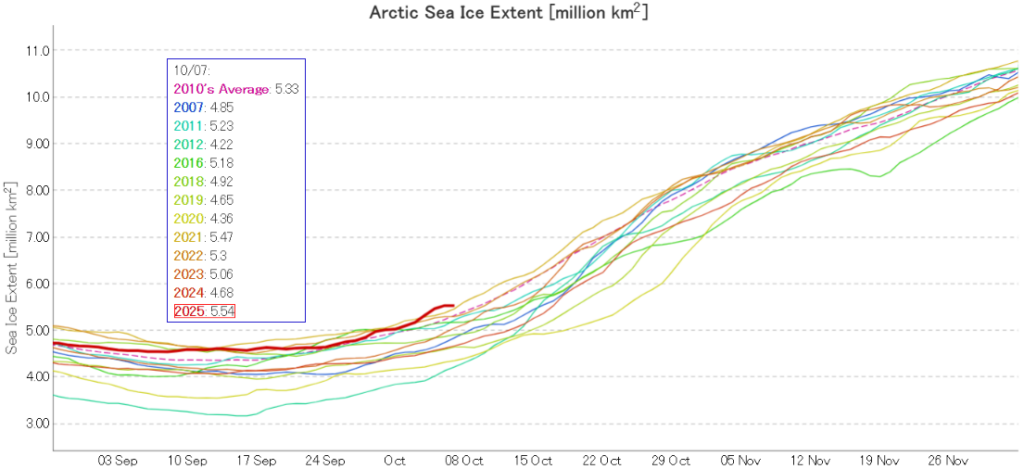
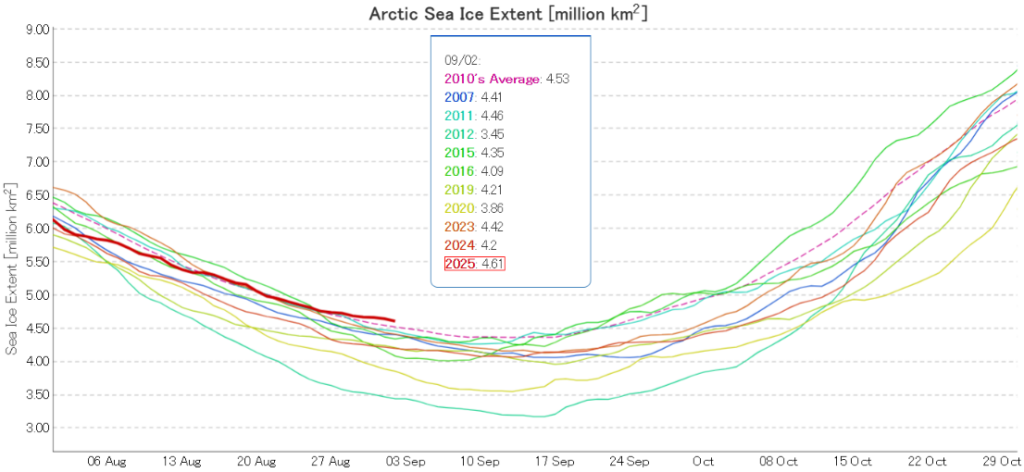
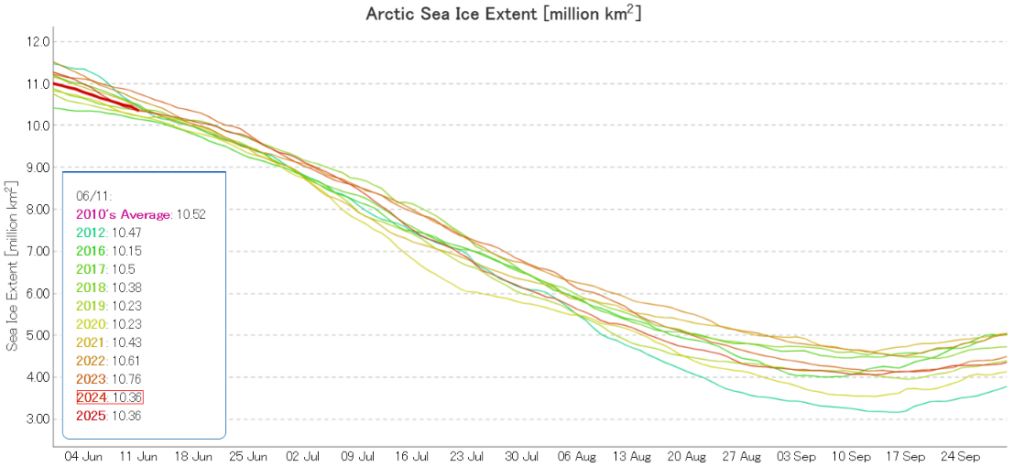
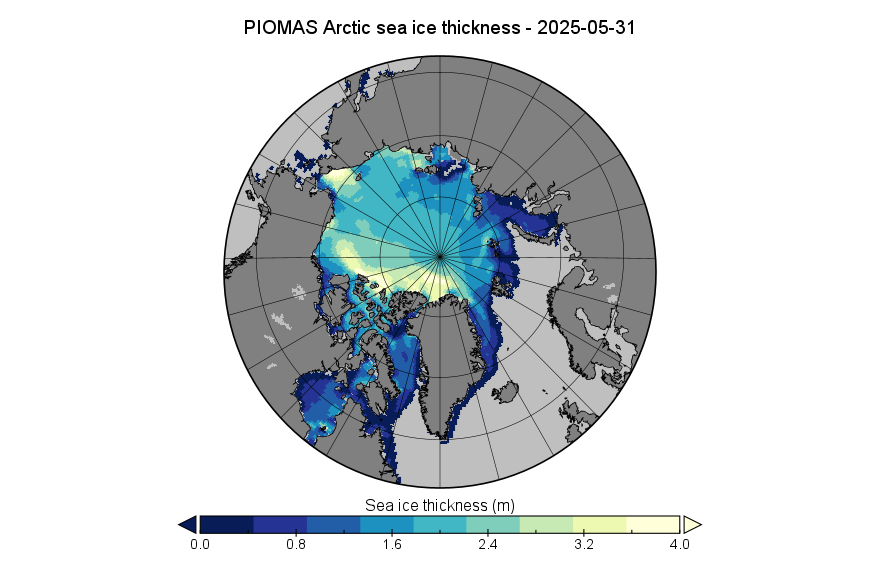
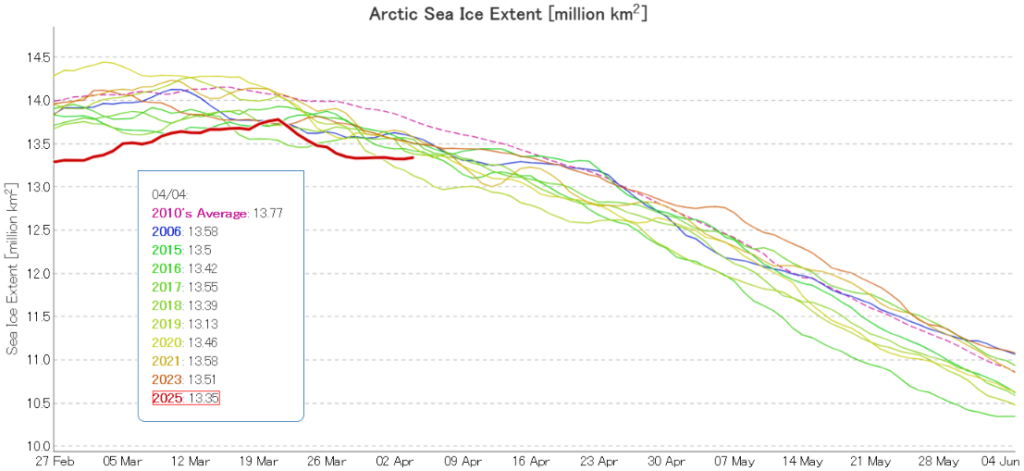
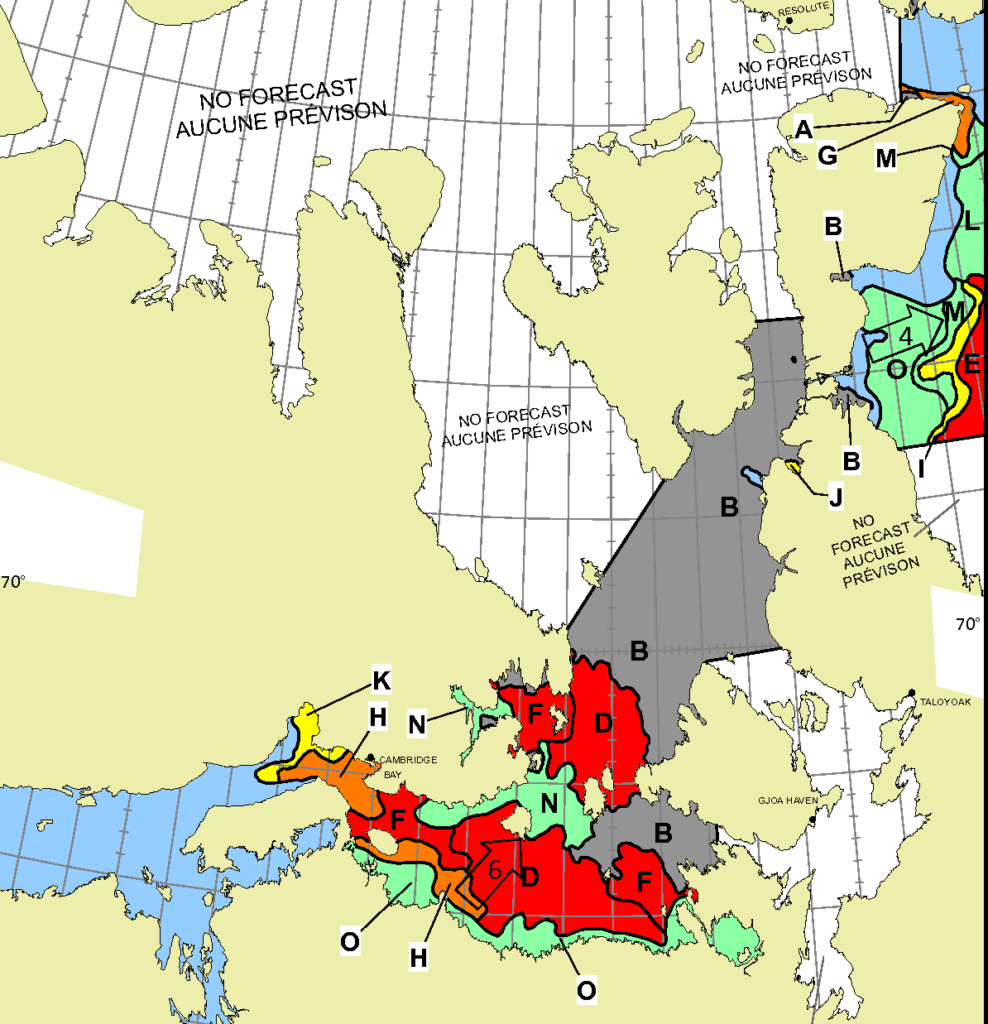
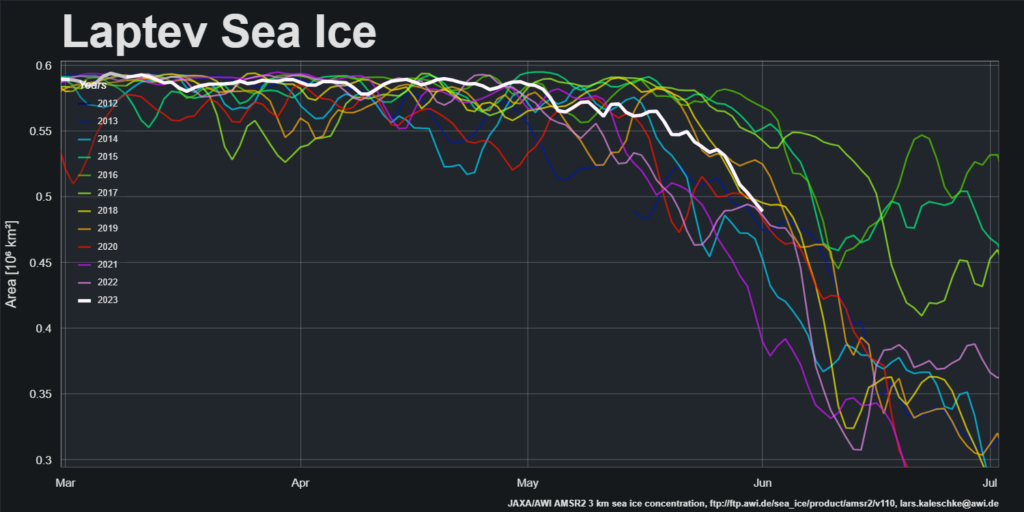
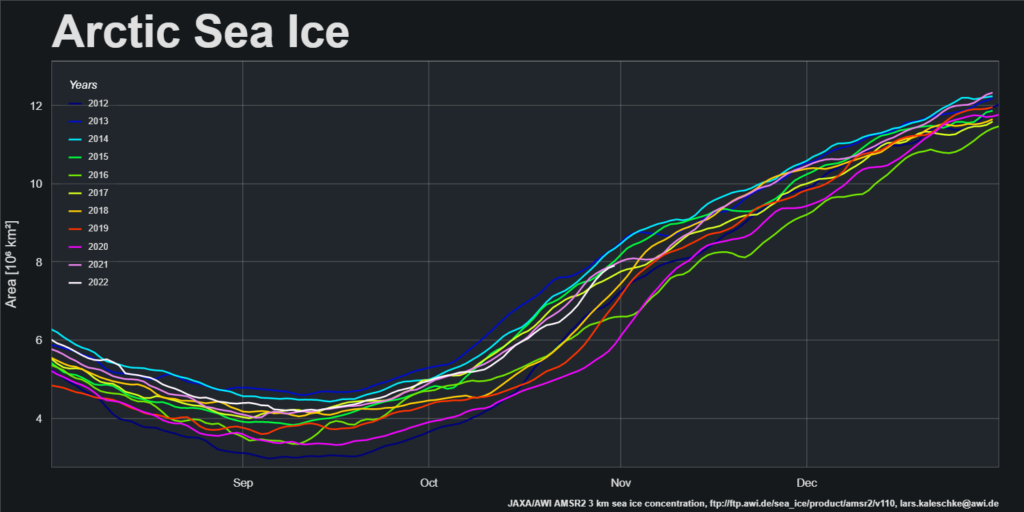
I was hoping that the September PIOMAS gridded thickness data would have been published by now, but no such luck. Reverting to JAXA/ViSHOP extent, after flatlining for most of