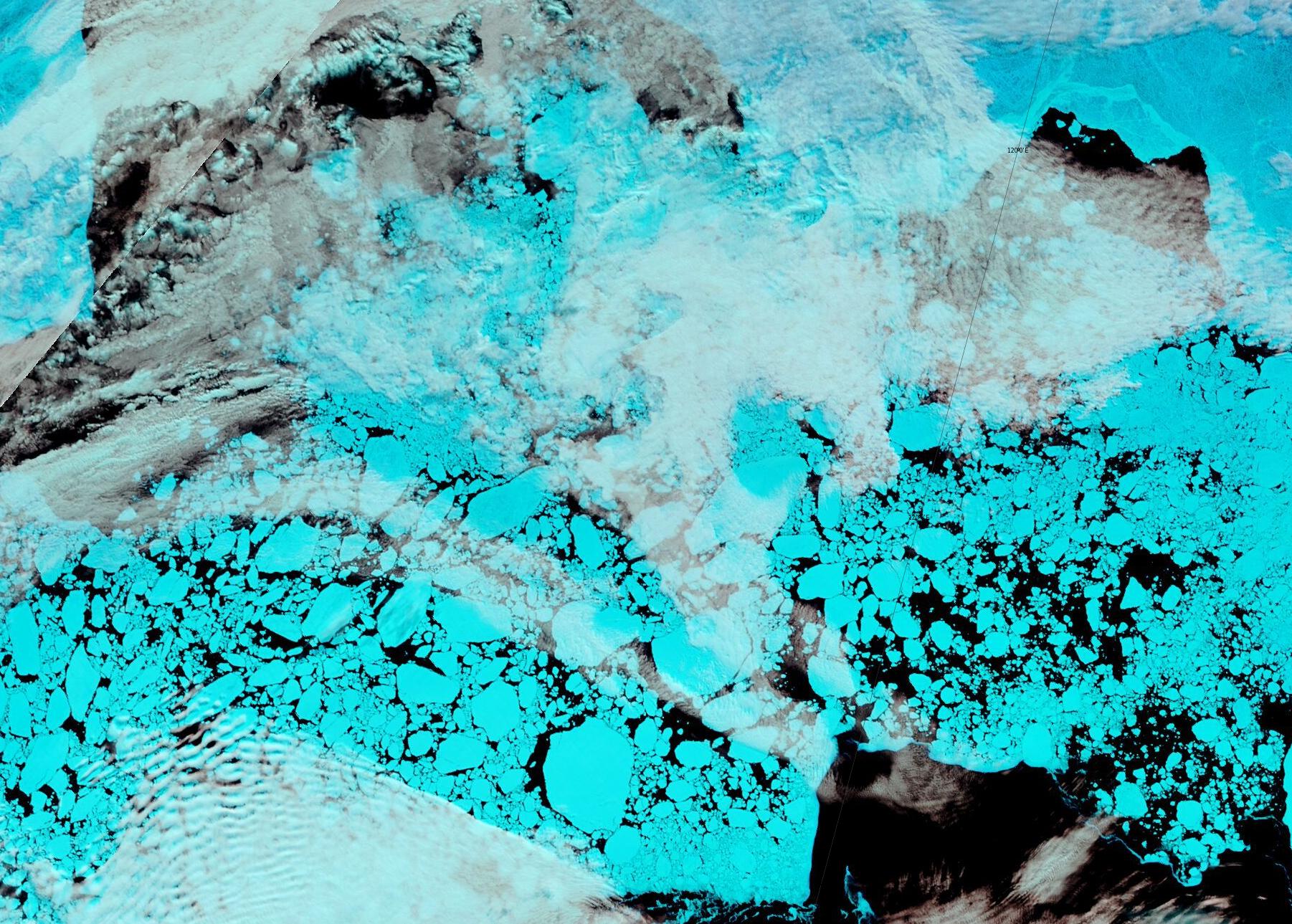
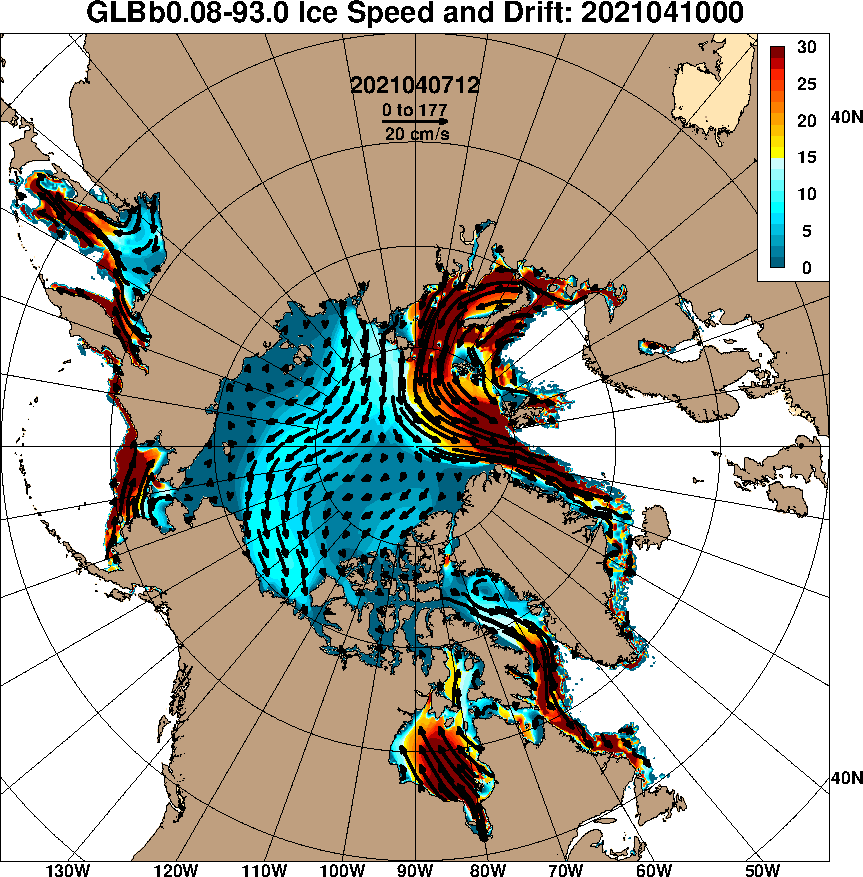
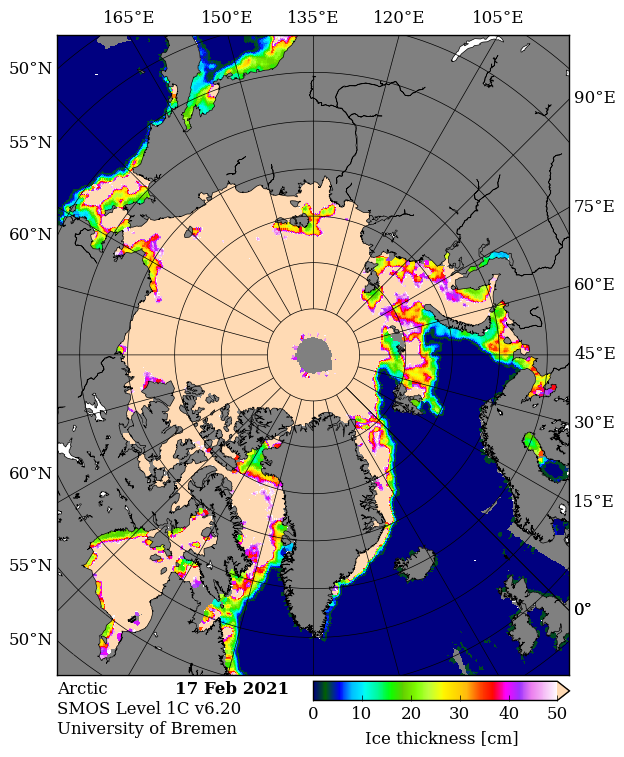
Christmas is coming. Santa’s secret summer swimming pool has frozen over. The time has come for a new monthly Arctic update.
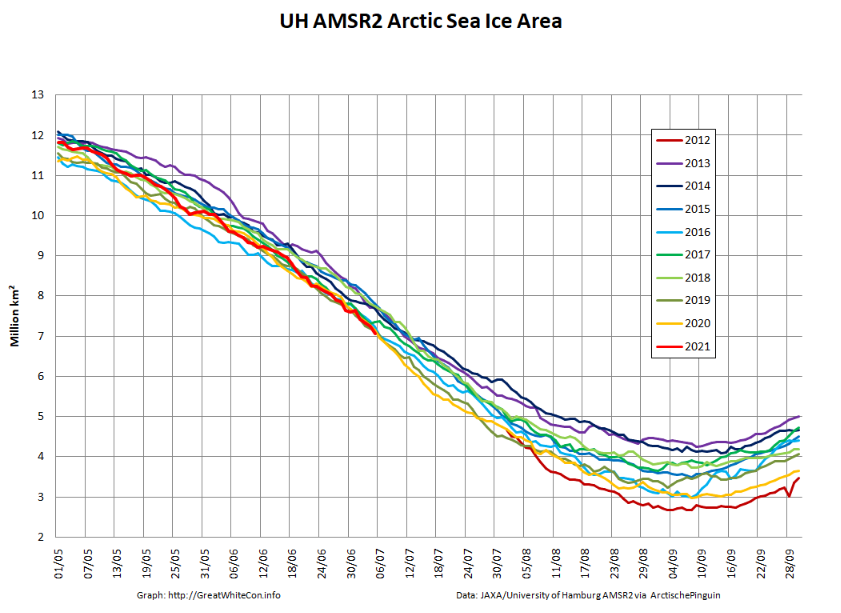
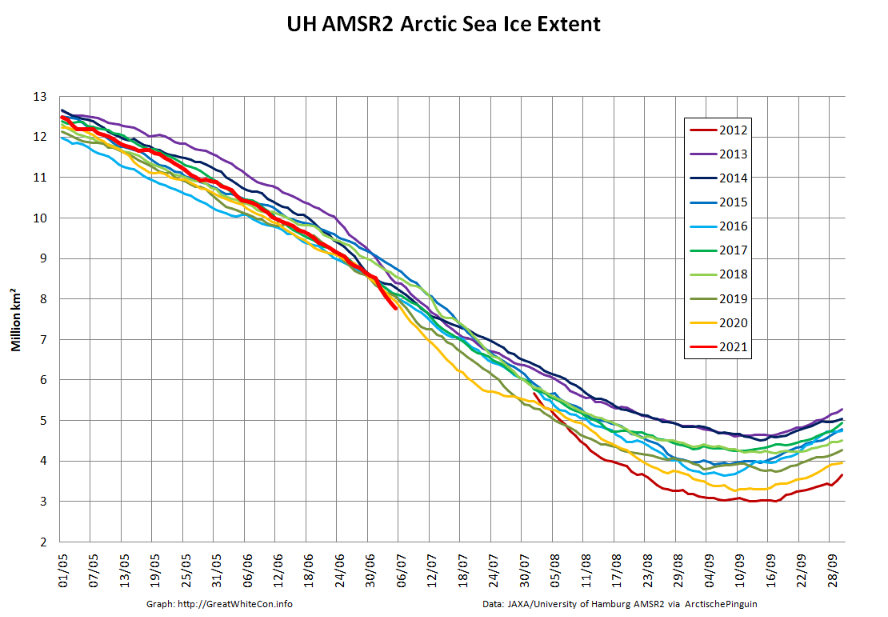
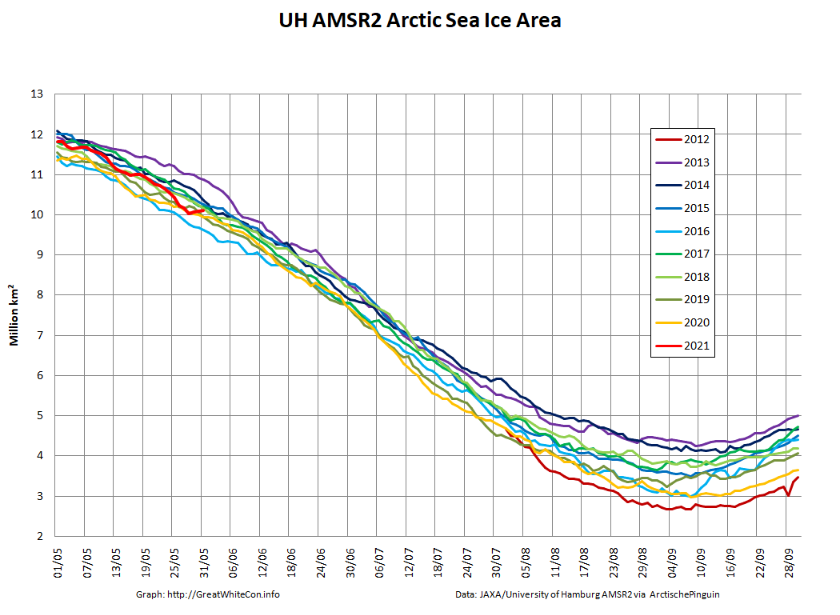
