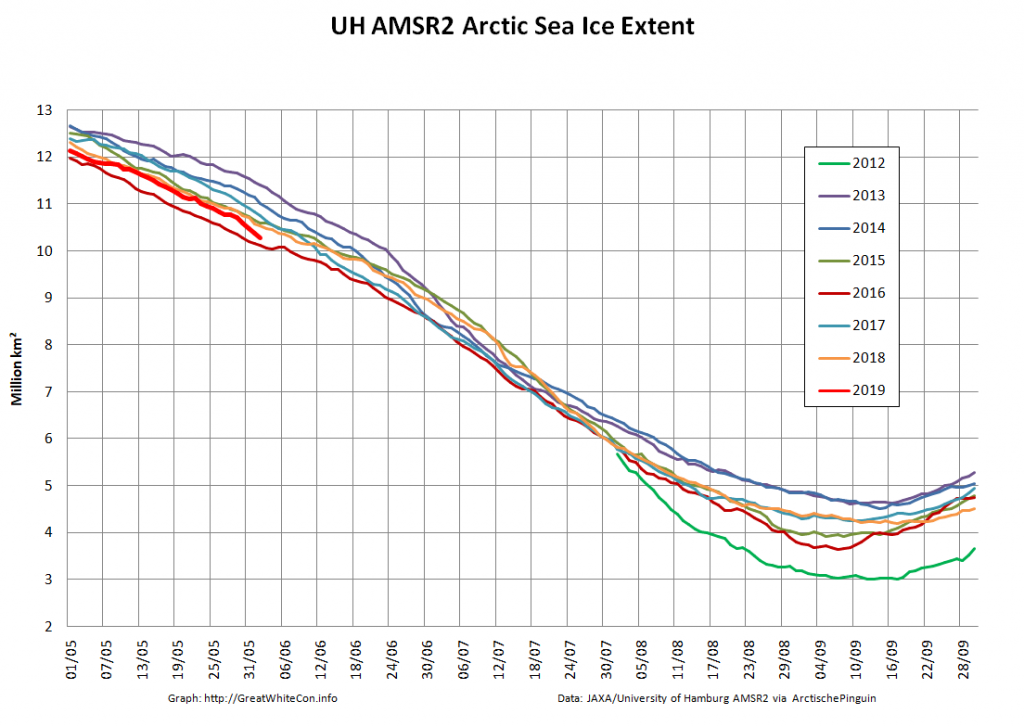
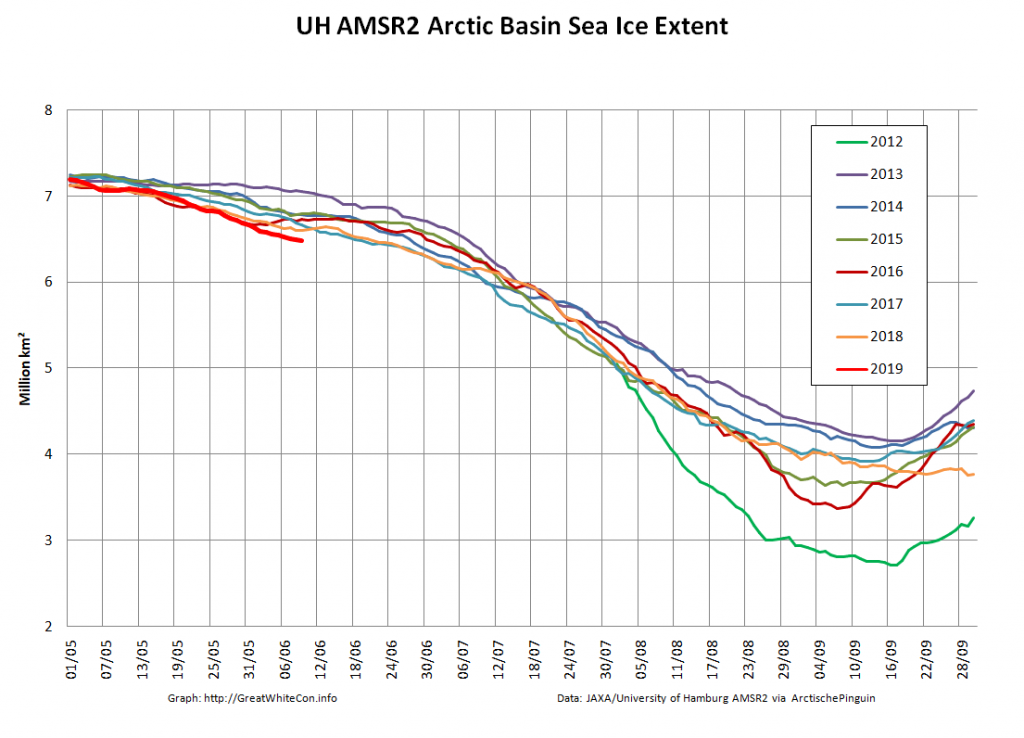
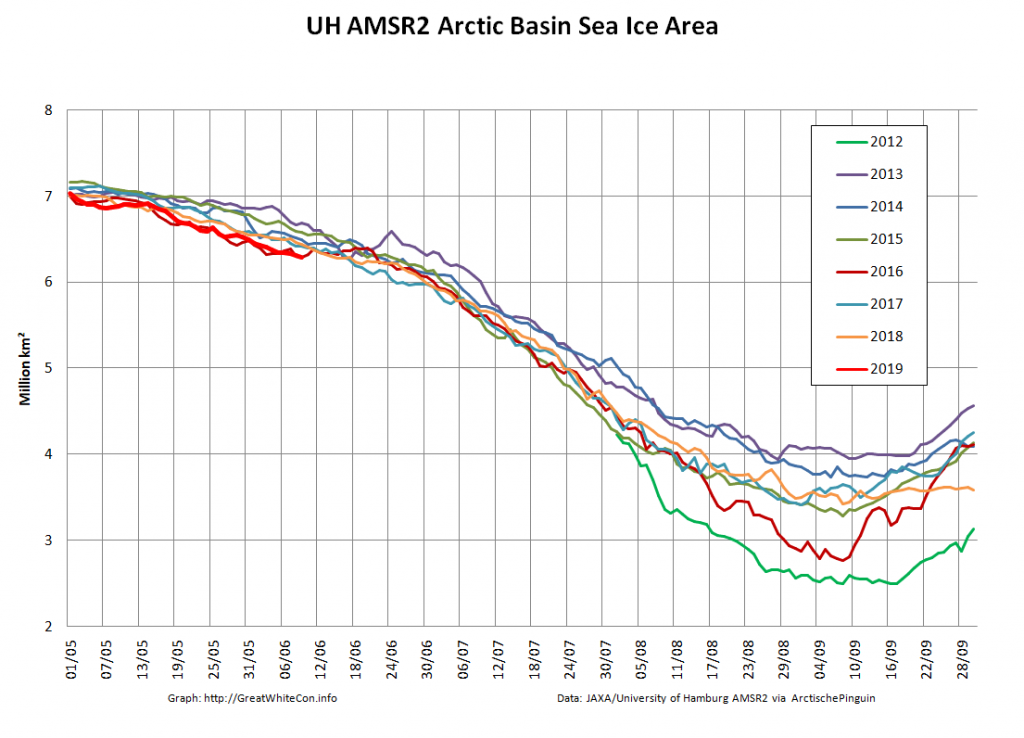
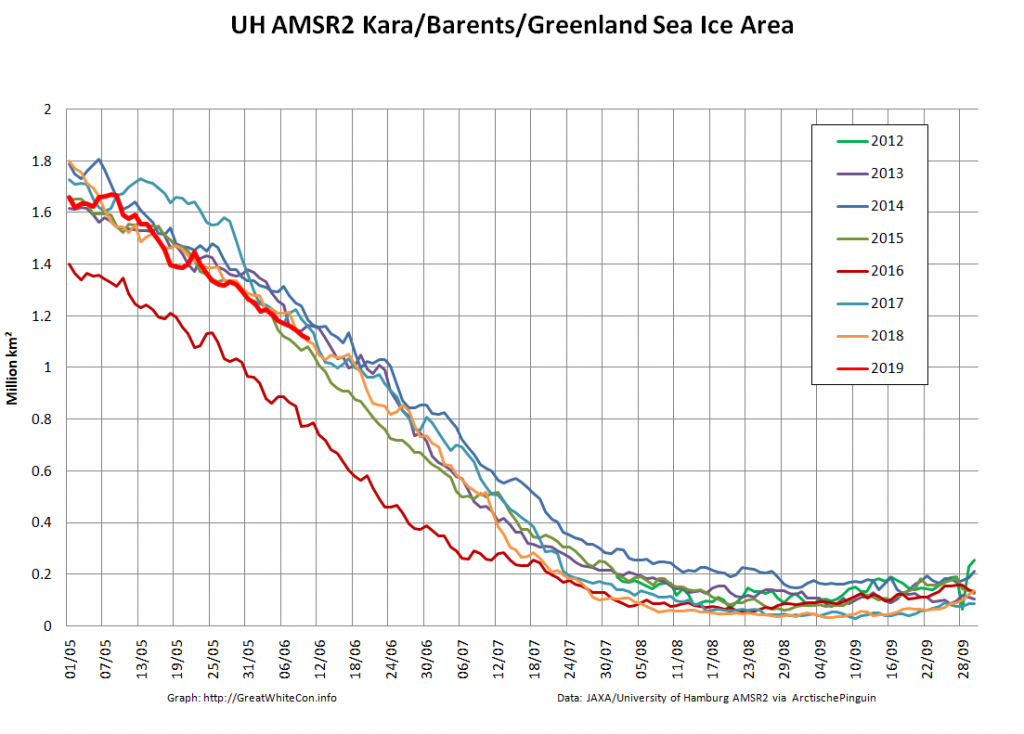
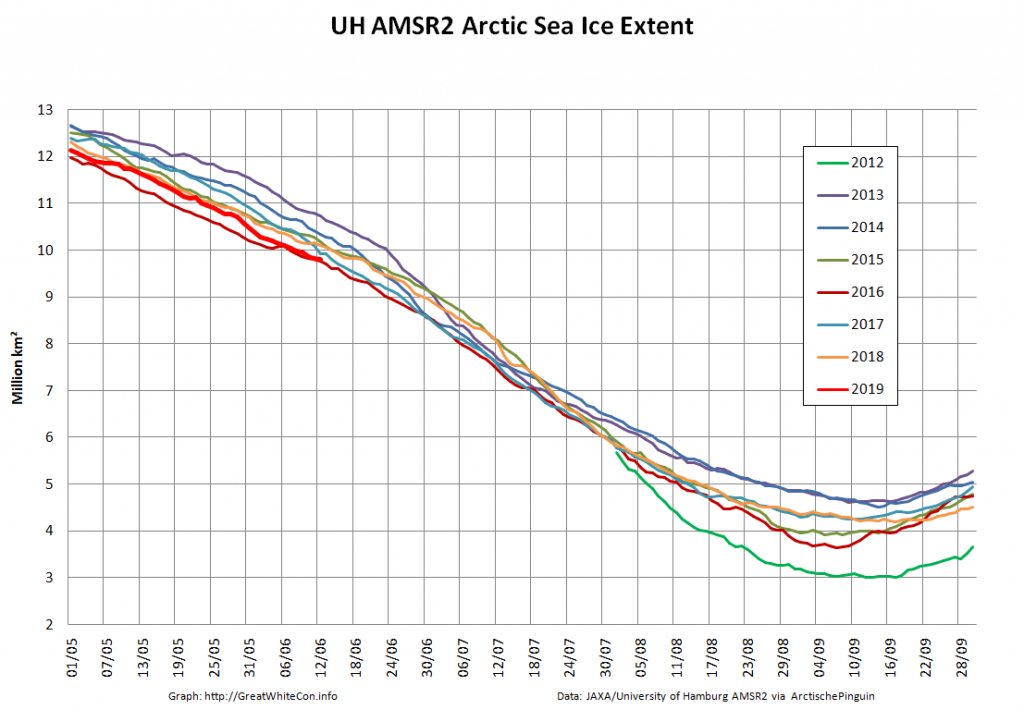
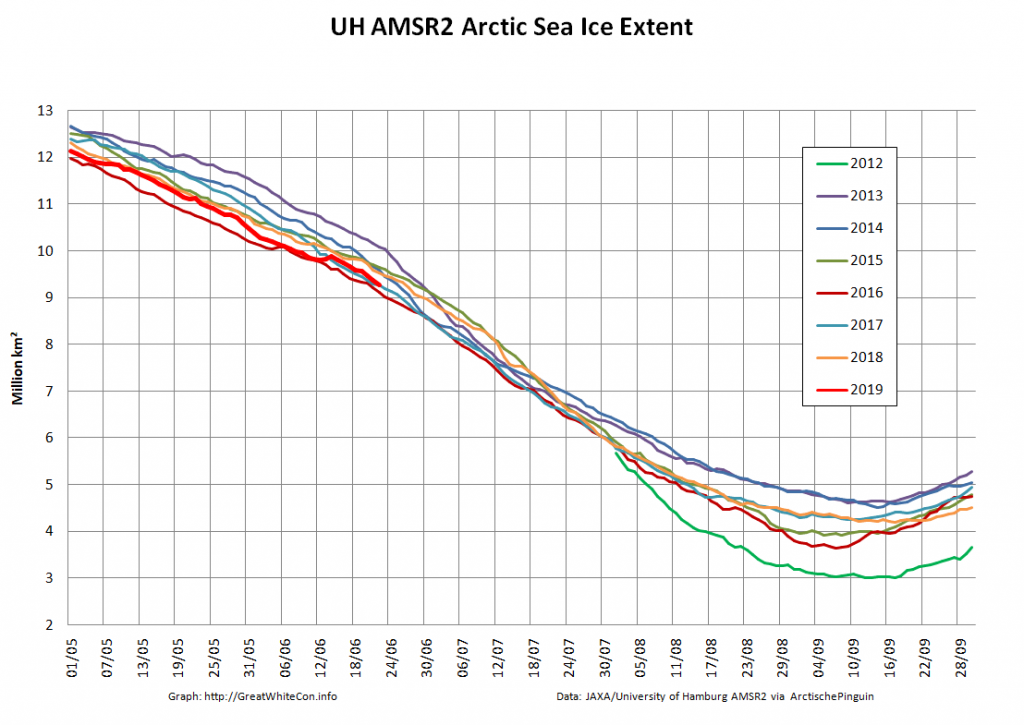
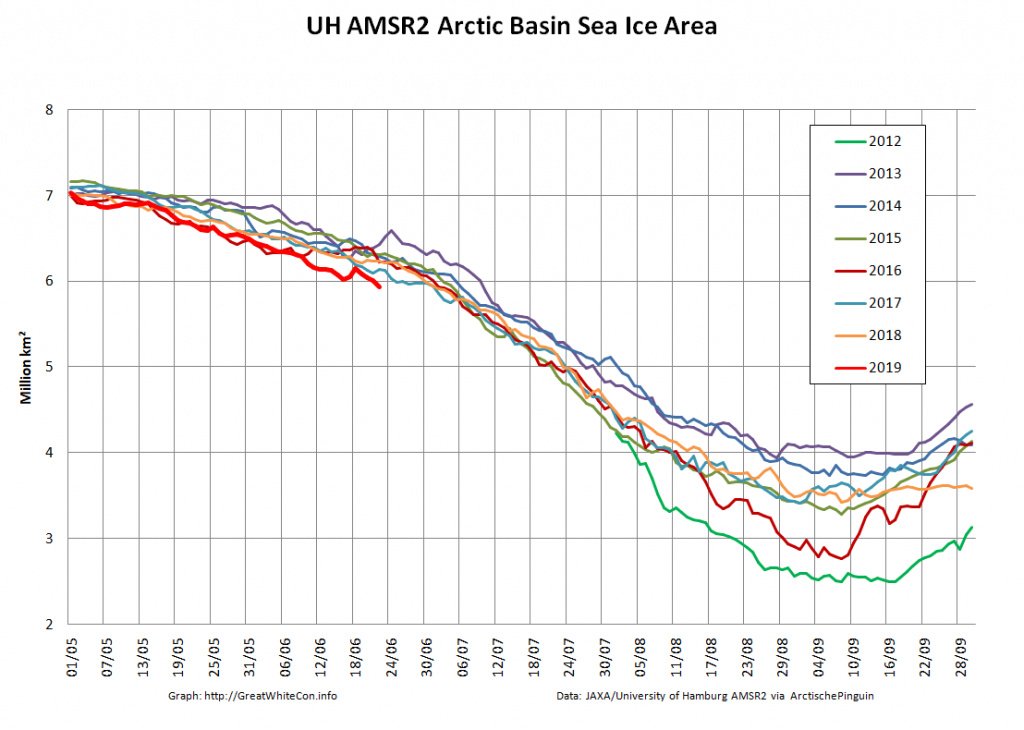
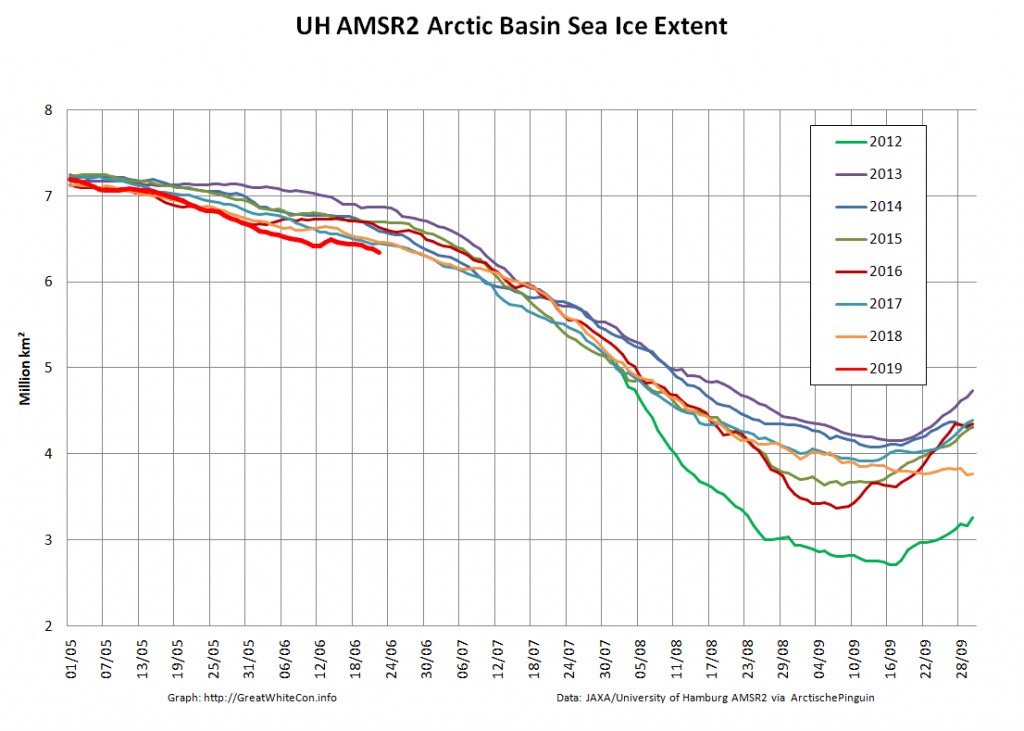
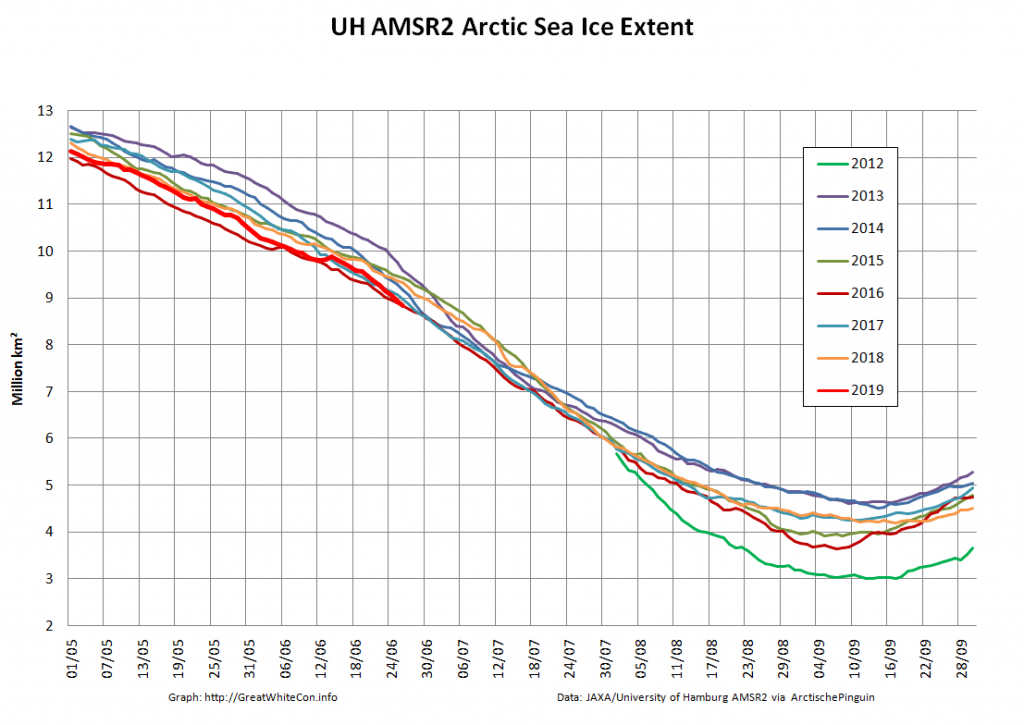
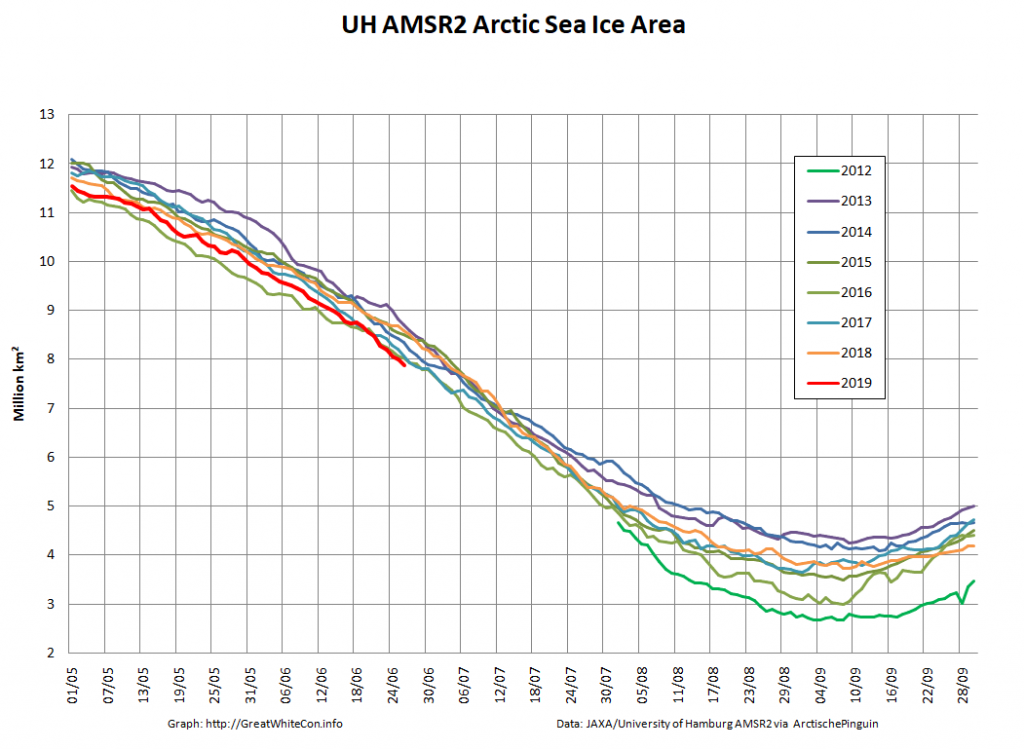
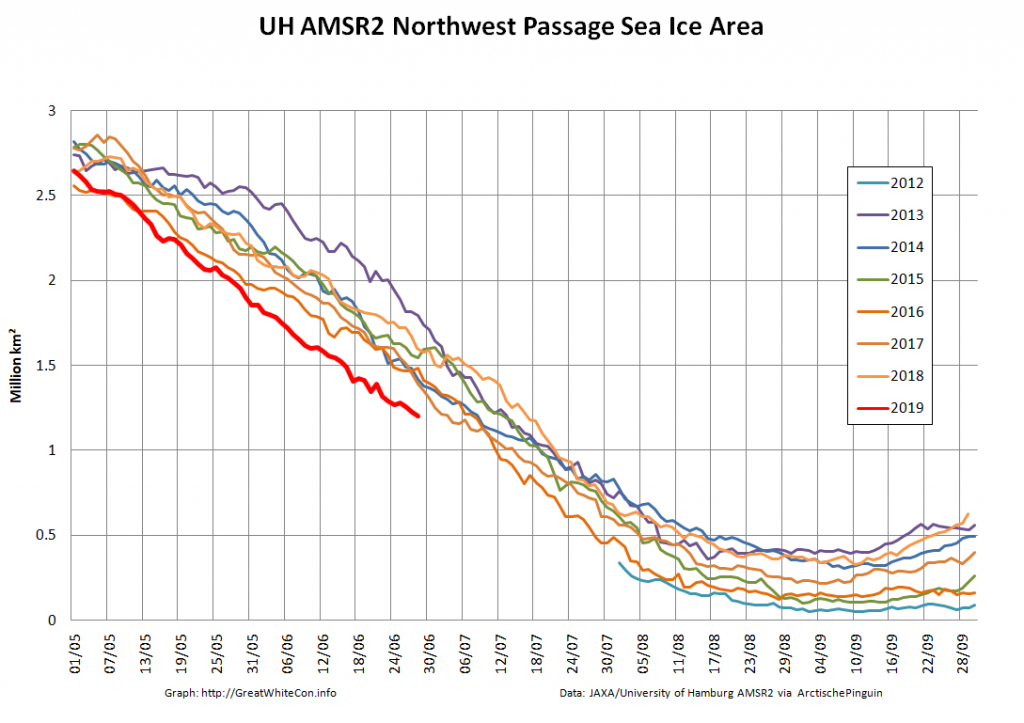
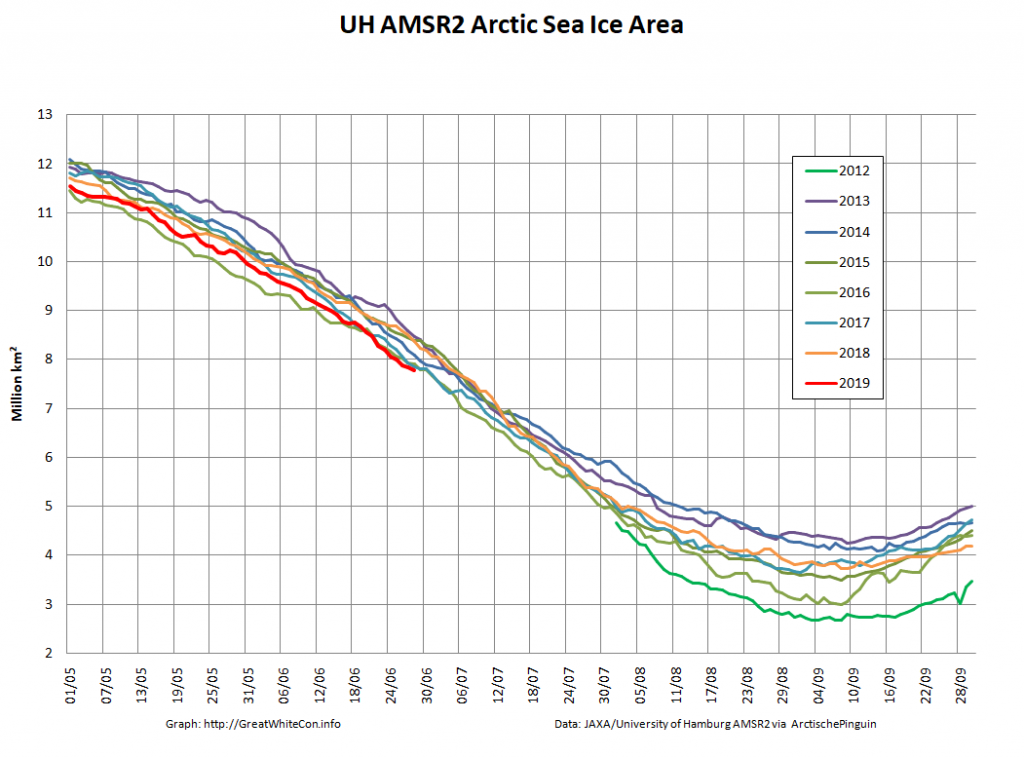
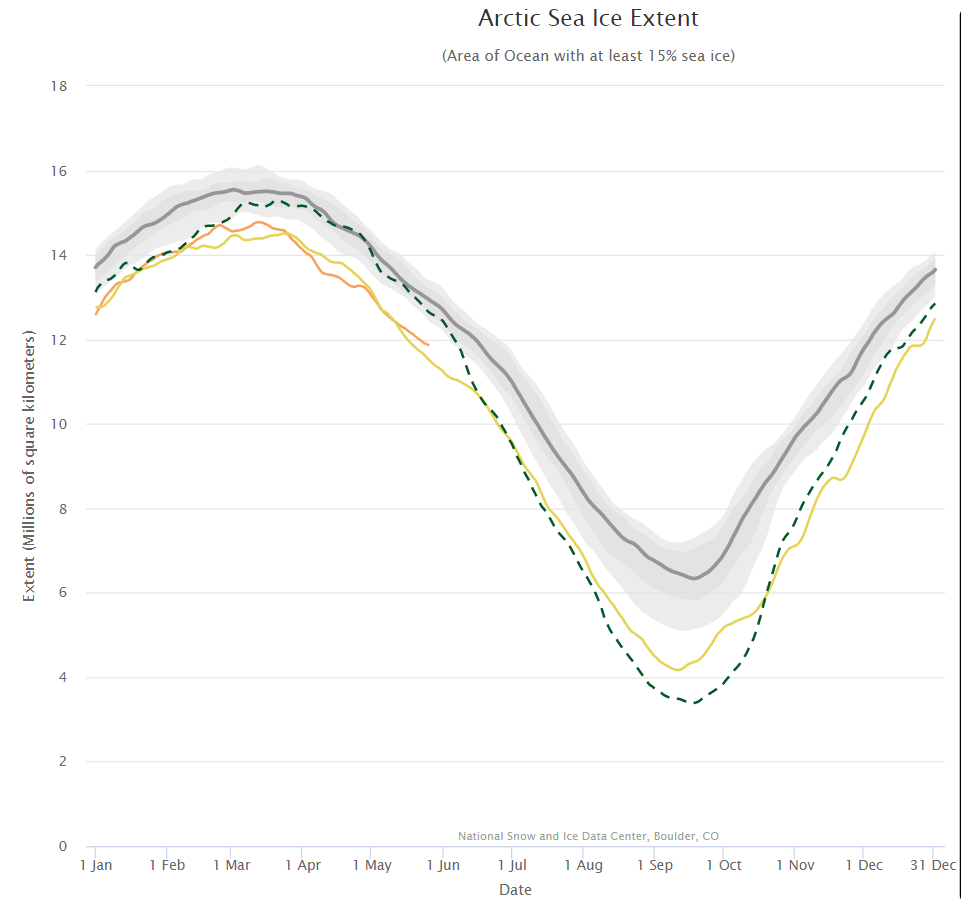
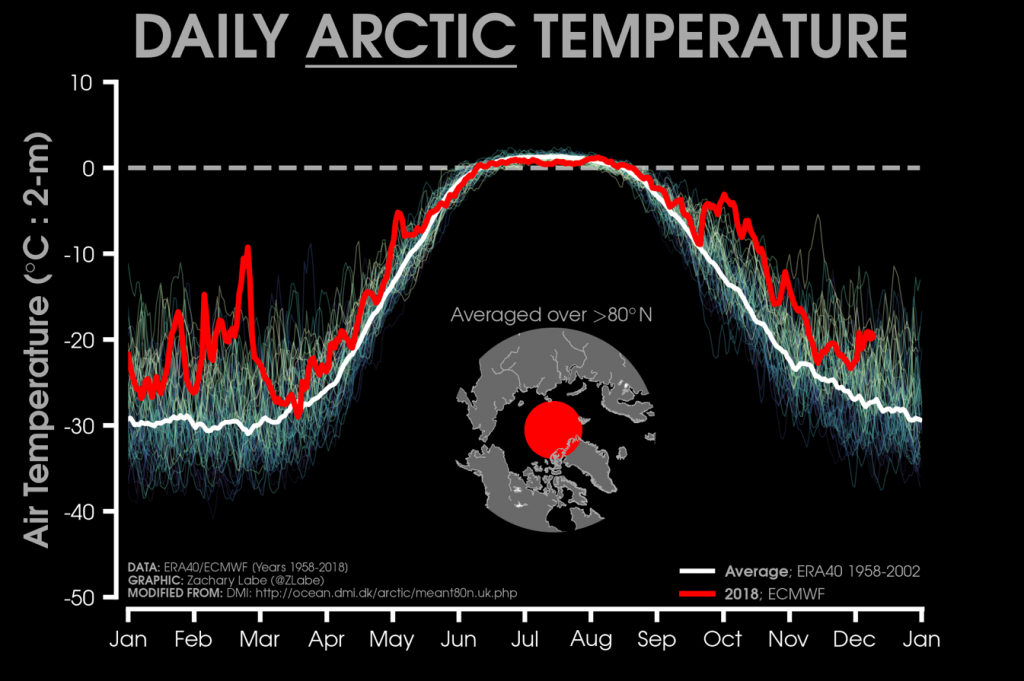
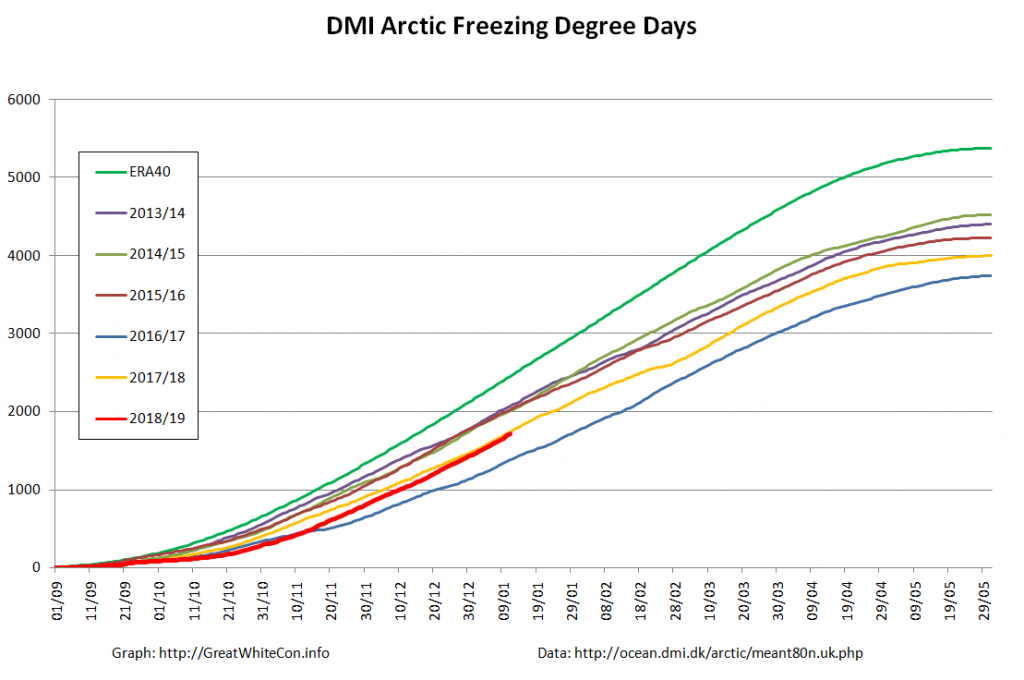
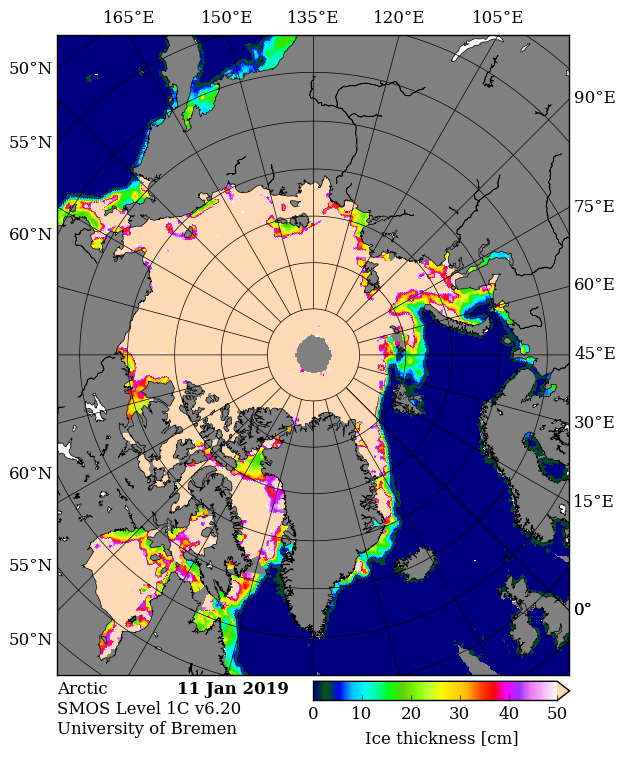
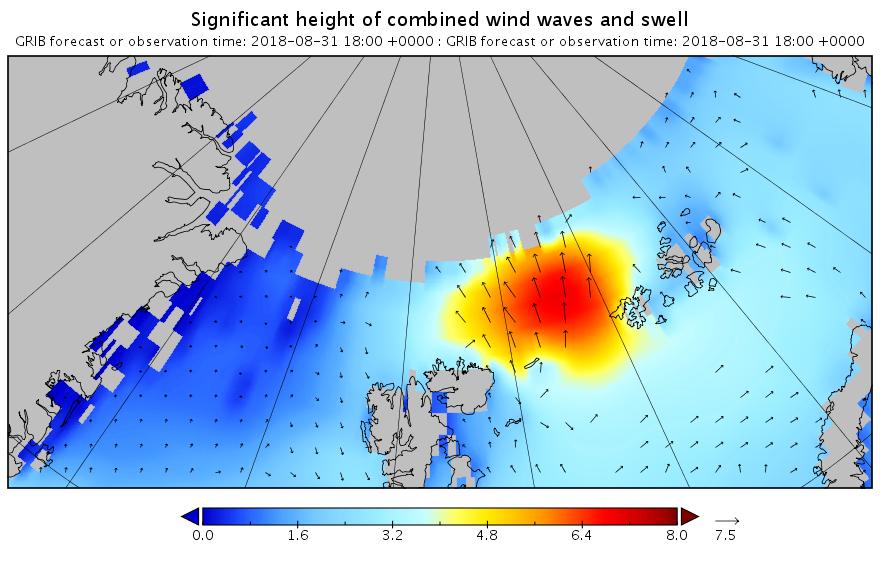
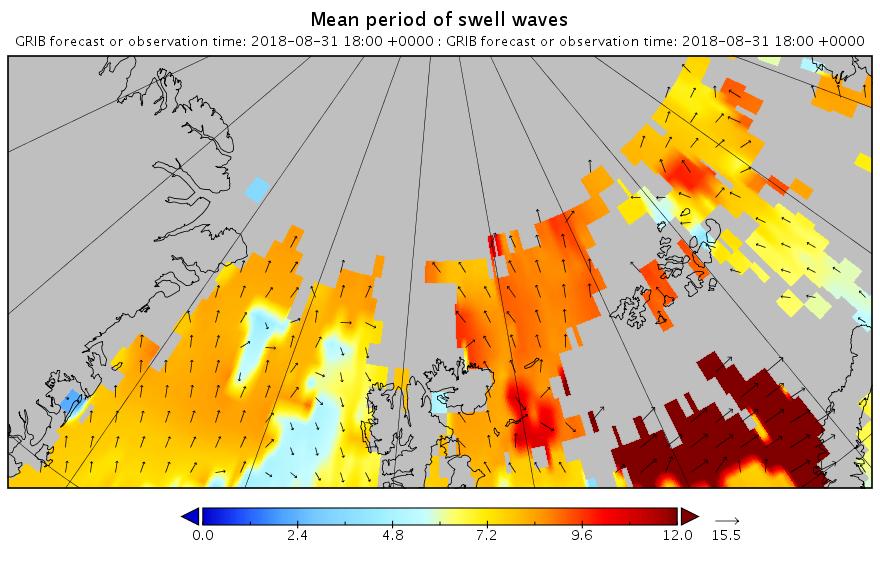
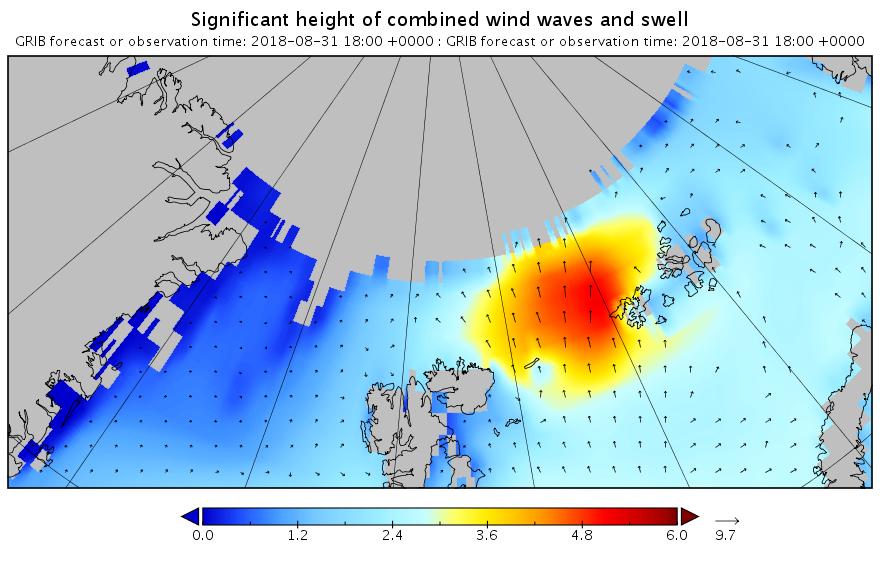
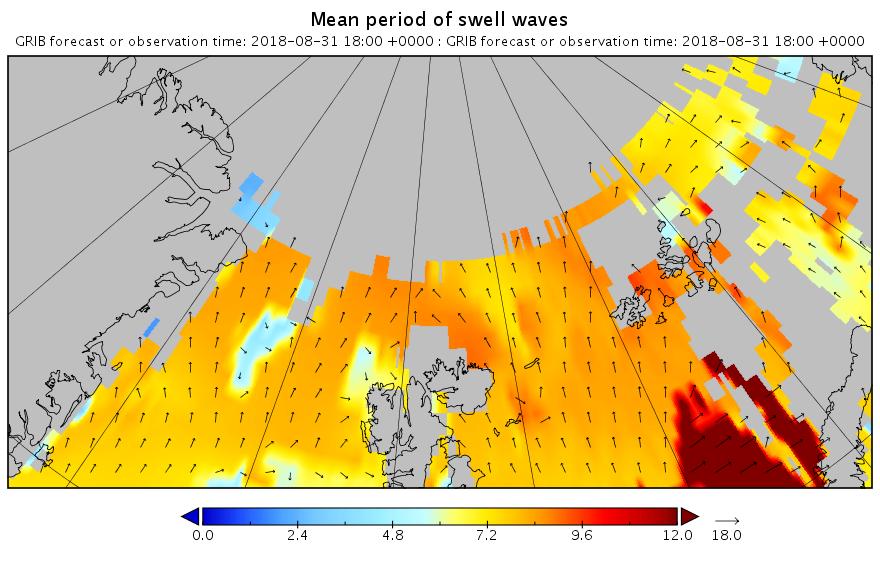
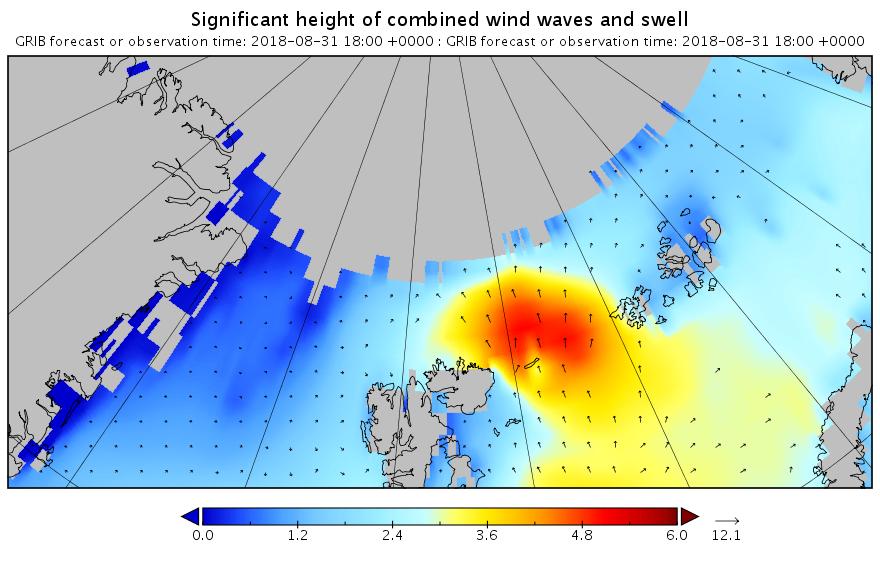
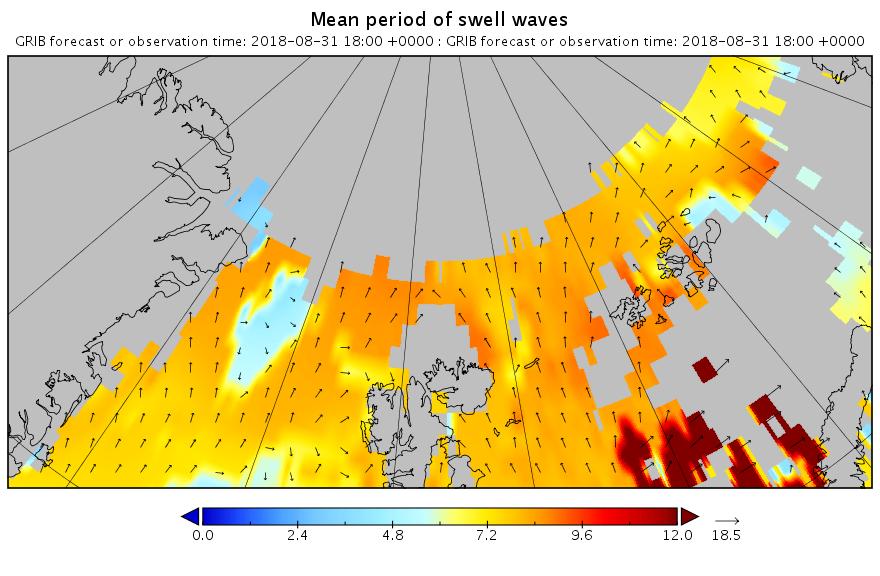
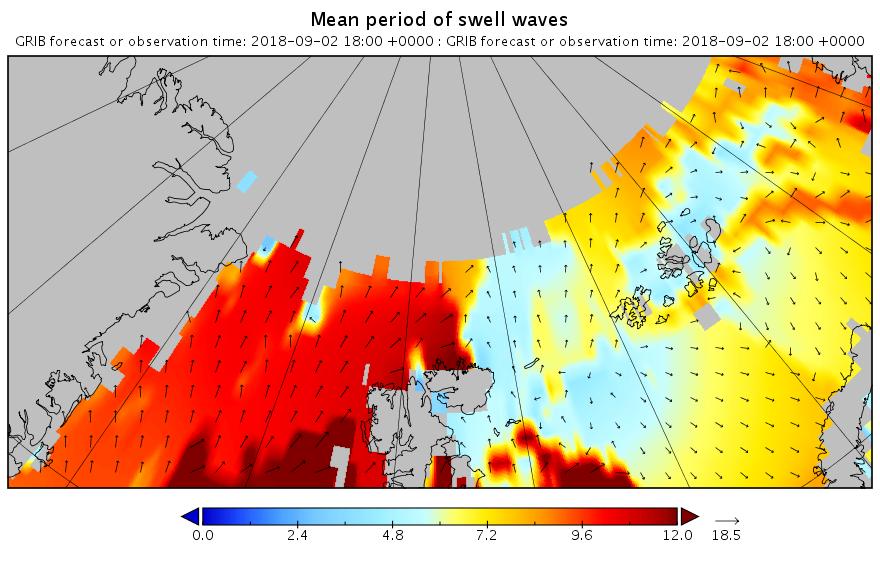
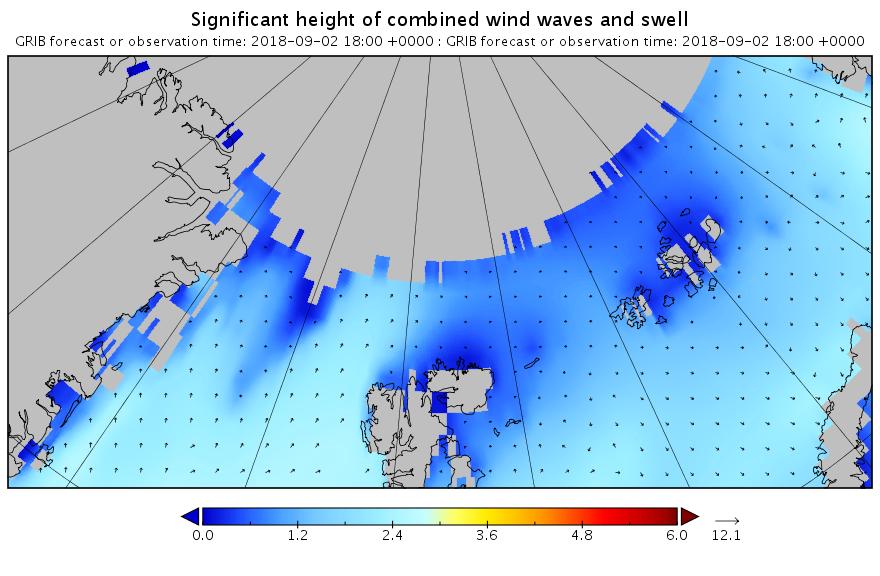
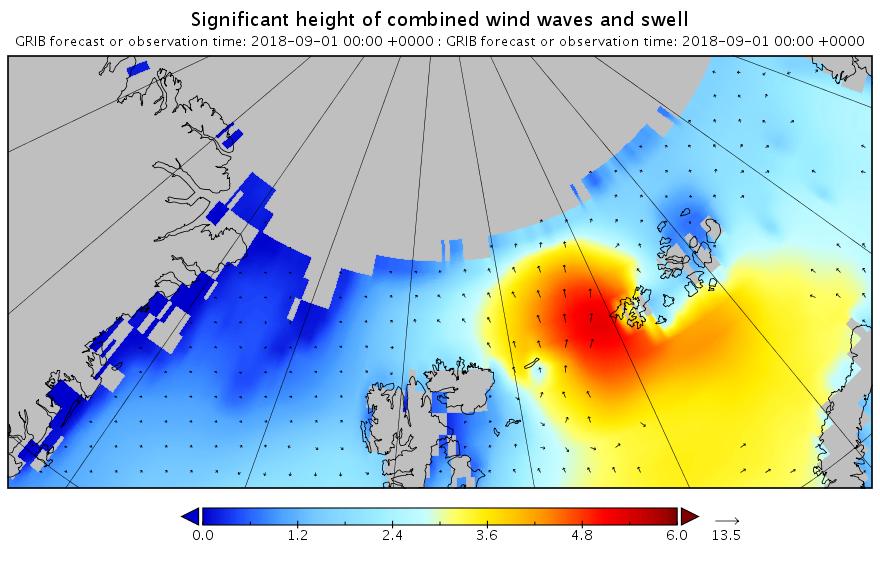
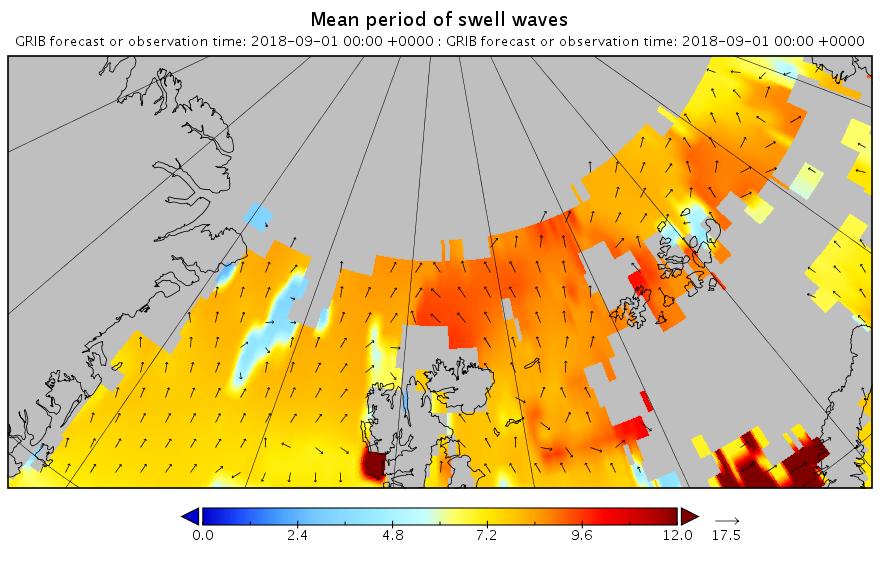
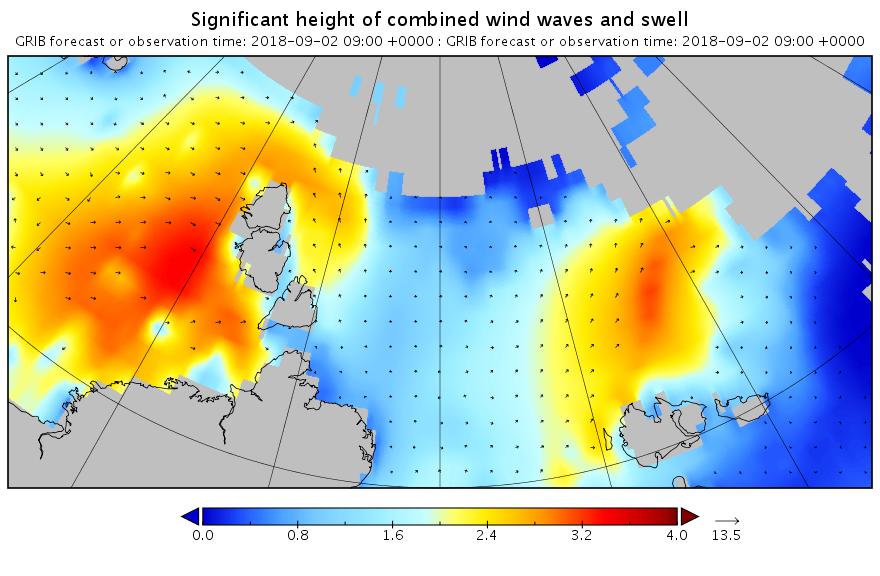
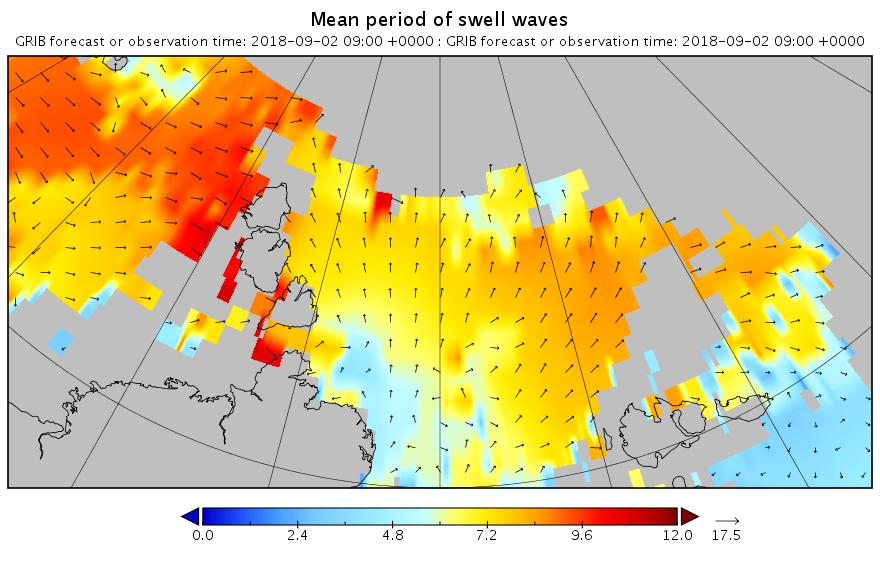
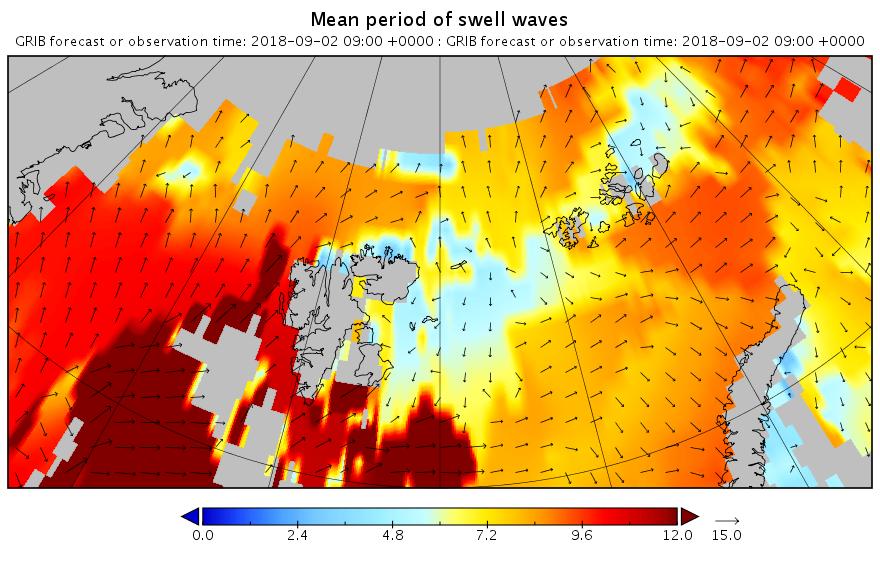
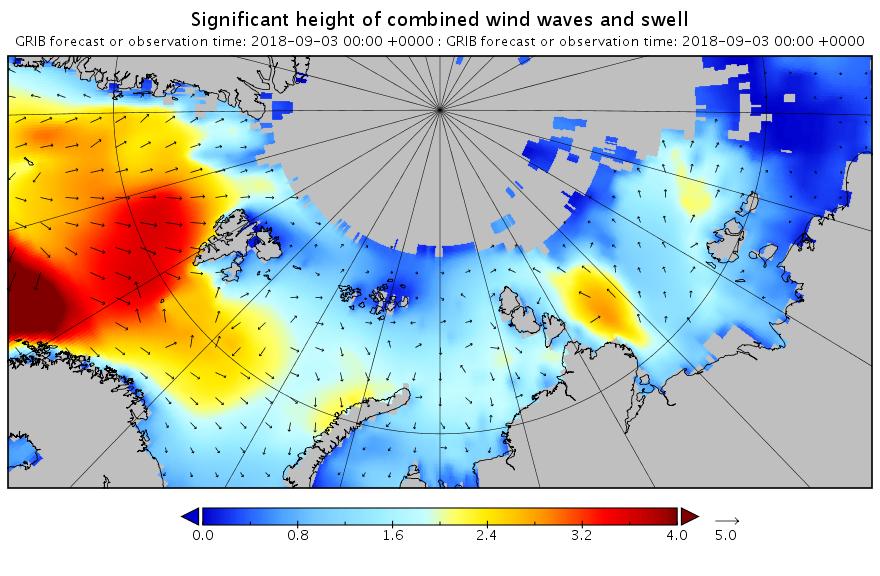
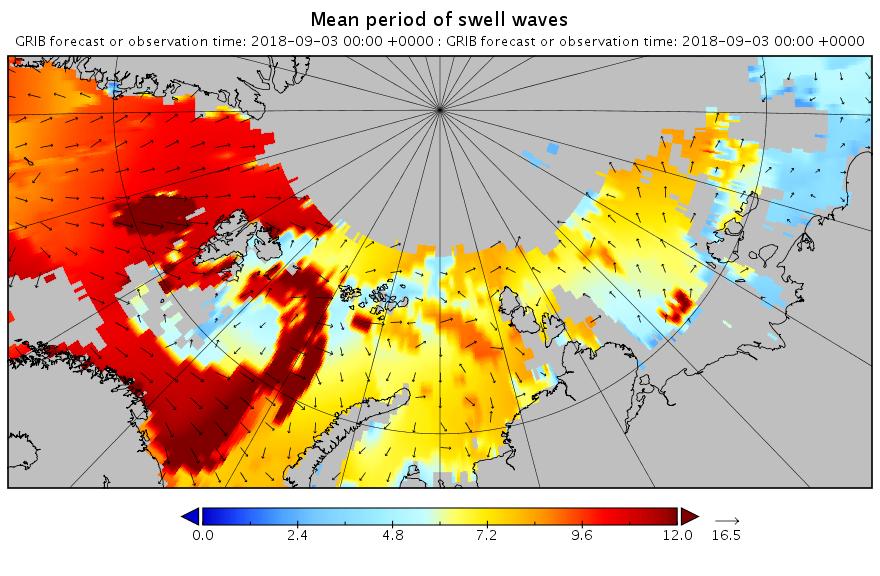
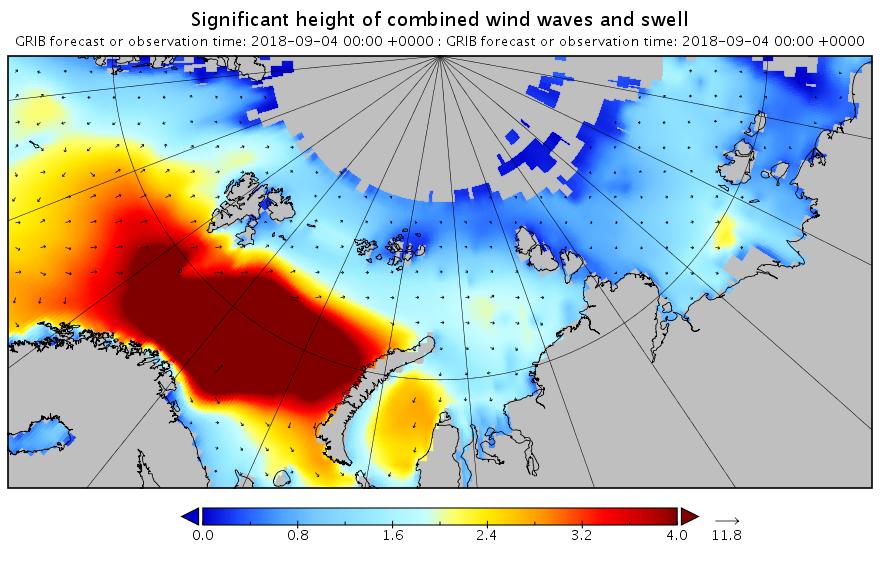
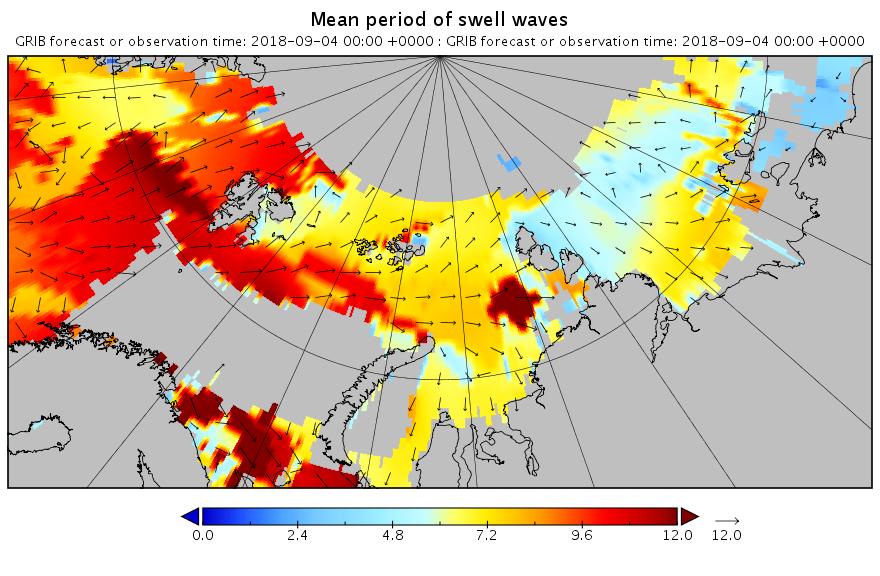