September the refreeze has started in earnest over the last two weeks. Extent is currently 12th lowest in the satellite era:
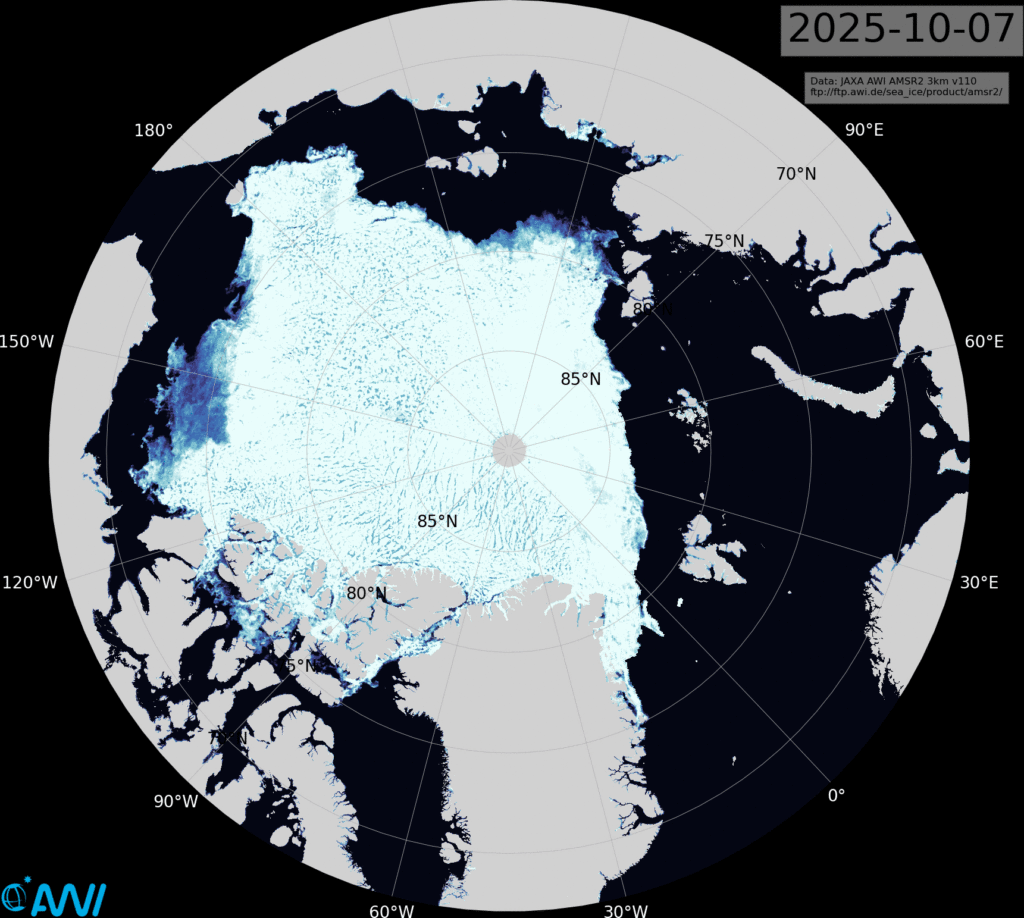
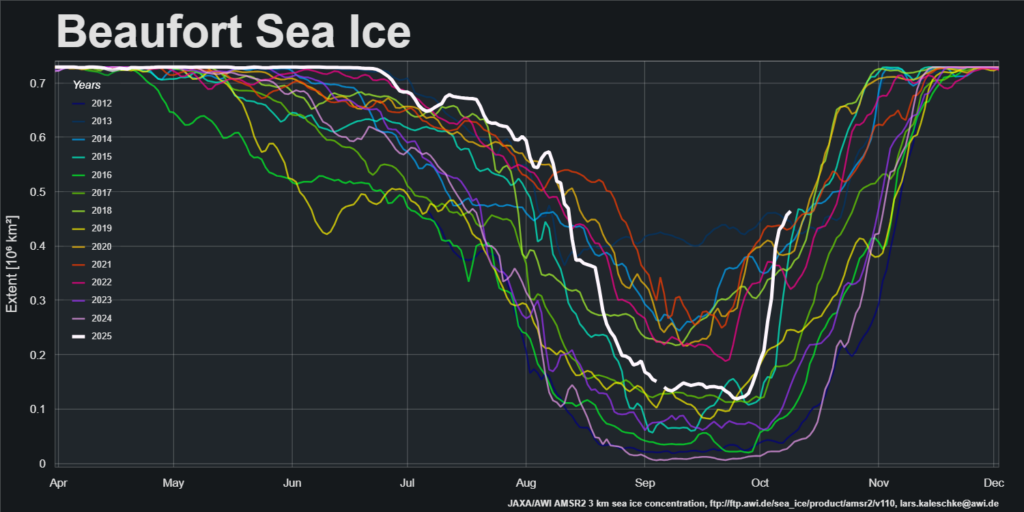
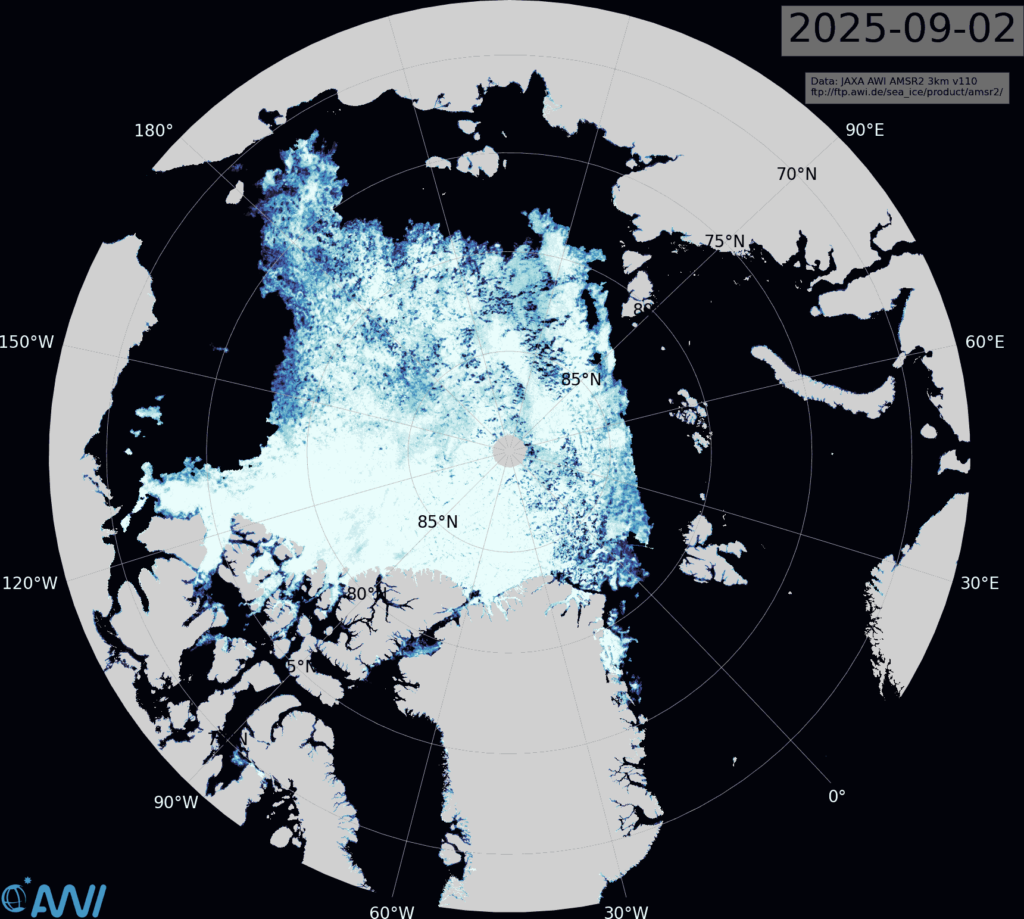
The latest sea ice concentration map from Lars Kaleschke of the Alfred Wegener Institute, based on AMSR2 data, reveals plenty of new ice in the Beaufort Sea, plus a bit more to the north of the Laptev Sea:
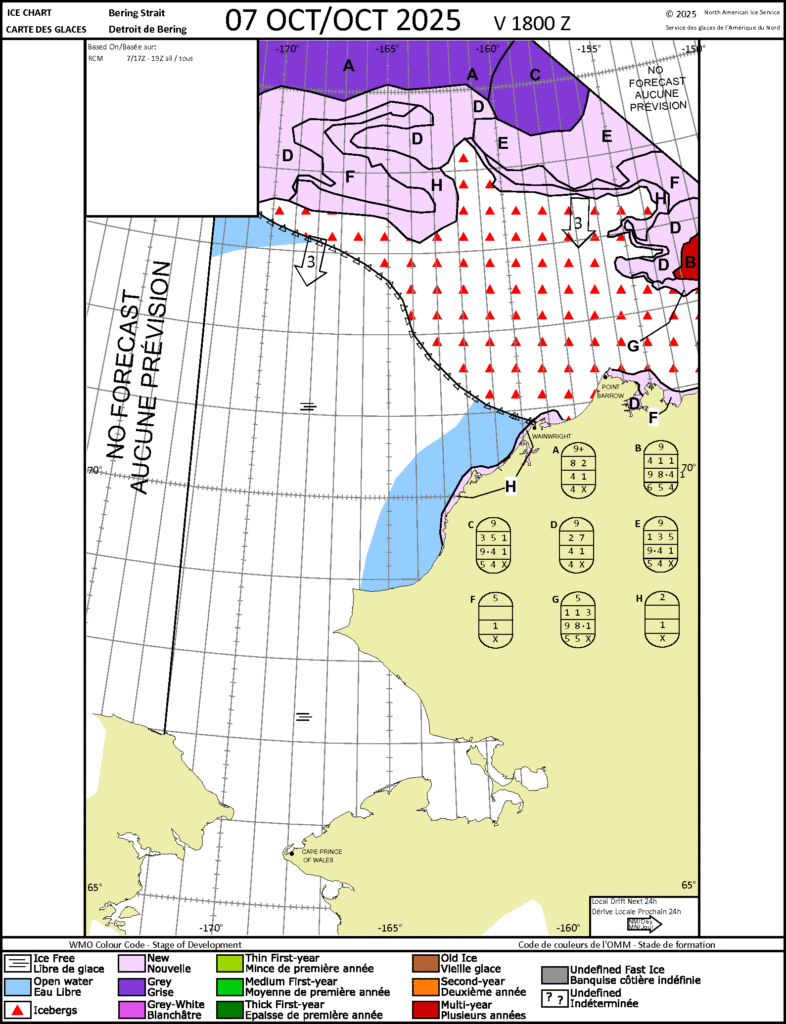