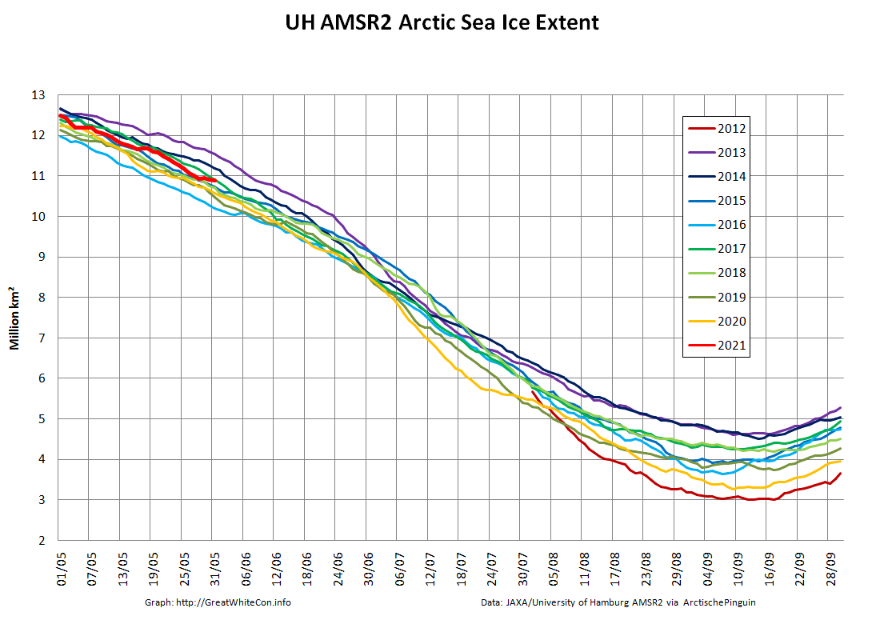
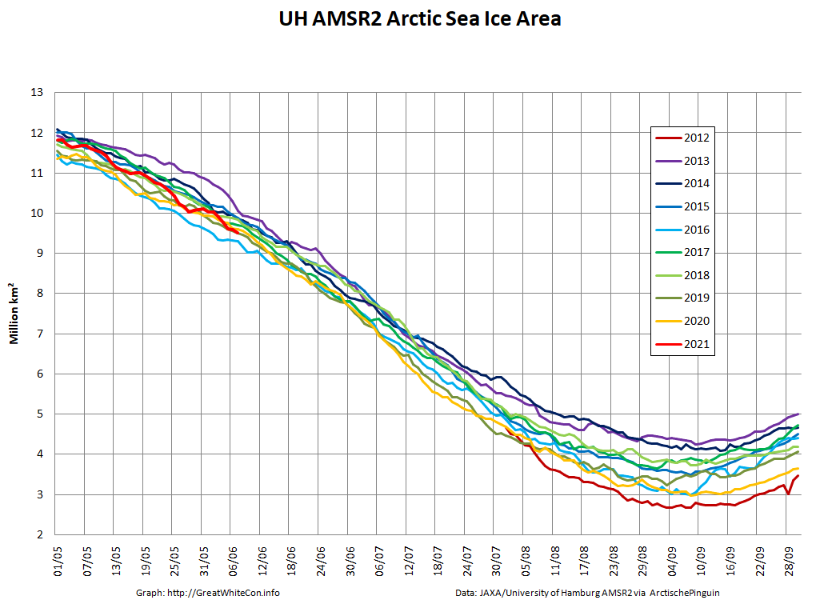
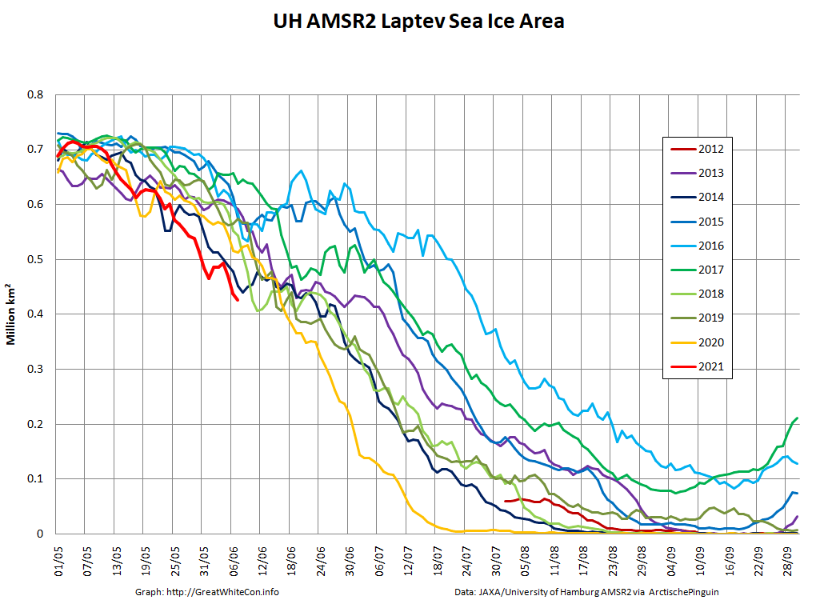
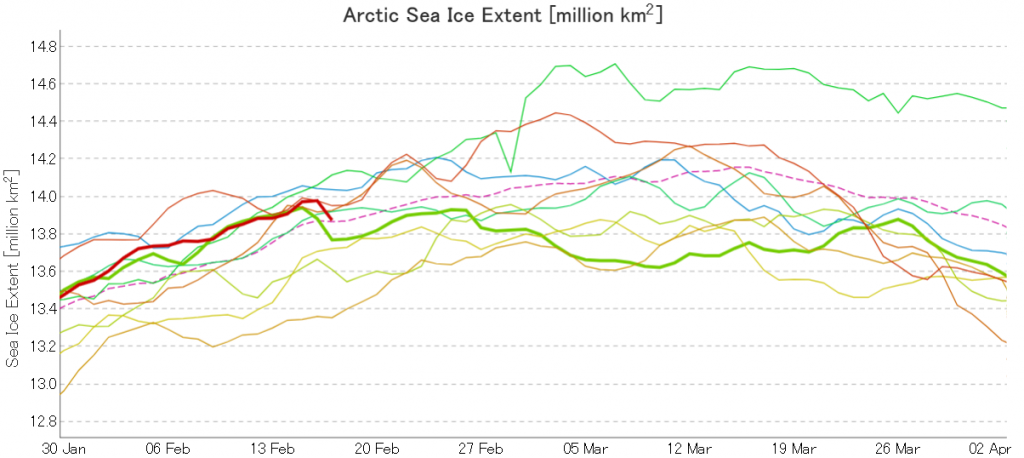
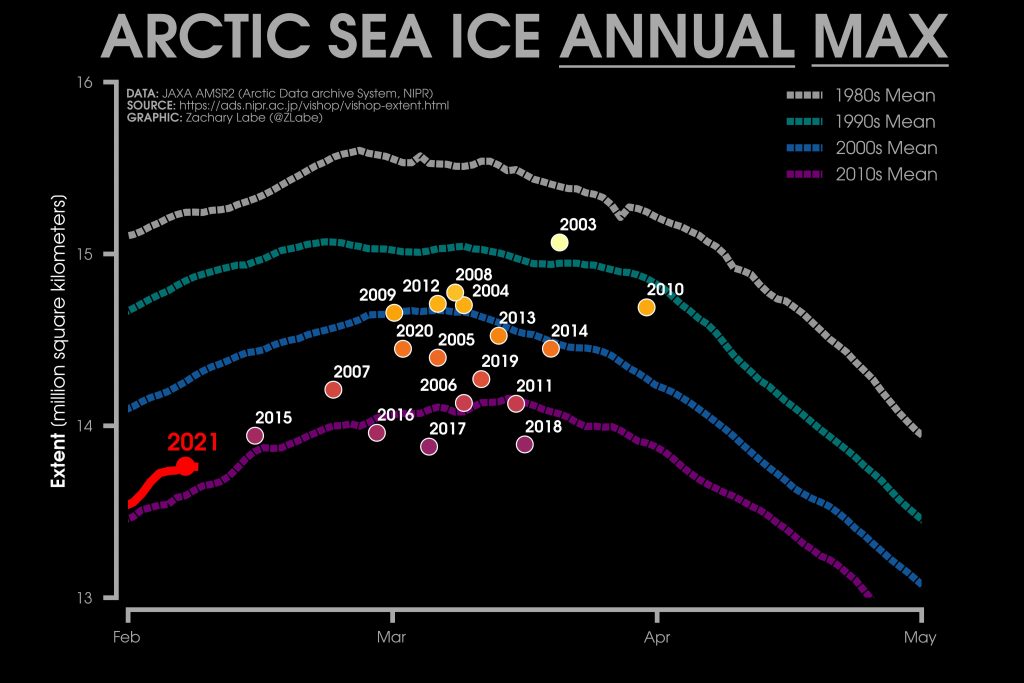
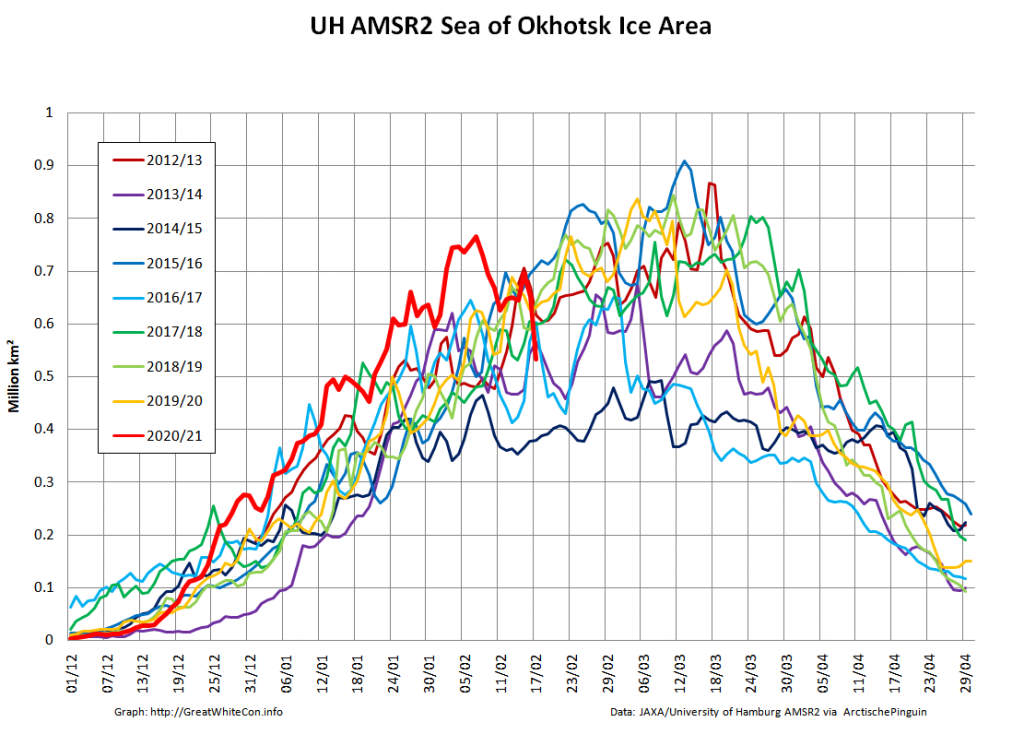
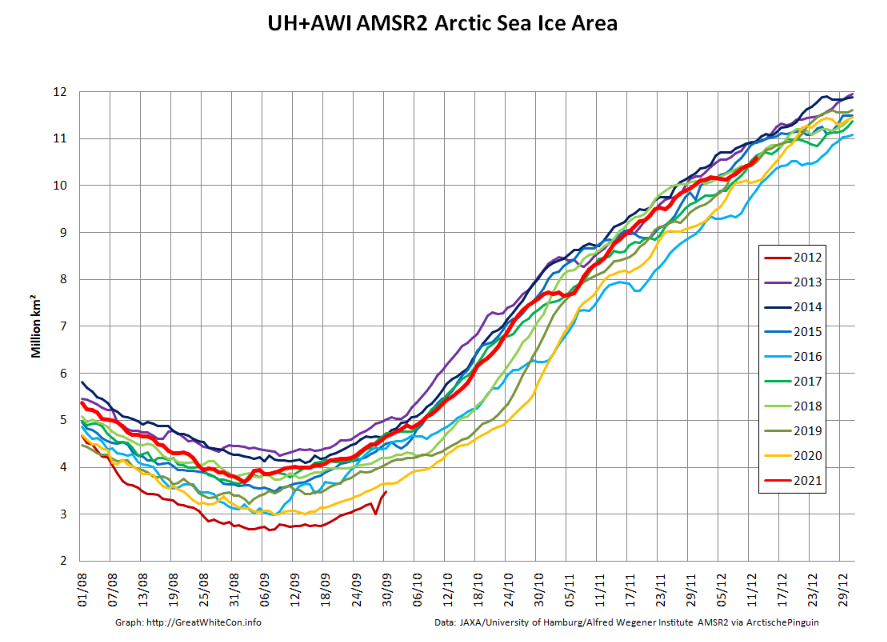
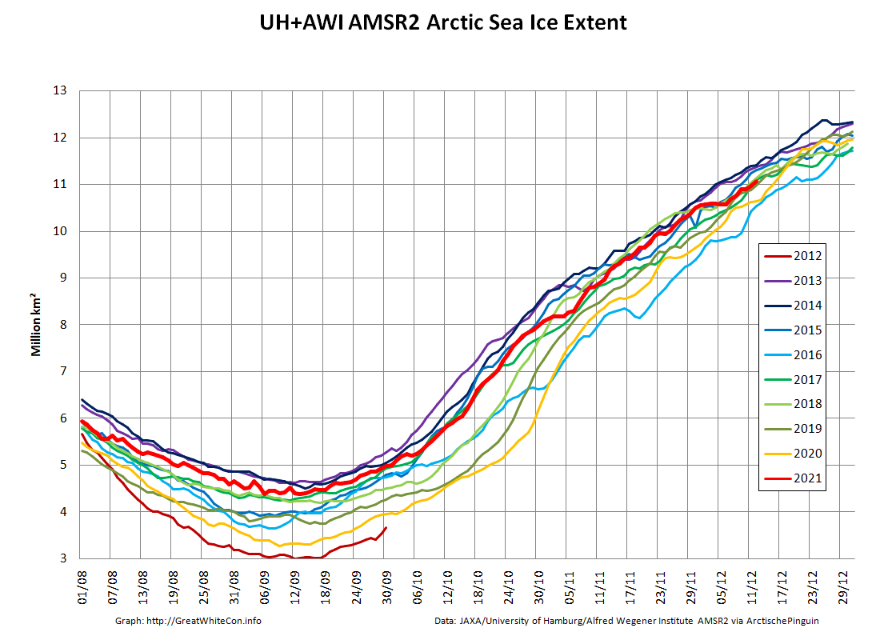
The JAXA/ADS/ViSHOP web site is undergoing maintenance for a week, so