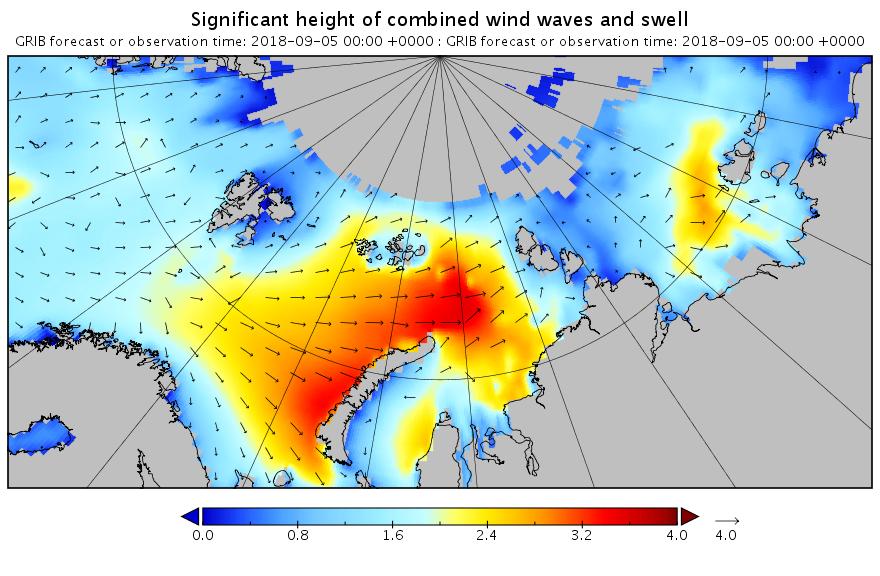
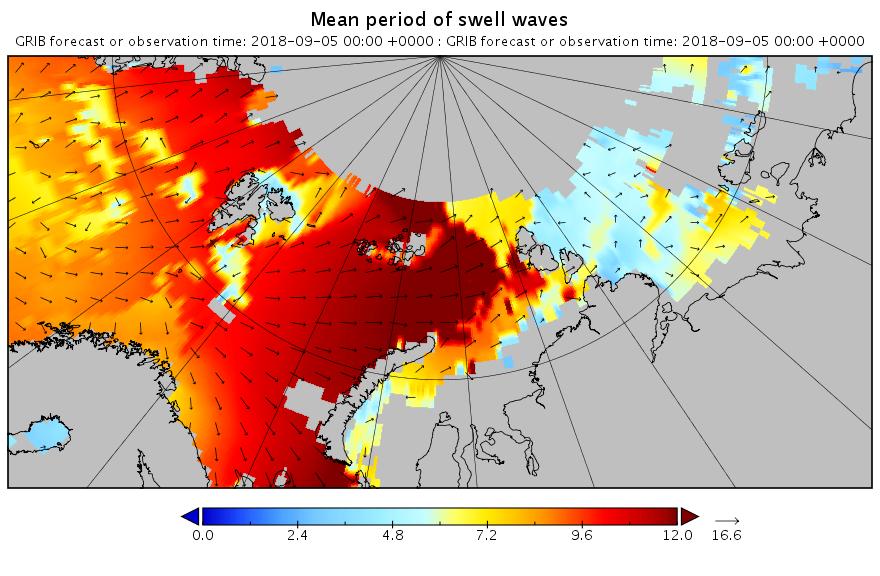
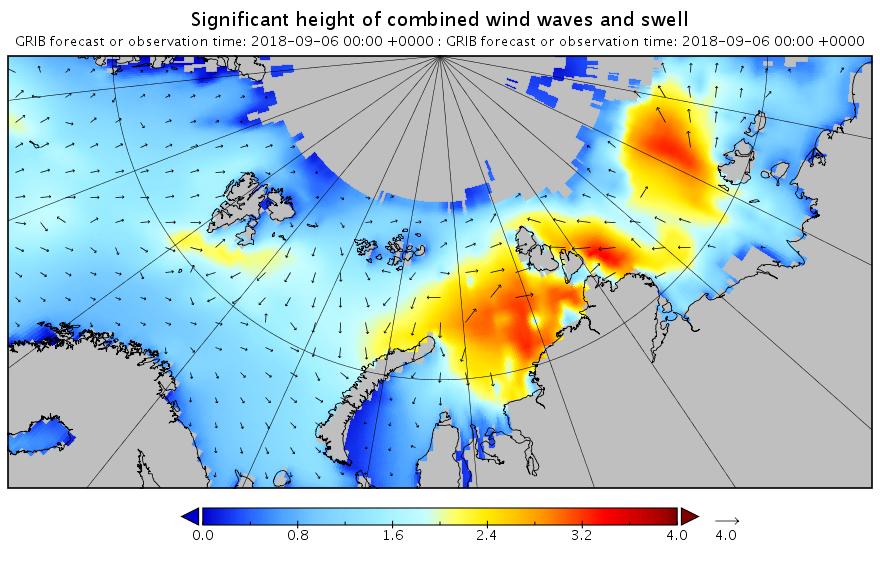
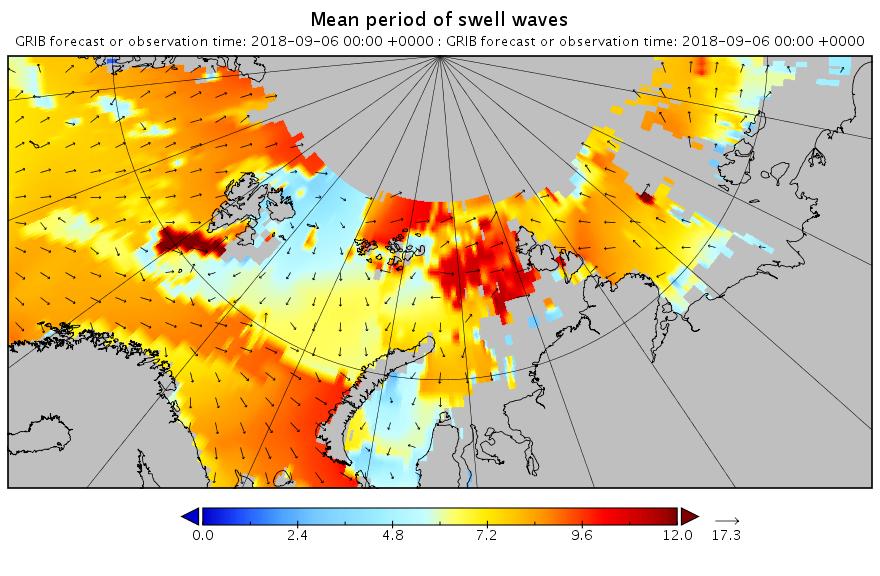
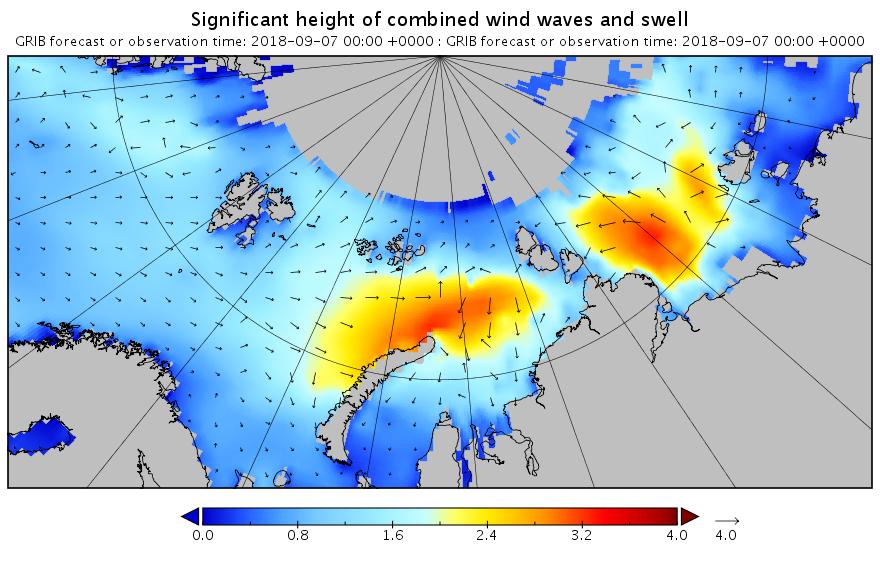
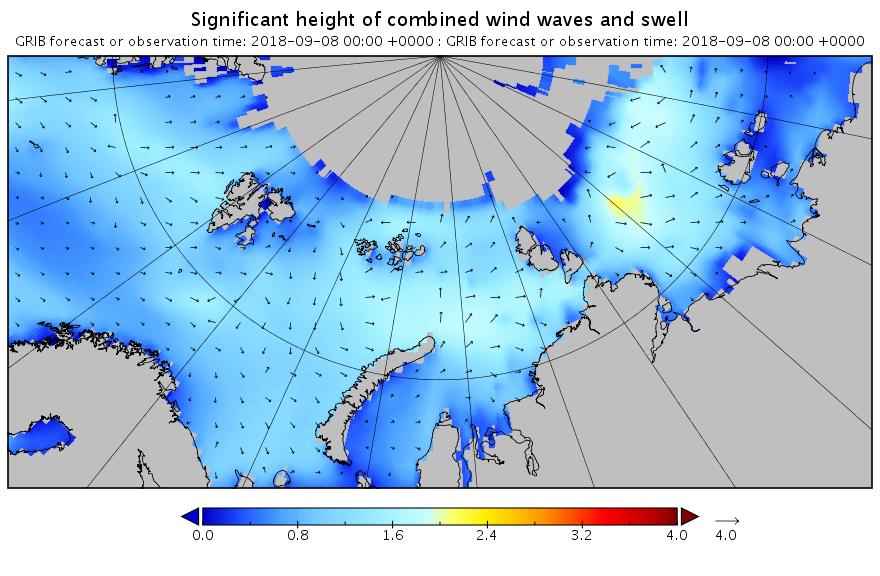
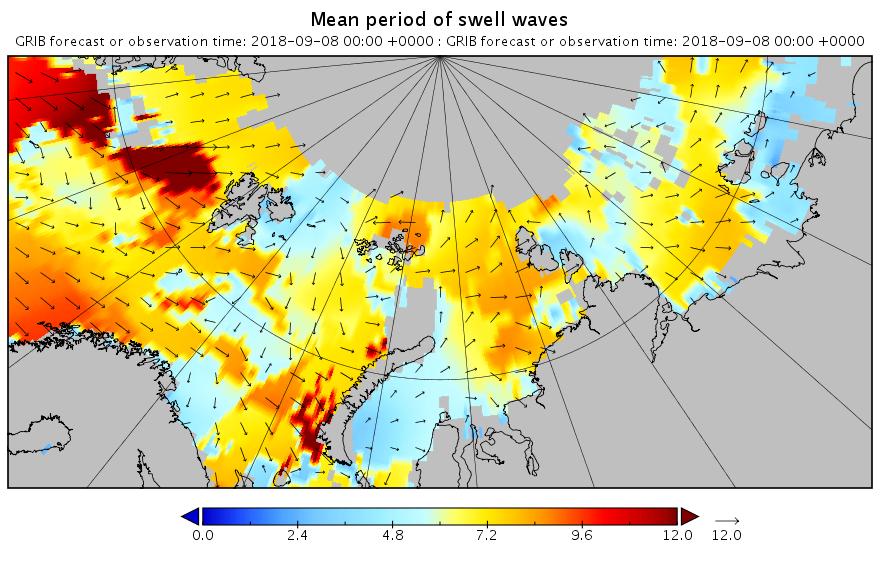
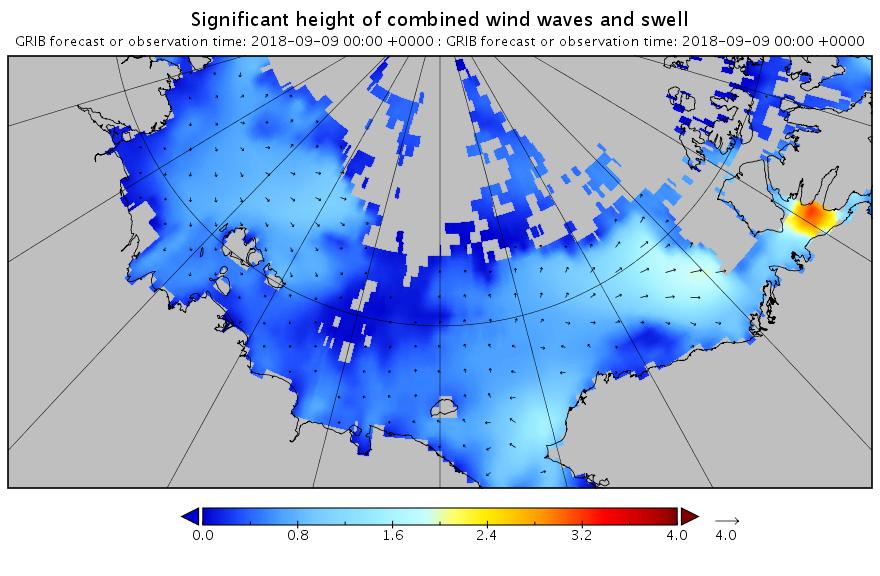
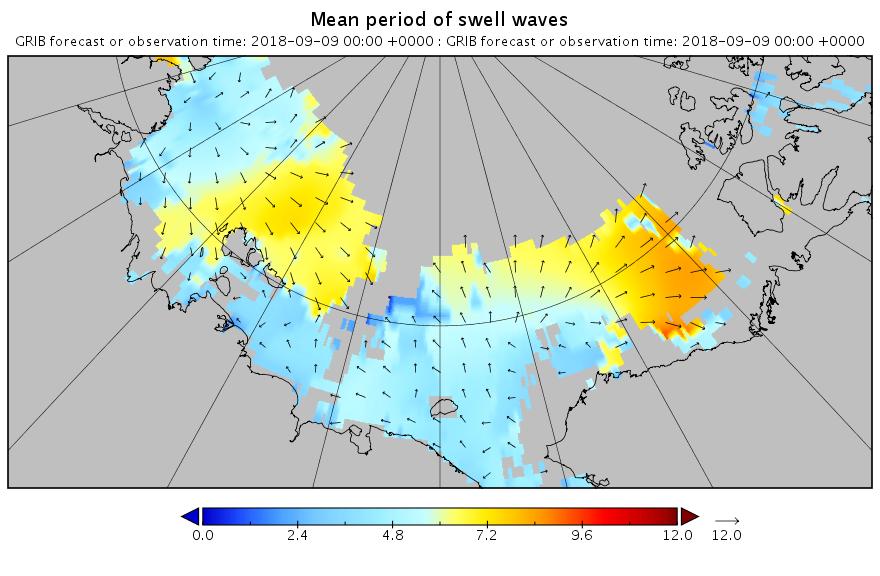
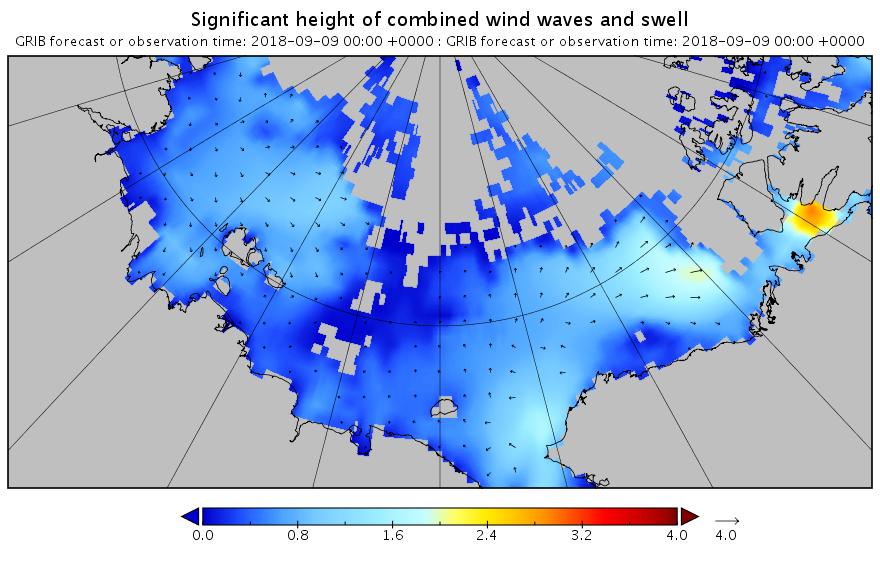
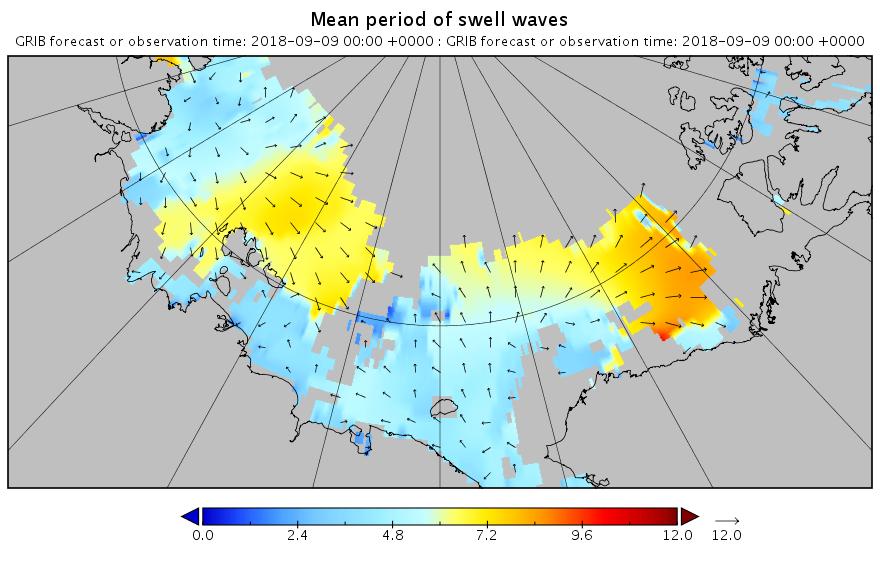
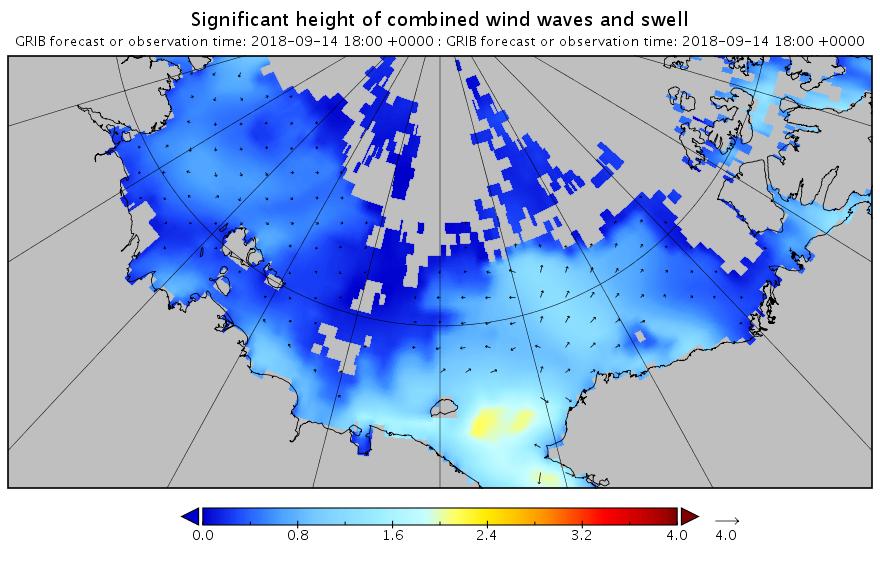
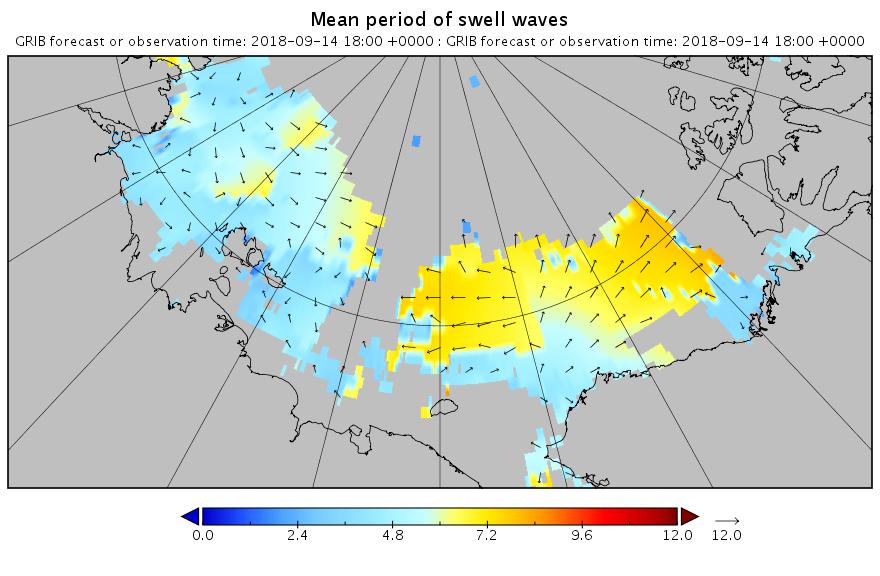
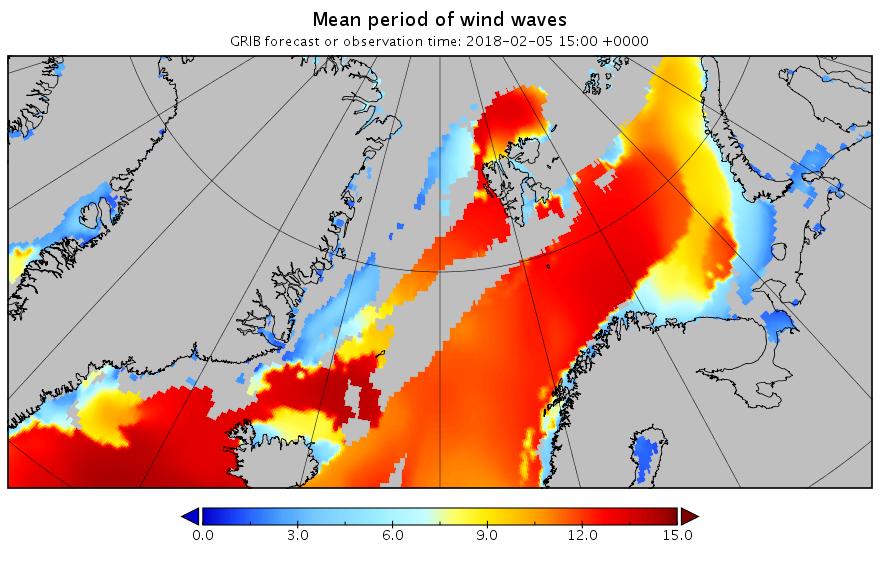
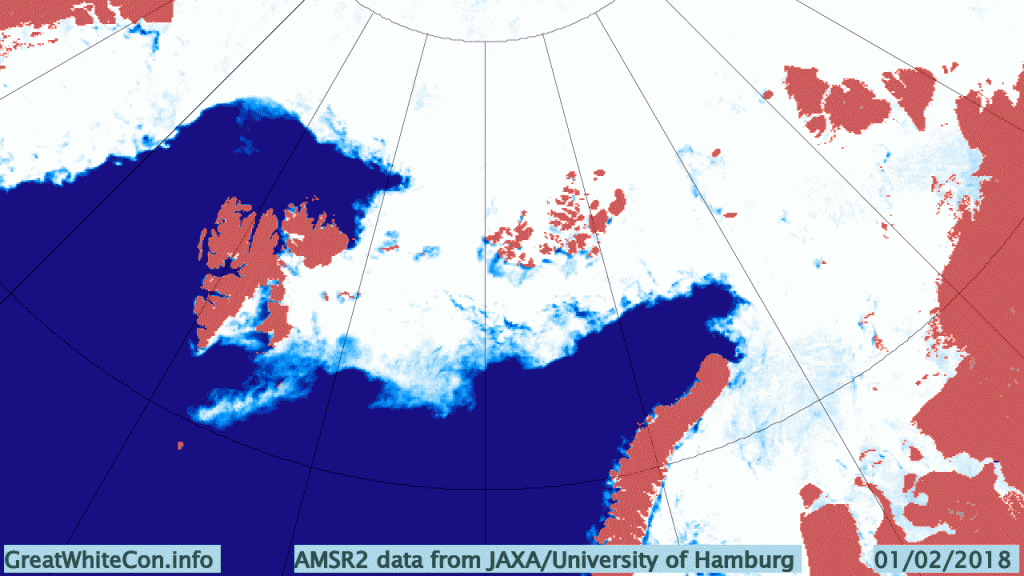
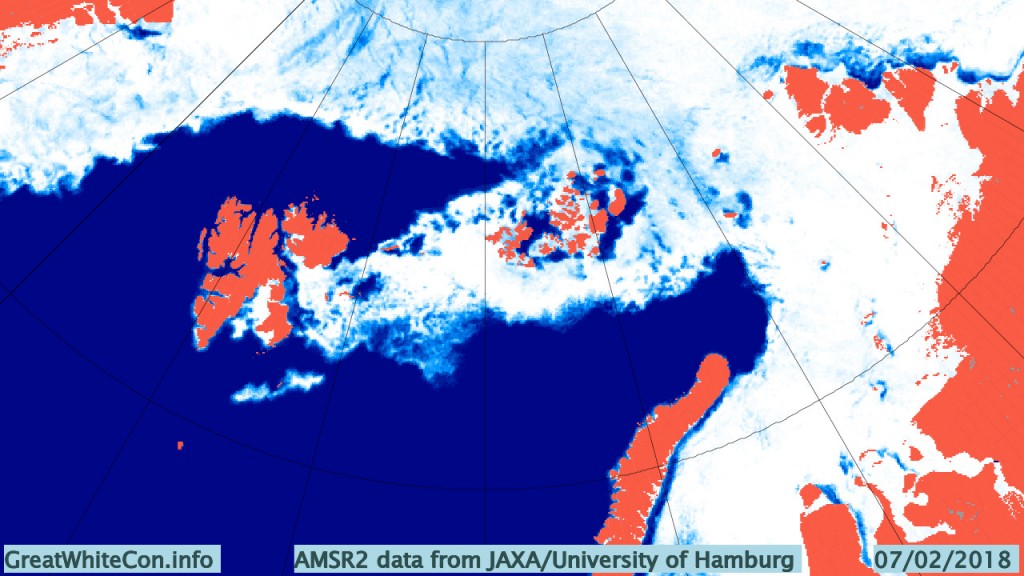
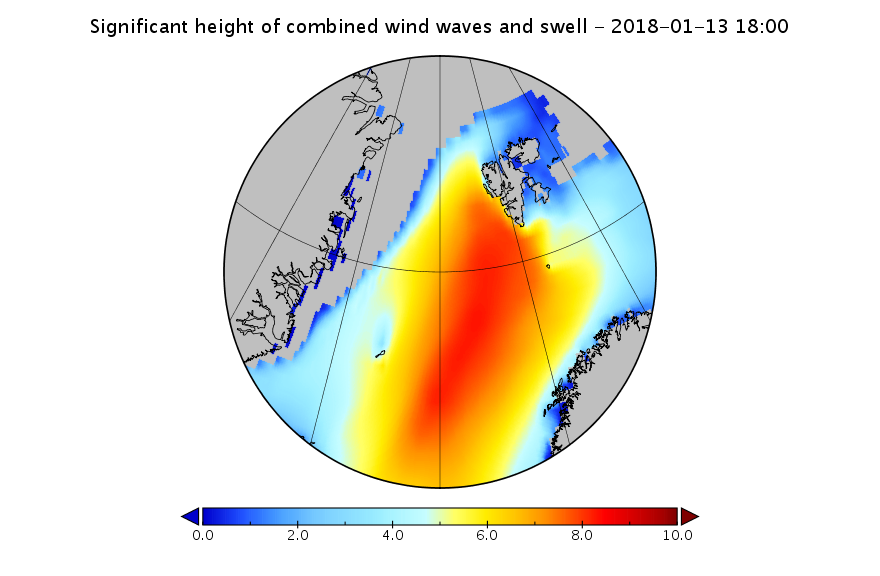
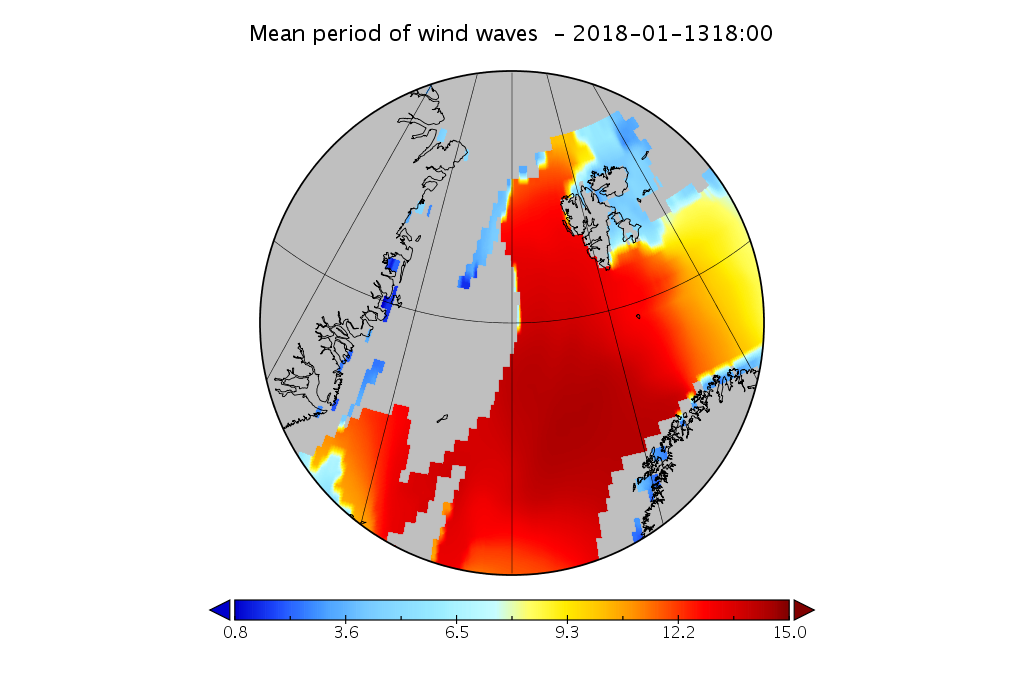
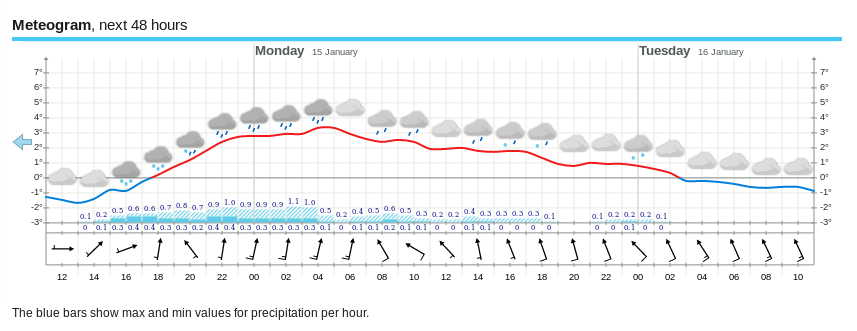
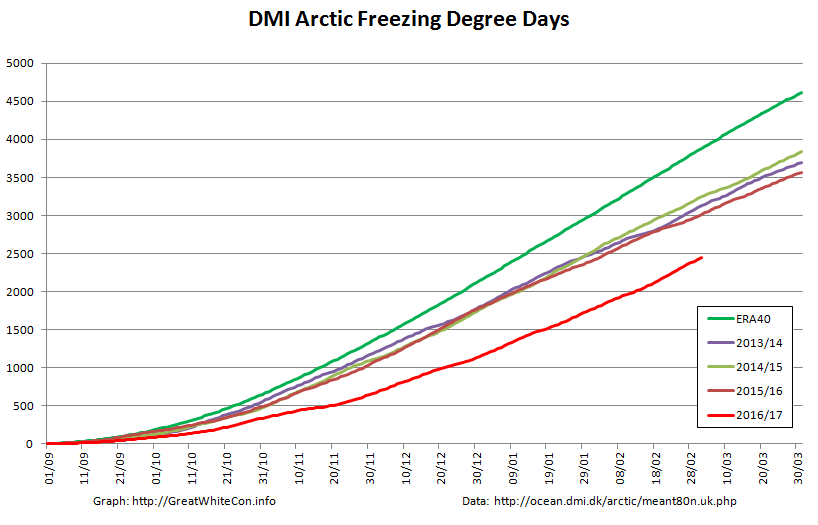
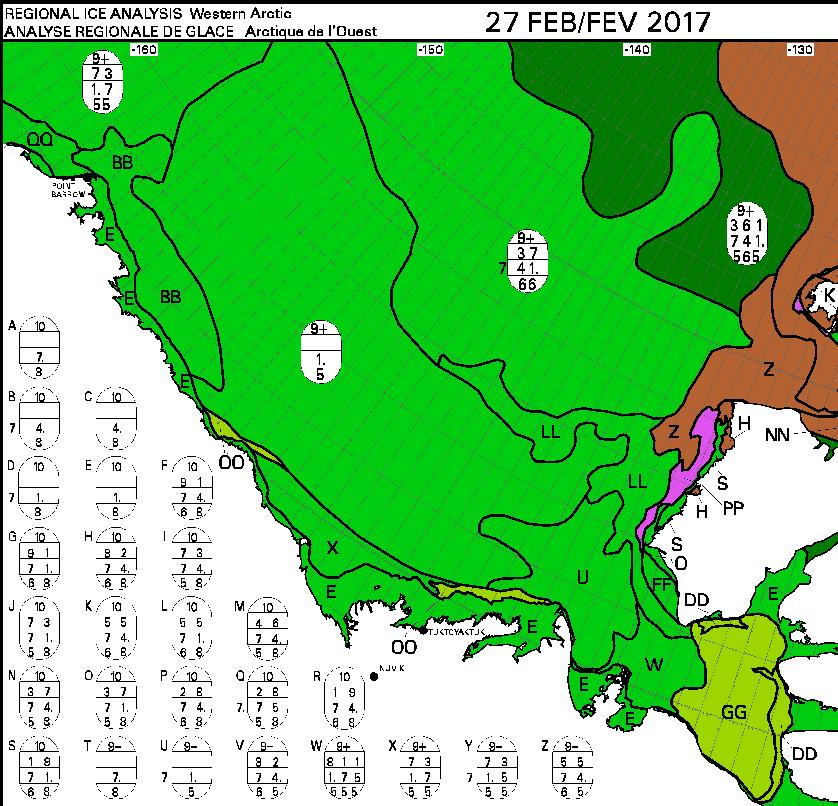
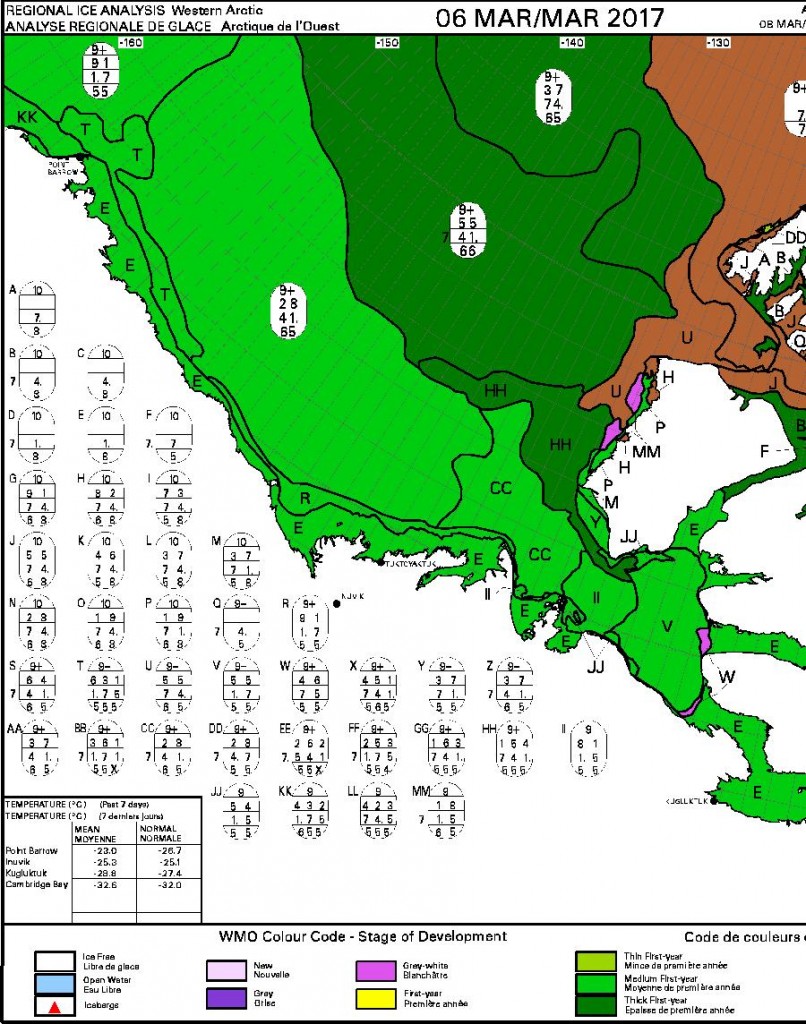
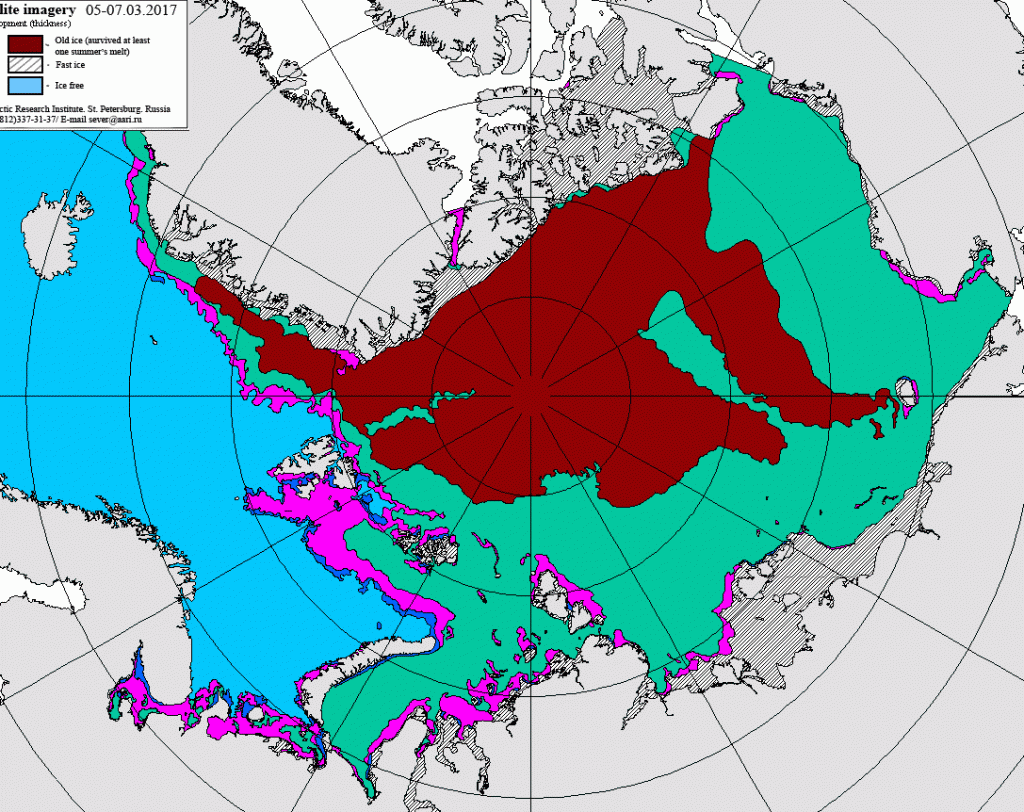
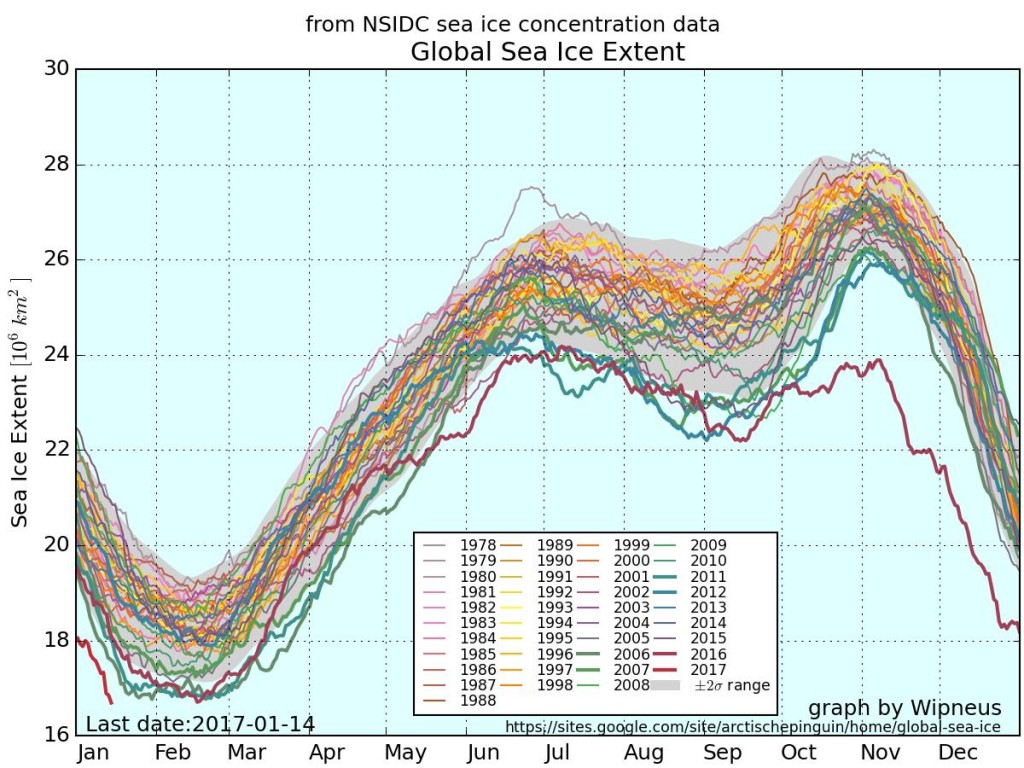
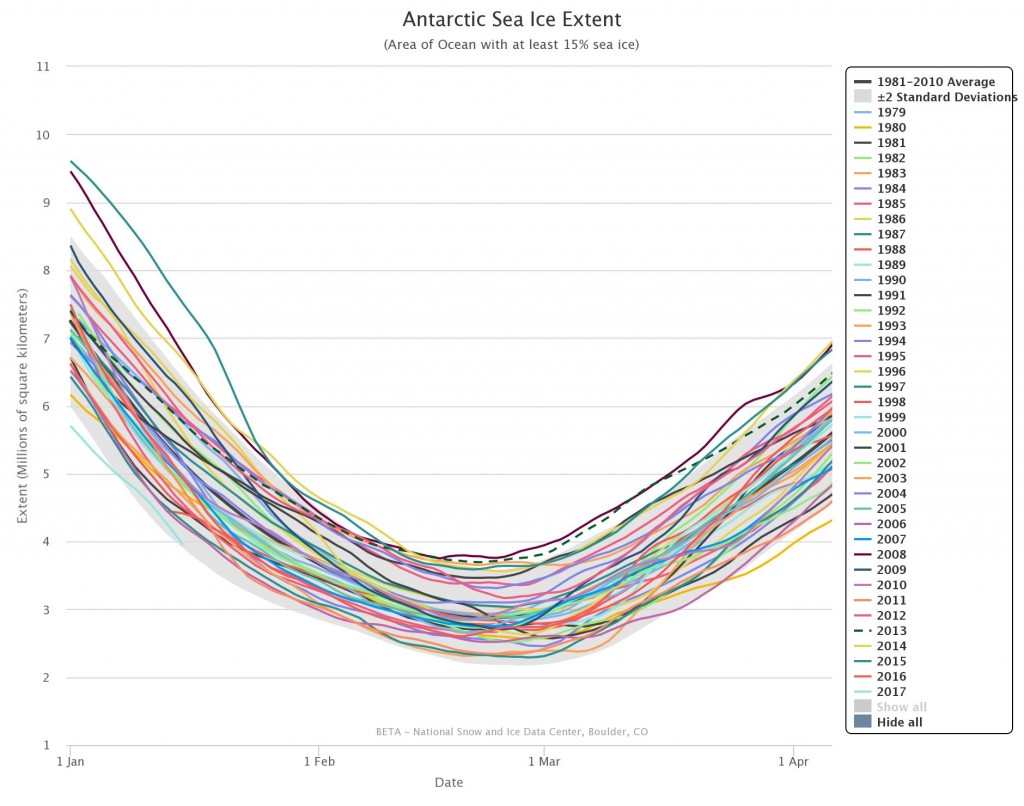
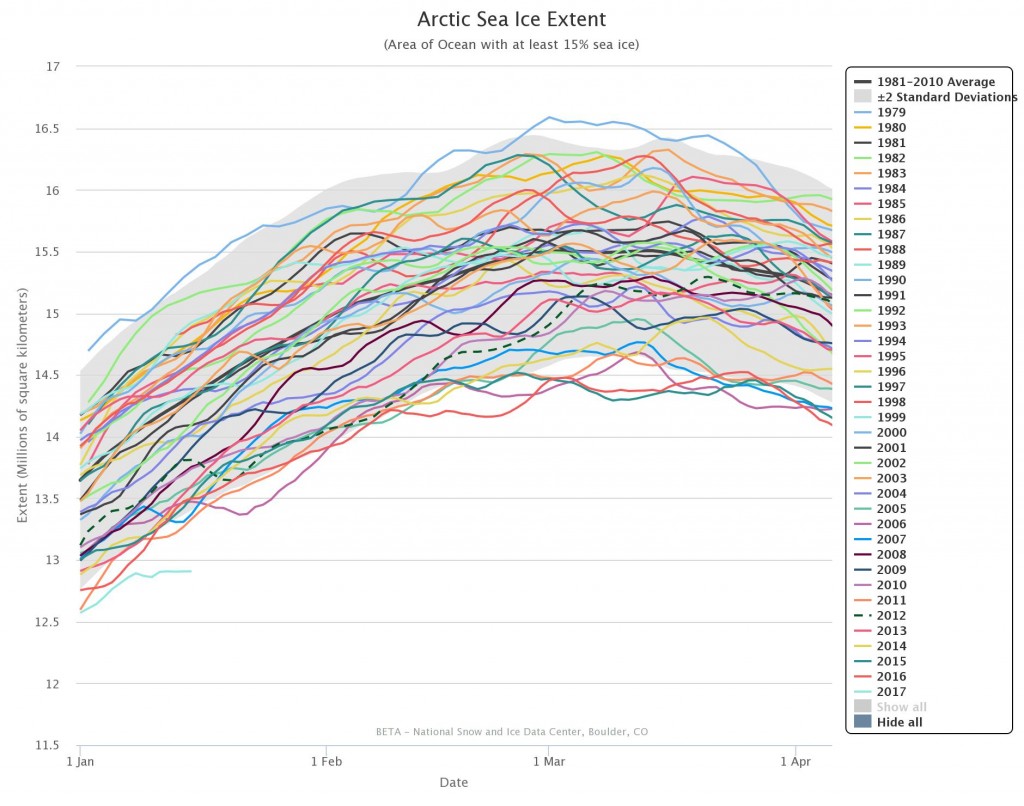
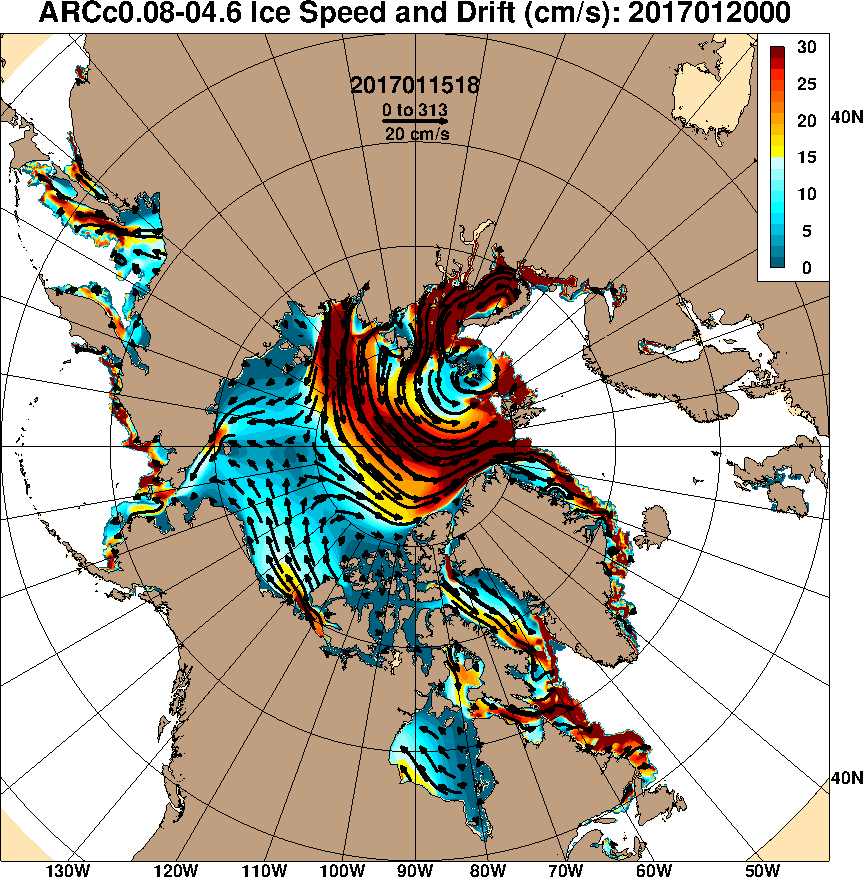
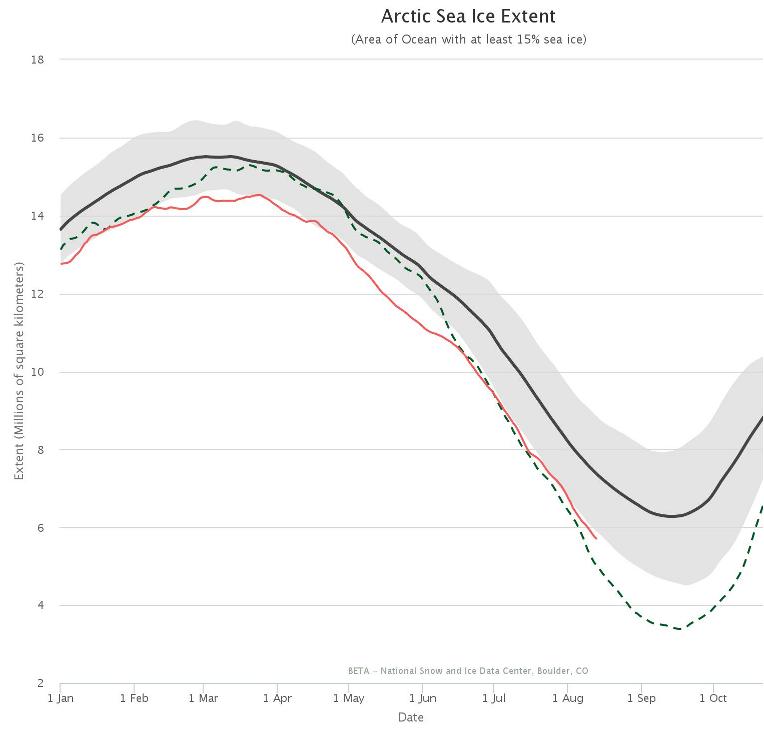
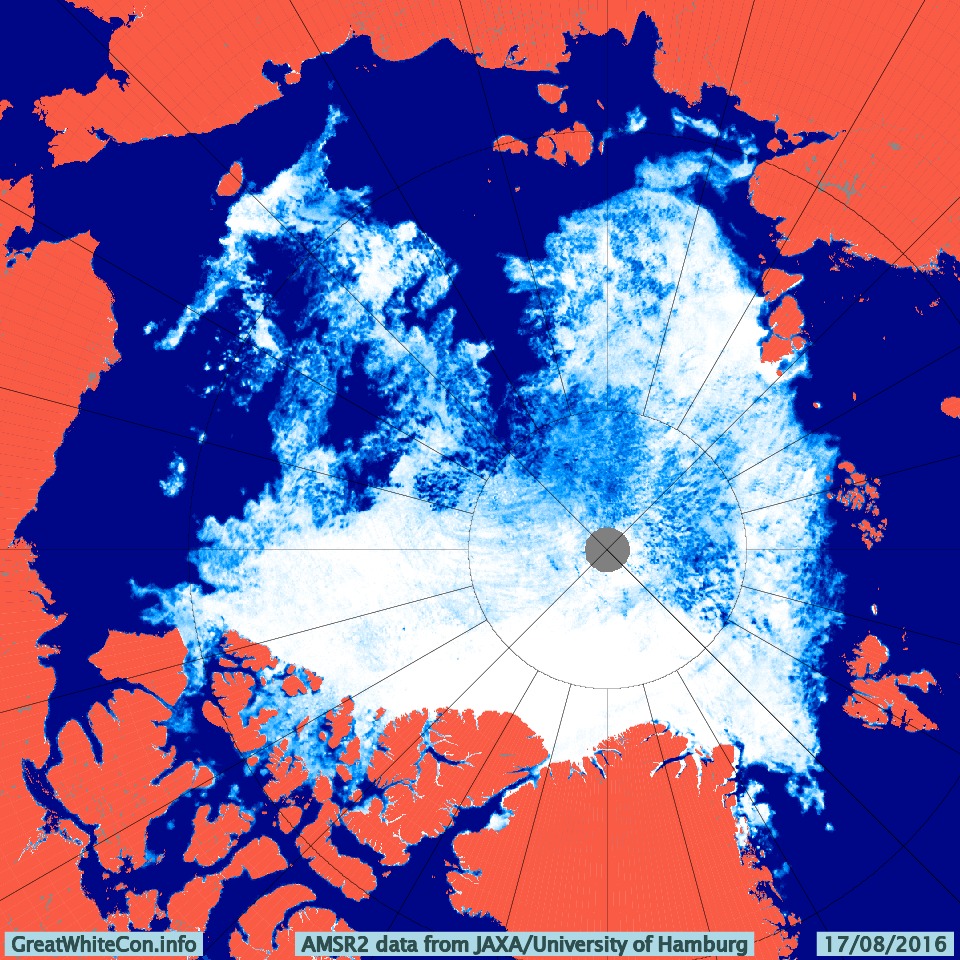
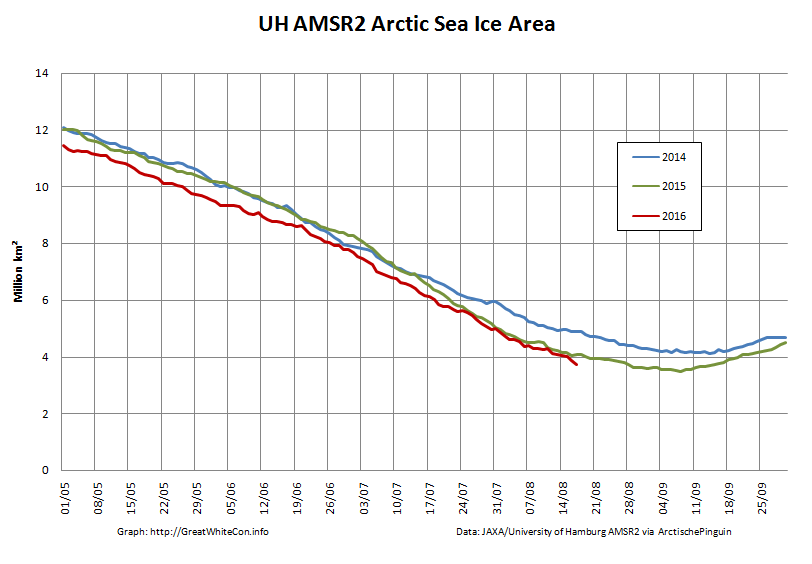
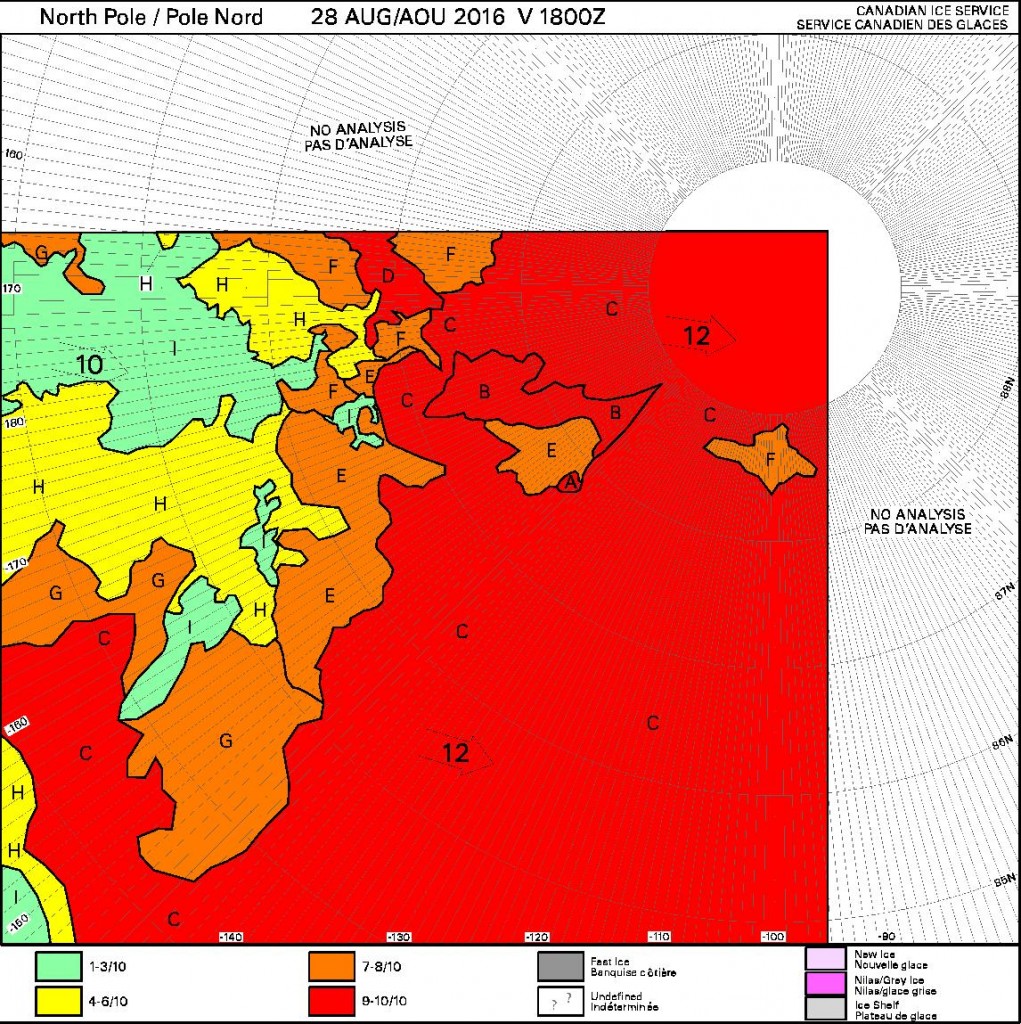
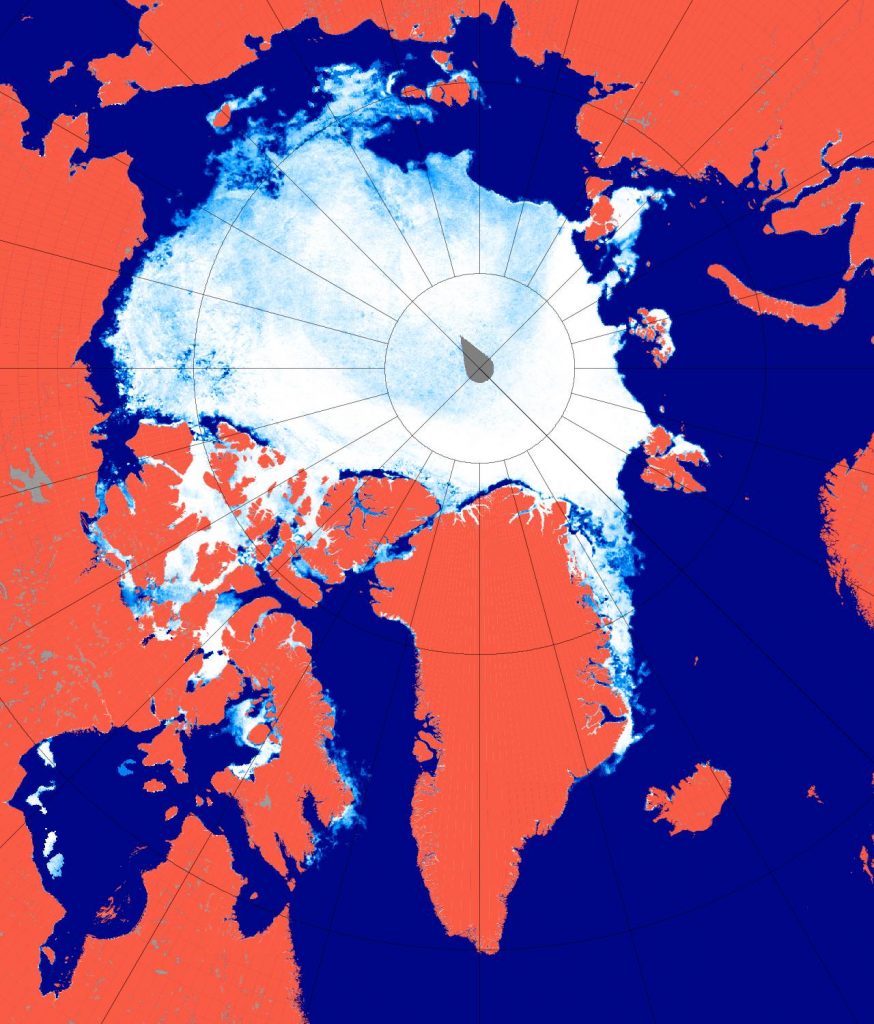