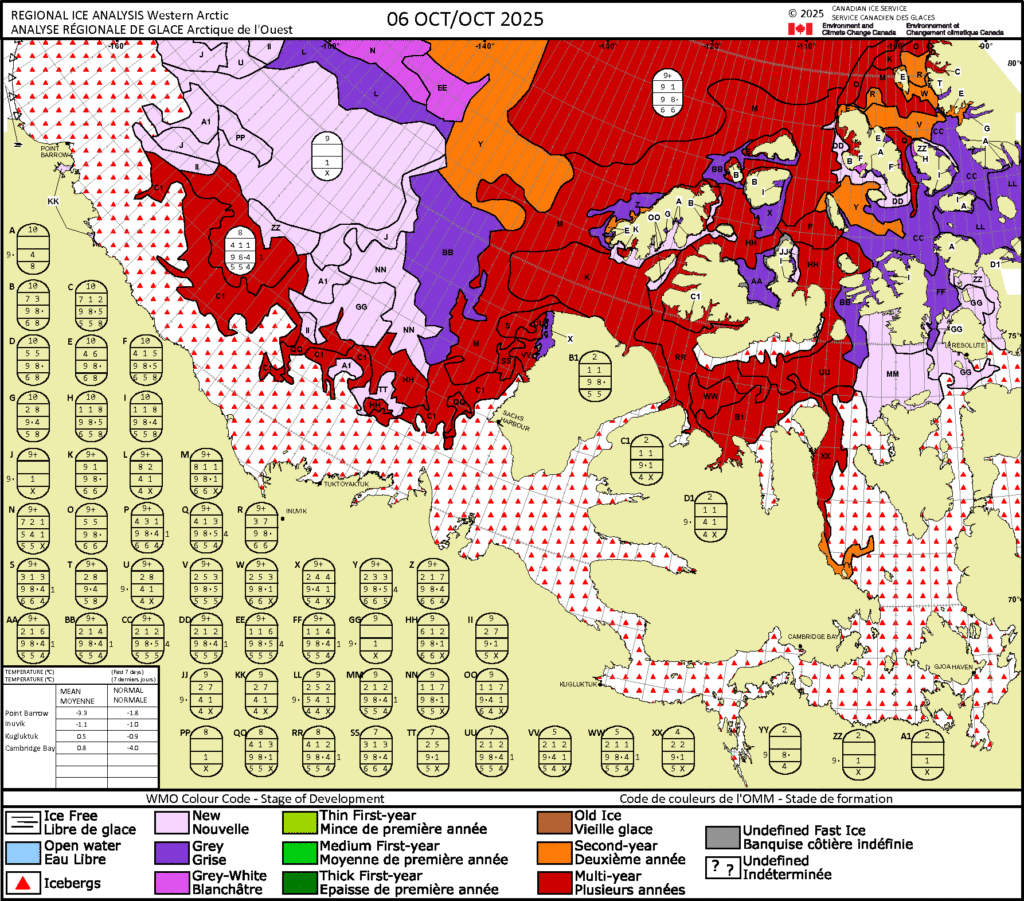
The latest sea ice “stage of development” charts from the Canadian Ice Service confirm that, and reveal more new ice that has yet to show up in the AMSR2 data:
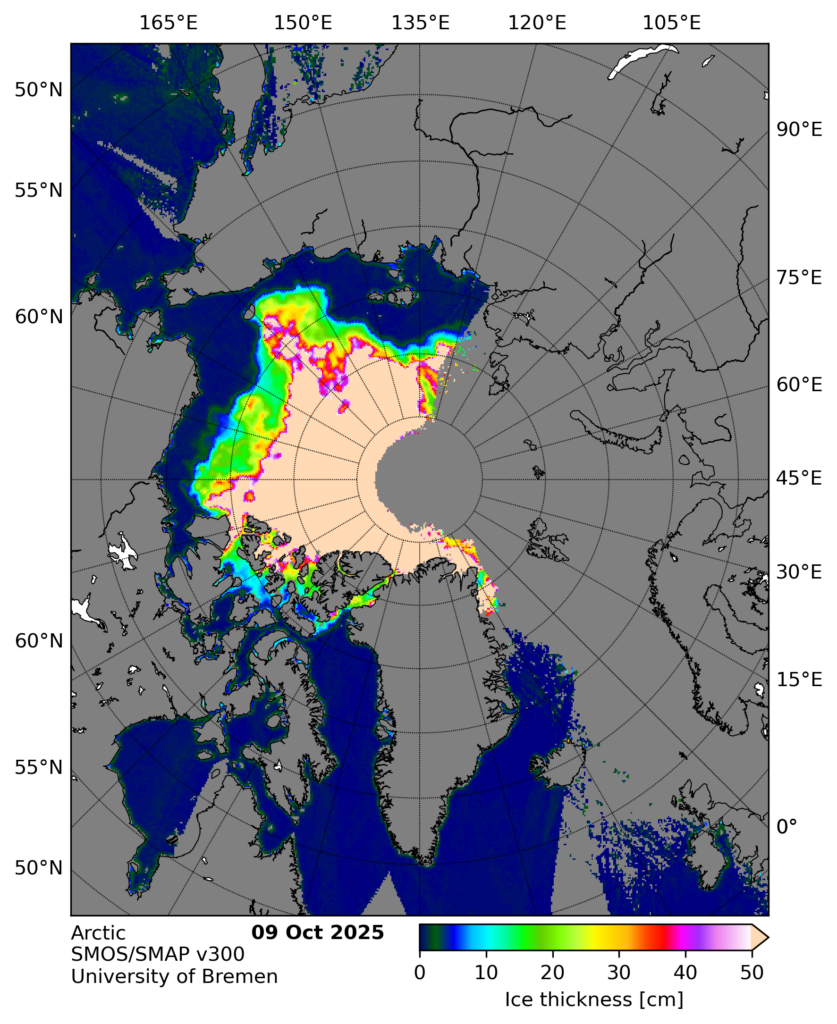
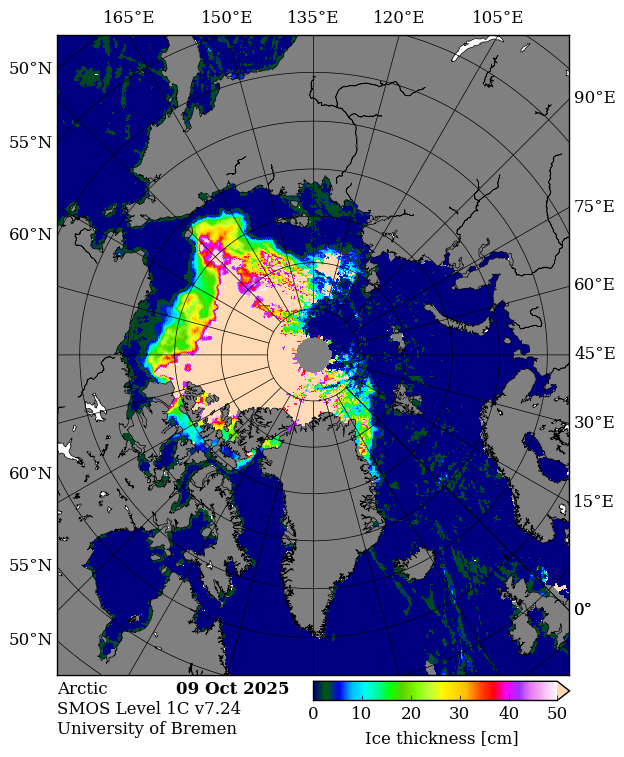
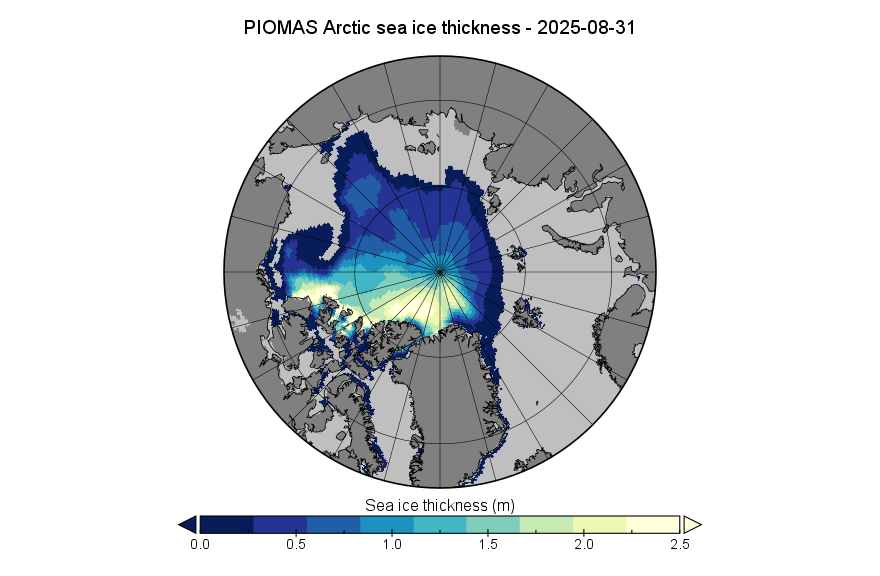
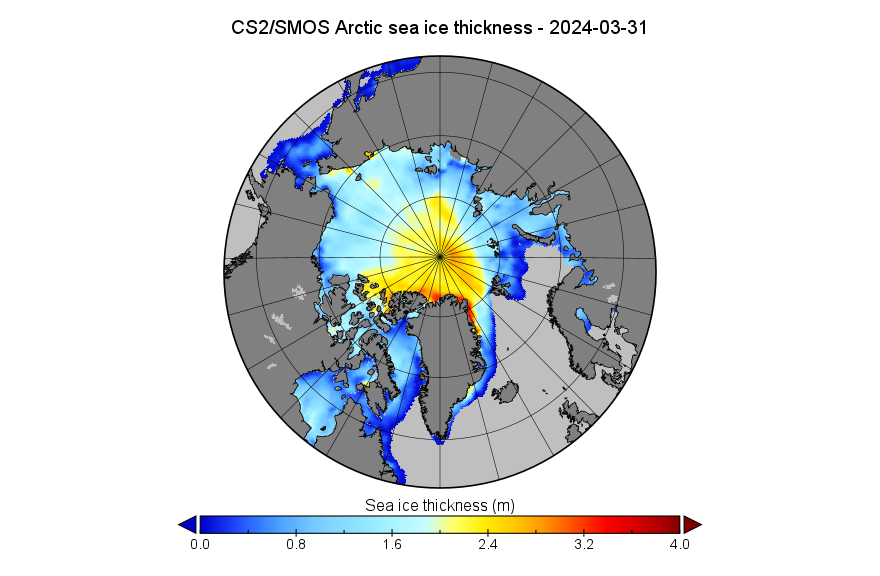
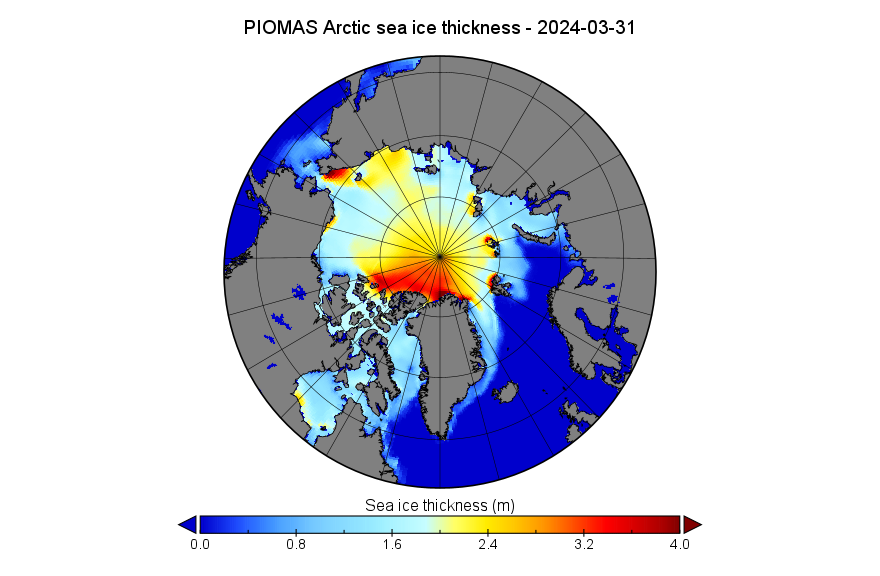
In the continuing absence of PIOMAS gridded thickness data (see below), here’s the latest SMOS/SMAP “thin ice thickness” map:
It appears to be badly affected by radio frequency interference on the Atlantic side of the Arctic. Here’s the raw SMOS map:
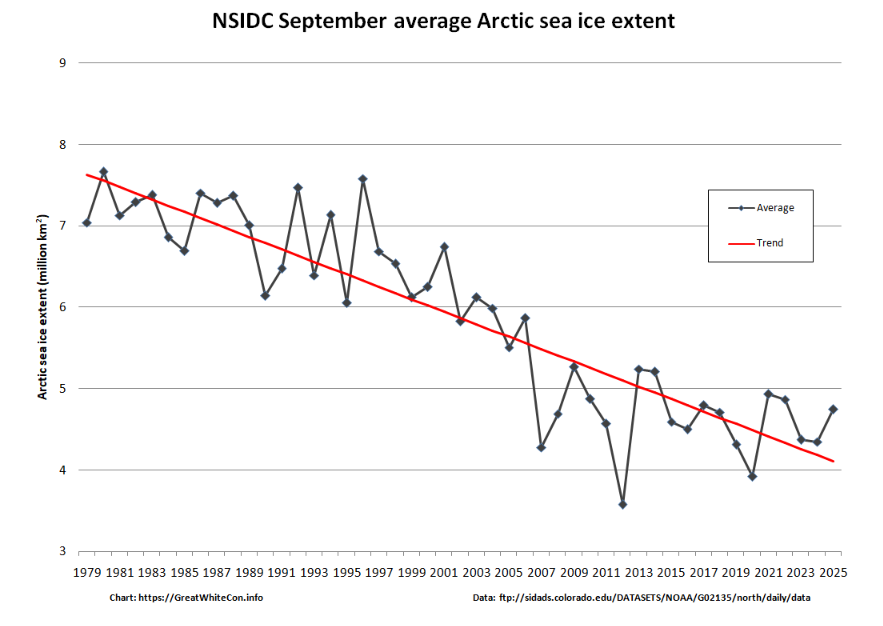
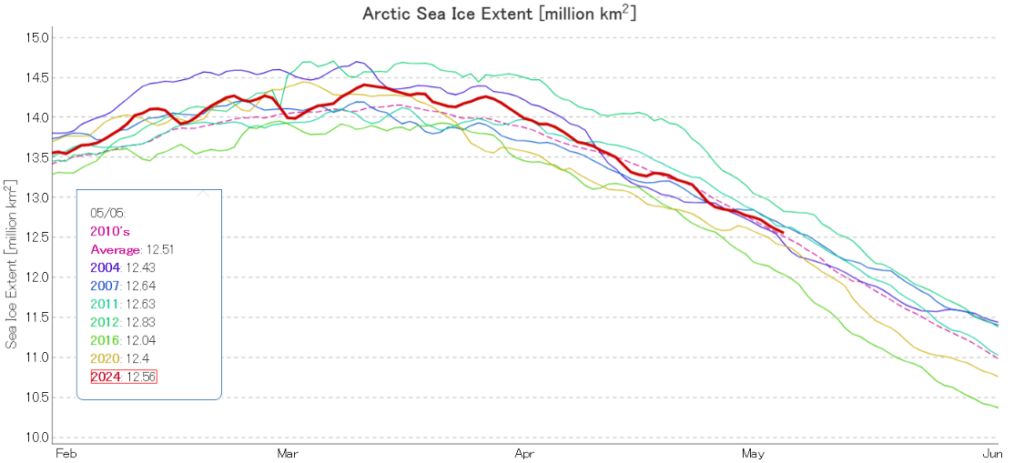
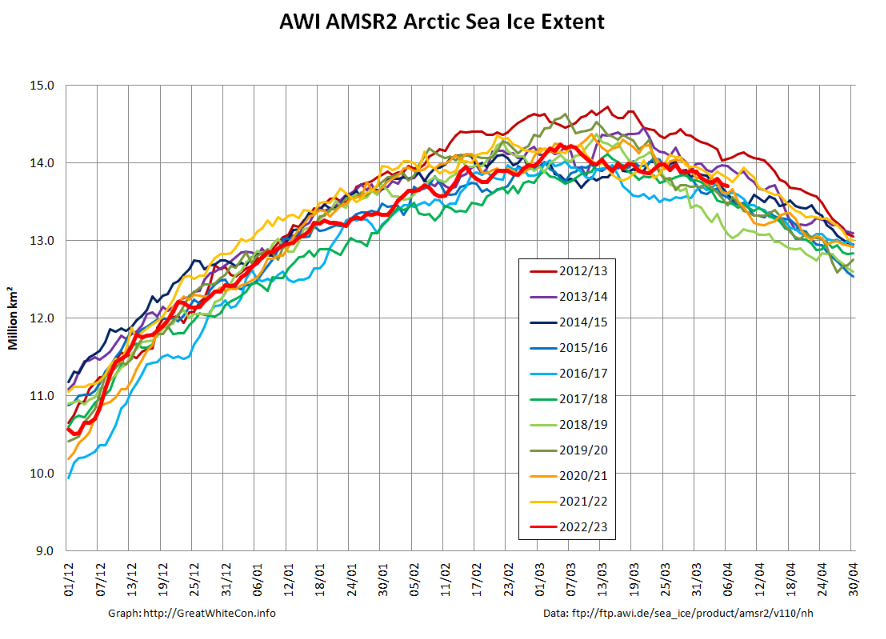
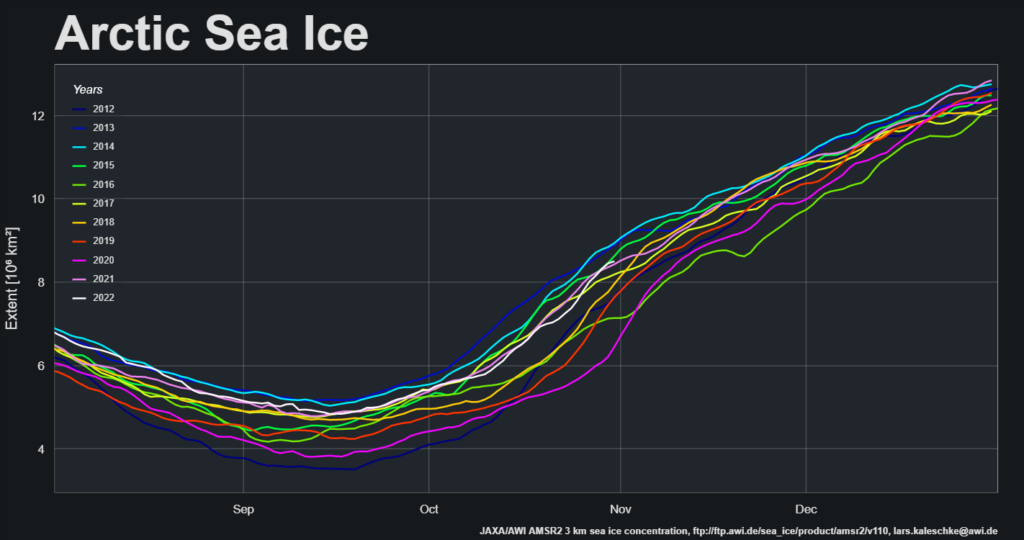
Further to a previous conversation on the subject, here’s the final NSIDC annual average extent graph for September:

As anticipated, 2025 annual average extent has proved to be the lowest in the satellite era.