let’s start the festive season with a look at high resolution AMSR2 area and extent:
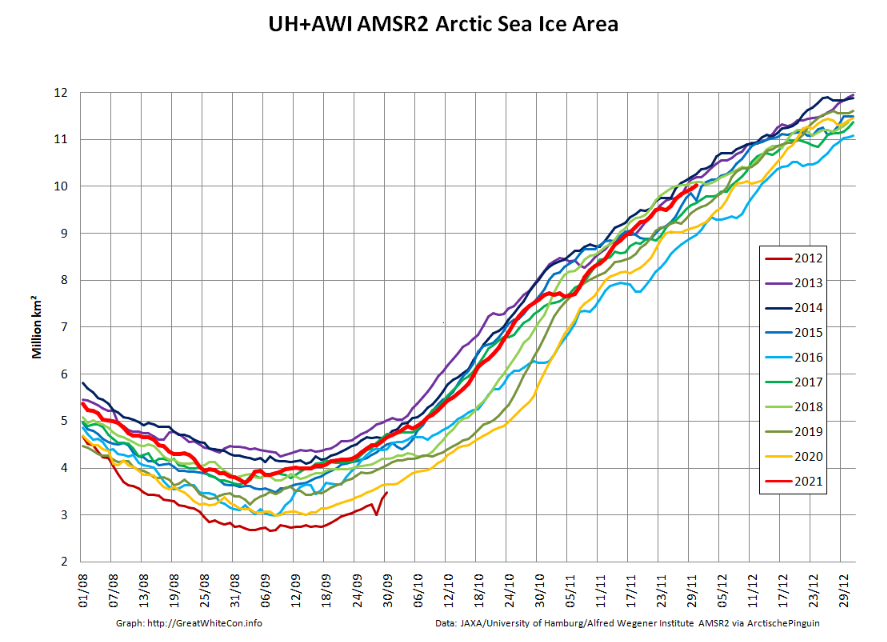
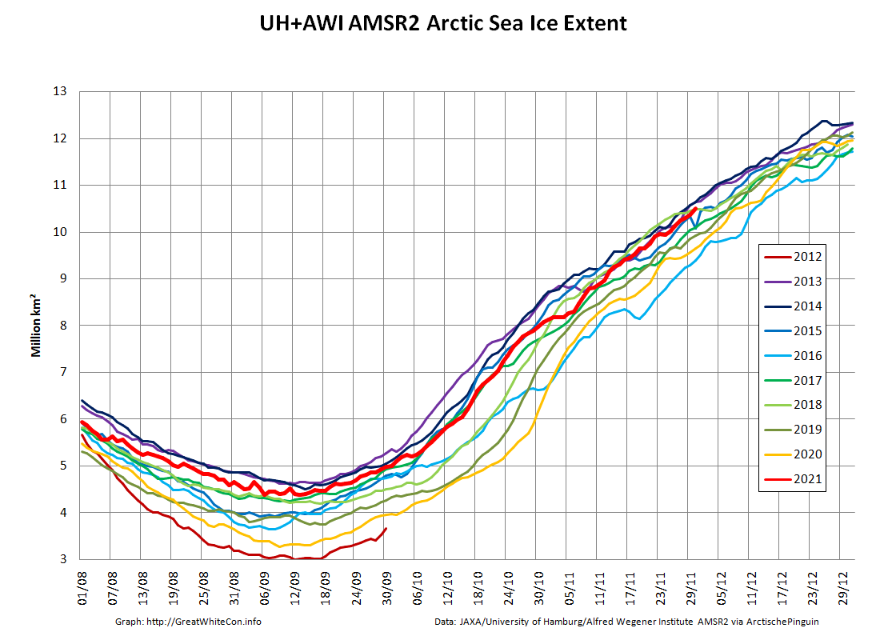
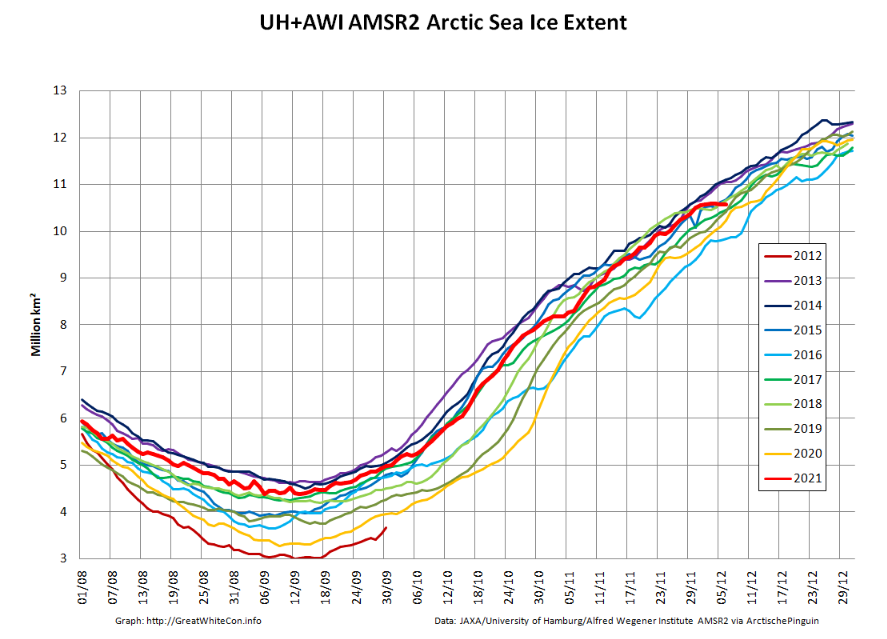
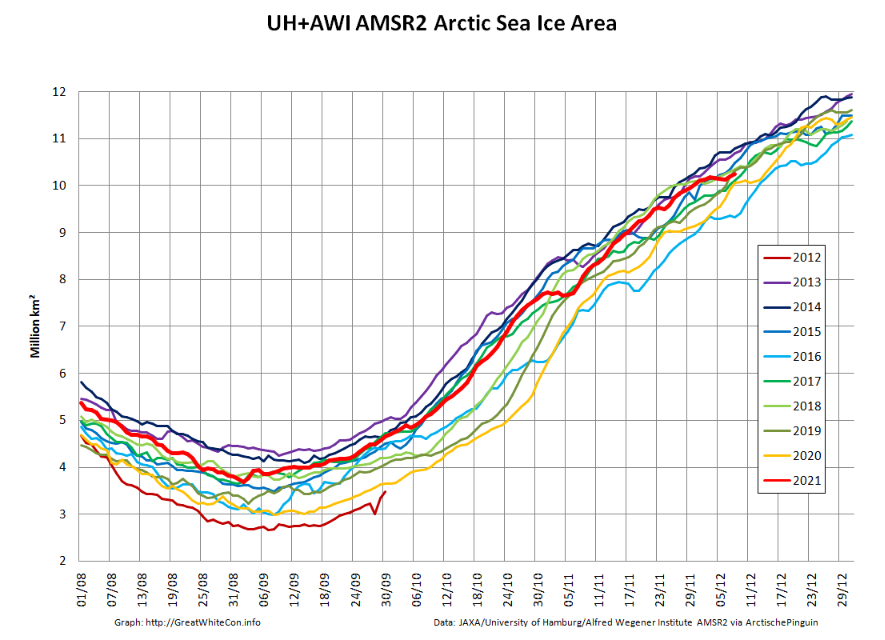
After a brief hiatus in early November both metrics are once again tracking within, but near the upper bound of the last 10 years.