The new month starts with JAXA extent “lowest for the date in the satellite record” by a whisker:
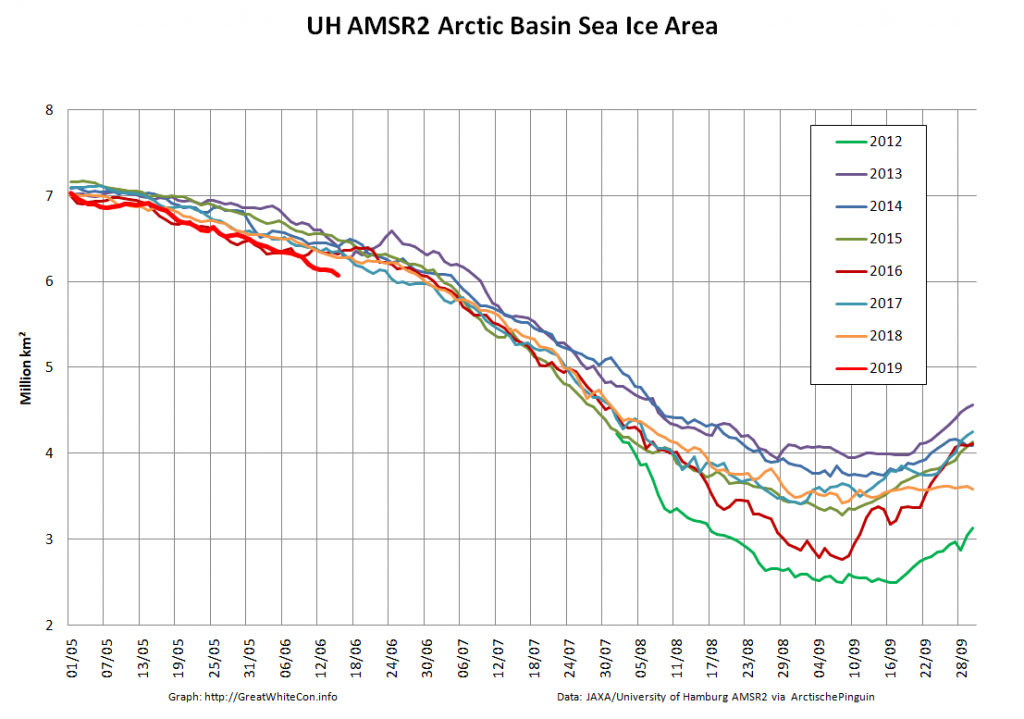
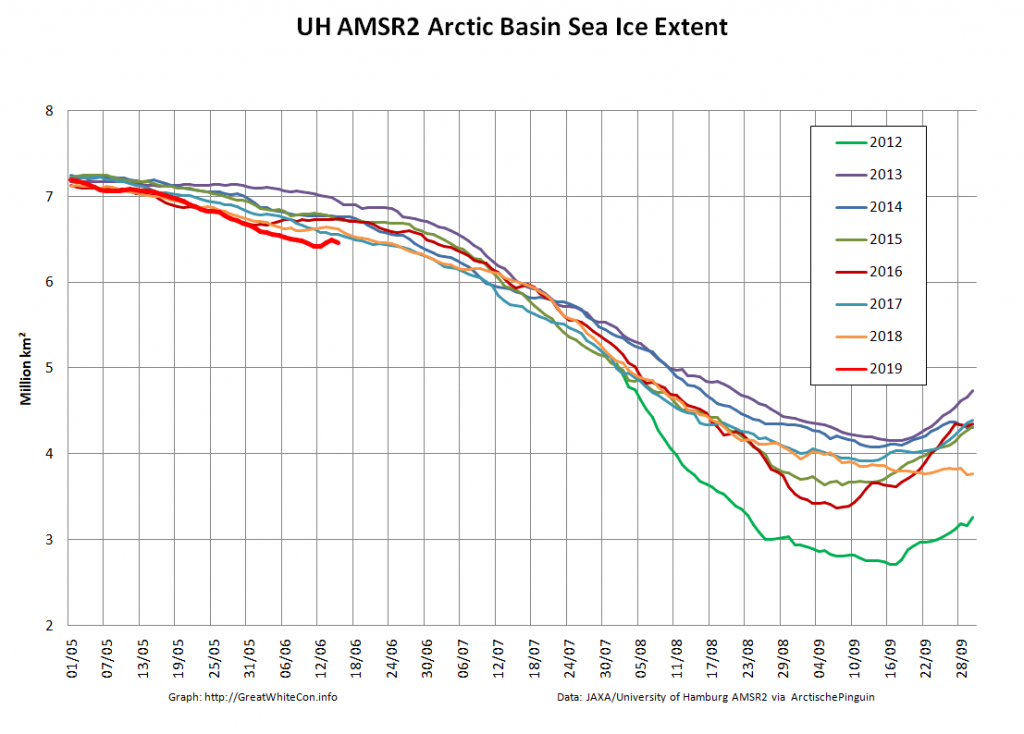
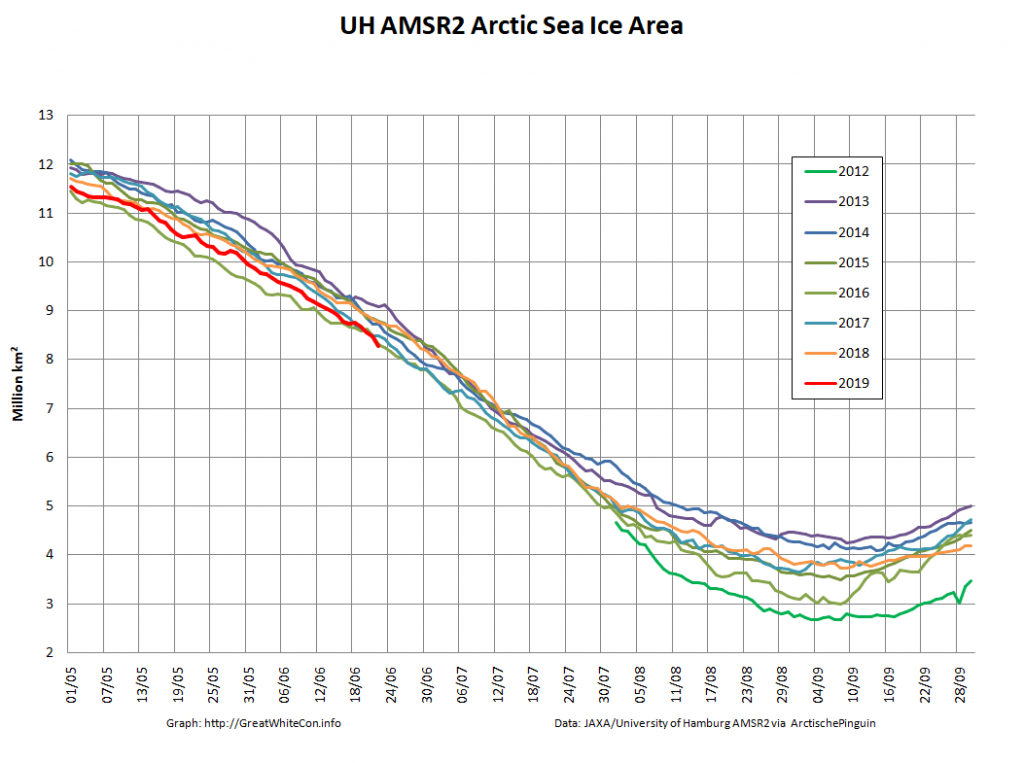
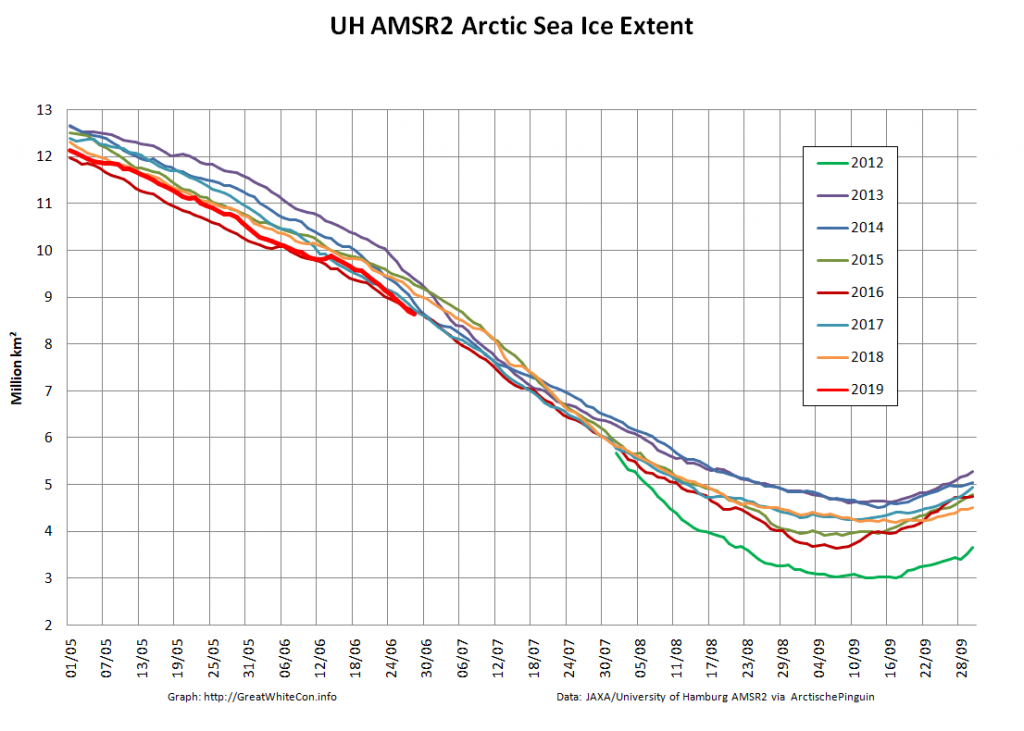
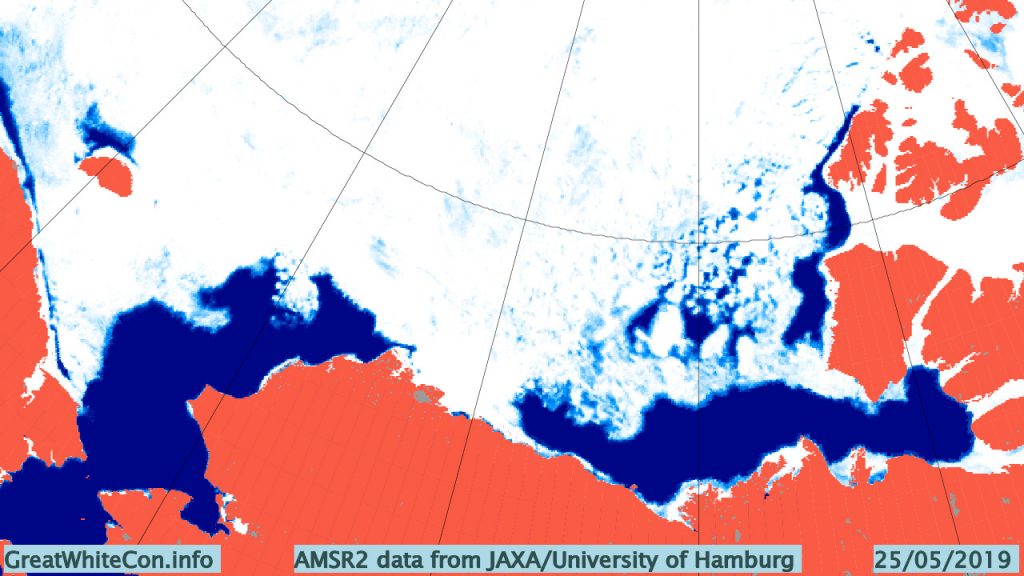
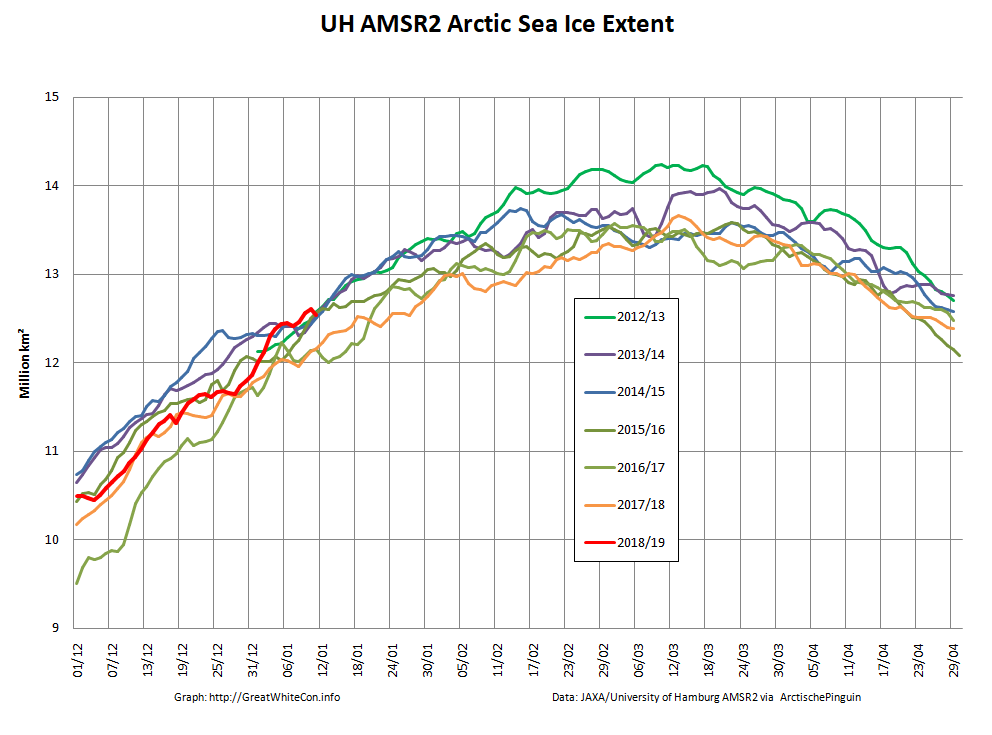
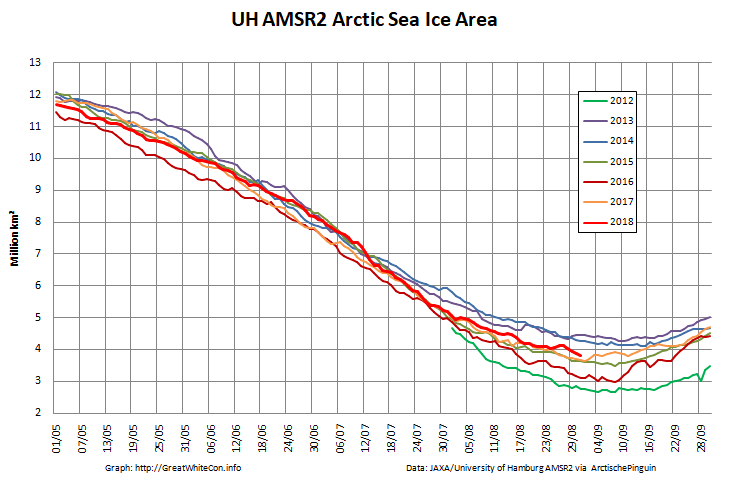
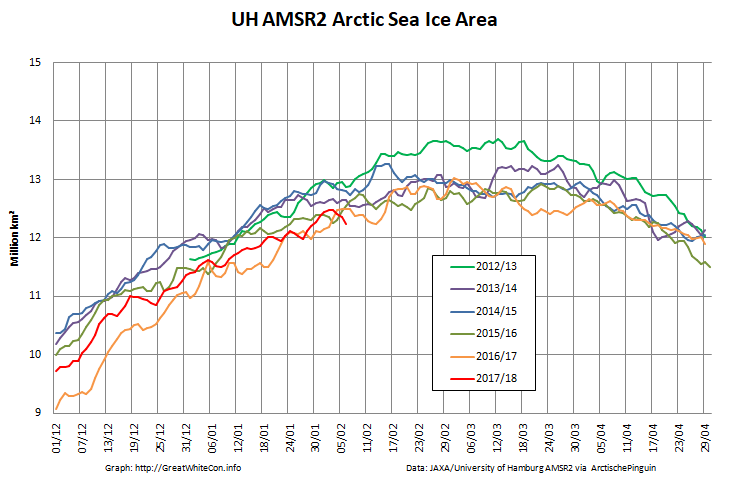
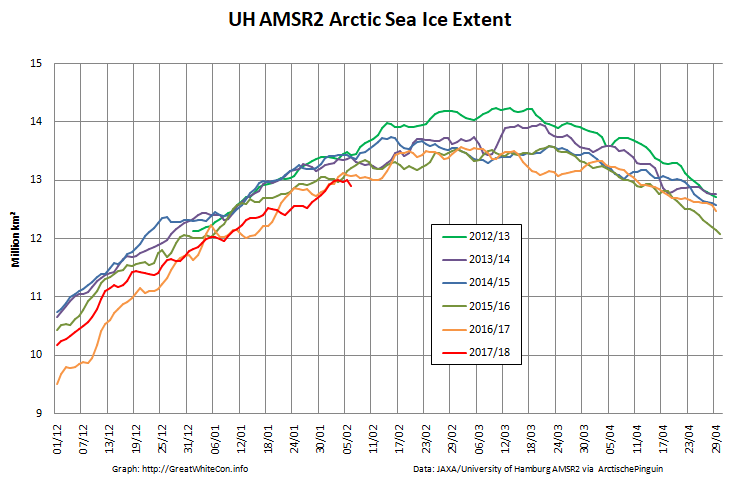
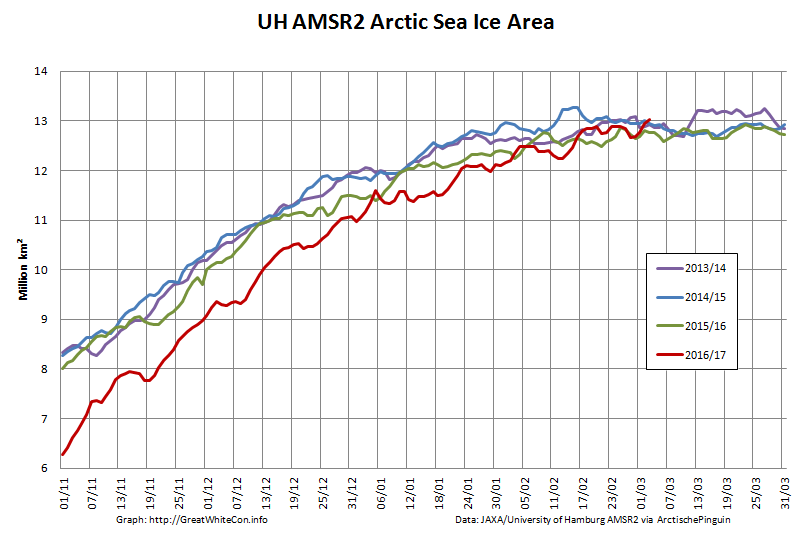
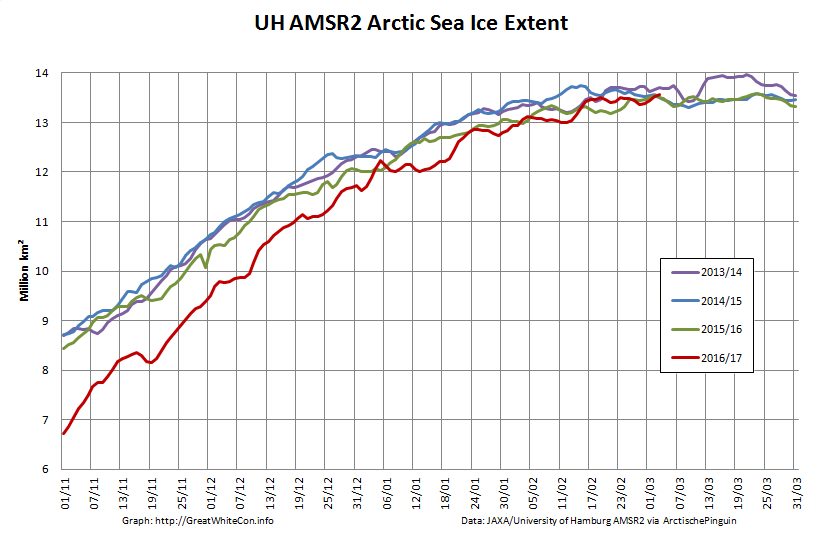
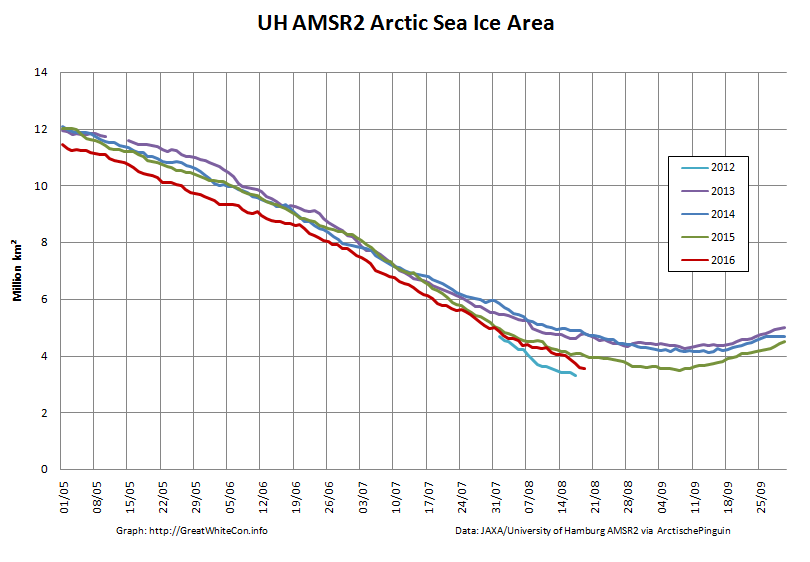
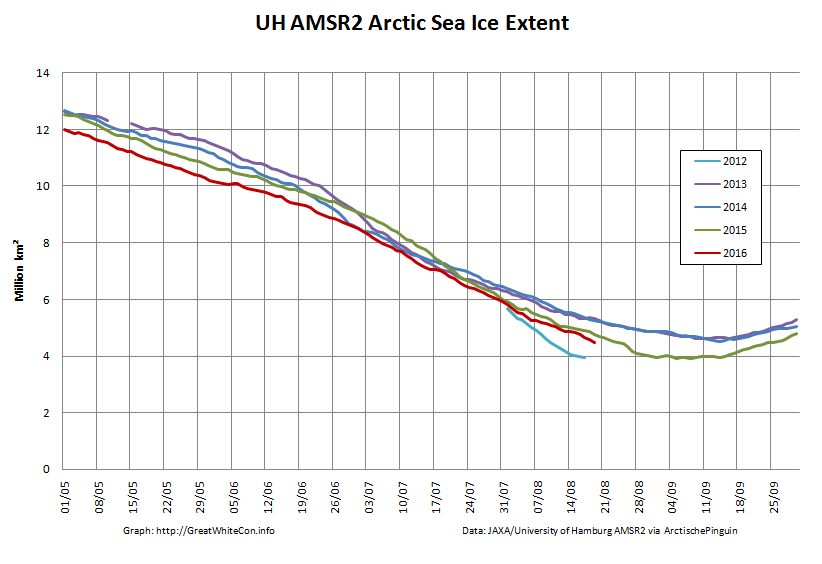
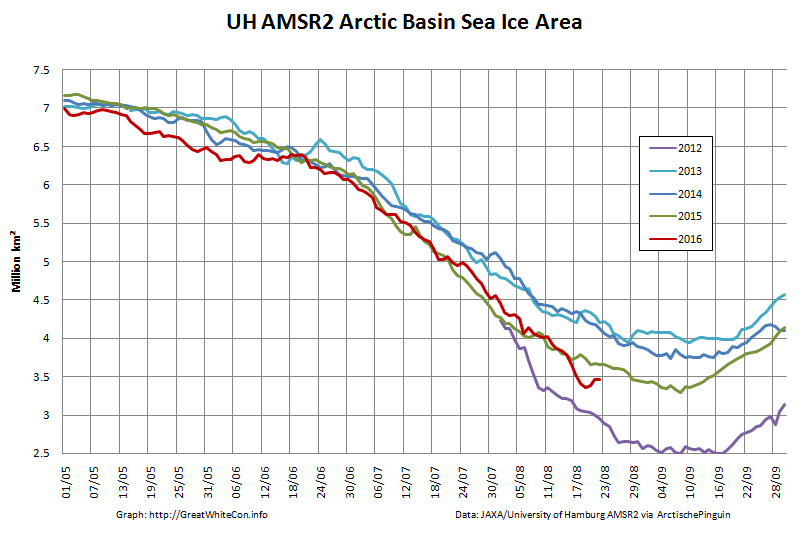
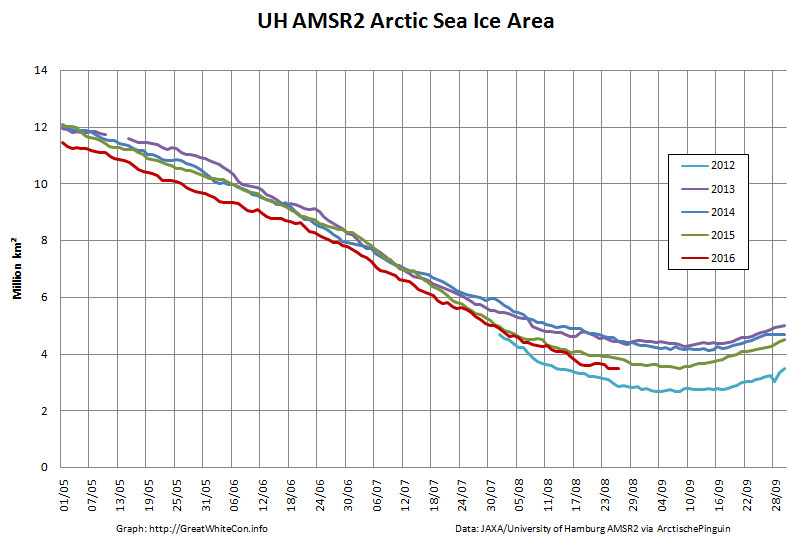
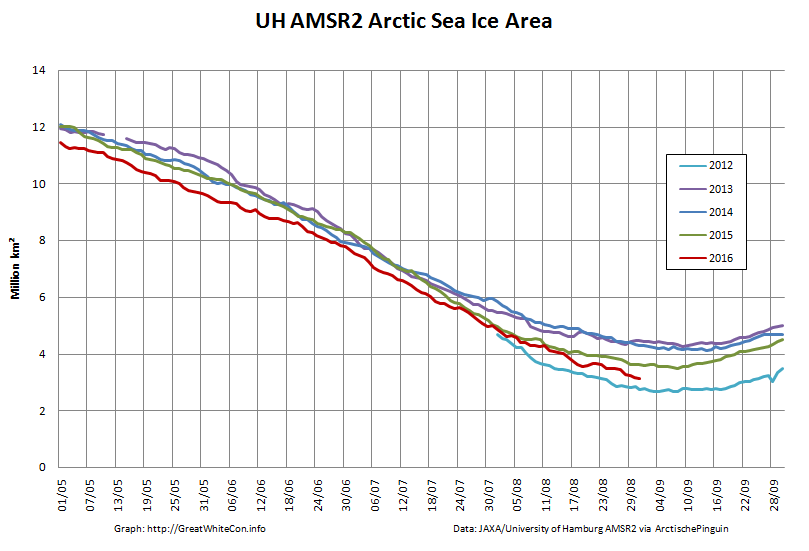
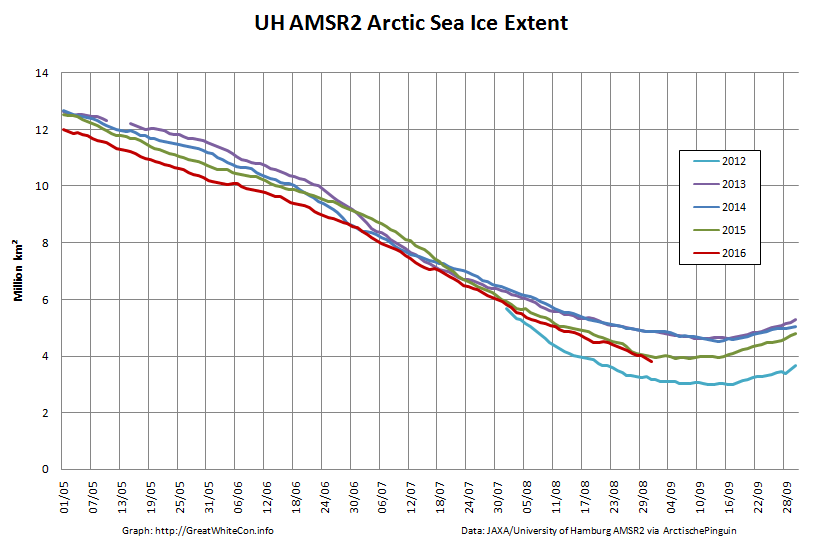
The high resolution Arctic sea ice area and extent graphs based on the University of Hamburg’s AMSR2 concentration data are also in “statistical ties” for that honour, in records going back to 2013:
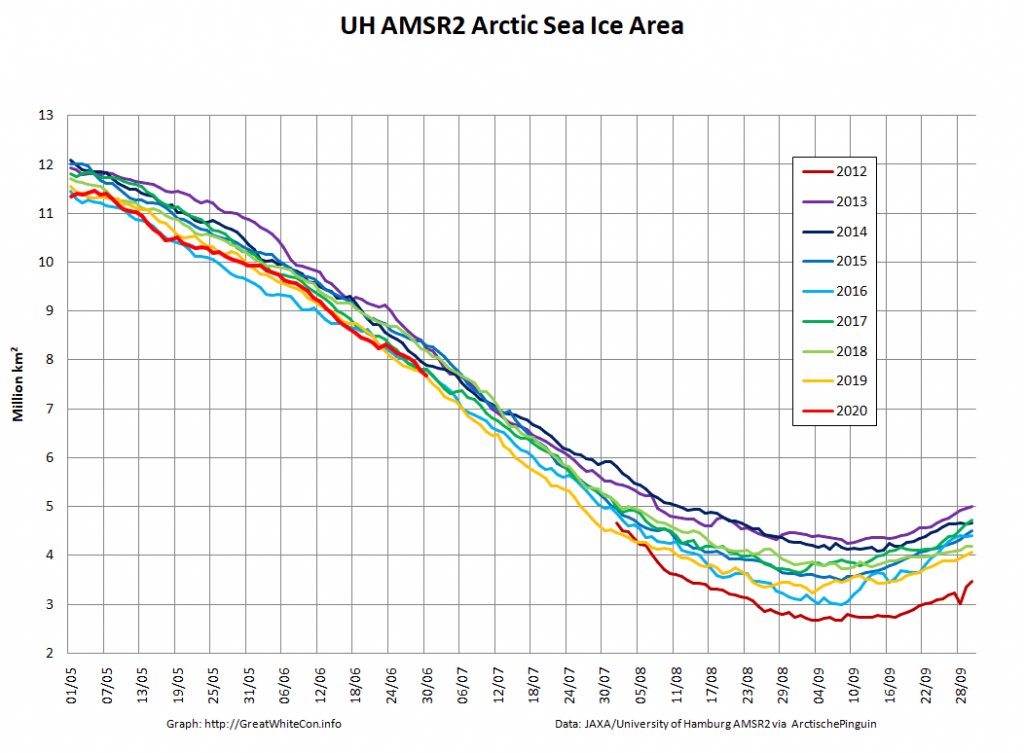
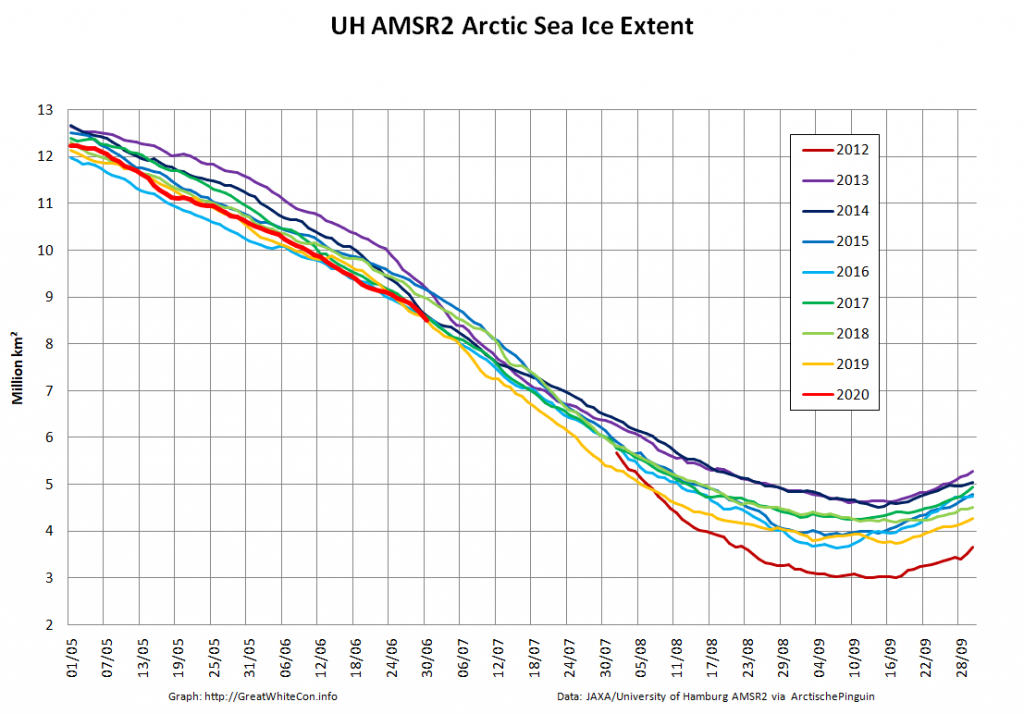
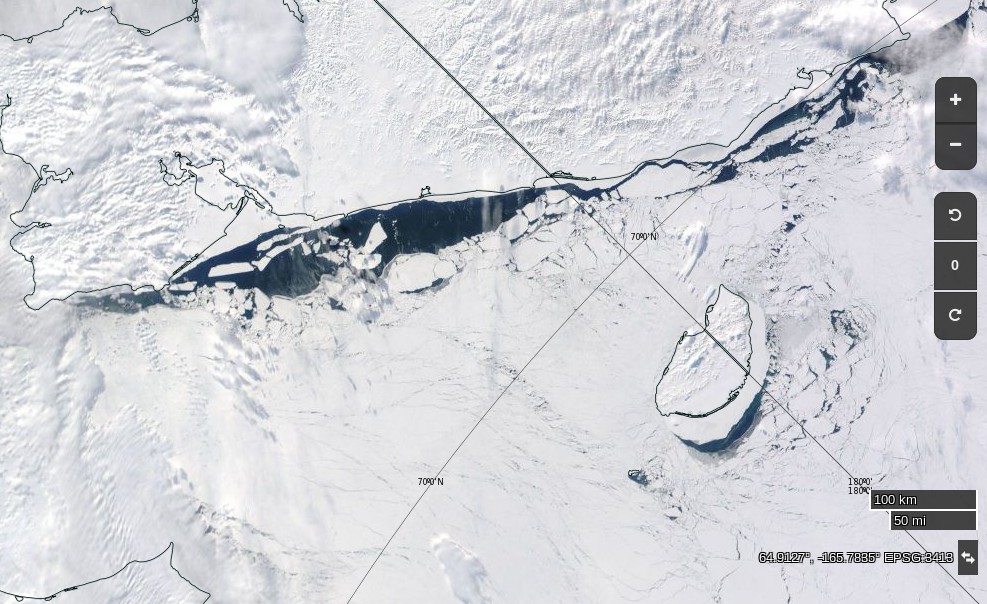
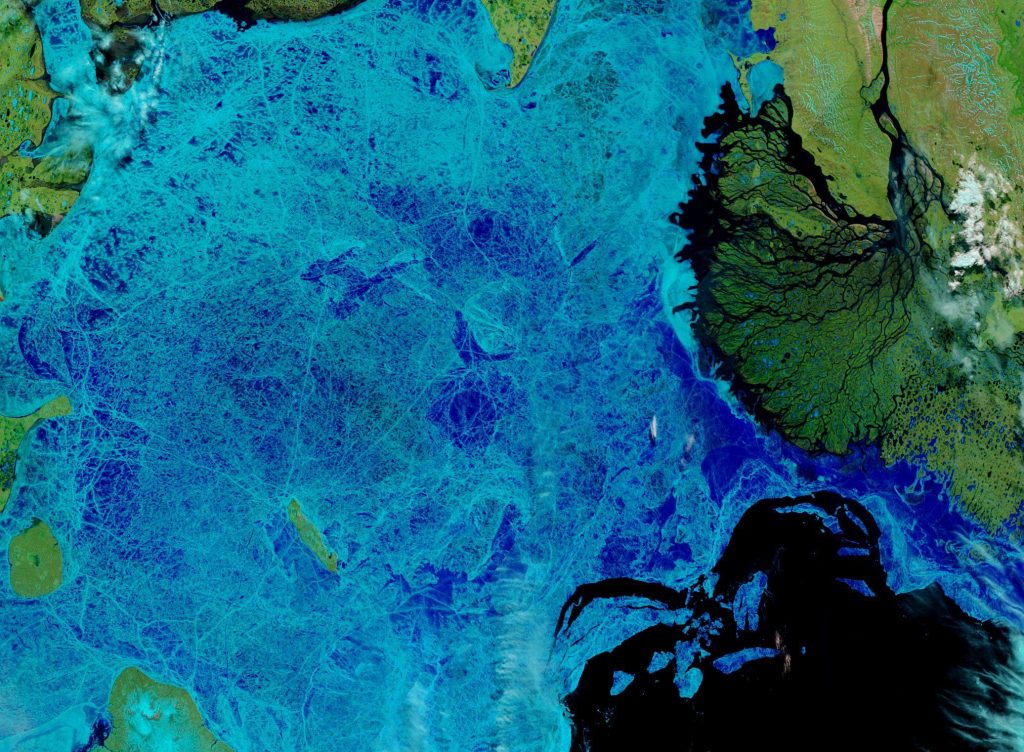
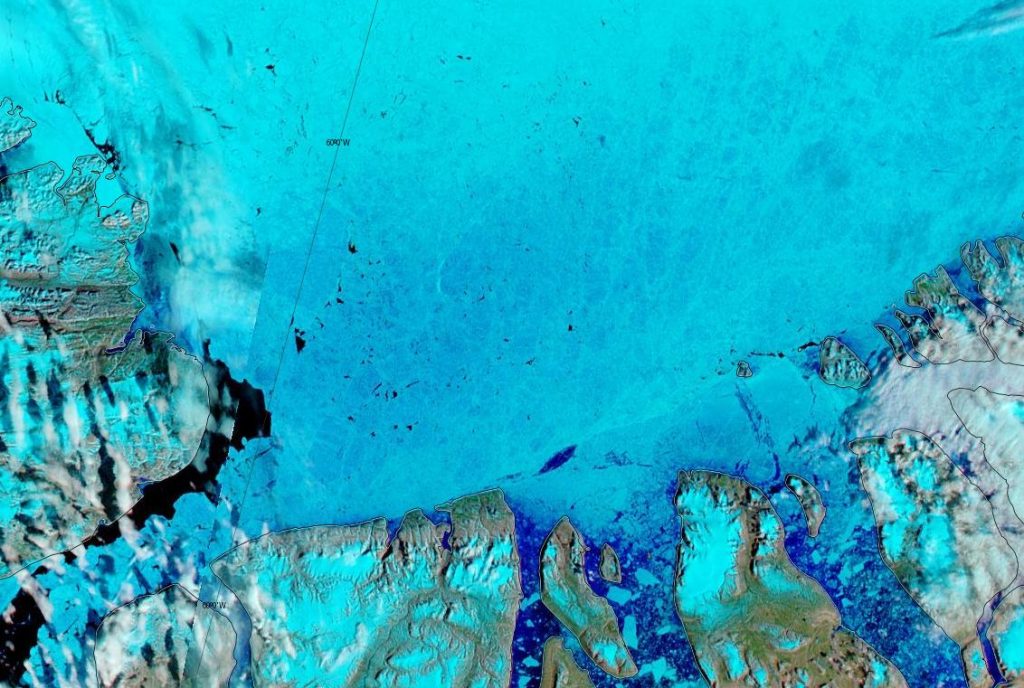
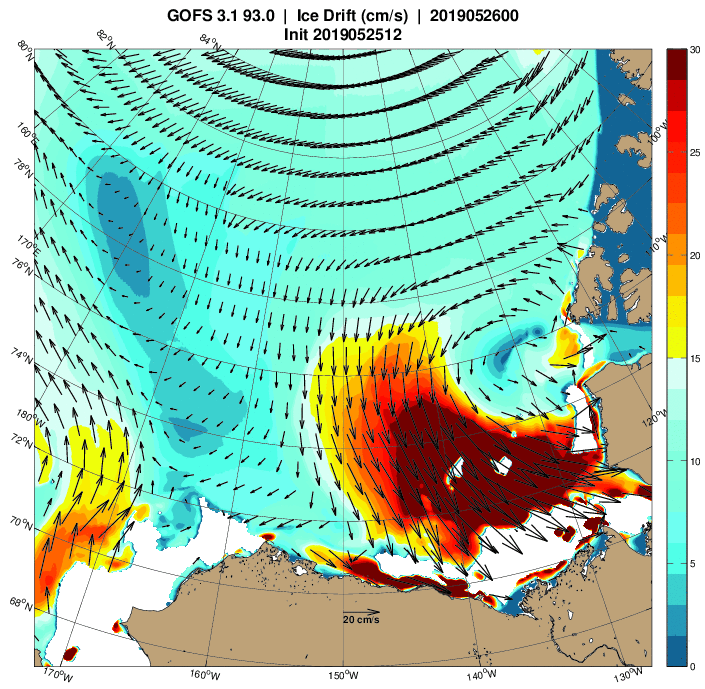
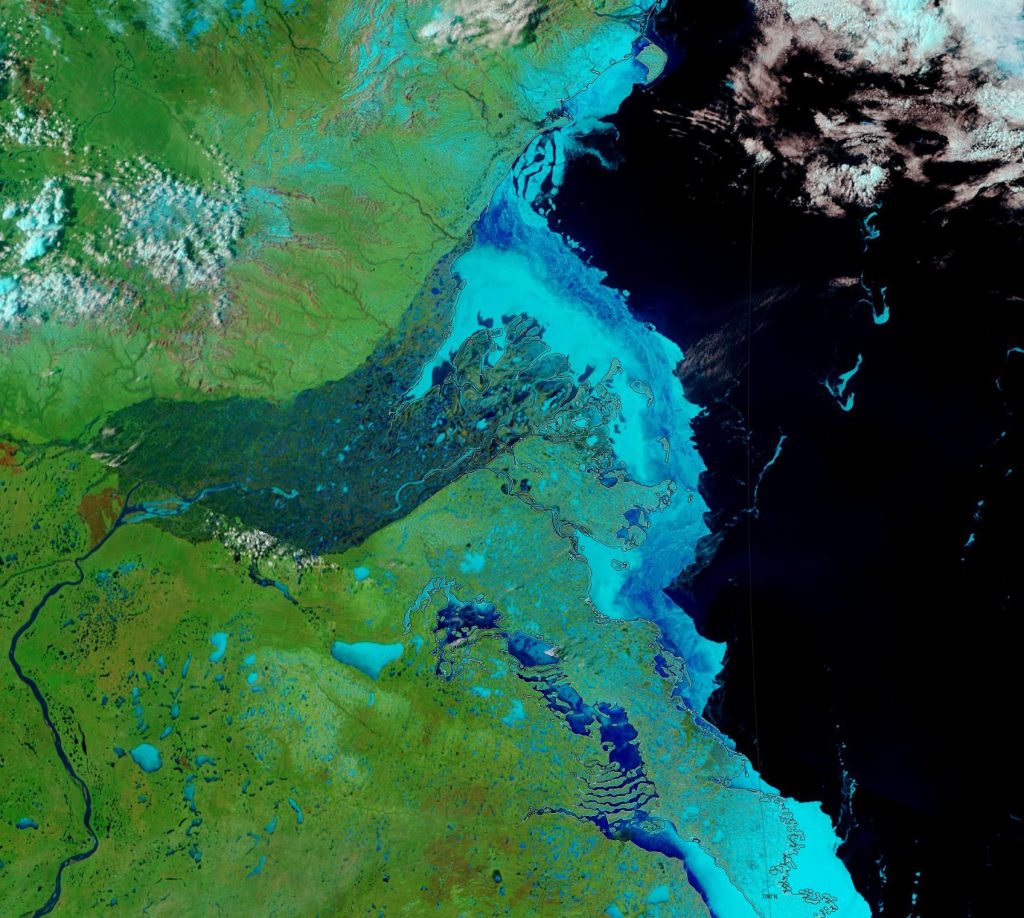
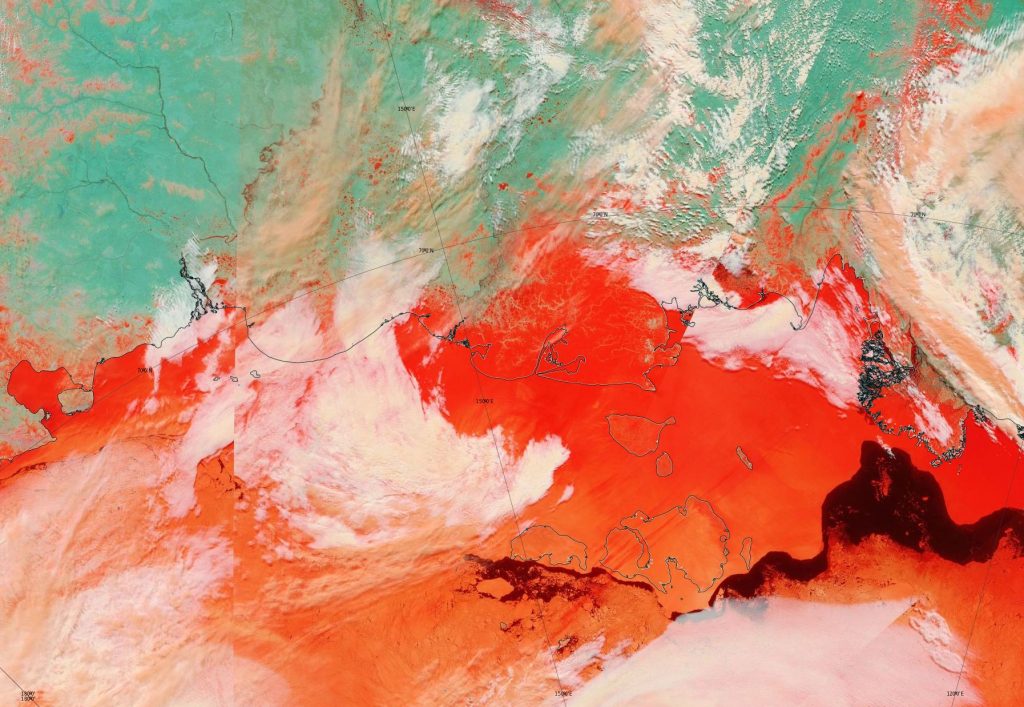
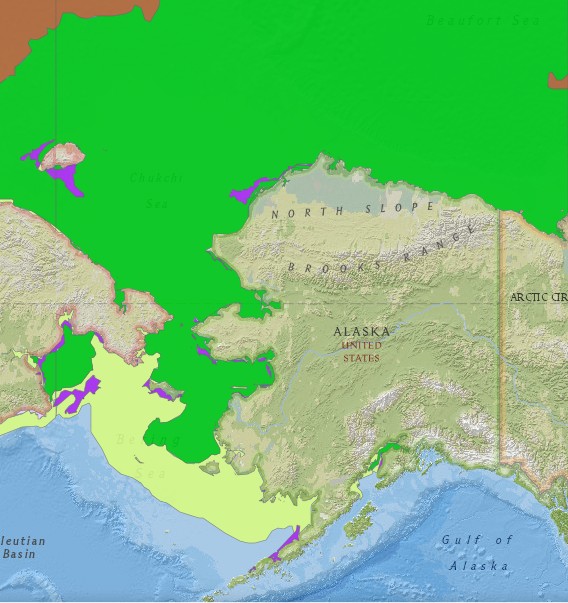