[Update – October 16th]I was hoping that the September edition of the NSIDC’s “Sea Ice Today” analysis would have been published by now, but no such luck. Here’s the latest data announcement from the NSIDC:
Effective October 15, 2025, due to non-renewed funding, NSIDC has suspended or reduced several Sea Ice Today tools and services.
Discontinued:
- New monthly and mid-month analysis posts
- Sea ice analysis tool
- Sea Ice Volume
- Sea ice extent spatial comparison tool
Persisting:
- Daily Arctic and Antarctic sea ice images
- ChArctic Interactive Sea Ice Graph
- Links to Sea ice analysis data spreadsheets from the NOAA Sea Ice Index
- Reduced user support
- Sea ice annual maximum and minimum announcements (typically occurring in March and September)
Previously-published Sea Ice Today analysis posts will remain online. The discontinued Sea Ice Today products will no longer update or be maintained, and will be removed in the next several weeks.
In Sea Ice Today’s absence, here’s the MSLP and 925 hPa temperature maps for September, usually contained in the monthly analysis articles:
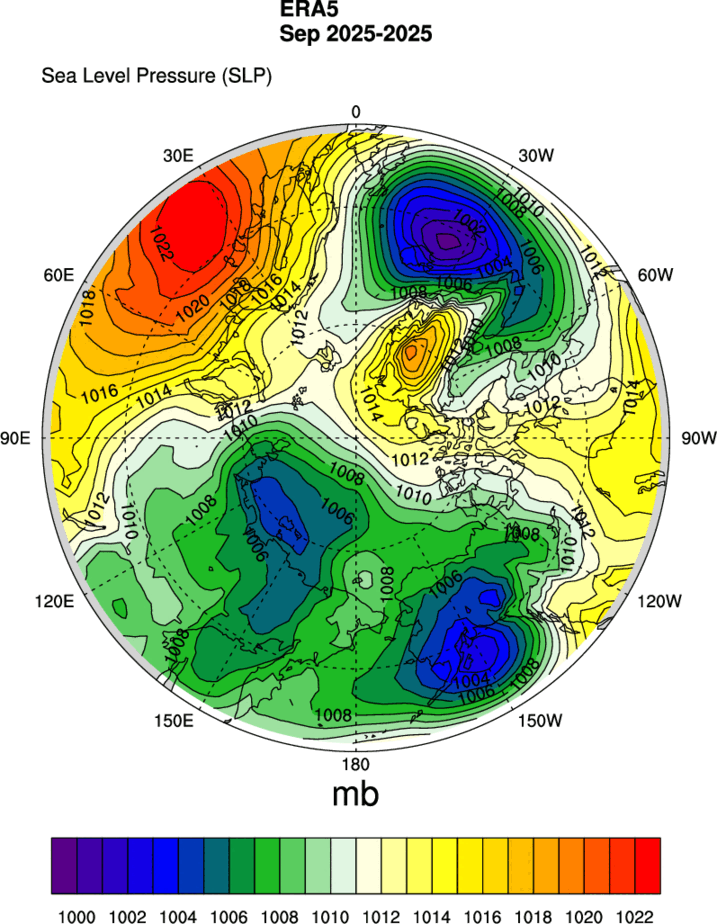
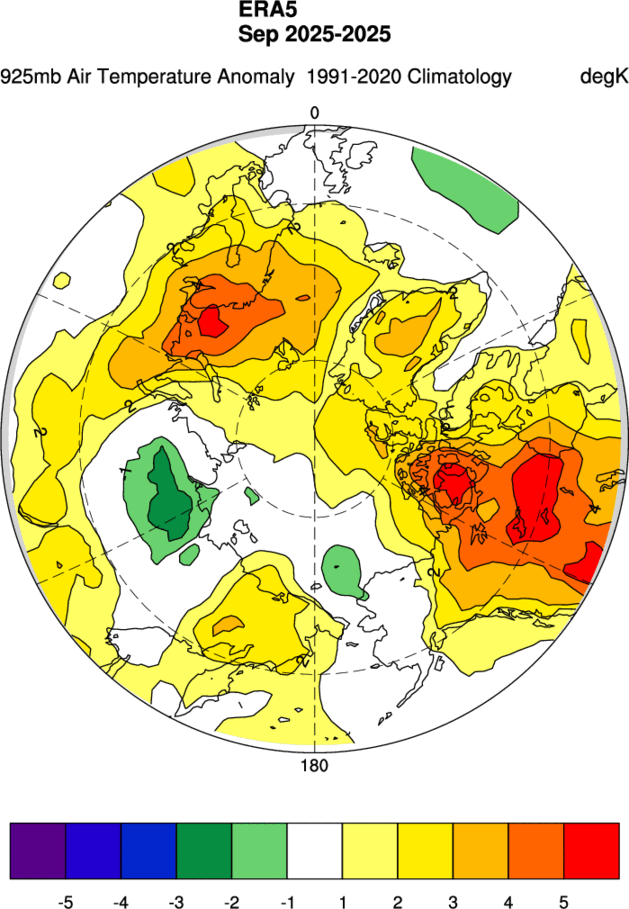
Plus a hastily constructed graph of the monthly average extent for September:
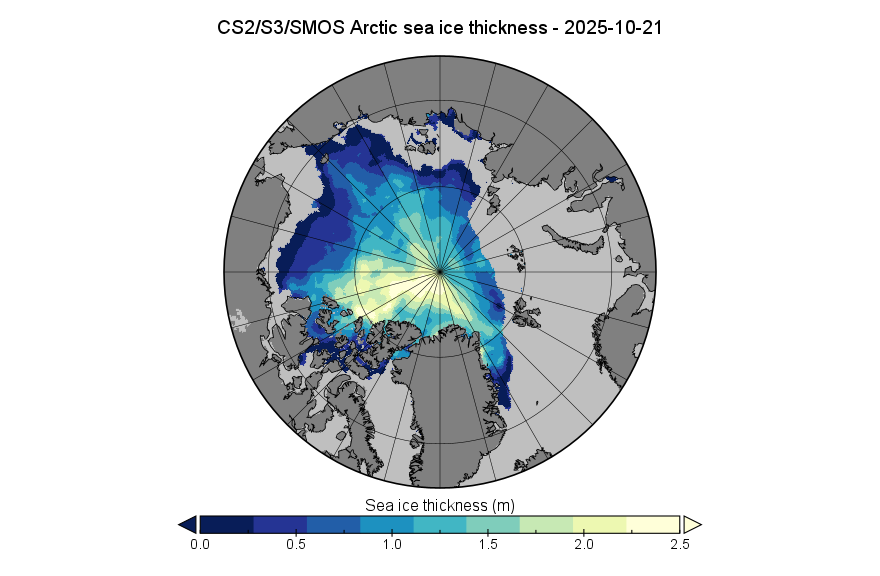
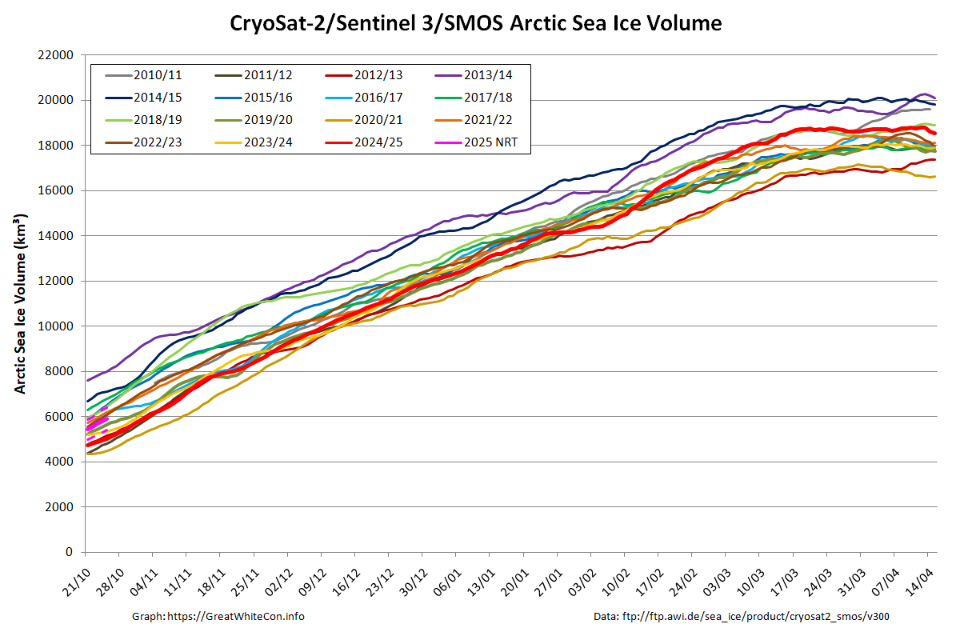
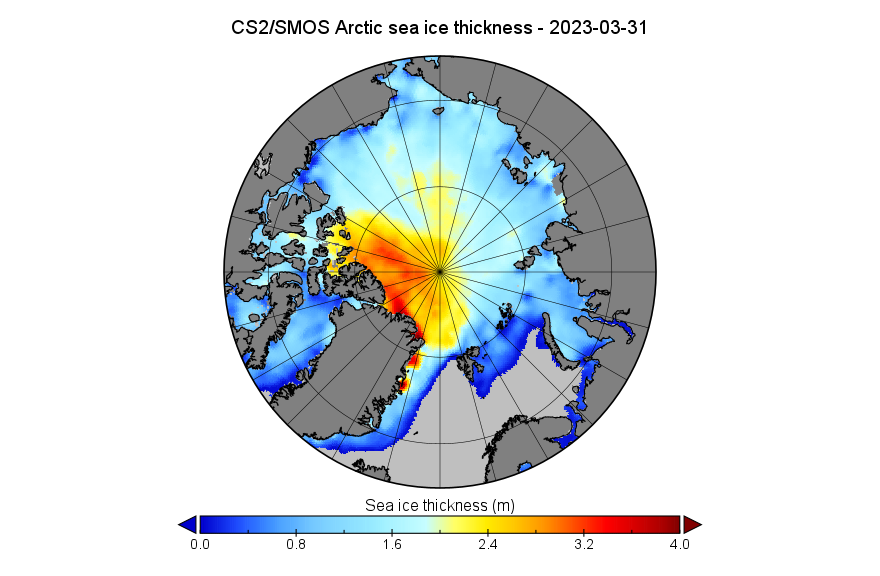
[Update – October 23rd]The Alfred Wegener Institute has published the first CryoSat-2/Sentinel 3/SMOS merged Arctic sea ice thickness data of Autumn 2025:
The Arctic sea ice volume derived therefrom is 5.43 thousand km³. The data is accompanied by the following “Product Degradation Warning”:
[Update – October 27th]SMOS input data continues to be affected by persistent and frequent radio-frequency interference (RFI) in the Barents, Kara, and Laptev Seas, resulting in missing thin ice thickness measurements. Consequently, sea ice thickness estimates for this region in the product will rely exclusively on radar altimeter data, which may lead to higher reported values than would have been obtained using SMOS.