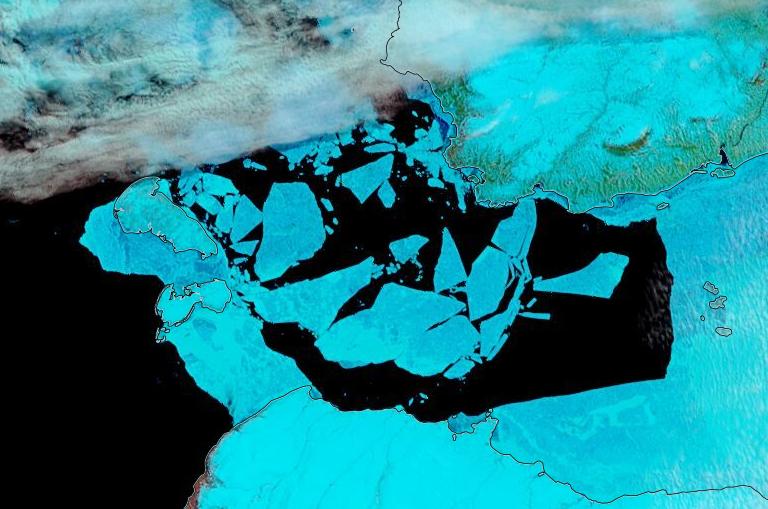
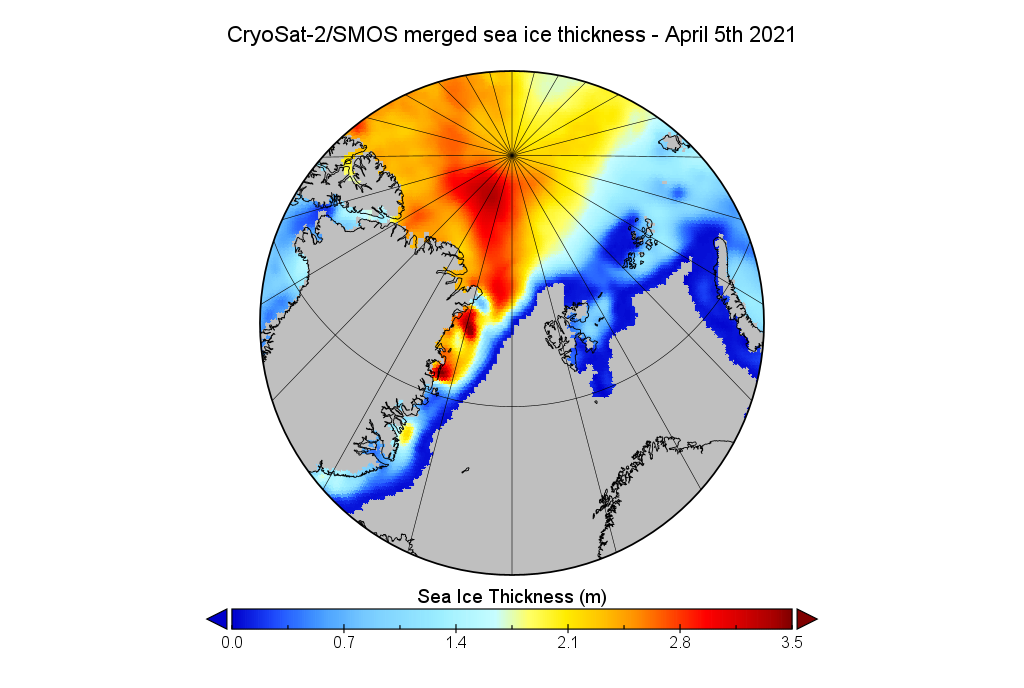
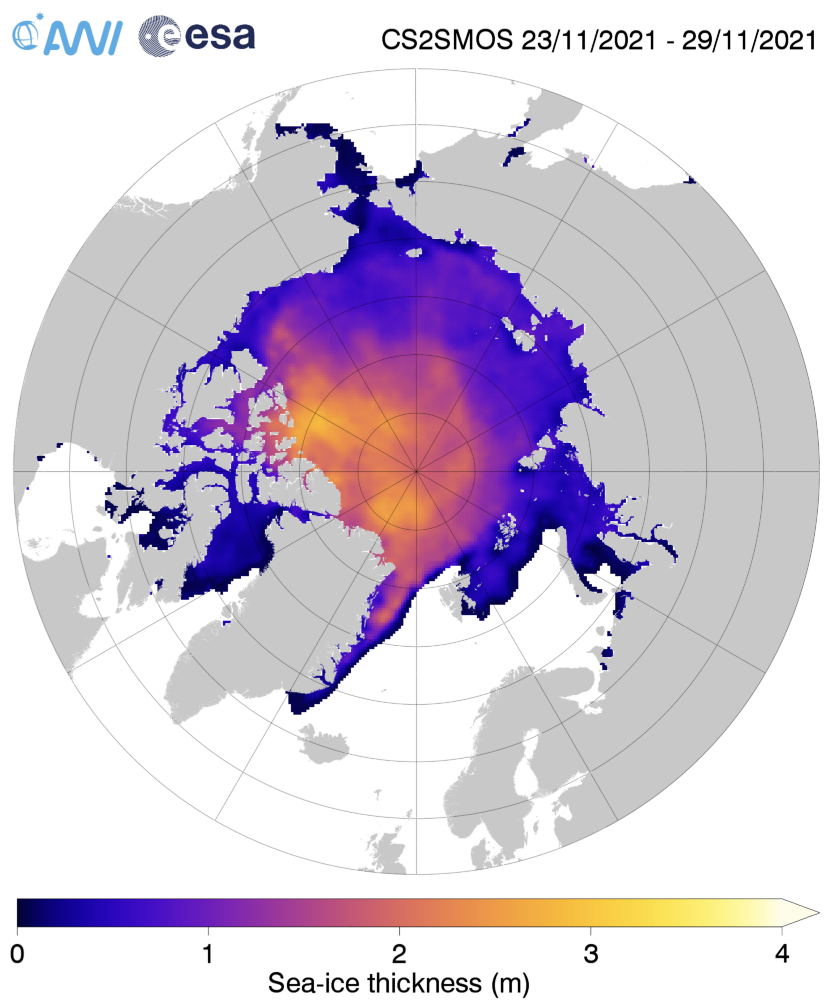
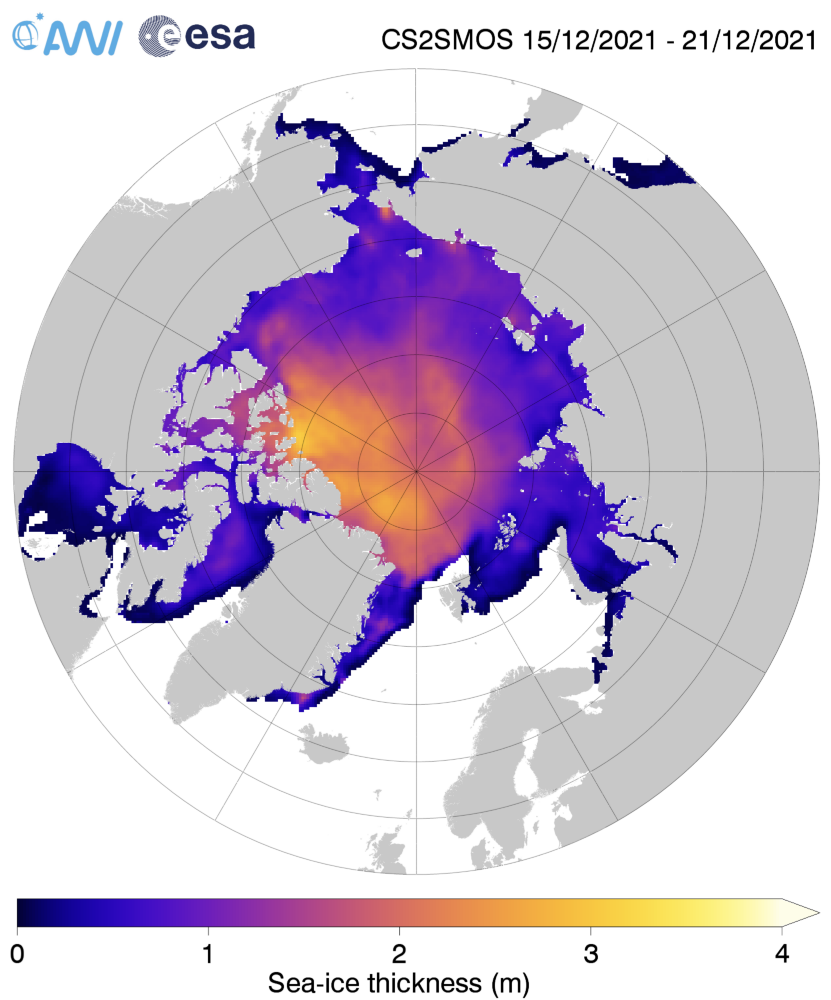
Next let’s take a look at the latest AWI CryoSat-2/SMOS thickness map:
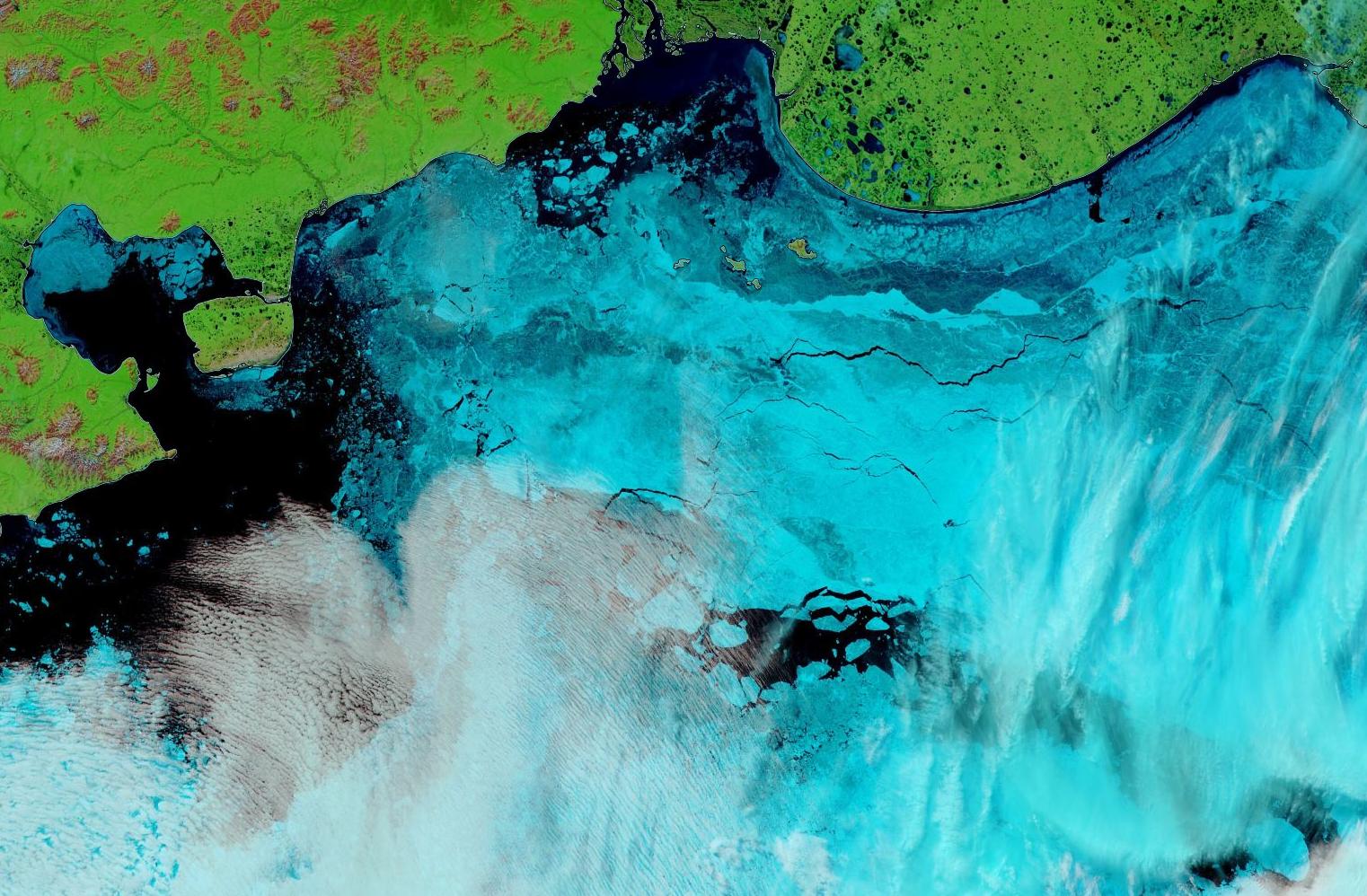
together with the anomaly map from the Finnish Meteorological Institute:
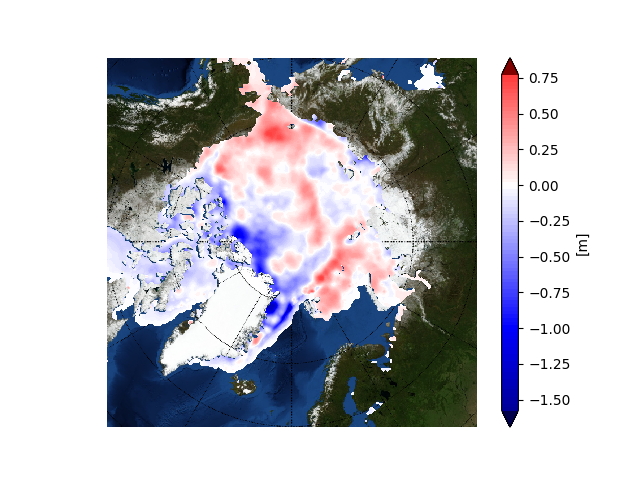
Still thinner than usual in the so called “last ice area” north of Greenland and Ellesmere Island, and thicker than usual on the Siberian side of the Arctic, particularly in the Chukchi Sea.