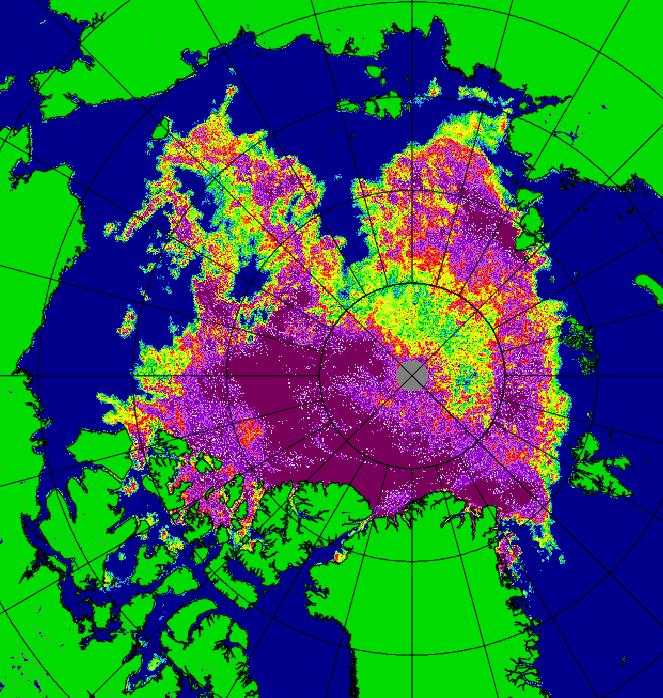
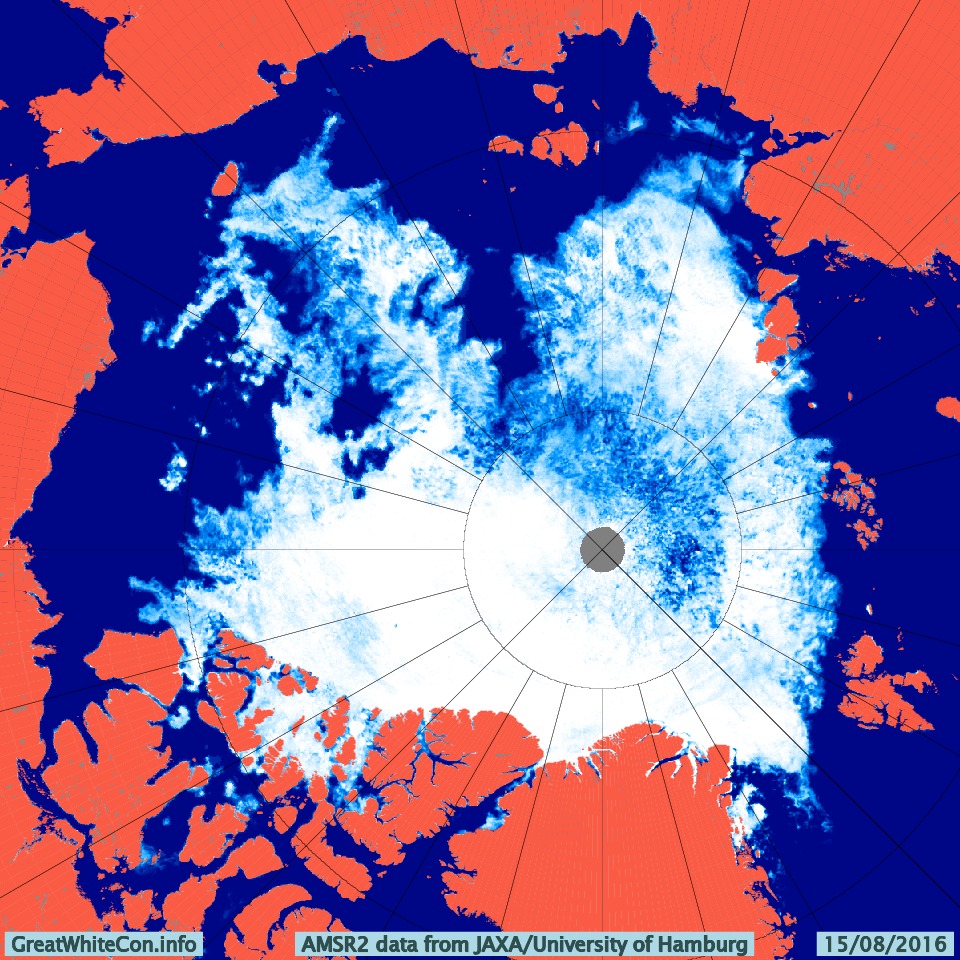
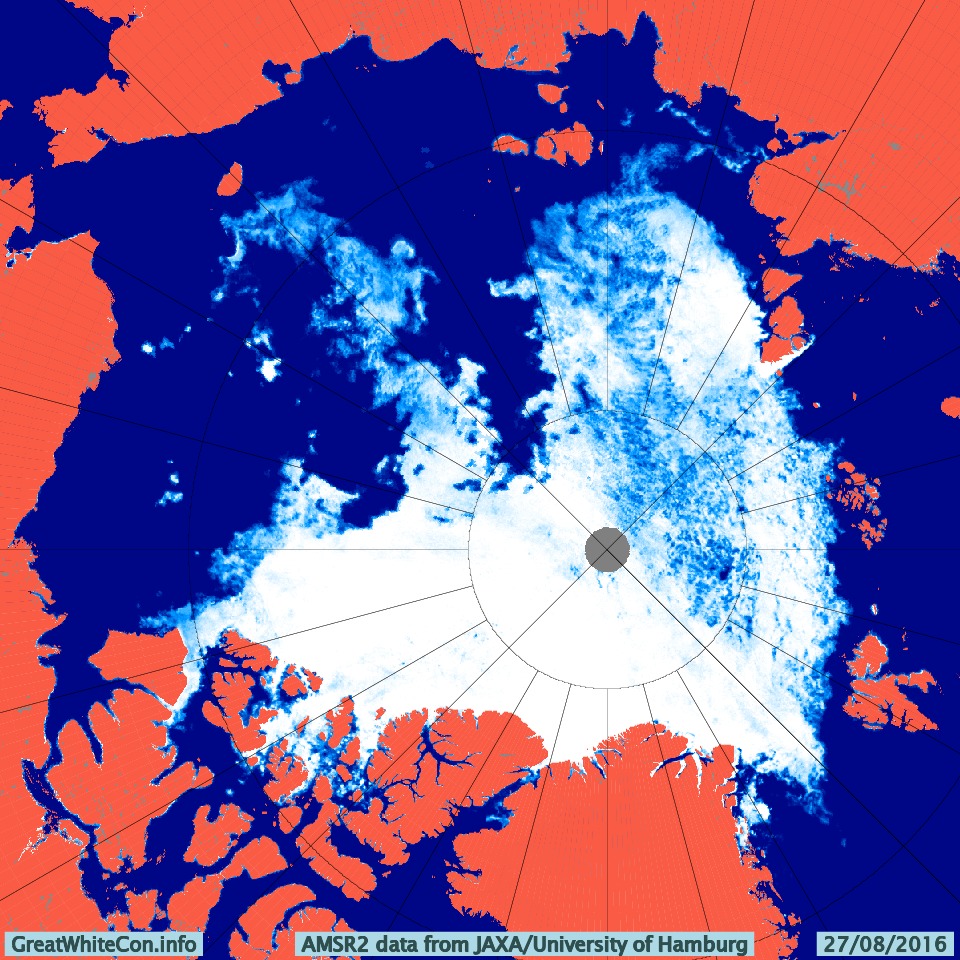
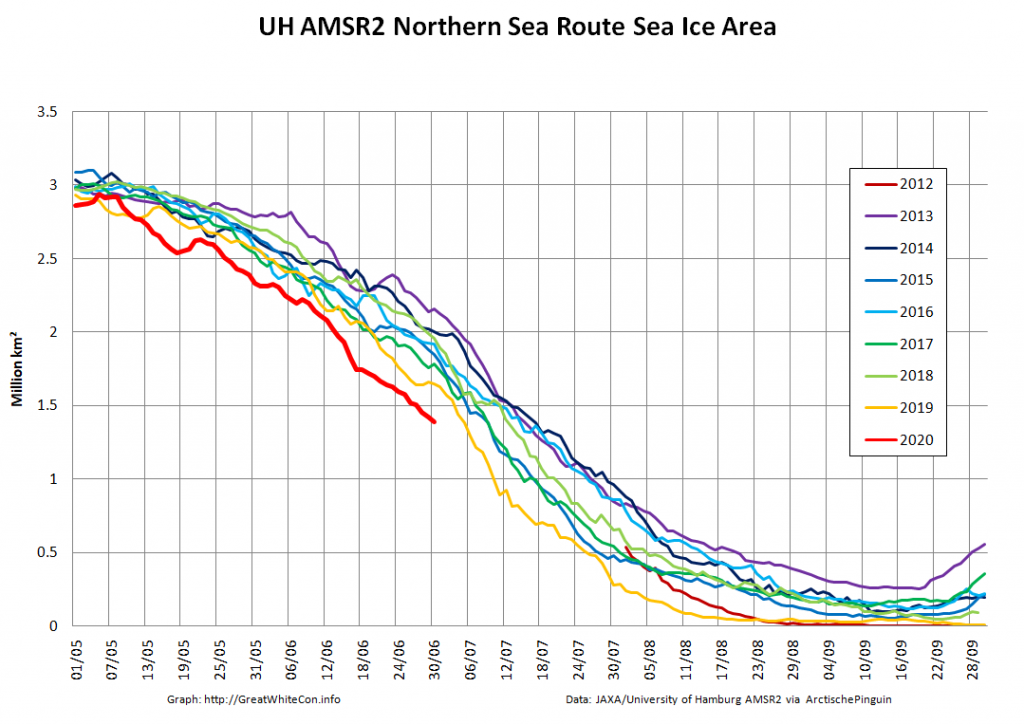
The 2020 melting season currently seems to be a game of two (geographical) halves. The sea ice on the Siberian side of the Arctic is currently at record lows:
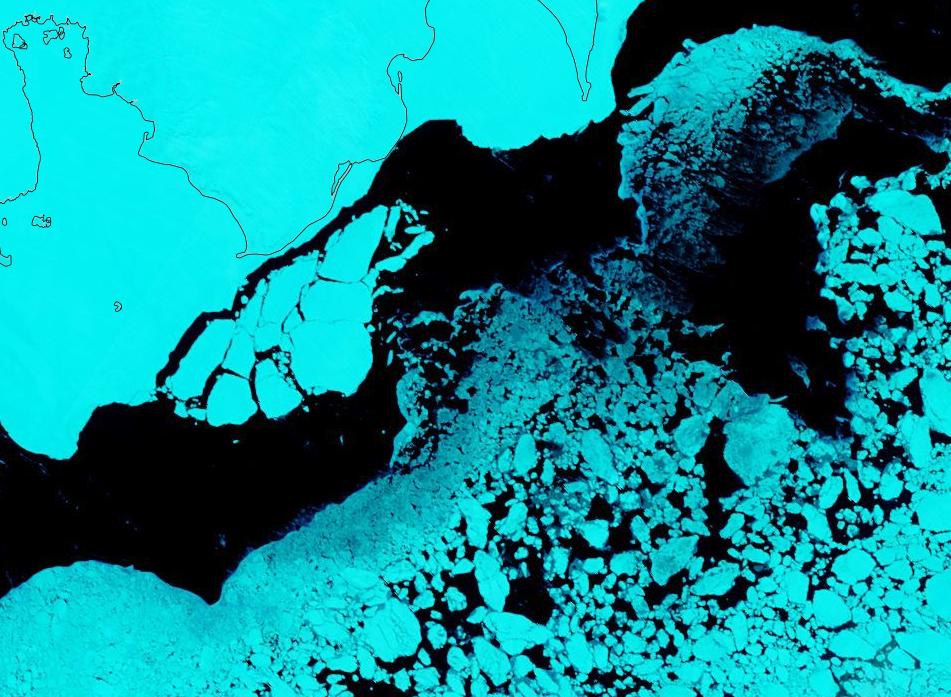
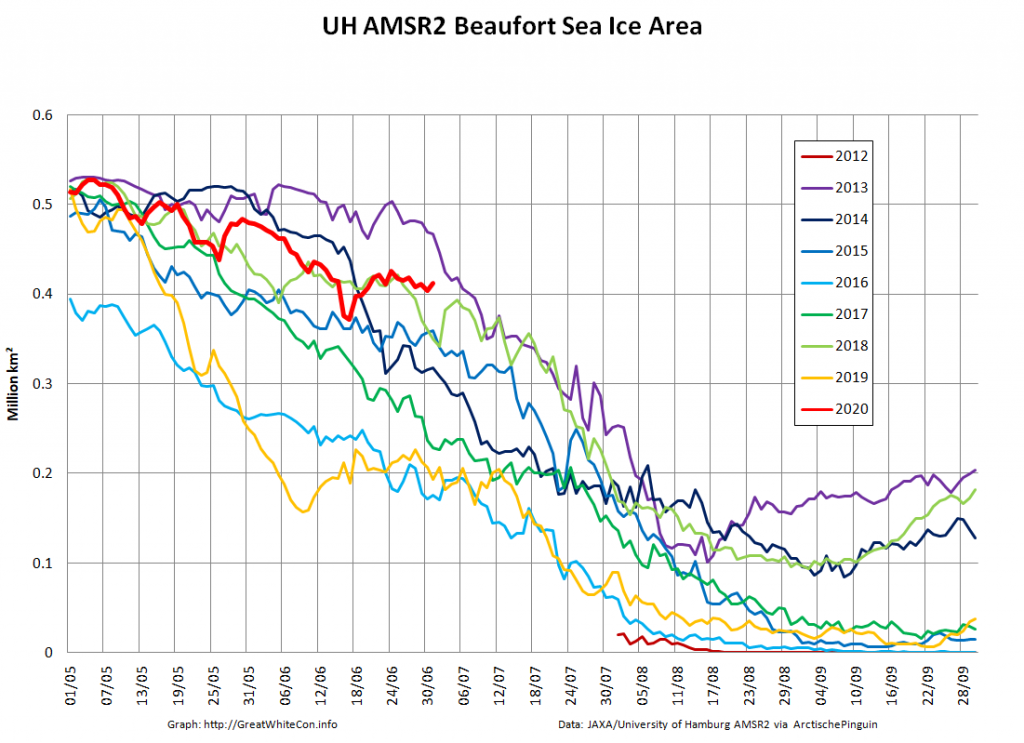
Whereas the Beaufort Sea is near a record high:
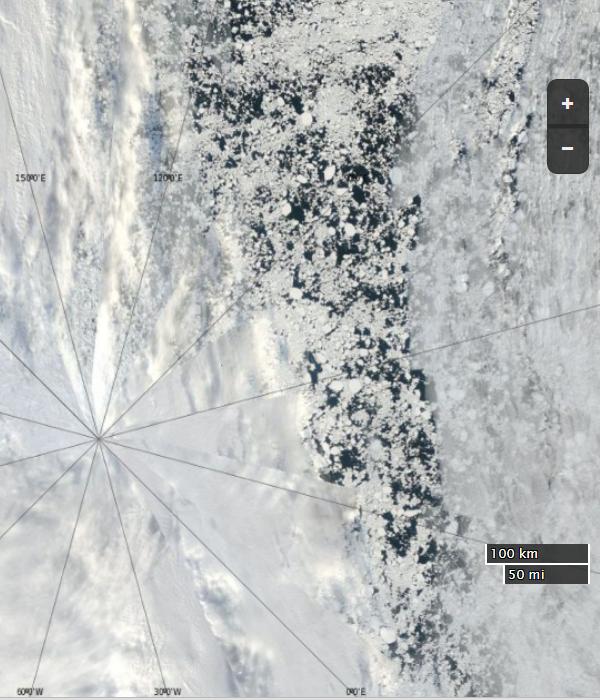
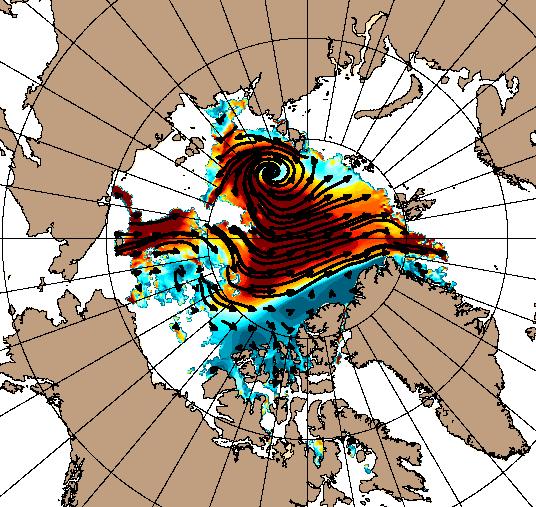
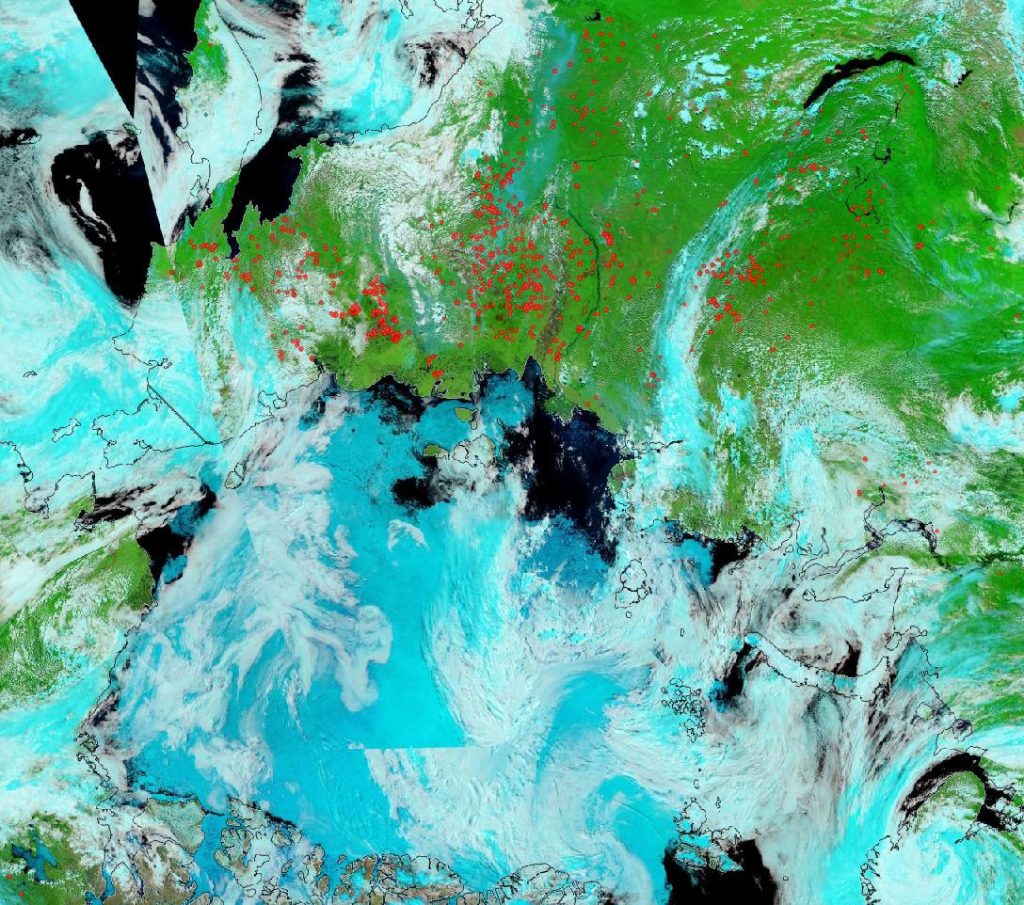
Currently the tell tale signs of surface melt are visible across most of the central Arctic, as are the large number of wildfires across Arctic Siberia:
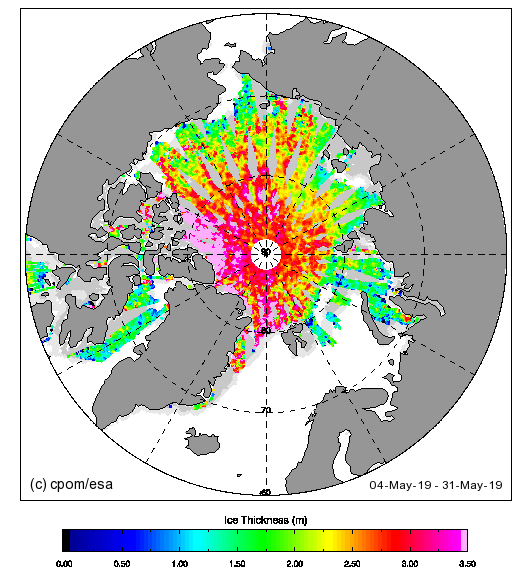
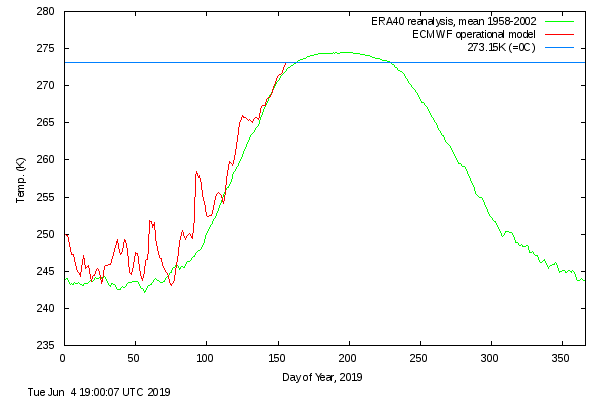
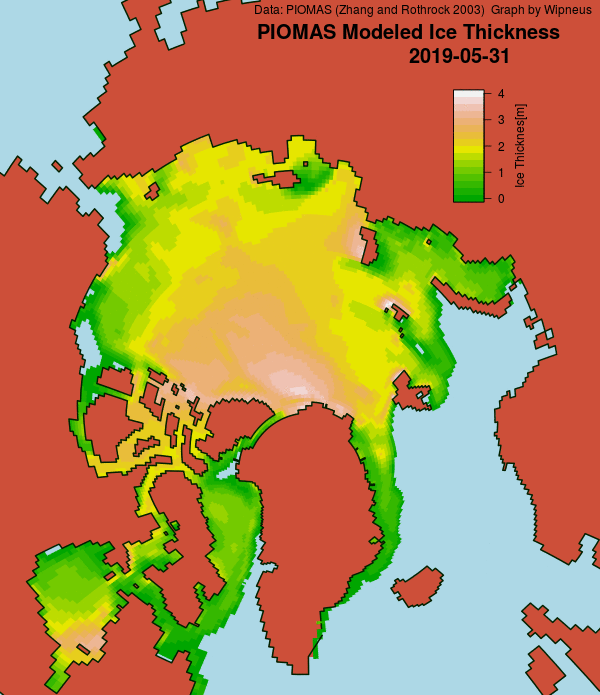
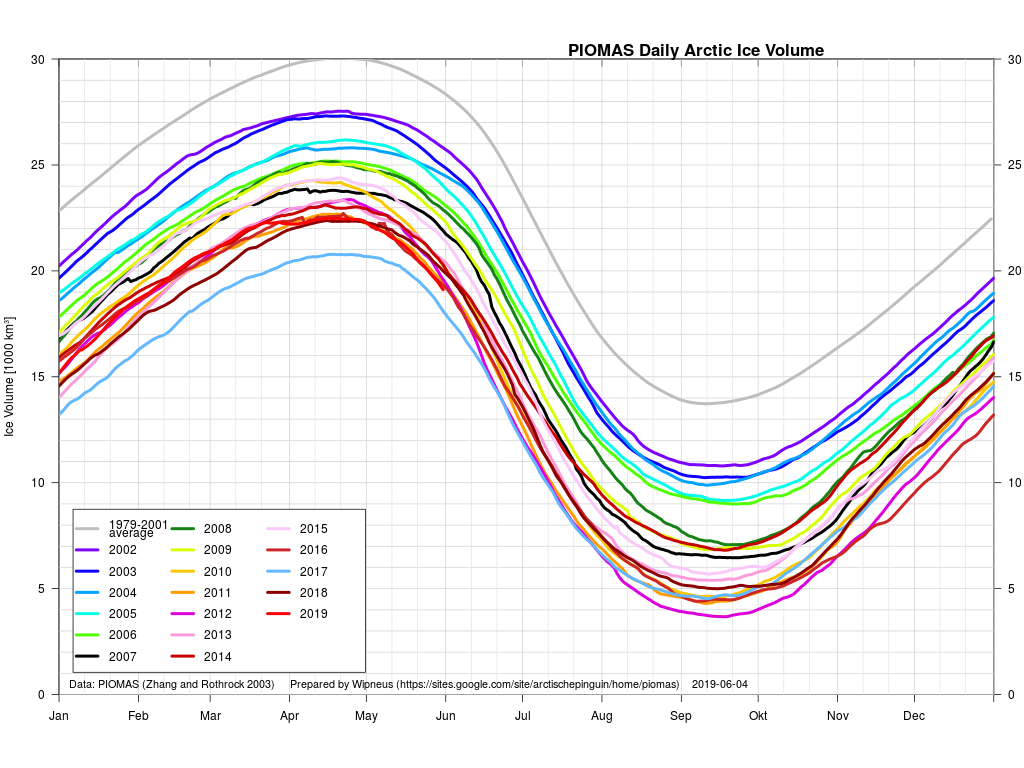
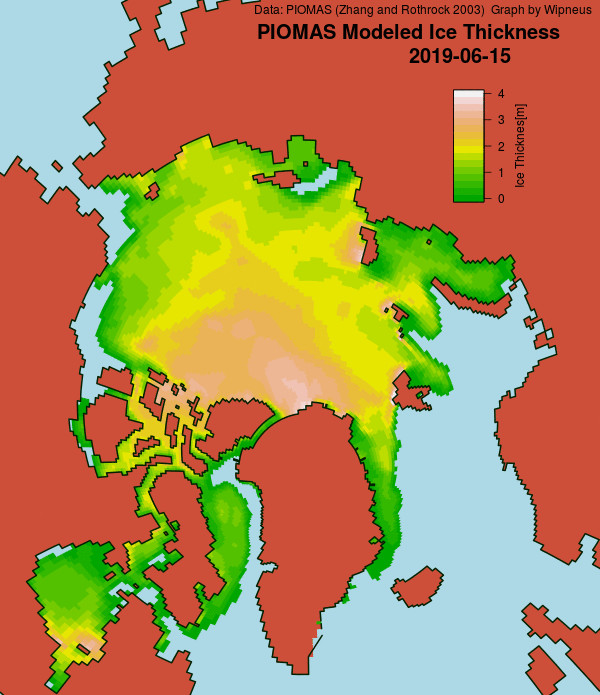
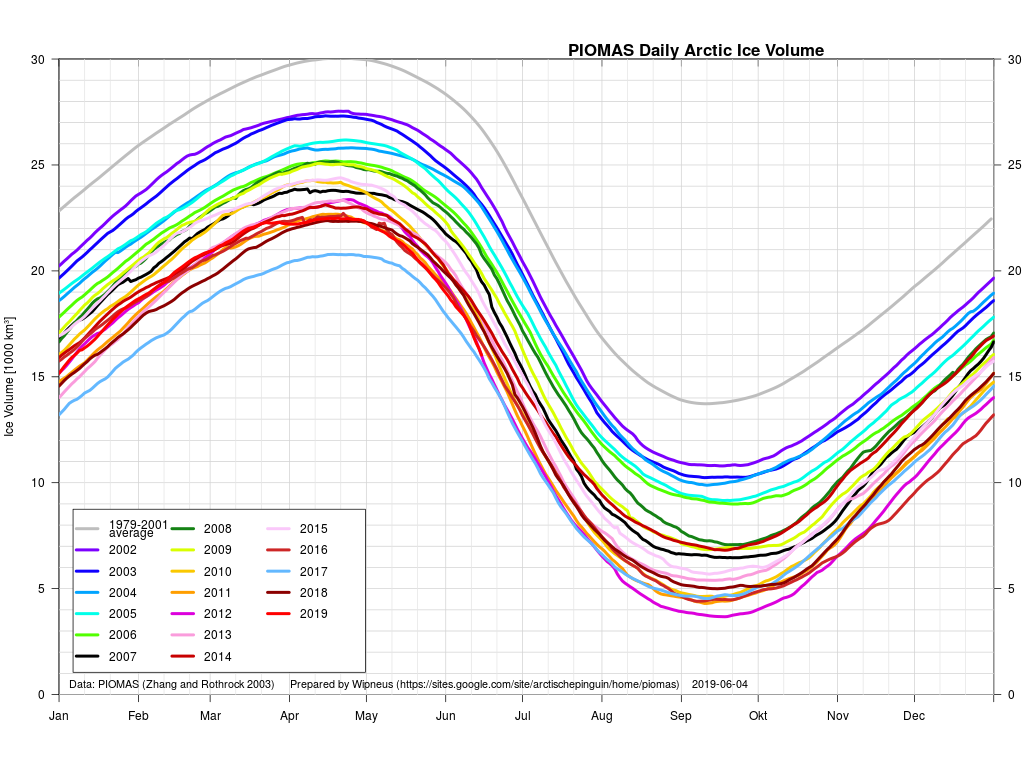
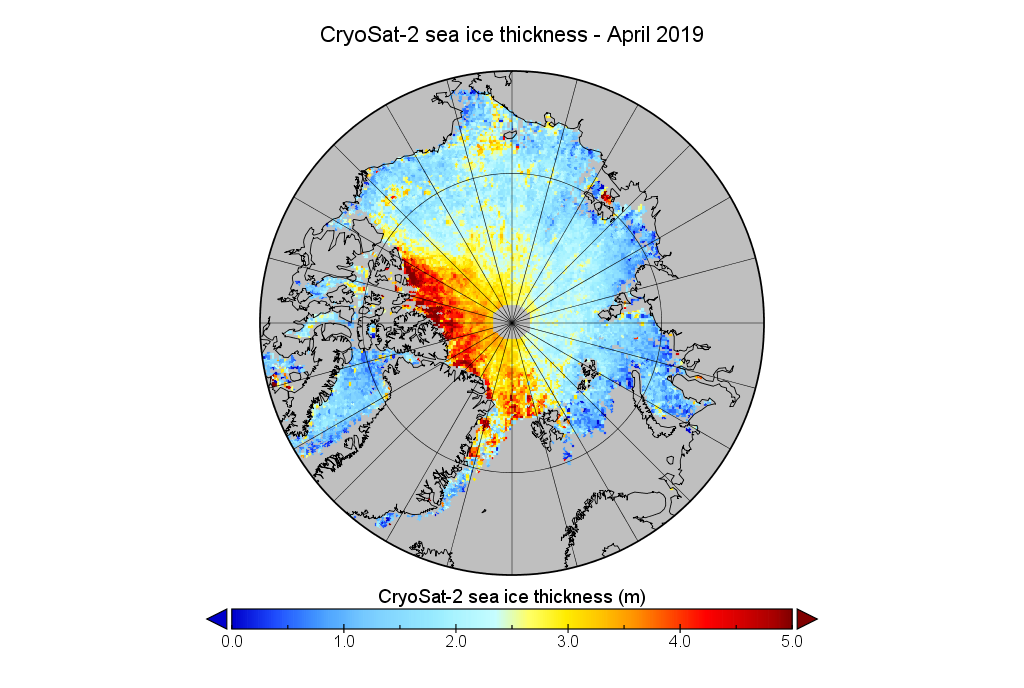
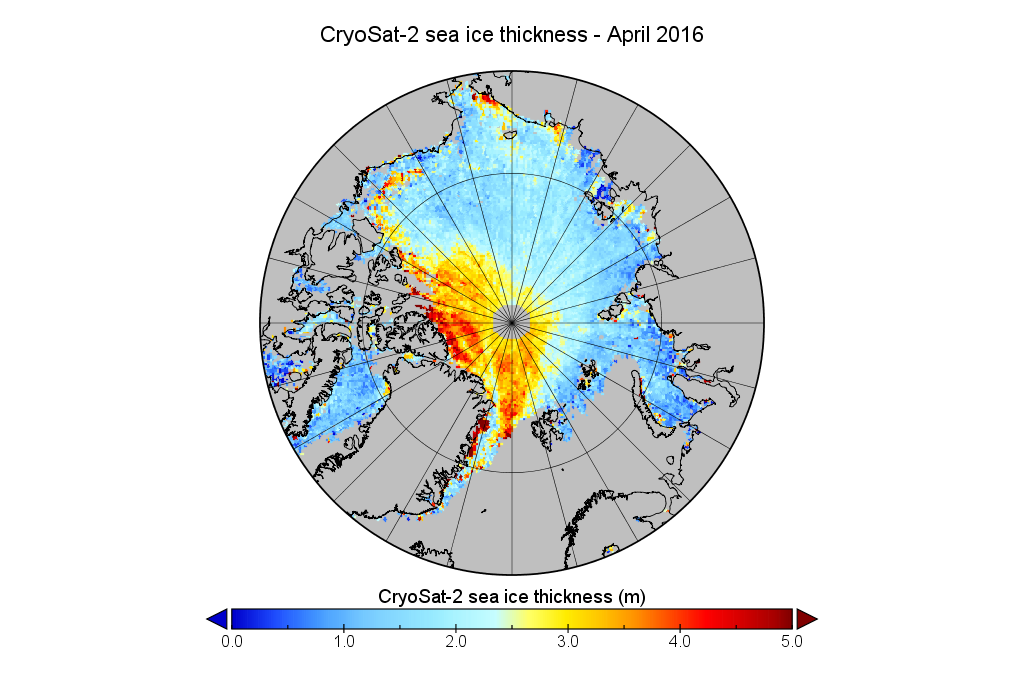
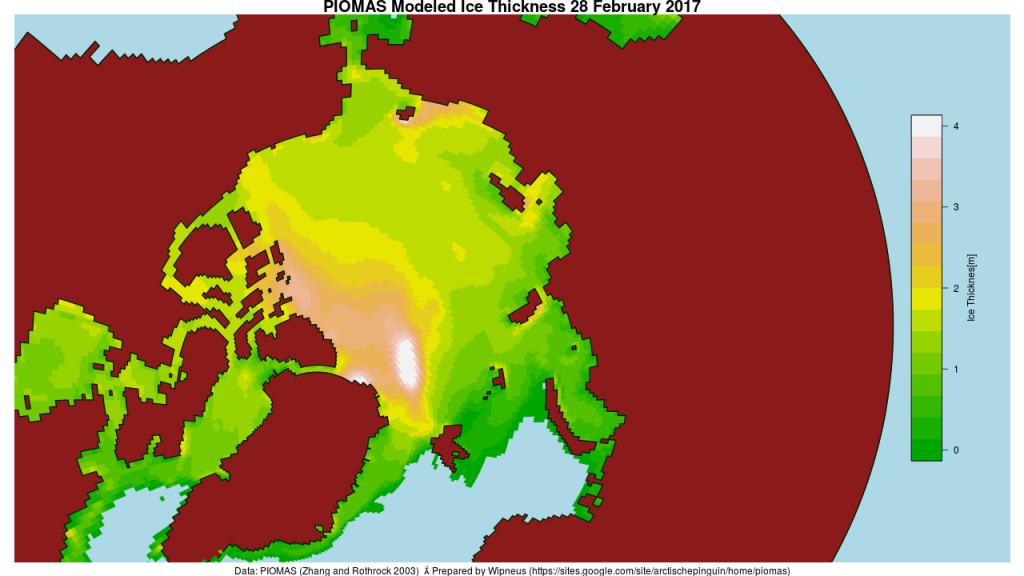
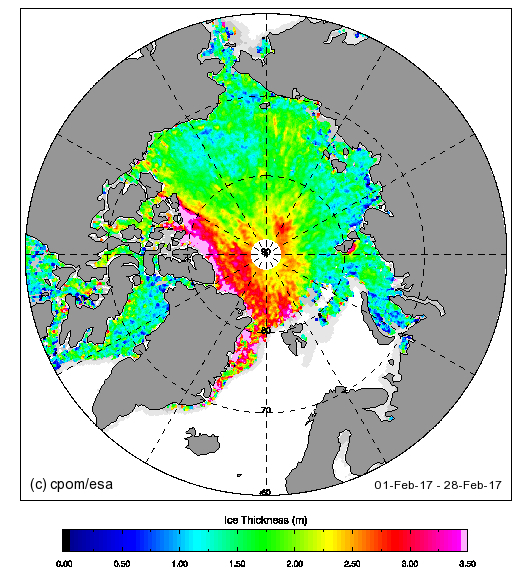
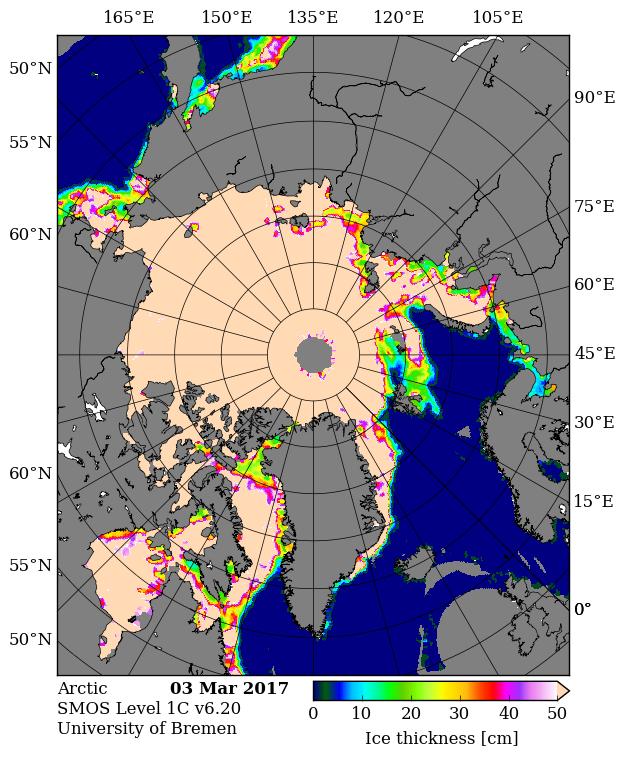
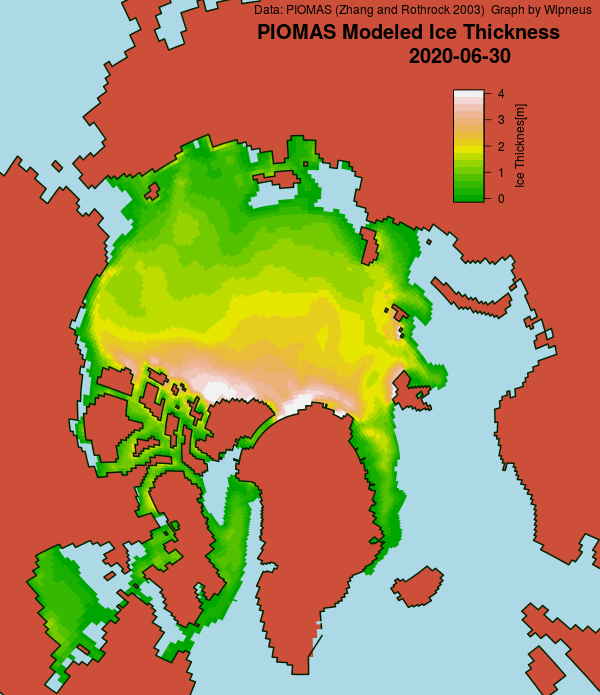
The June 30th PIOMAS gridded thickness numbers have been released, and here are the results of Wipneus’s number crunching:
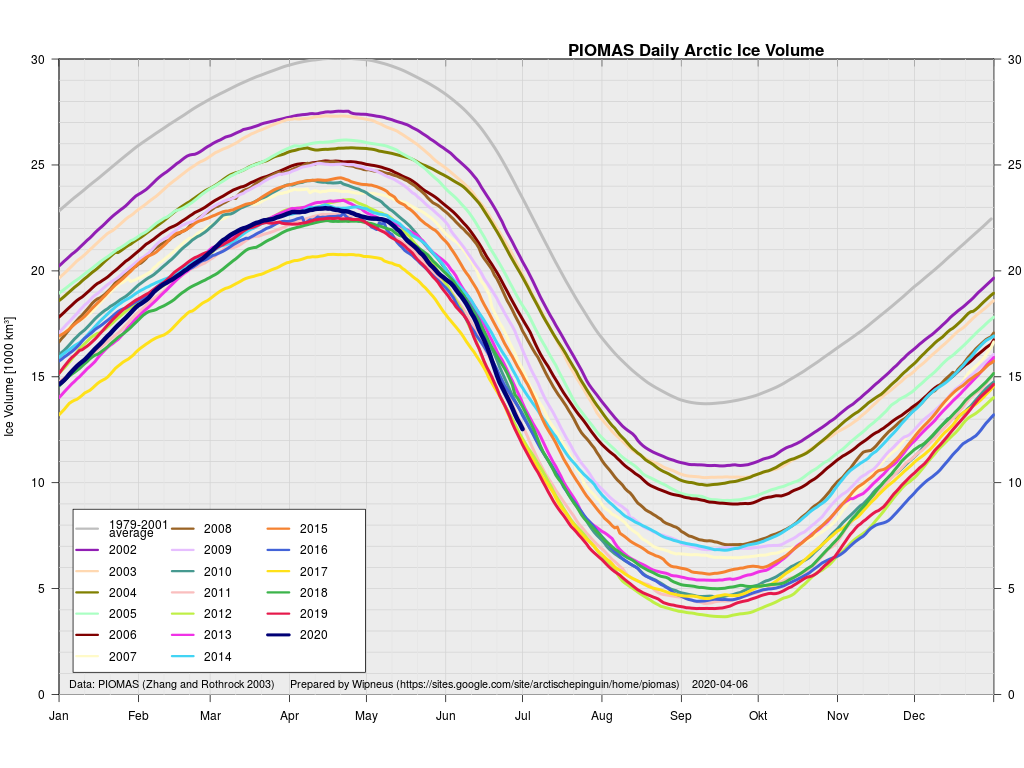
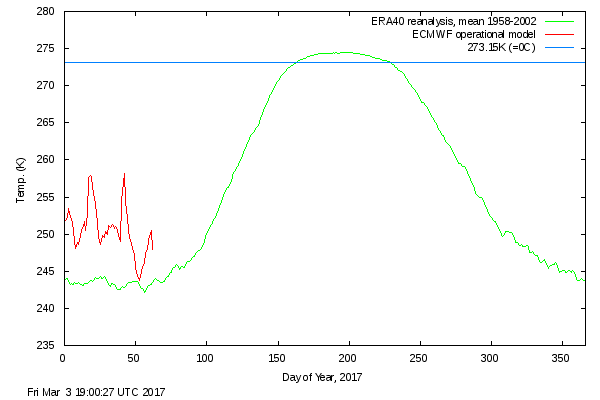
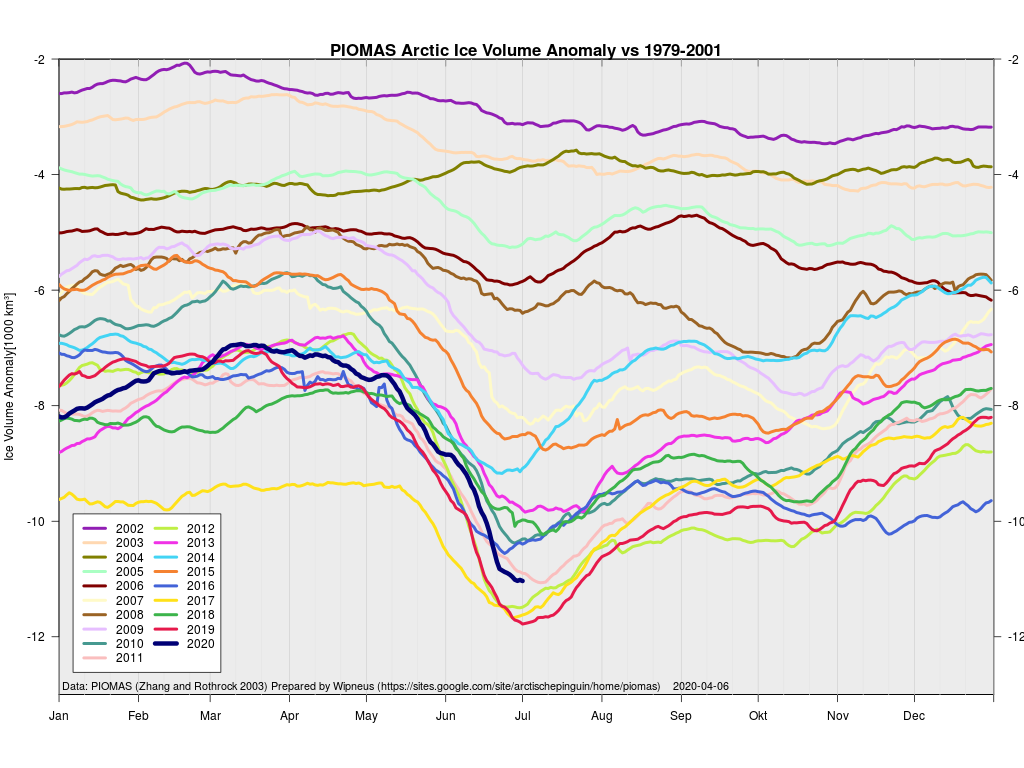
This month including a visualisation of the increasing negative anomaly:
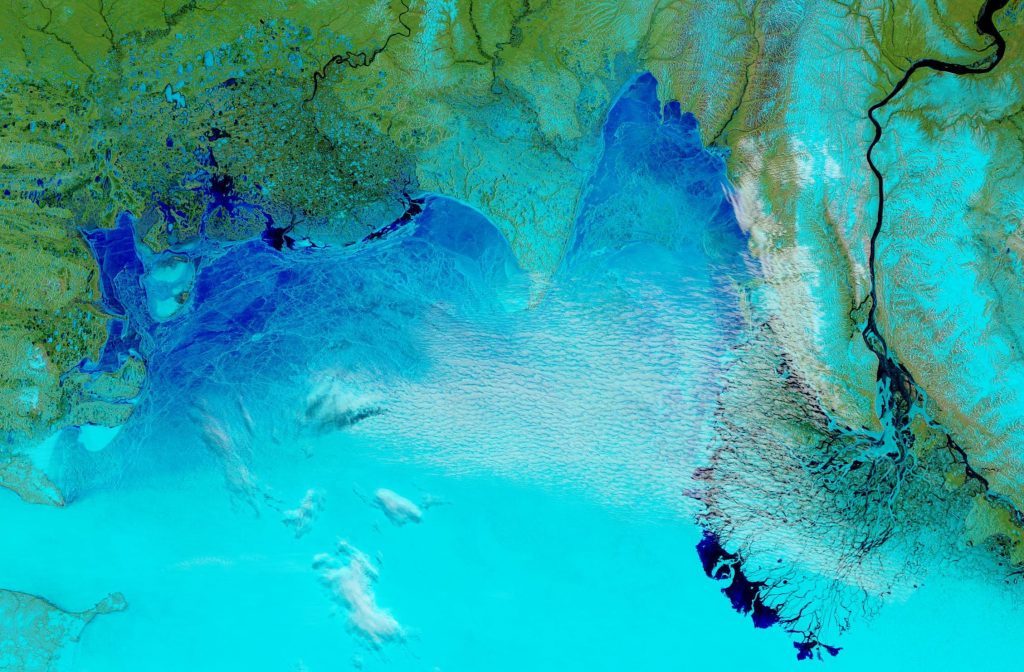
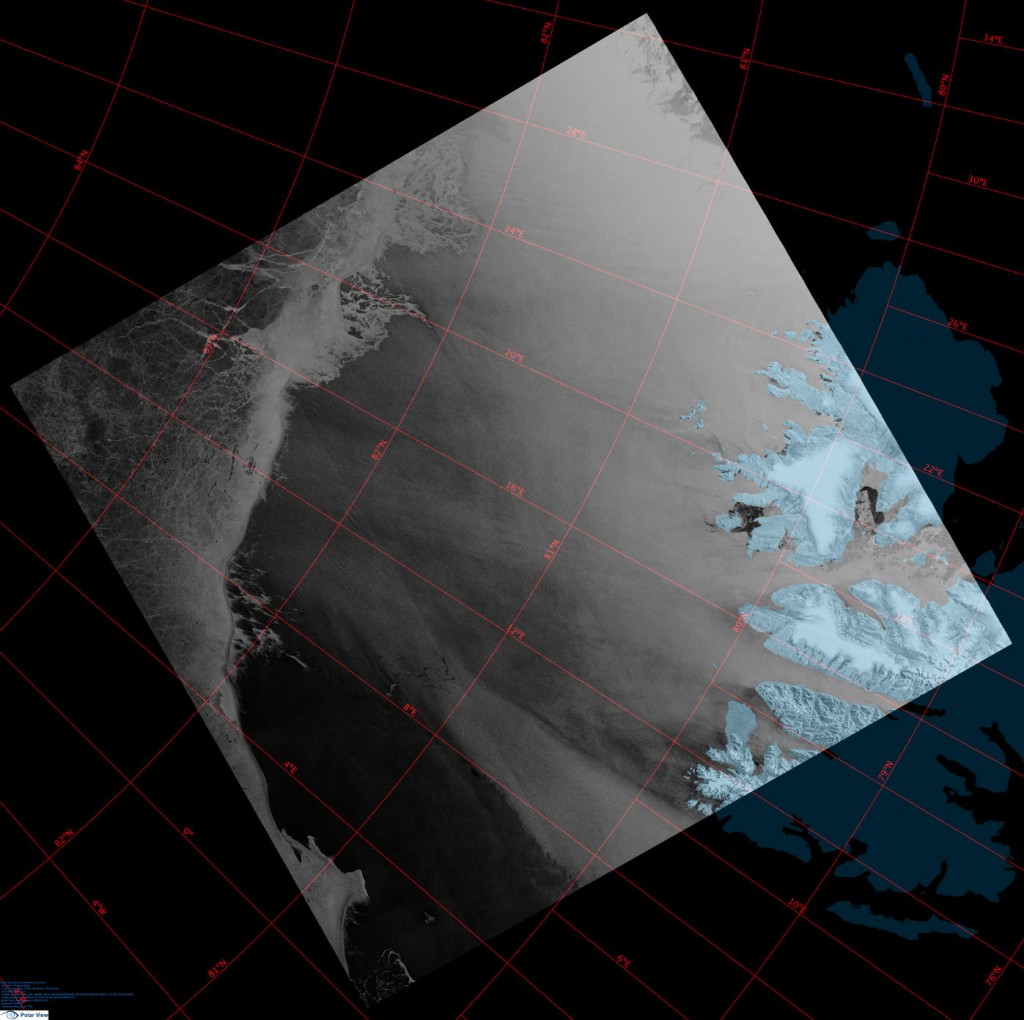
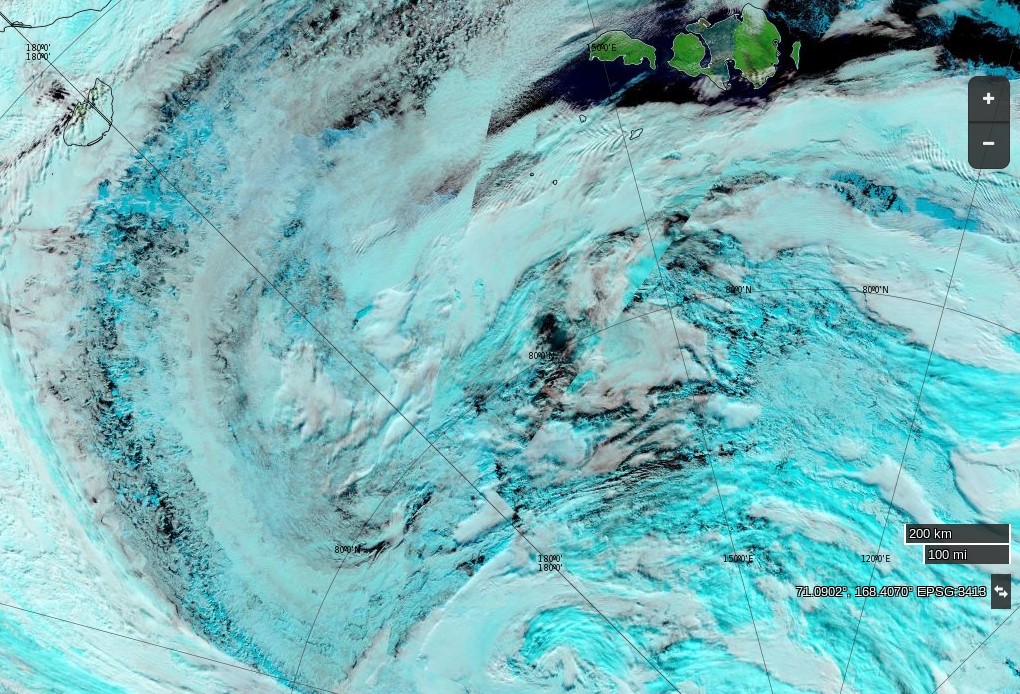
A break in the clouds over the North Pole reveals the onset of surface melt:
After a brief hiatus there are once again some ice mass balance buoys installed at assorted locations across the Arctic. Some have ceased to function, but one of the buoys installed as part of the MOSAiC expedition is still sending back data as it heads towards the Fram Strait. Buoy 387850 is currently located at 81.66 N, 4.19 E. Here’s its ice mass balance plot:
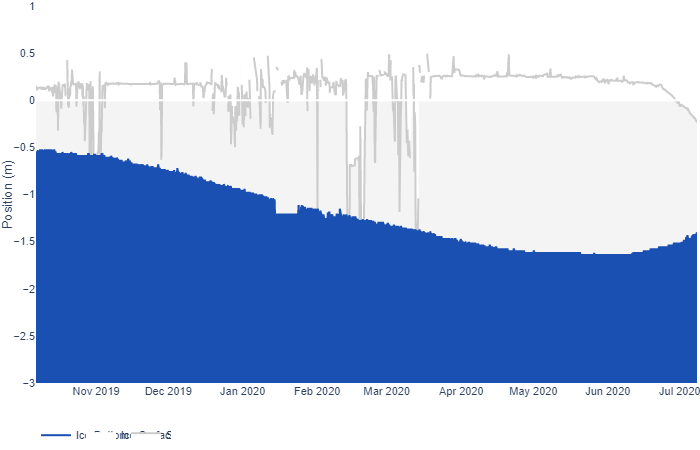
As you can see, both surface and bottom melt are well under way, with just over a meter of ice still remaining.
Now let’s take a look at buoy 386840, currently located at 74.30 N, 132.60 W in the Beaufort Sea:
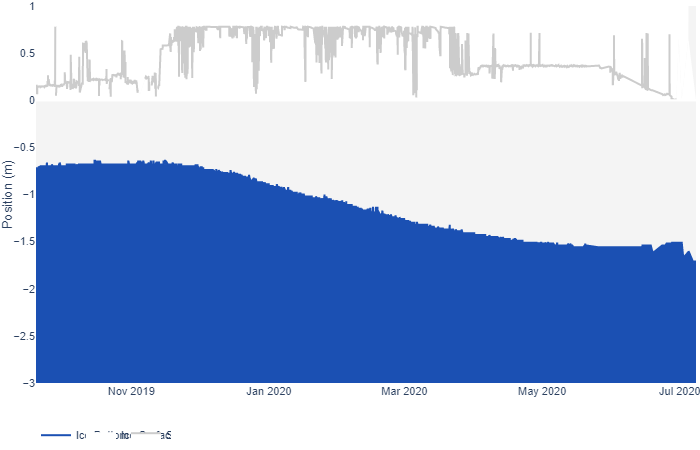
It looks as though the ice thickness has increased, but surely that can’t be right at this time of year? To try and find out I downloaded the raw data and plotted the temperature readings from the buoy’s thermistor string:
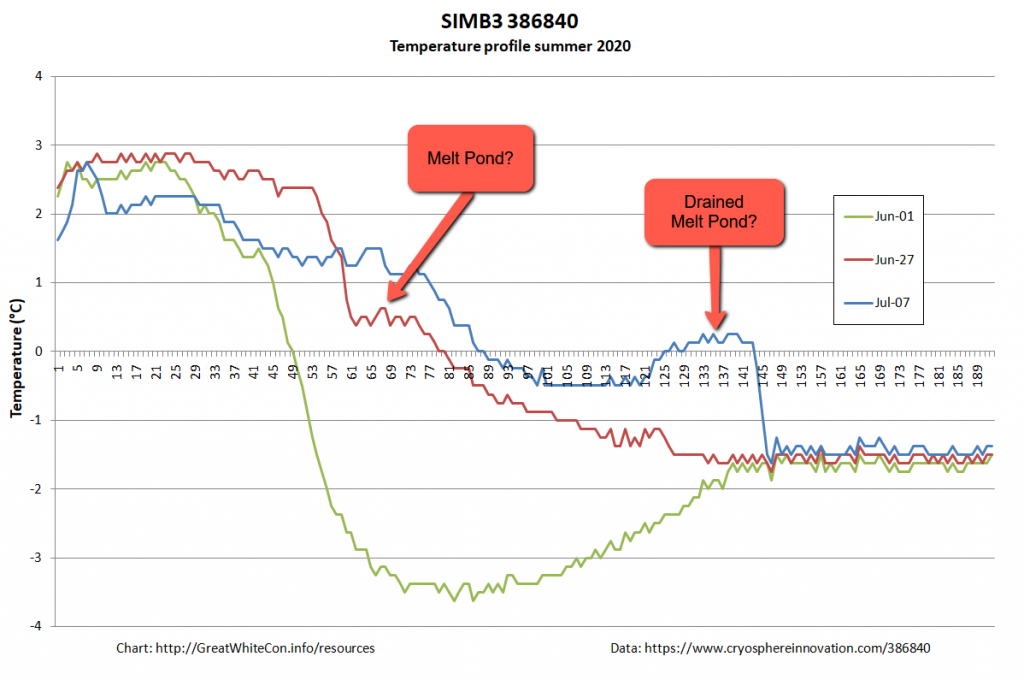