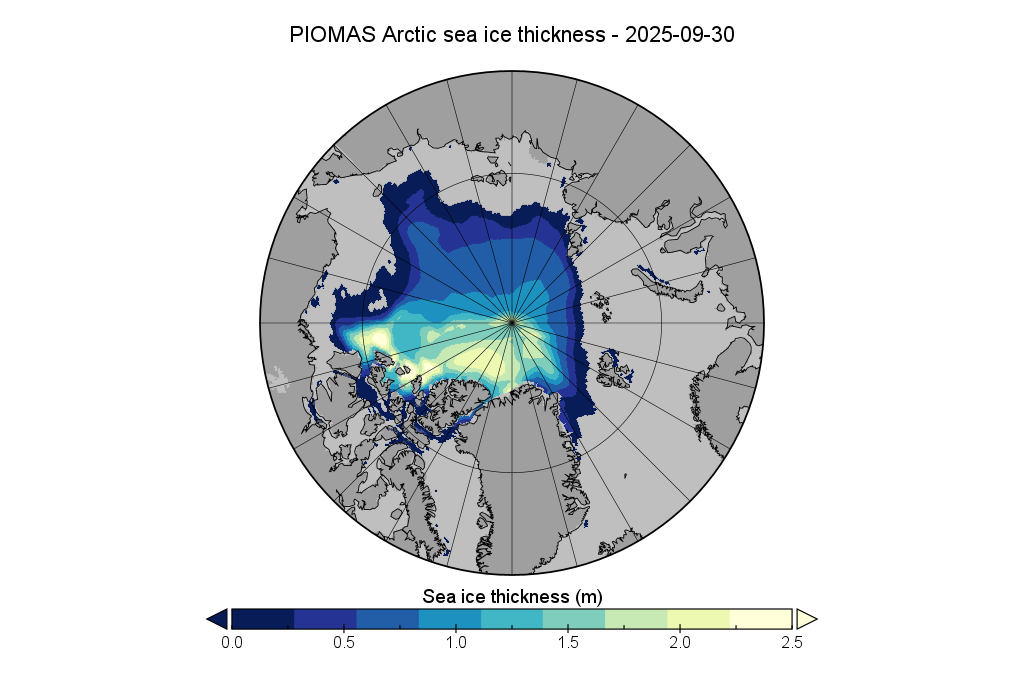
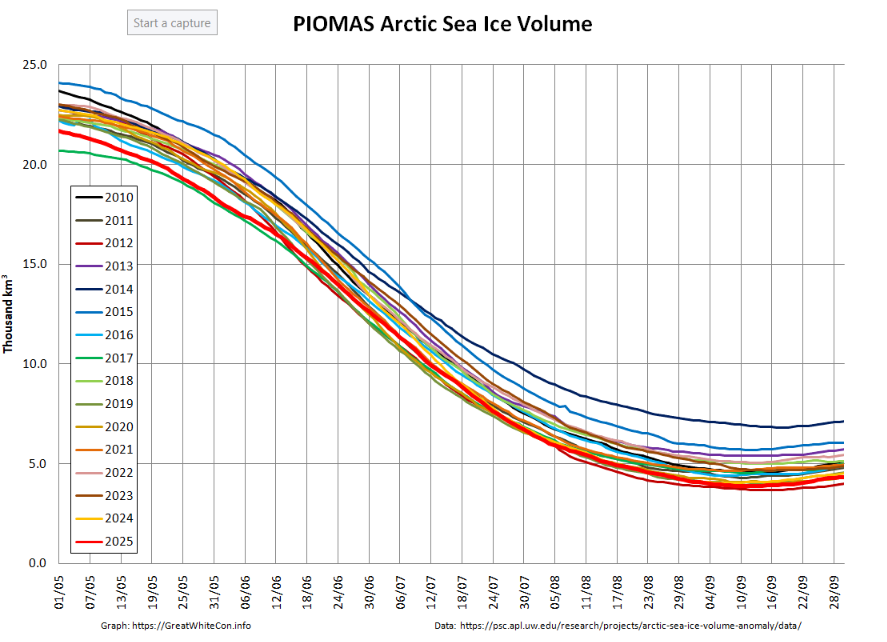
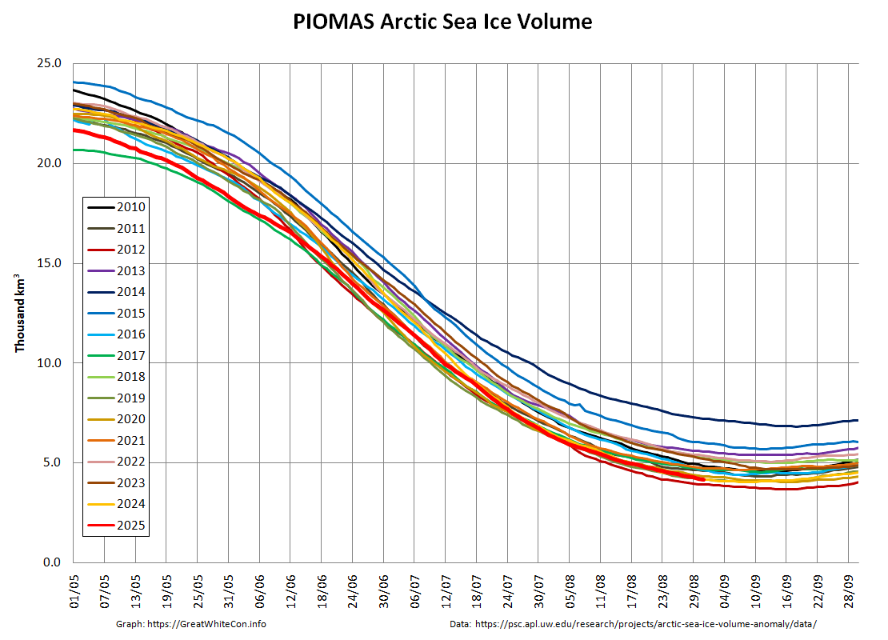
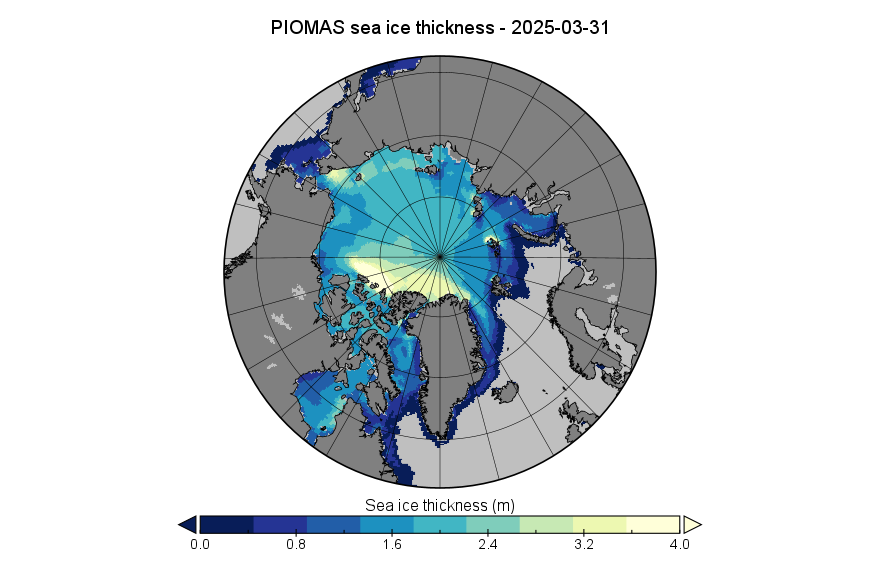
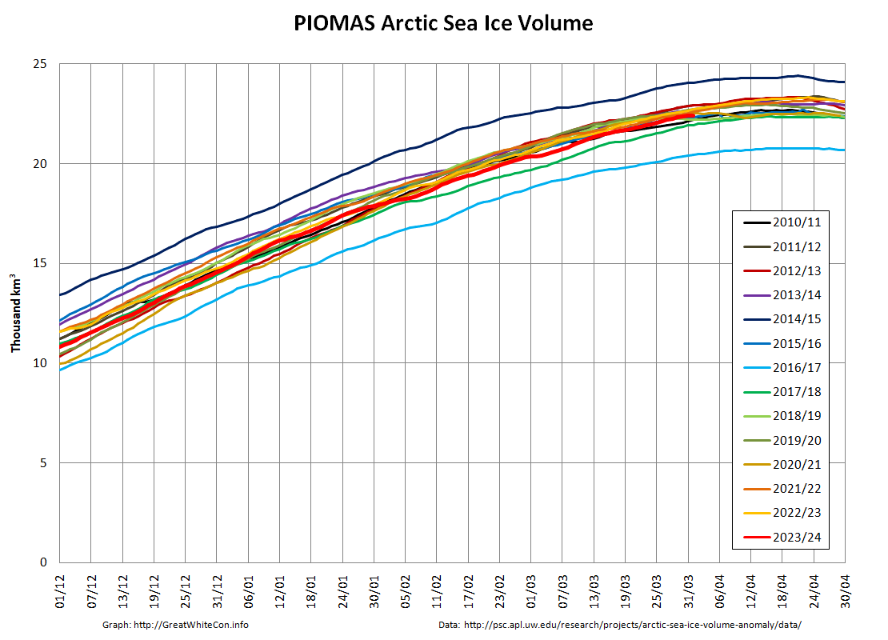
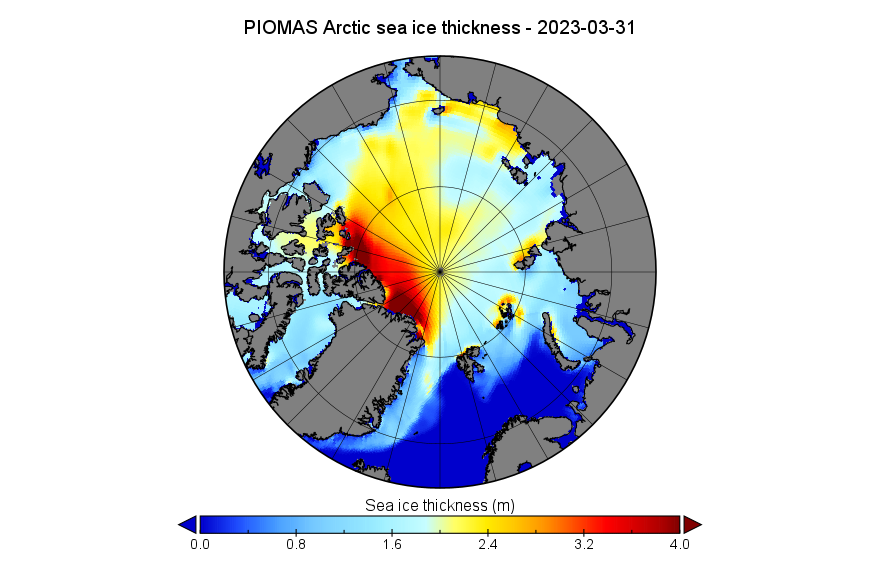
The PIOMAS gridded thickness data for September 2025 has been belatedly released:
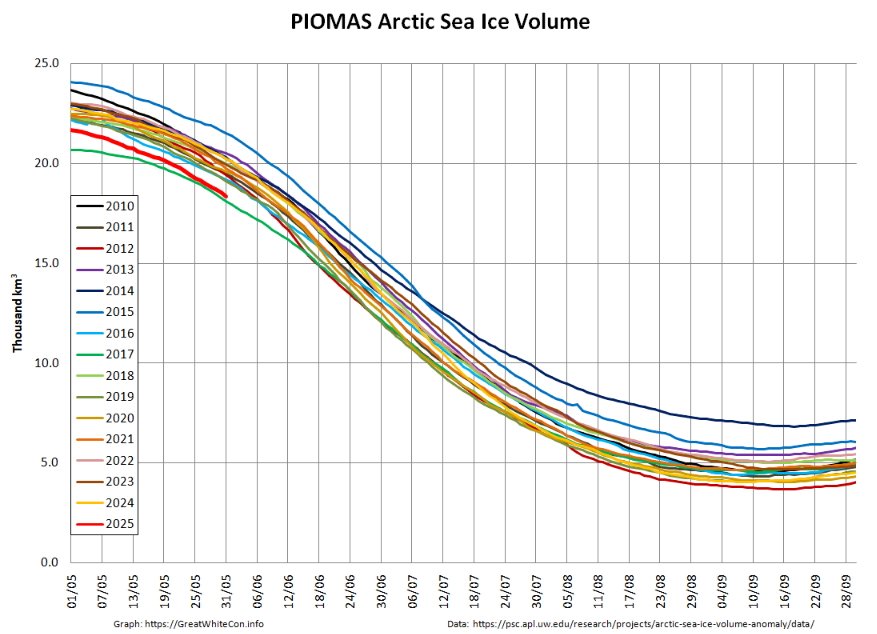
The associated volume graph reveals that the 2025 minimum modelled Arctic sea ice volume was 3.87 thousand km³ on September 12th, which is the 2nd lowest minimum in the PIOMAS record going back to 1979:
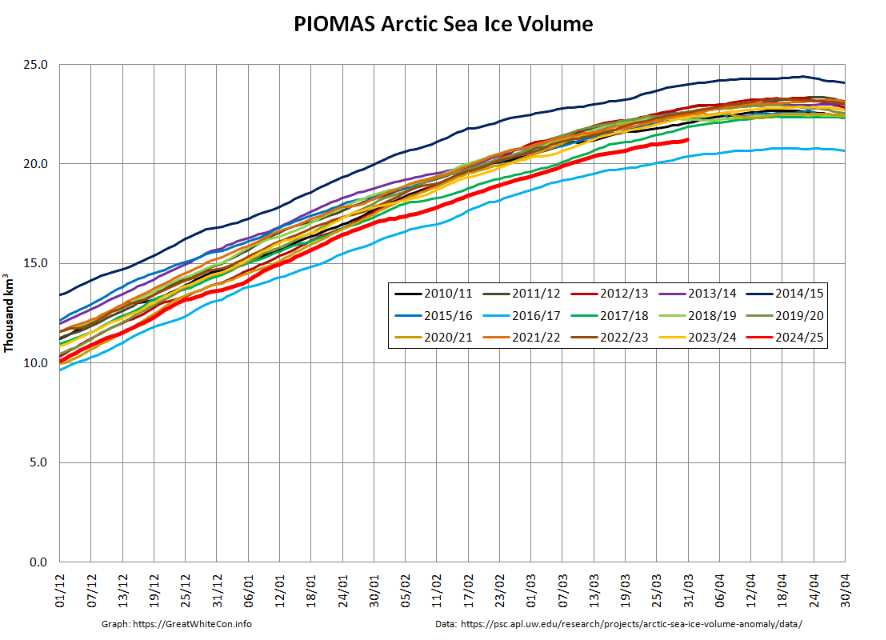
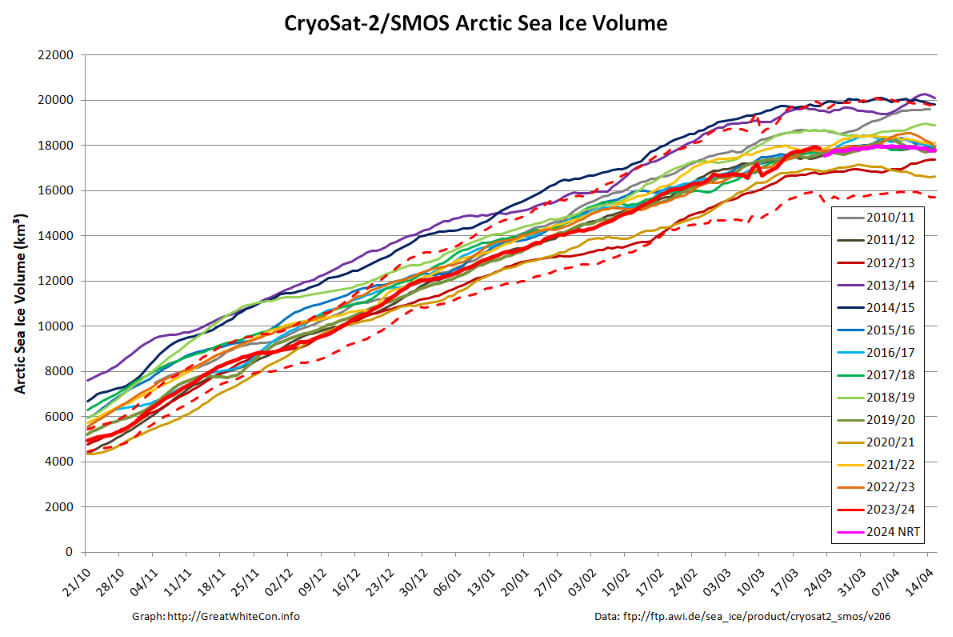
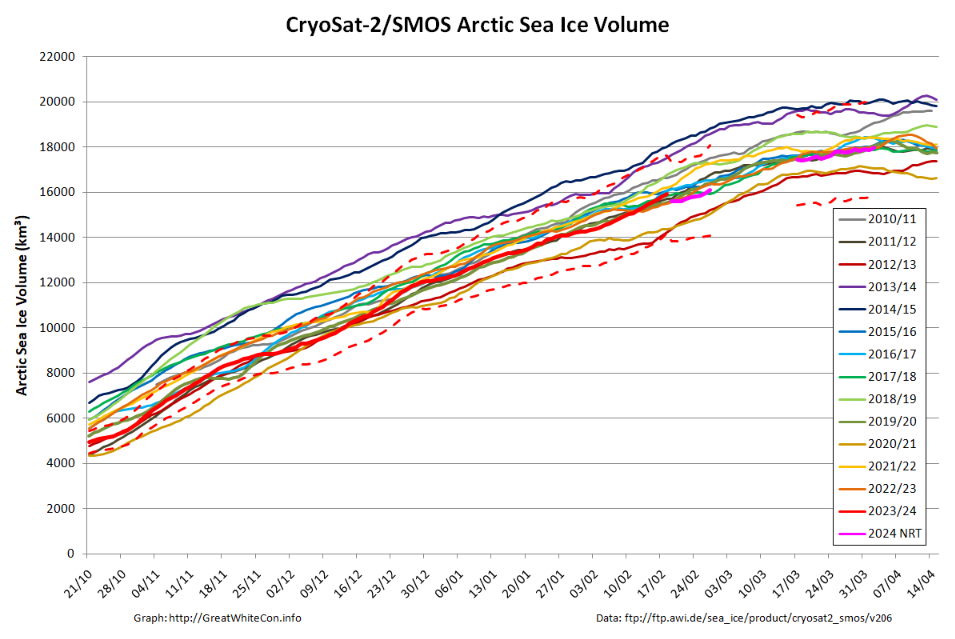
Whilst we’re on the topic of sea ice volume, here’s the latest “measured” volume graph:
Note the proviso about recent SMOS data above, and also that the version 3.00 data from AWI is currently only available beginning in Autumn 2023. Prior years shown on the graph above are based on version 2.06 data, which amongst other things does not incorporate Sentinel 3 data.
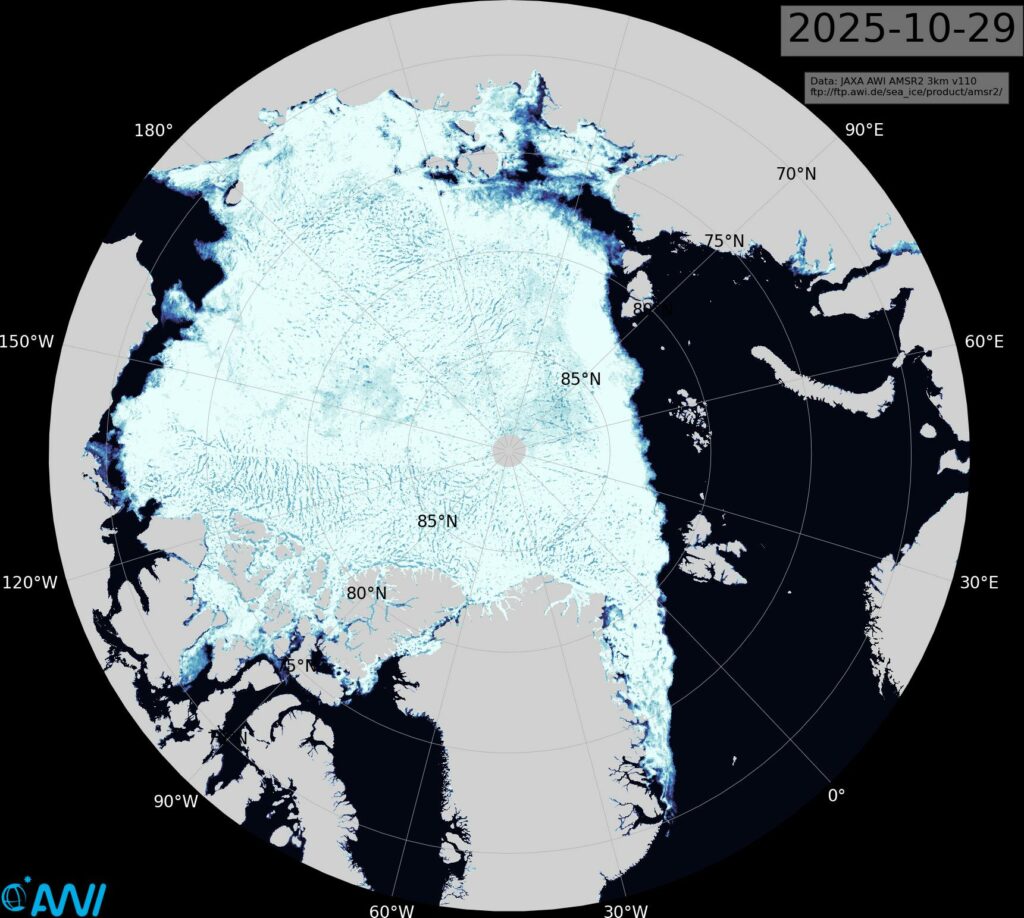
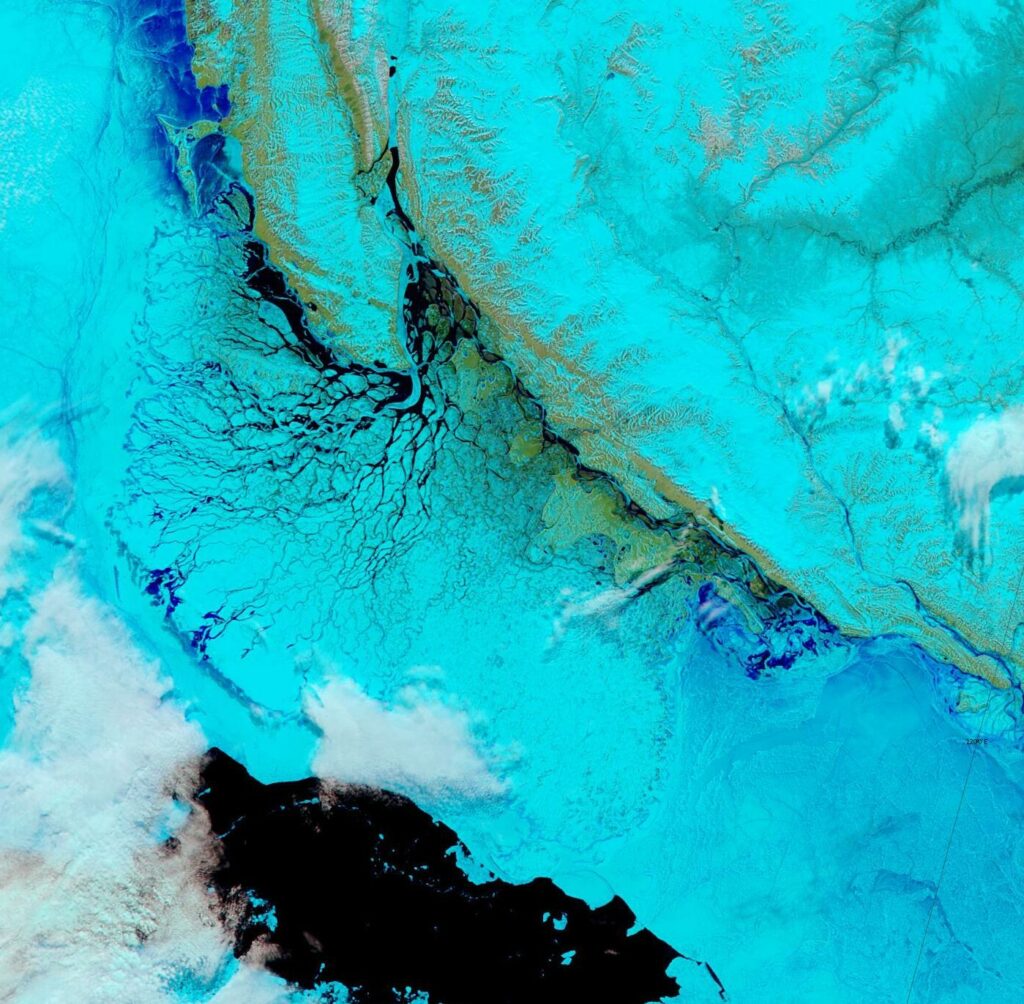
[Update – October 29th]Much of the Siberian side of the Arctic Ocean has now refrozen:
There is a significant difference between progress of the refreeze on the the Pacific and Atlantic sides of the Arctic. Extent in the Chukchi Sea is currently highest for the date in the AMSR2 record:
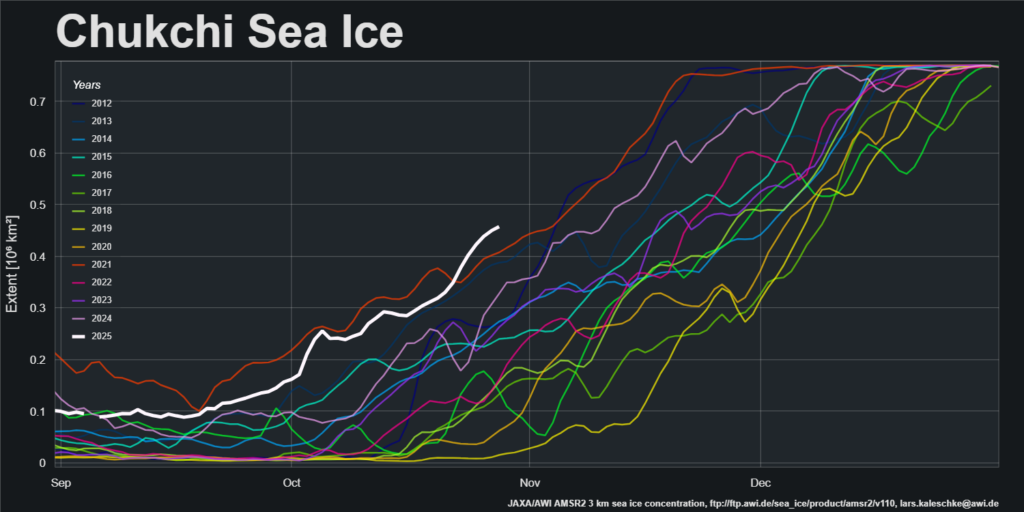
However, refreeze of the Kara Sea has yet to begin, and extent is currently lowest for the date in the AMSR2 record:
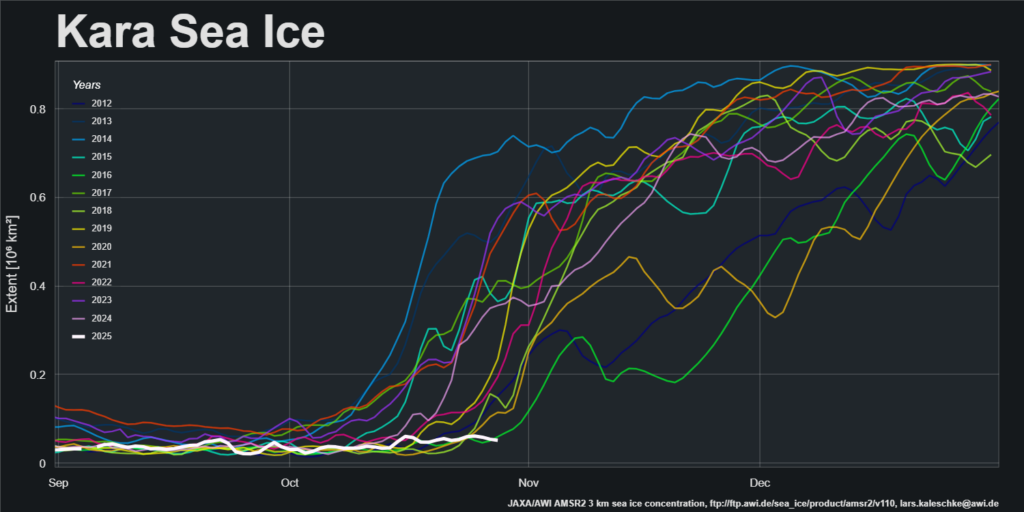
Pan Arctic JAXA/ViSHOP extent is now 6th lowest in the satellite era:
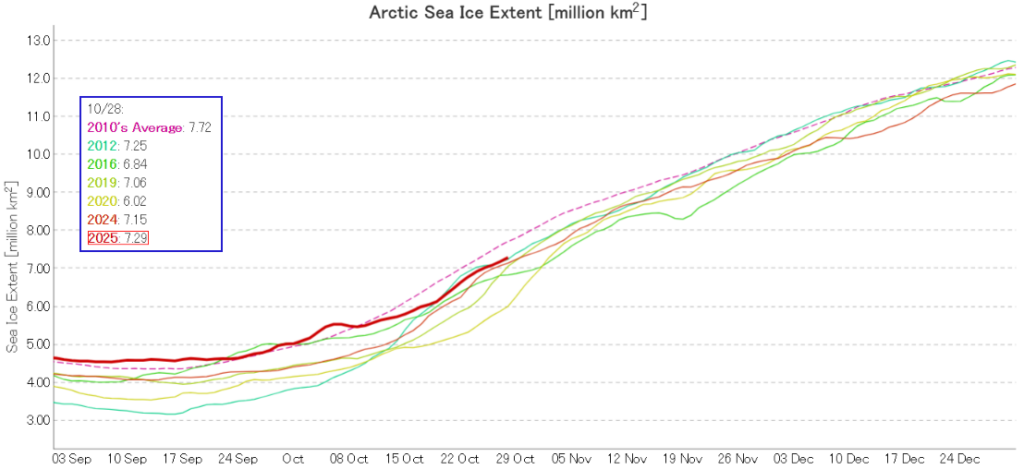
The conversation continues over on the November open thread.