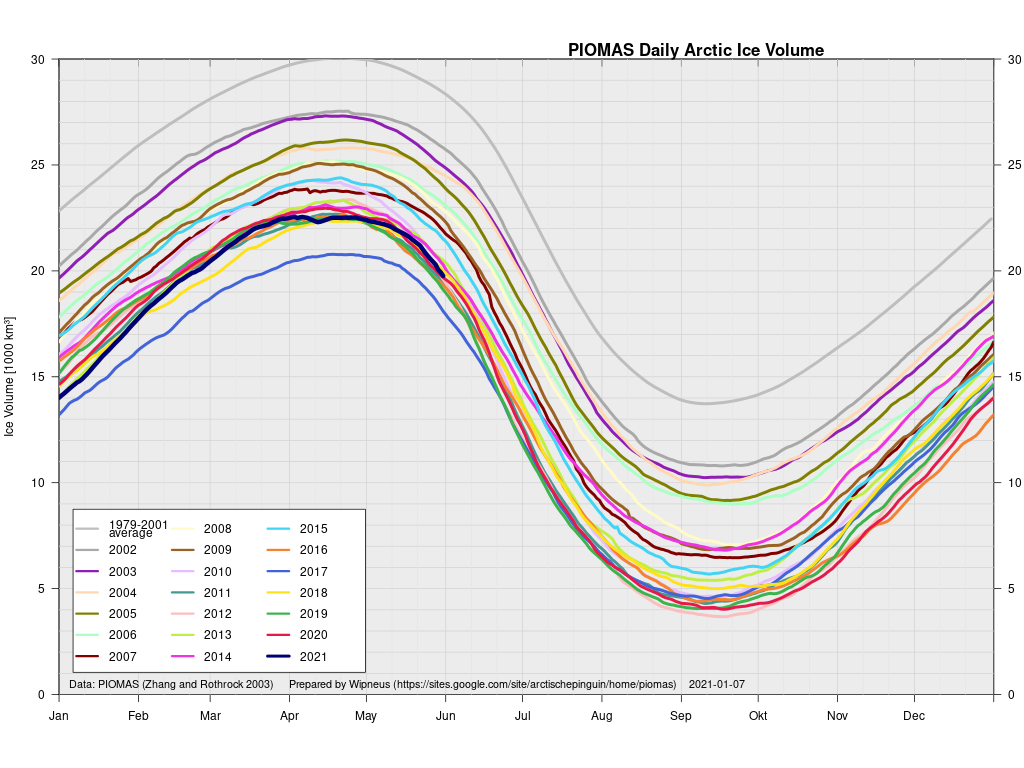
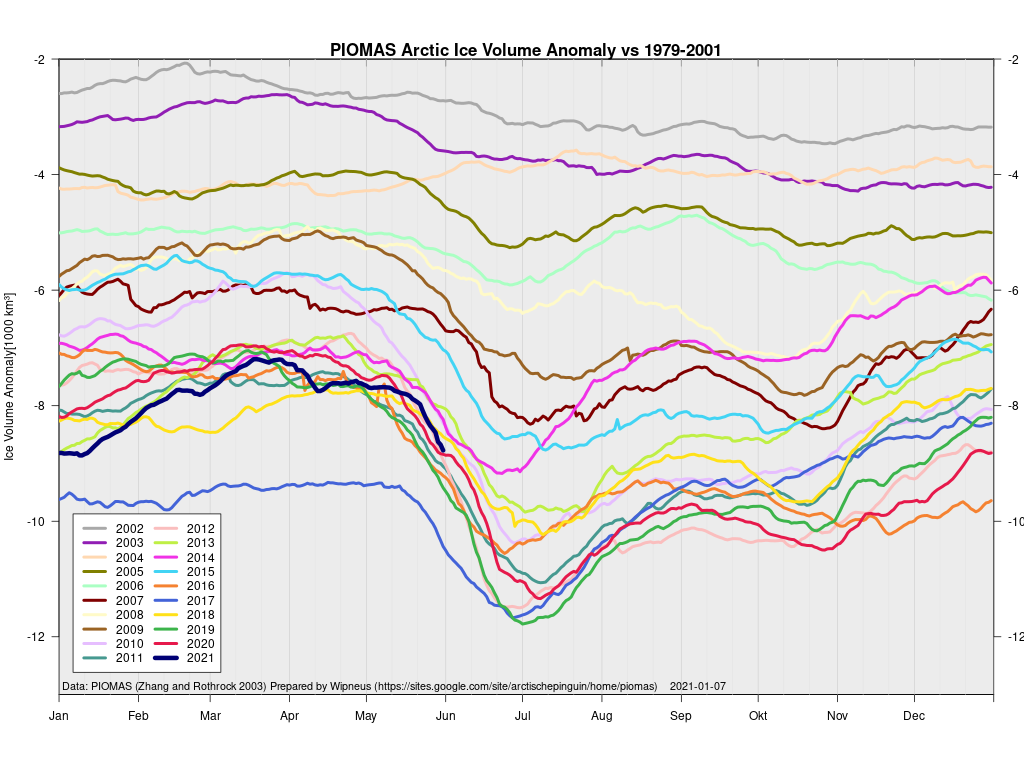
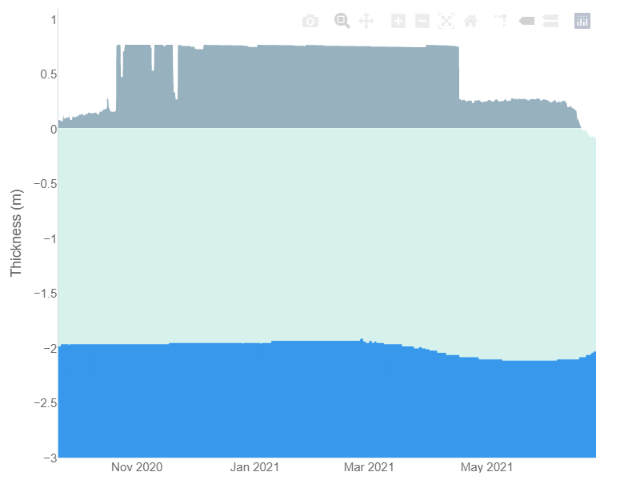
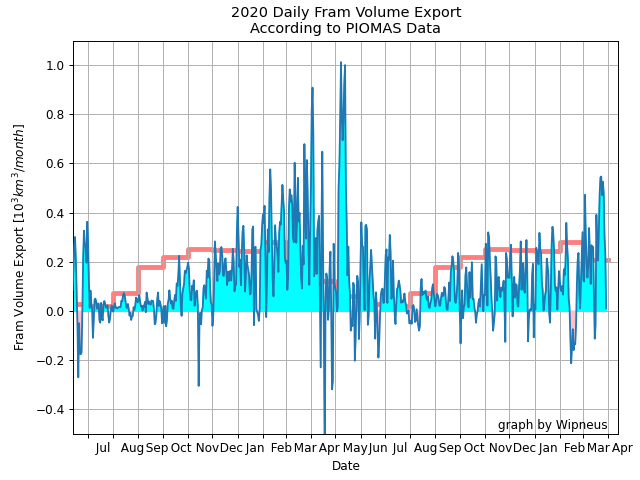
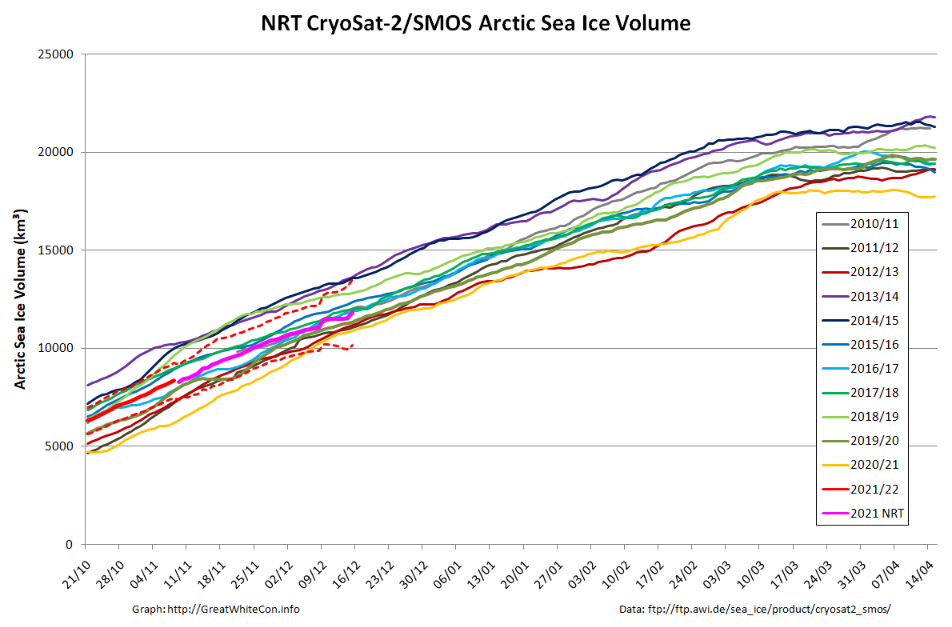
Finally, for the moment at least, here’s the latest CryoSat-2/SMOS volume graph:
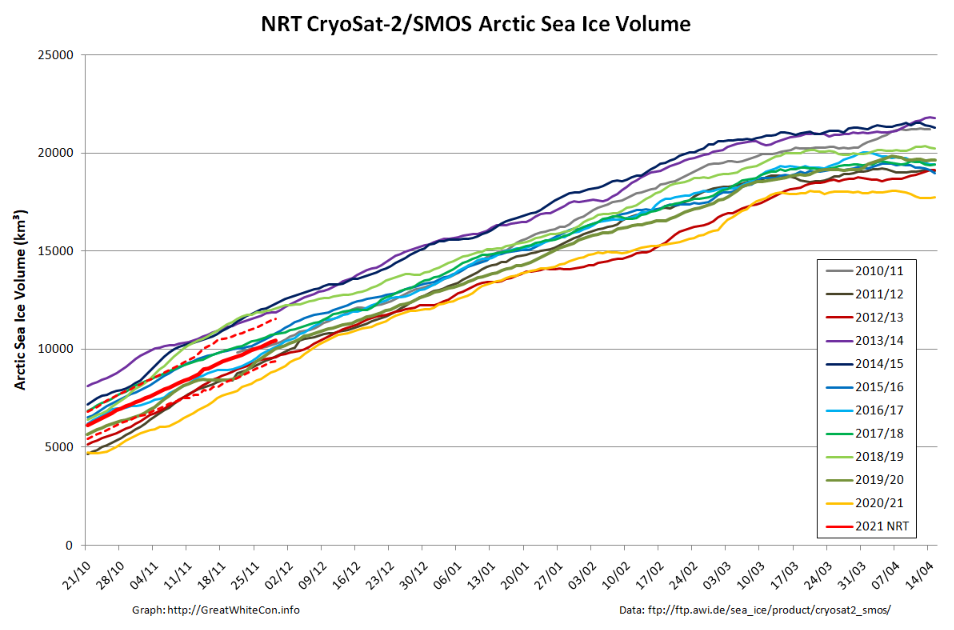
Unlike the previous metrics, this particular one is close to the middle of the pack.
[Edit – December 5th]The National Snow and Ice Data Center issued their latest monthly Arctic Sea Ice News update earlier than usual this month:
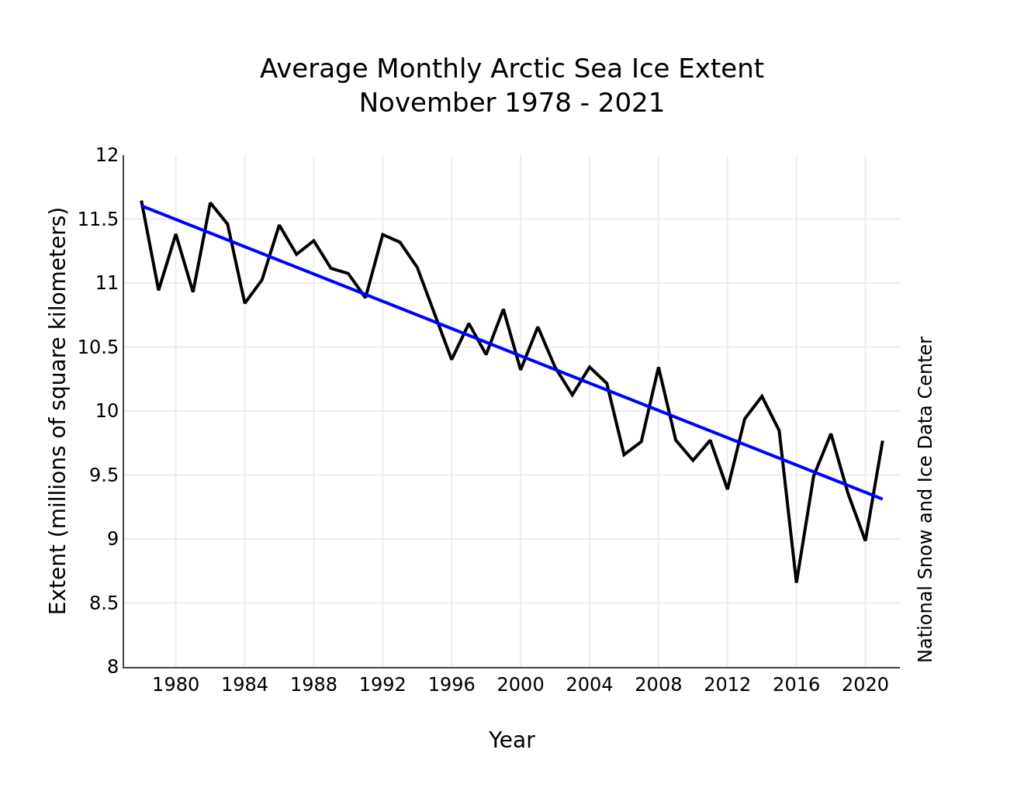
Sea ice extent increased at a faster than average pace through November and by the end of the month, extent was just within the interdecile range. Extent was above average in the Bering Sea, but Hudson Bay remained unusually ice free through the month.