It looks to me as though the ice floe carrying the buoy is currently floating on some warm fresh water from a recently drained melt pond, which is confusing the sensor designed to measure the position of the bottom of the ice. There certainly seems to be far less than the claimed “1.653 m snow and ice thickness” still remaining to be melted!
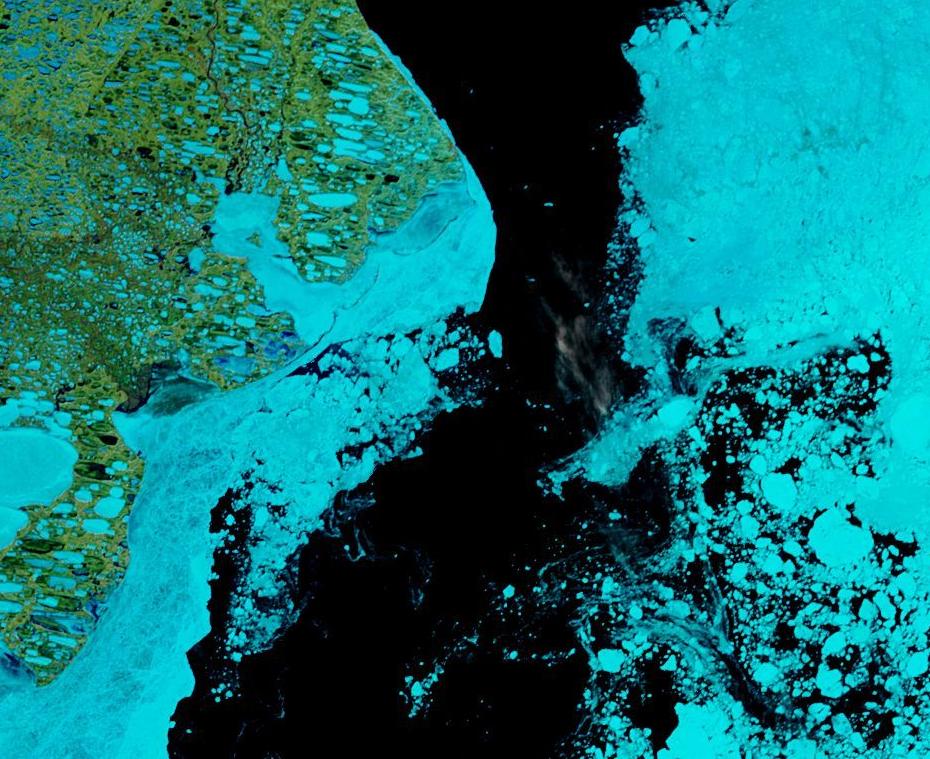
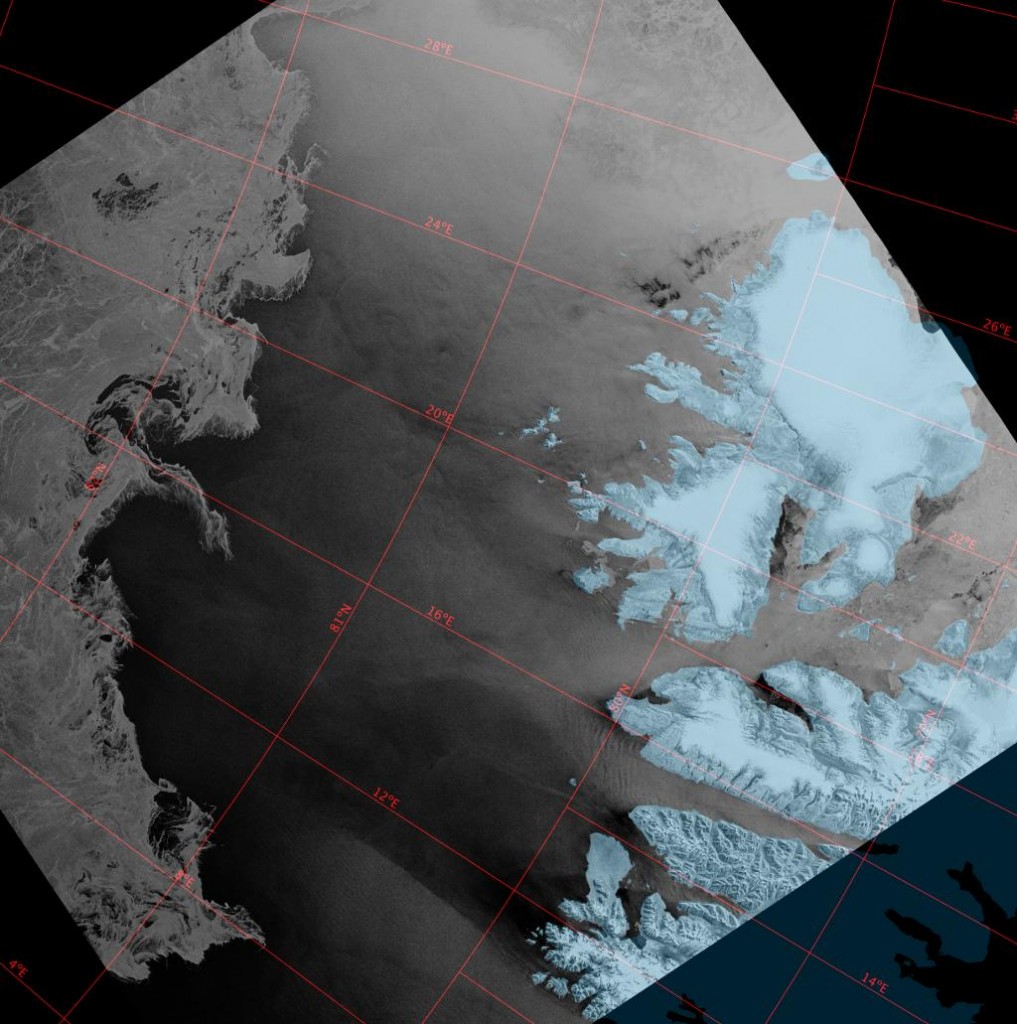
A very unusual image. Hardly a cloud in the sky over the North Pole yesterday:

The July 2020 extent “plummet” shows no signs of ending just yet. Here’s the JAXA/ViSHOP version:
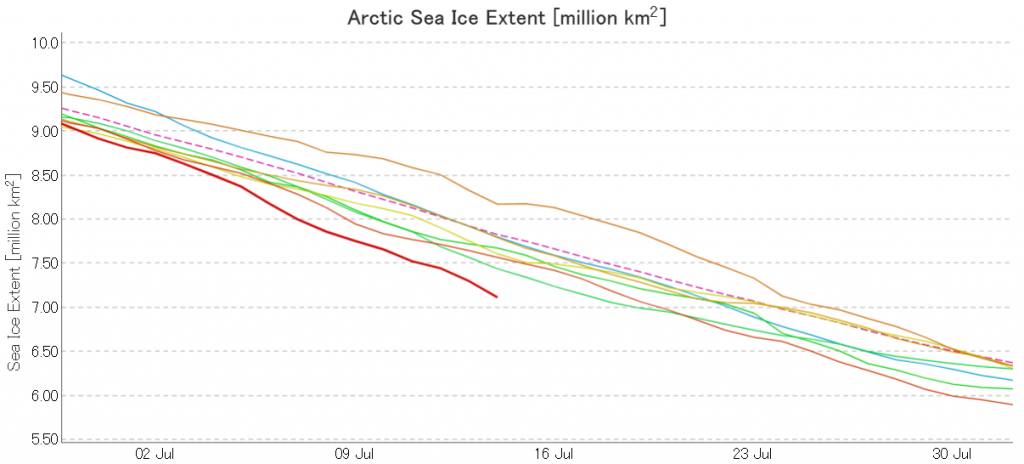
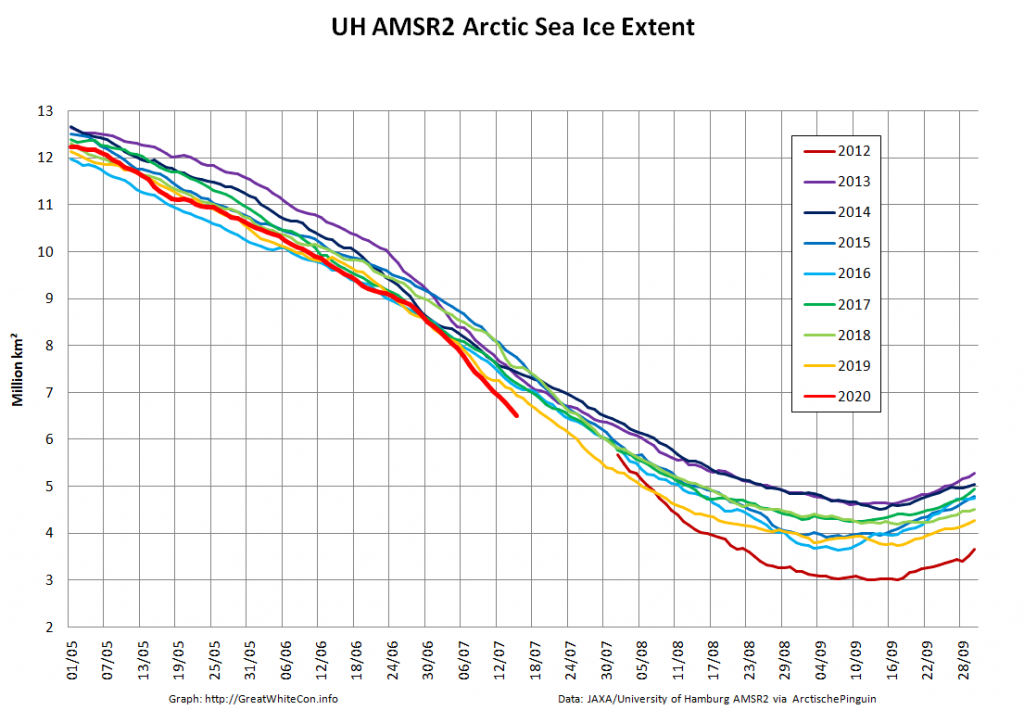
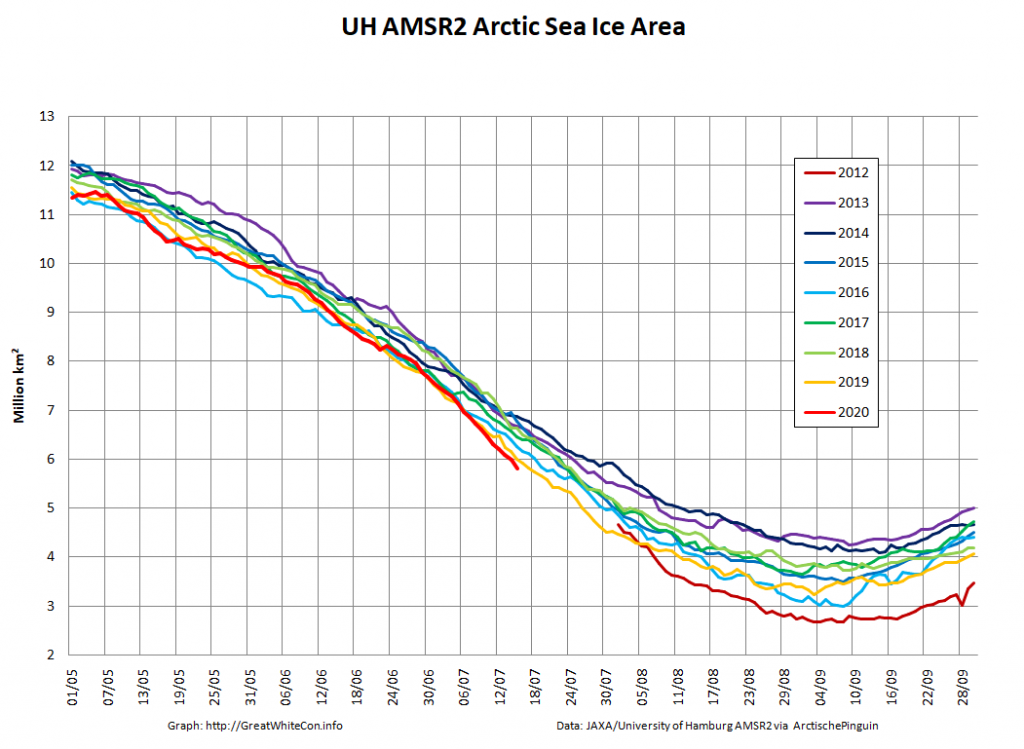
JAXA AMSR2 extent is now below 7 million km², and the high resolution version is lower still:
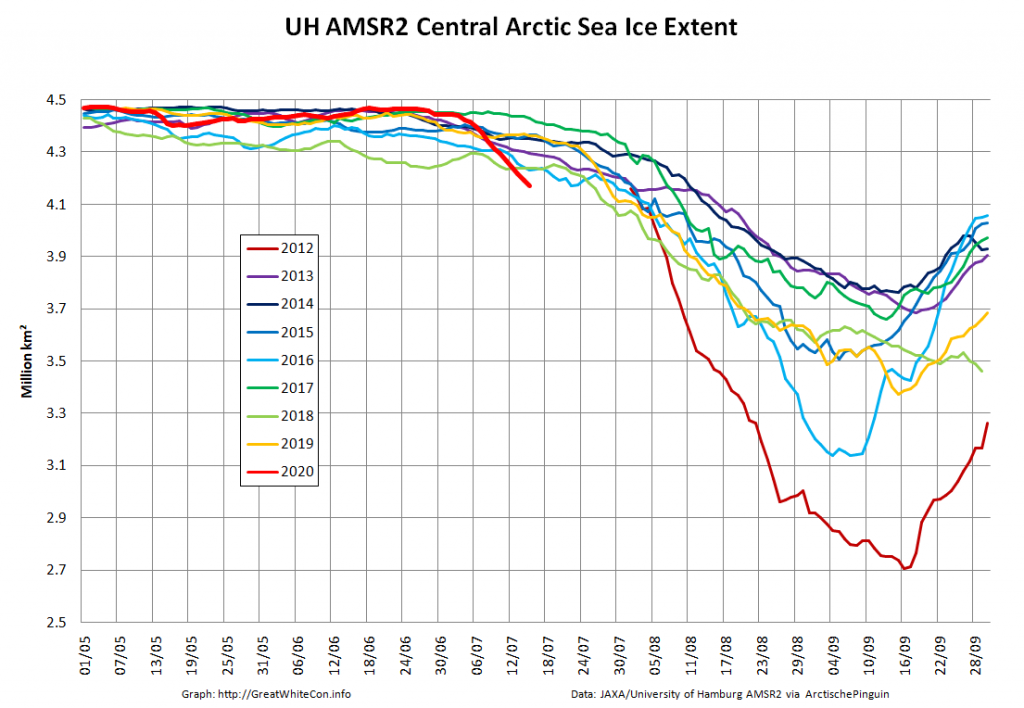
As the “Laptev Bite” and the Atlantic periphery of open water extends further towards the North Pole, Central Arctic Basin extent is now also at record lows for the date in the AMSR2 record:
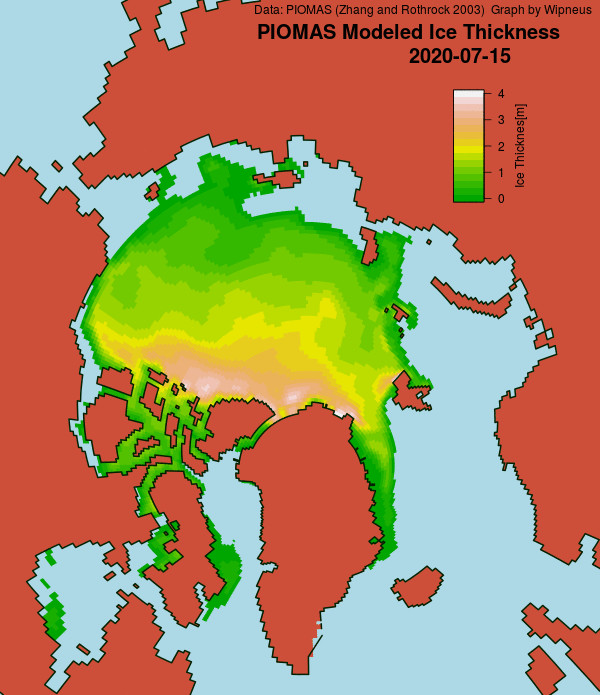
Wipneus has crunched the mid month PIOMAS gridded thickness numbers, and here are the results:
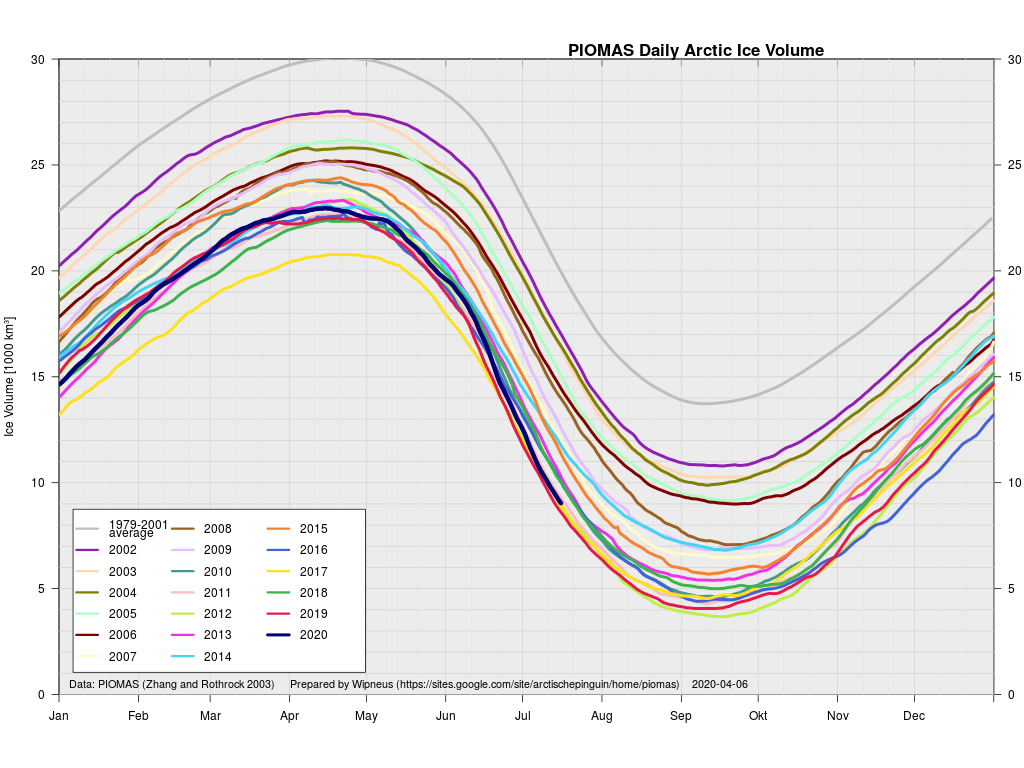
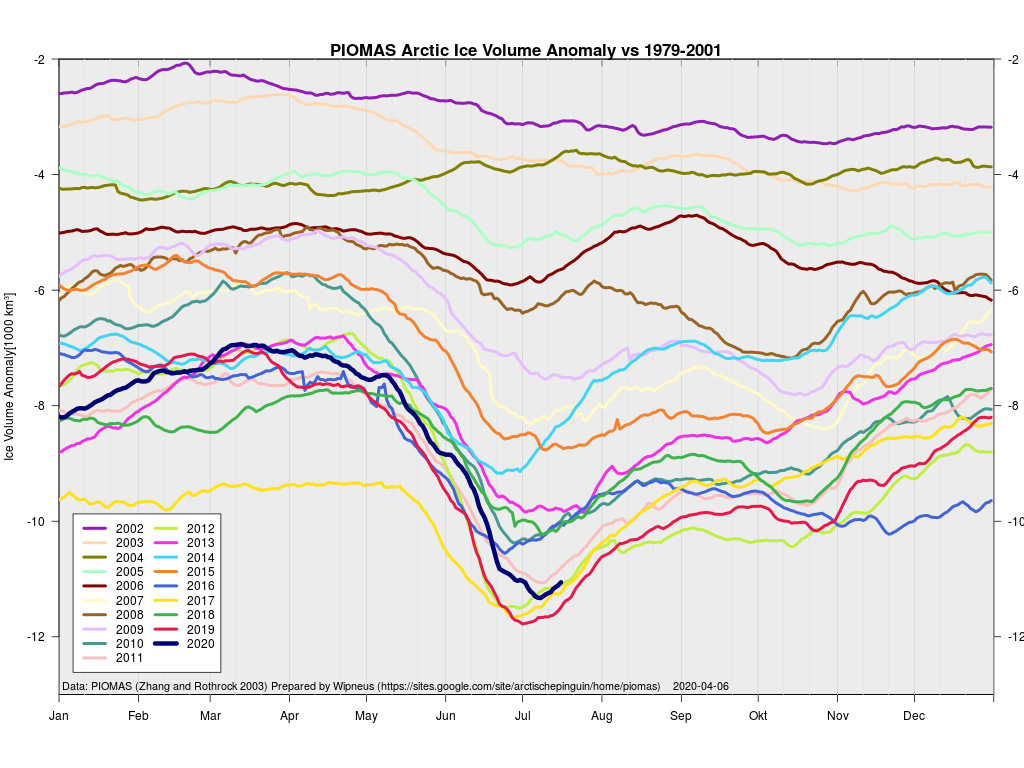
Extent is currently lowest in the satellite era by a long way, but modelled volume is only fourth lowest!
