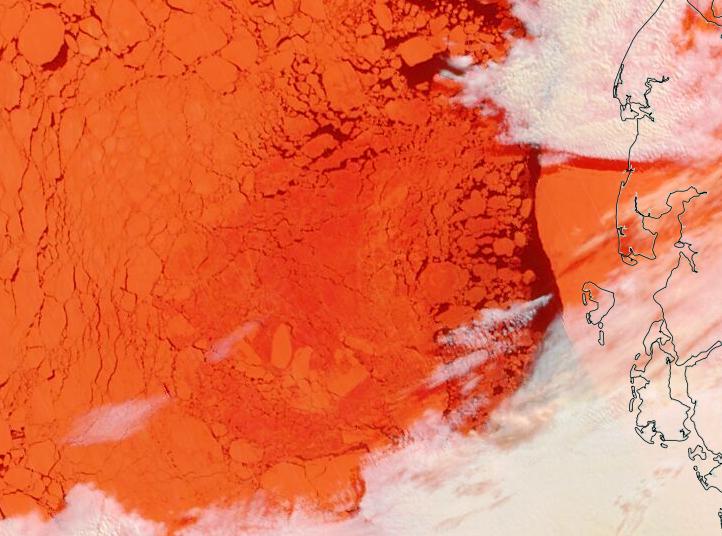
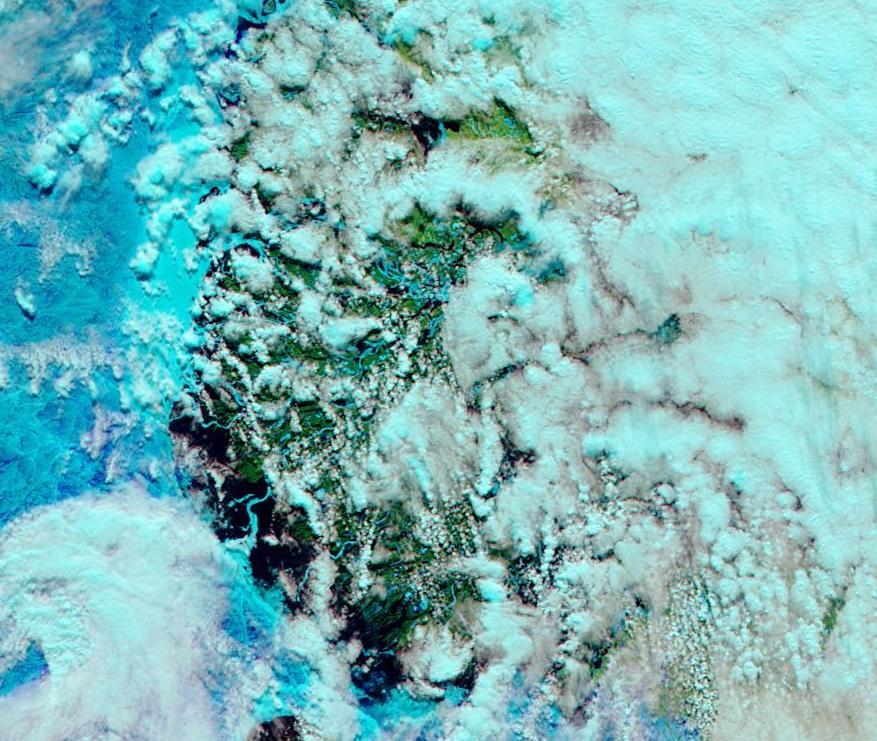
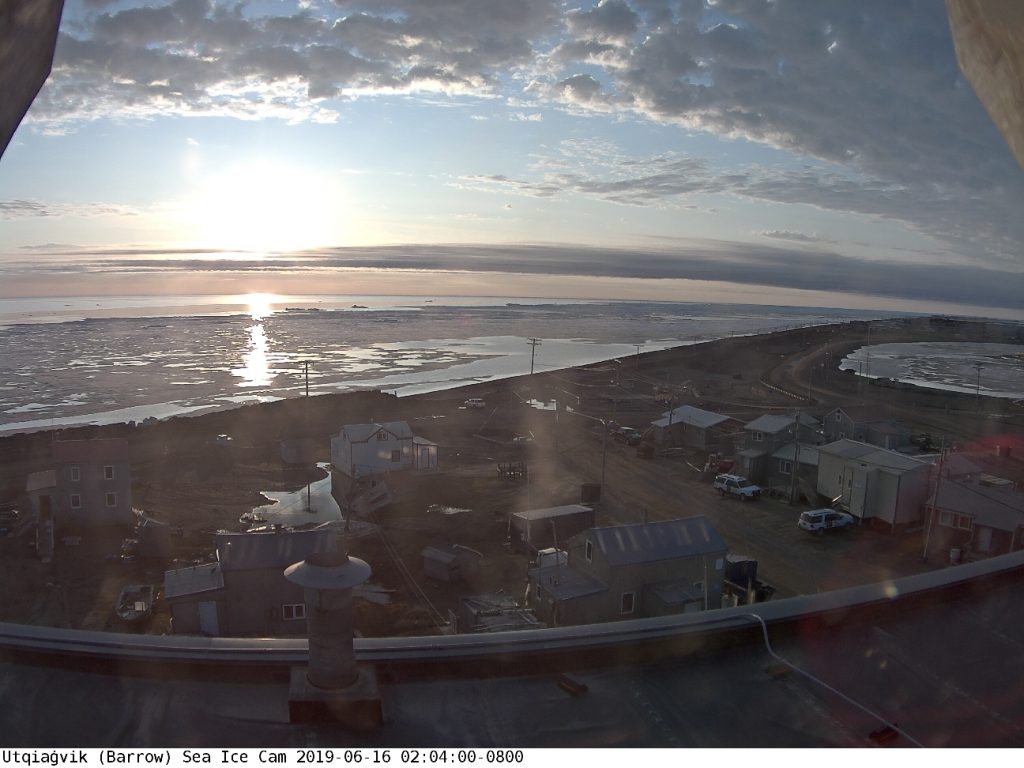
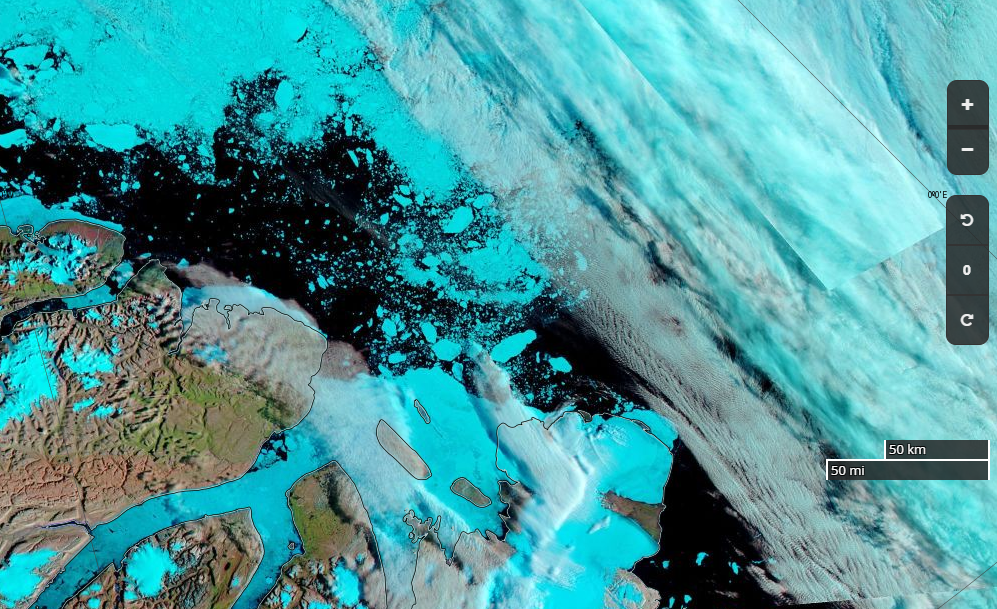
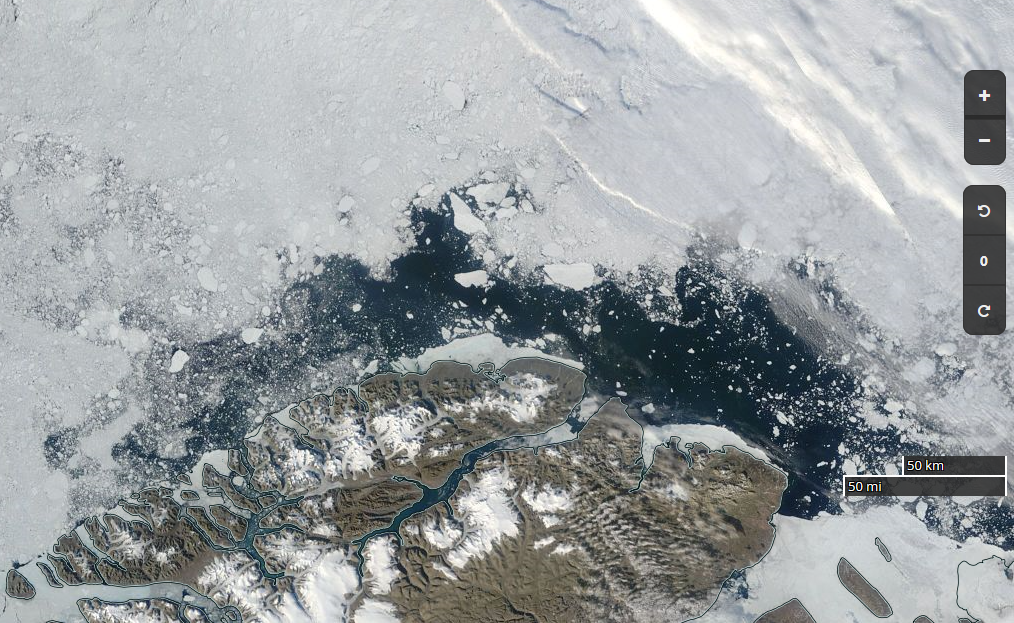
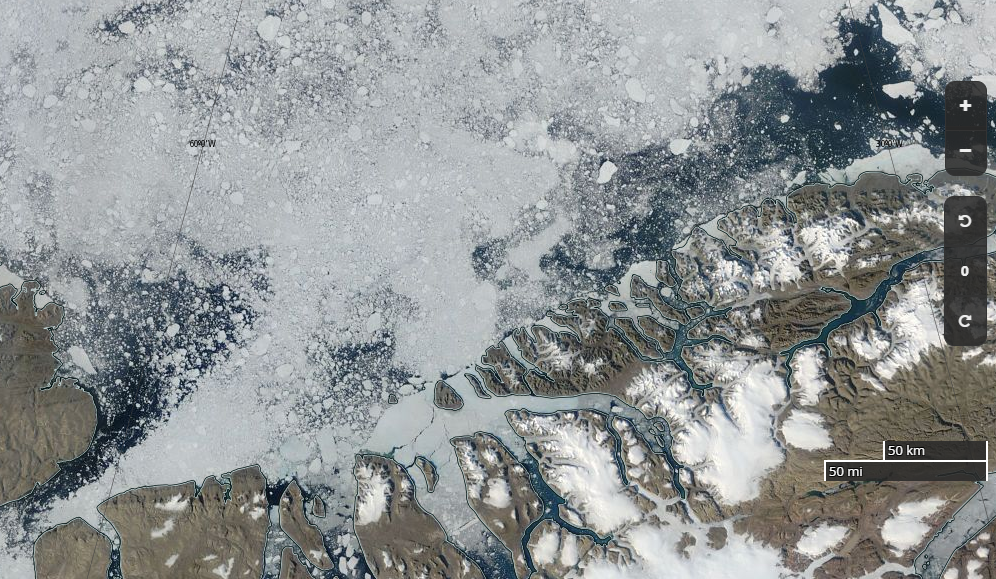
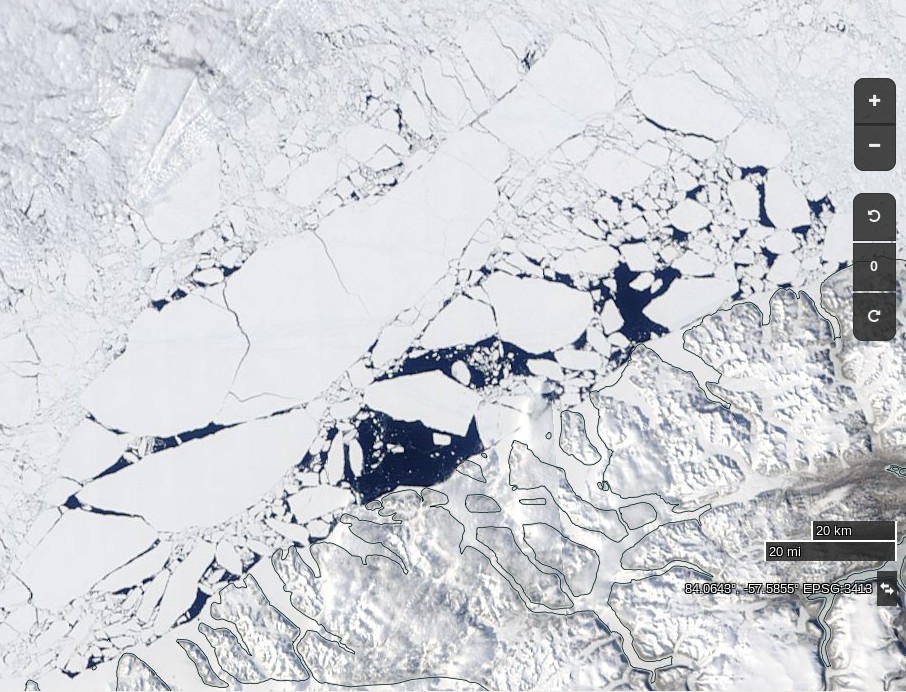
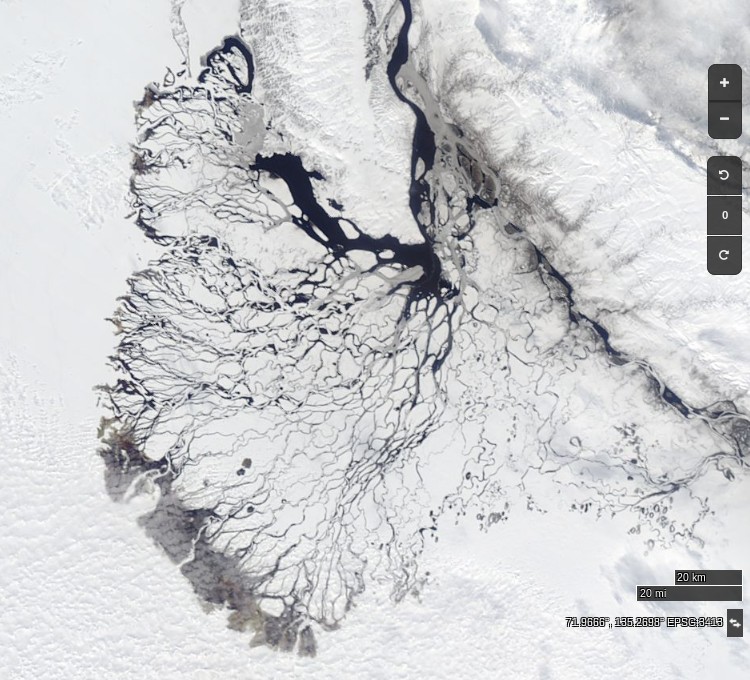
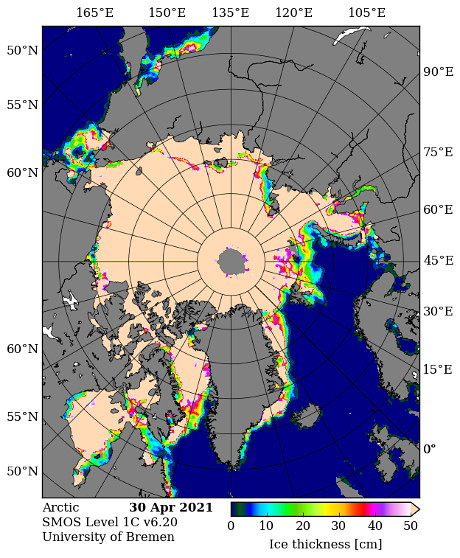
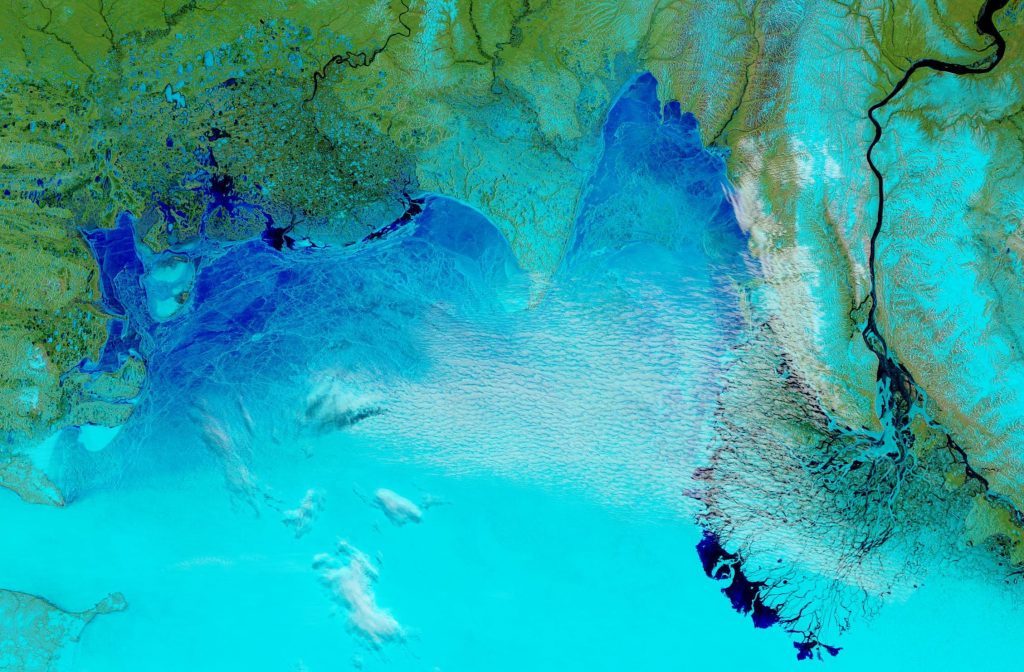
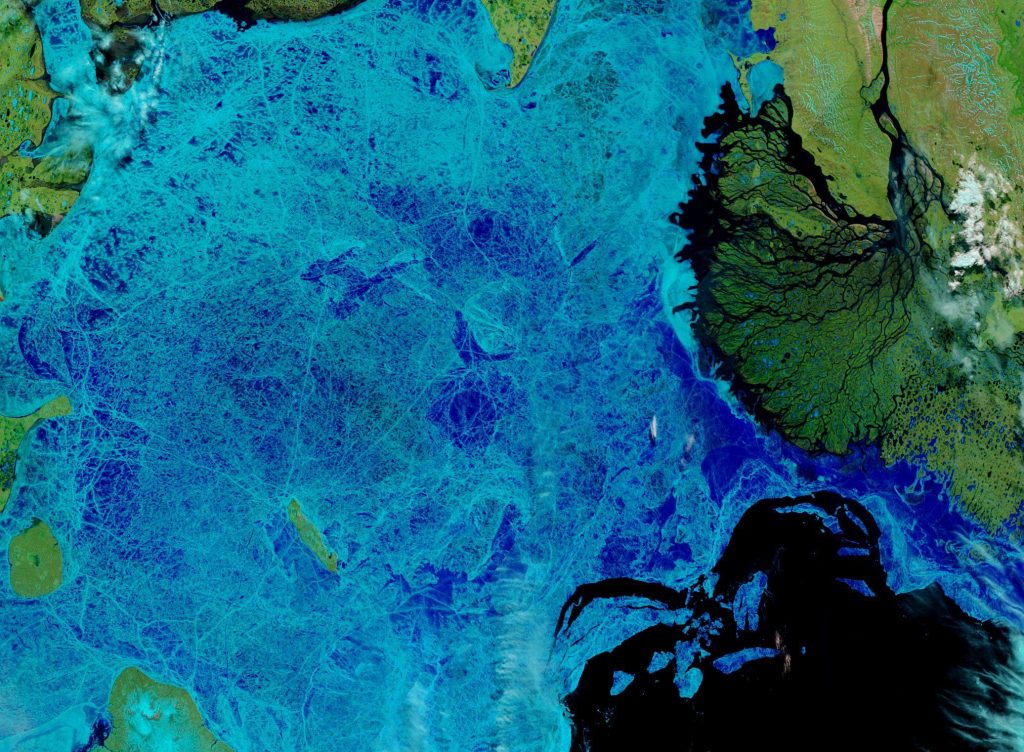
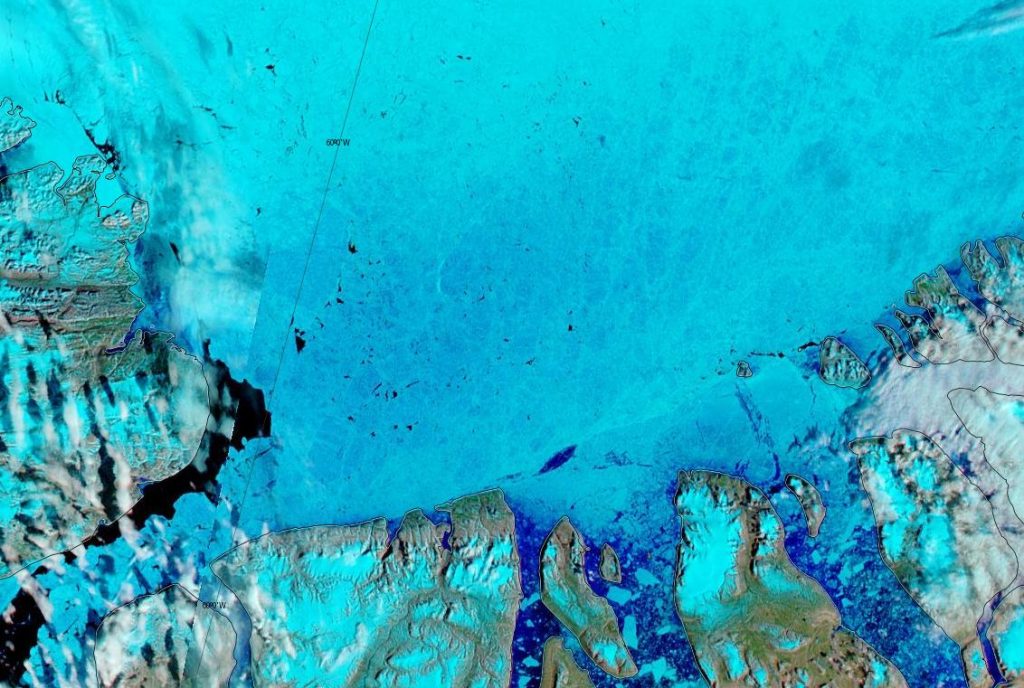
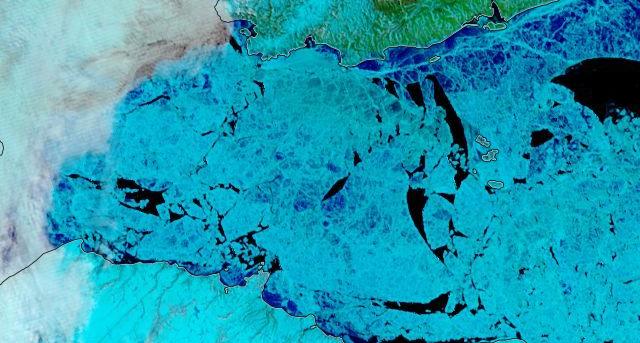
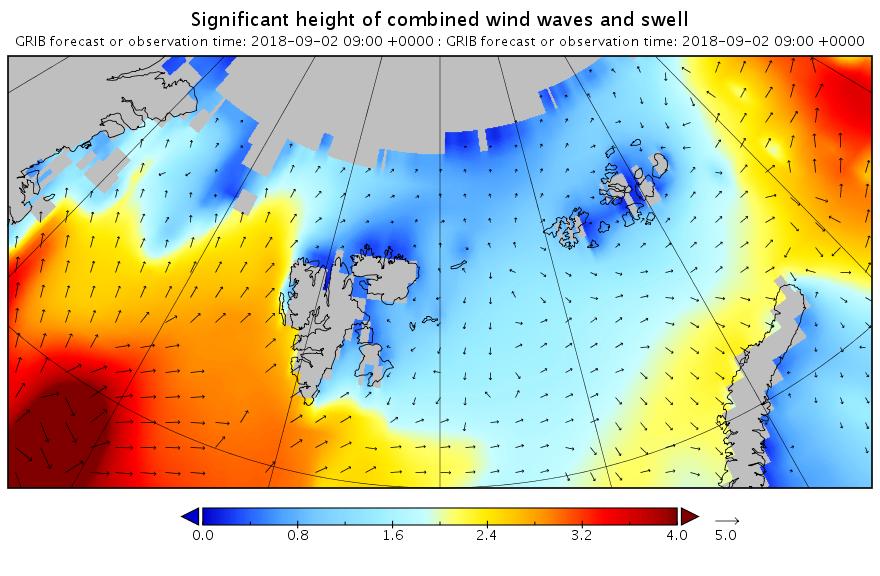
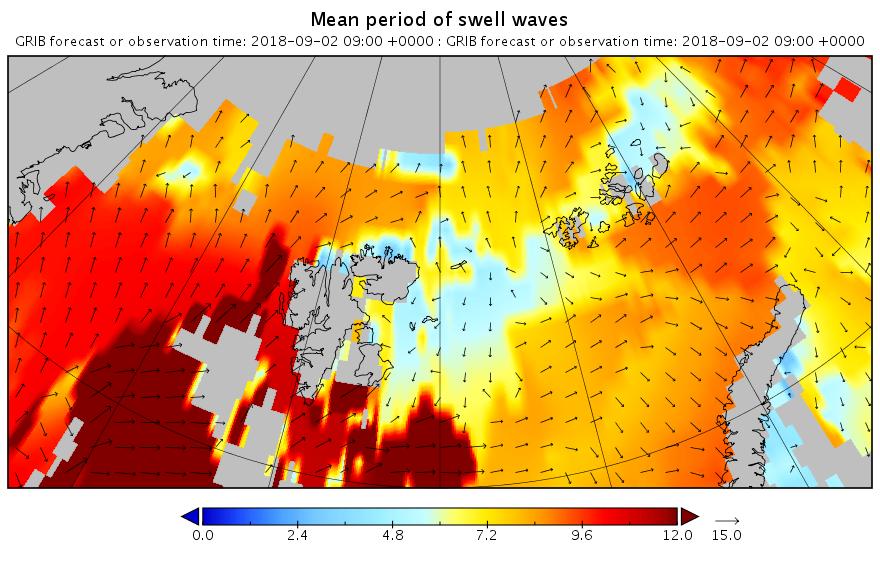
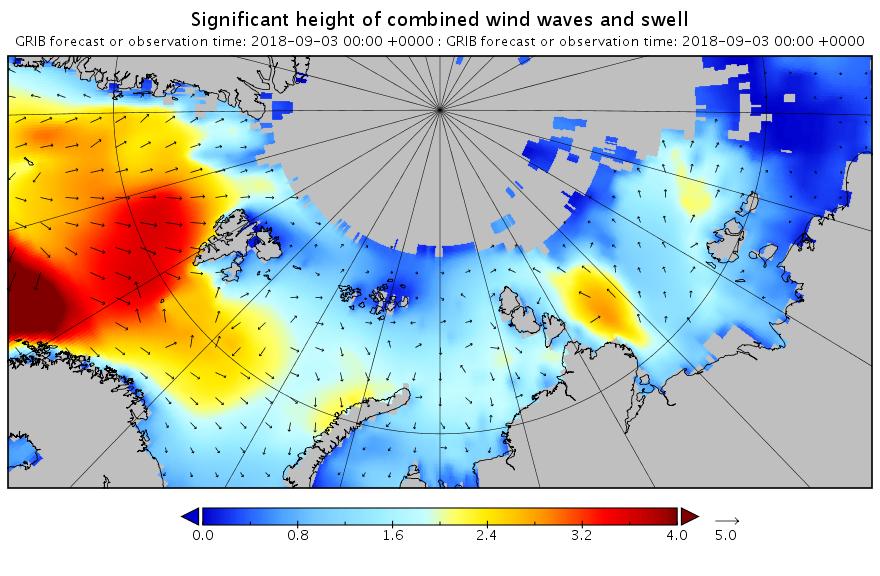
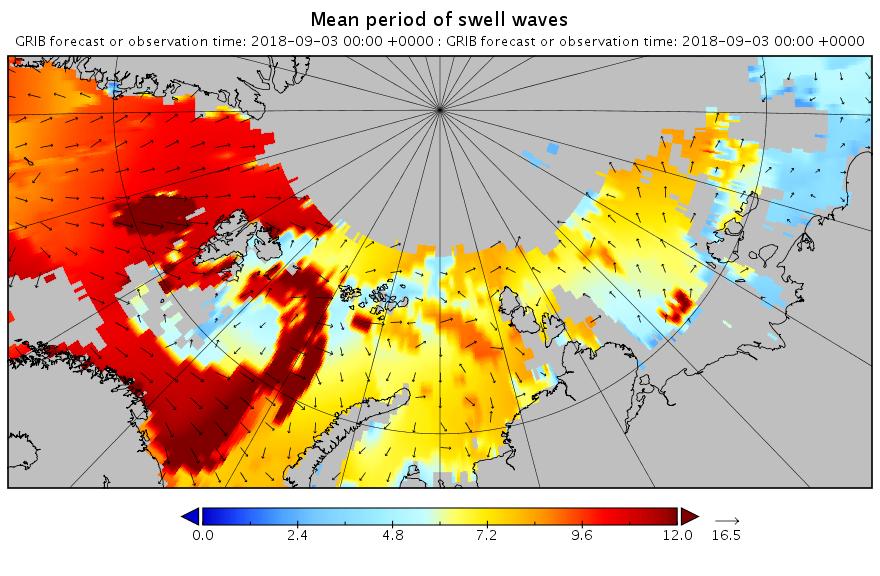
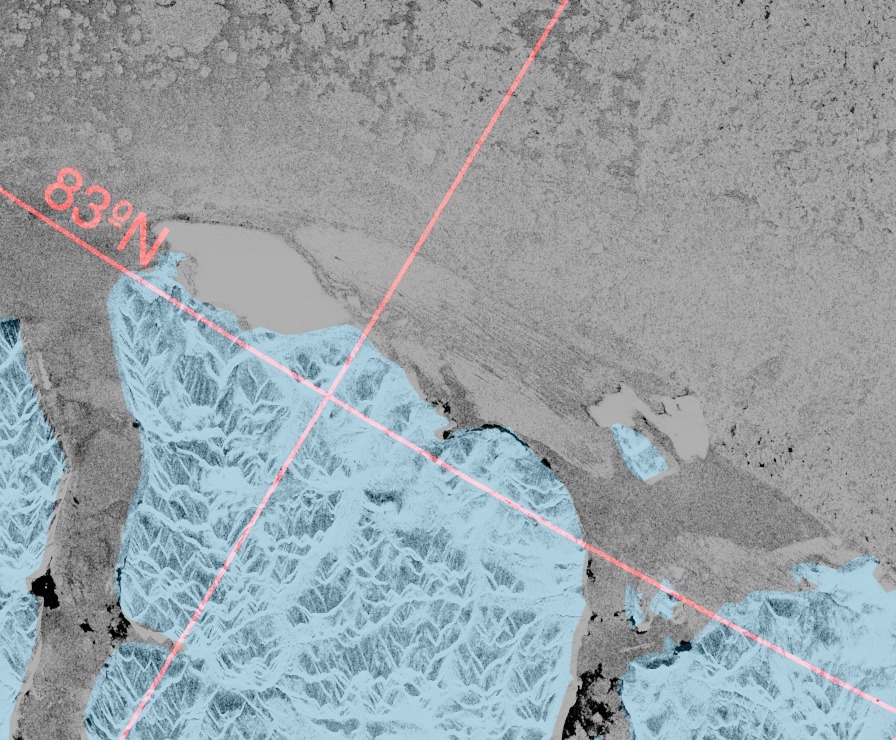
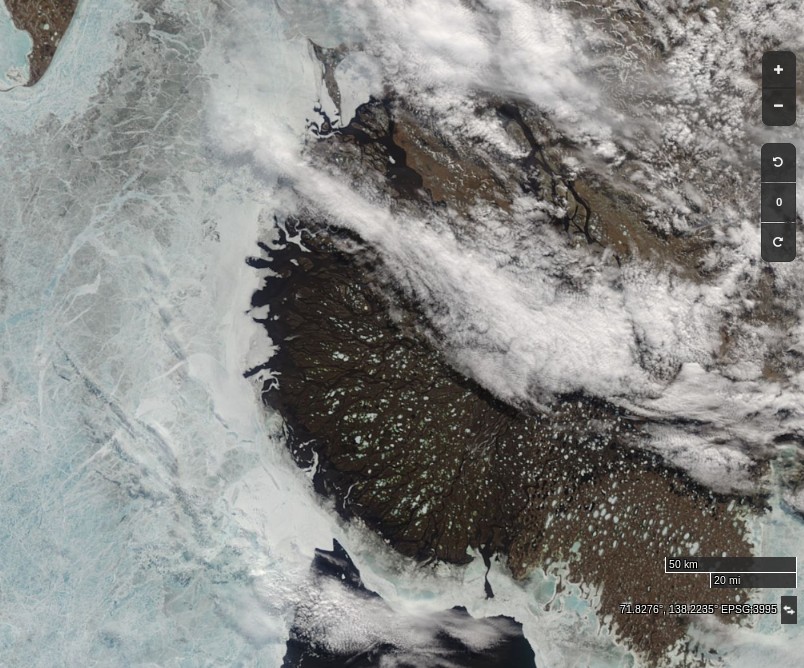
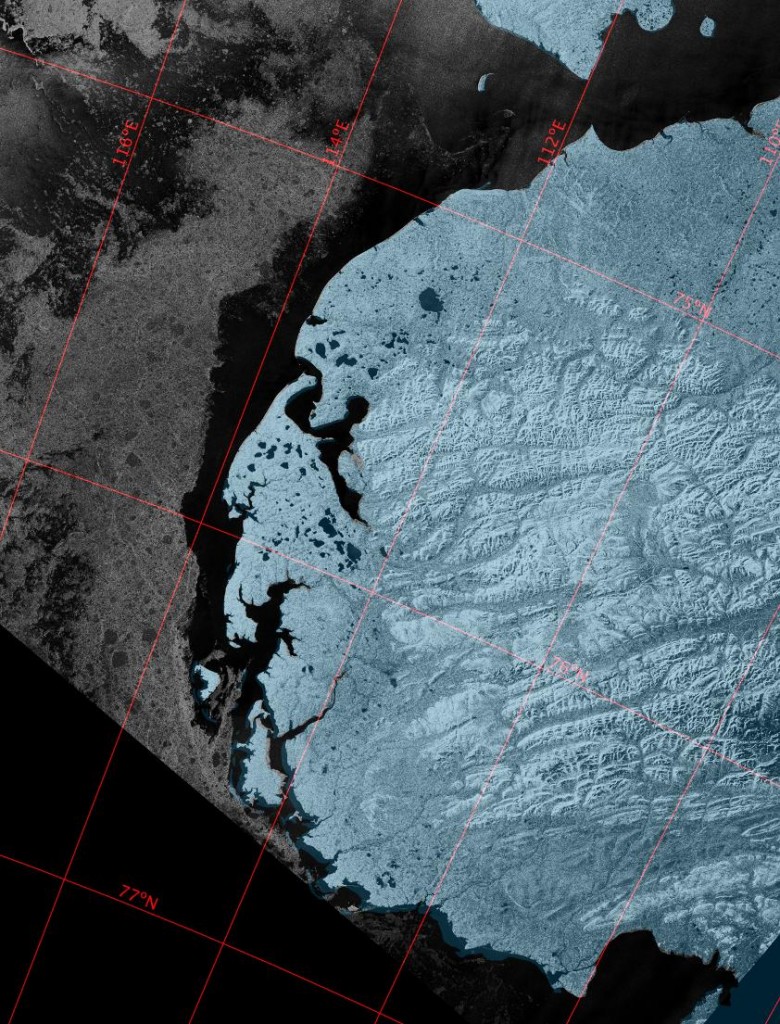
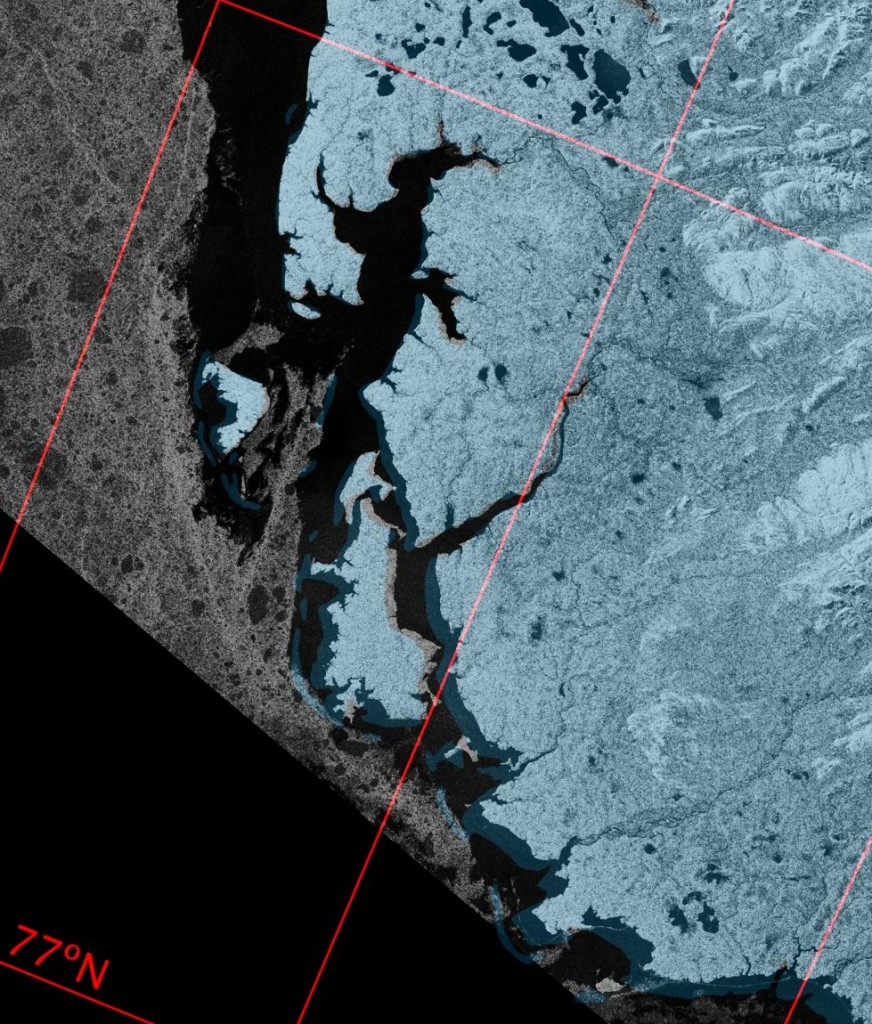
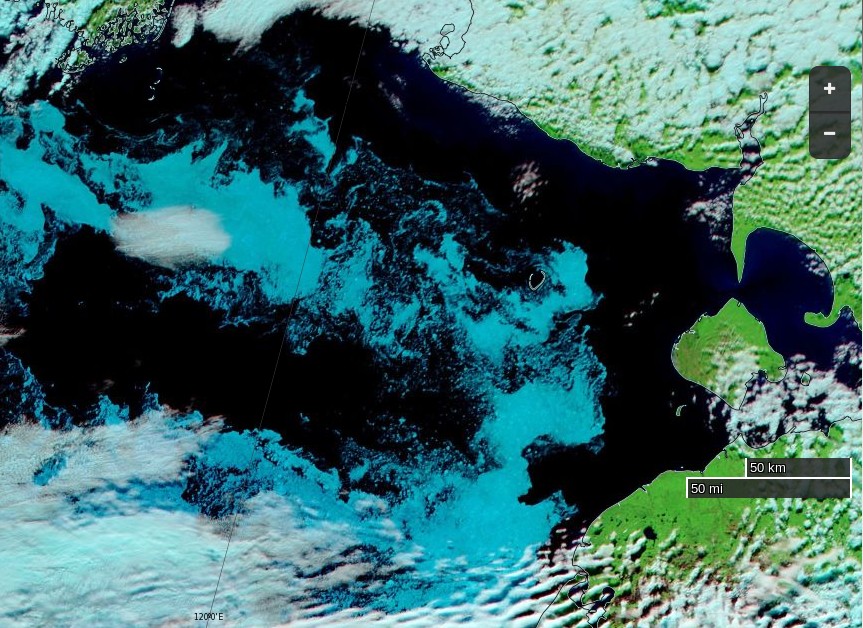
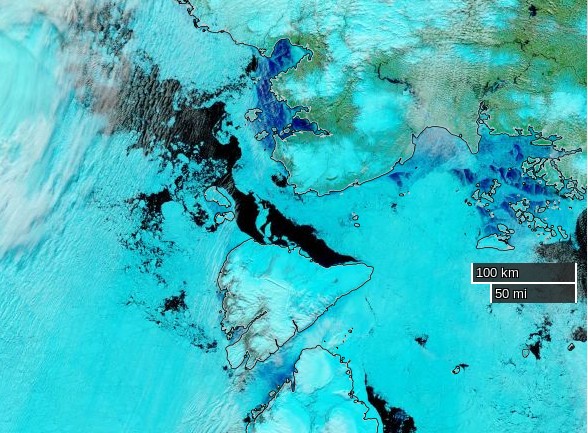