The November 2021 monthly average extent was 9.77 million square kilometers (3.77 million square miles), which ranked tenth lowest in the satellite record. The 2021 extent was 930,000 million square kilometers (359,000 million square miles) below the 1981 to 2010 long-term average. Extent was higher than average in the Bering Sea, but is extremely low in Hudson Bay.
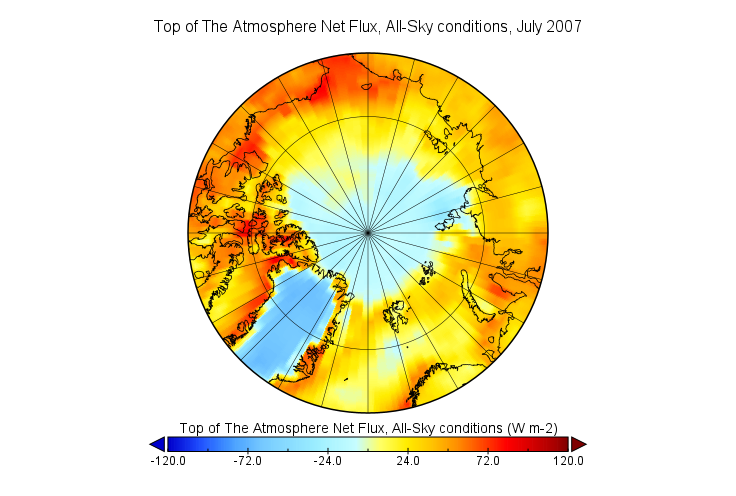
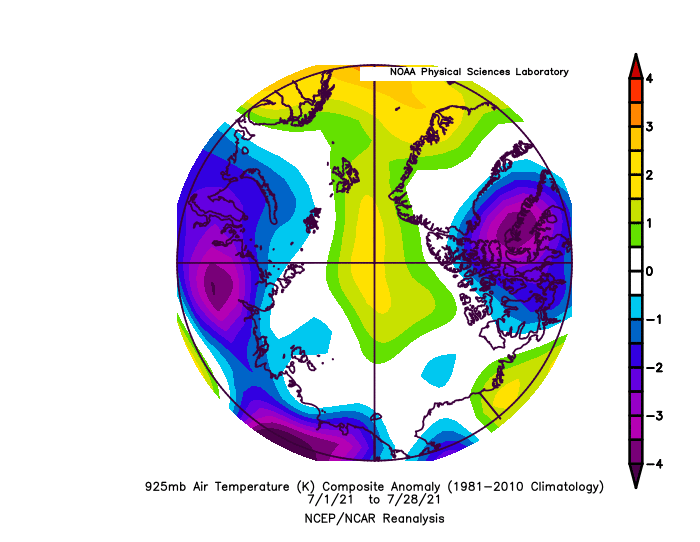
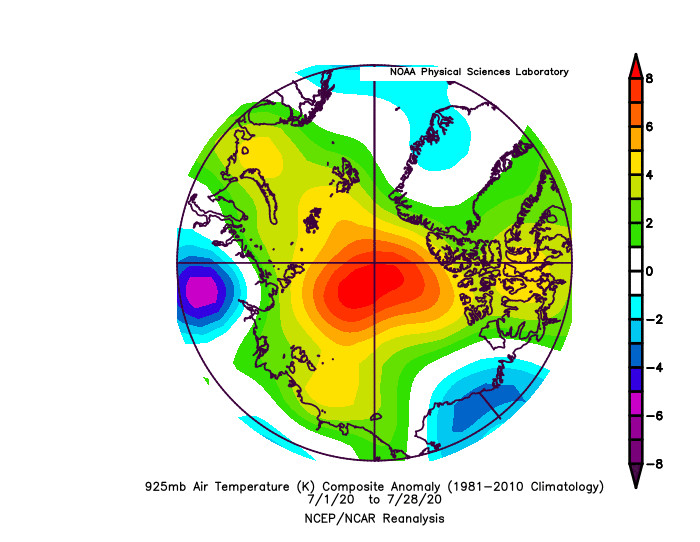
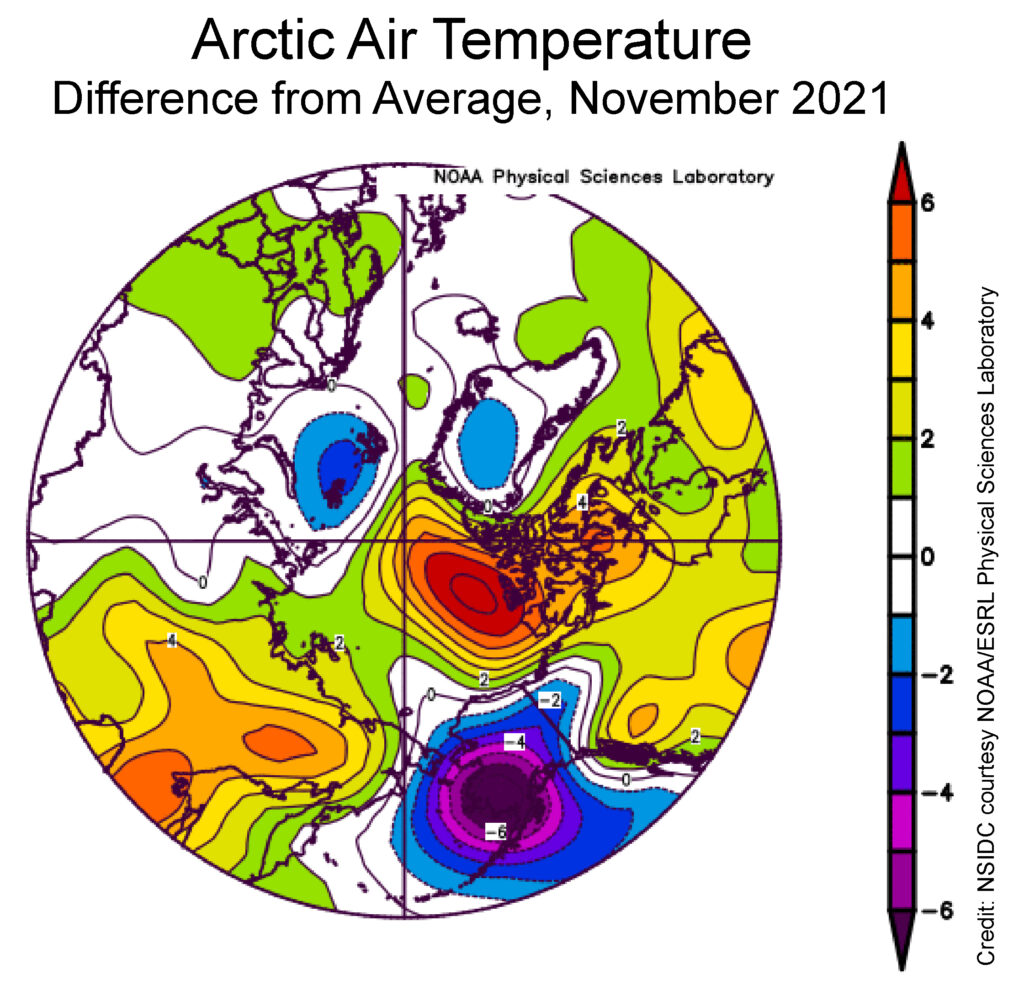
Air temperatures at the 925 millibar level (about 2,500 feet above the surface) were well above average north of the Canadian Archipelago, by as much as 6 degrees Celsius. Conversely, temperatures over southwest Alaska and the eastern sector of the Bering Sea were as much as 6 degrees Celsius below average:
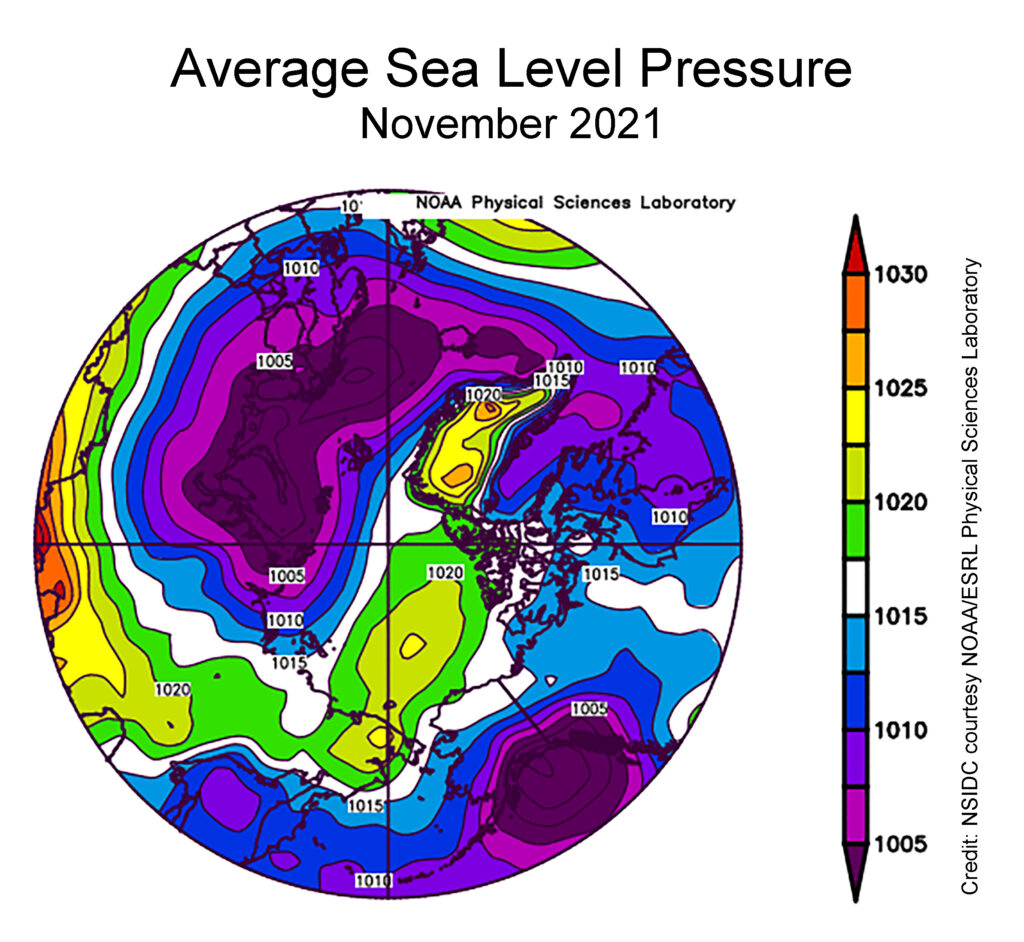
The sea level pressure pattern for November featured widespread low pressure over the Atlantic side of the Arctic and extending into the Barents and Kara Seas, paired with a moderately strong Beaufort Sea High. Strong low pressure over the Gulf of Alaska resulted in a circulation pattern in the eastern Bering Sea that brought cold air from the north. This pattern was favorable for sea ice growth, and can explain the above average ice extent in the region:
Since the start of December high resolution AMSR2 extent has been flatlining:
Sea ice area has even declined slightly over the past few days:

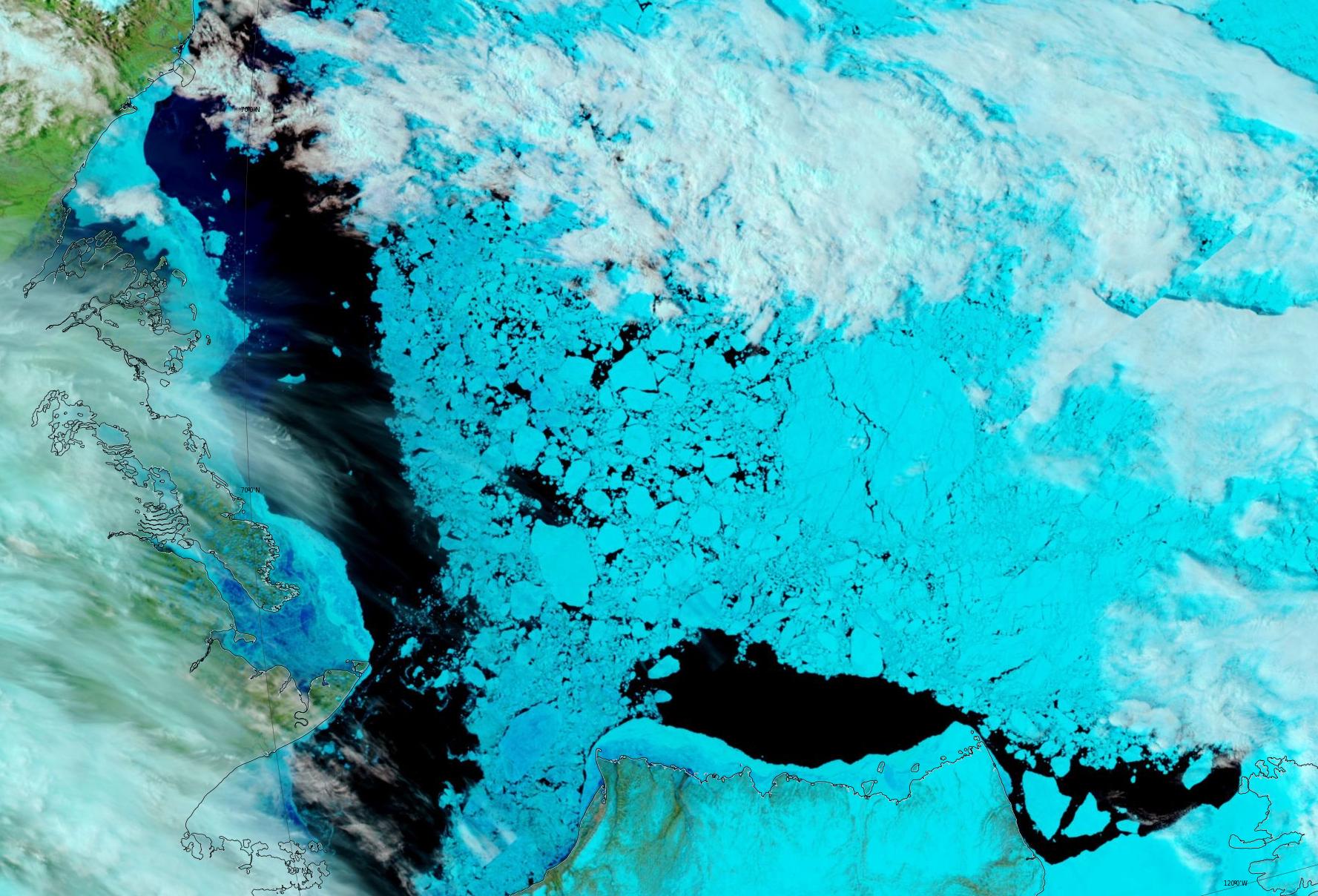
Here too is an animation created by Uniquorn on the Arctic Sea Ice Forum using AWI ASMR2 data to reveal ice movement through the Nares Strait during December:
[Edit – December 9th]The JAXA/ADS/ViSHOP web site is down again, so let’s take another look at high resolution AMSR2 area and extent:
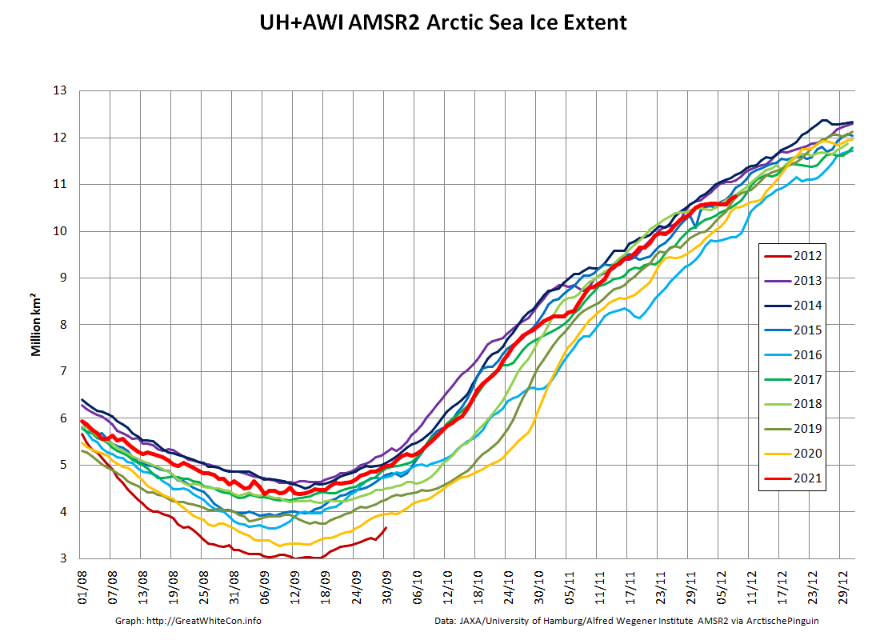
It seems that the “brief hiatus” is over, and extent is now in a “statistical tie” with 2018/19 at 4th lowest for the date amongst recent year.
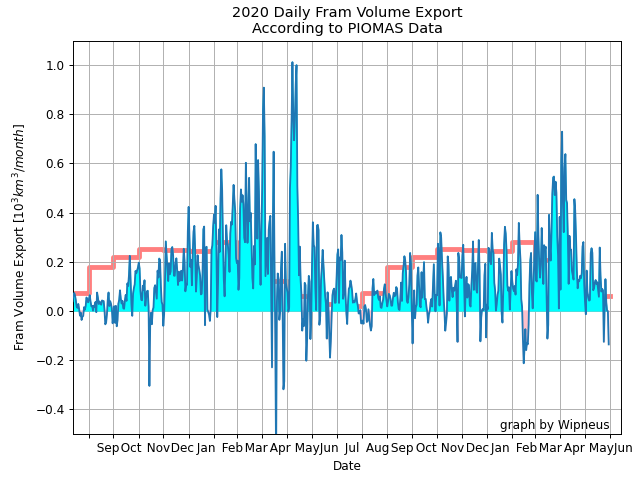
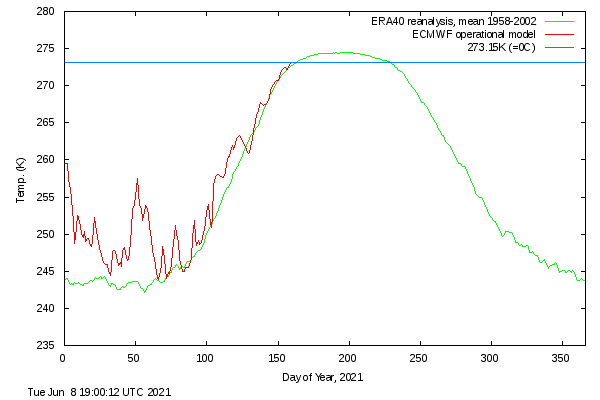
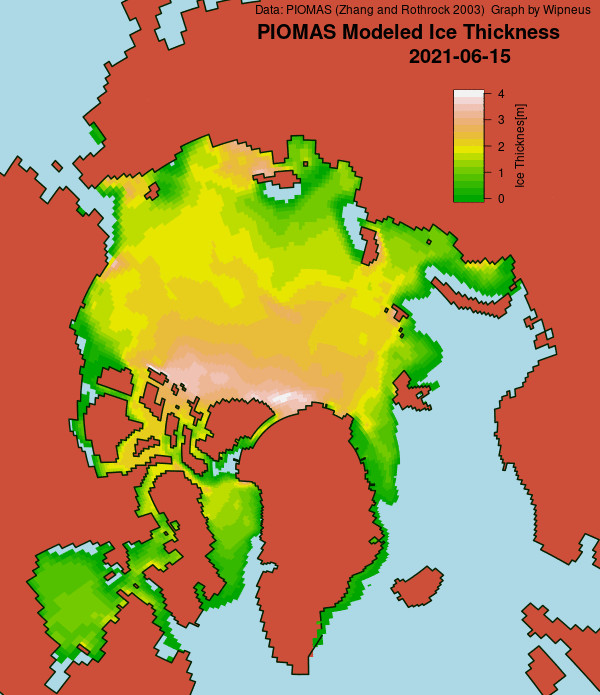
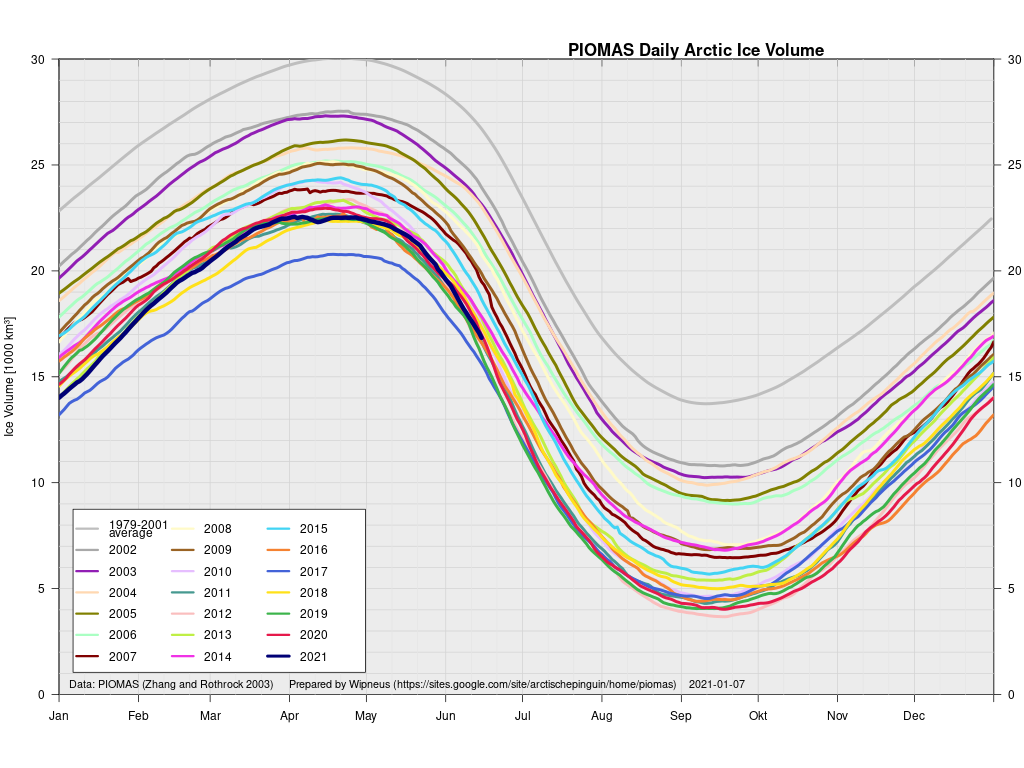