Watch this space!
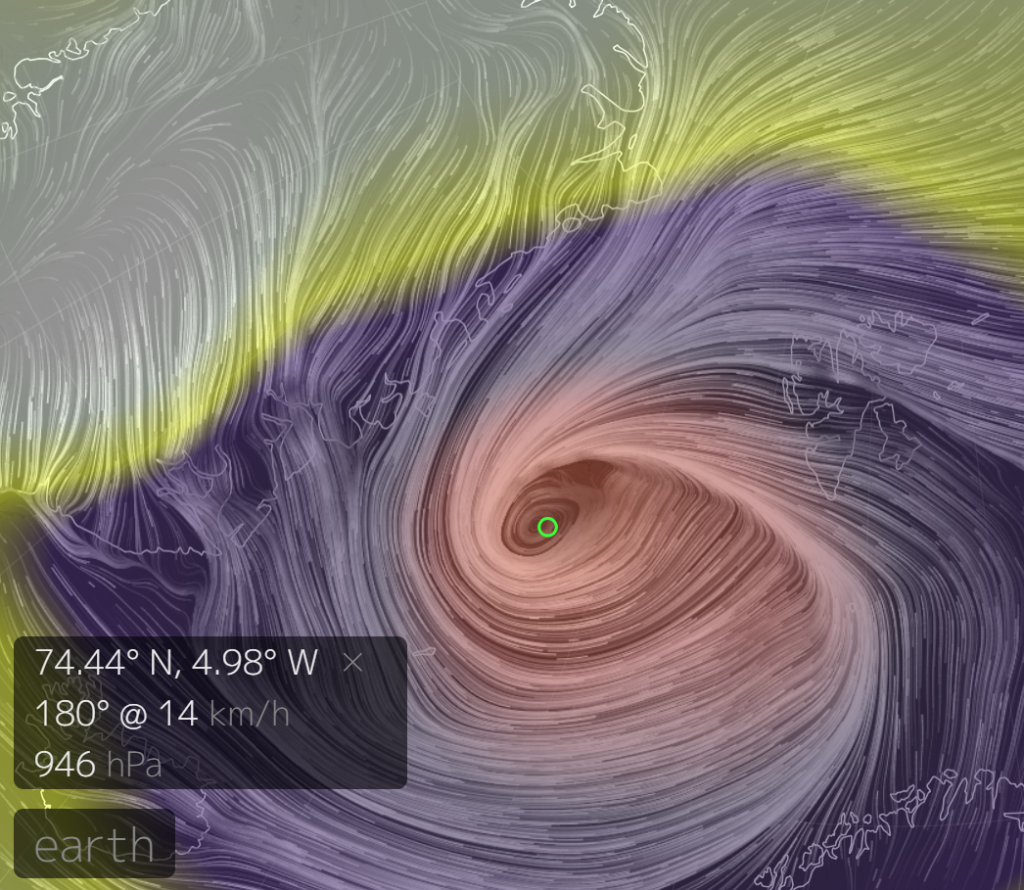
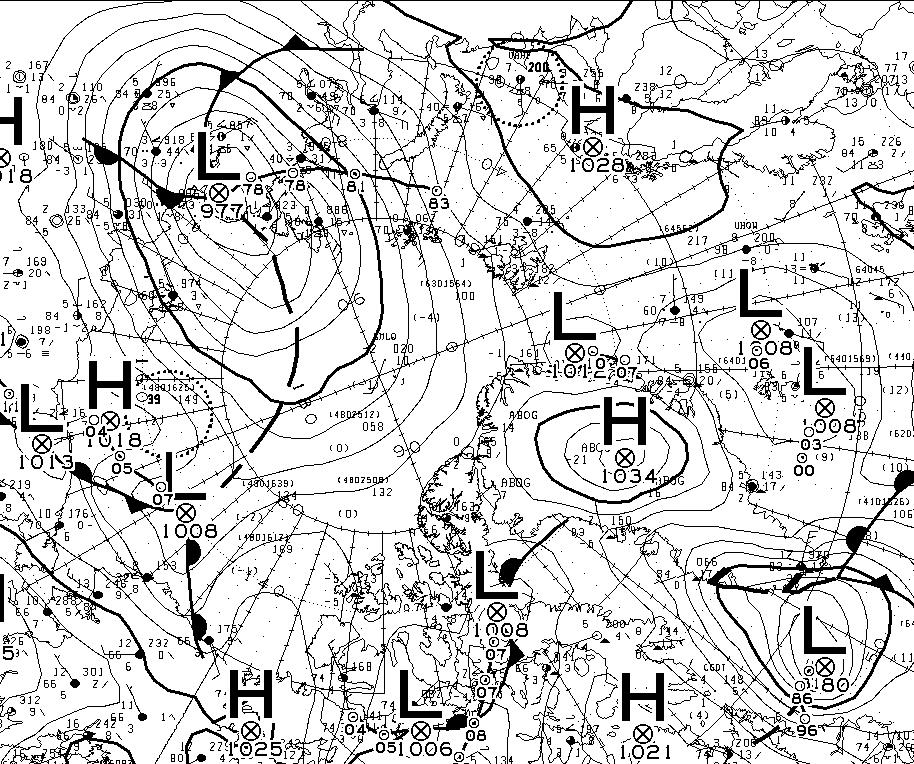
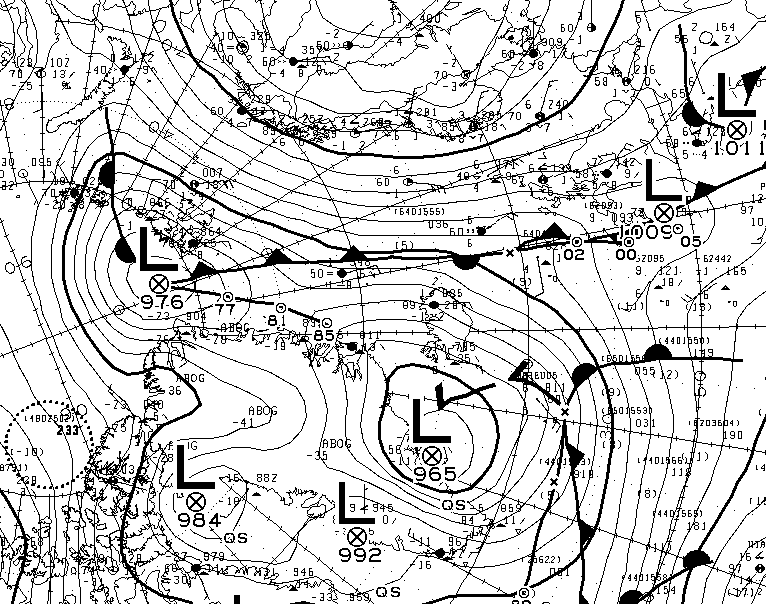
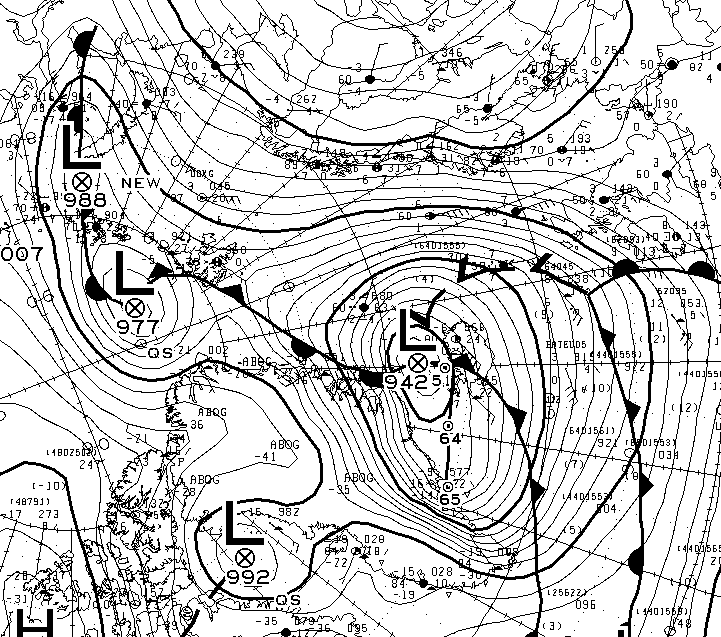
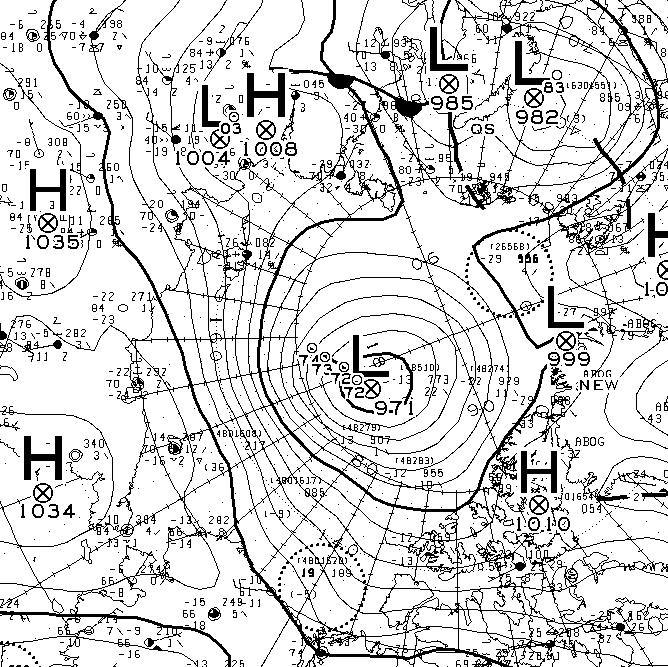
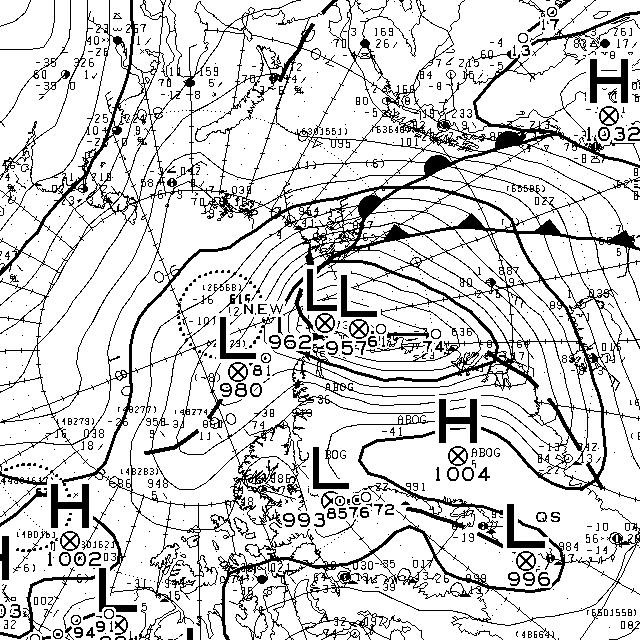
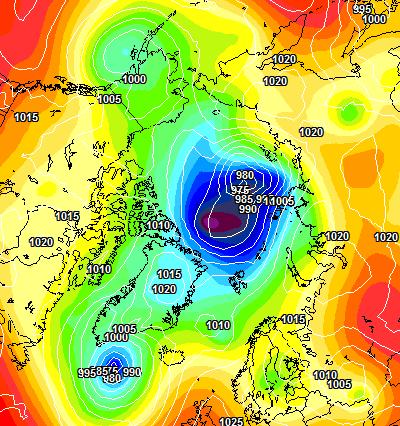
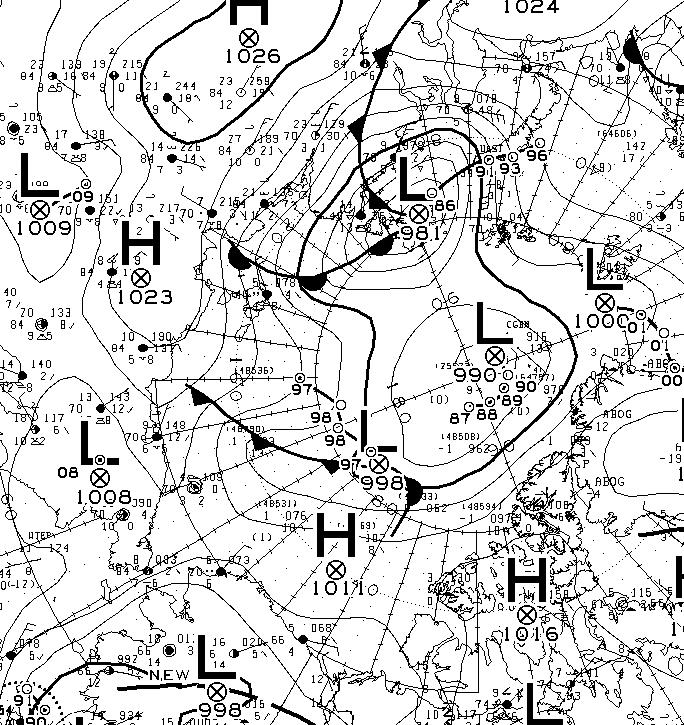
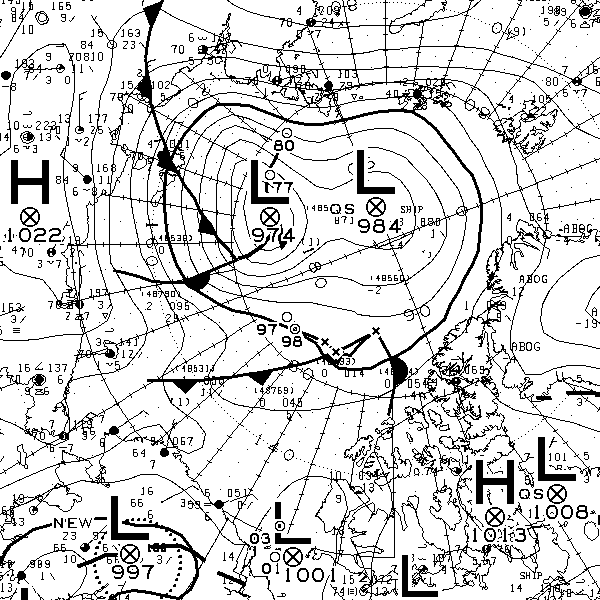
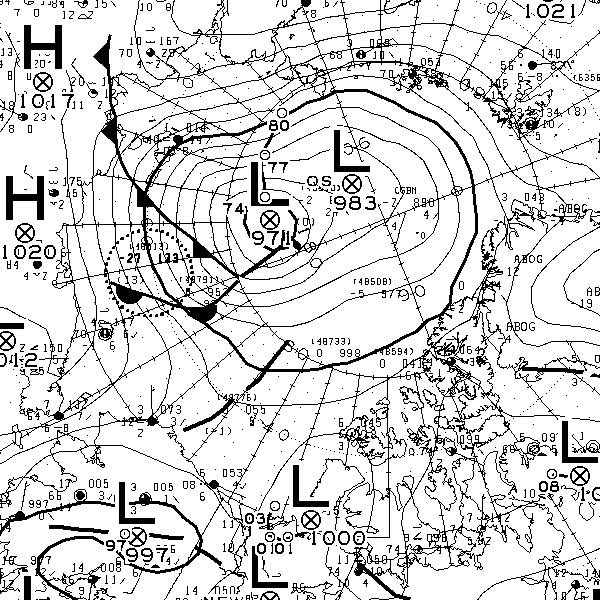
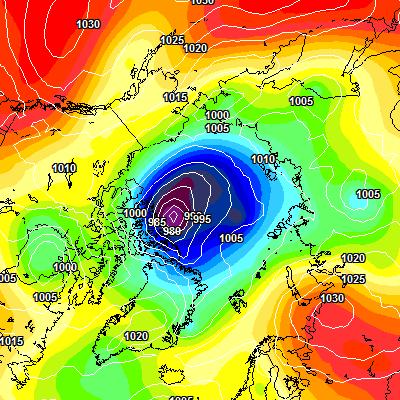
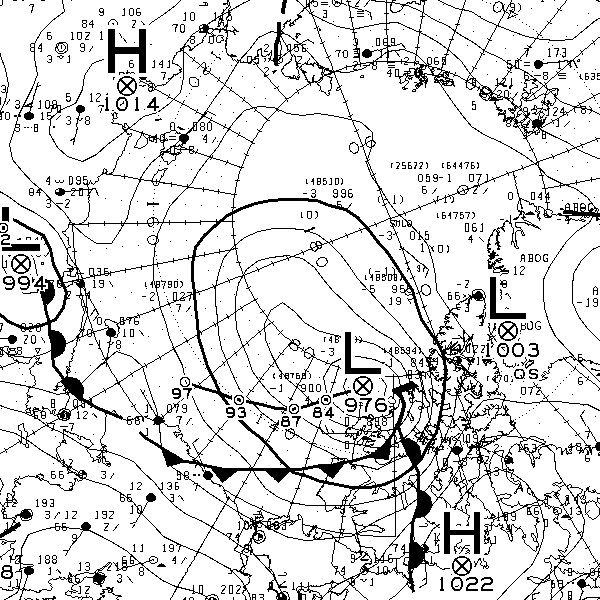
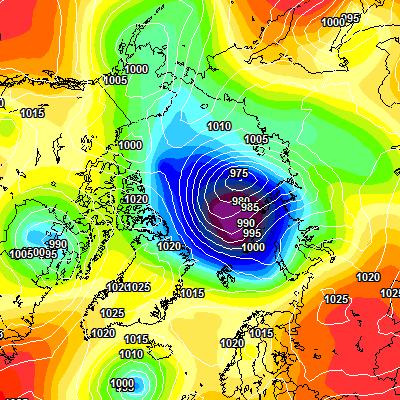
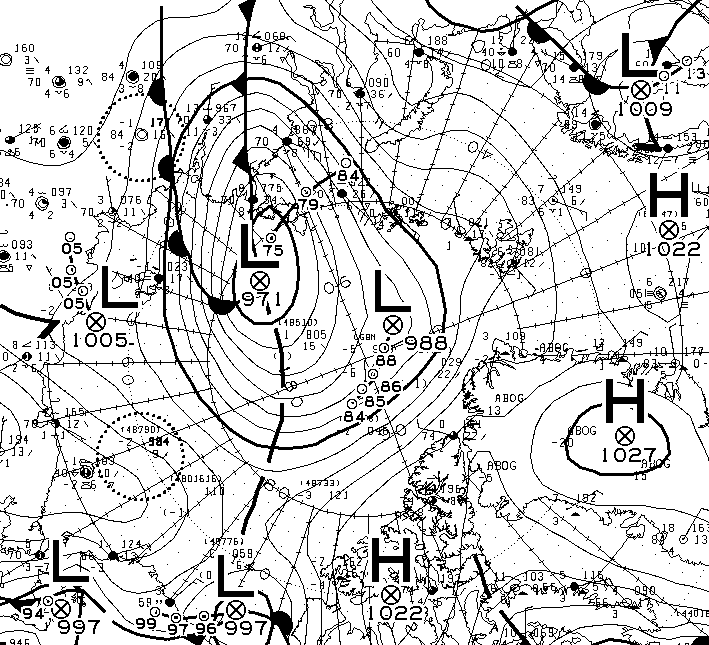
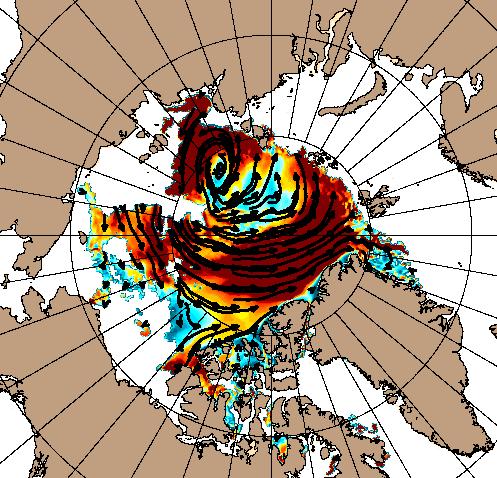
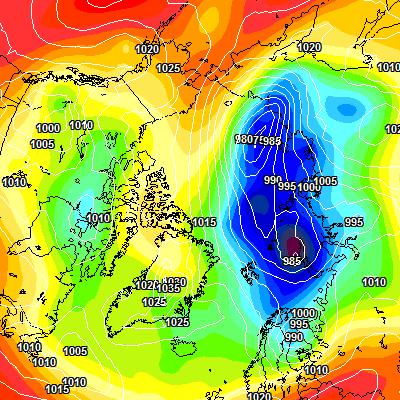
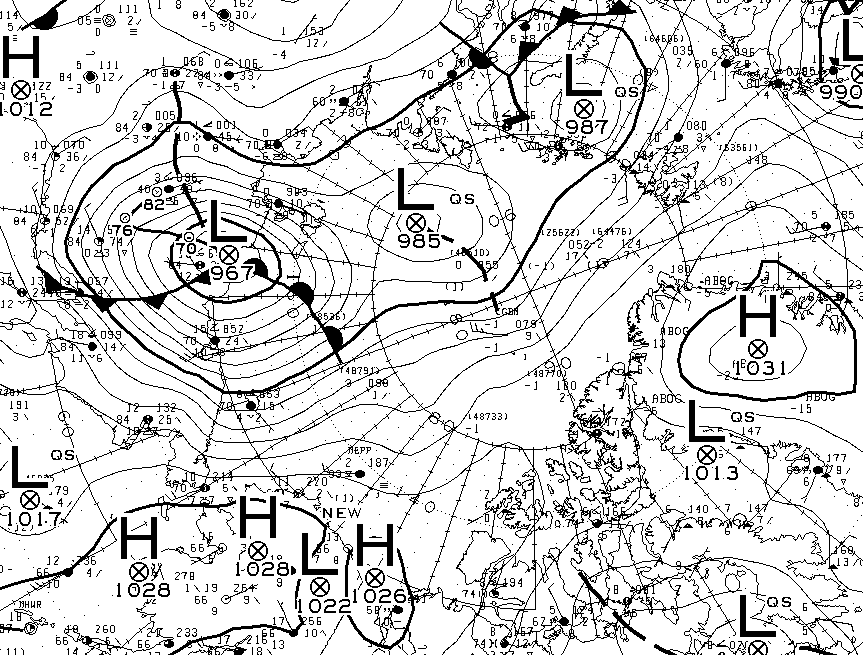
At long last there’s a sub 1000 hPa MSLP low pressure area slowly wending its way across the central Arctic:
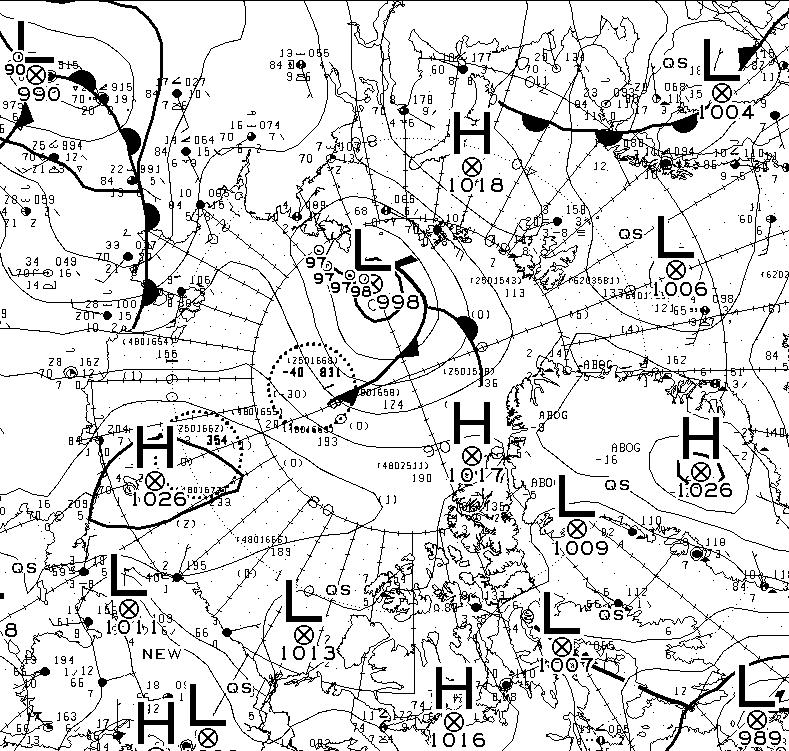
It seems to have bottomed out at 997 hPa. Perhaps this will inhibit the ongoing “plummet” in extent? JAXA extent fell by 114,342 km2 yesterday.
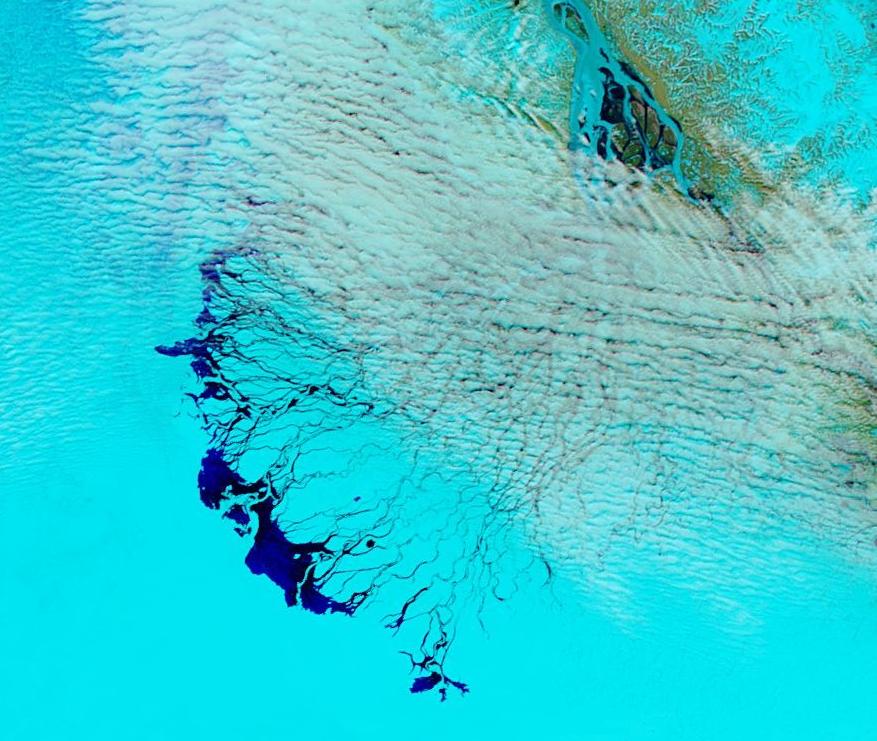
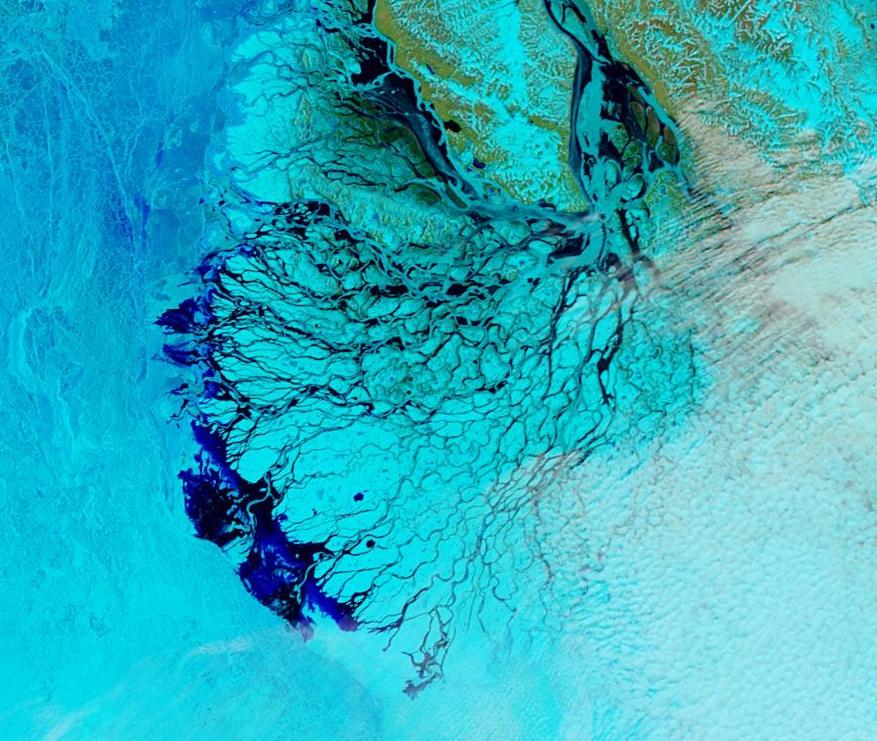
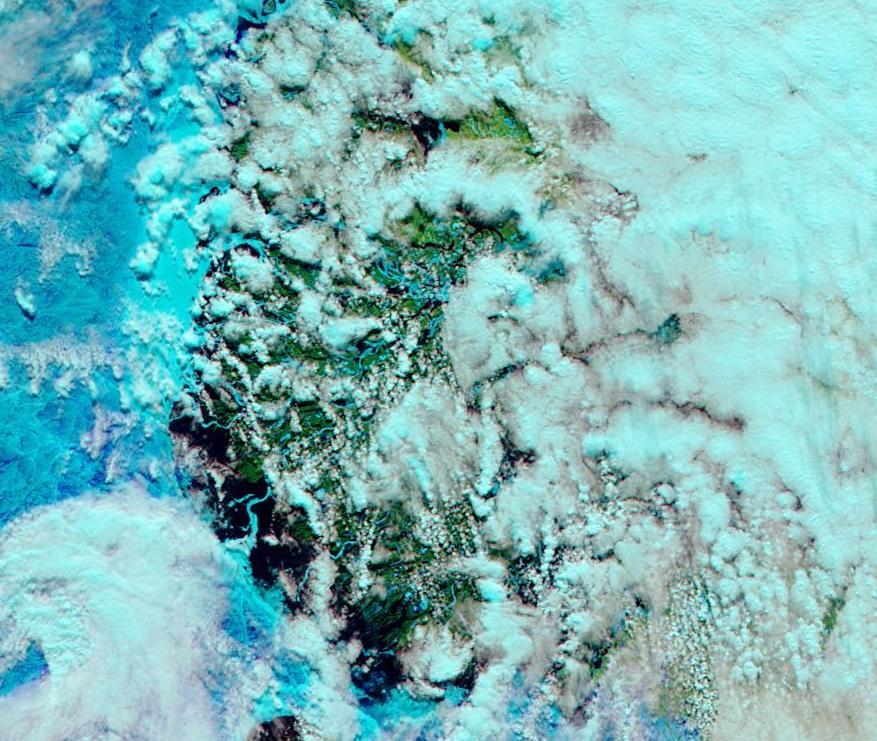
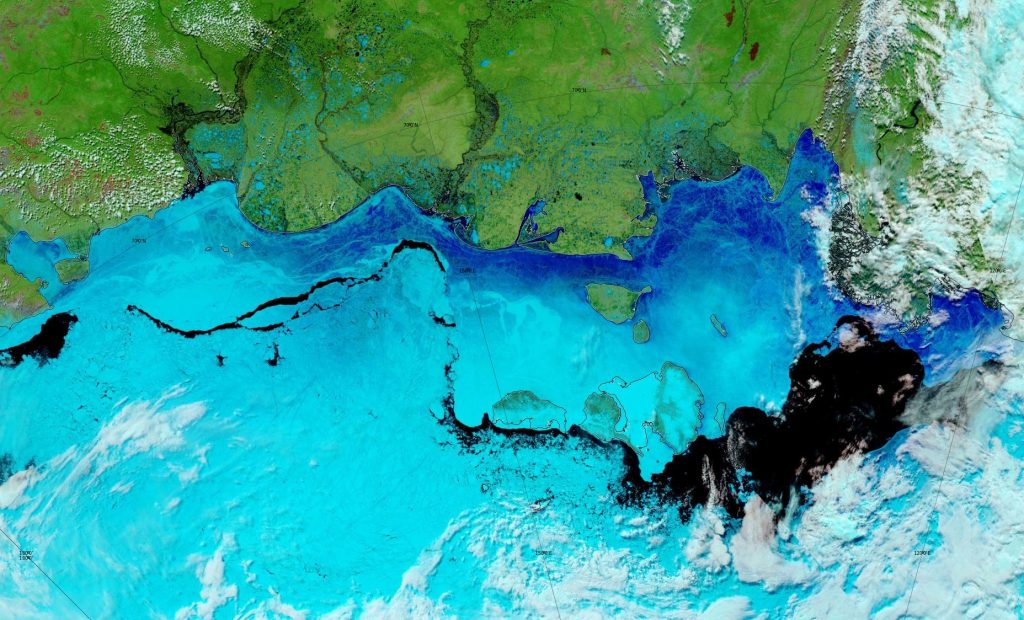
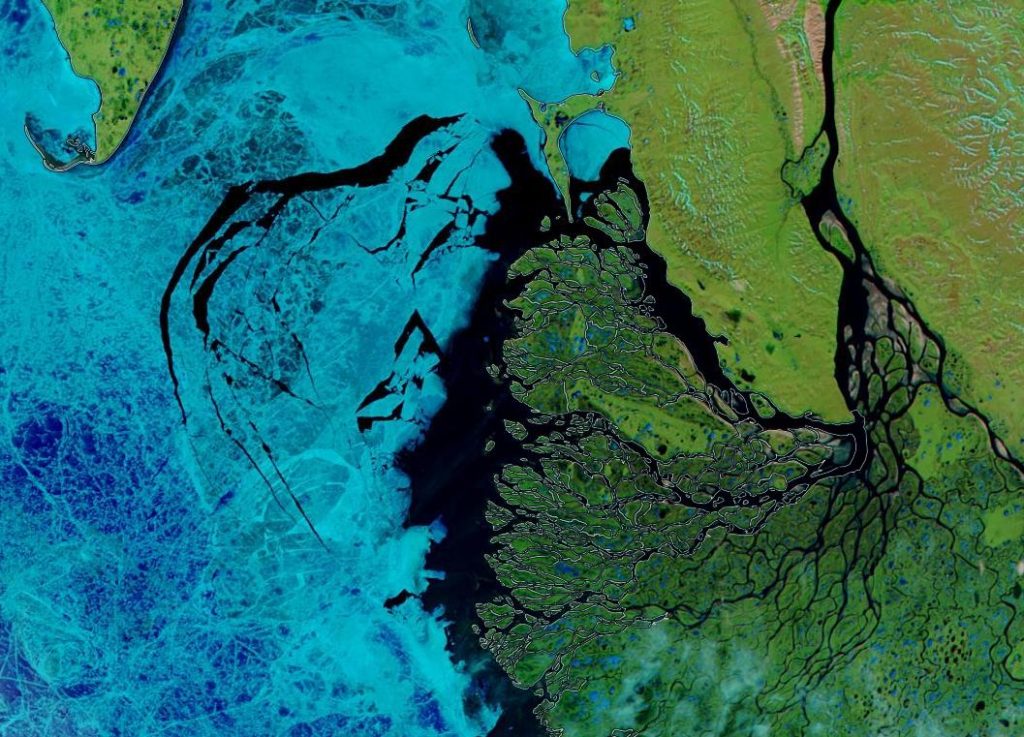
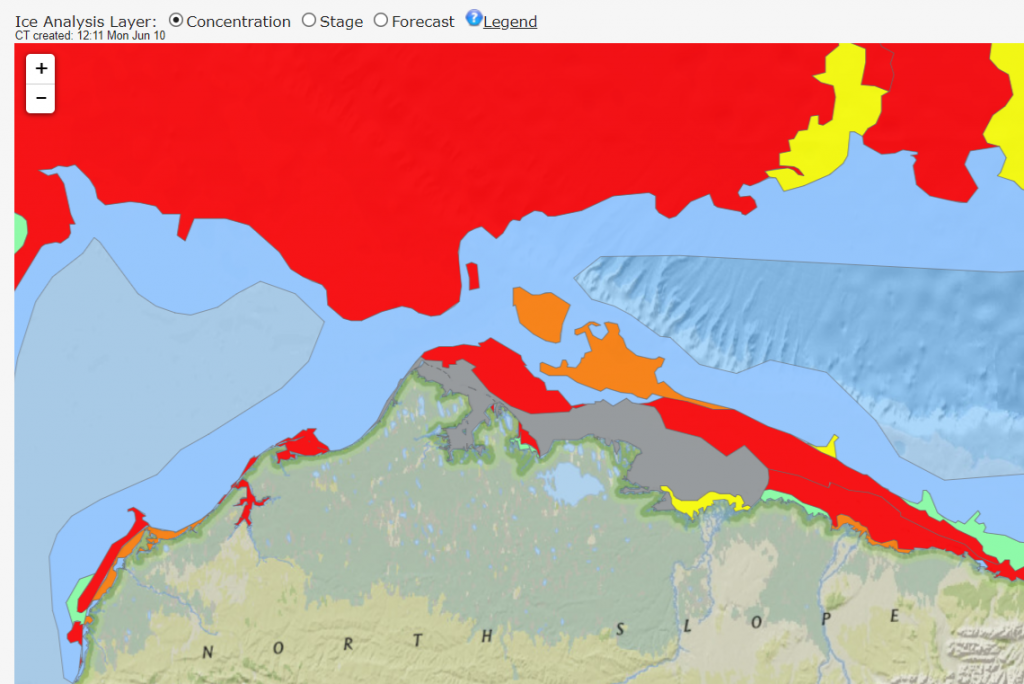
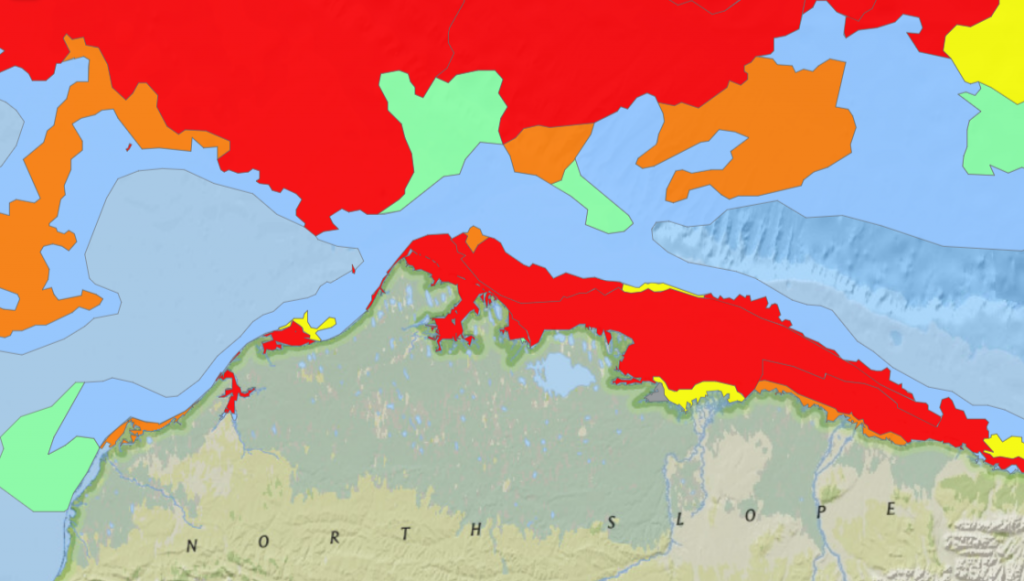
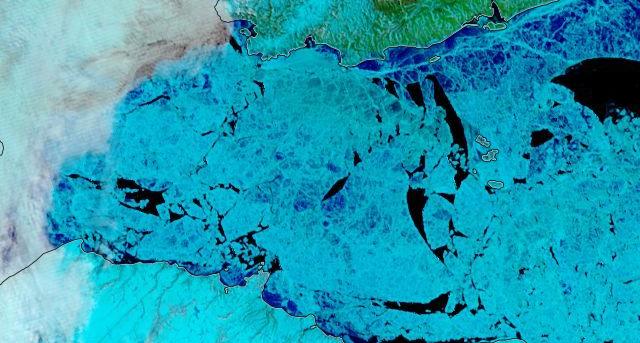
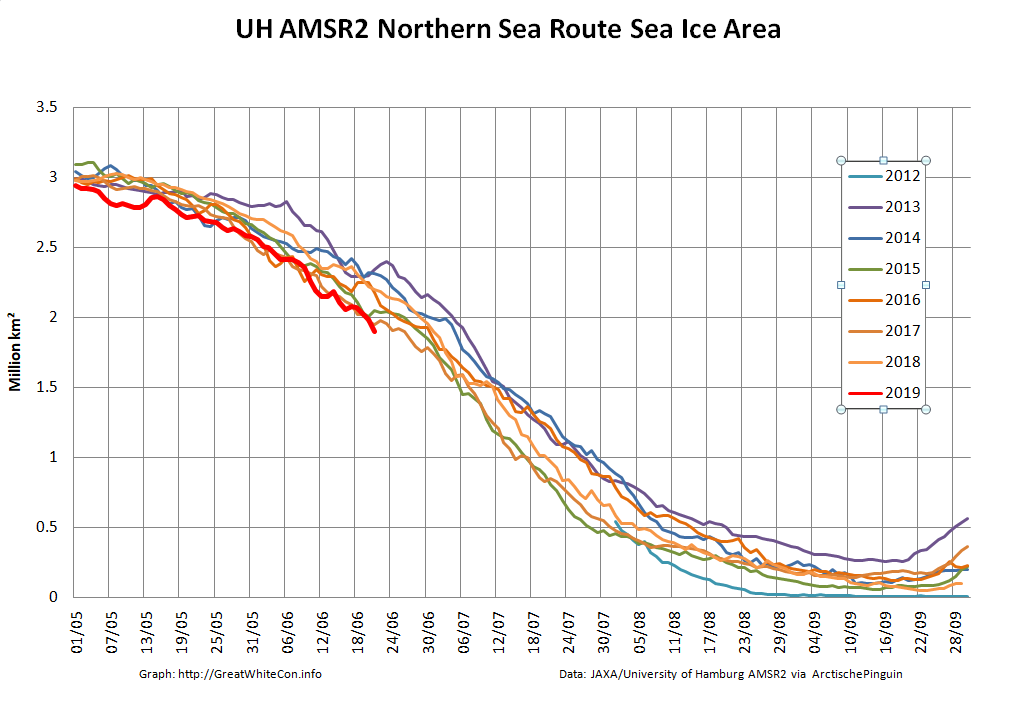
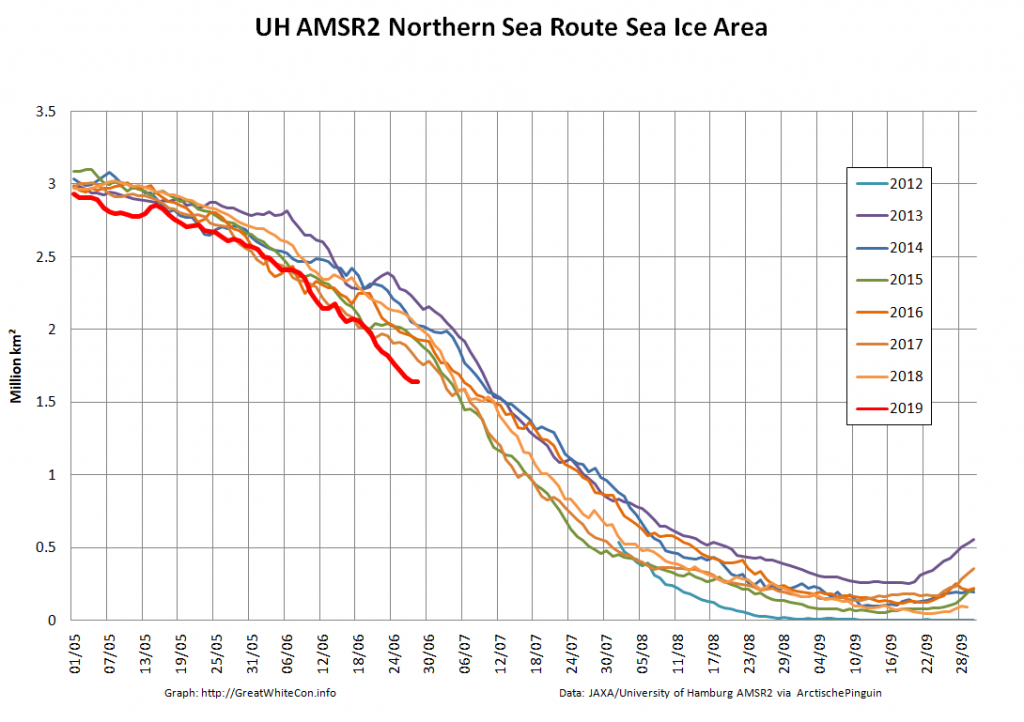
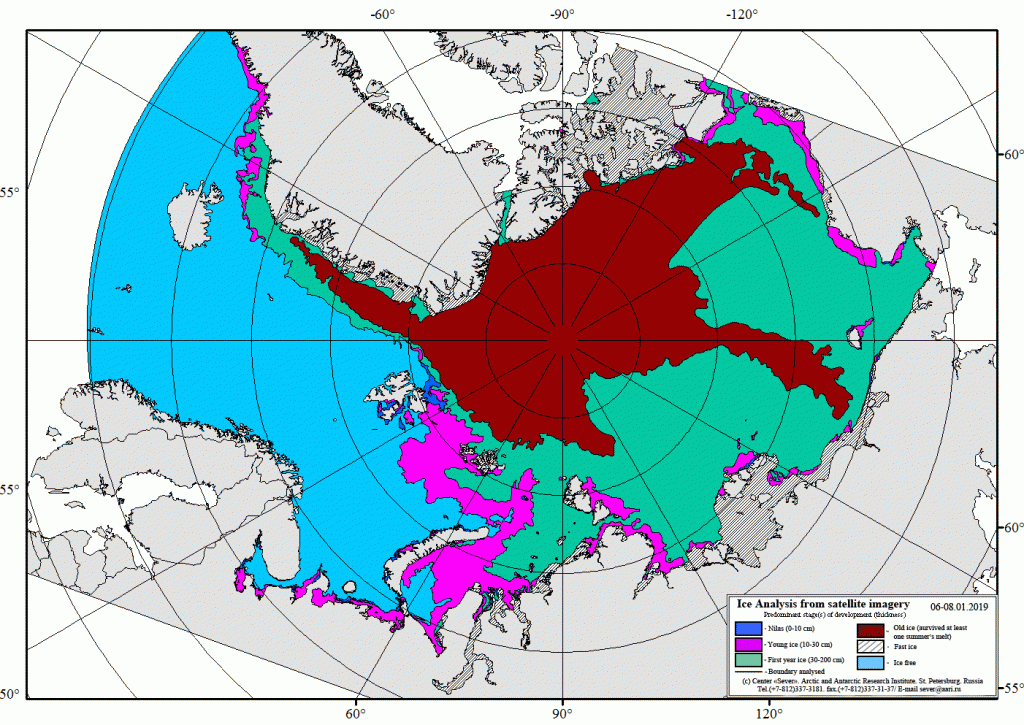
The Northern Sea Route has opened unusually early this year:
Based on the AMSR2 concentration maps from the University of Hamburg that happened on July 13th. The final choke point, as is so often the case, was the Vilkitsky Strait. According to the charts from the Russian Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute, by the 14th there was a narrow way through occupied by no more than 3/10 concentration ice:
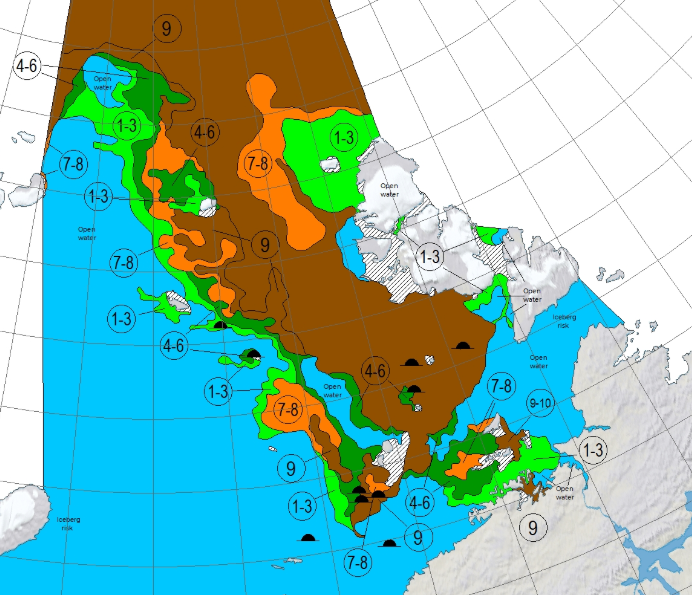
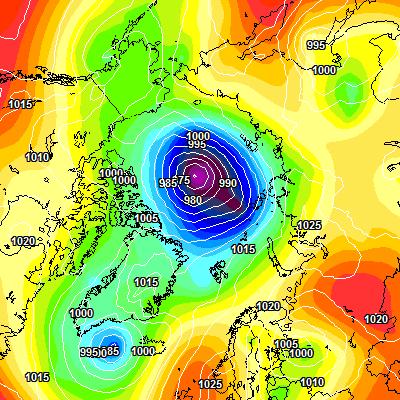
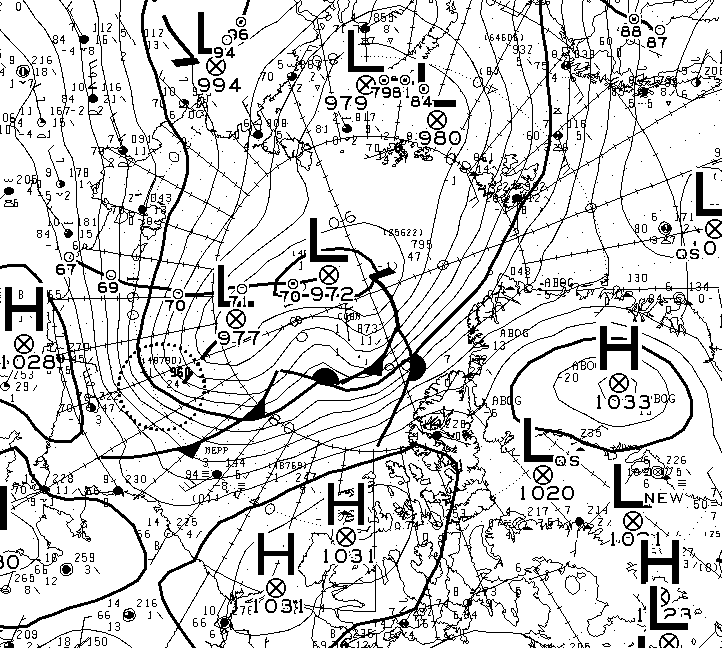
A mere three days away, and the GFS and ECMWF forecasts are in agreement, so there is a decent chance this setup will materialise in the real world:
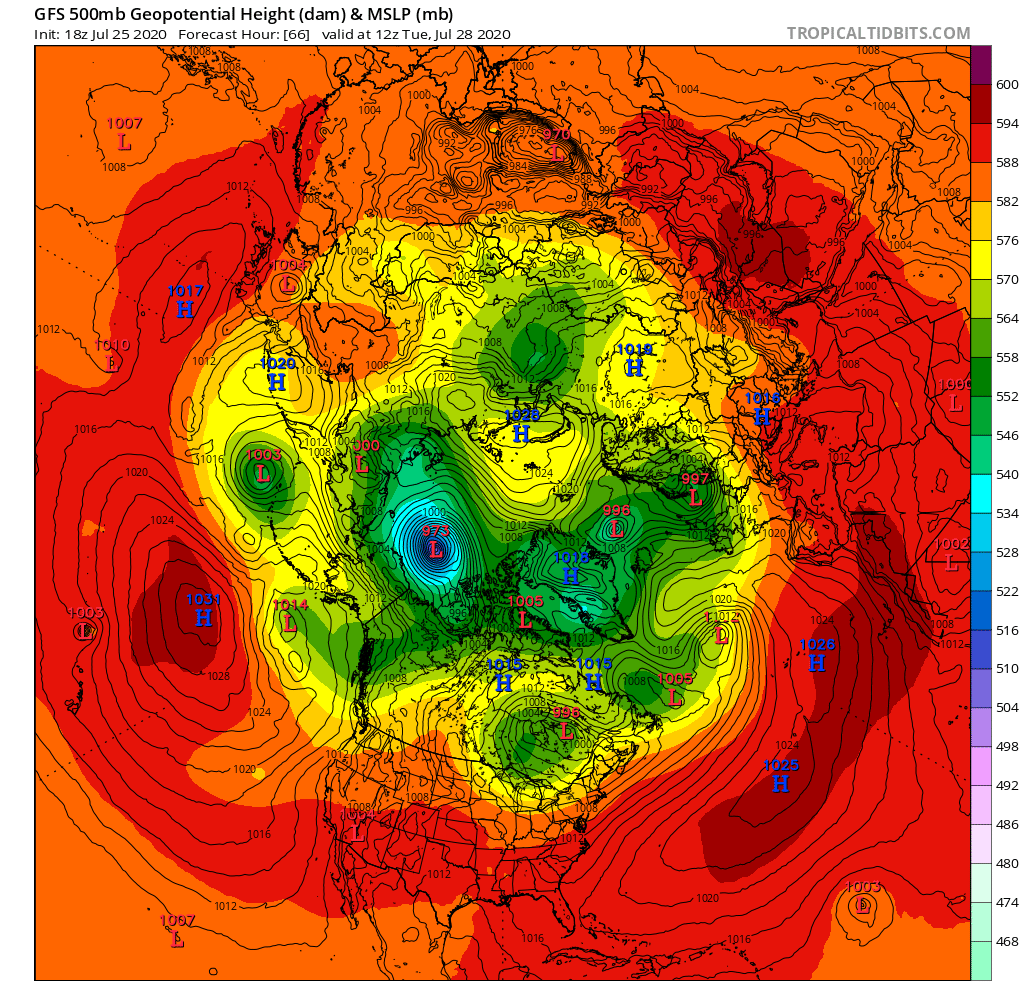
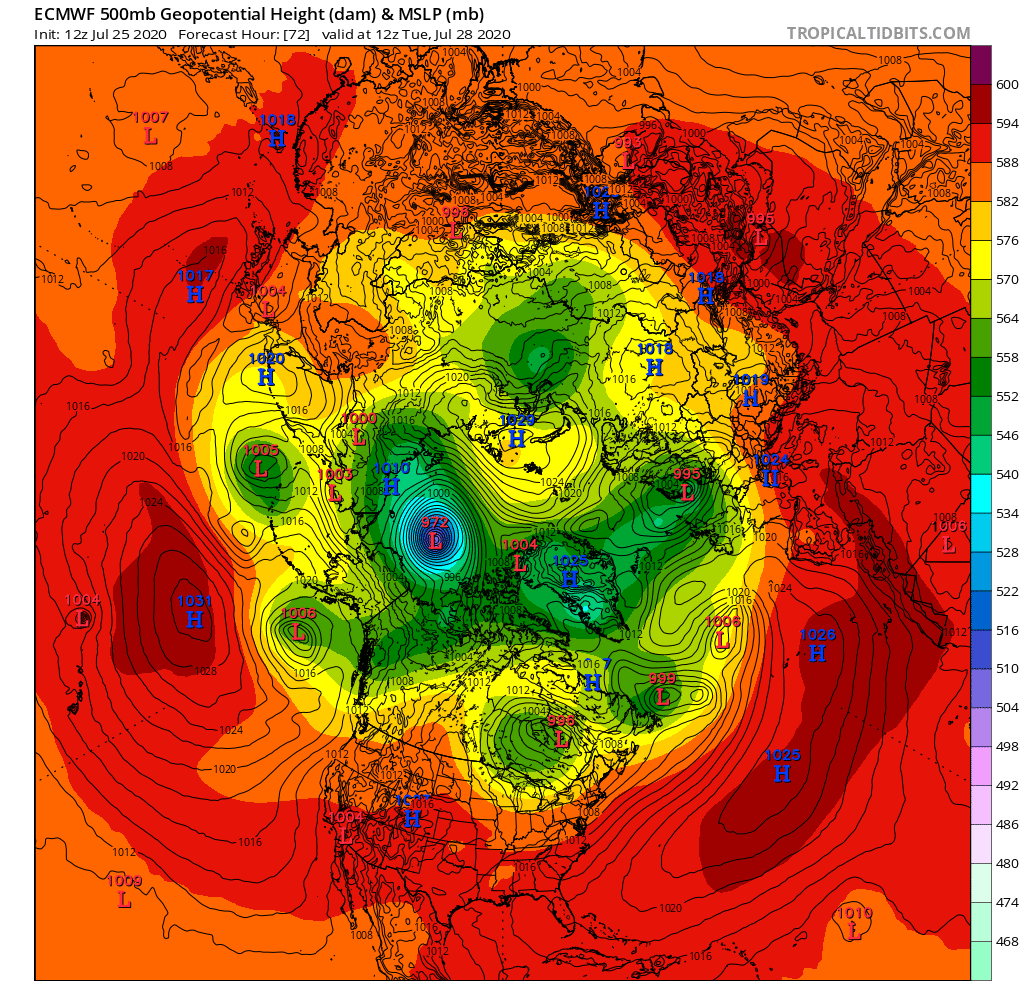
A 972(ish) hPa MSLP cyclone sitting over the ice Beaufort Sea by 12Z on Tuesday.
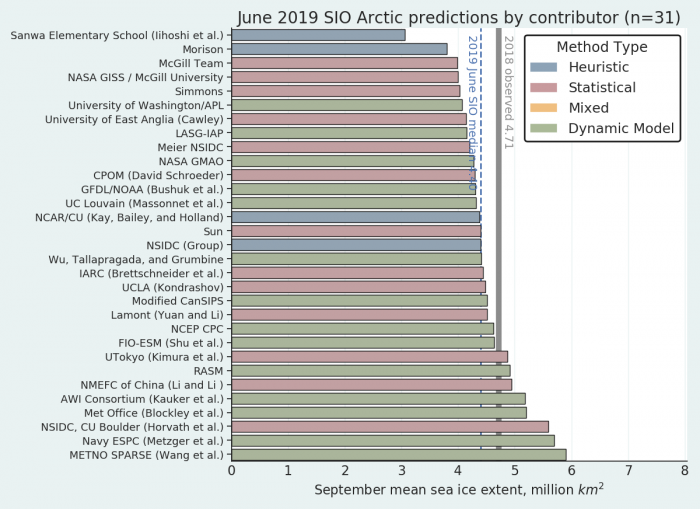
The Sea Ice Prediction Network July forecast for this year’s September minimum extent have been released. Here’s the graphical overview:
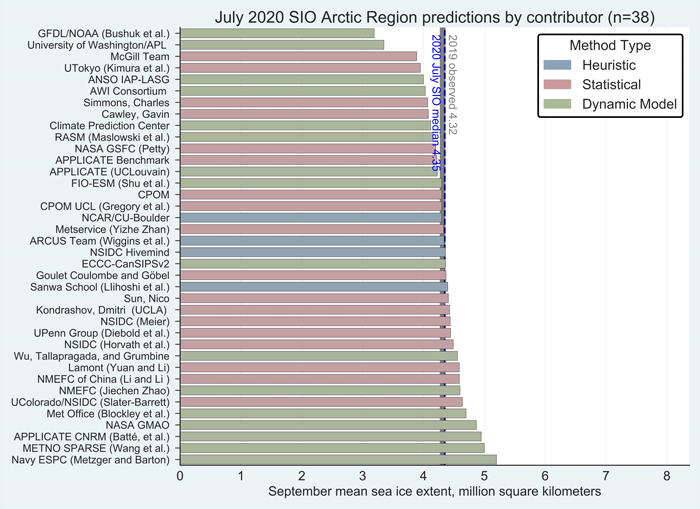
This year’s median projected value from the July forecasts of 4.3 million square kilometers is essentially identical to the median from the June forecasts. Quartiles are 4.1 and 4.6 million square kilometers. As was also the case for June, only two projections, both by dynamic models, are for a new record low, below the mark of 3.57 million square kilometers set in 2012. One dynamical model predicts the September sea-ice extent above 5.0 million square kilometers, compared to two in the June report.
Note that the numbers quoted are for the average NSIDC extent across the month of September, not the lowest daily JAXA extent, which I suggested earlier would be “below 4 million km²” this year.
Meanwhile over on Twitter this evening (UTC):
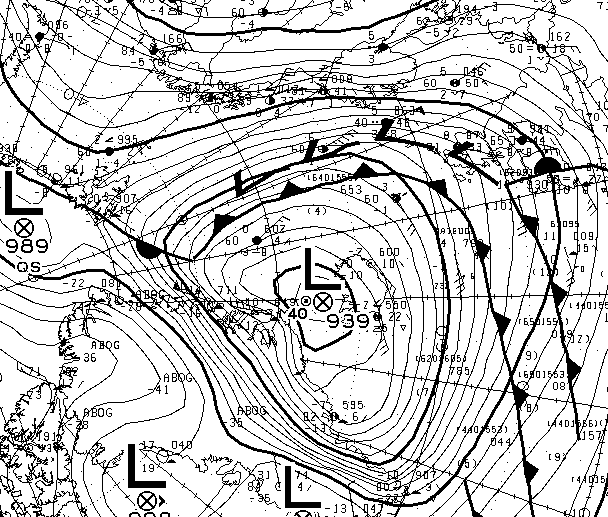
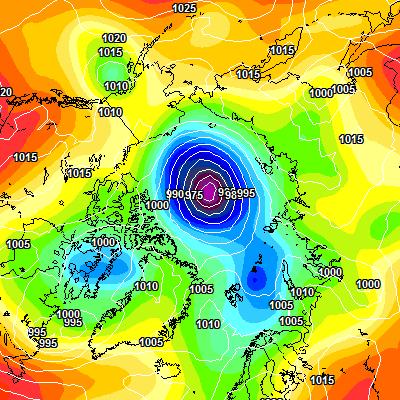
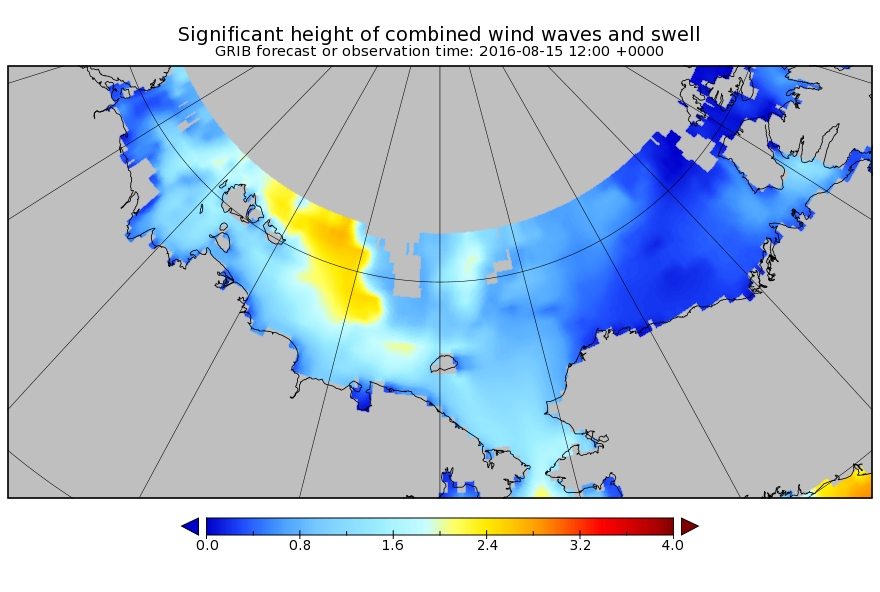
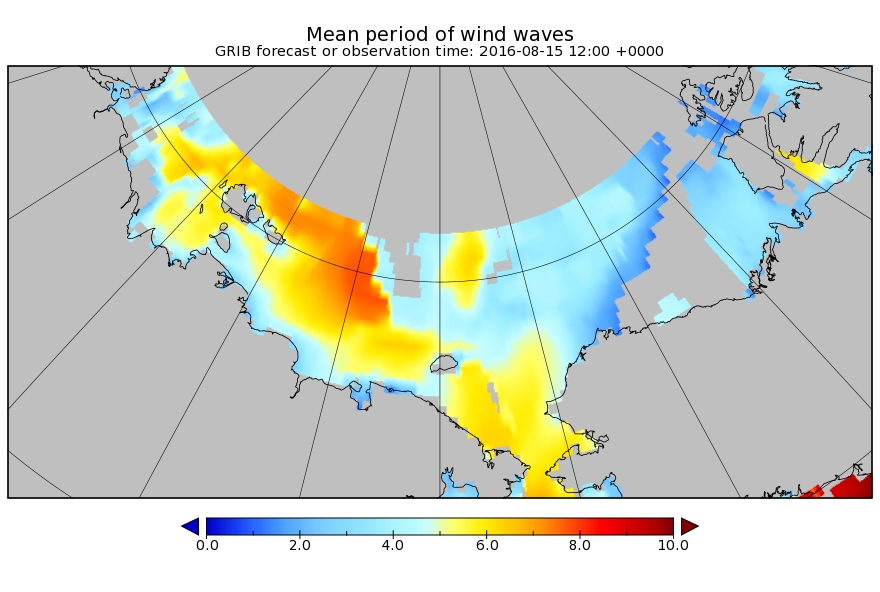
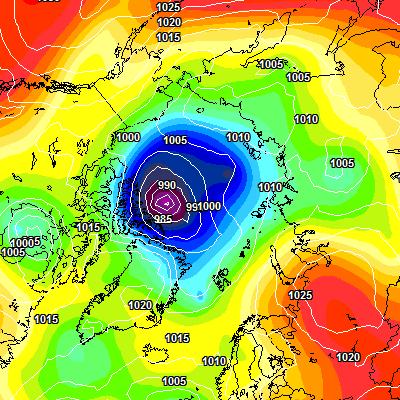
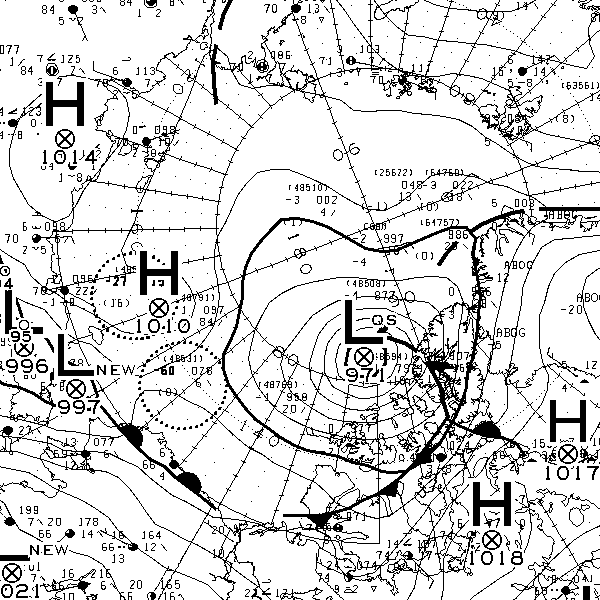
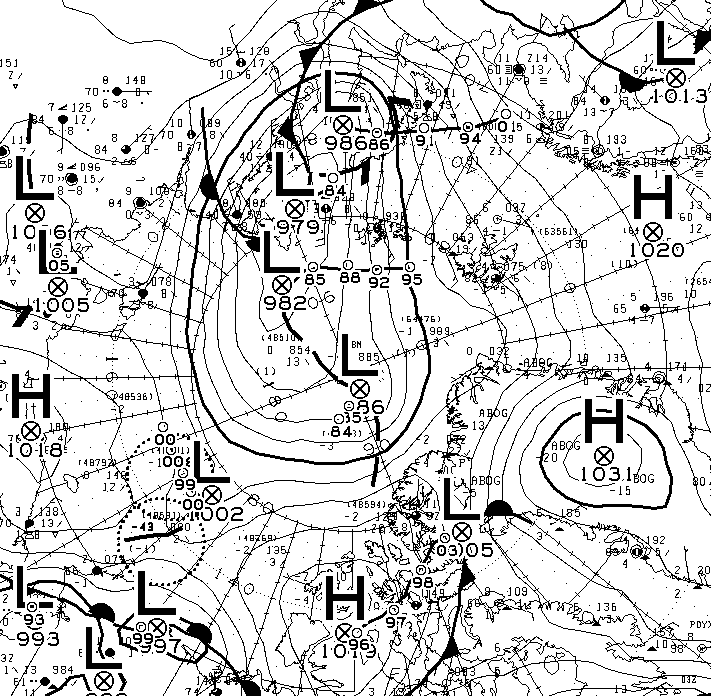
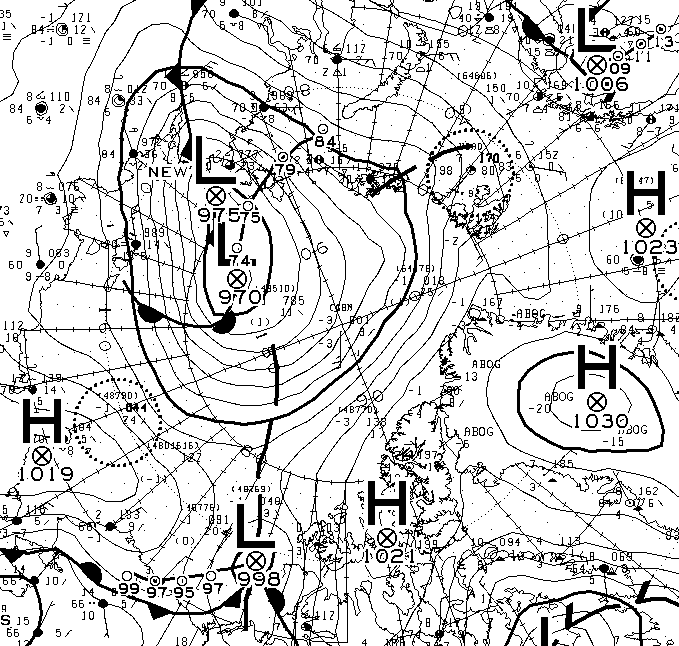
The MSLP of the (Great?) Arctic cyclone sank below 970 hPa overnight:
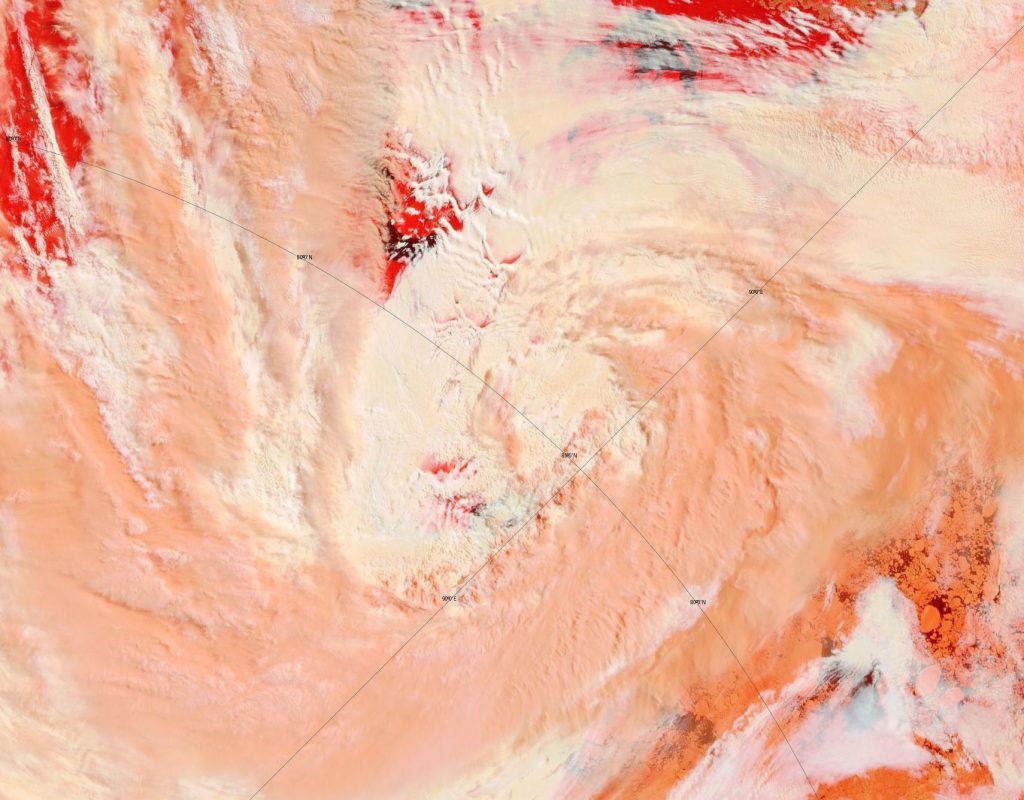
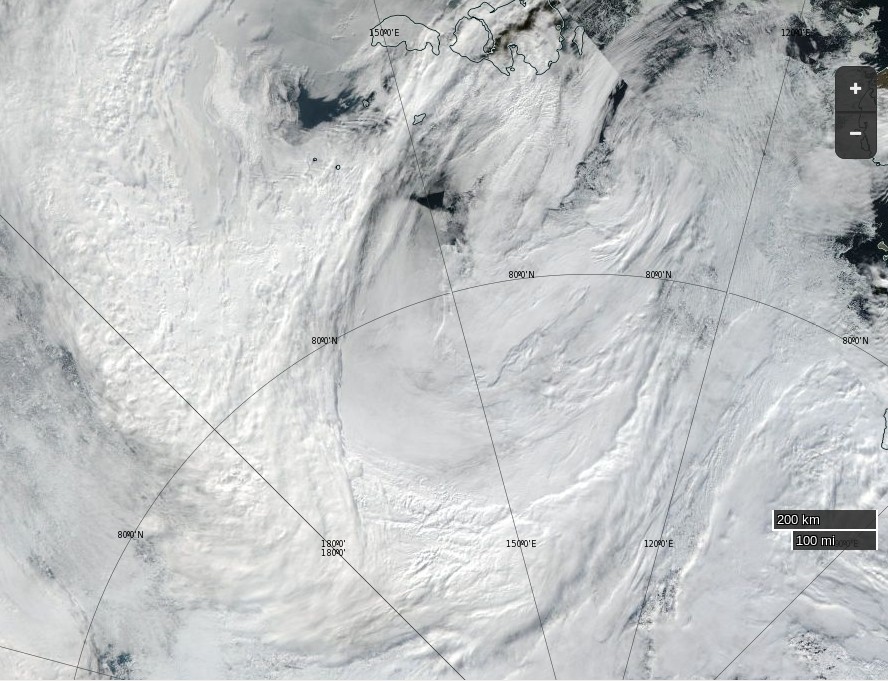
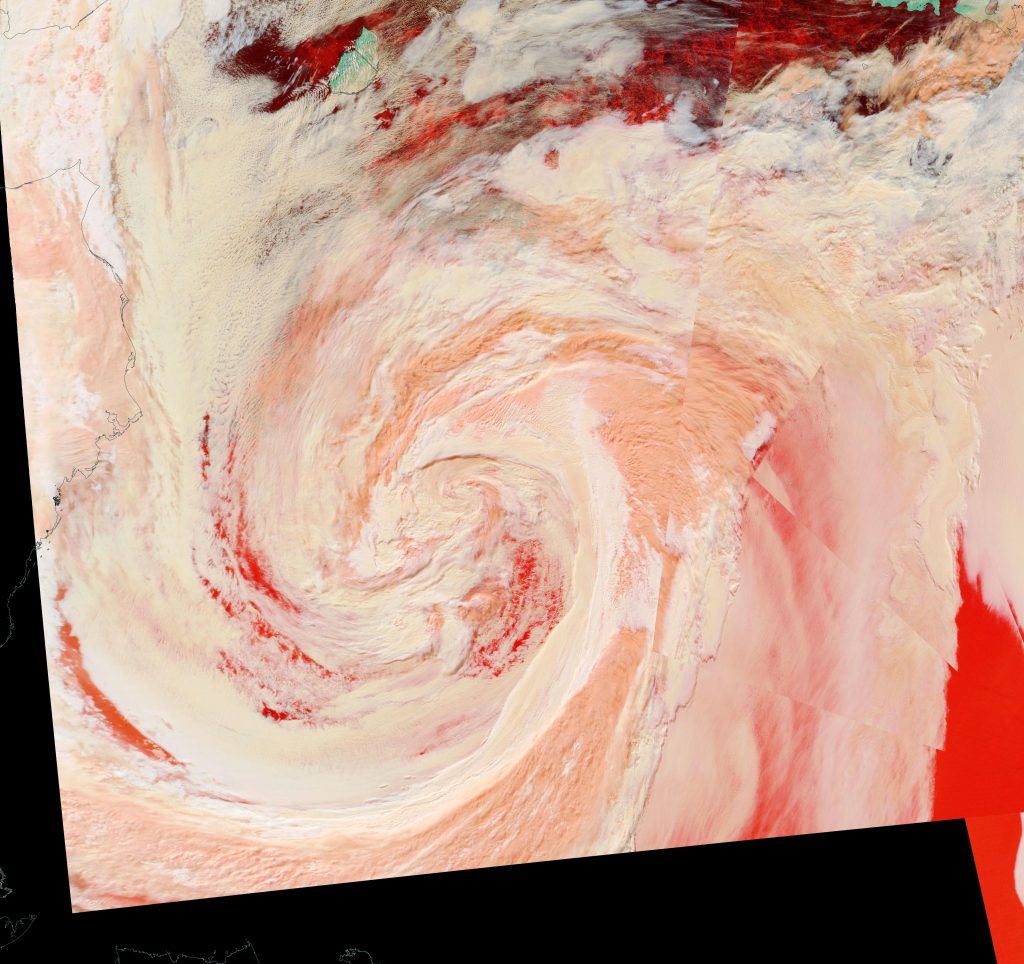
Here’s an early false colour snapshot of how (s)he looks from on high this afternoon (UTC), courtesy of the MODIS instrument on the Terra satellite:

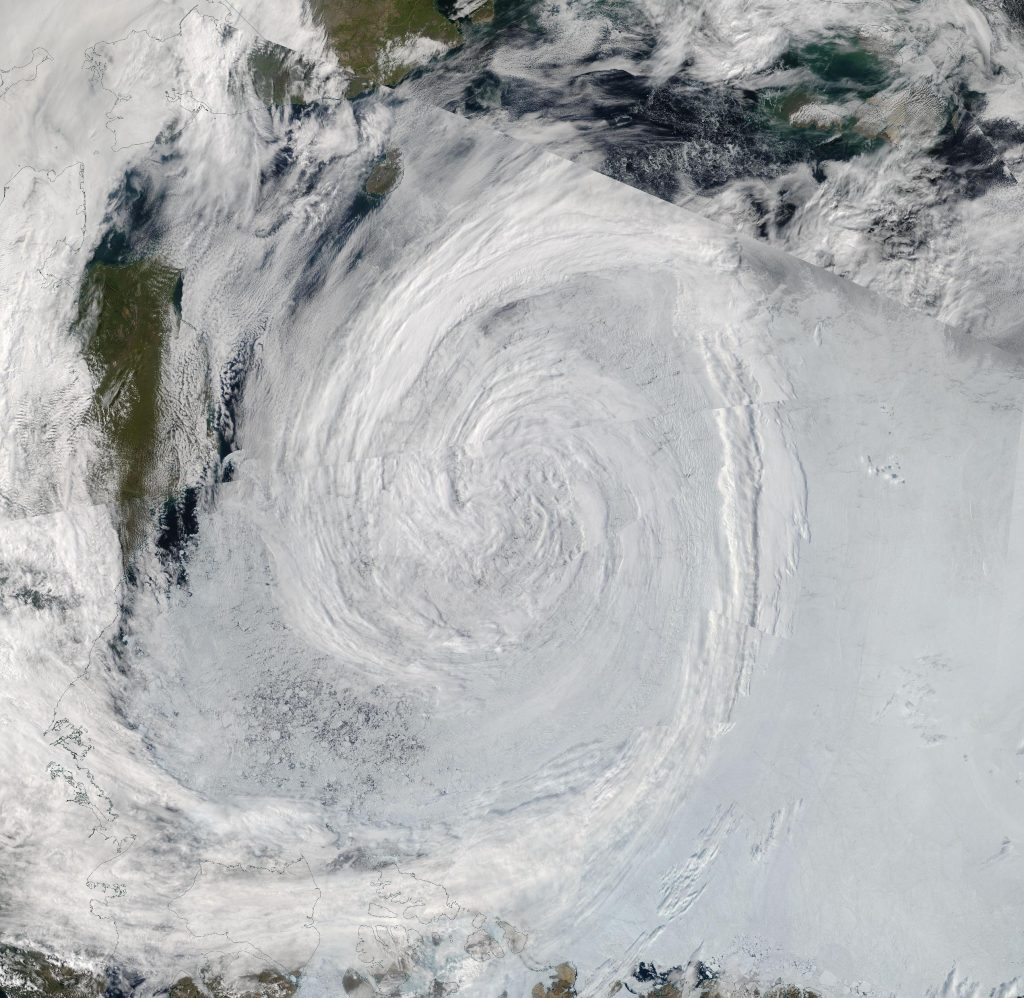
First up today we have a more complete “true colour” image of the cyclone doing its worst yesterday, including a fairly clear view in the bottom left corner of the initial damage to the sea ice covering the eastern Beaufort Sea. This one is from the Aqua satellite:

Watch this space!