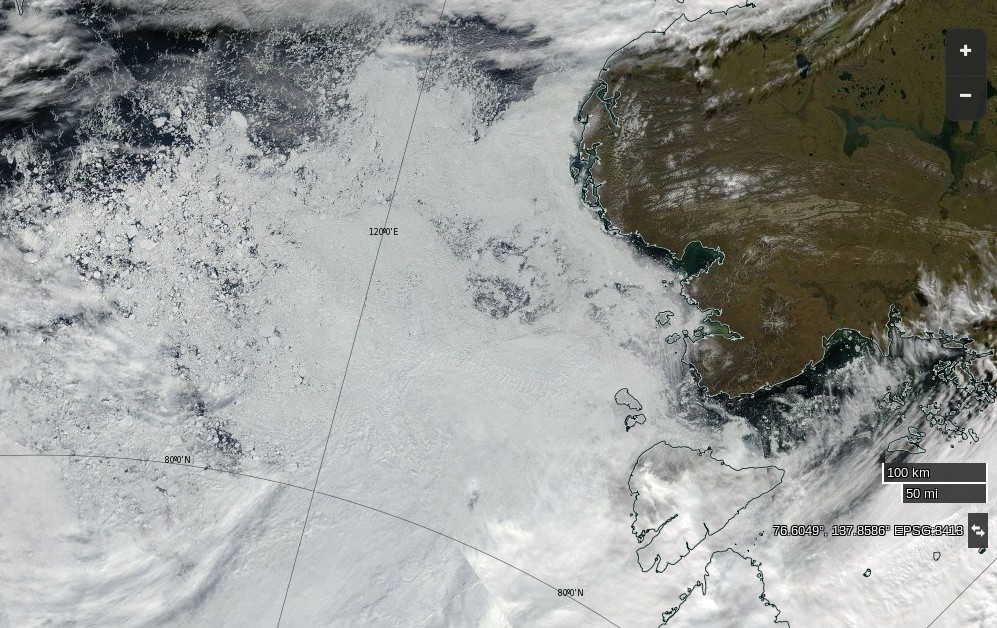
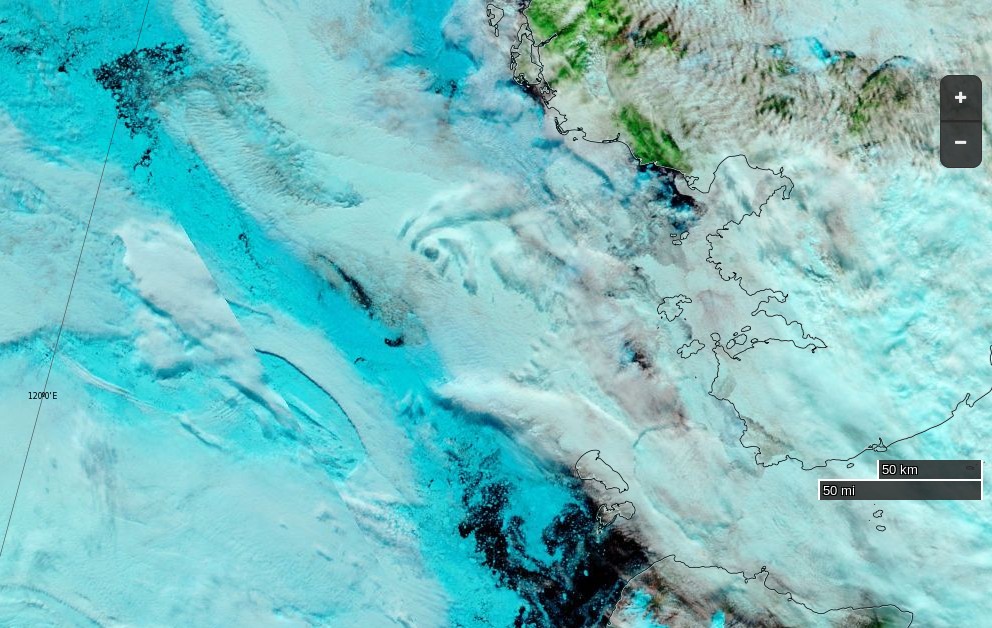
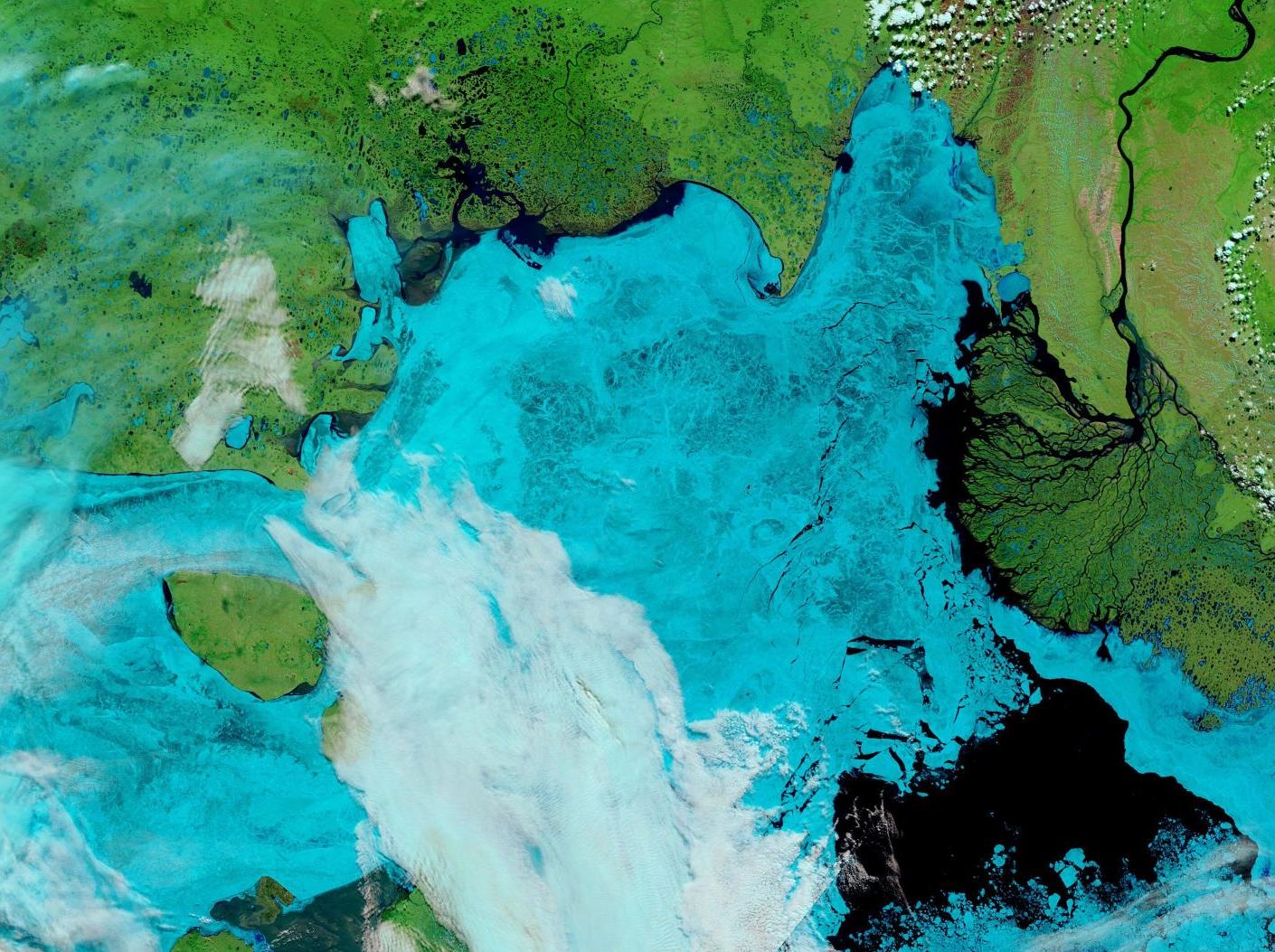
Let’s begin the month with a “true colour” image from the Terra satellite of the Laptev Sea and thereabouts:

The blueish tinge indicates the appearance of melt ponds almost everywhere over the land-fast ice currently covering the majority of the Laptev Sea.
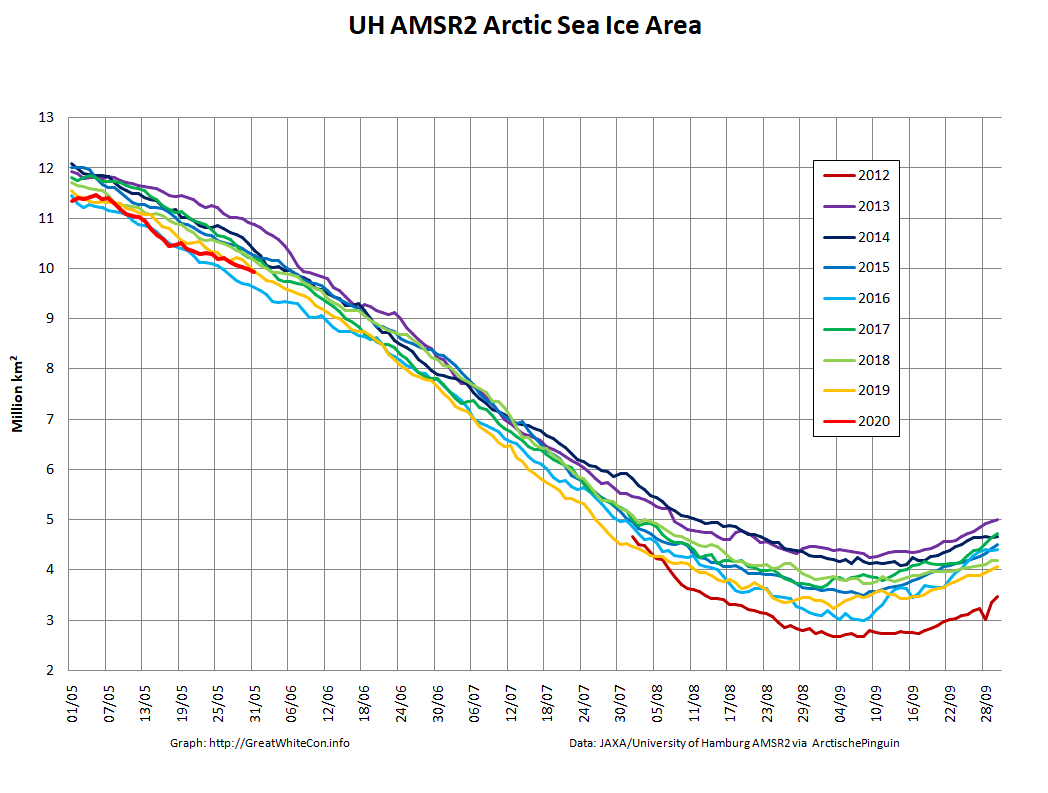
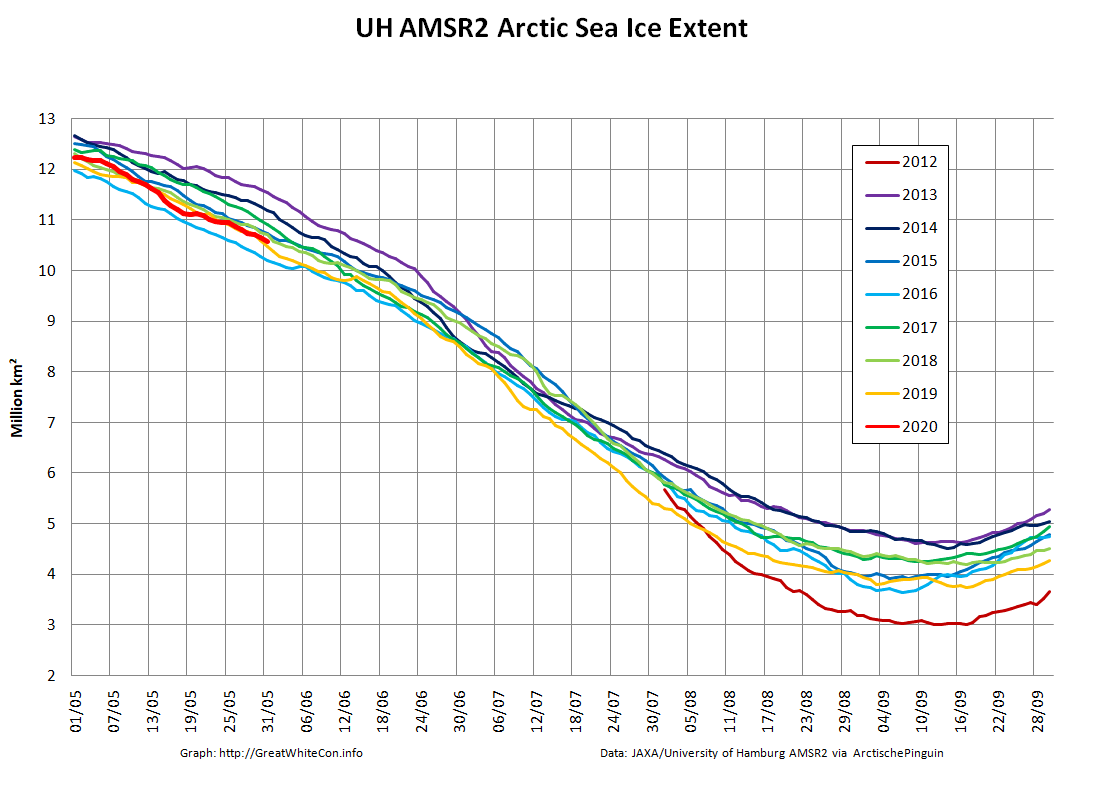
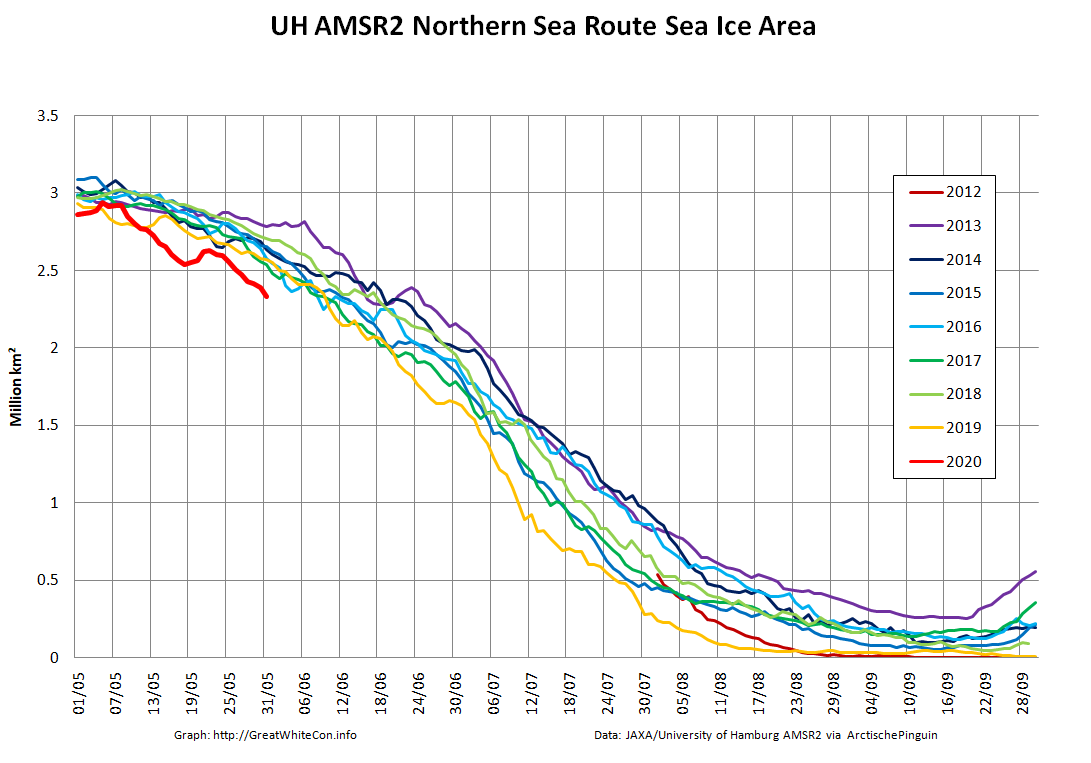
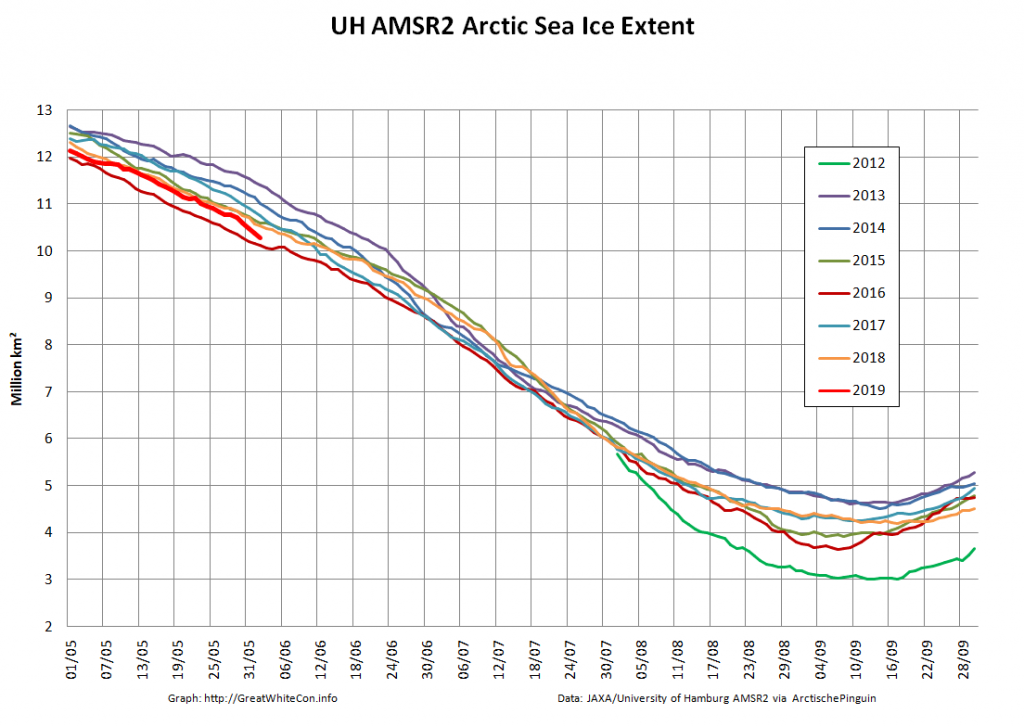
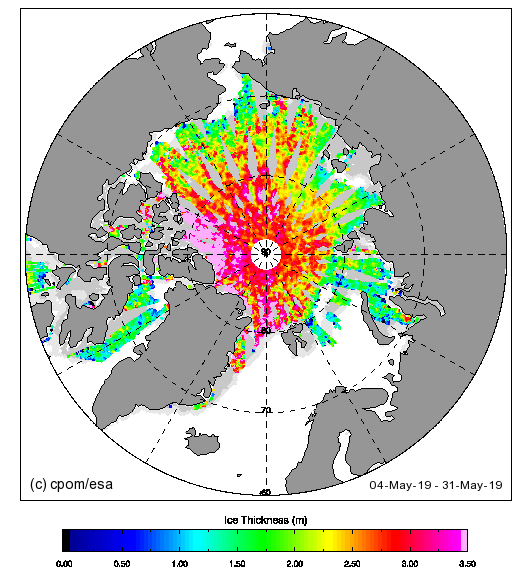
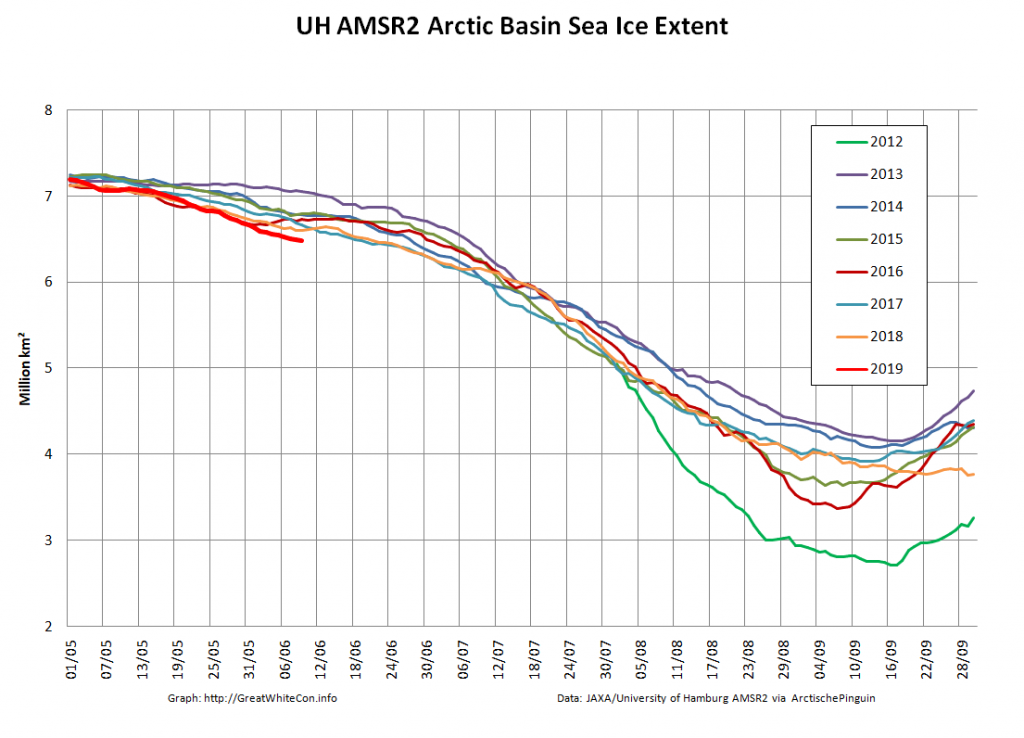
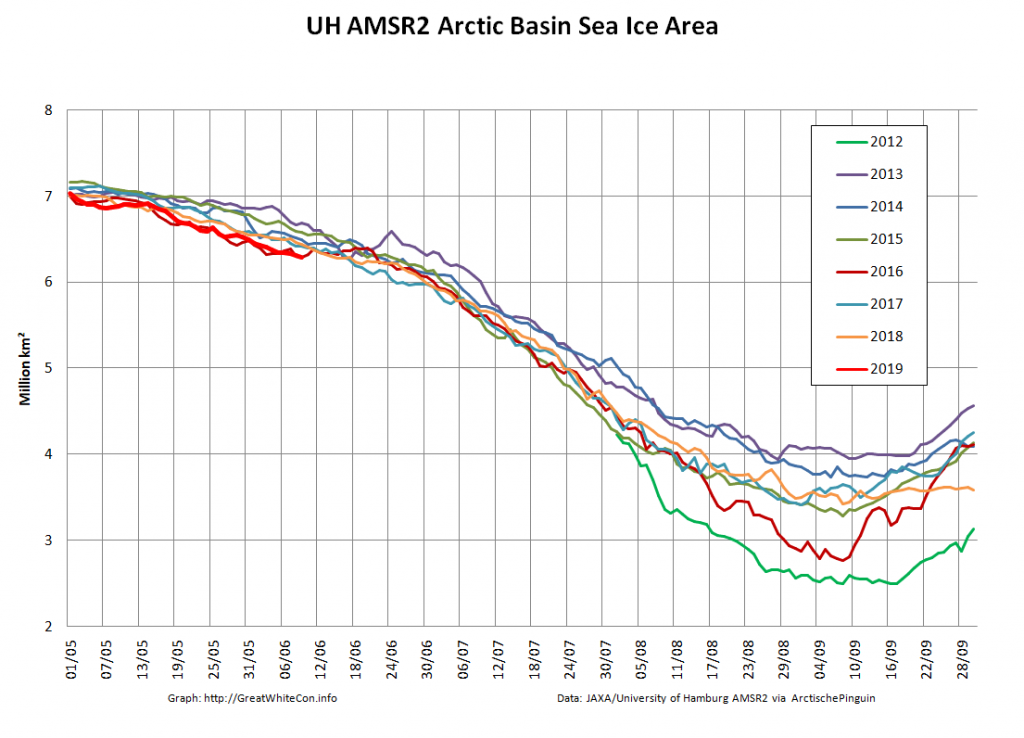
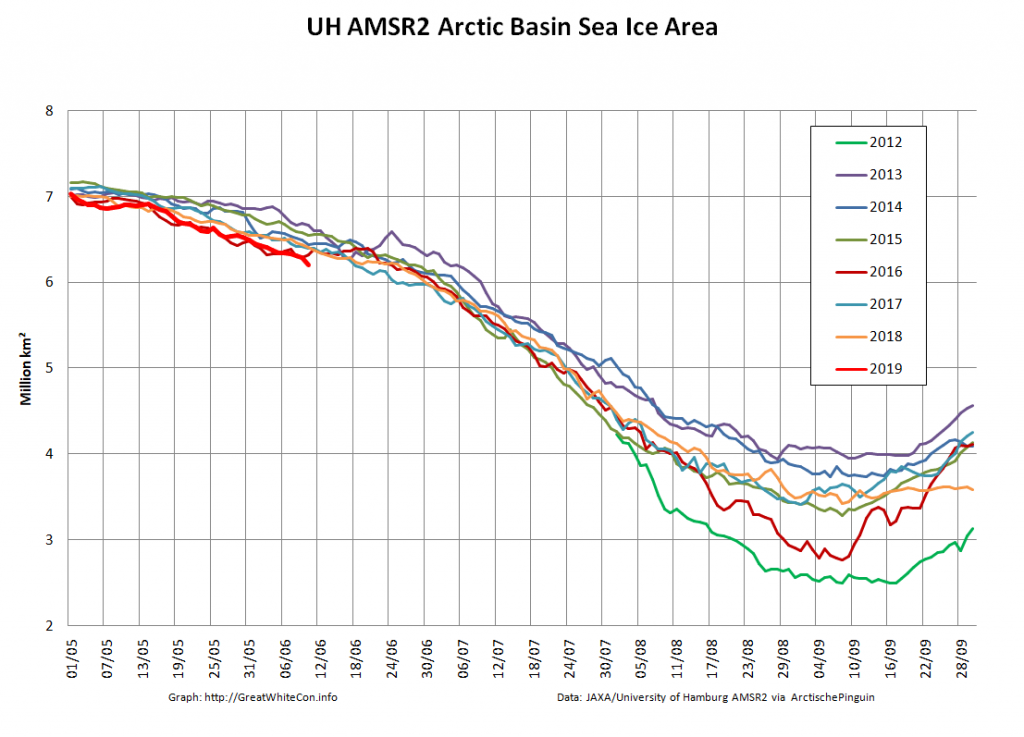
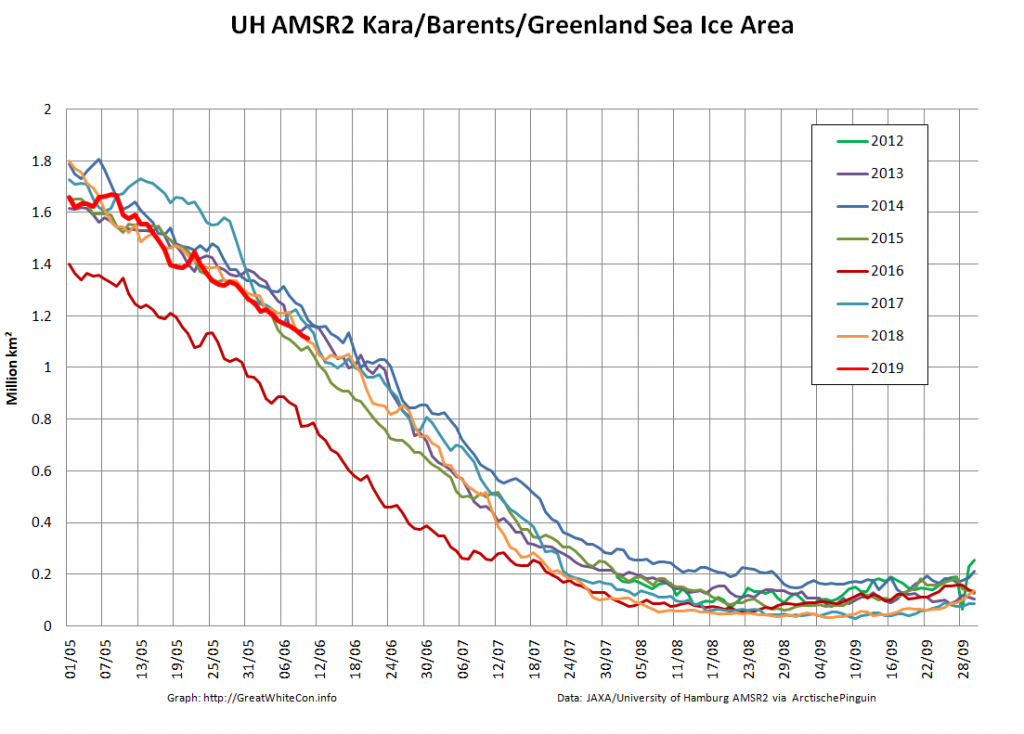
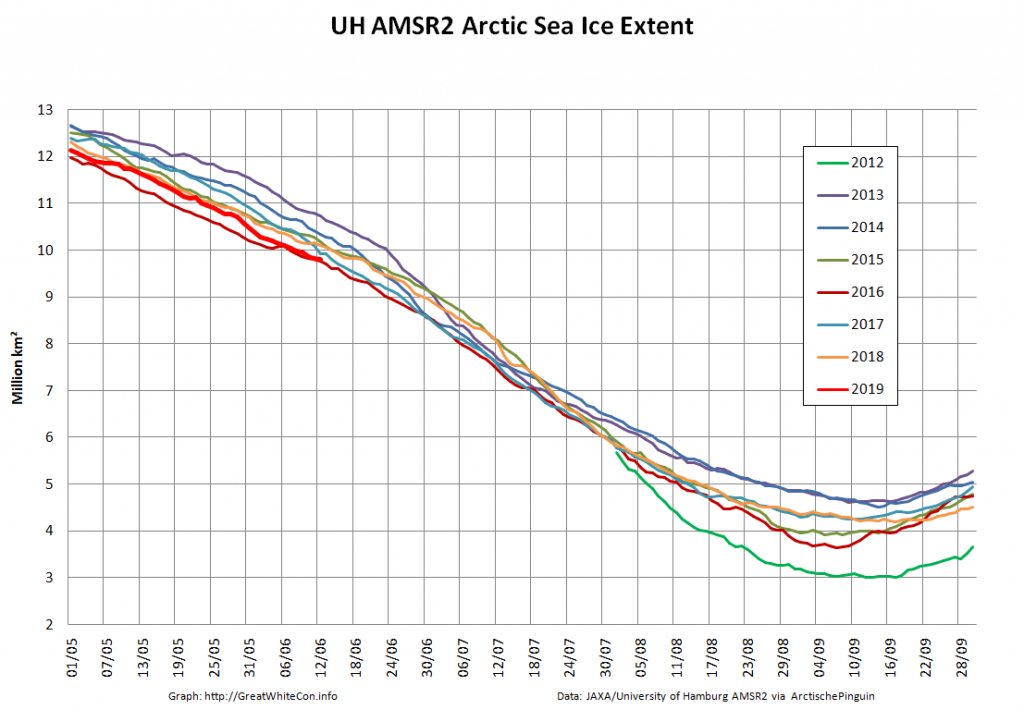
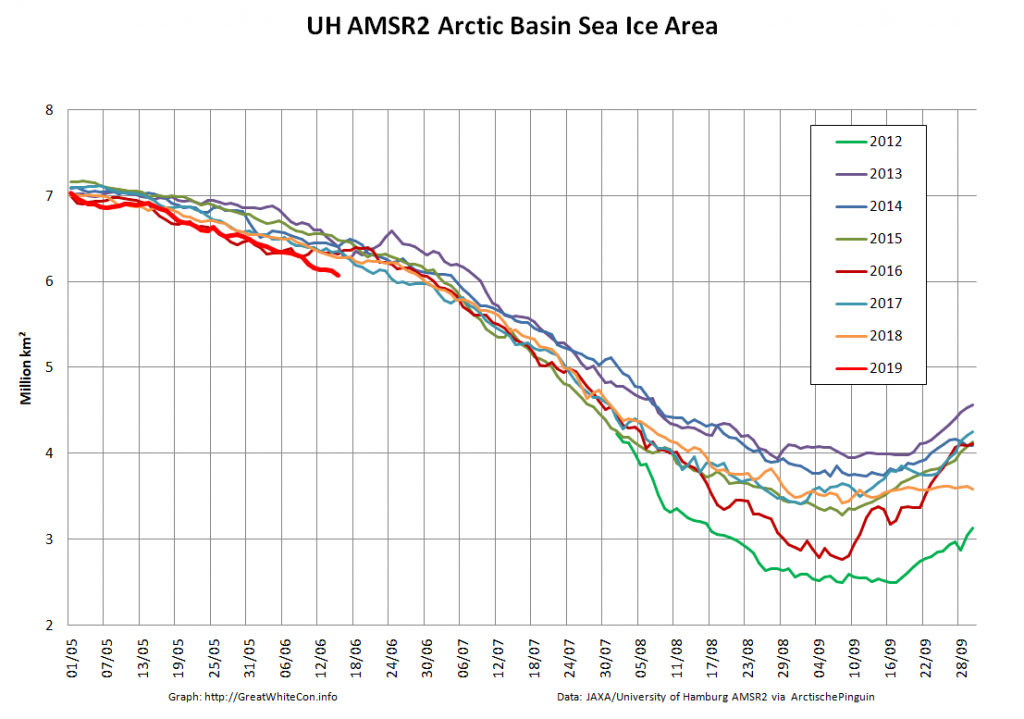
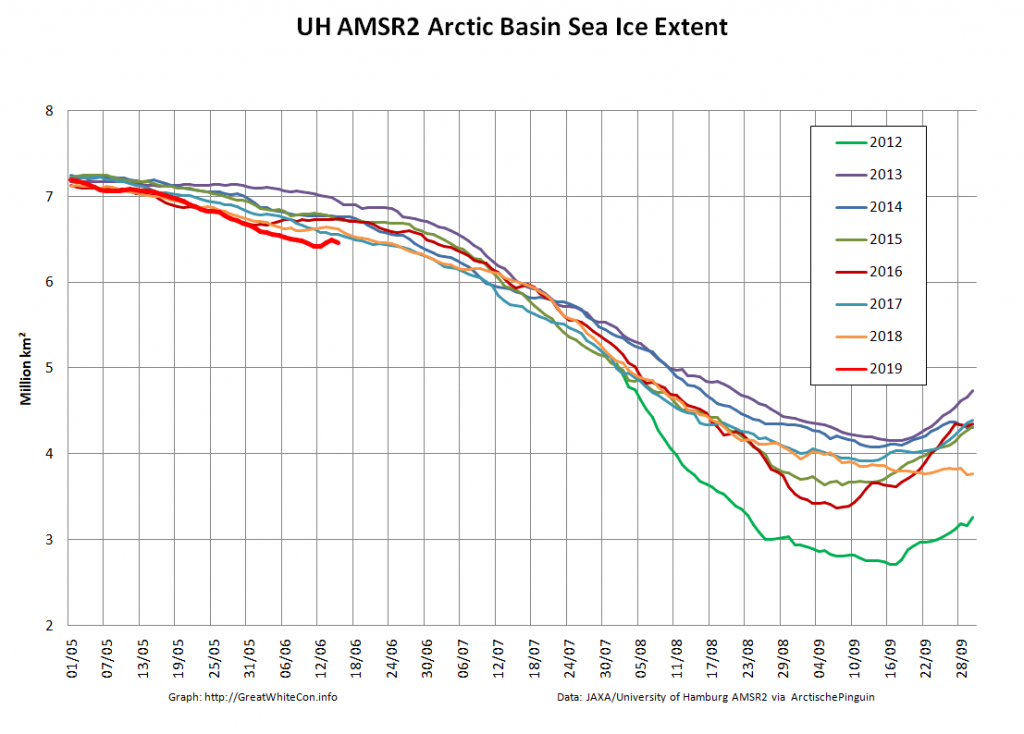
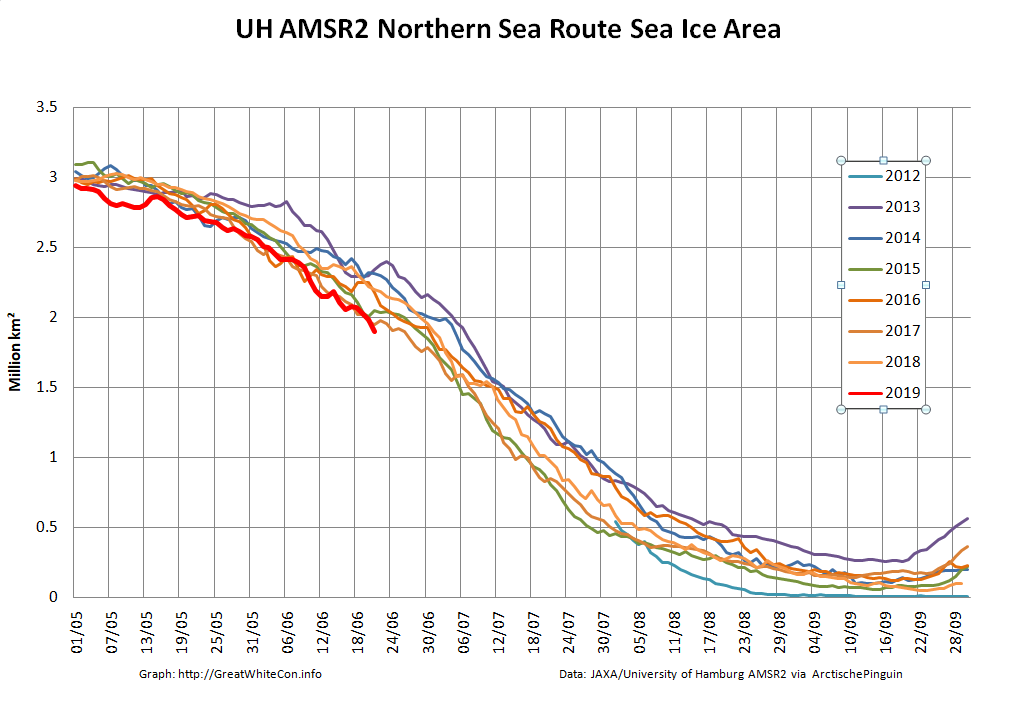
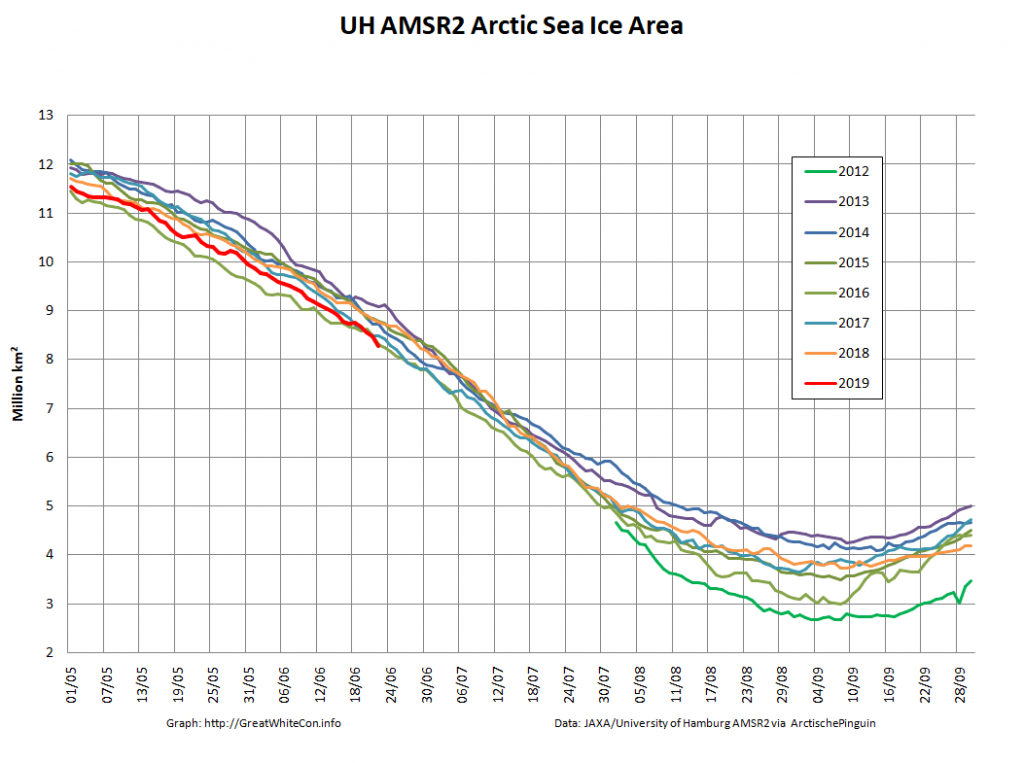