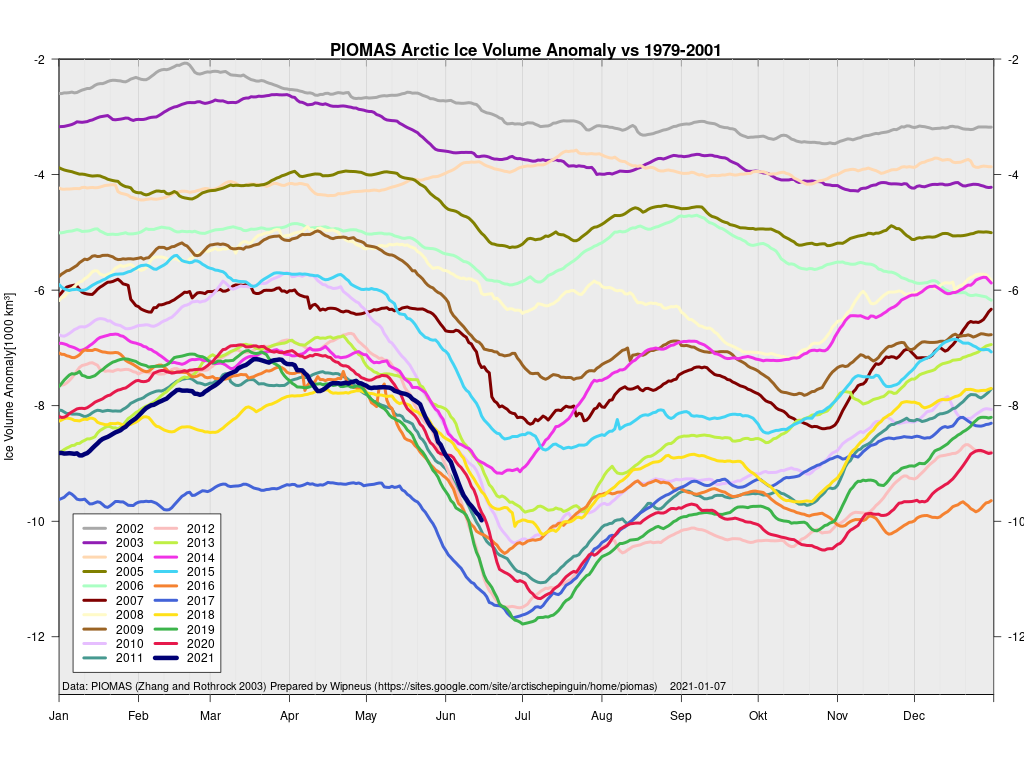
[Edit – December 13th]The PIOMAS Arctic sea ice volume data for November 2021 has been released:
Average Arctic sea ice volume in November 2021 was 7,830 km3. This value is the 7th lowest on record for November, about 1600 km3 above the record set in 2016. Monthly ice volume was 61% below the maximum in 1979 and 45% below the mean value for 1979-2020. Average November 2021 ice volume was about one sigma above the 1979-2020 trend line. October saw relative rapid ice growth for recent years bringing the mean ice thickness (above 15 cm thickness) above the recent low values:
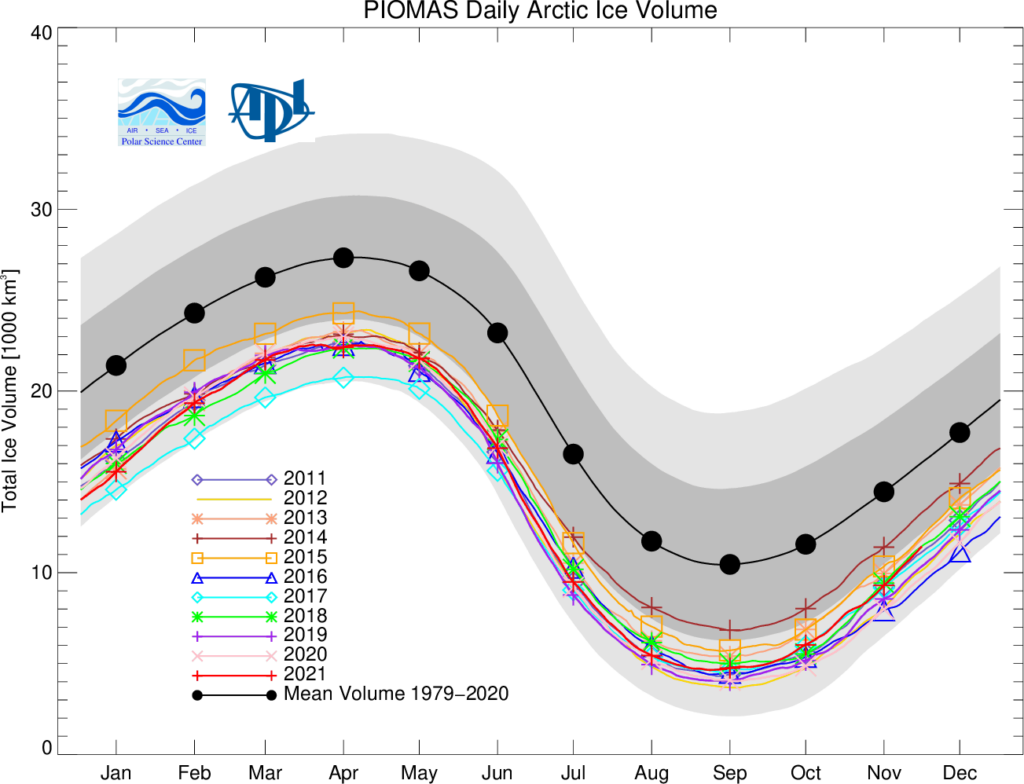
The ice thickness anomaly map for November 2021 relative to 2011-2020 continues to show anomalies divided into positive and a negative halves with areas of positive anomalies increasing since the two prior months. Negative anomalies stretching from North of Greenland and along the Canadian Archipelago across the Eastern Arctic into the Barents Sea. Areas North of Greenland again feature very low ice thickness as in prior years (see our recent paper). Positive anomalies are notable in the Beaufort and Chukchi seas due to advection of thicker older ice into the areas during the previous winter (See recent paper on this). The Alaskan summer has also been relatively cold contributing to unusually thick ice in this area:
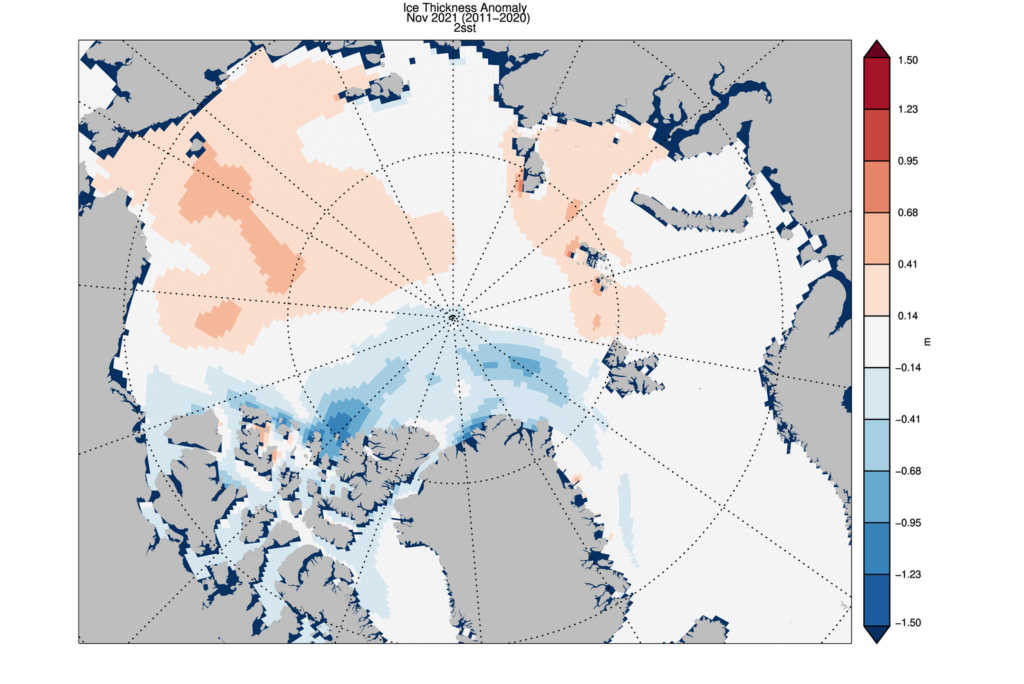
CryoSat-2 ice thickness shows a similar picture sea ice thickness anomalies but with the maxima slightly displaced which maybe due to temporal sampling of the composite:
The JAXA web site is still down, so here’s another set of high resolution AMSR2 graphs:
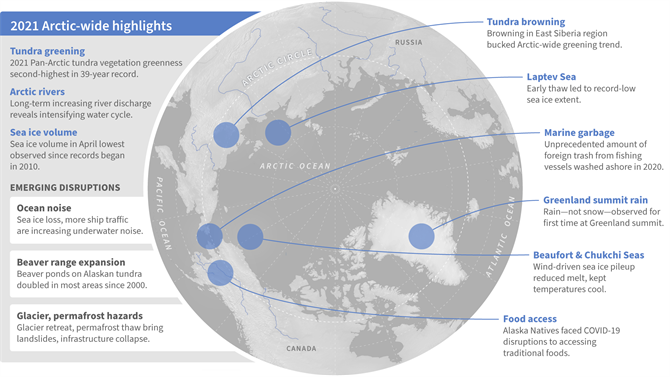
NOAA have just released their 2021 Arctic Report Card. Here’s the introductory video:
and here is the report itself:
Ice hardened LNG tanker Vladimir Vize is about to enter the Vilkitsky Strait on the Northern Sea Route:
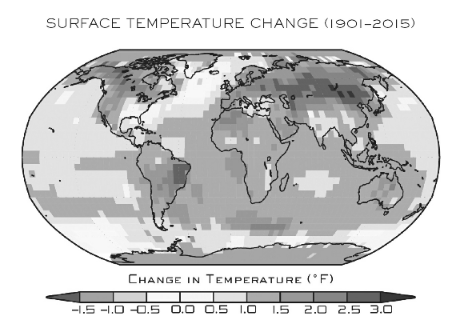
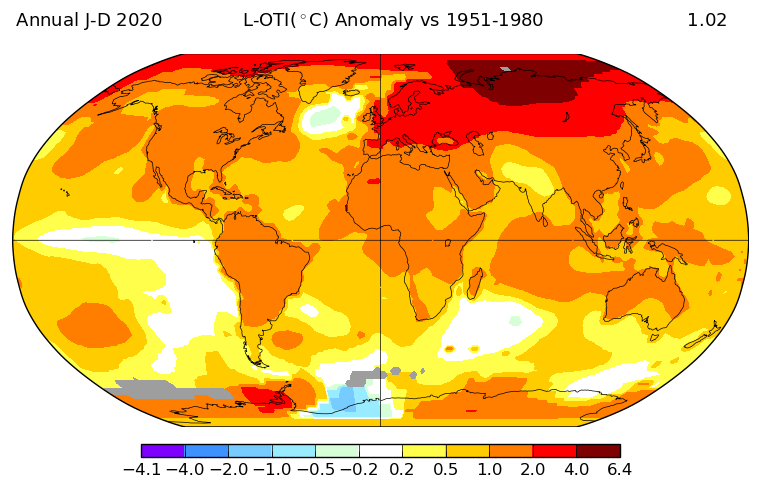
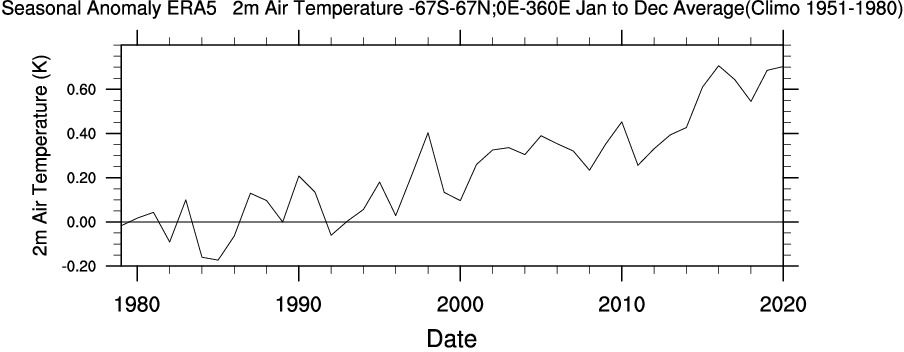
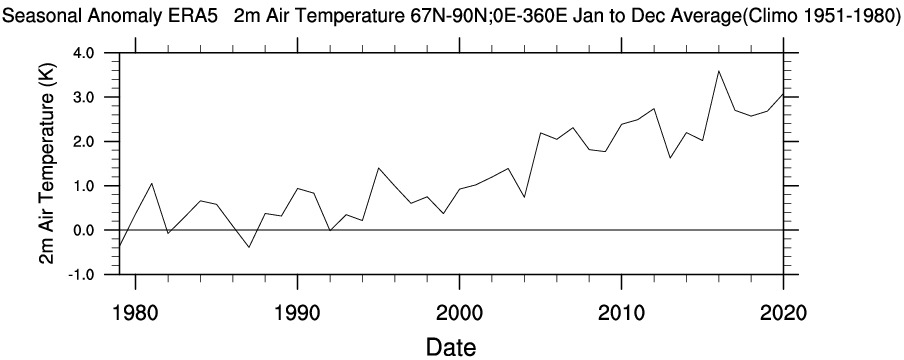
Meanwhile Science.org reports that “The Arctic is warming four times faster than the rest of the world“:
[Edit – December 23rd]“Everybody knows [the Arctic] is a canary when it comes to climate change,” says Peter Jacobs, a climate scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, who presented the work on 13 December at a meeting of the American Geophysical Union. “Yet we’re misreporting it by a factor of two. Which is just bananas.”
Jacob’s co-authors include researchers who oversee several influential global temperature records, and they noted the faster Arctic warming as they prepared to release the global temperature average for 2020. NASA’s internal peer reviewer challenged the higher figure, suggesting the scientific literature didn’t support it. But the researchers have found the four times ratio holds in record sets from both NASA (3.9) and the United Kingdom’s Met Office (4.1), and they hope to soon include the Berkeley Earth record. (Their work also has company: In July, a team at the Finnish Meteorological Institute posted a preprint also arguing for the four times figure.)
The researchers found Arctic warming has been underestimated for a couple of reasons. One is climate scientists’ tendency to chop each hemisphere into thirds and label the area above 60°N as the “Arctic”—an area that would include, for example, most of Scandinavia. But the true definition of the Arctic is defined by Earth’s tilt. And, as has been known for centuries, the Arctic Circle is a line starting at 66.6°N. When researchers lump in the lower latitudes, “you’re diluting the amount of Arctic warming you’re getting,” Jacobs says. “That is not a trivial thing.”
The other difference is the choice of time periods over which the warming rate is calculated. Jacobs and his colleagues focused on the past 30 years, when a linear warming trend emerged for the Arctic. Analyses that look at longer term trends see less divergence between the Arctic and the world.
Here is the latest CryoSat-2/SMOS volume graph, now including some reanalysed data which seems to have come in slightly higher than the earlier “near real time” numbers:
Plus the AWI thickness map:
Further discussion of the divergence between volume and extent continues in the new New Year 2022 thread: