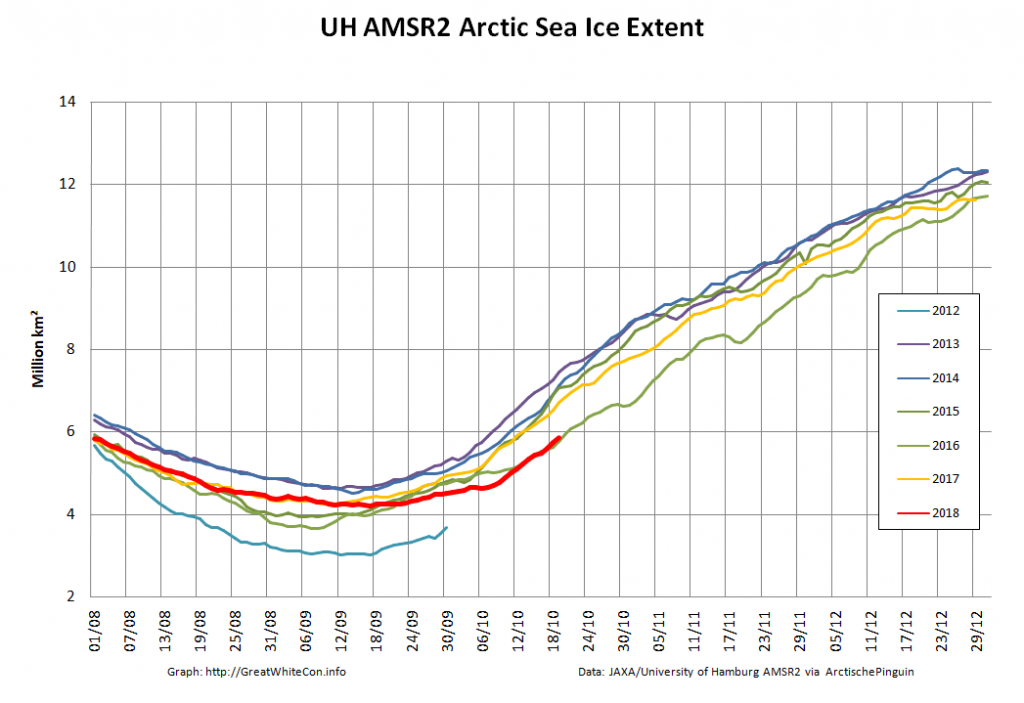
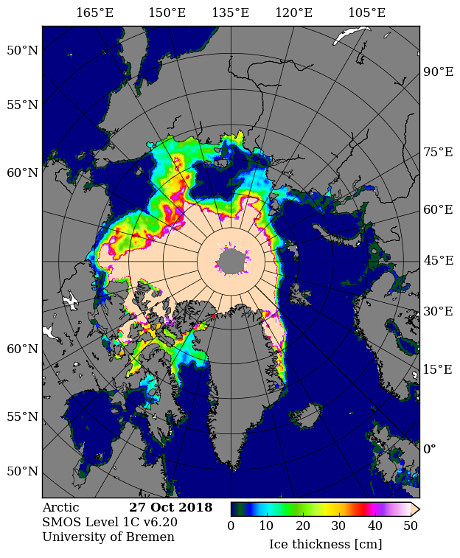
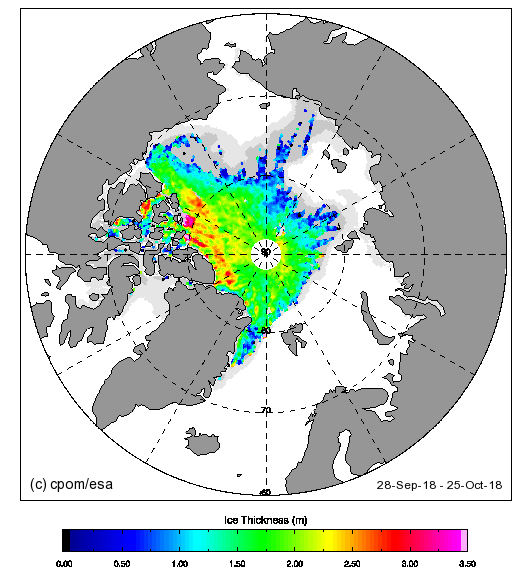
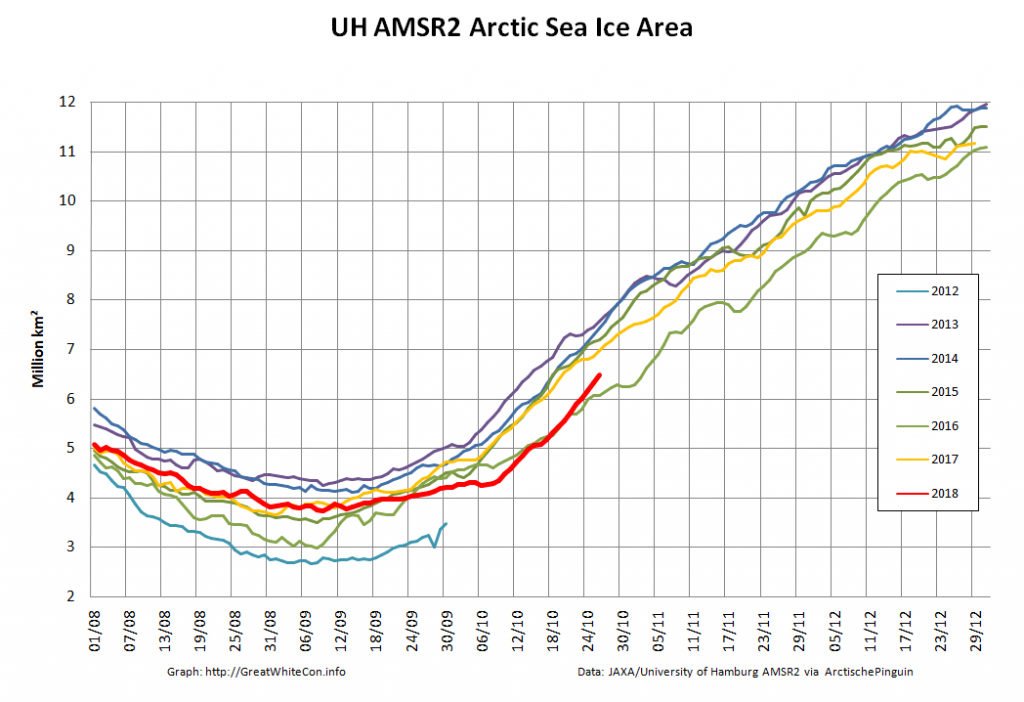
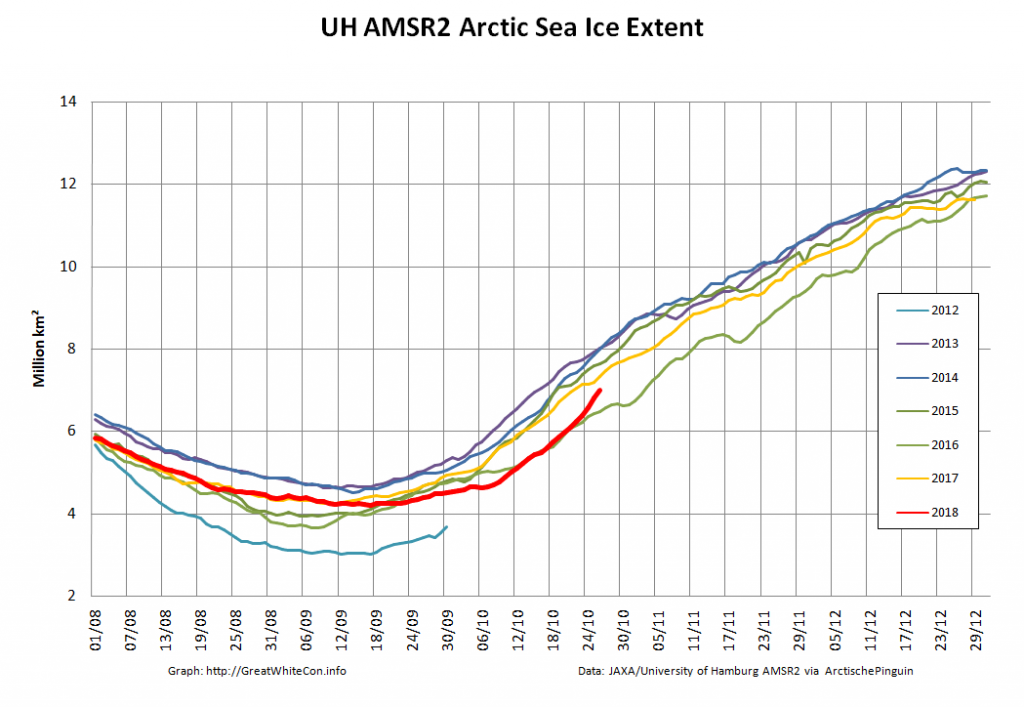
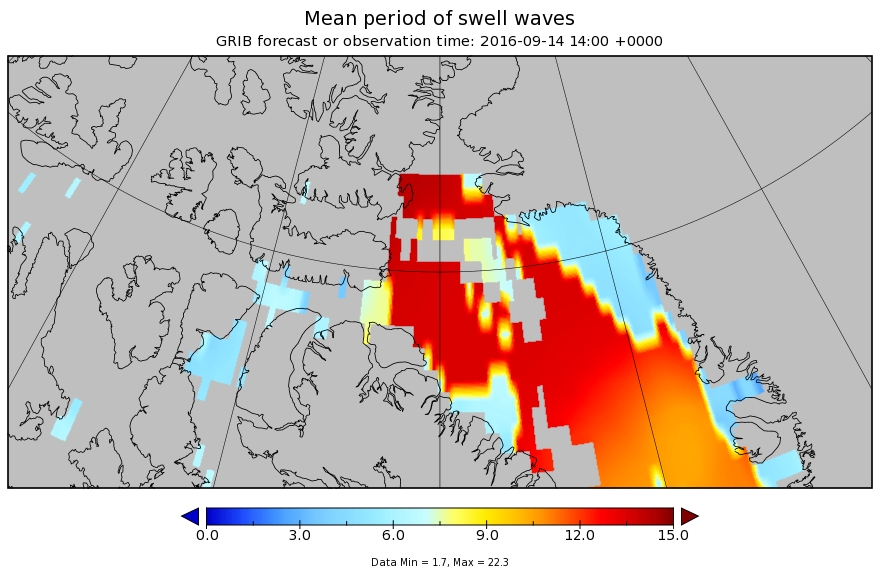
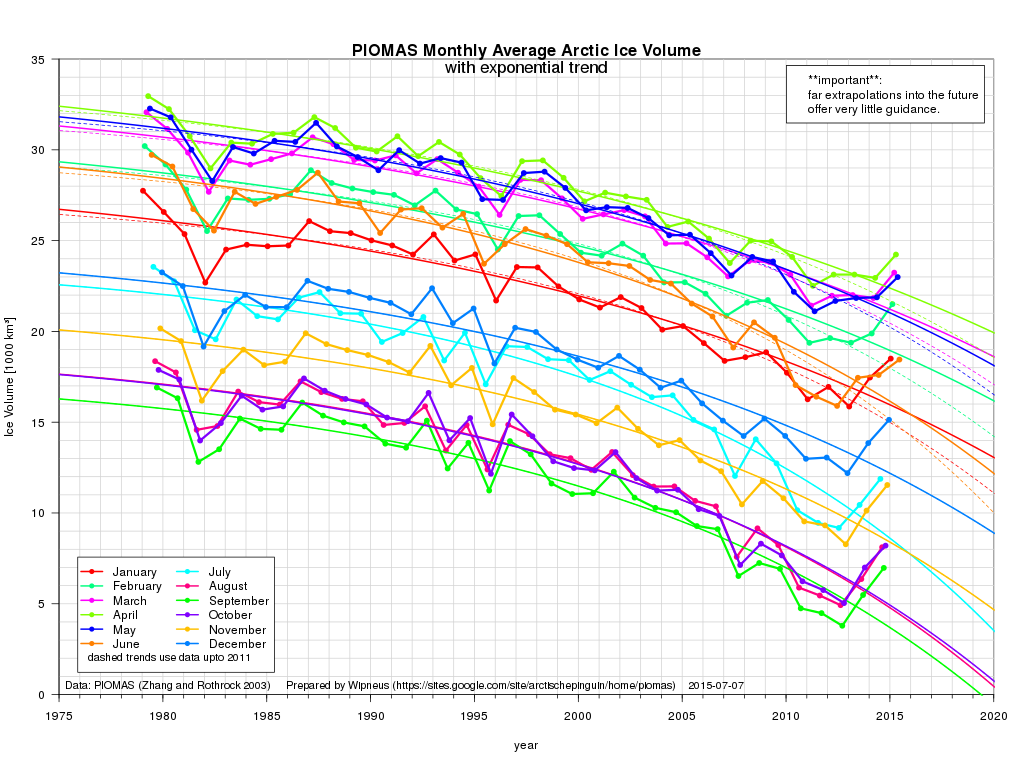
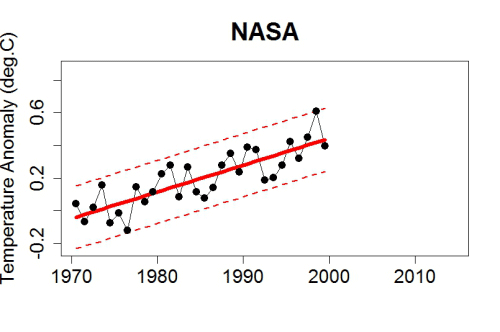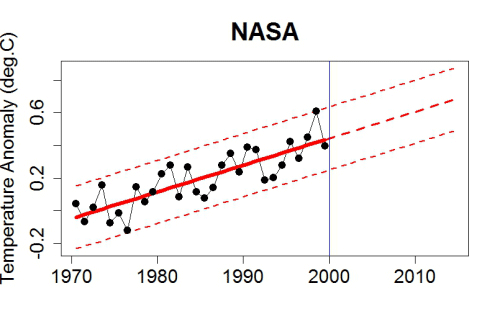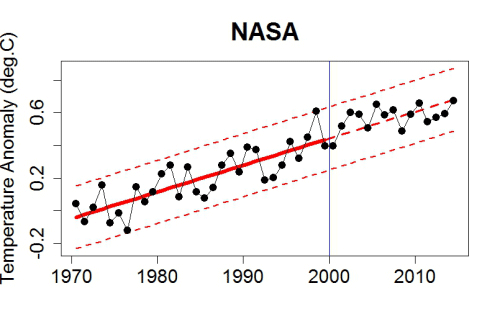
This month has begun with a couple of CryoSat-2 related papers. First we have one that I unexpectedly I found out about via Twitter:
Regular readers will recall that the thickness in mid April by the AWI’s CryoSat-2/SMOS metric seemed remarkably low, so I had to ask this question:
Whilst we wait on those SnowModel-LG results does the CPOM’s new analysis offer any cause for comfort concerning sea ice thickness in 2021? I’m afraid not. Here’s an extract from the conclusions:
We found that interannual variability in average sea ice thickness of the marginal seas was increased by more than 50 % by accounting for variability in the snow cover. On a seasonal timescale we find that variability in the snow cover makes an increasing contribution to the total variability of inferred sea ice thickness, increasing from around 20 % in October to more than 70 % in April.
We also observed that the trends in SnowModel-LG data propagated through to the sea ice thickness time series, amplifying the decline in regions where it was already significant and introducing significant decline where it did not previously exist. This occurred in spite of the compensating effect of enhanced interannual variability.
Next there is a preprint from Arttu Jutila et al. at the Alfred Wegener Institute. According to “Retrieval and parametrisation of sea-ice bulk density from airborne multi-sensor measurements“:
Knowledge of sea-ice thickness and volume depends on freeboard observations from satellite altimeters and in turn on information of snow mass and sea-ice density required for the freeboard-to-thickness conversion. These parameters, especially sea-ice density, are usually based on climatologies constructed from in situ observations made in the 1980s and before while contemporary and representative measurements are lacking. Our aim with this paper is to derive updated sea-ice bulk density estimates suitable for the present Arctic sea-ice cover and a range of ice types to reduce uncertainties in sea-ice thickness remote sensing. Our sea-ice density measurements are based on over 3000 km of high-resolution collocated airborne sea-ice and snow thickness and freeboard measurements in 2017 and 2019.
Some slightly strange English in there, but interesting nonetheless and an complement to Robbie Mallett’s paper above.
In addition to the paper itself Stefan Hendricks has posted an explanatory thread on Twitter:
From Stefan’s Twitter thread:
Main findings: The density values are higher than what we get with the climatology values, more so for multi-year sea ice than for first-year ice. Part of the explanation is that with the airborne data we also tried to get the bulk density of deformed ice that includes sea water.
We also found a robust relationship between ice freeboard and ice density. This will be useful for the freeboard to thickness conversion of satellite data.
If I’ve understood the 2 papers correctly Robbie’s change to estimated snow thickness implies less overall sea ice volume in CPOM’s future product, whereas Arttu’s change to estimated sea ice density implies increased sea ice volume in AWI’s version.
All in all I’m anticipating the summer 2021 high Arctic melting season with even greater trepidation than at the start of this month. Uncertainty is exceedingly unsettling!
[Edit – June 17th]
News arrives via an AWI press release, which also refers to the Ricker et al. paper we mentioned last month, of a new paper. The lead author of “Interannual variability in Transpolar Drift summer sea ice thickness and potential impact of Atlantification” is Jakob Belter. Some more famous names in the “et al.” section include Igor Polyakov, Robert Ricker and Stefan Hendricks.
According to the press release:
AWI sea-ice physicists report on the first indications that the rising ocean heat is also slowing ice formation in the Laptev Sea, which also includes measurements of the ice floe from the one-year MOSAiC expedition in late summer 2020. In it, the researchers analyse the long-term data from their sea-ice thickness measuring programme in the Arctic, ‘IceBird’, and trace the origins of the unusually thin sea ice that they observed from the research aeroplane in the northern Fram Strait in summer 2016. At that time, the ice was just 100 centimetres thick, making it 30 percent thinner than in the previous year – a difference that the researchers were initially unable to explain. “To solve the puzzle, we first retraced the ice’s drift route with the help of satellite images. It originated in the Laptev Sea,” explains AWI sea-ice physicist Dr Jakob Belter. The experts then examined the weather along the route. However, the atmospheric data for the period 2014 to 2016 didn’t show any abnormalities.
That meant the answer had to lie in the ocean – and indeed: from January to May 2015, experts from the University of Alaska Fairbanks recorded unusually high temperatures in the waters north of the Laptev Sea. We now know that the heat rose from the depths with Atlantic water masses, and slowed the winter ice growth. “Using the satellite data, we were able to show that the thin ice that we sampled in Fram Strait in July 2016 had previously passed through this unusually warm area off the Russian continental shelf,” says Belter. Furthermore, the ocean heat wave must have been so extreme that its effects on the growth in sea-ice thickness couldn’t be compensated for during its drift across the Arctic Ocean.

The conclusions from the paper itself include:
Further investigations and measurements are required to monitor the development of Atlantification in the eastern marginal ice zones. But in order to strengthen our conclusion that Atlantification is able to precondition sea ice and that this preconditioning persists far beyond the eastern Arctic, additional uninterrupted SIT time series are vital along the pathways and at the exit gates of Arctic sea ice. The presented summer SIT time series at the end of the Transpolar Drift is an important effort to establish long-term and large-scale measurements of SIT, especially during the melt season. Airborne EM measurements of SIT during IceBird campaigns provide the necessary accuracy and areal coverage that is unmatched by any other non-satellite SIT measurement approach. Russian shipborne SIT measurements show significant differences to EM-based measurements, but their regularity and spatial consistency enable the depiction of regime shifts in SIT that are hardly resolved by the presented EM SIT time series. Obtaining SIT distributions over large areas and developing and continuing long-term SIT time series will provide unique input data for modelling efforts and ultimately will improve predictions of Arctic sea ice and its thickness in the future.
Getting back to the conclusion of the press release:
The two new studies highlight the importance of long-term datasets for sea-ice research in the Arctic. “If we are to understand the changes in the Arctic sea ice, long-term observations of ice thickness using satellites and aircraft are vital. Combined with modelling data they provide an overall picture that is sufficiently detailed to allow us to identify the key processes in the changing Arctic,” explains Jakob Belter.