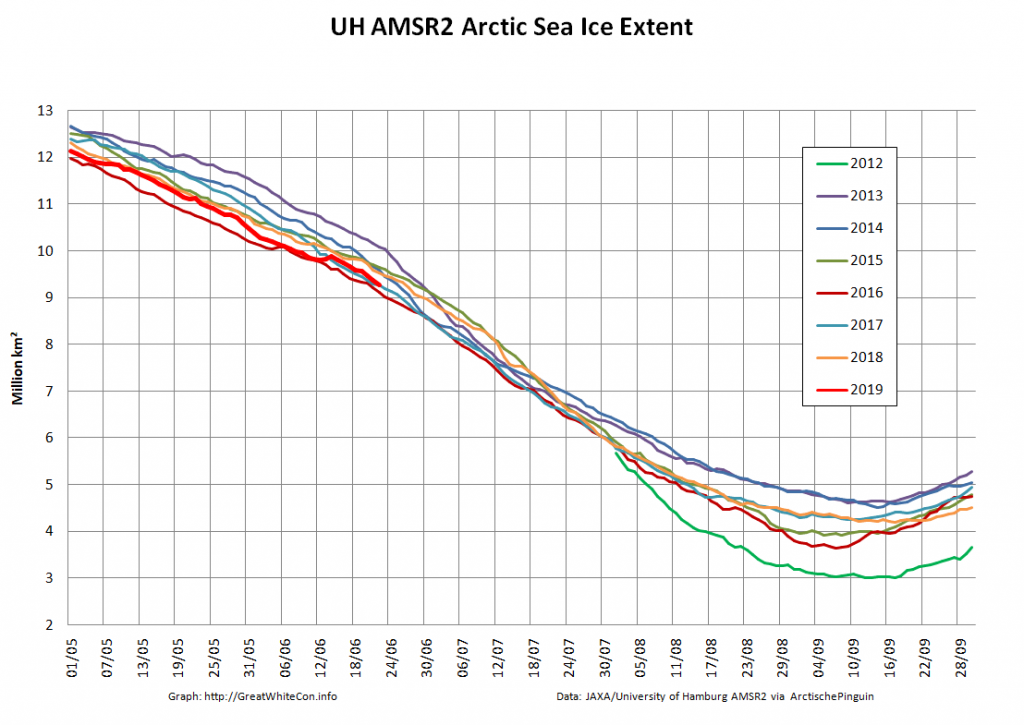
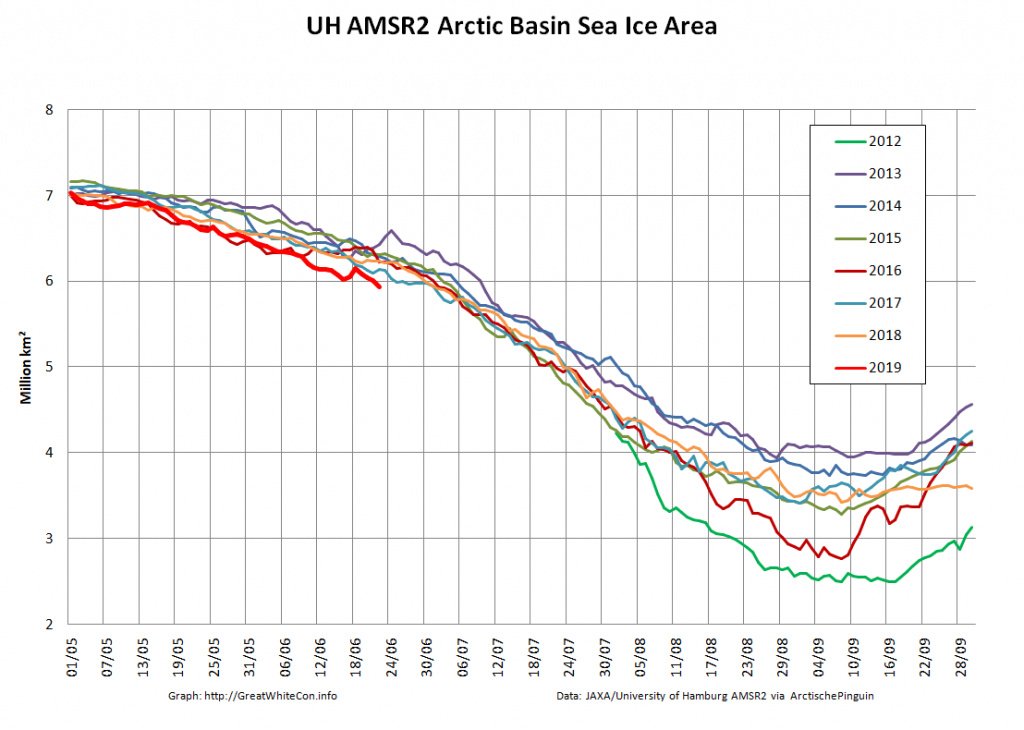
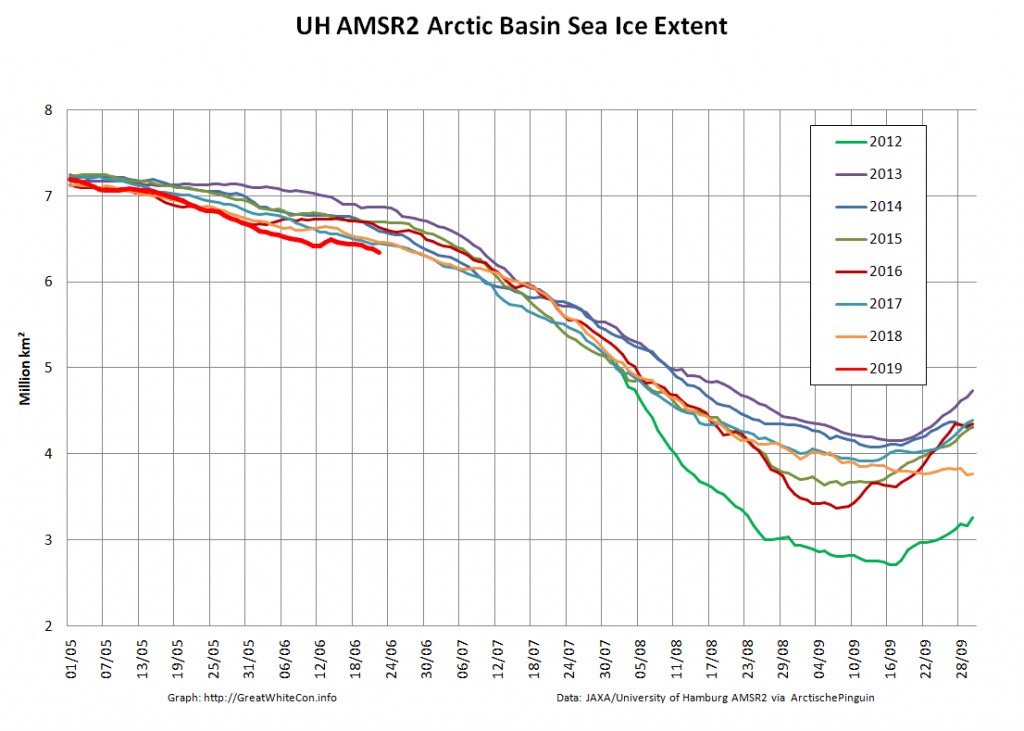
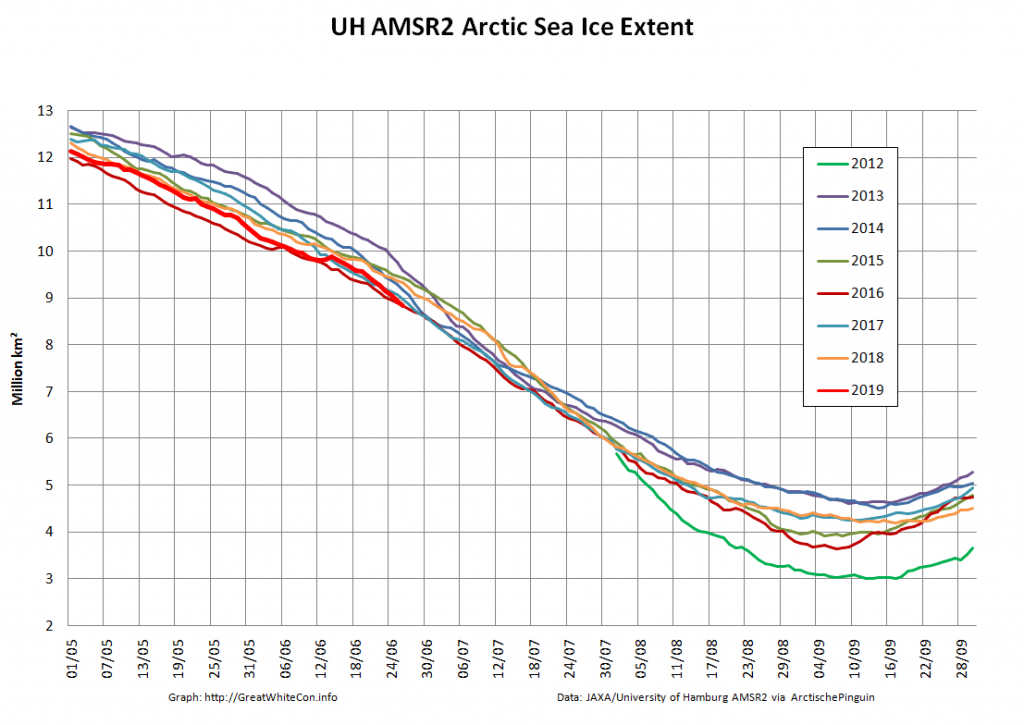
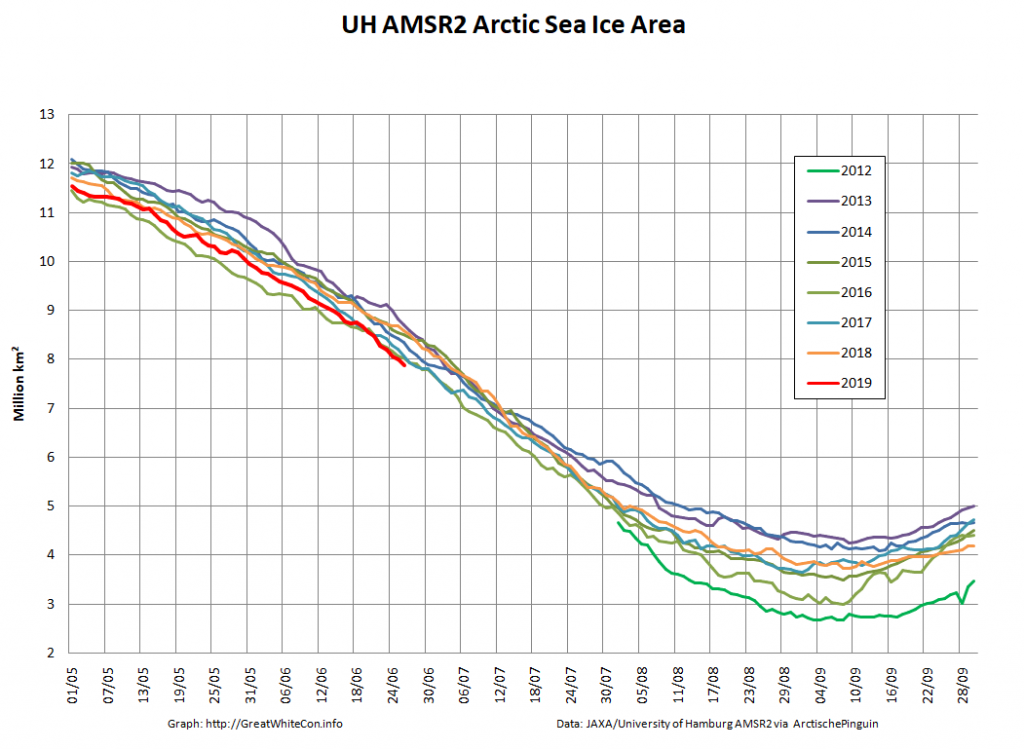
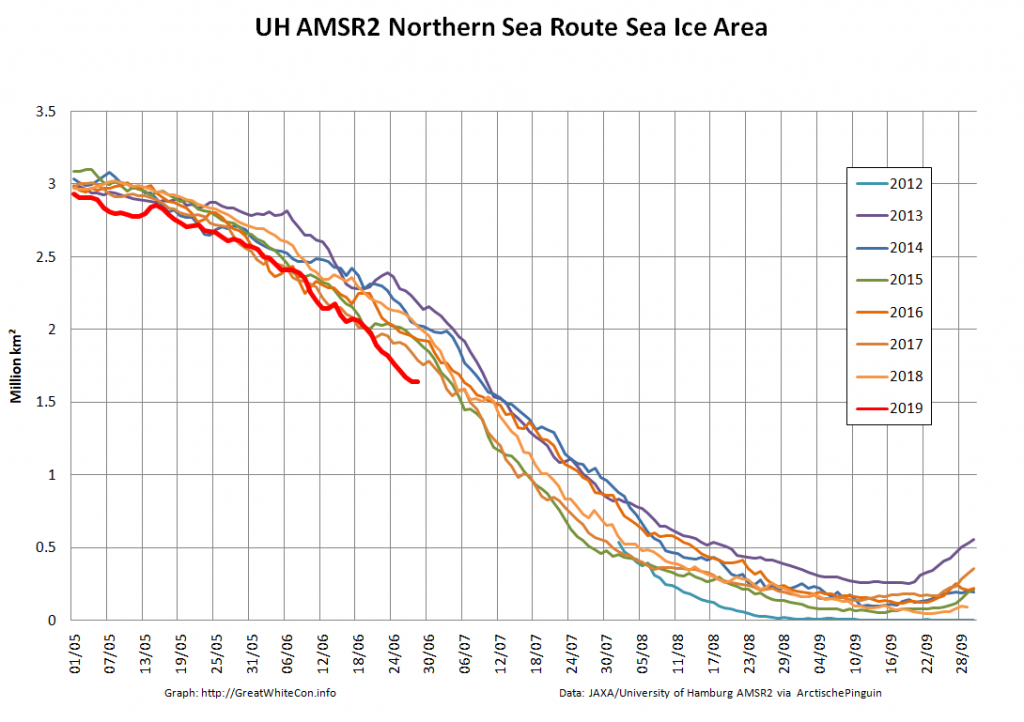
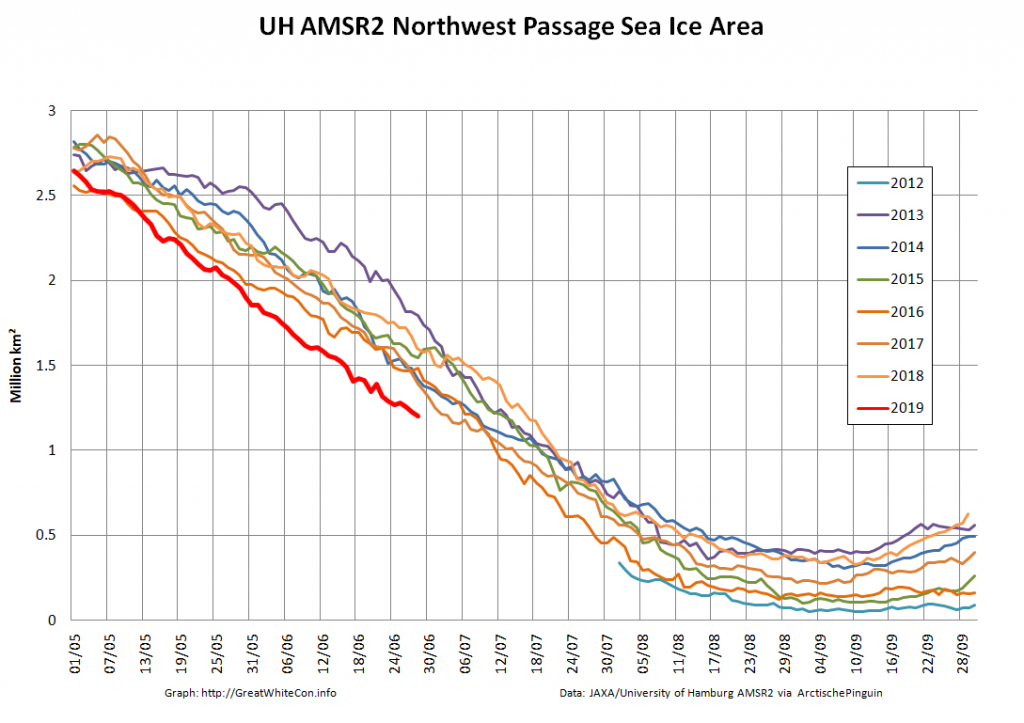
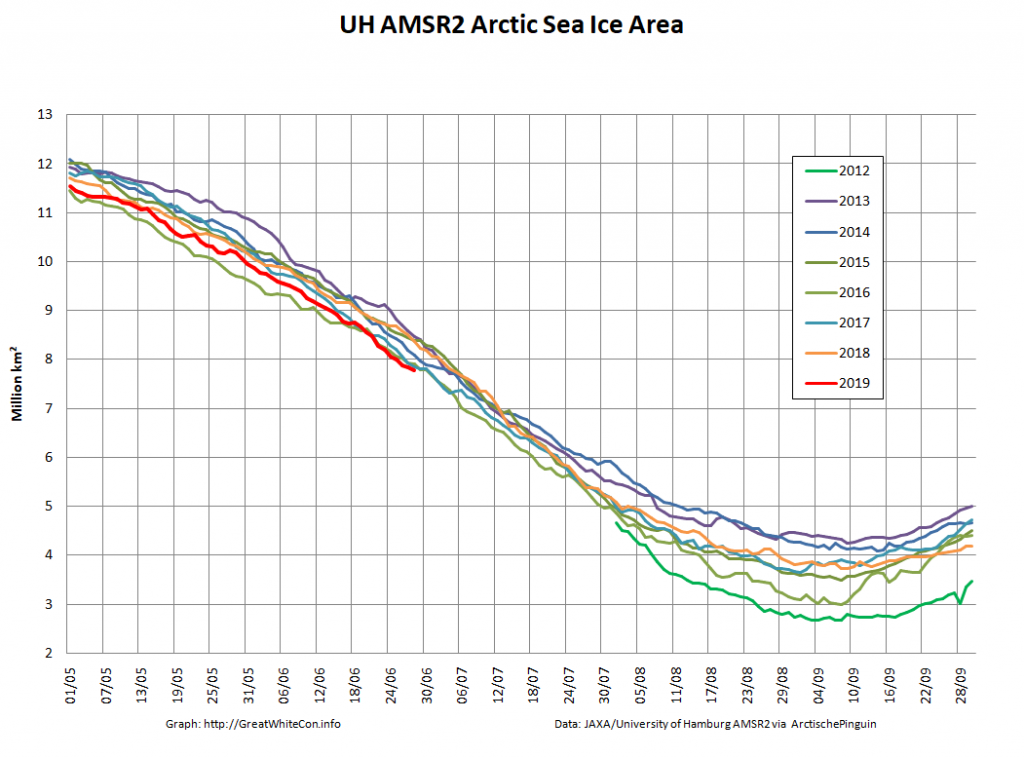
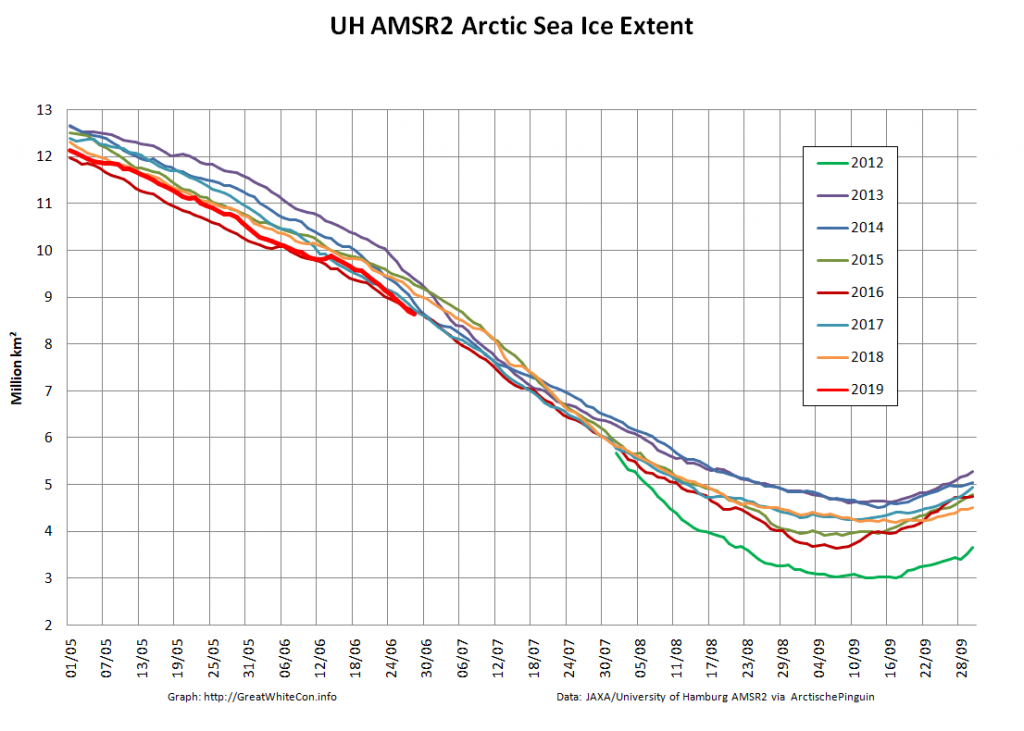
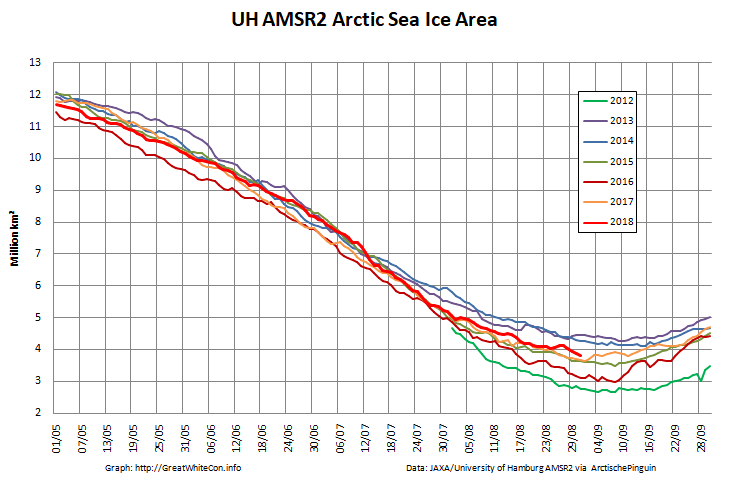
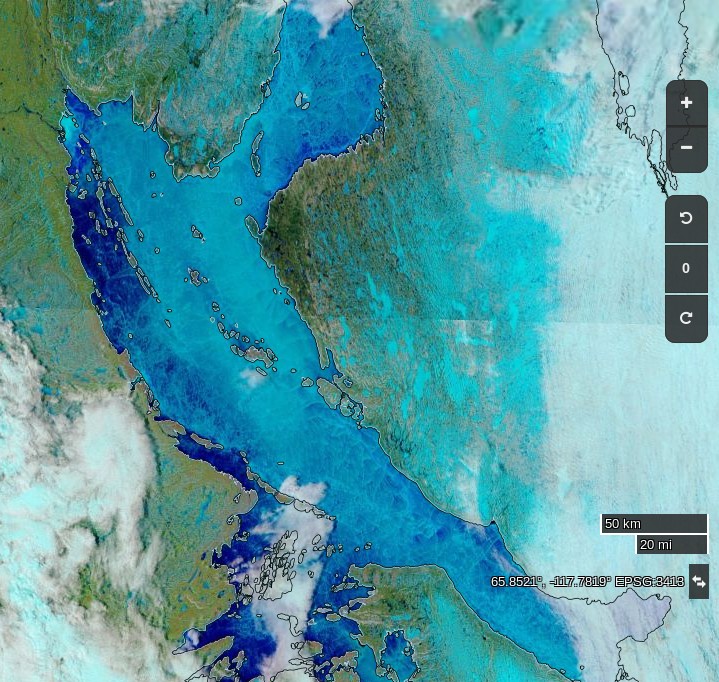
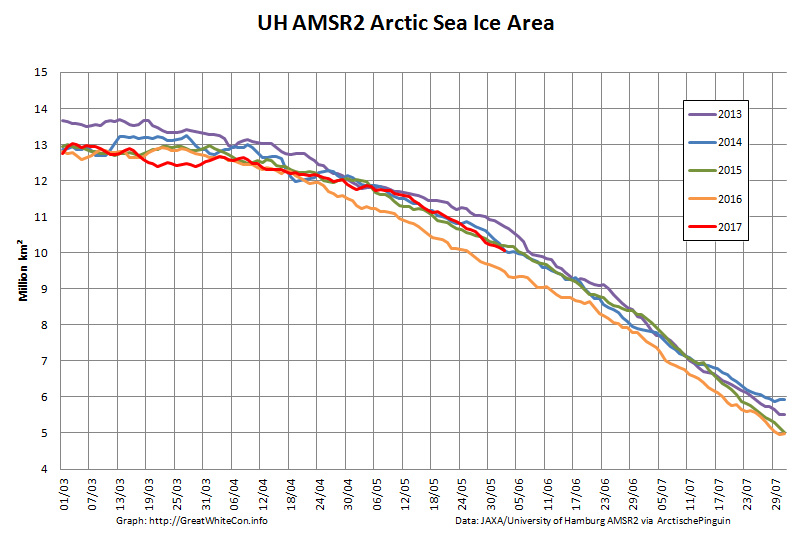
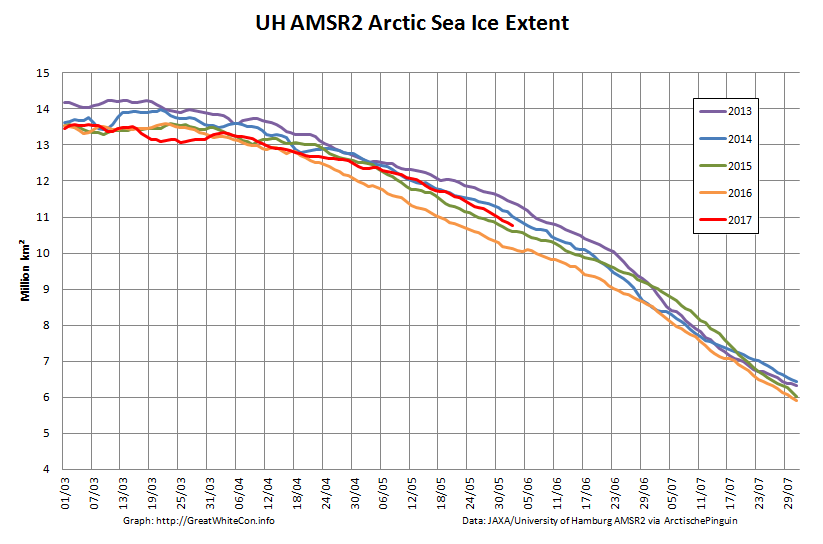
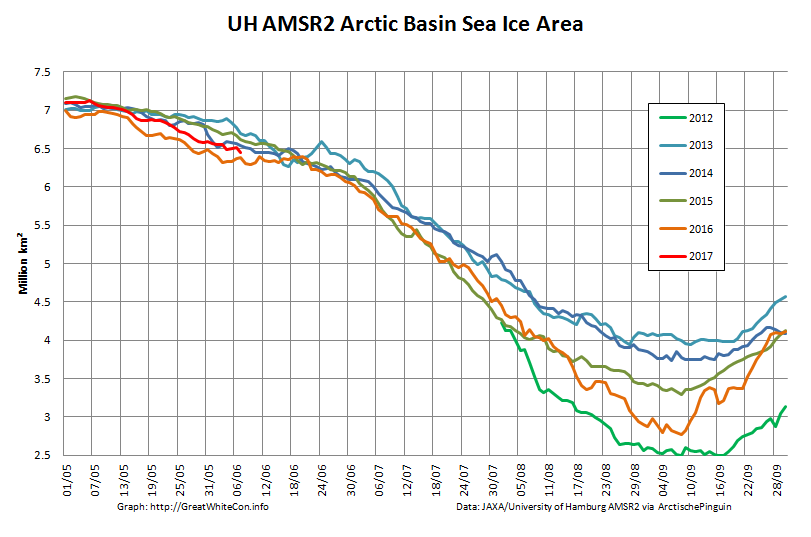
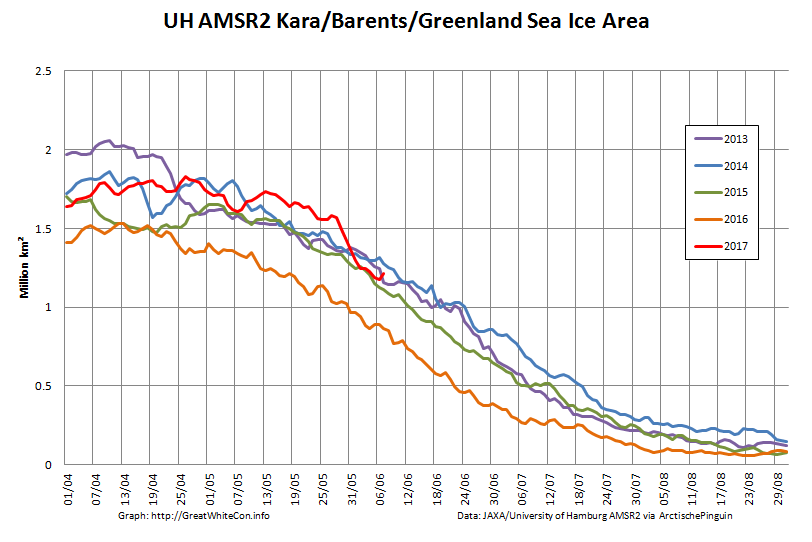
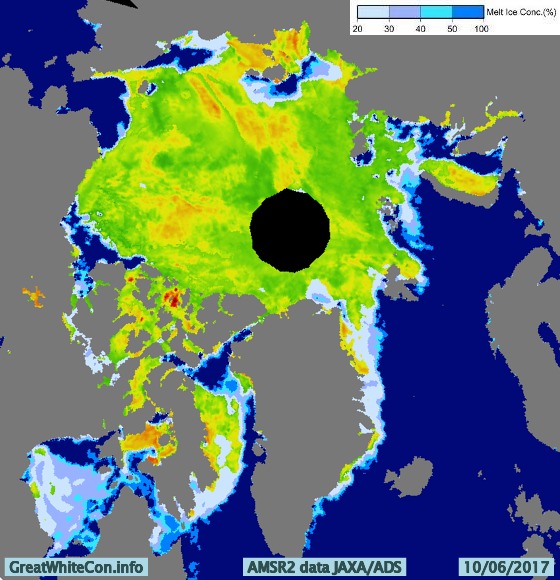
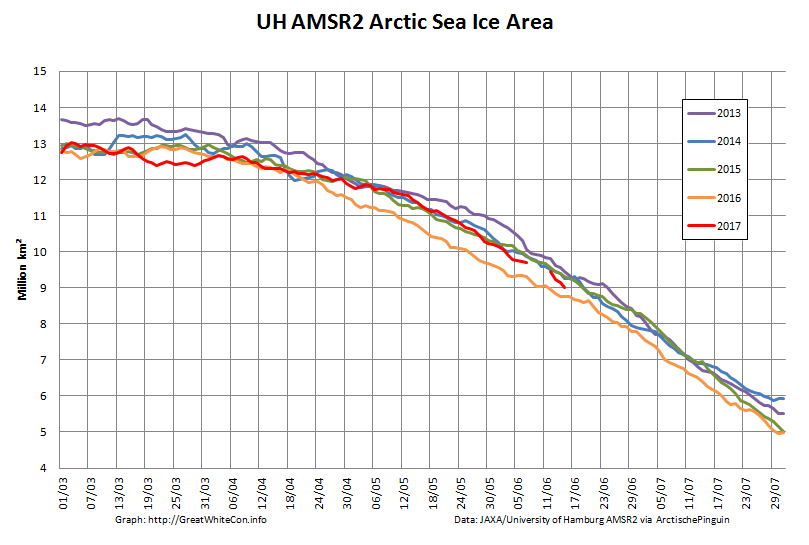
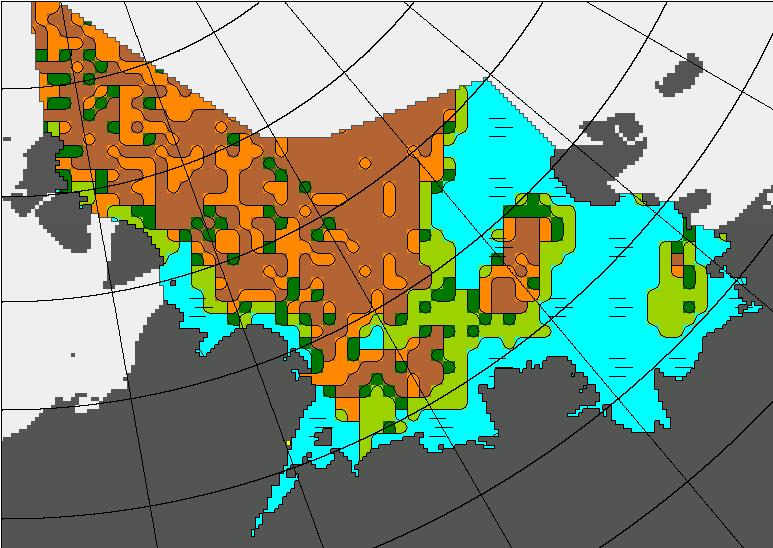
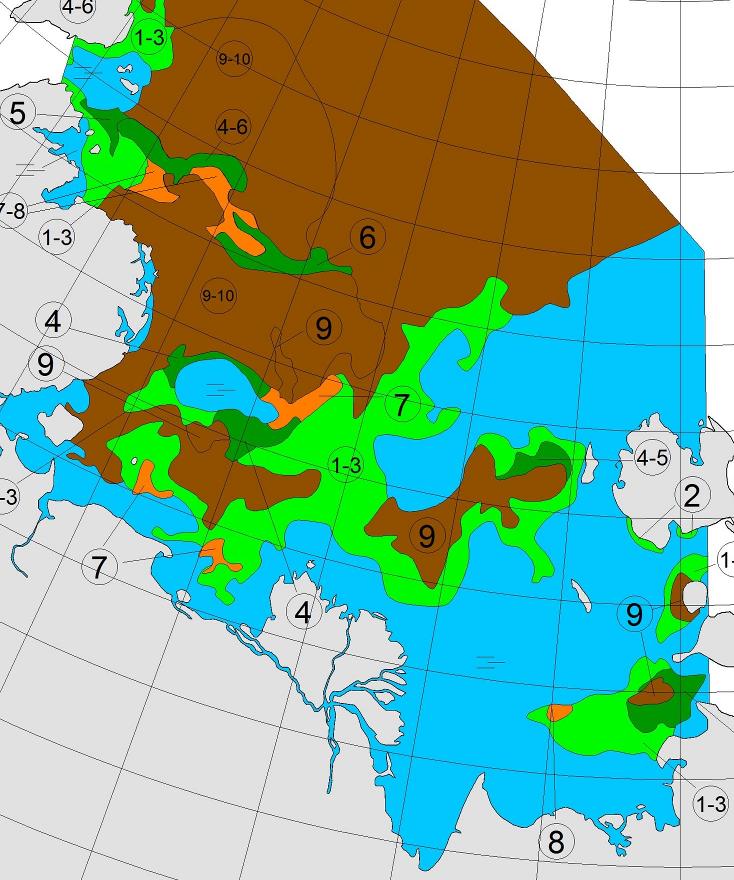
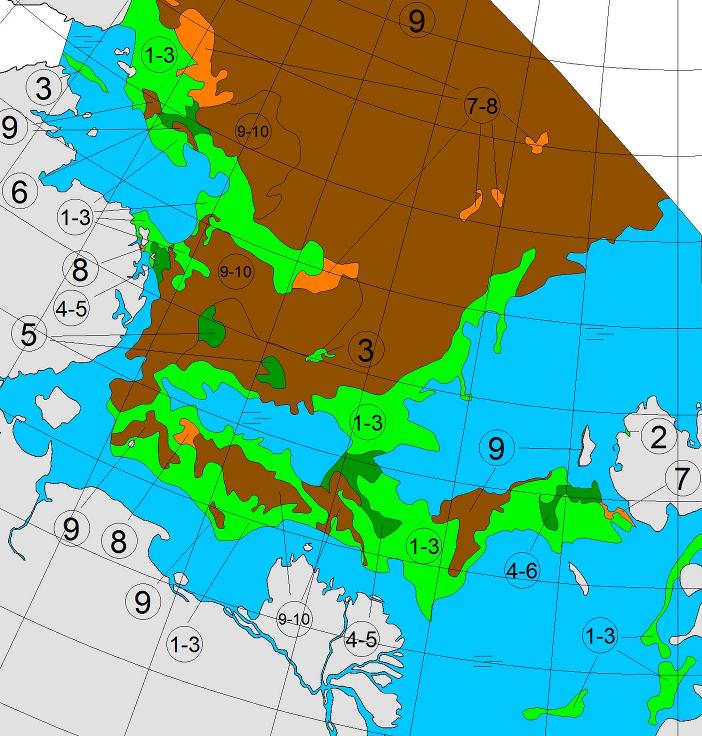
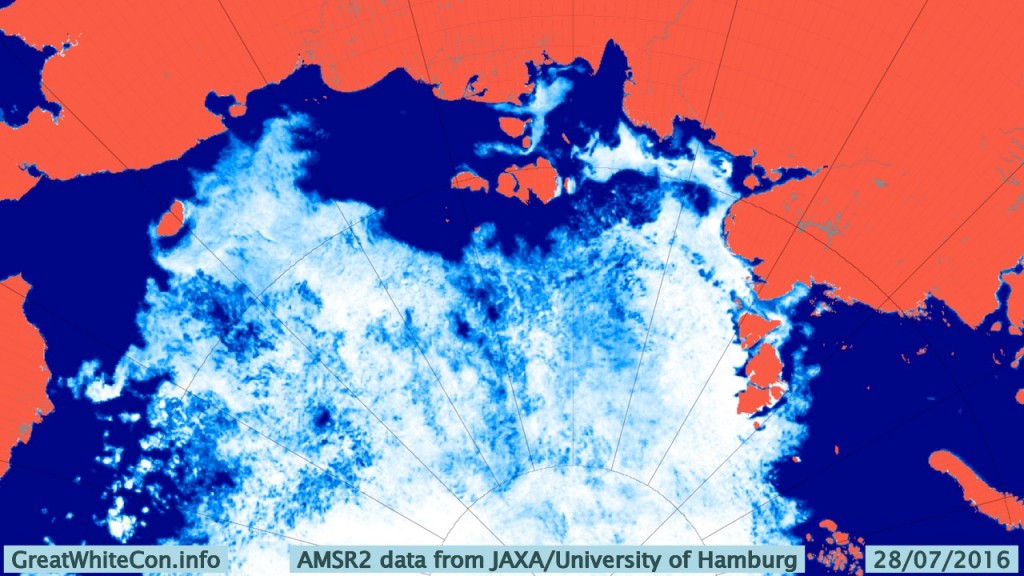
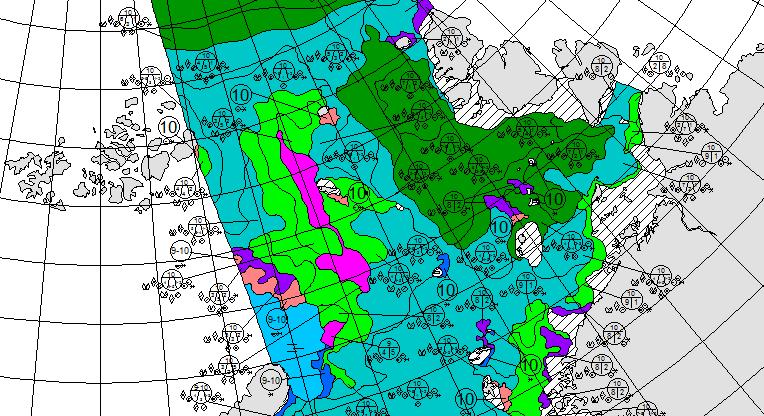
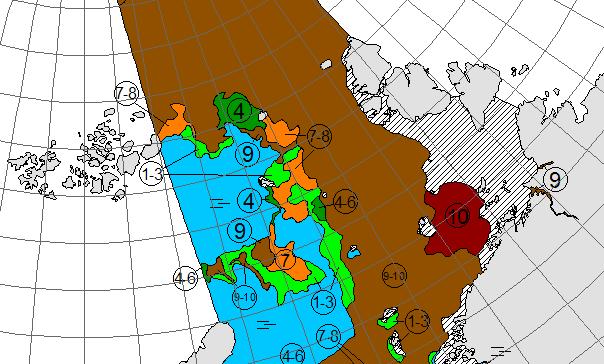
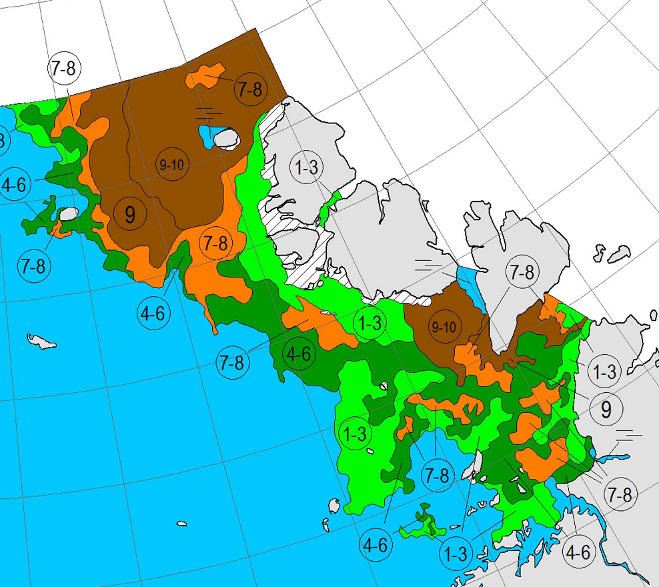
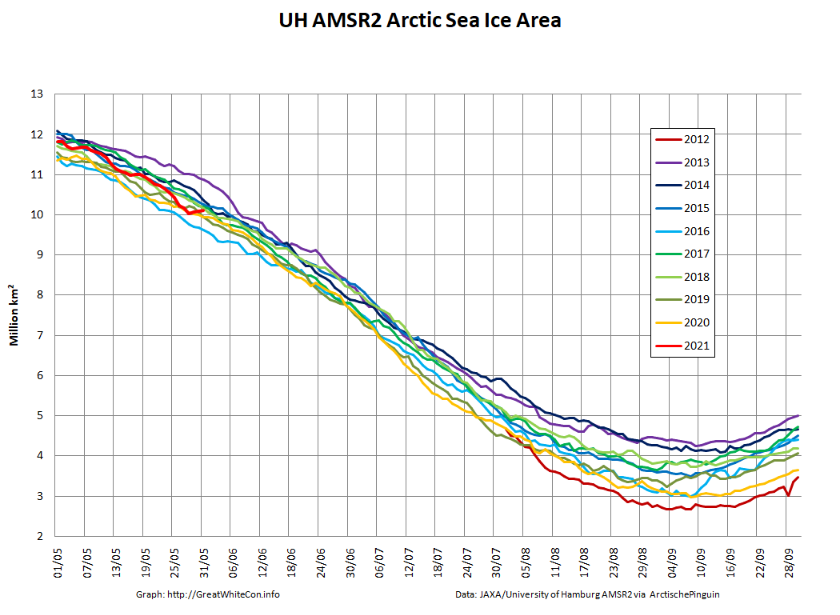
Let’s also take a look at the high resolution AMSR2 metrics for the end of May 2021:
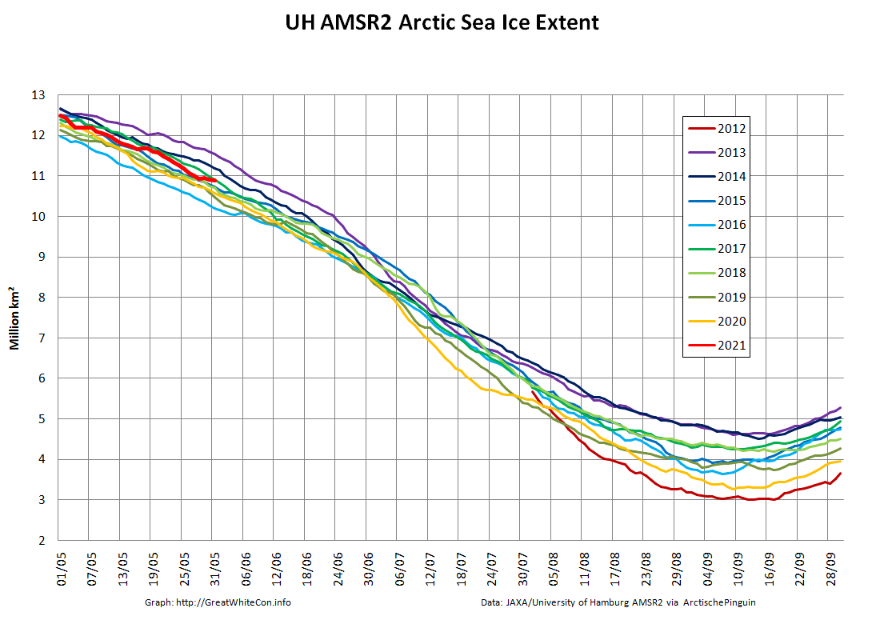
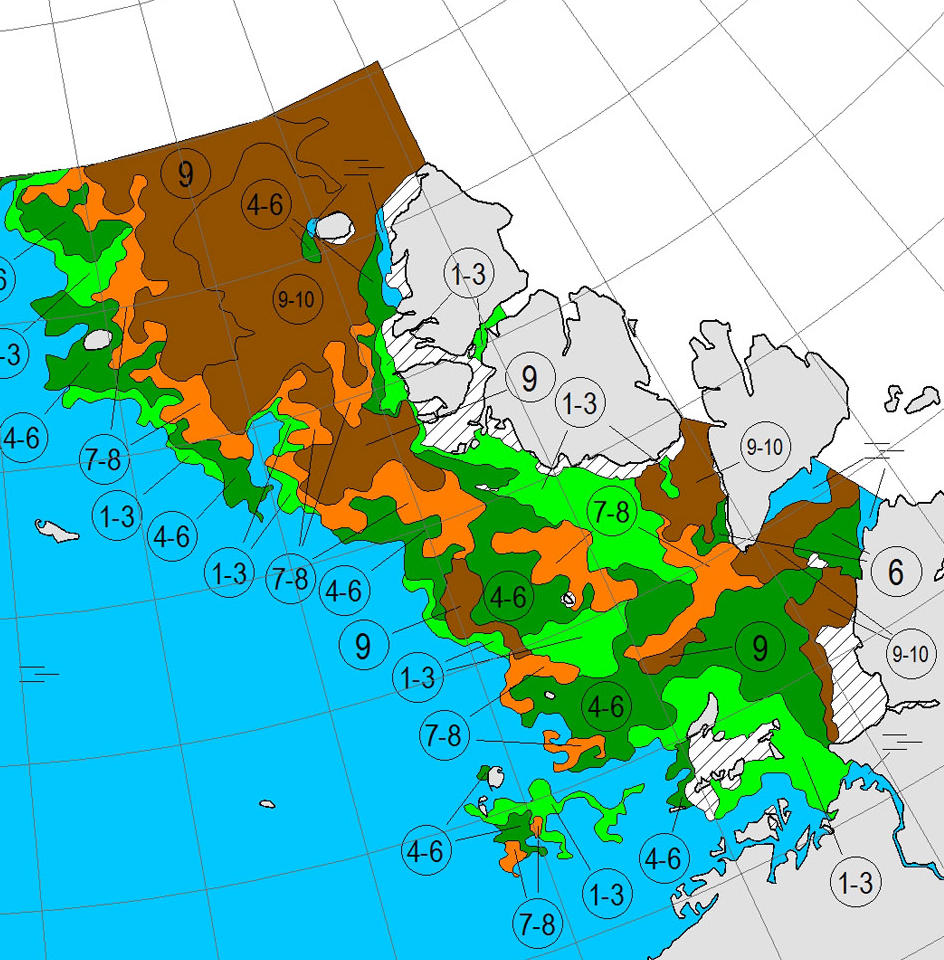
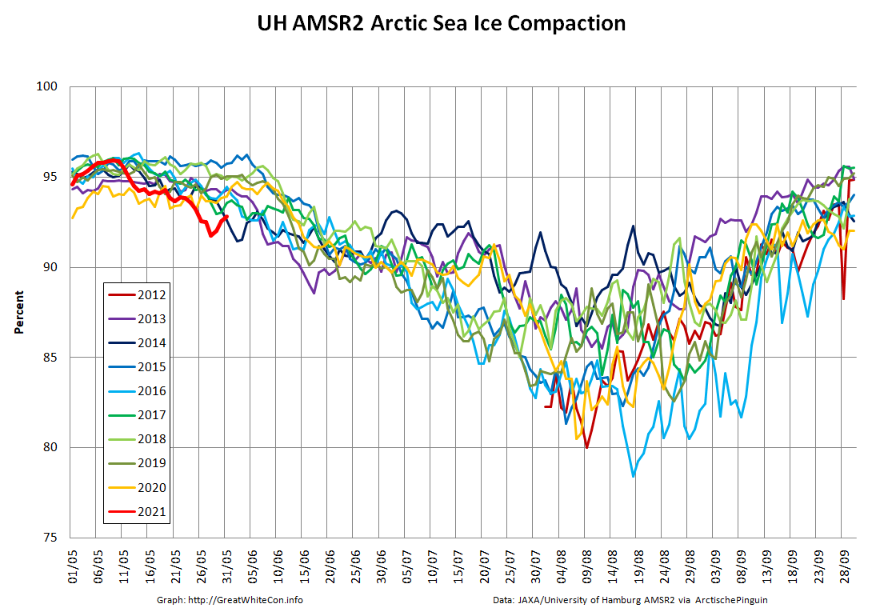
Thanks to the recent “brief hiatus” in areal decline, Arctic wide compaction is no longer in record territory:
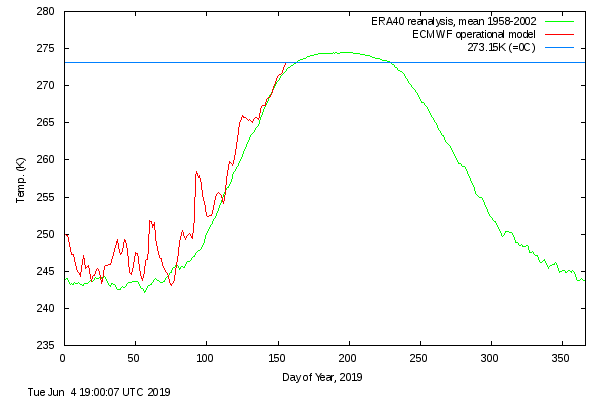
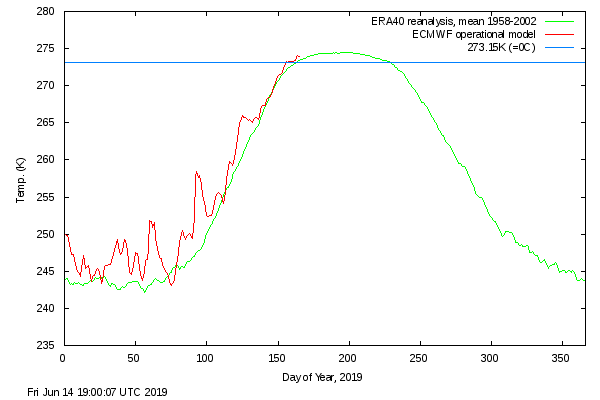
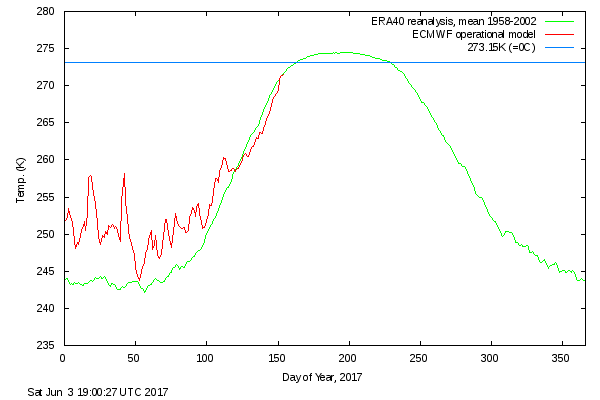
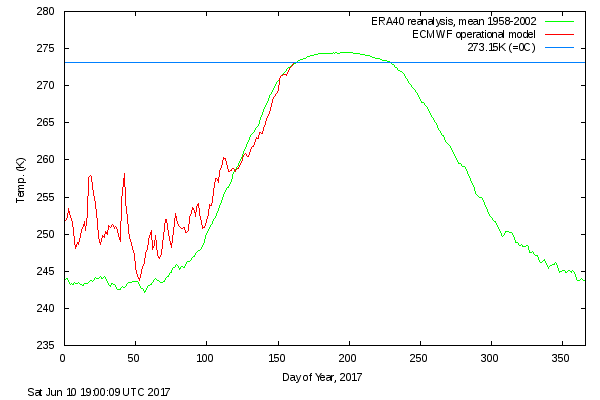
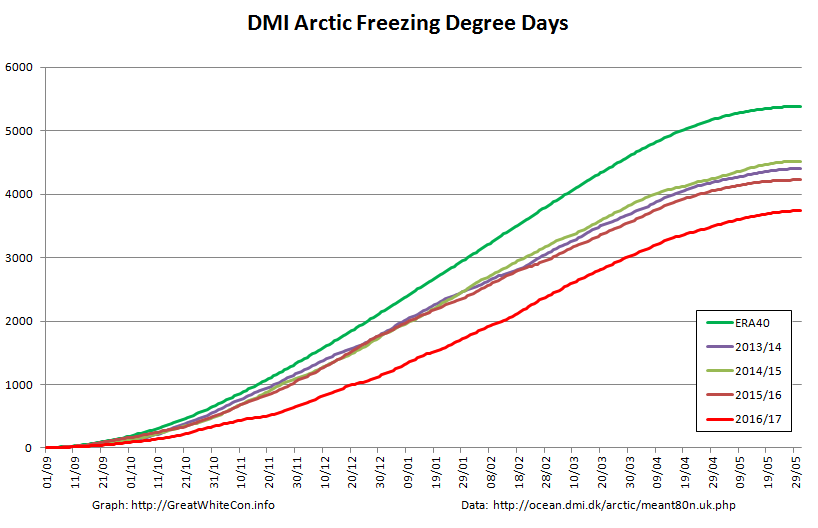
Finally, for the moment at least, here is the Danish Meteorological Institute’s high Arctic temperature data in the form of a graph of freezing degree days:
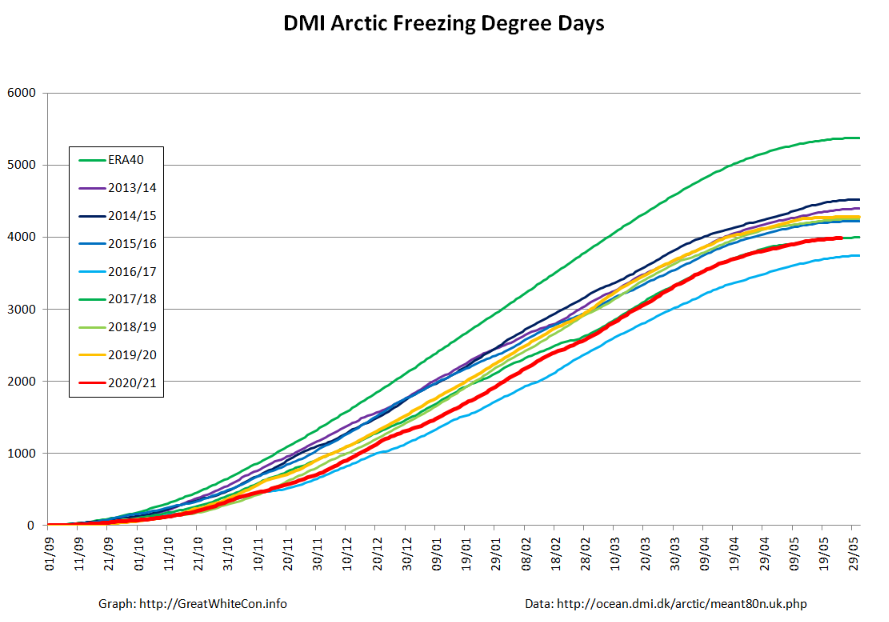
For some reason the data file still doesn’t include data to the end of May, but things won’t change much by then. Over the winter as a whole only 2016/17 was significantly warmer.
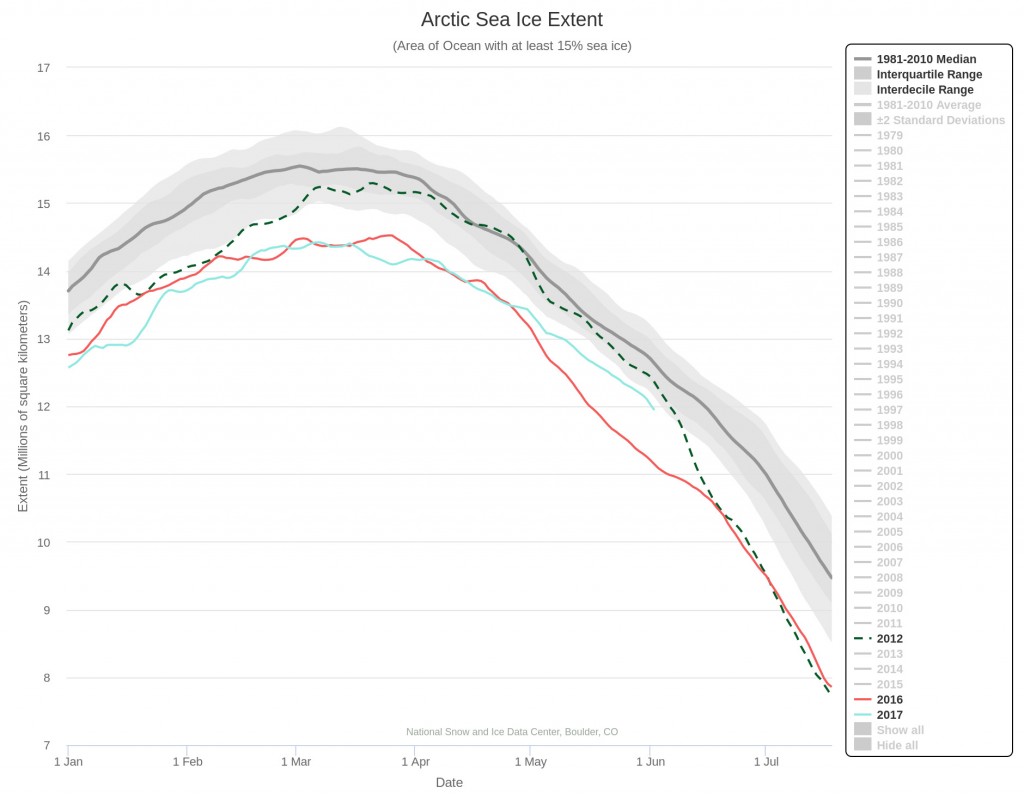
Let the 2021 Arctic sea ice summer melting season officially begin!
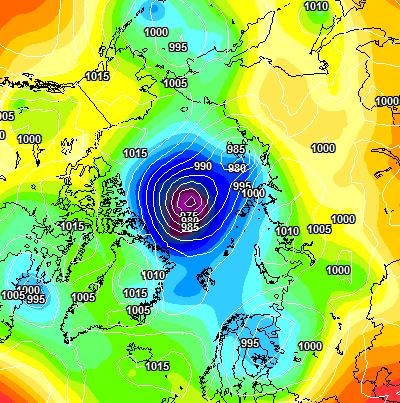
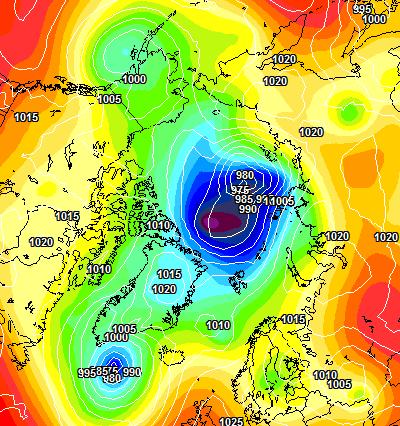
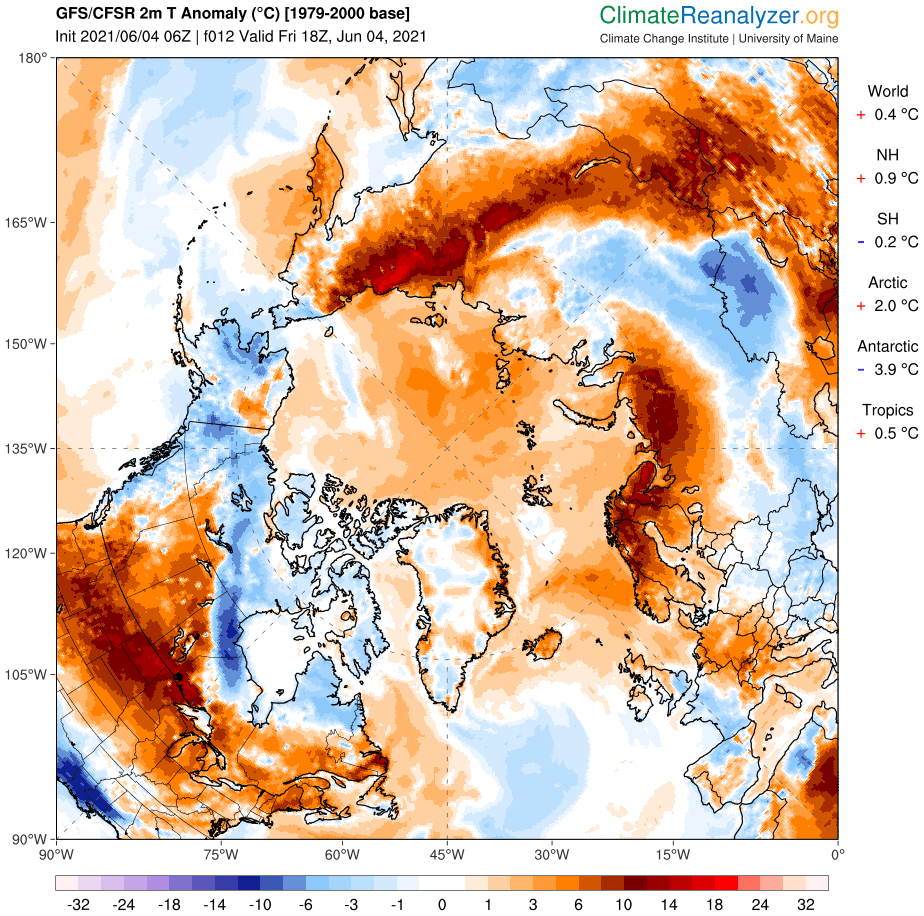
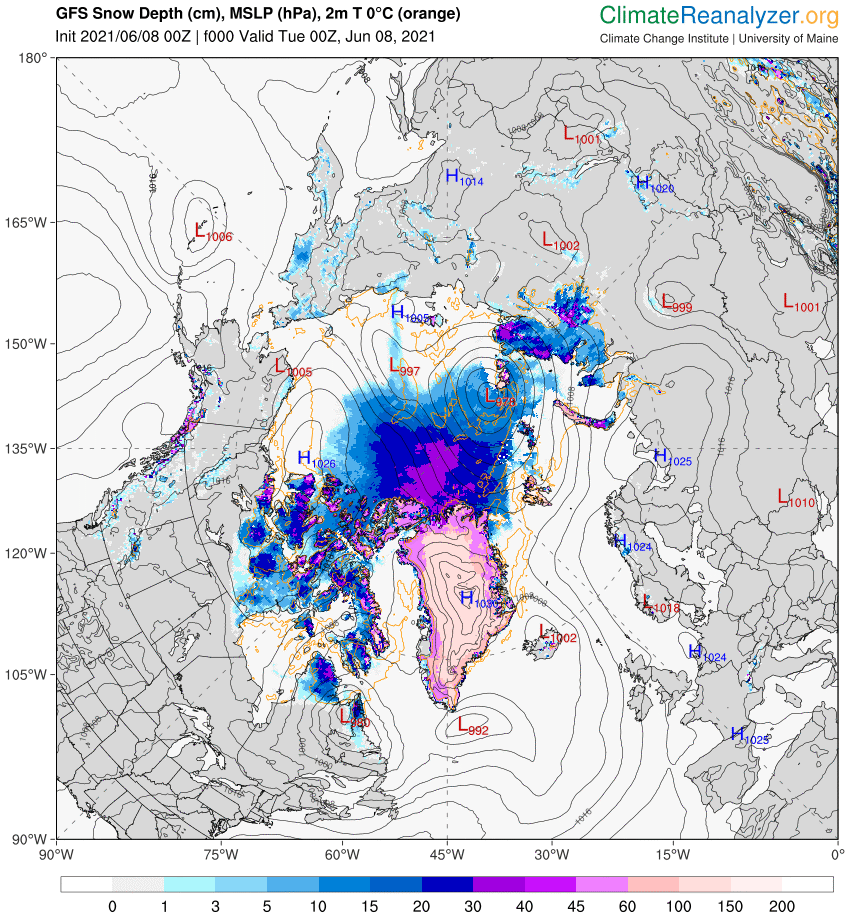
[Edit – June 4th]Perhaps unsurprisingly the GFS forecast from four days ago hasn’t quite worked out as predicted. The Arctic as a whole is certainly on the warm side, with a +2 C anomaly at this moment:
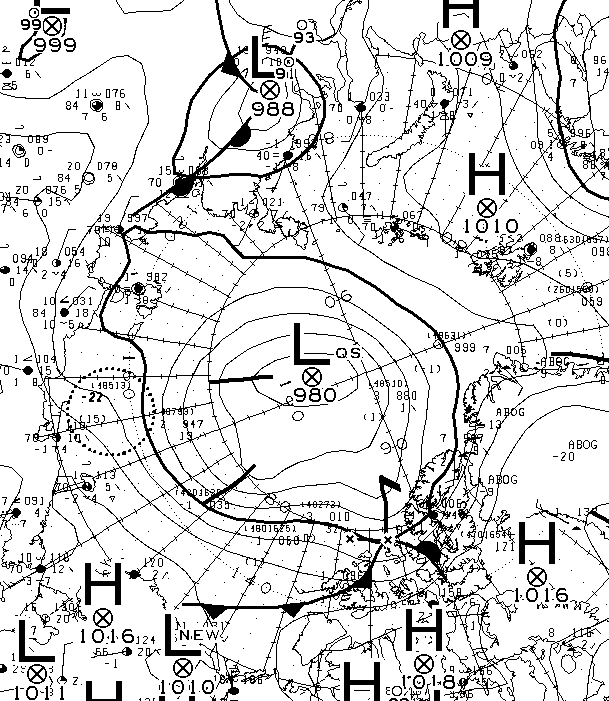
However the 966 hPa MSLP cyclone predicted for Monday is now forecast to be a mere 978 hPa:
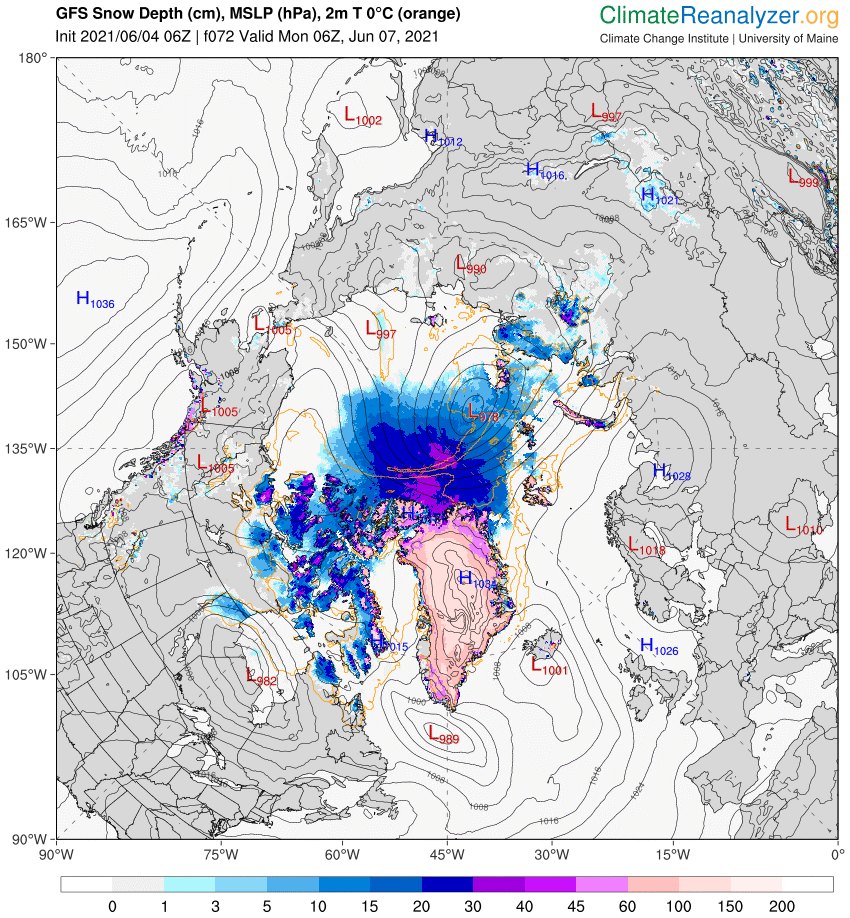
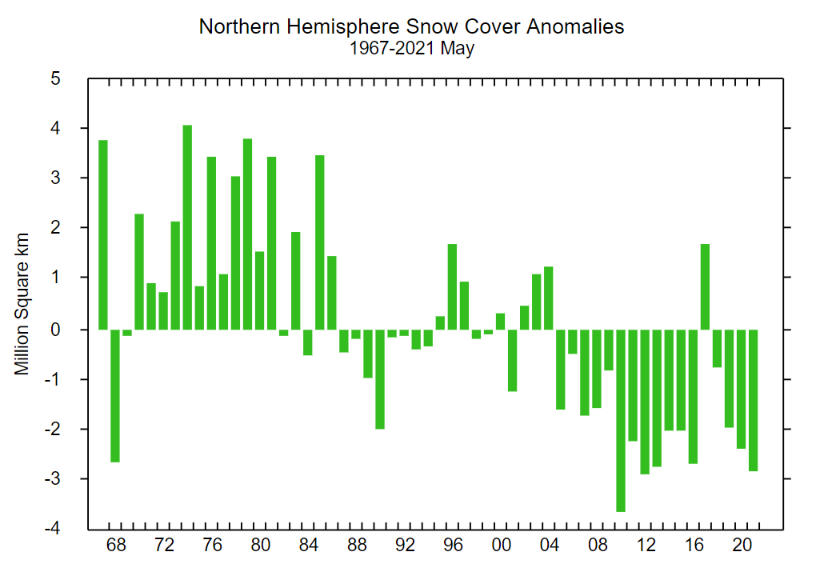
With 3 days to go there is a reasonable chance of it verifying in the “New Arctic” of 2021. As you can see from the map above a large area of the Central Arctic has now lost its snow cover. This is confirmed by the Rutgers Snow Lab northern hemisphere data for May:
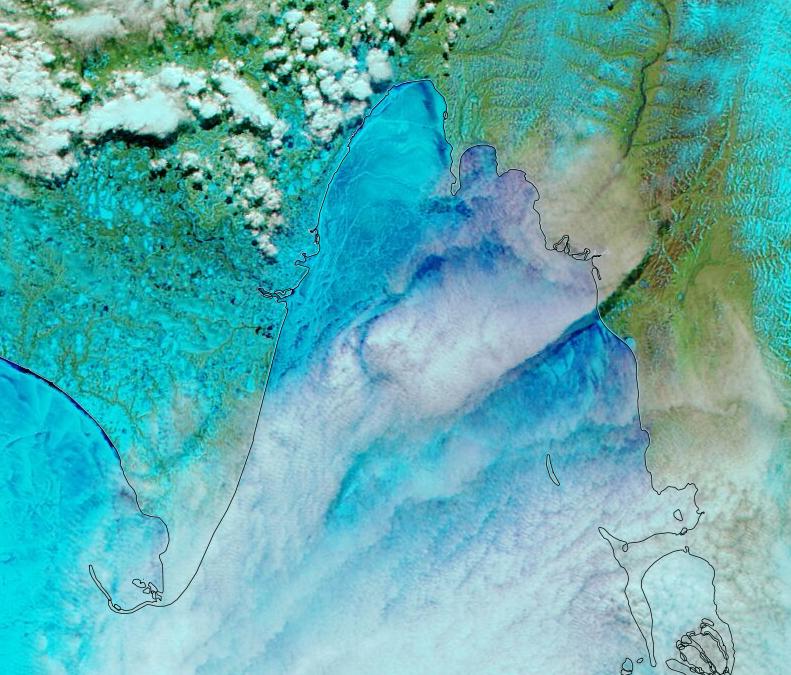
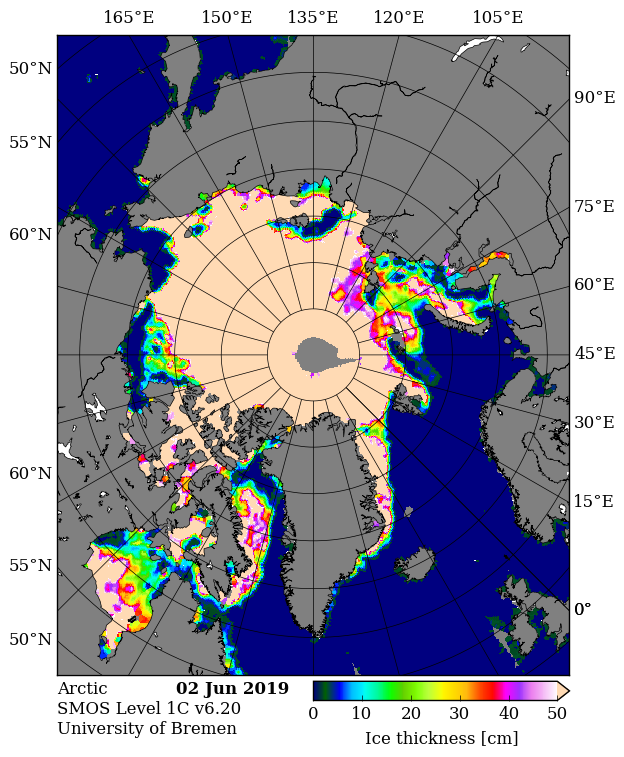
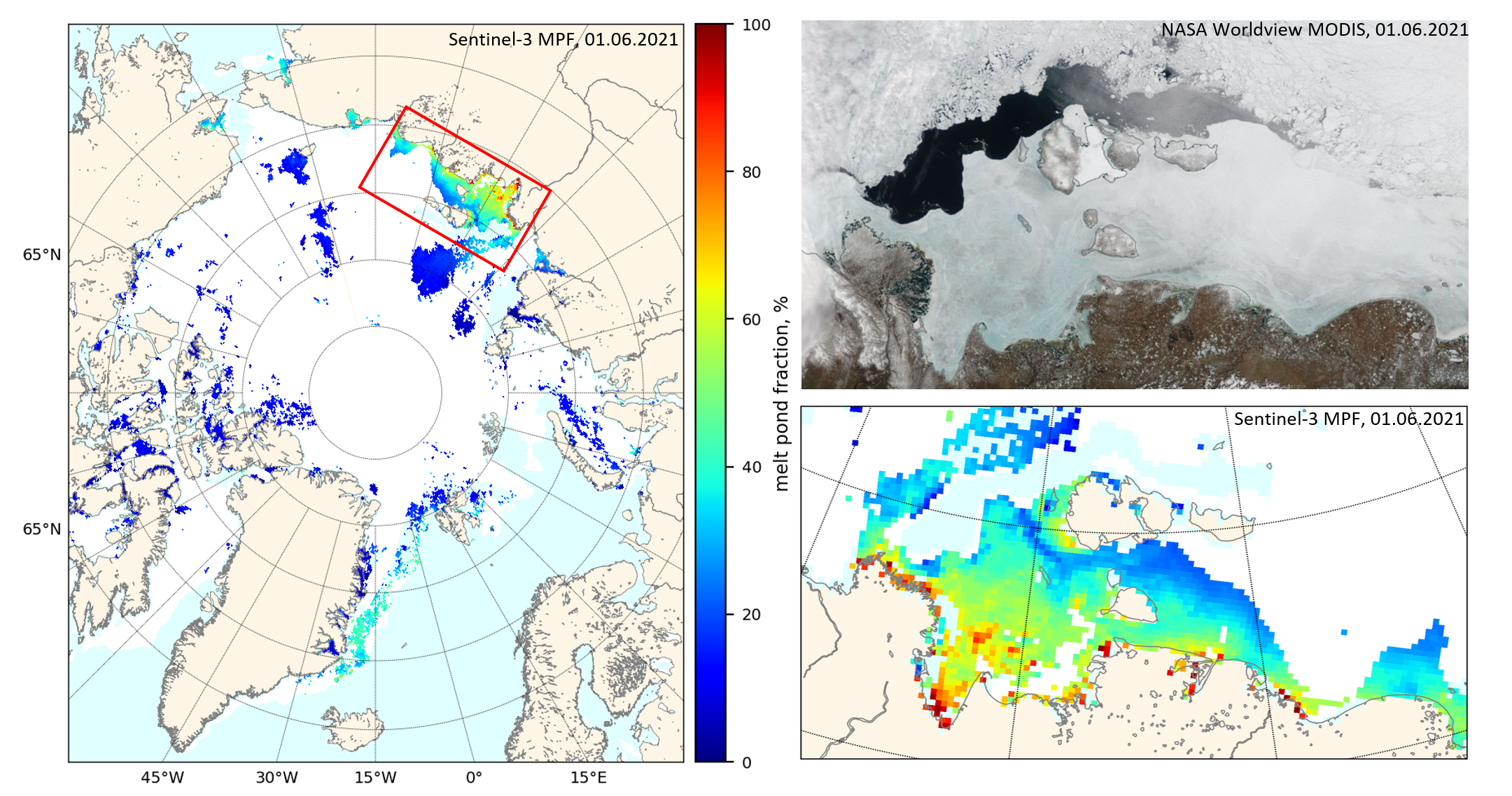
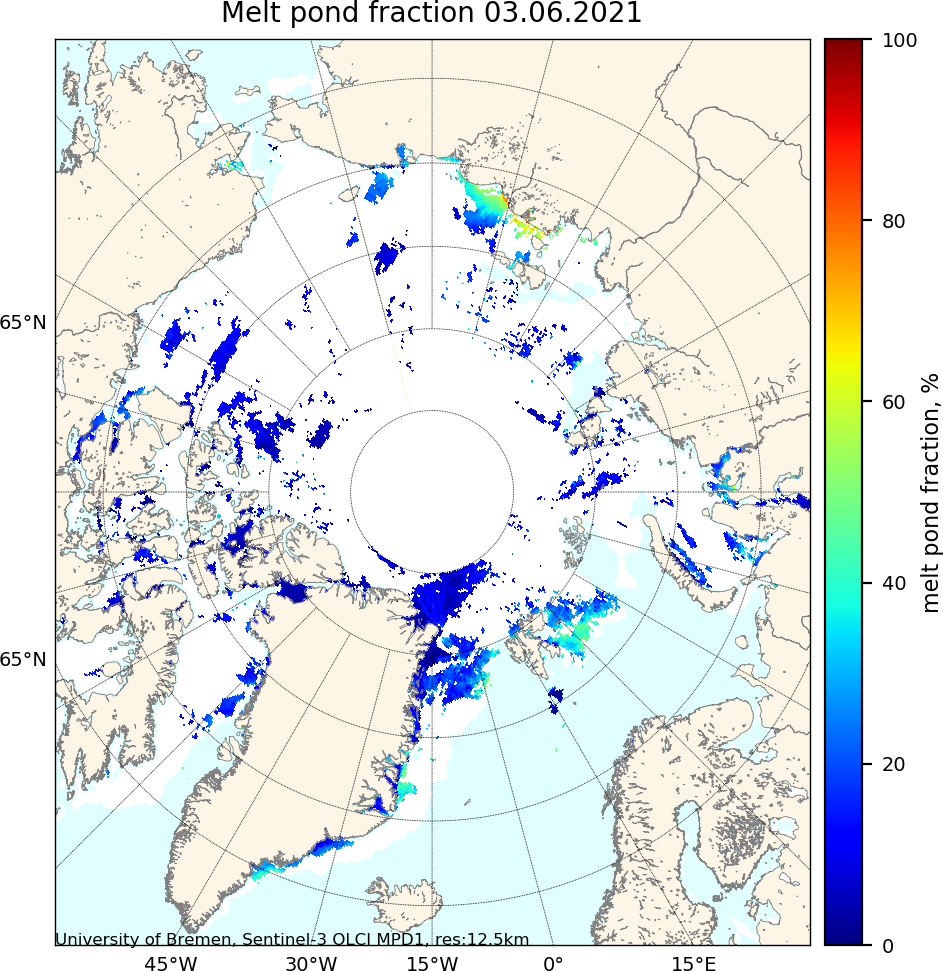
A new Sentinel 3 melt pond fraction product from the University of Bremen confirms that on the fast ice in the Laptev & East Siberian Seas snow cover has departed and melt ponds have arrived:
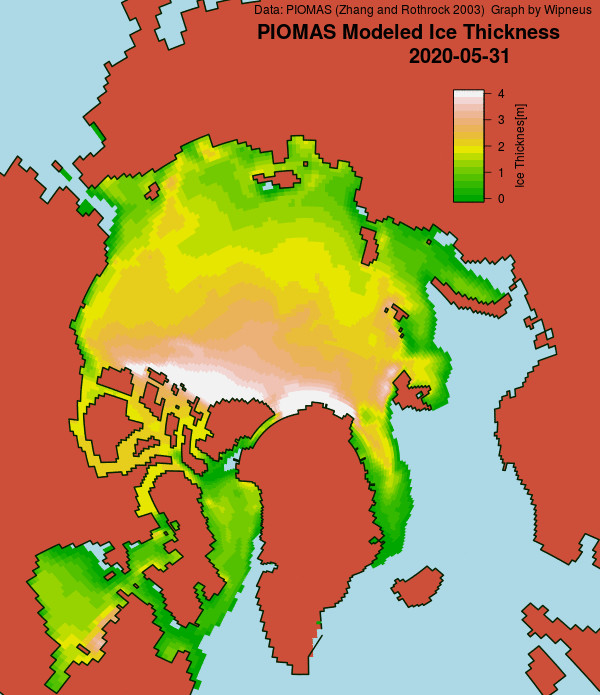
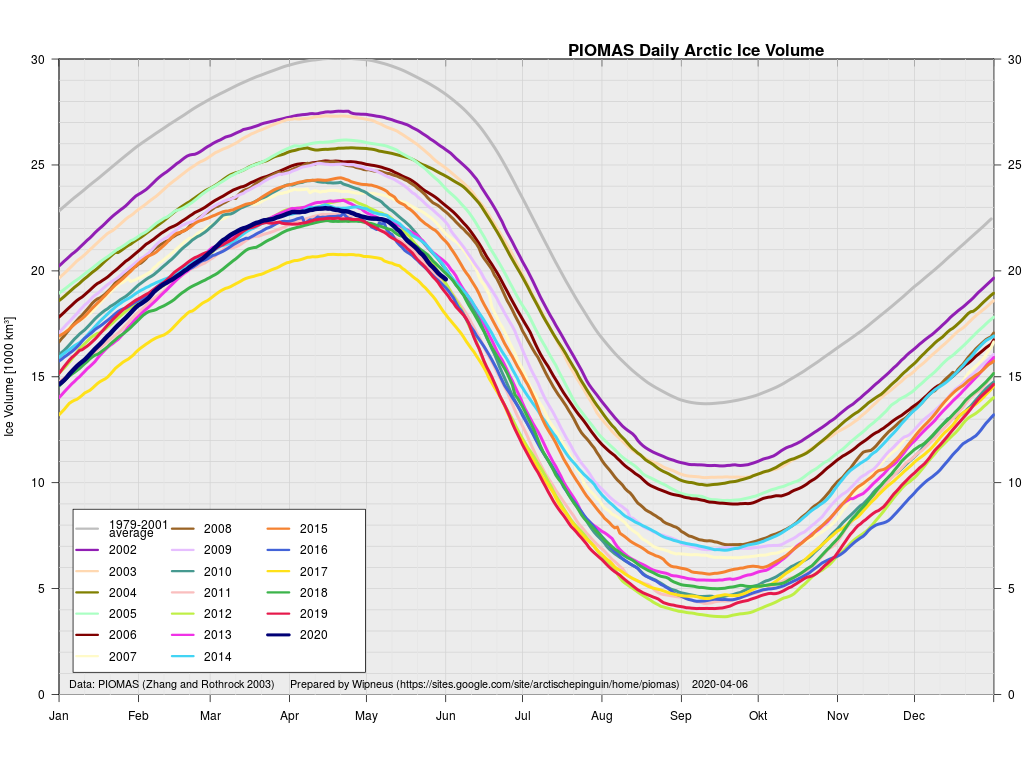
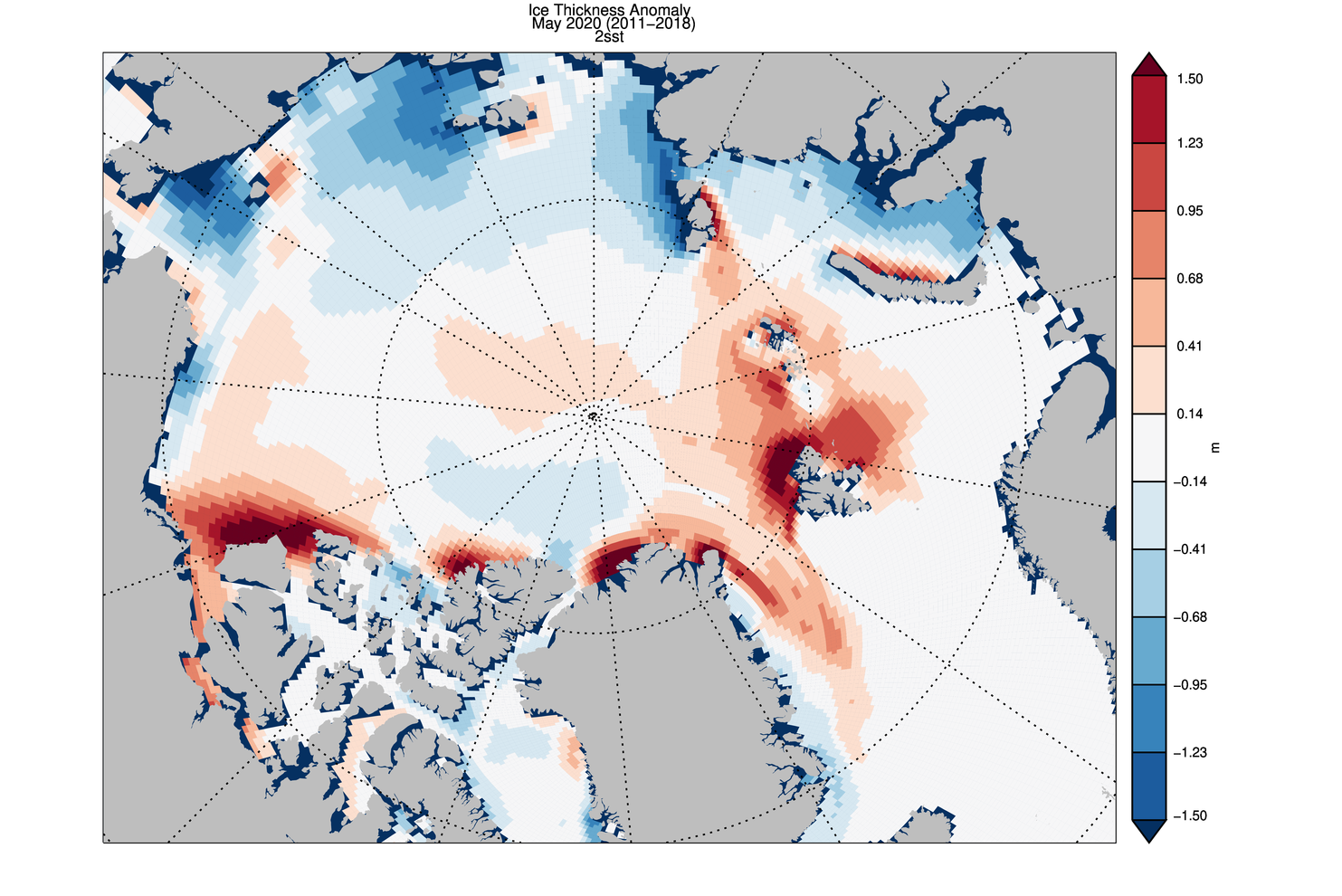
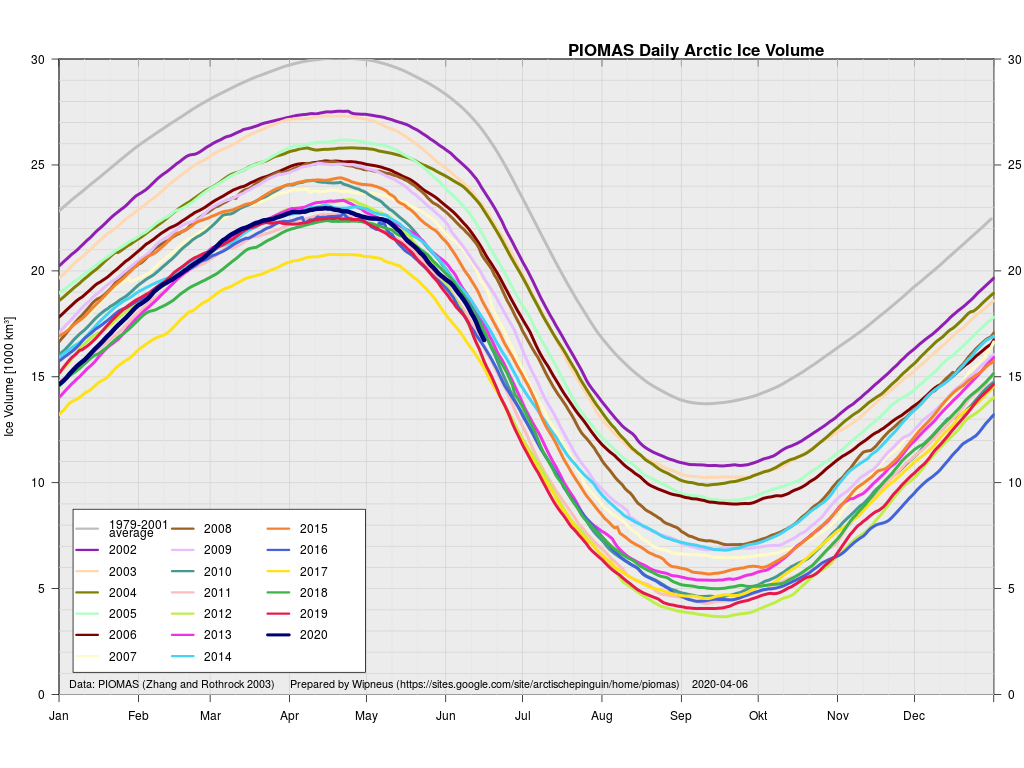
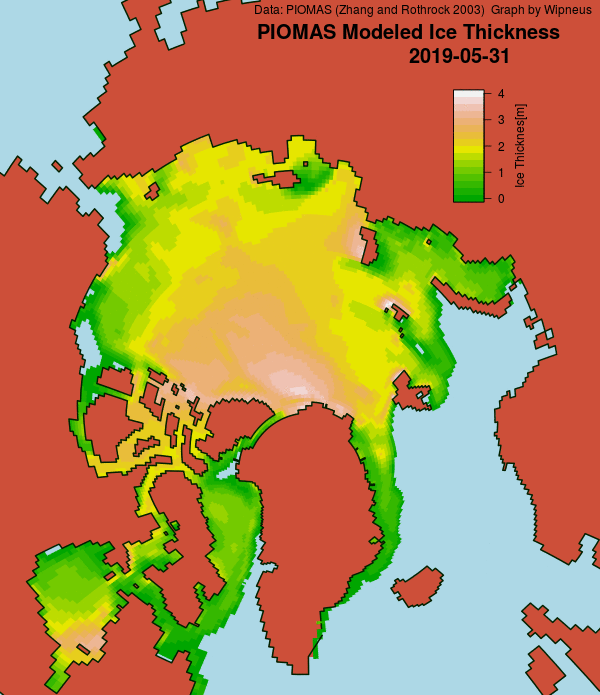
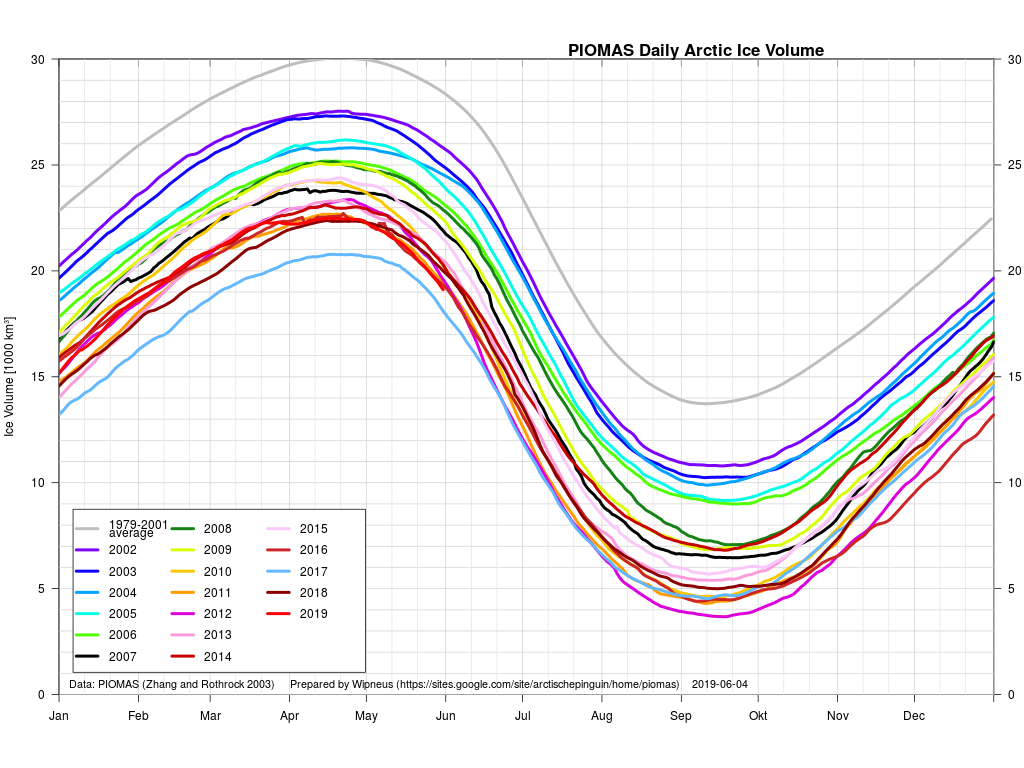
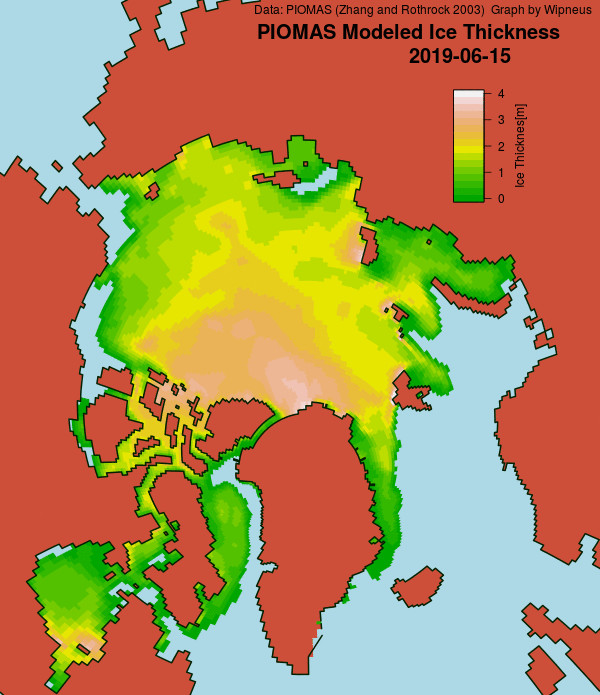
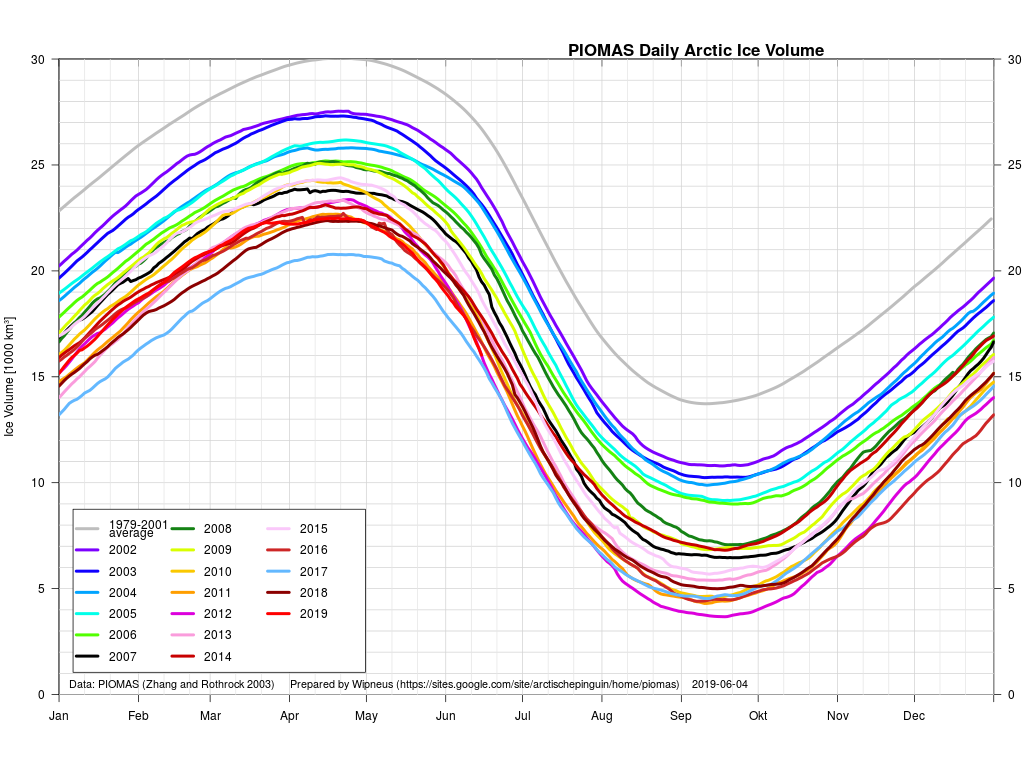
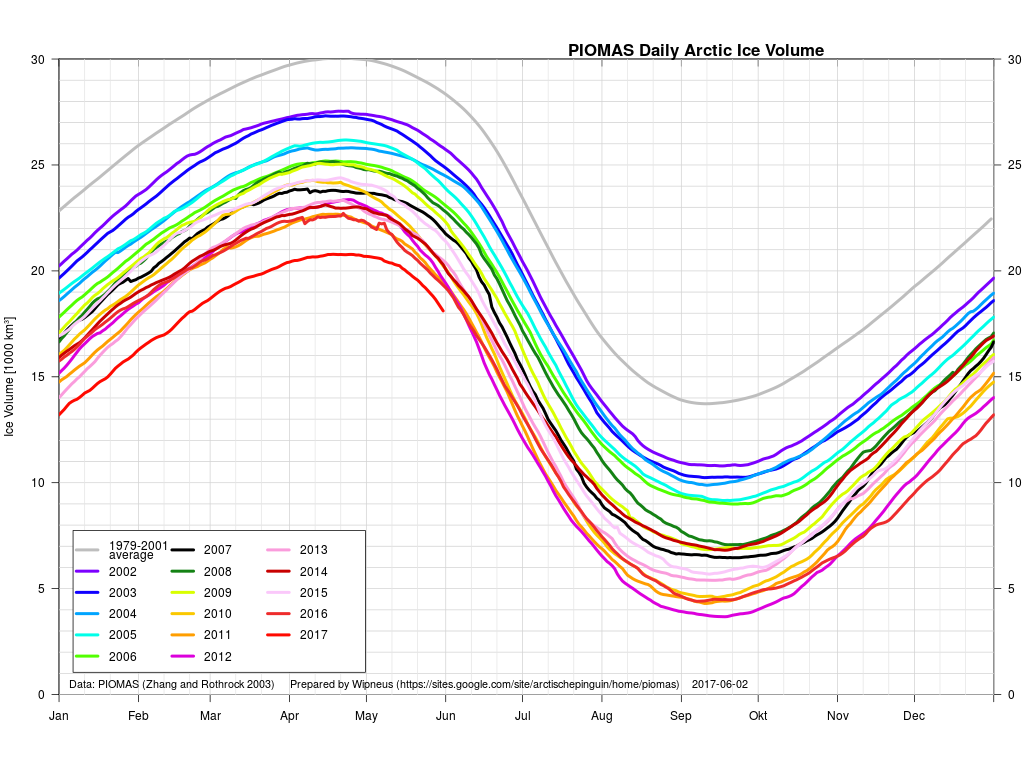
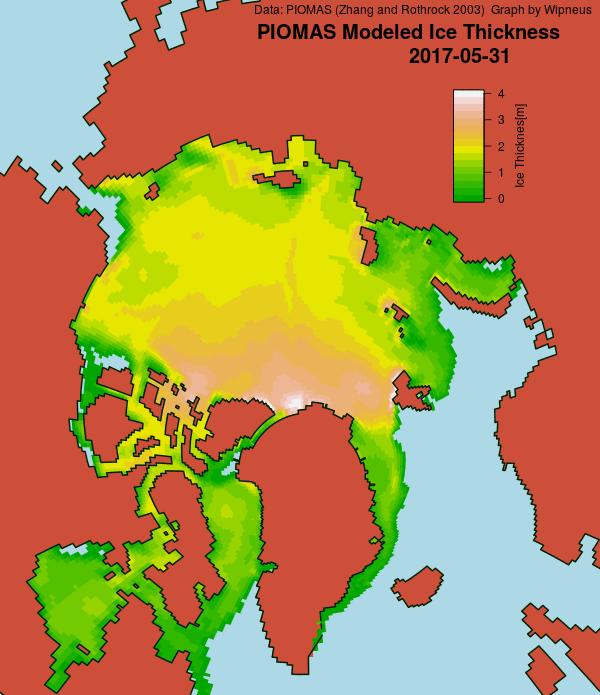
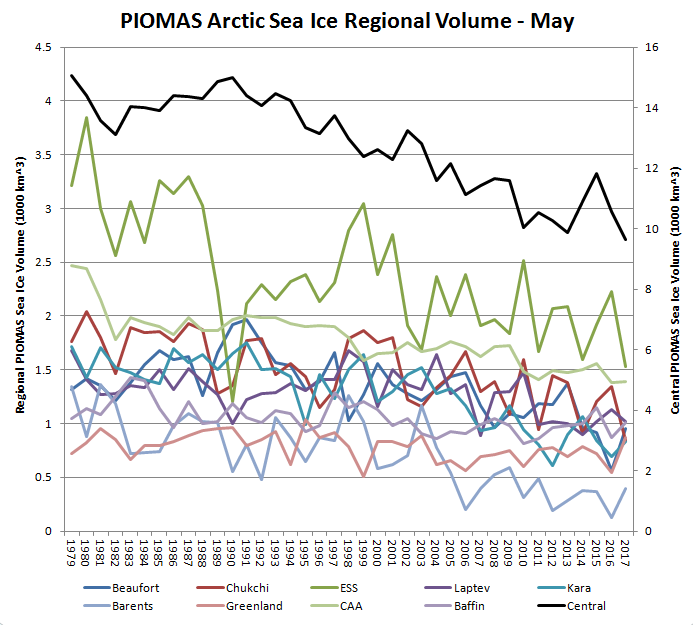
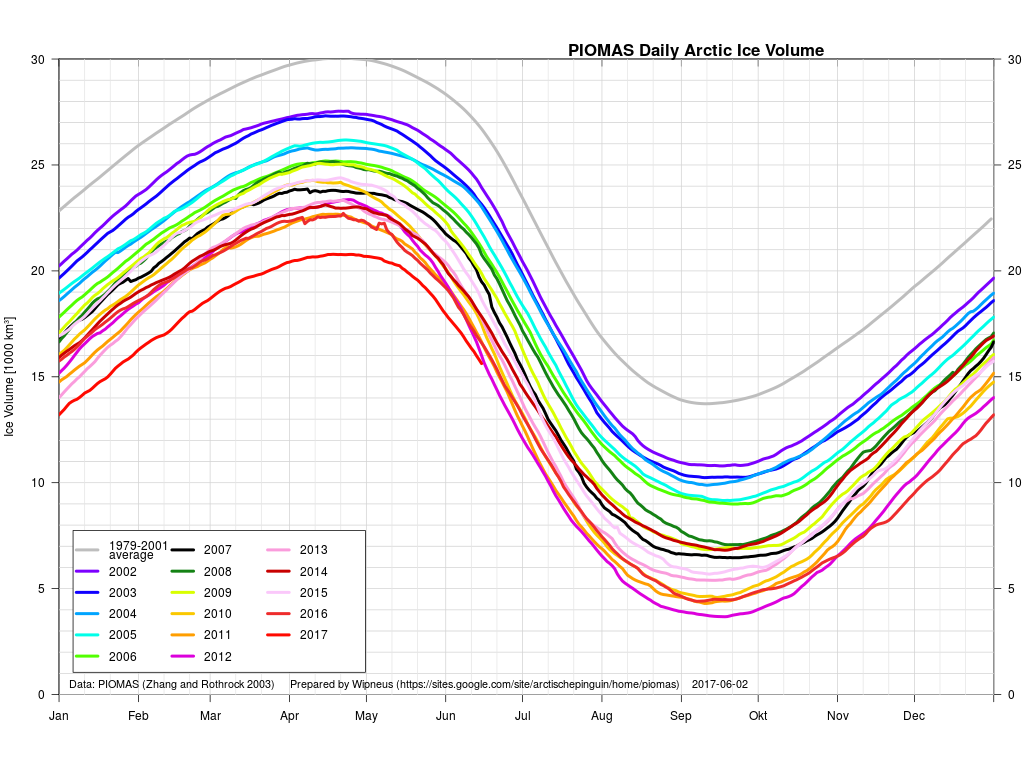
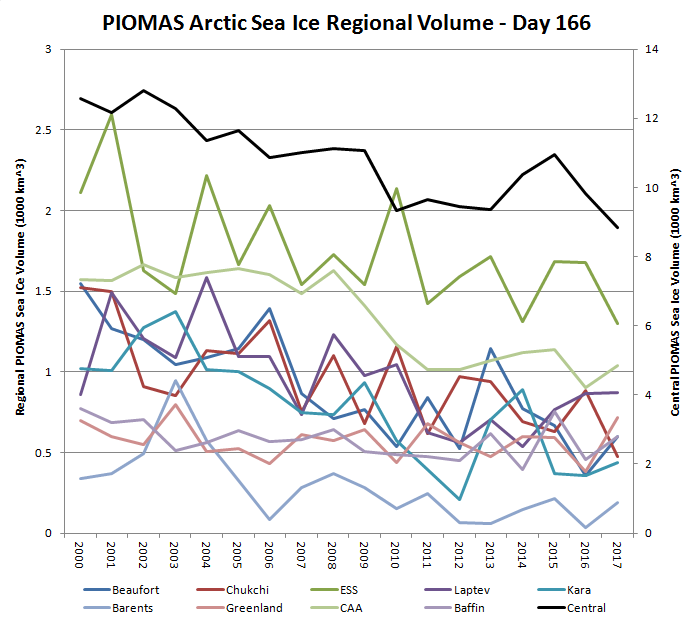
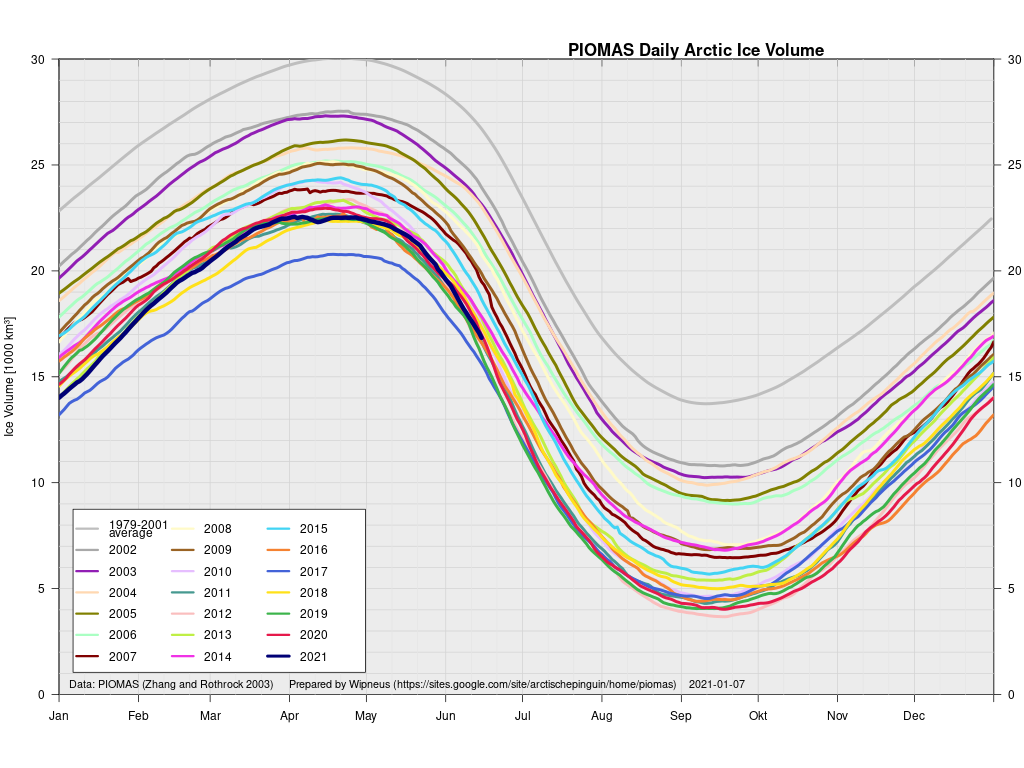
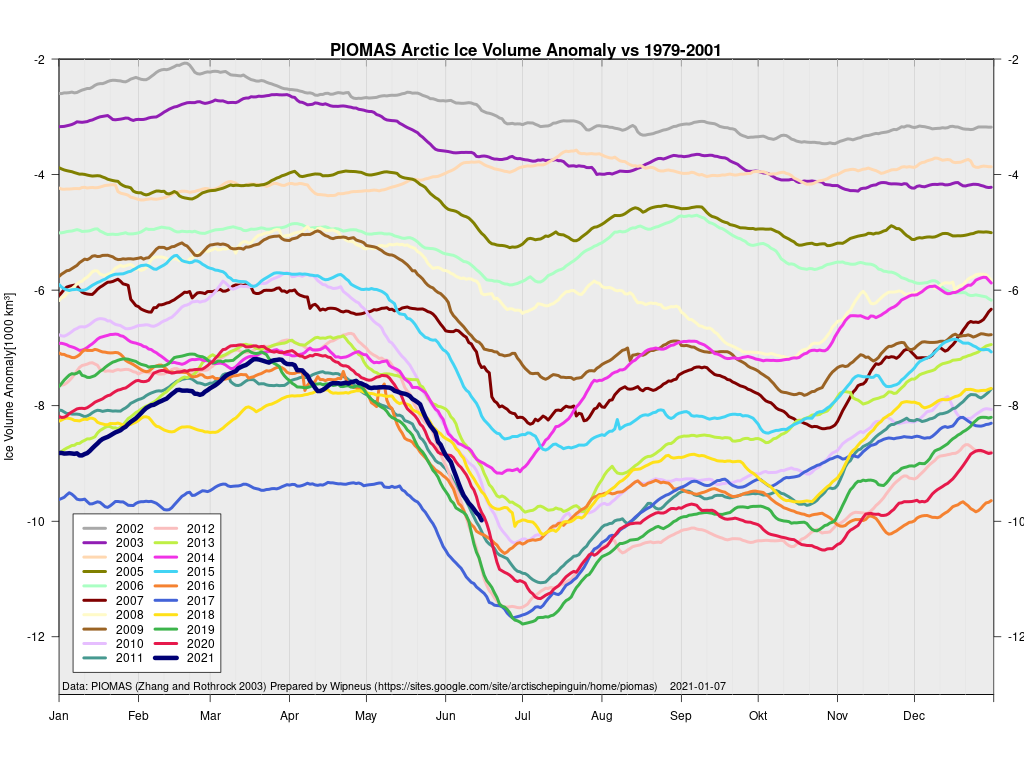
In other news Wipneus has released the latest PIOMAS gridded thickness and volume data on the Arctic Sea Ice Forum:
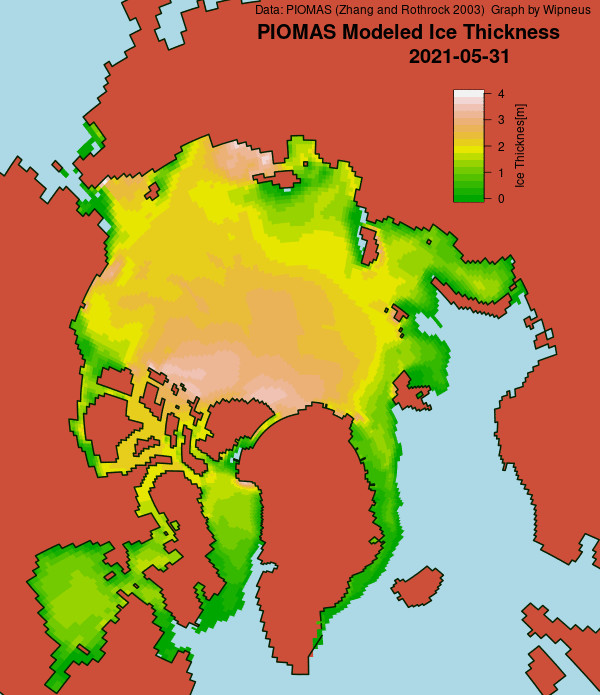
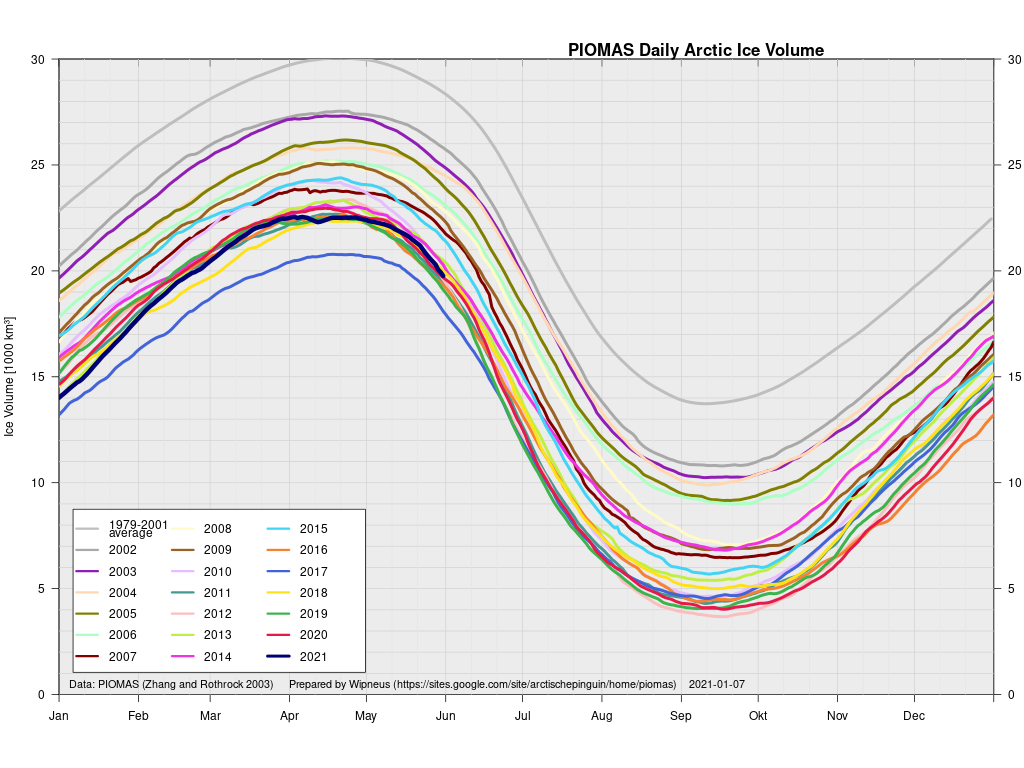
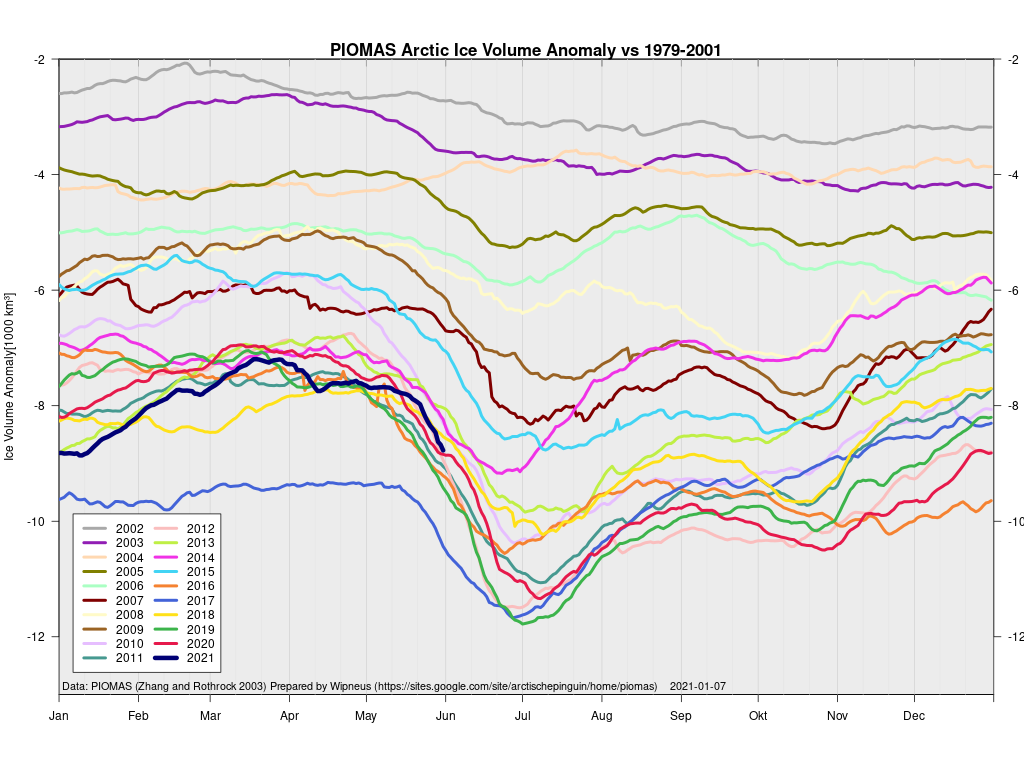
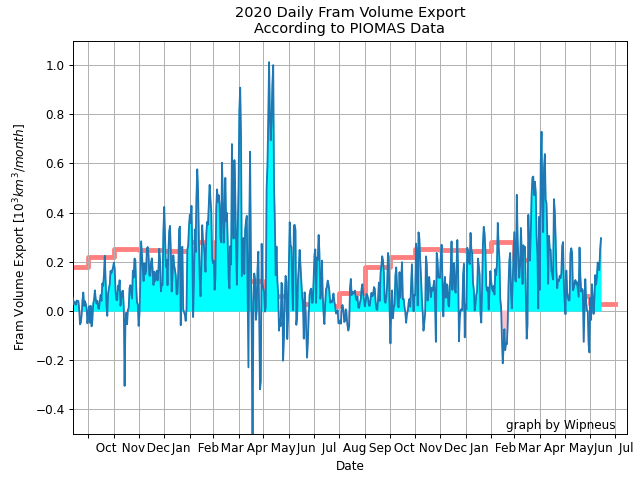
For some strange reason 2021 volume at the end of May is almost identical to 2012 and 2020! Plus of course there’s the modelled volume export from the Central Arctic via the Fram Strait:
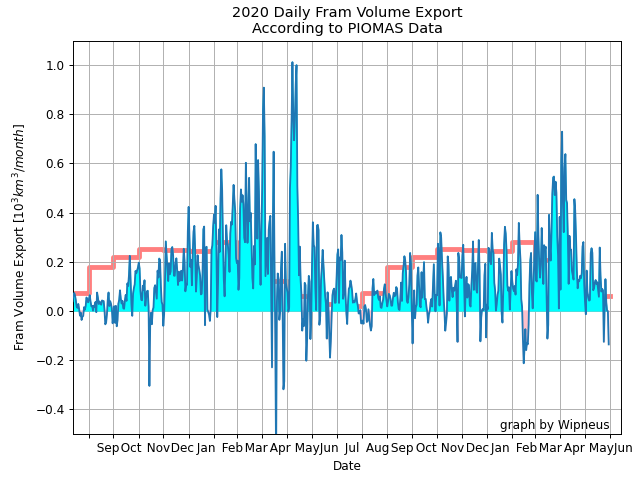
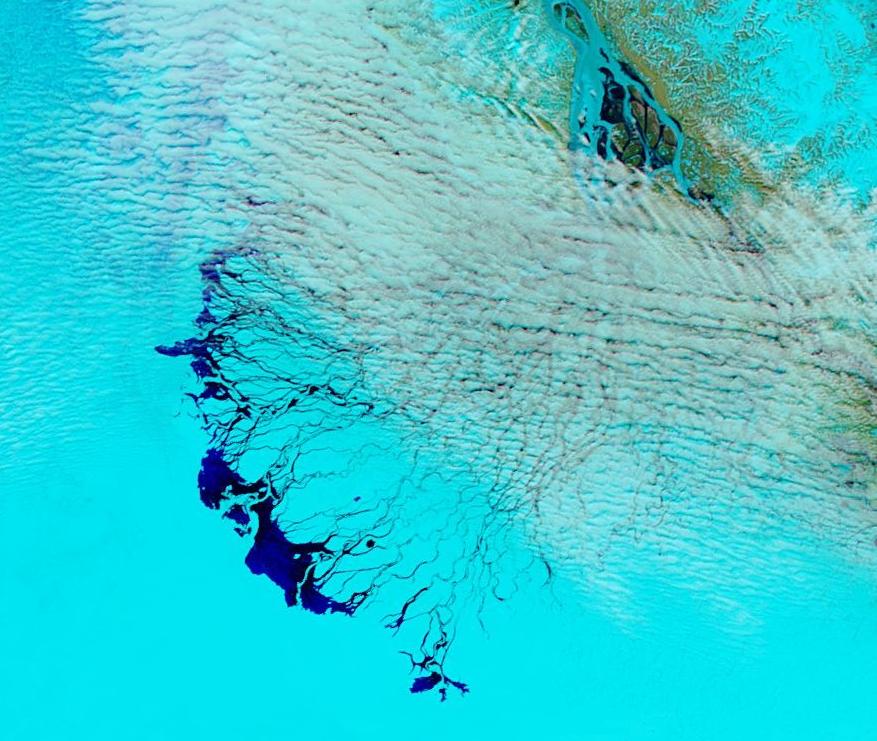
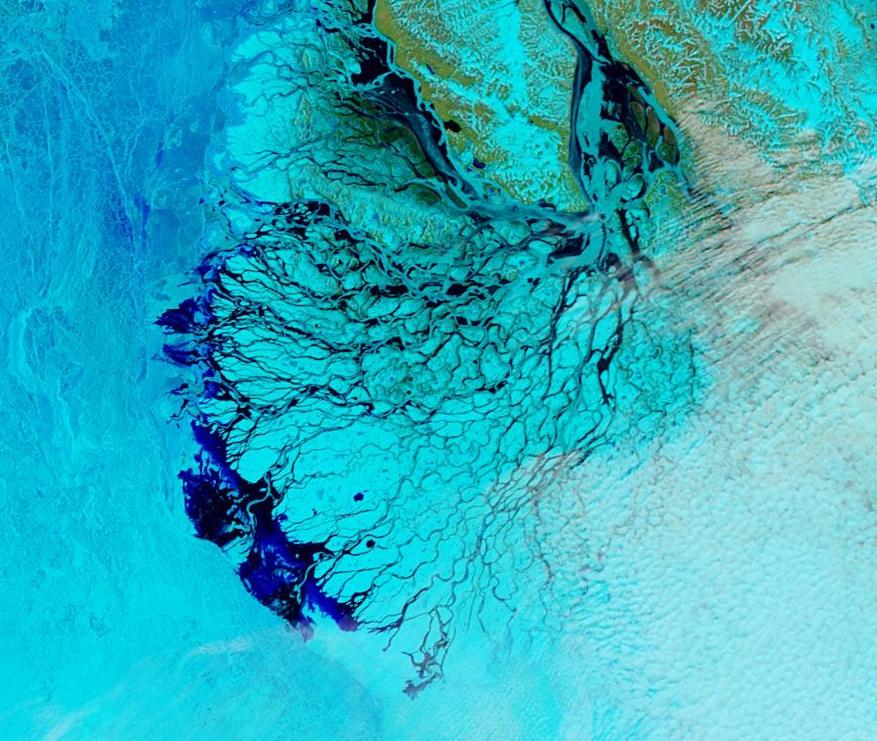
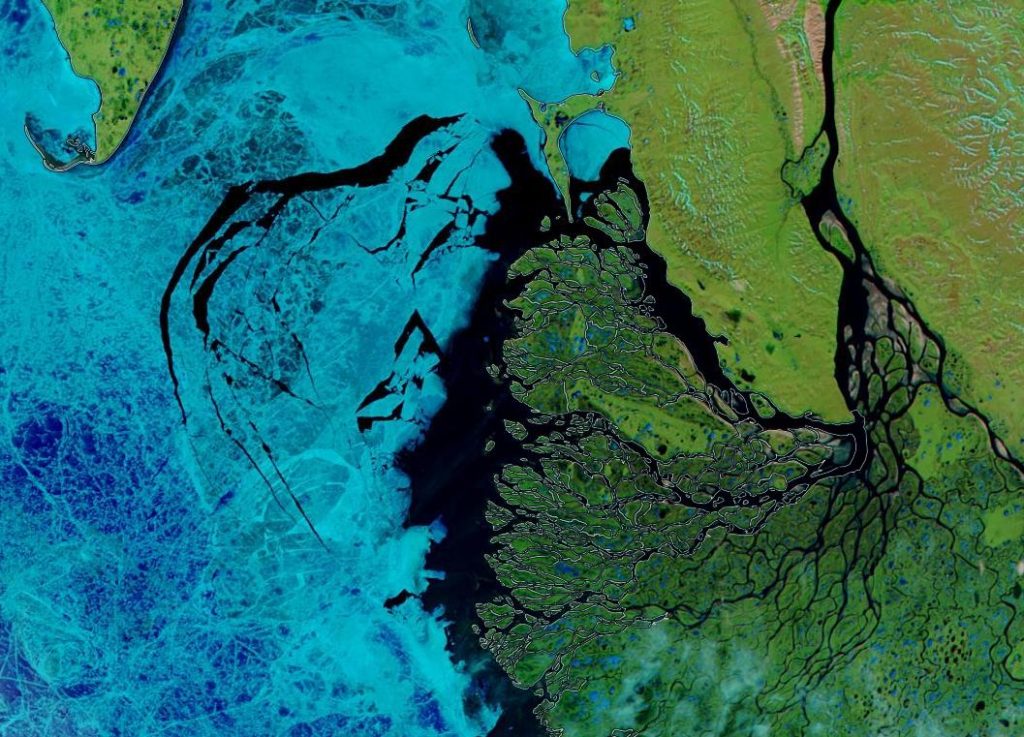
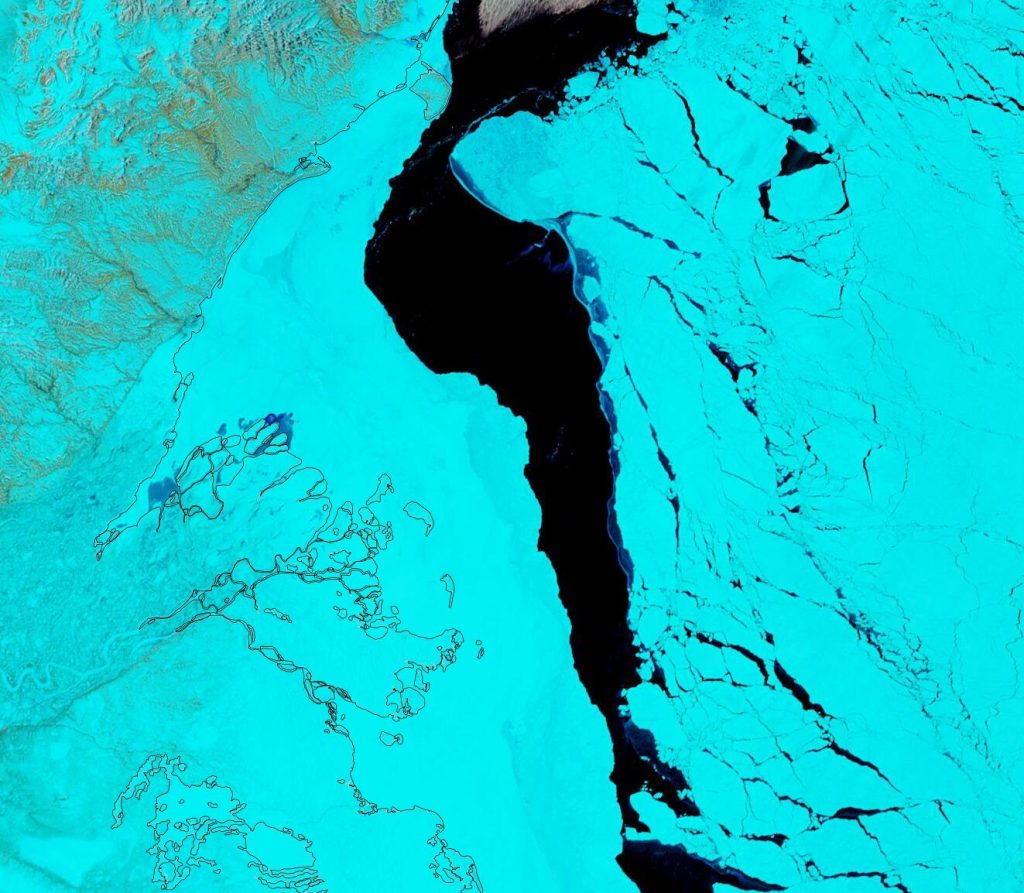
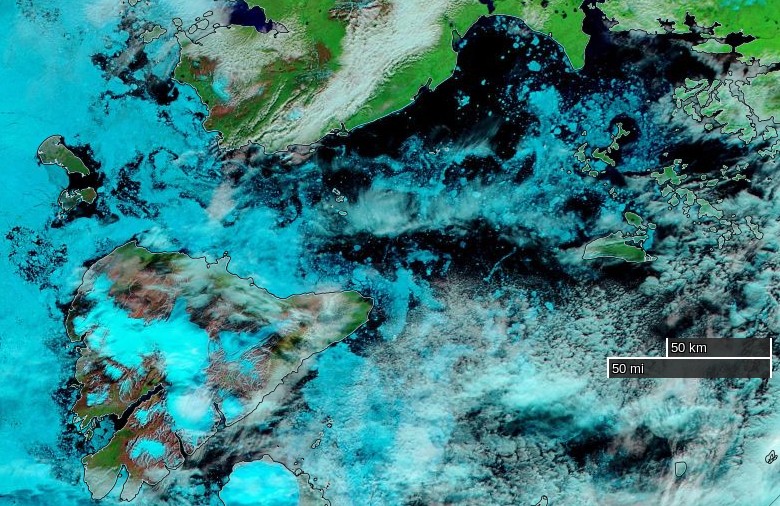
This “false colour” image reveals that there’s virtually no snow cover left on land, and this “false colour” image reveals that the land-fast ice in the East Siberian Sea is now awash with melt ponds:

The forecast low pressure area appears to have bottomed out near the Severnaya Zemlya islands with a 978 hPa MSLP:
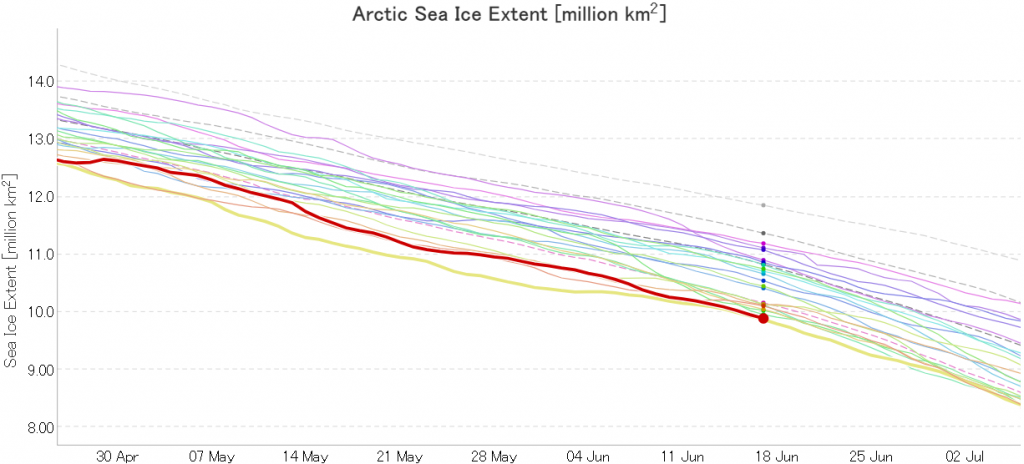
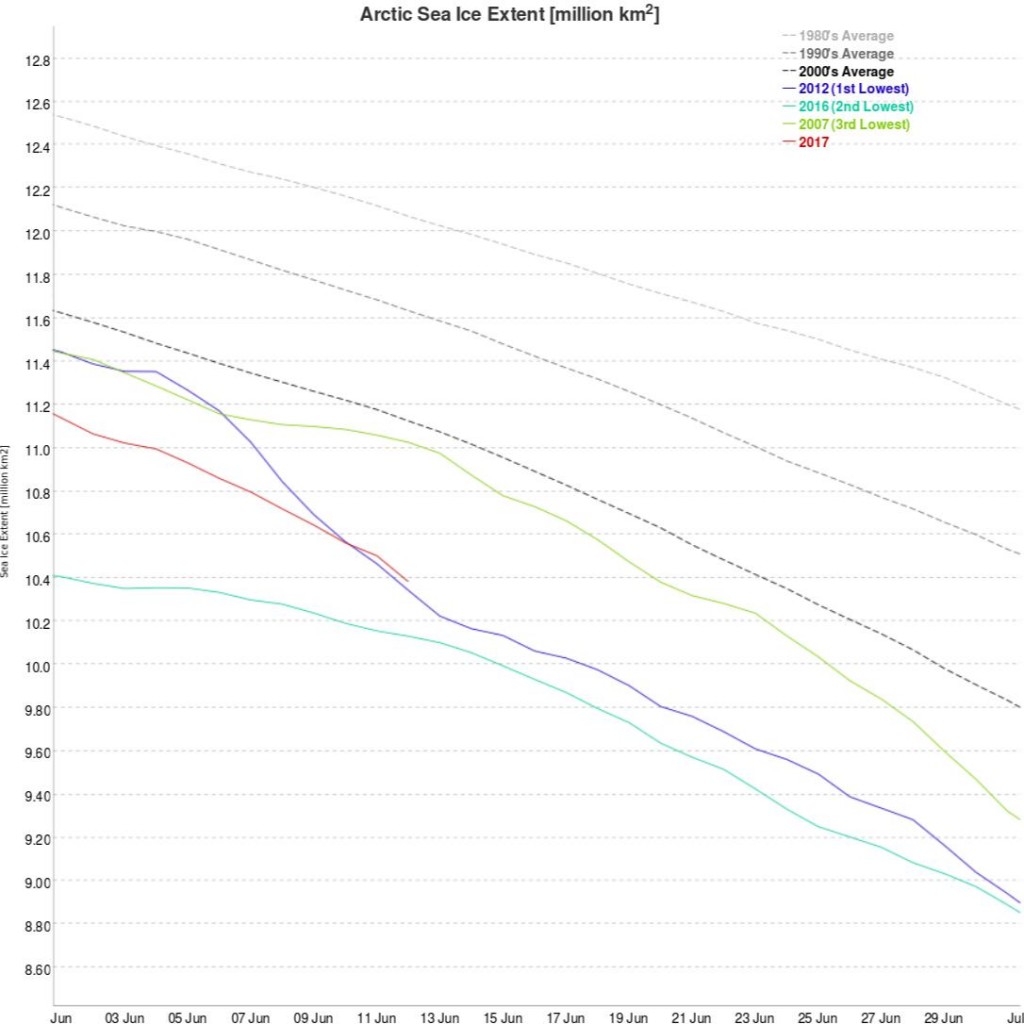
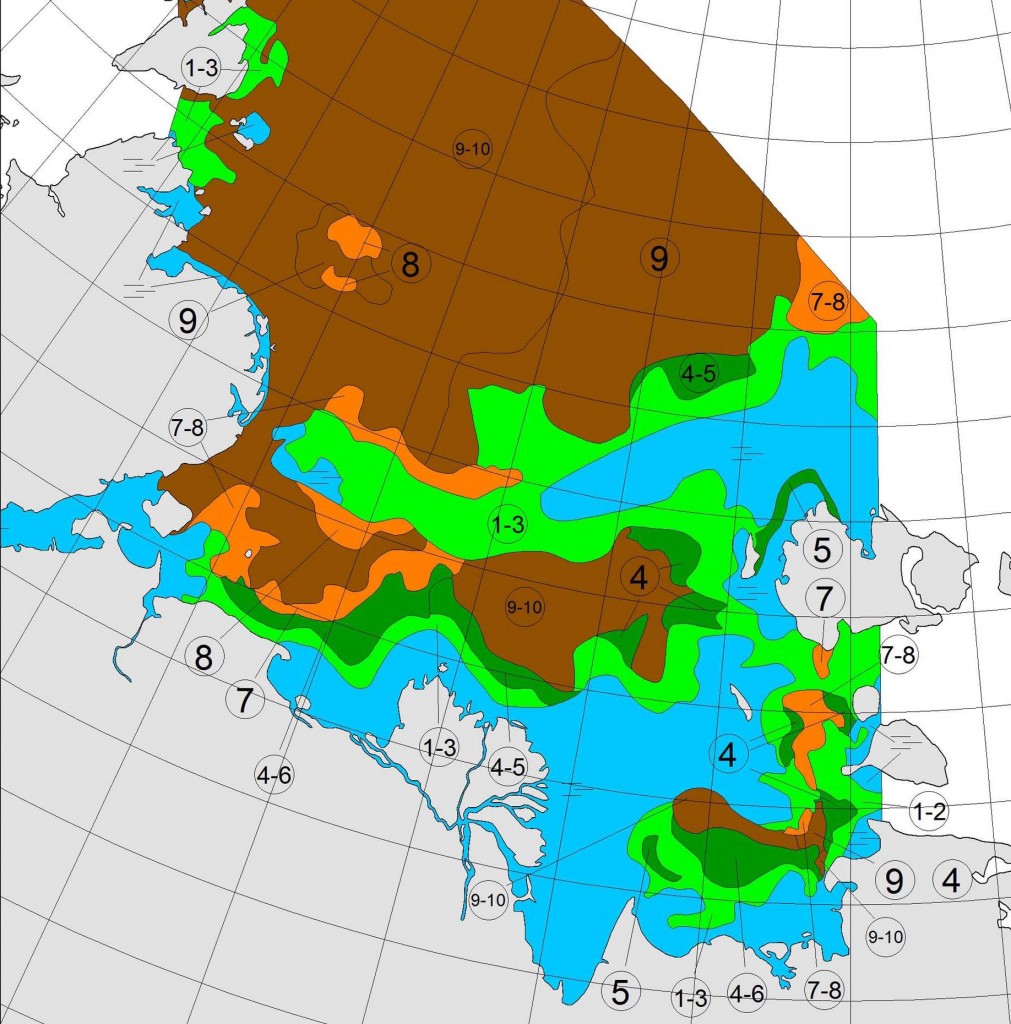
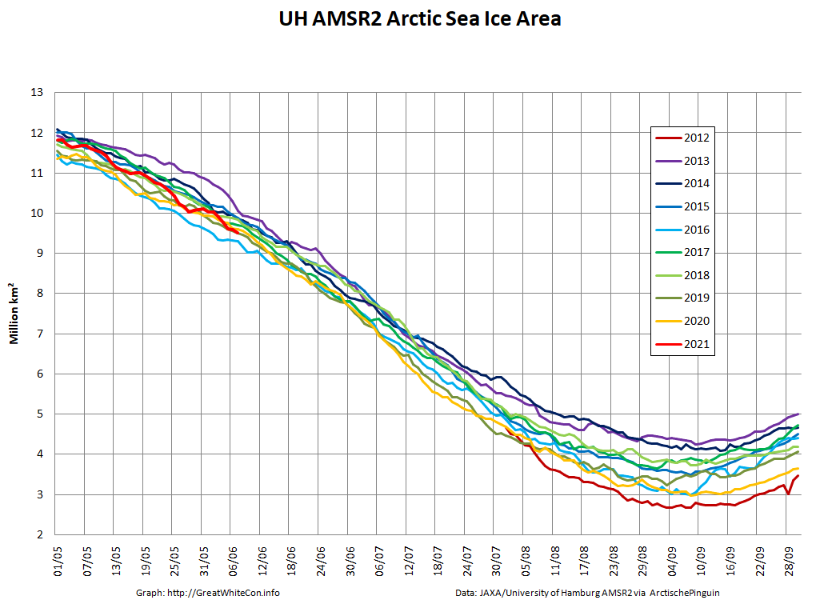
High resolution AMSR2 Arctic sea ice area is now 2nd lowest for the date after 2016:
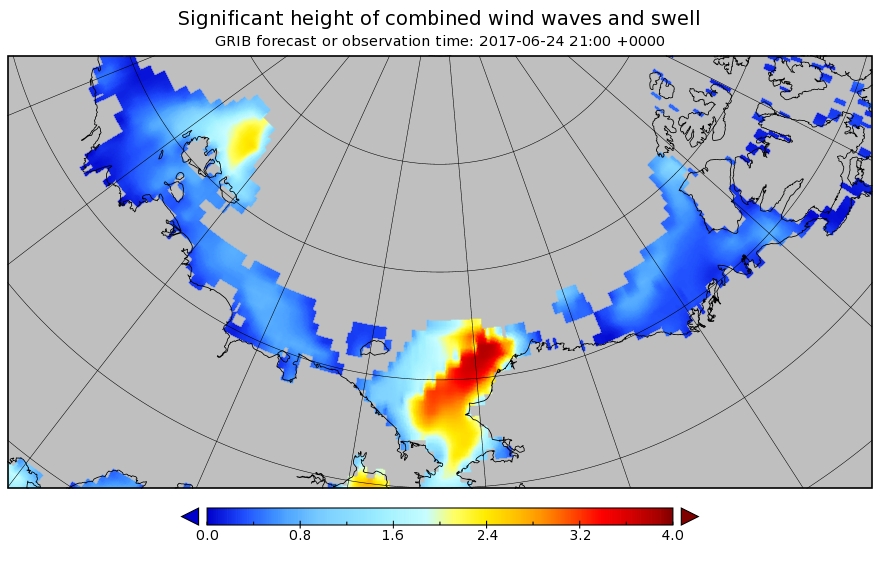
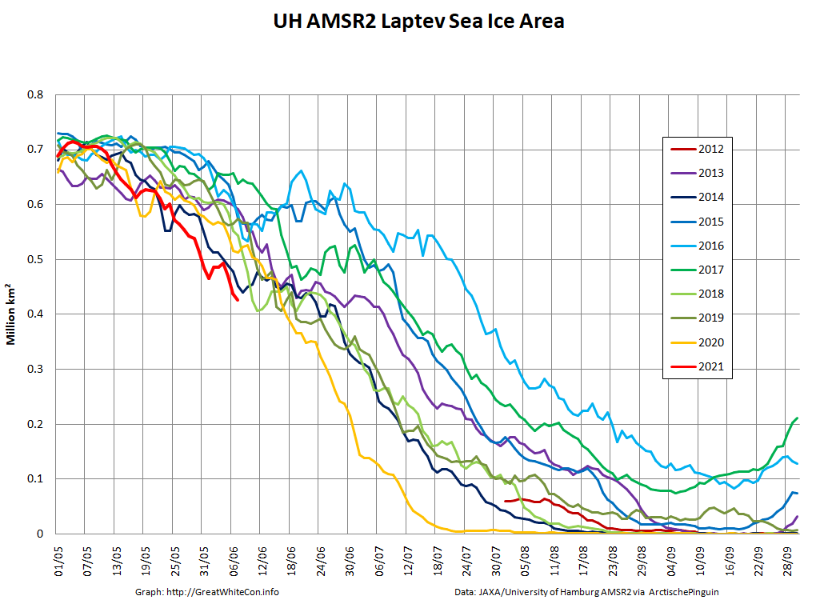
Laptev sea ice area is still lowest for the data, and looks as though it will retain that position for a while:
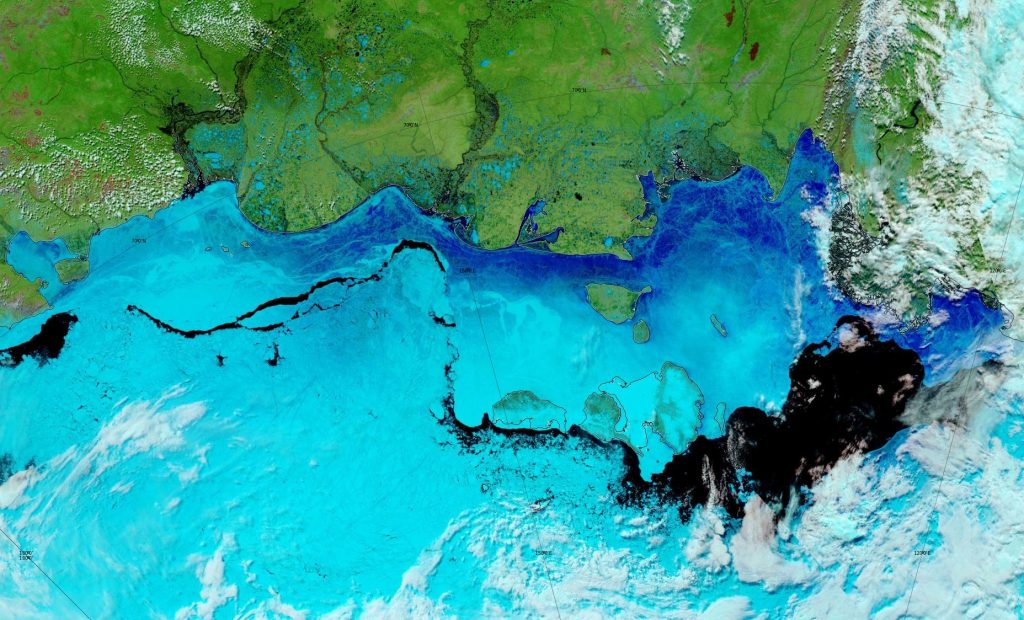
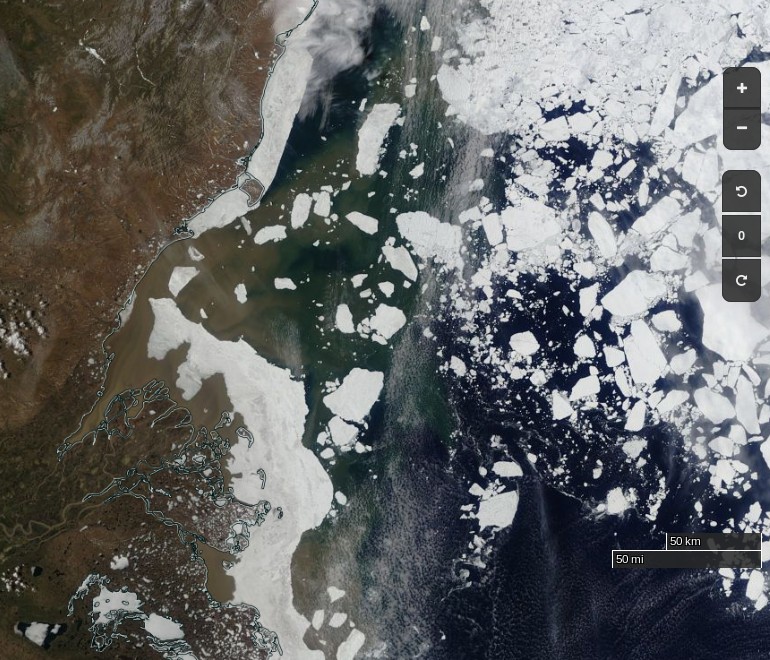
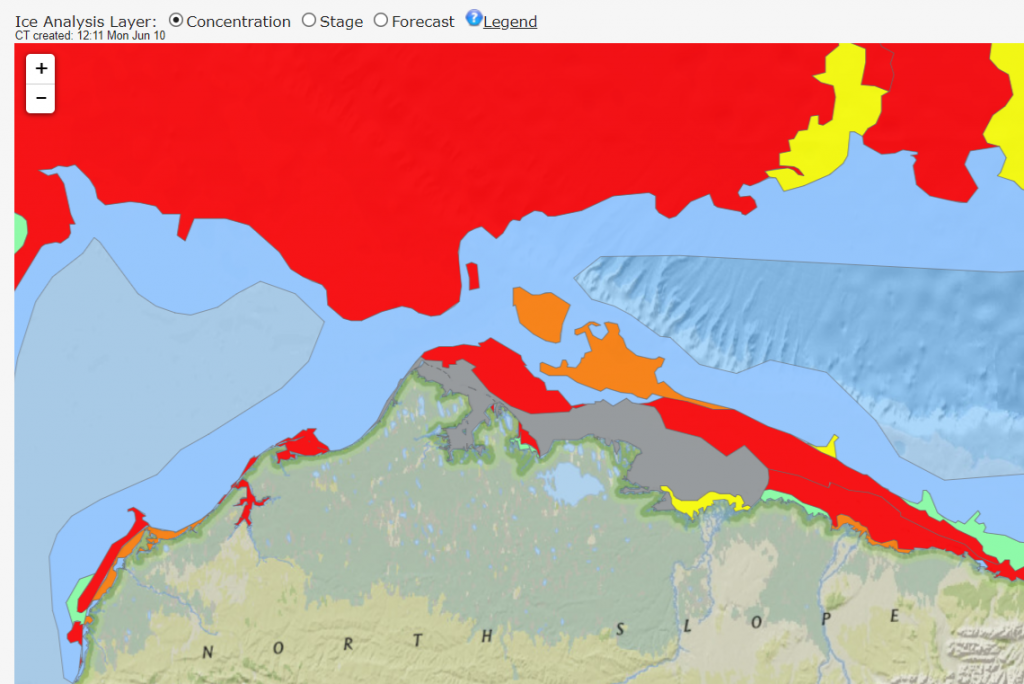
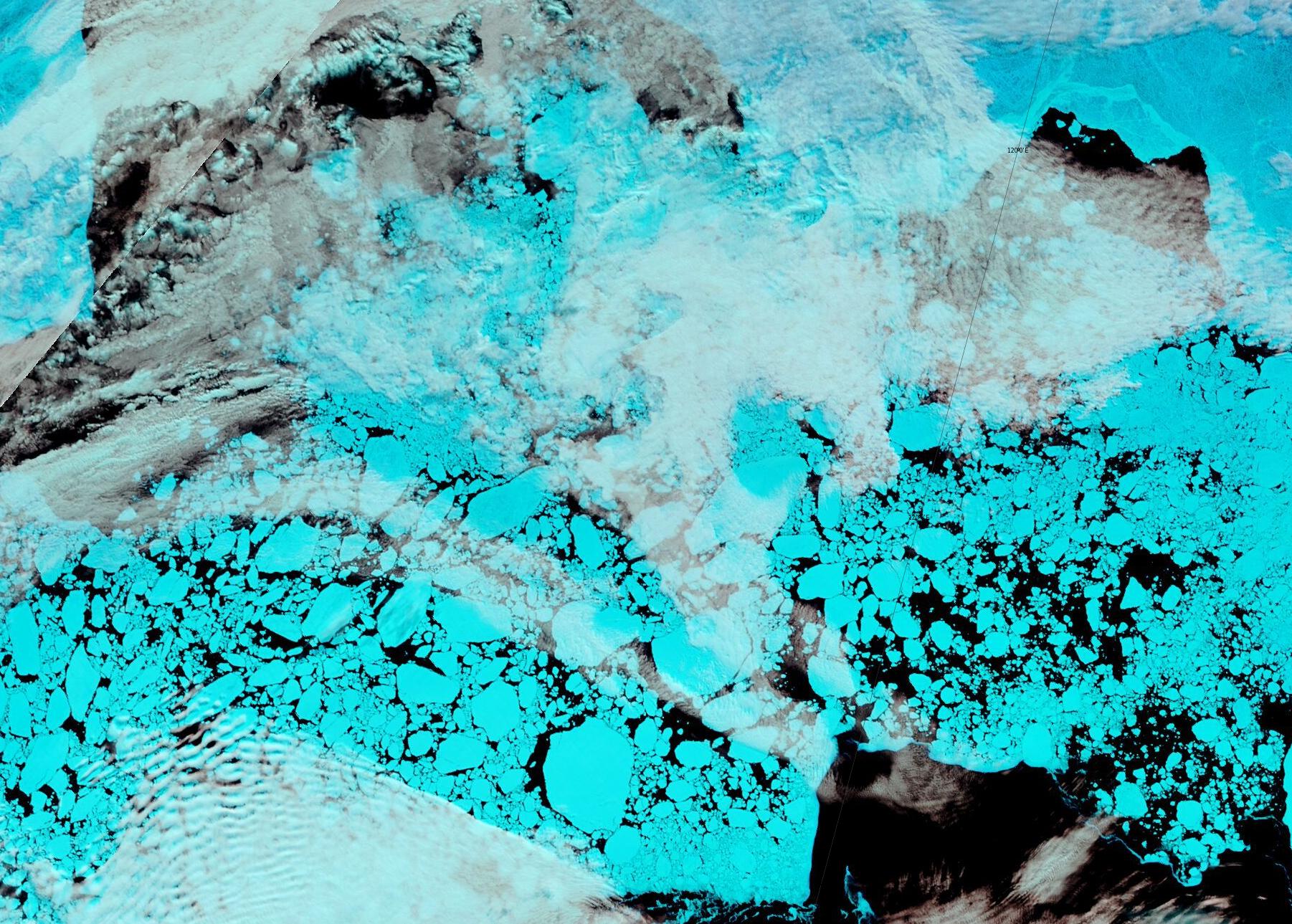
The effect of the recent heat and wind on the remaining sea ice in the Laptev Sea is now all too apparent:
It’s also evident in the DMI >80N temperature graph, which has now reached sea ice “melting point” ahead of the climatology:
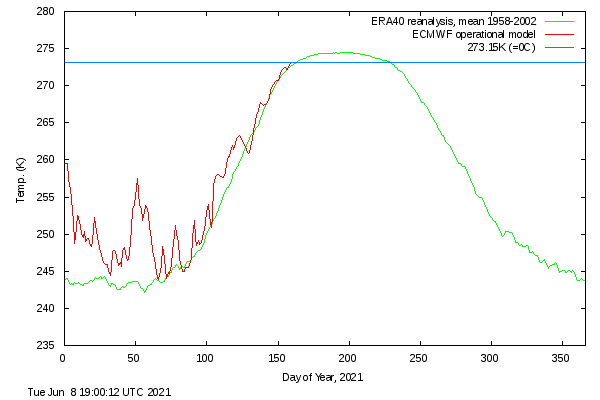
Note that the blue line is actually above the “freezing point” of salty Arctic sea water.
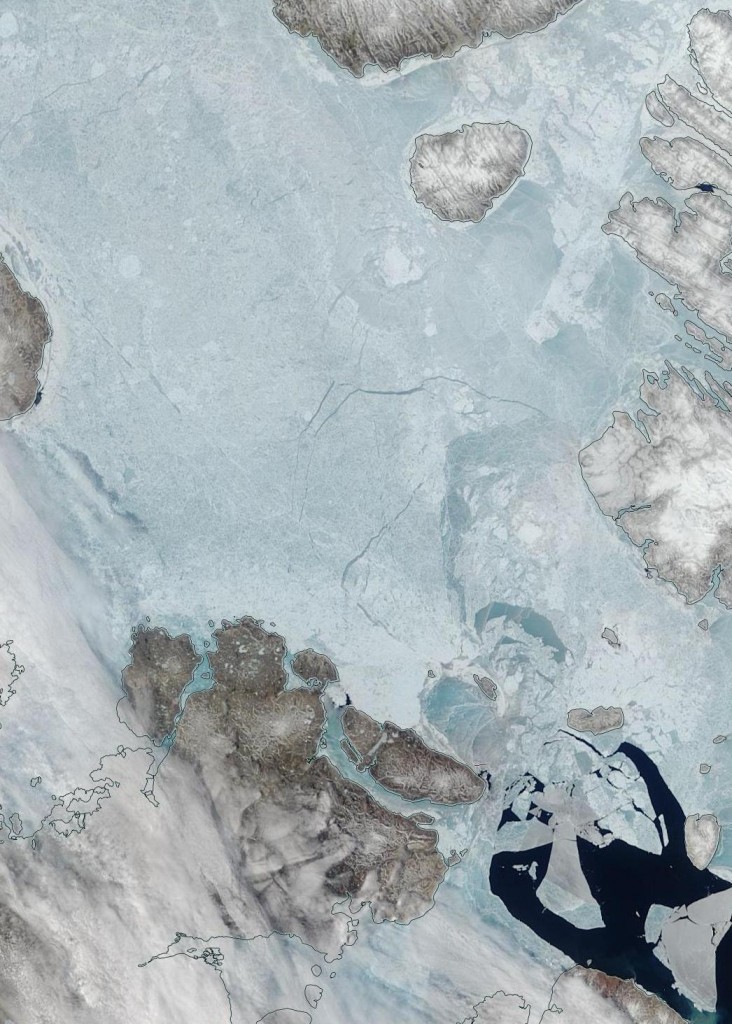
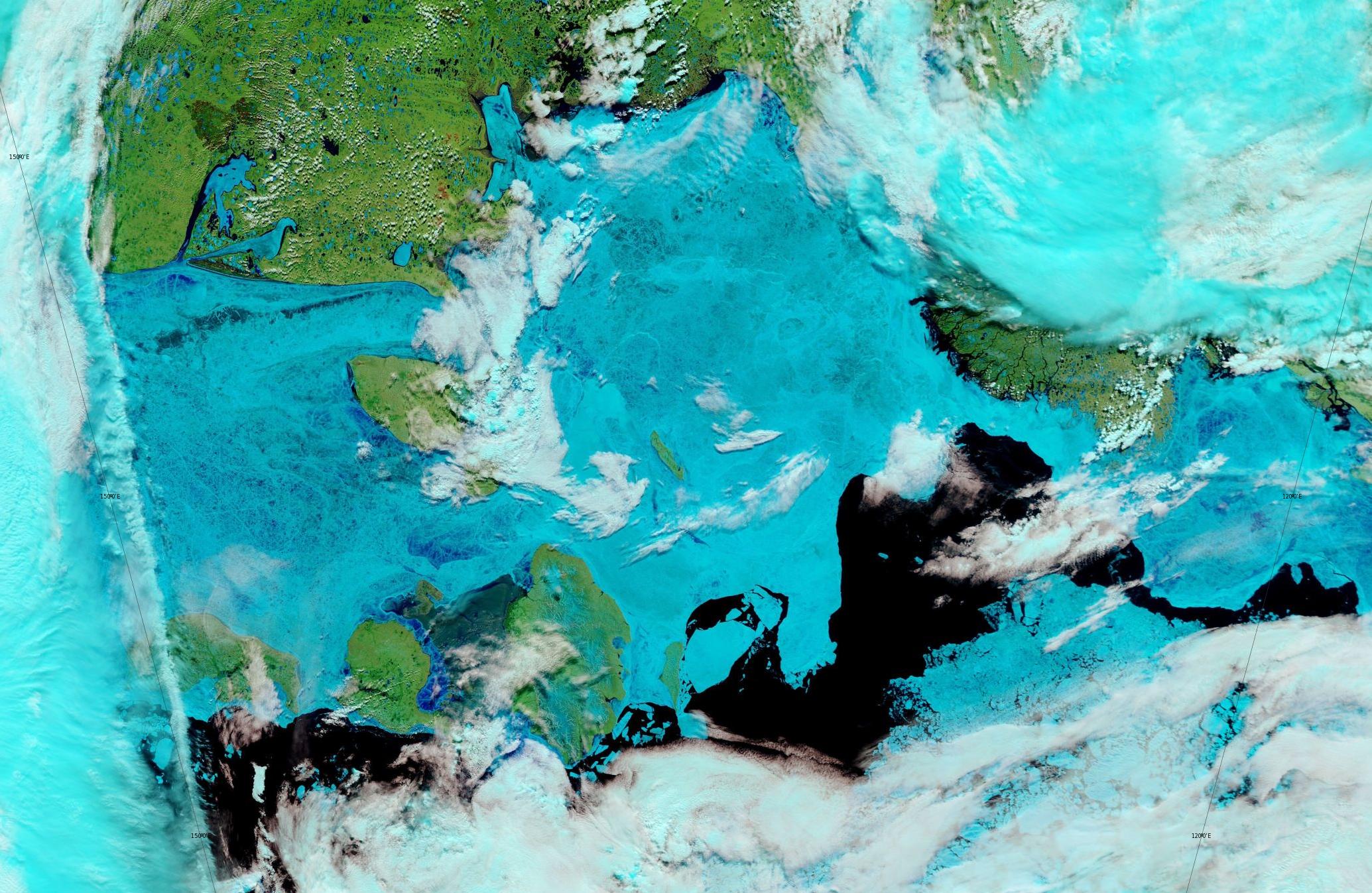
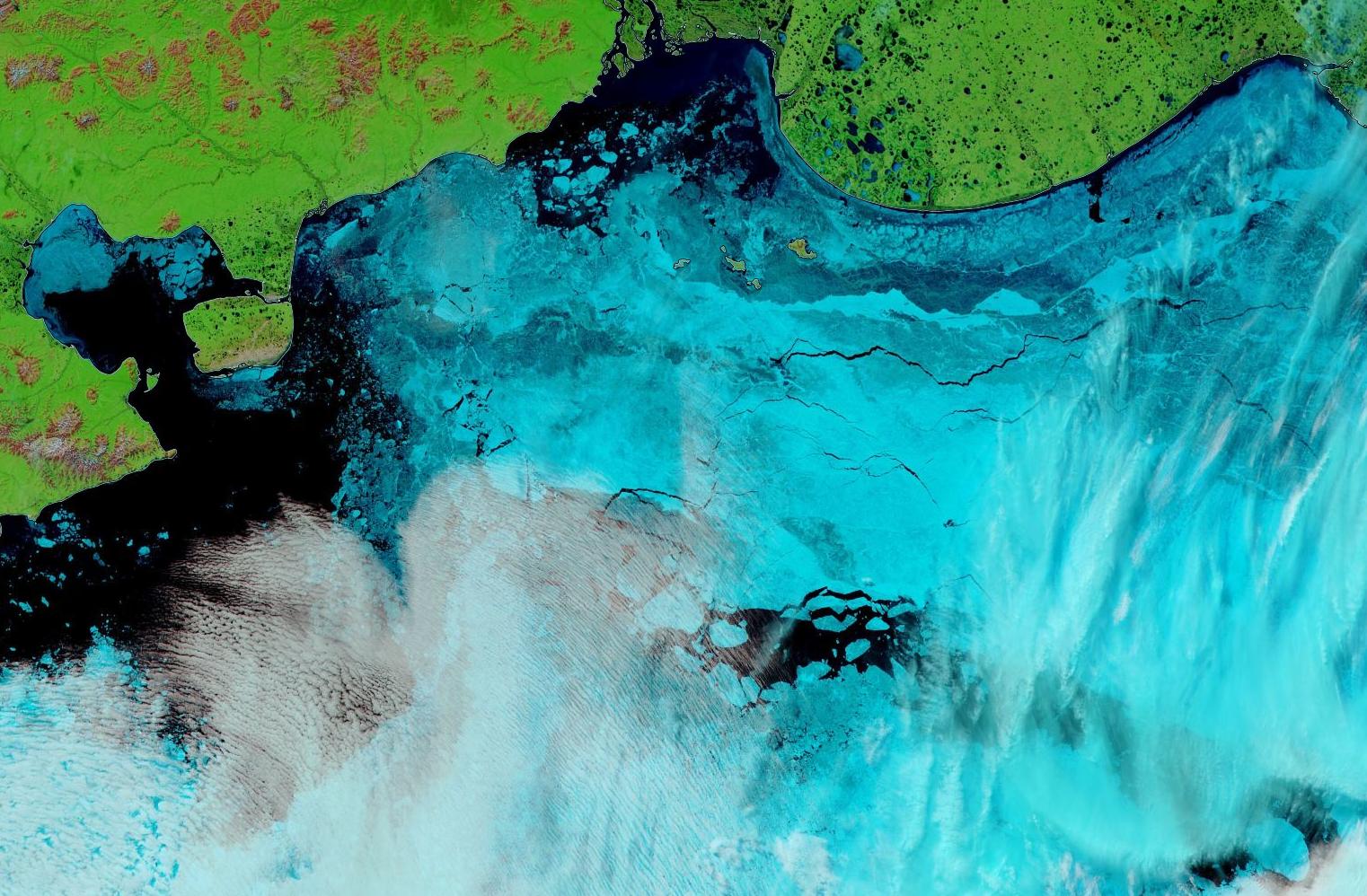
[Edit – June 13th]Fairly clear skies over the Laptev Sea and the western East Siberian Sea, revealing wall to wall melt ponds and the land-fast ice starting to break up near the coast as well as on the edge of the now open ocean:
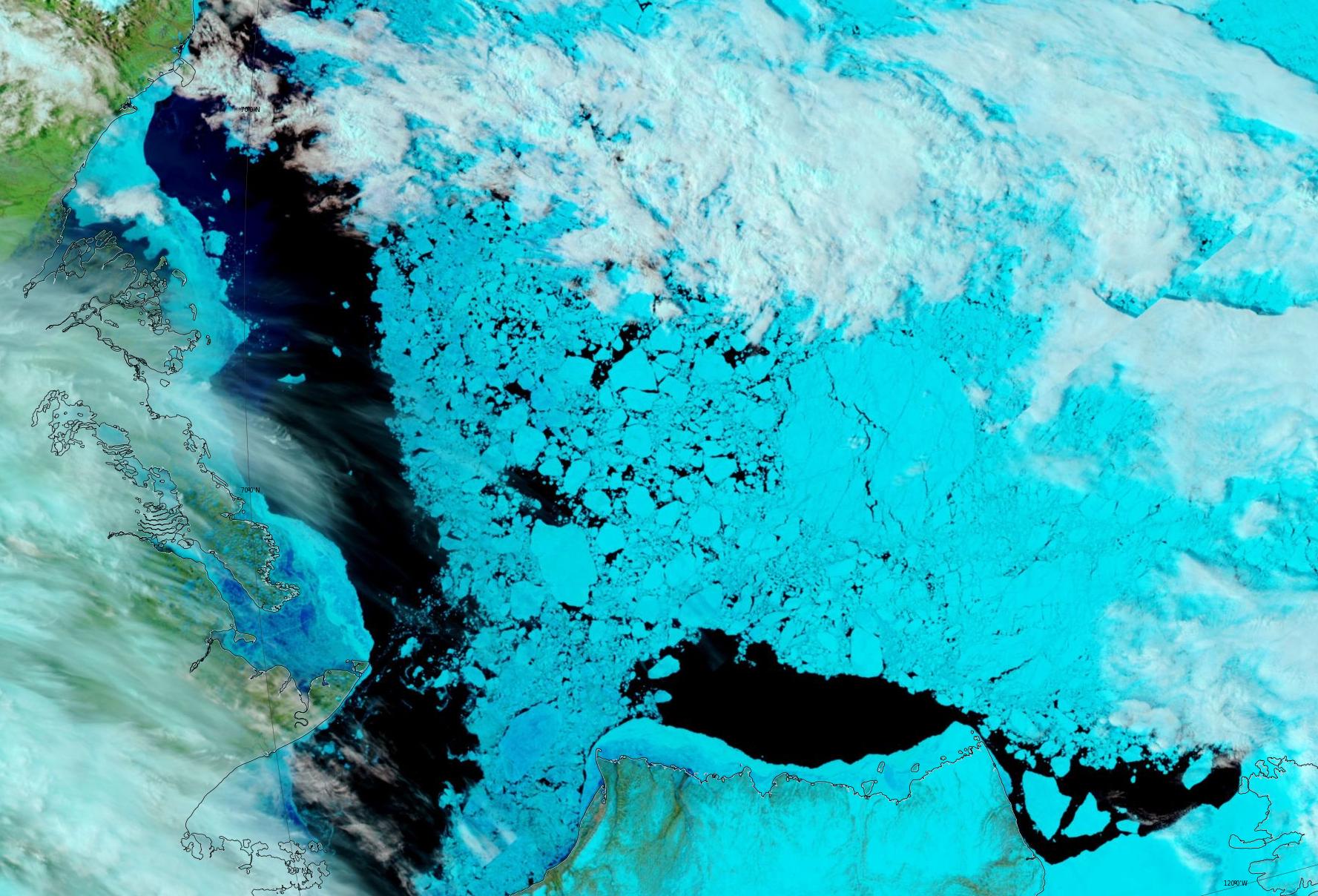
Plus yesterday’s view of the Beaufort Sea, revealing fast ice breaking up in the western entrance to the McClure Strait:
[Edit – June 18th]
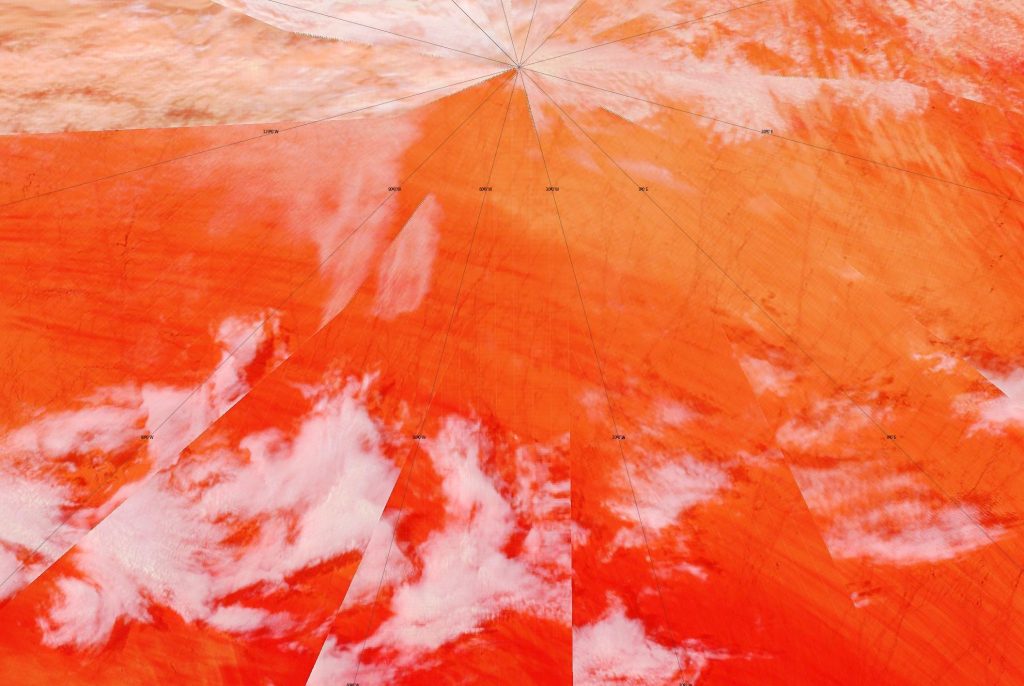
A clearish view of the Laptev Sea today, revealing assorted cracks in a variety of locations:

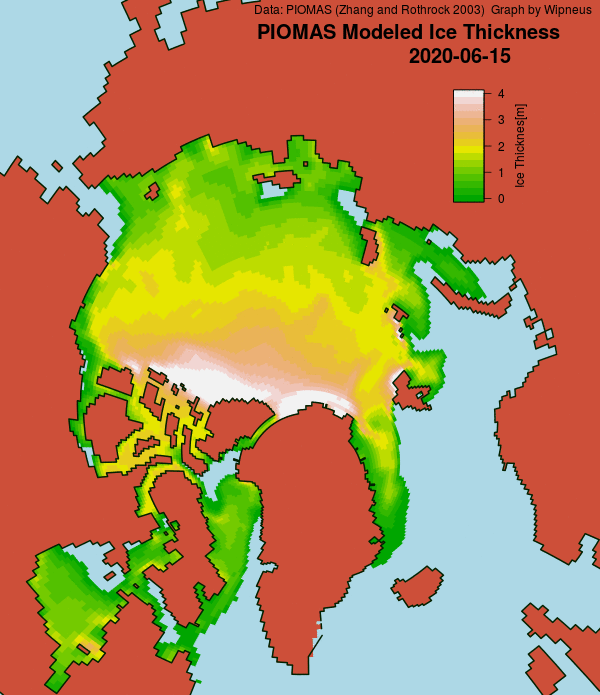
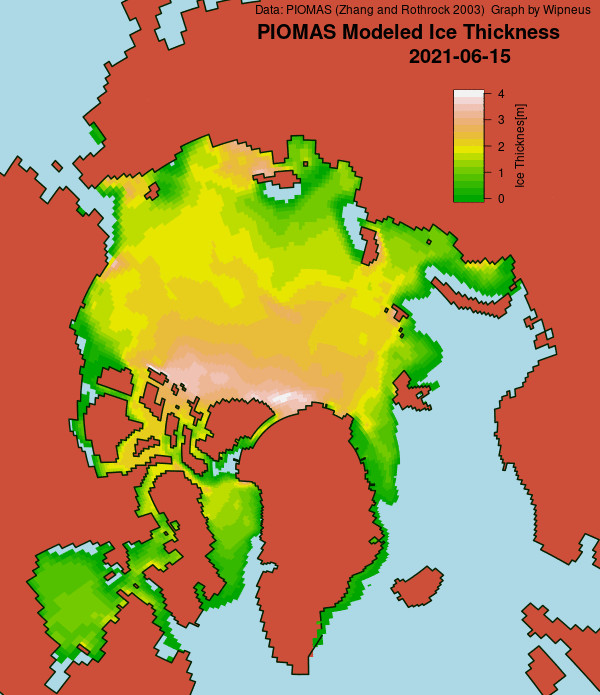
The latest mid-month PIOMAS thickness/volume numbers have been released:
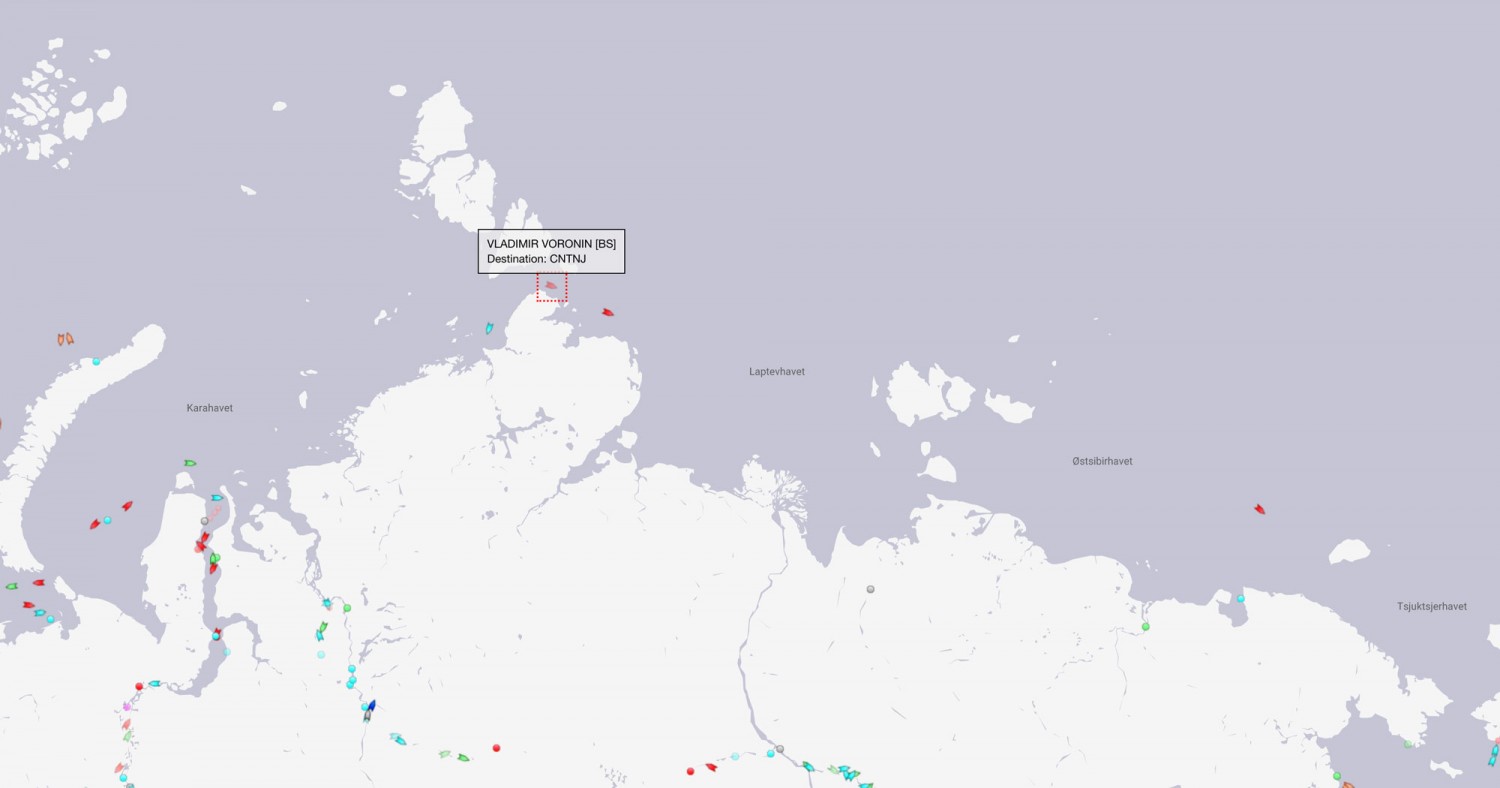
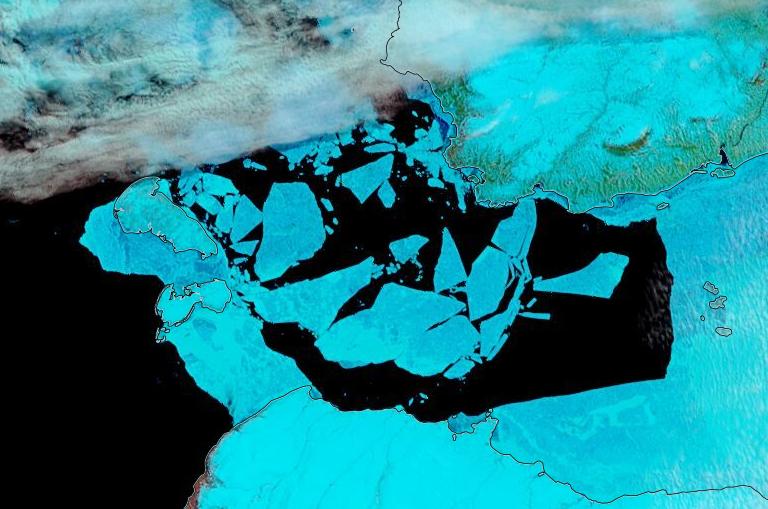
The skies over the Vilkitsky Strait have been cloudy for a few days. However a fairly clear view yesterday reveals that breakup is well under way in what is usually one the last areas along the Northern Sea Route to become navigable:
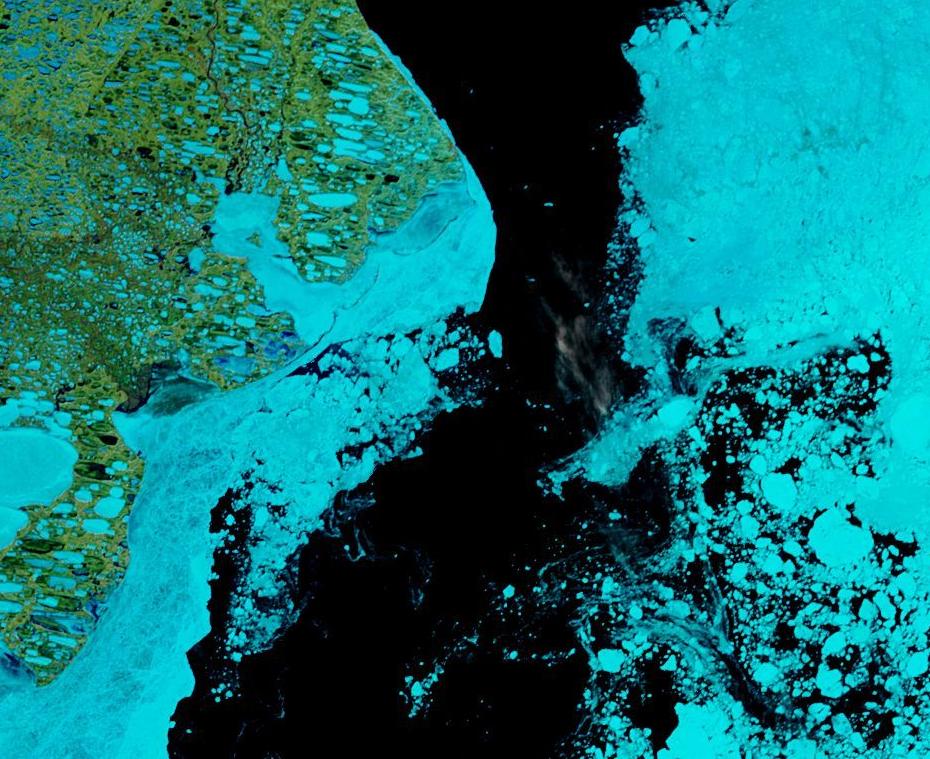
The land-fast ice in the East Siberian Sea has started to disintegrate en masse:
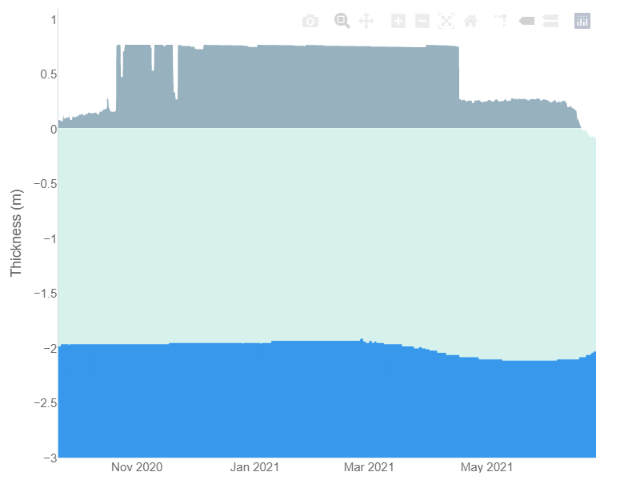
Data from ice mass balance buoy 441910, currently located at 76.1 N, 151.1 W in the Beaufort Sea, reveals the onset of both surface and bottom melt:
Watch this space!