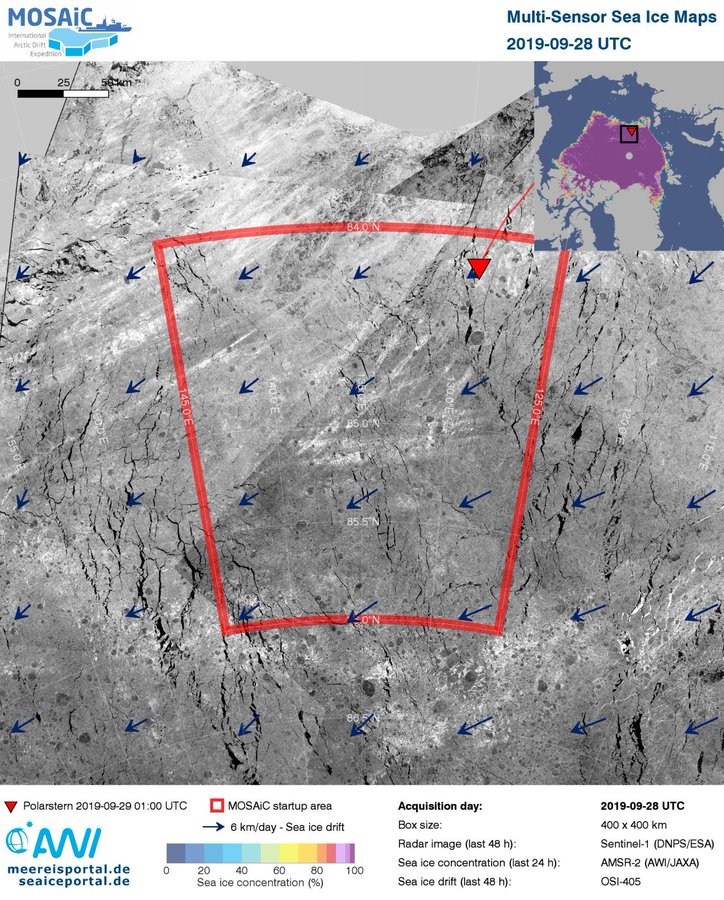
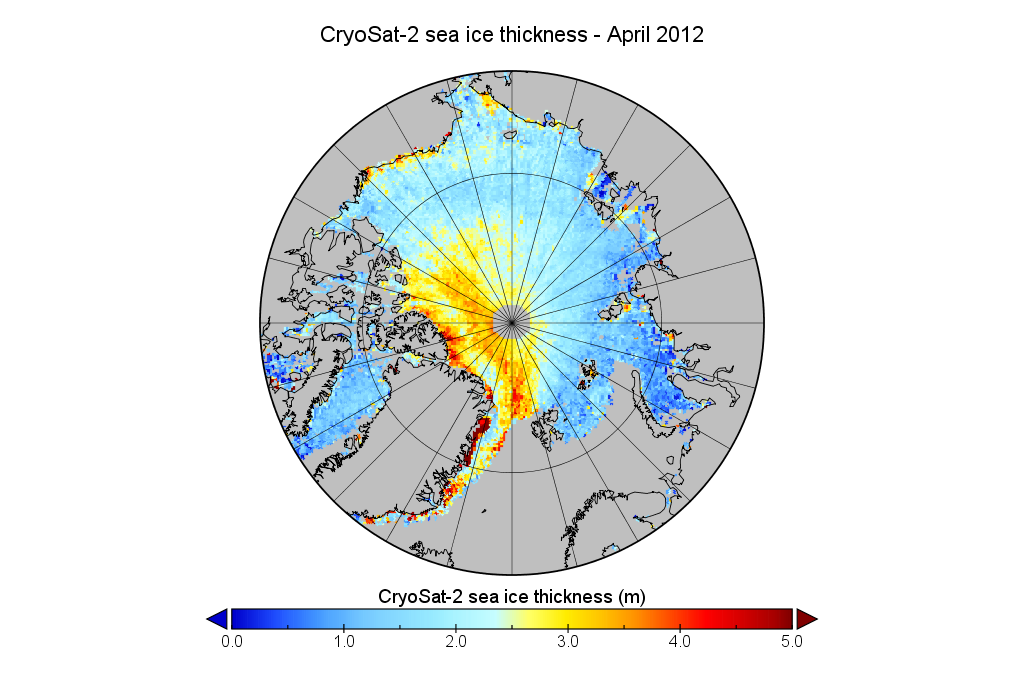
In the absence of the usual mid month PIOMAS Arctic sea ice volume update I’m being moaned at by “angech” over on Judith Curry’s “Climate Etc.” blog:
Any ideas on why PIOMAS mid month update not out, other than not wanting to show a big recovery?
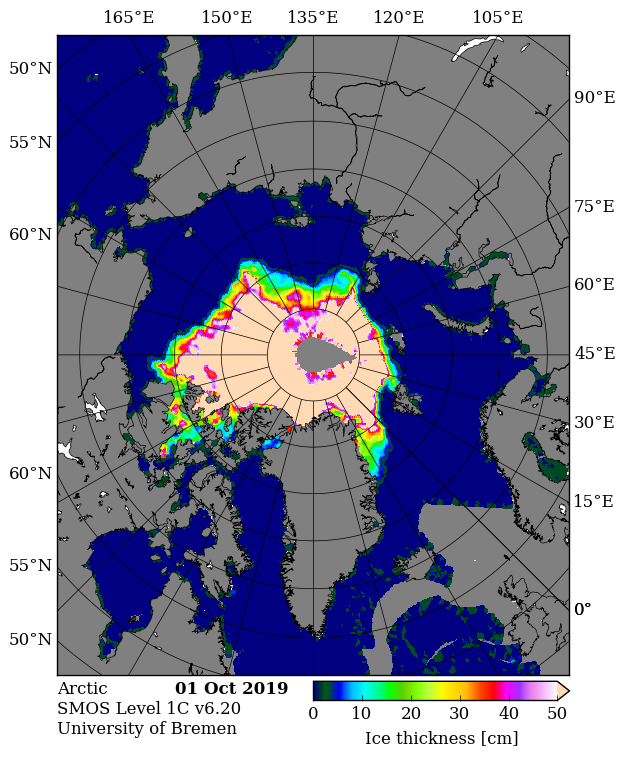
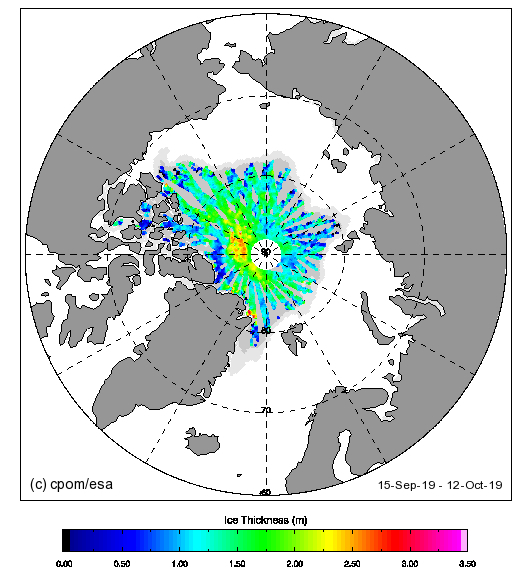
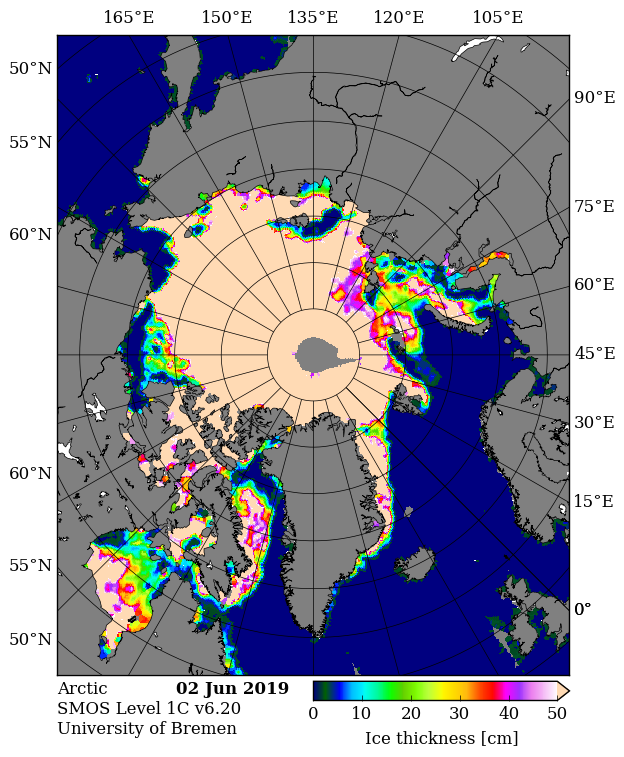
Unlike any of Judy’s denizens I checked out the comparatively new merged CryoSat-2 plus SMOS thickness maps from the Alfred Wegener Institute. “Measured” rather than “modelled” data must be a good thing surely?
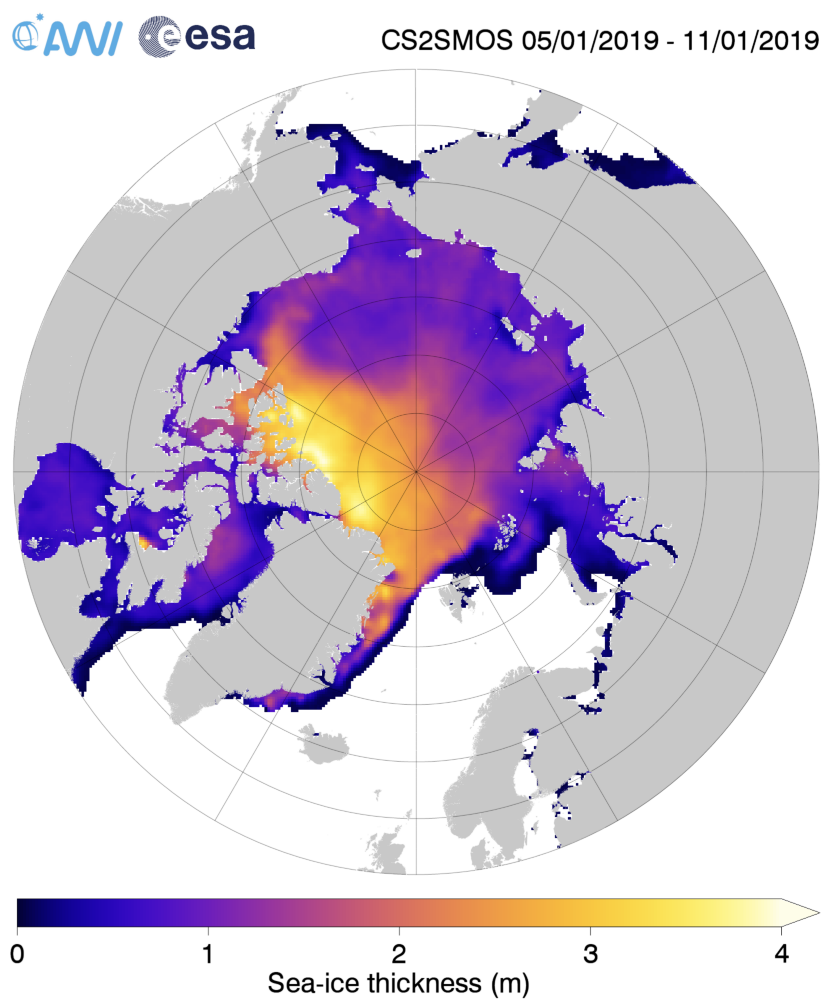
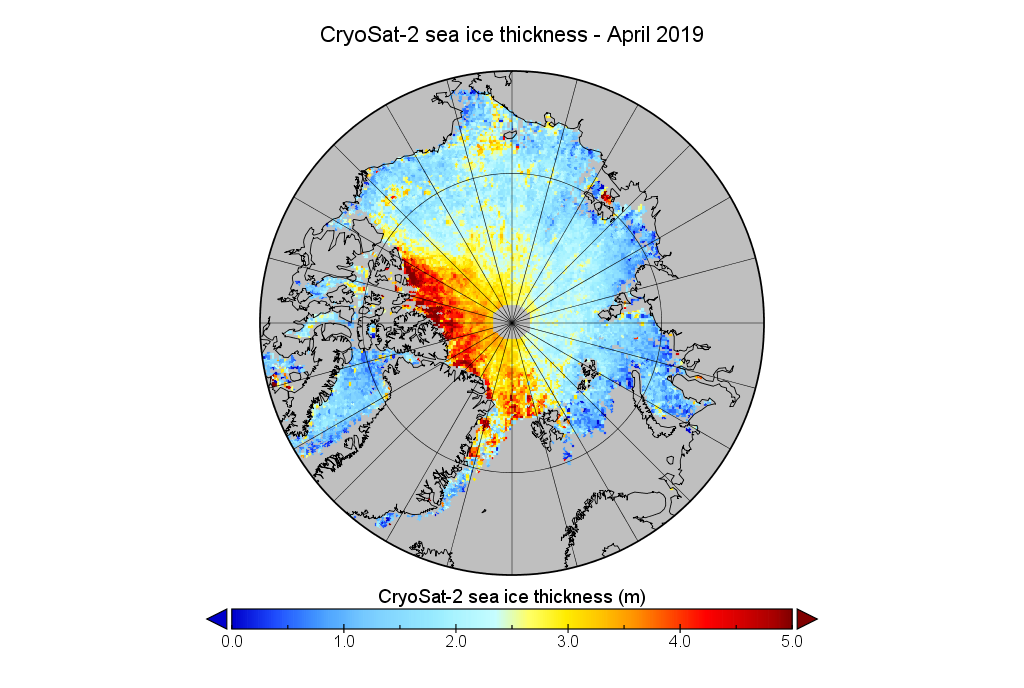
Just in case there’s some significant difference between the “reanalysis” and “operational” versions of that product, here is the AWI’s most recent reanalysed Arctic sea ice thickness map, for the week ending January 11th: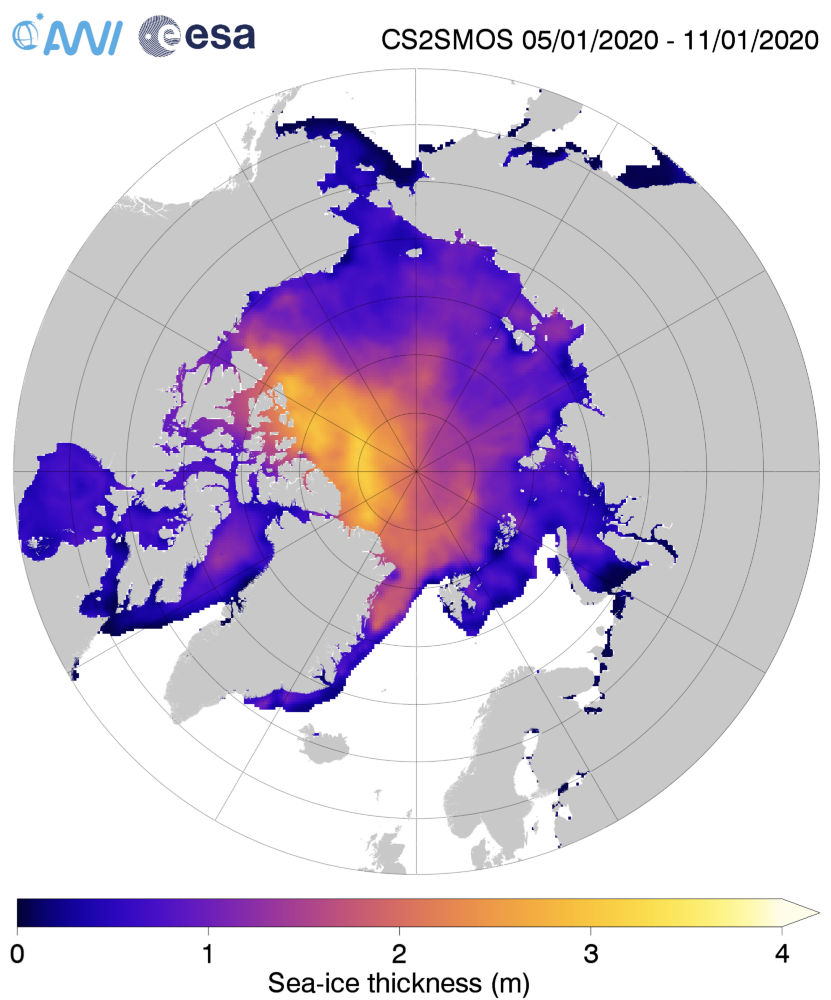
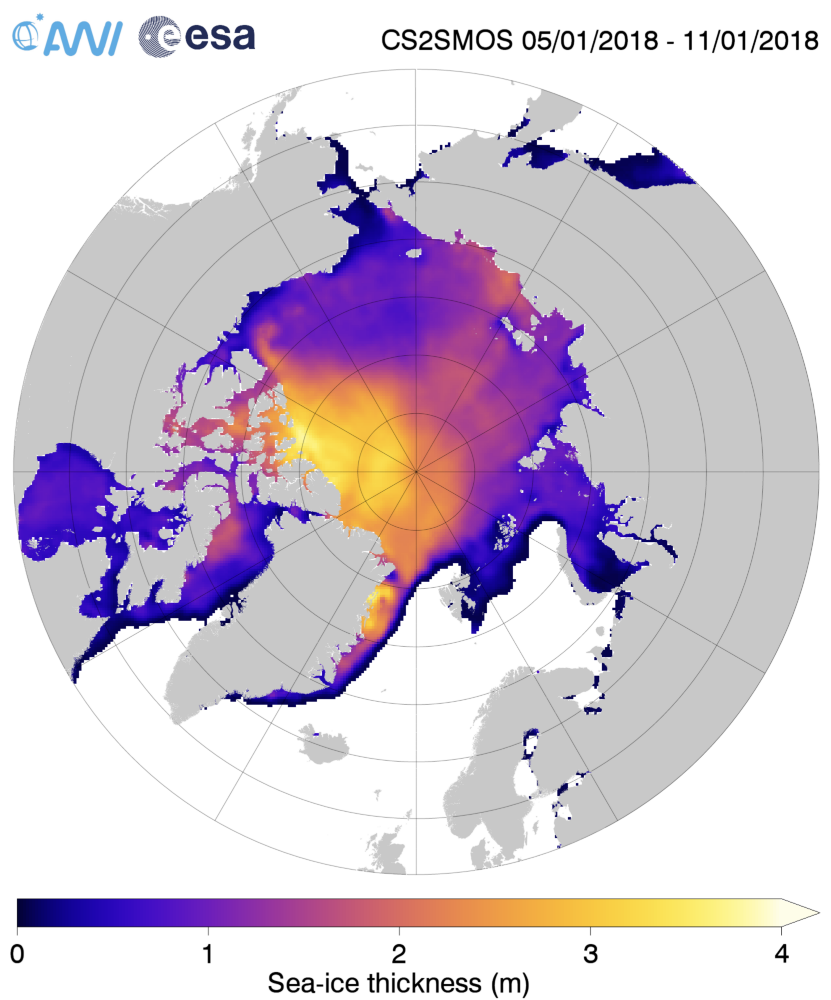
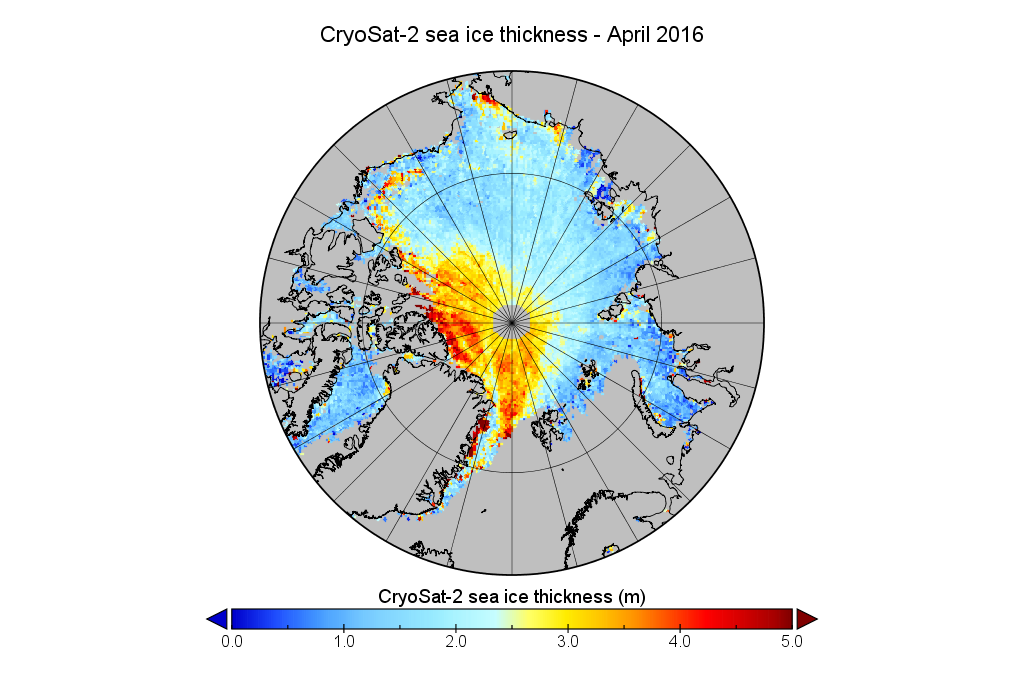
together with the same date from the previous two years:
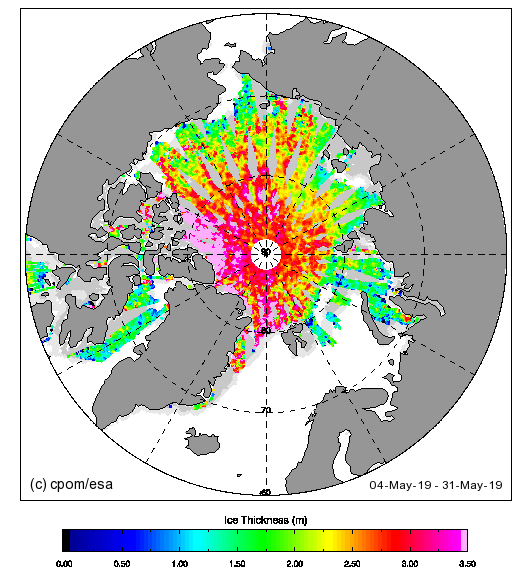
Make sure to take a close look at the white areas north of Greenland and the Canadian Arctic Archipelago showing sea ice over 4 metres thick.
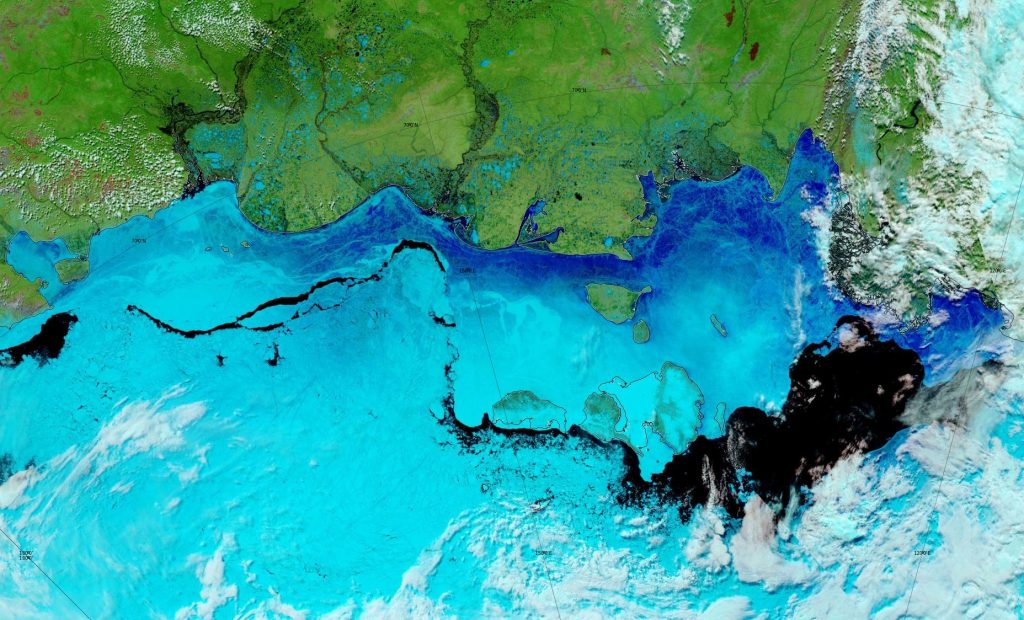
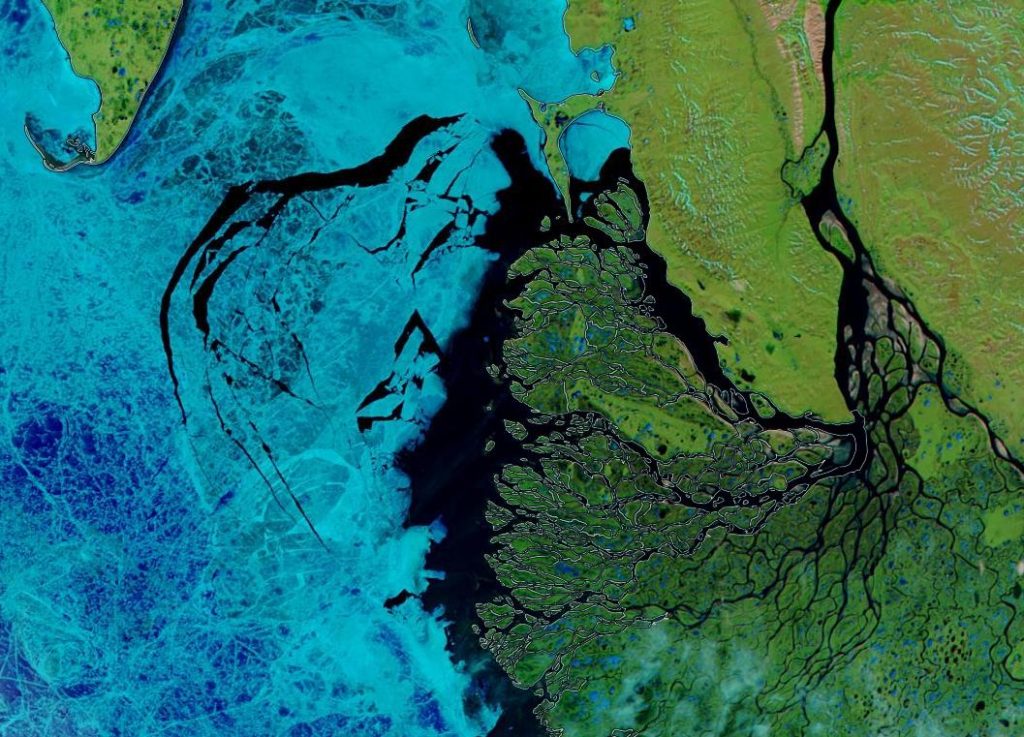
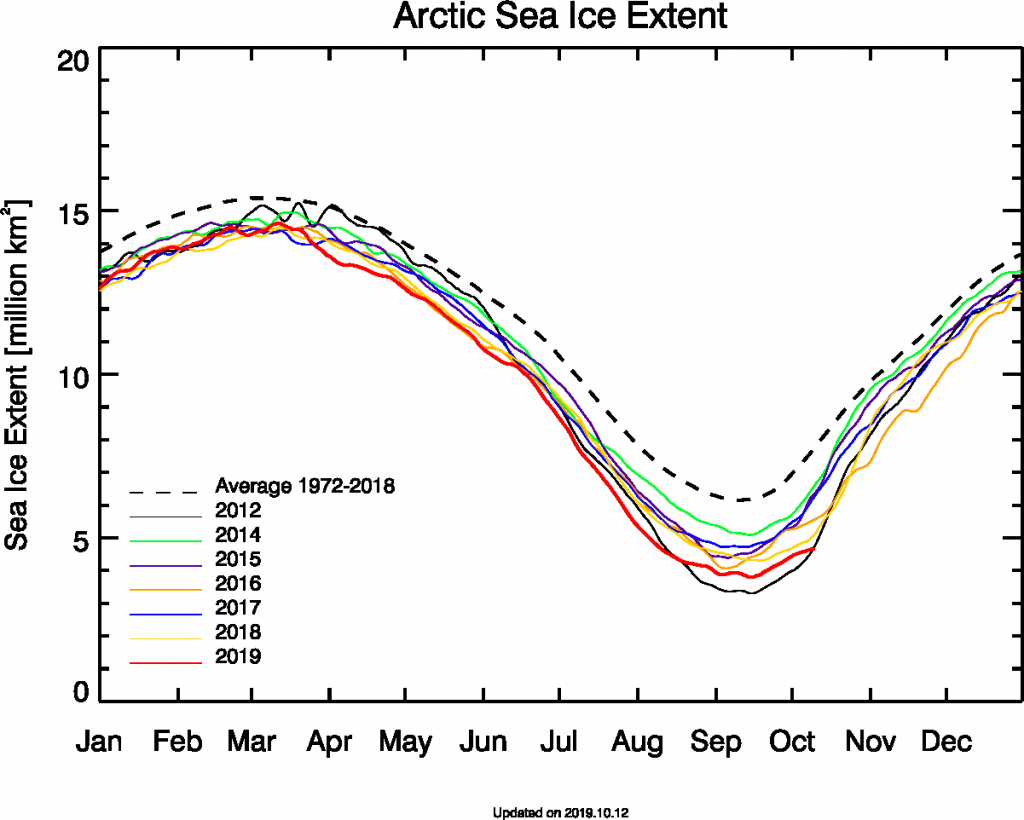
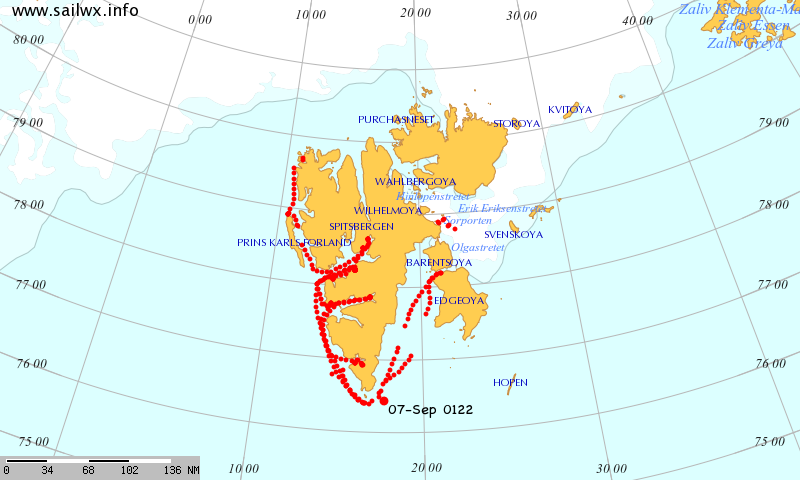
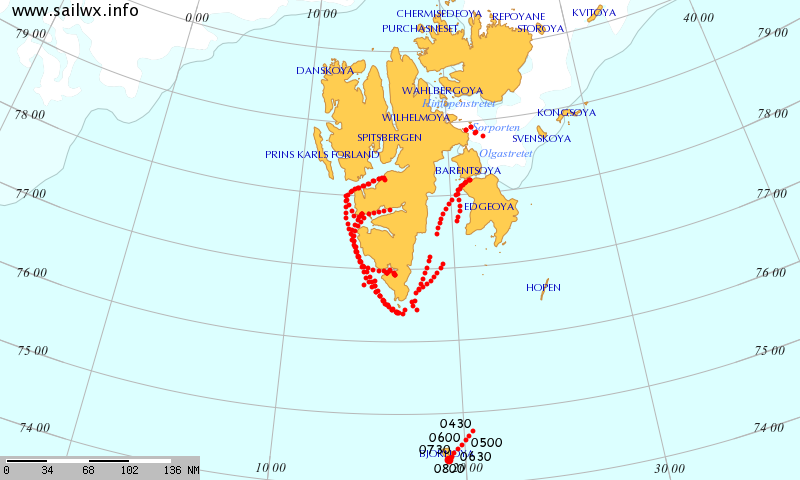
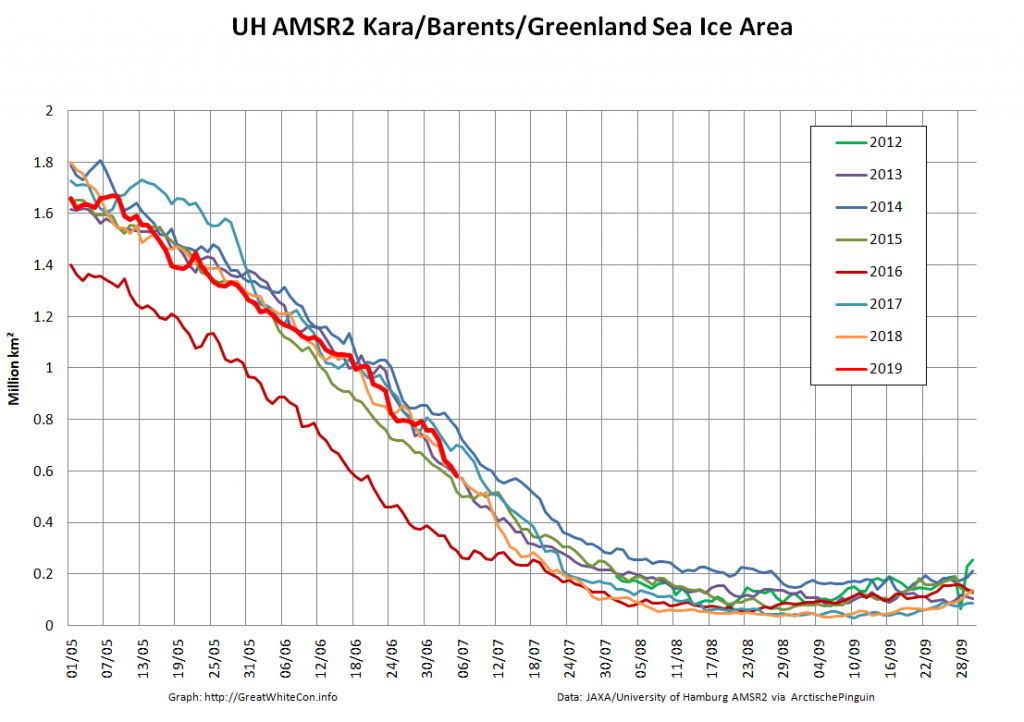
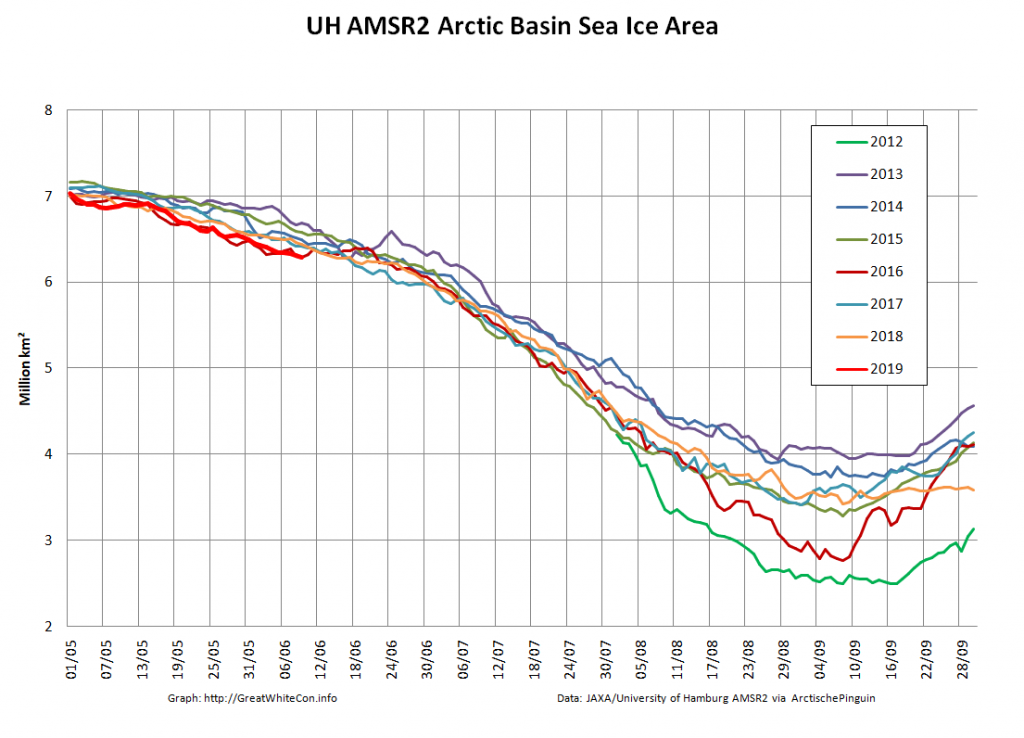
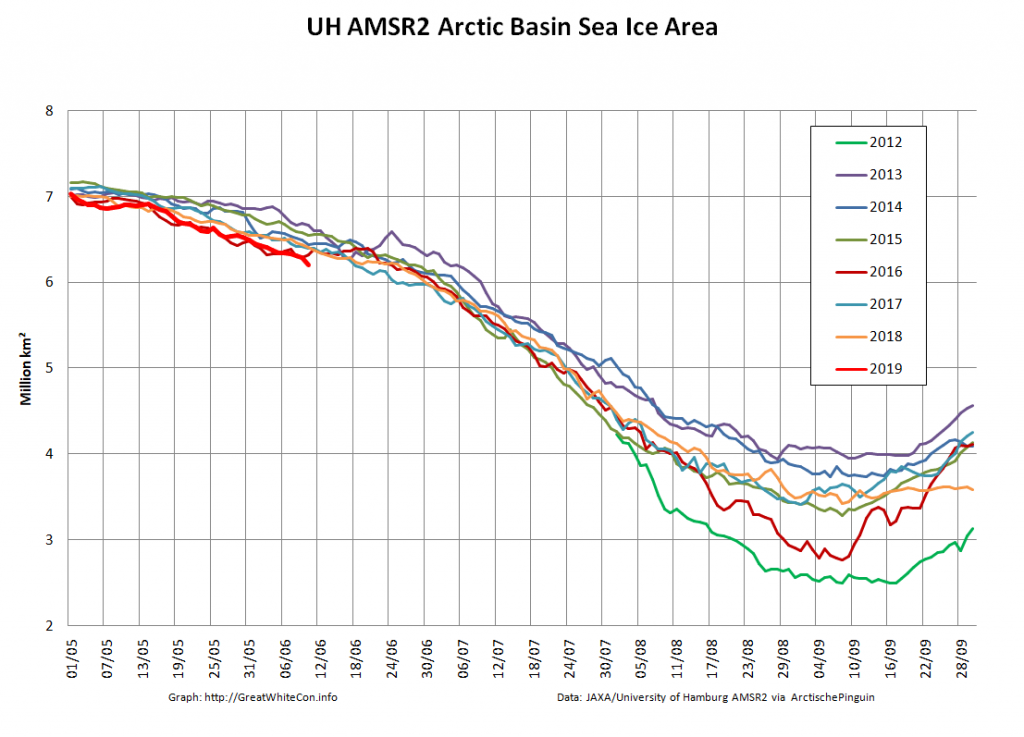
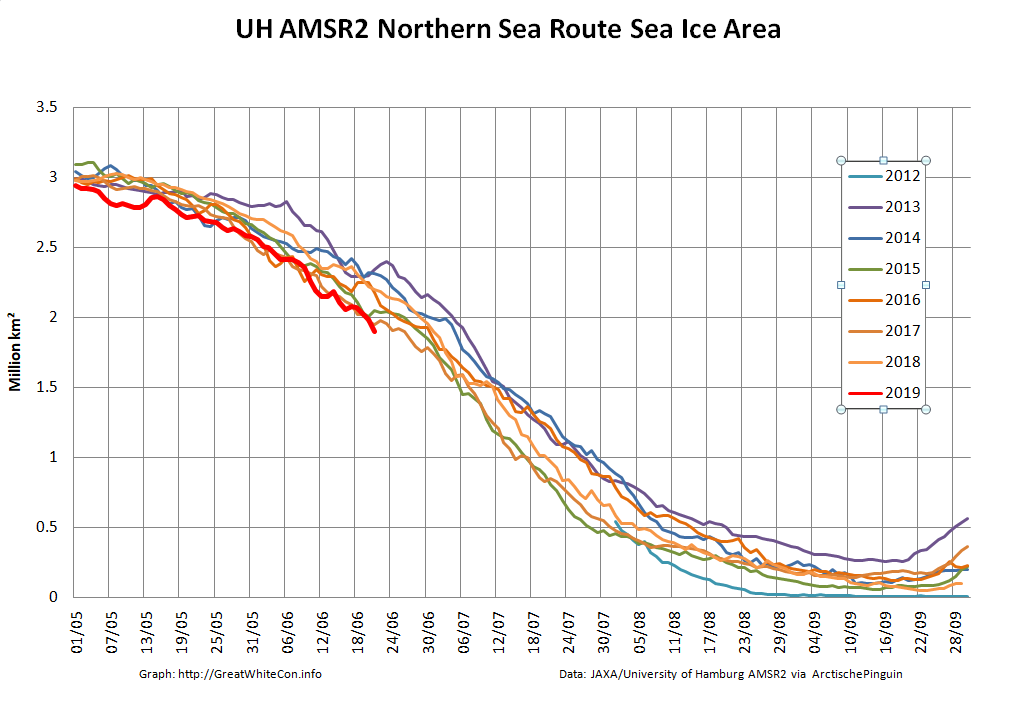
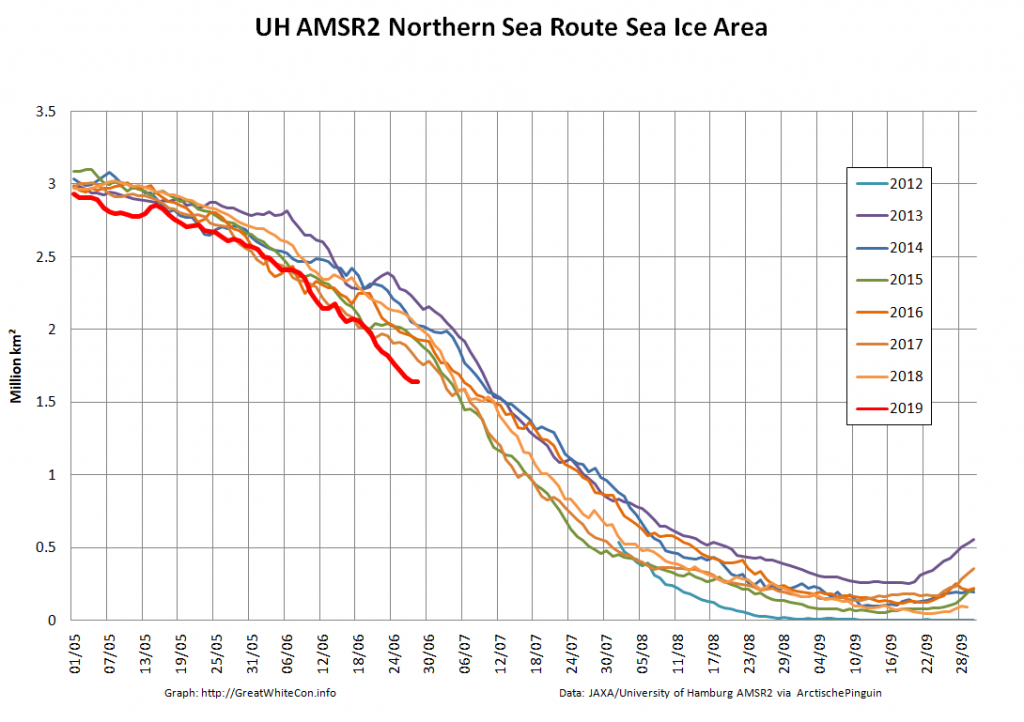
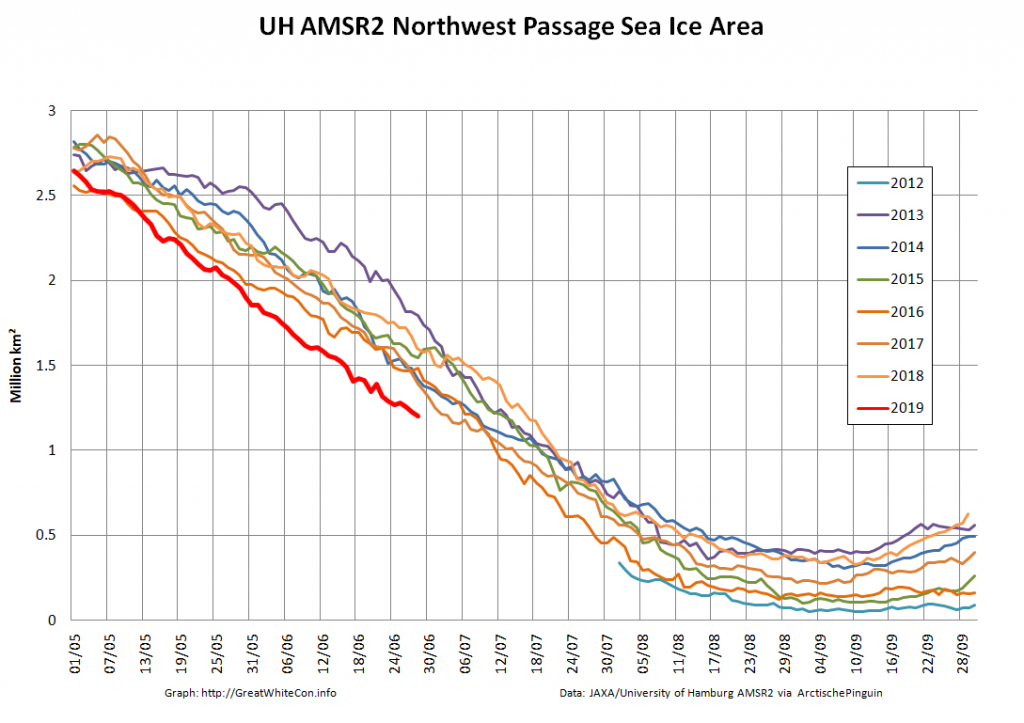
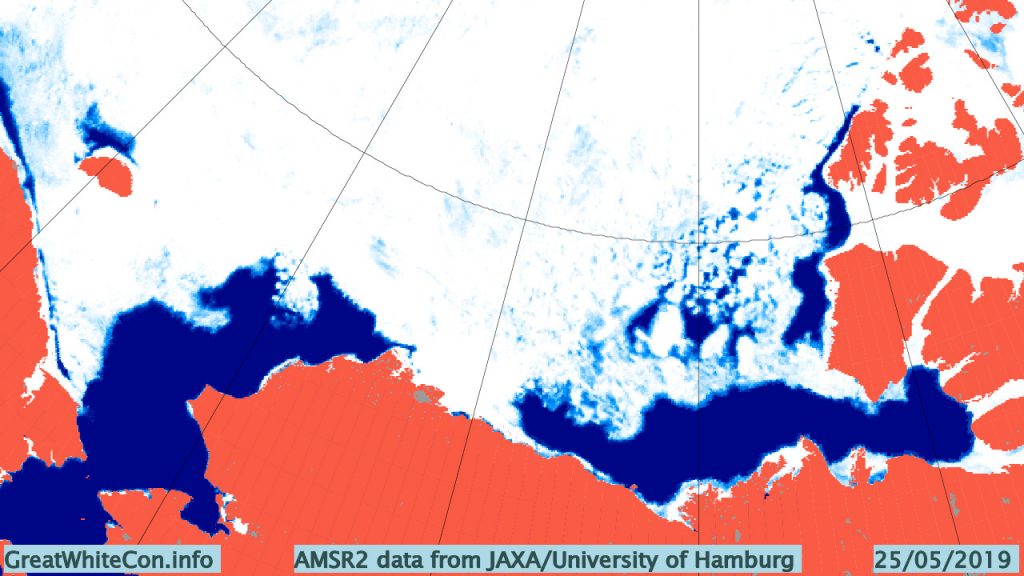
Over the winter of 2018/19 ASCAT revealed that there was a relentless movement of multi-year ice towards both the North Atlantic and the Beaufort Sea.
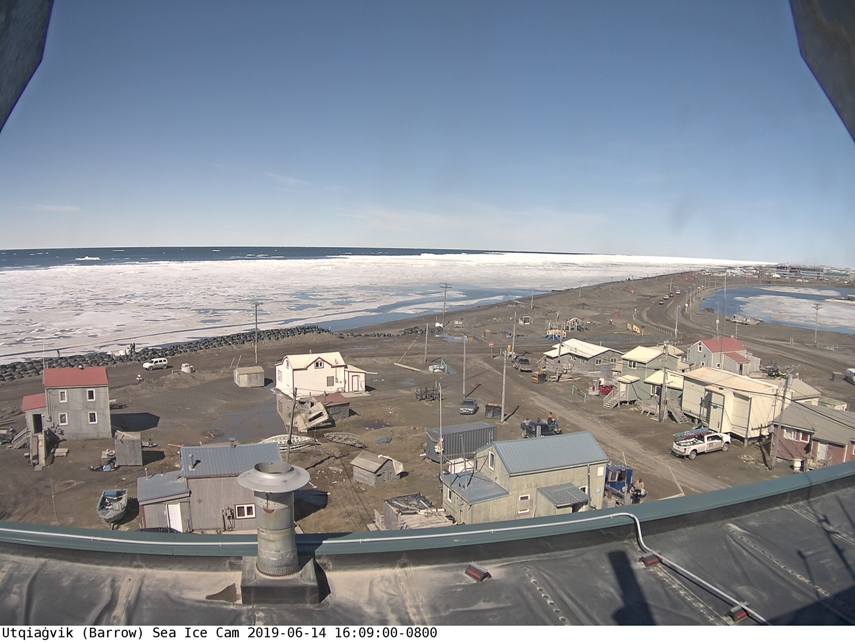
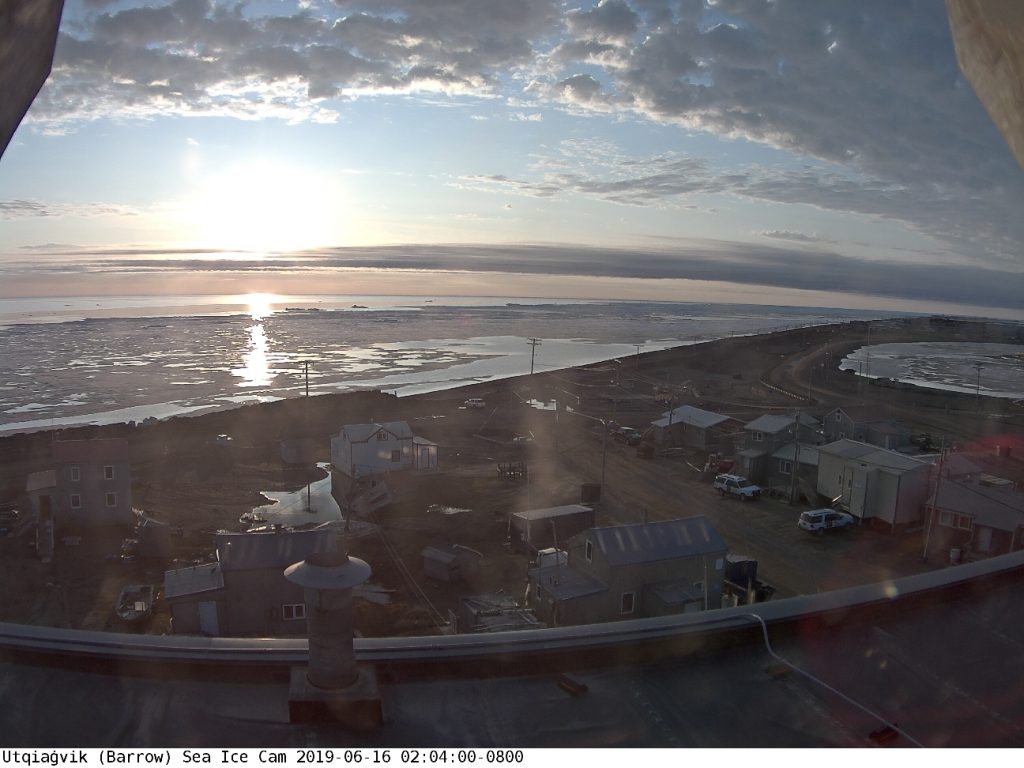
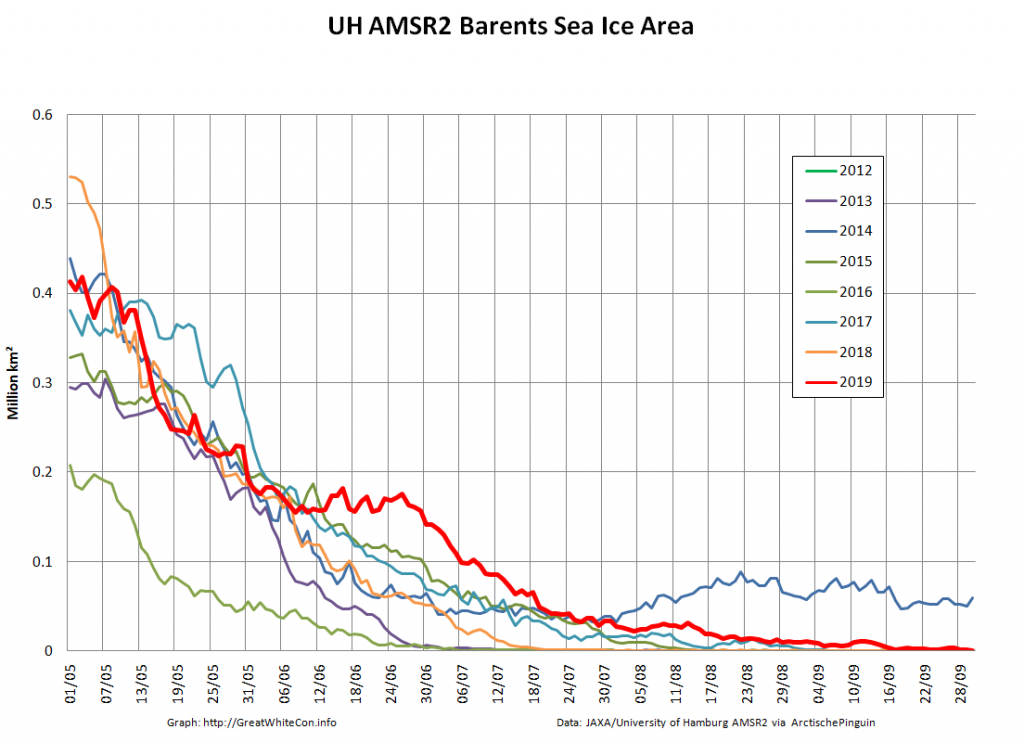
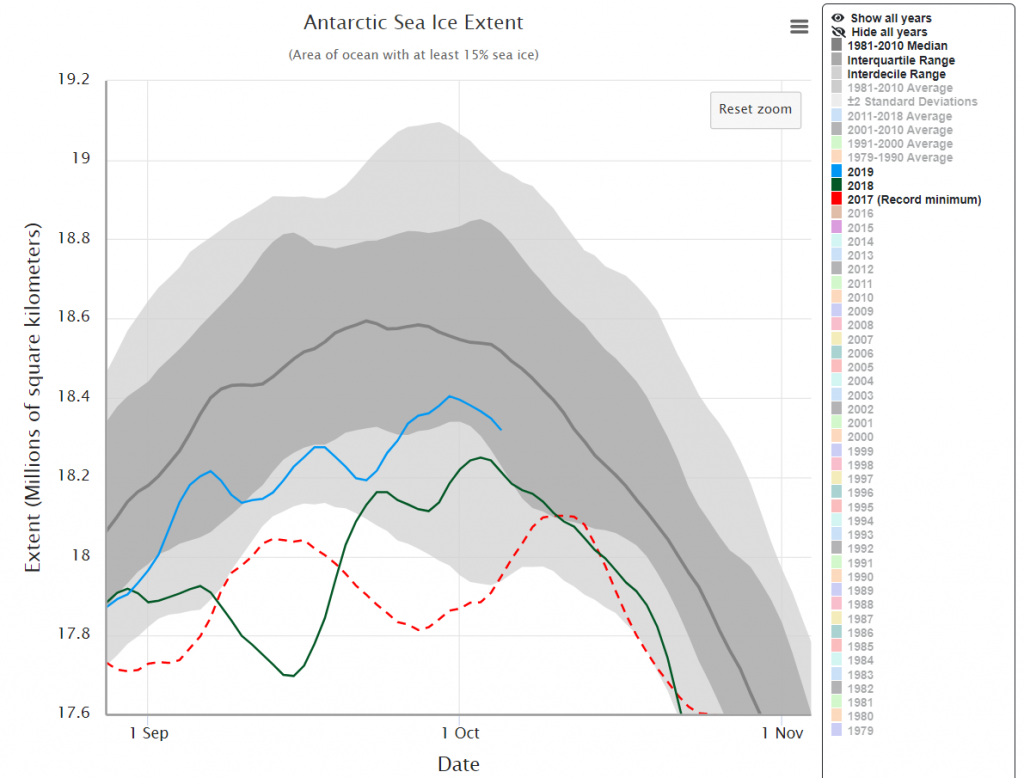
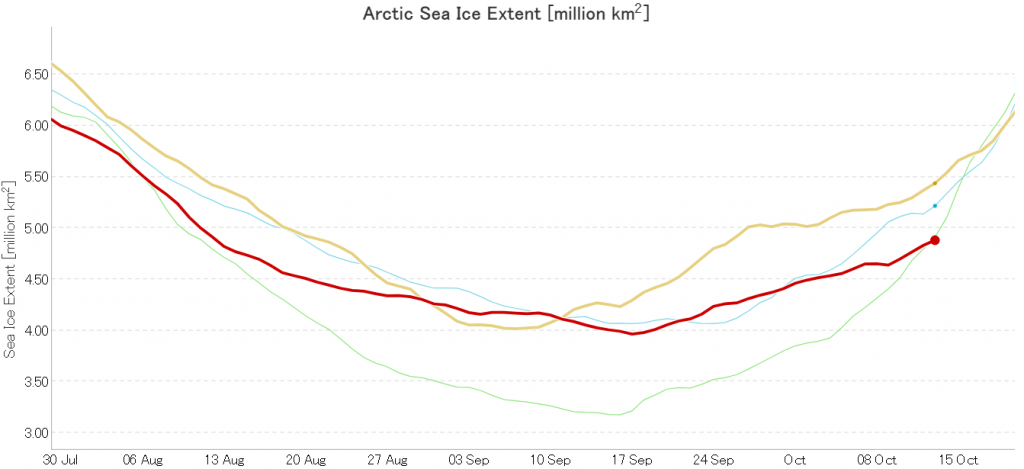
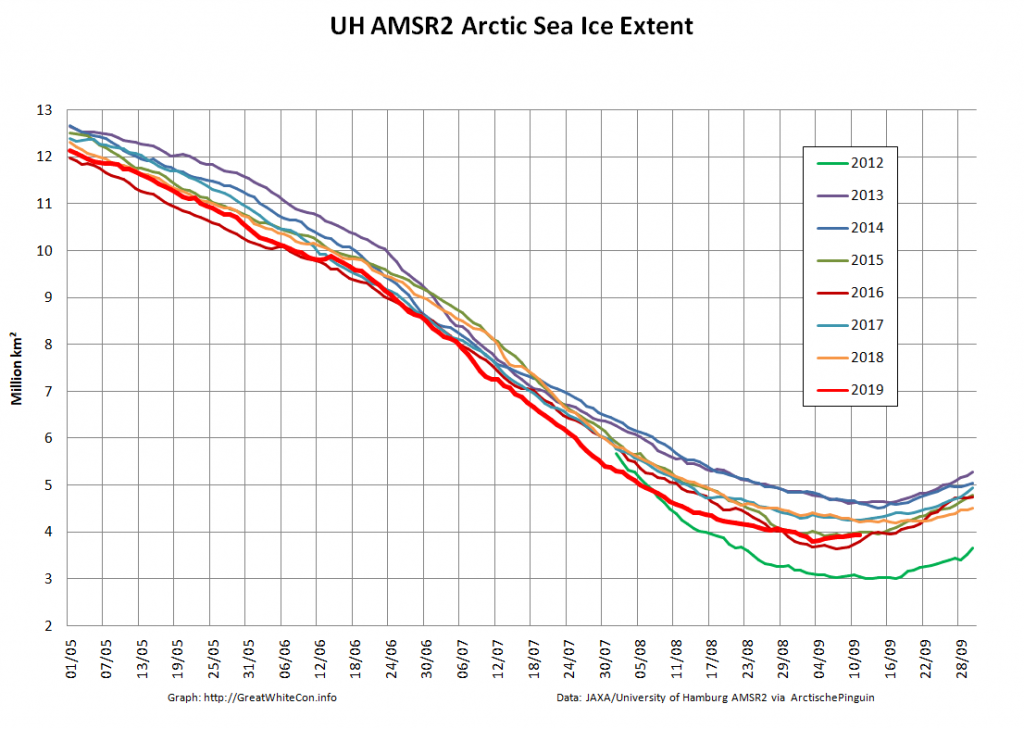
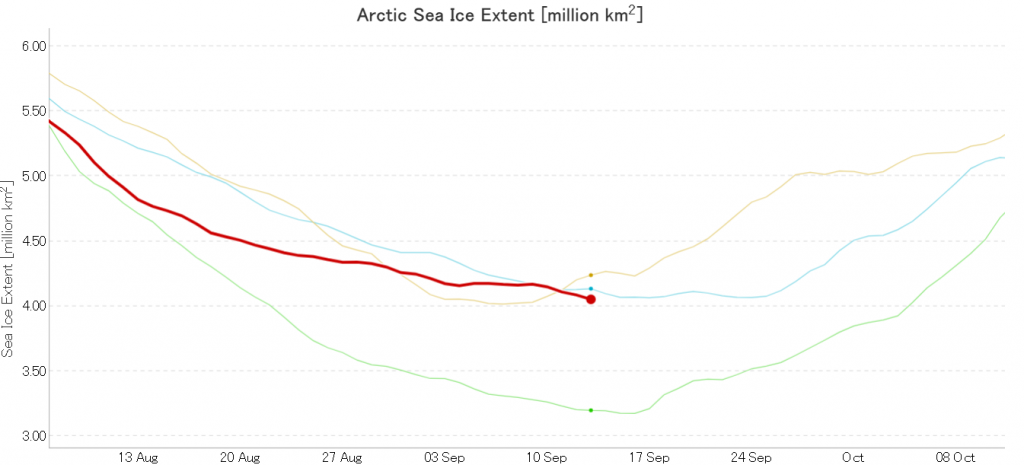
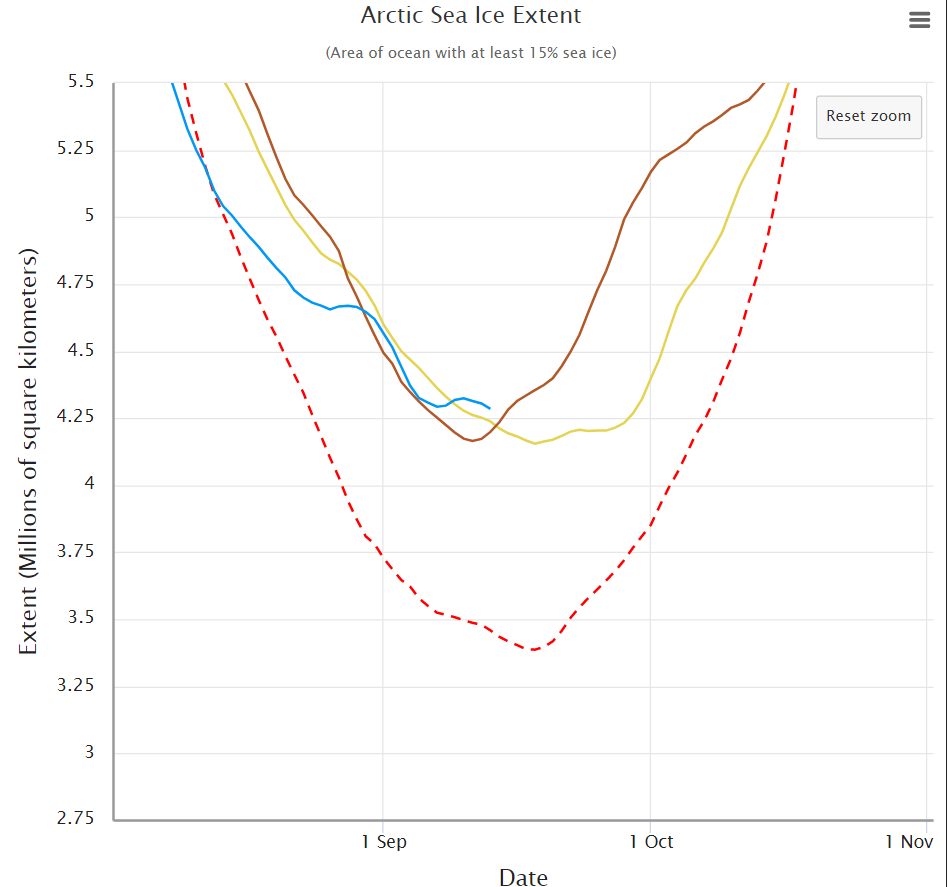
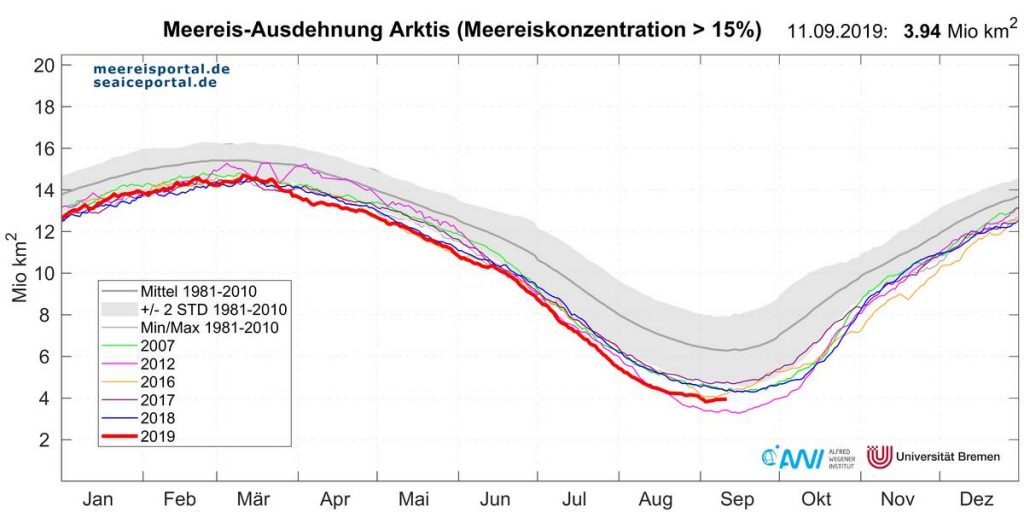
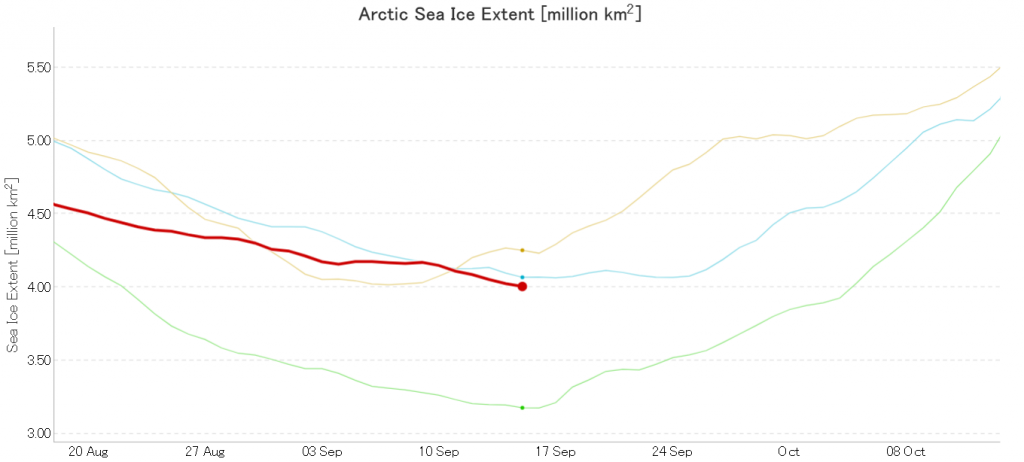
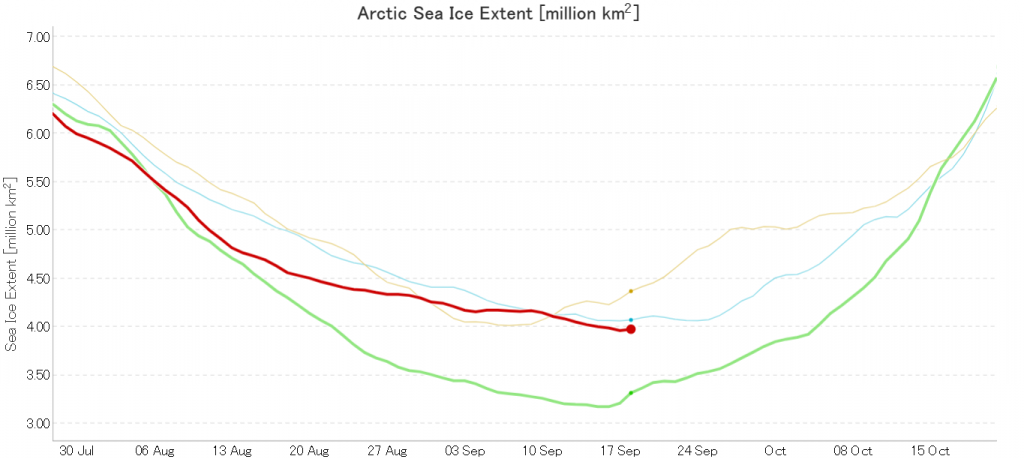
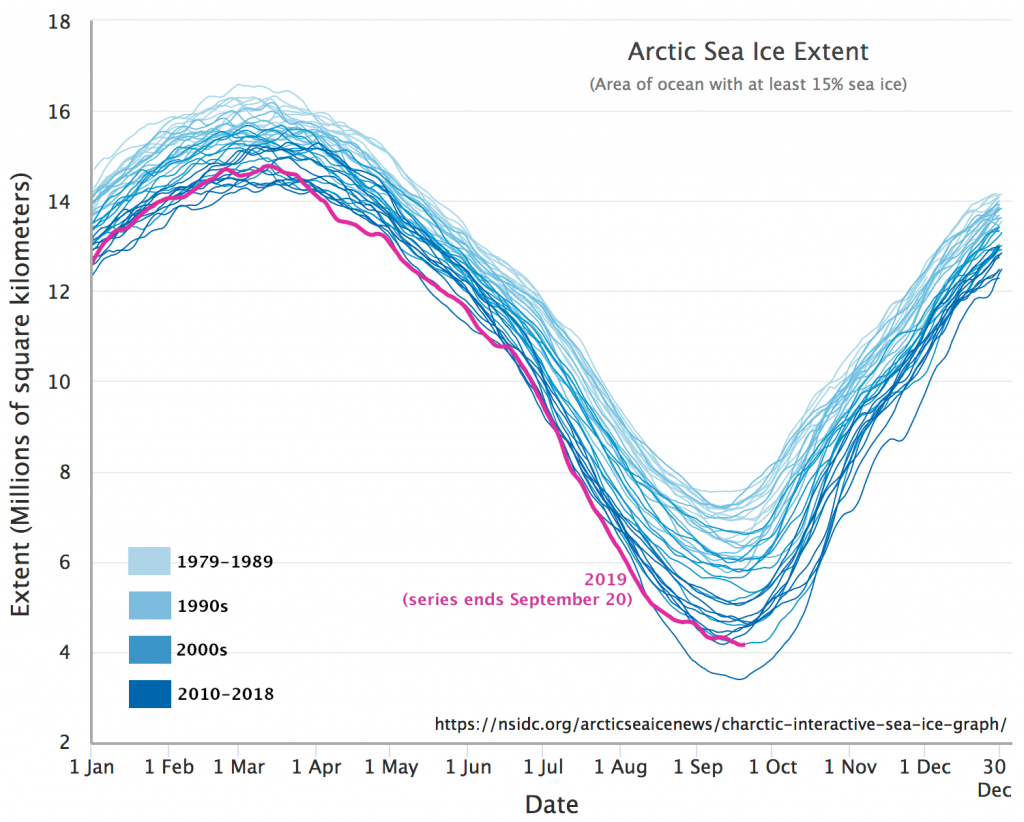
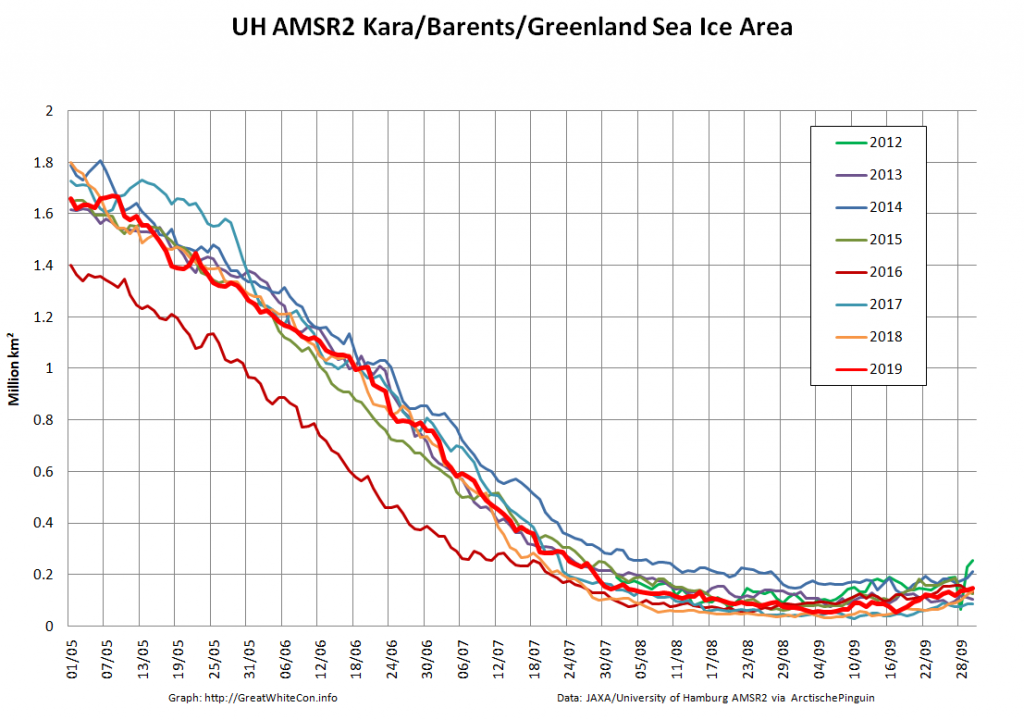
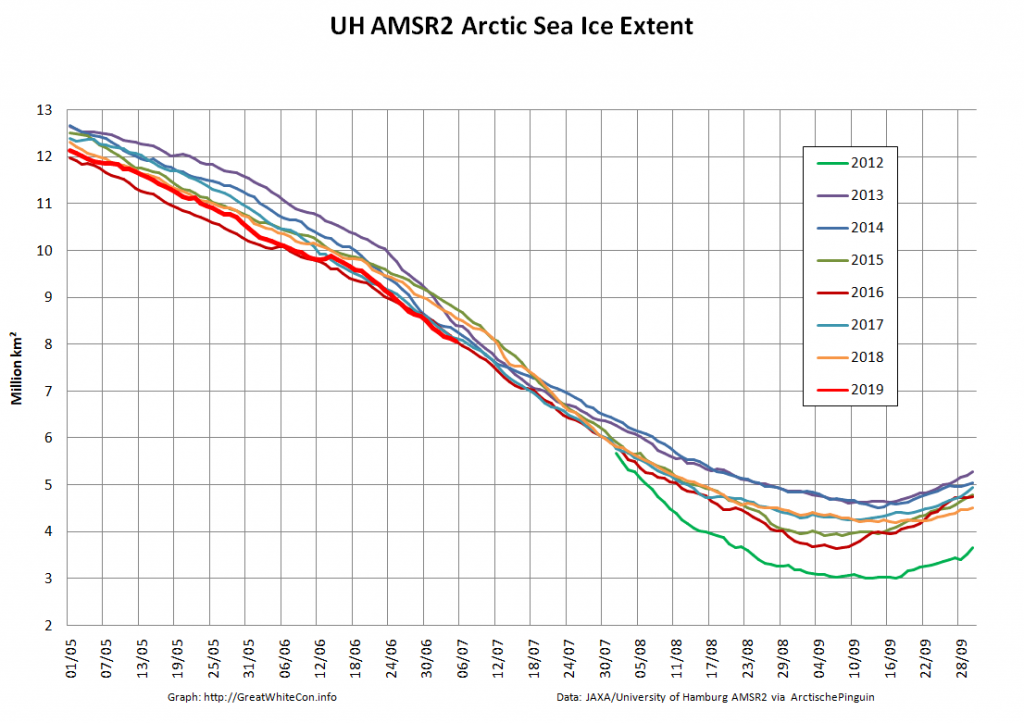
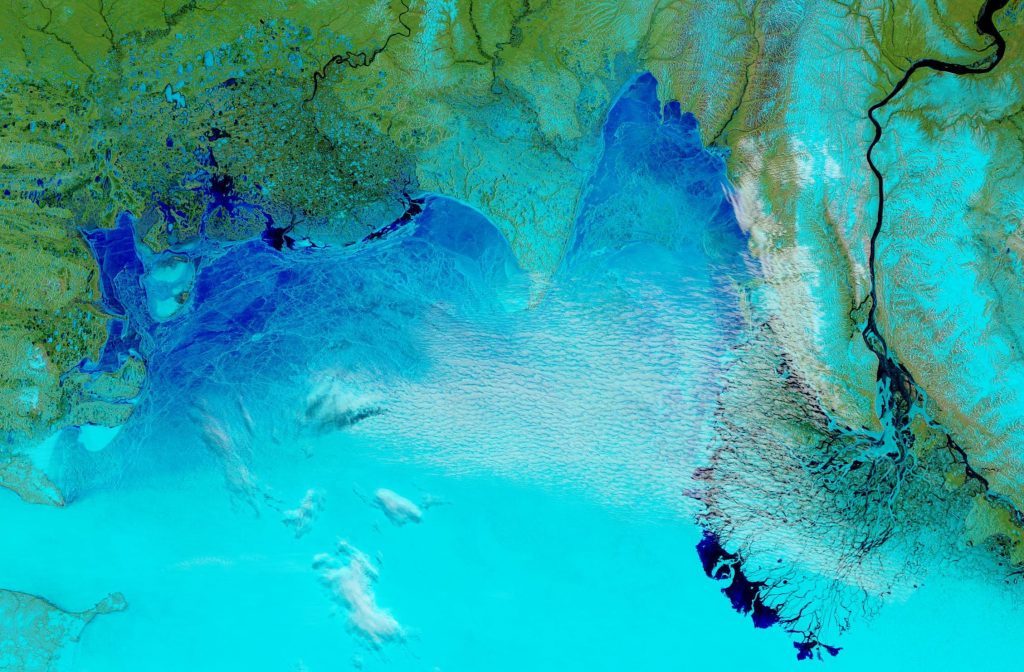
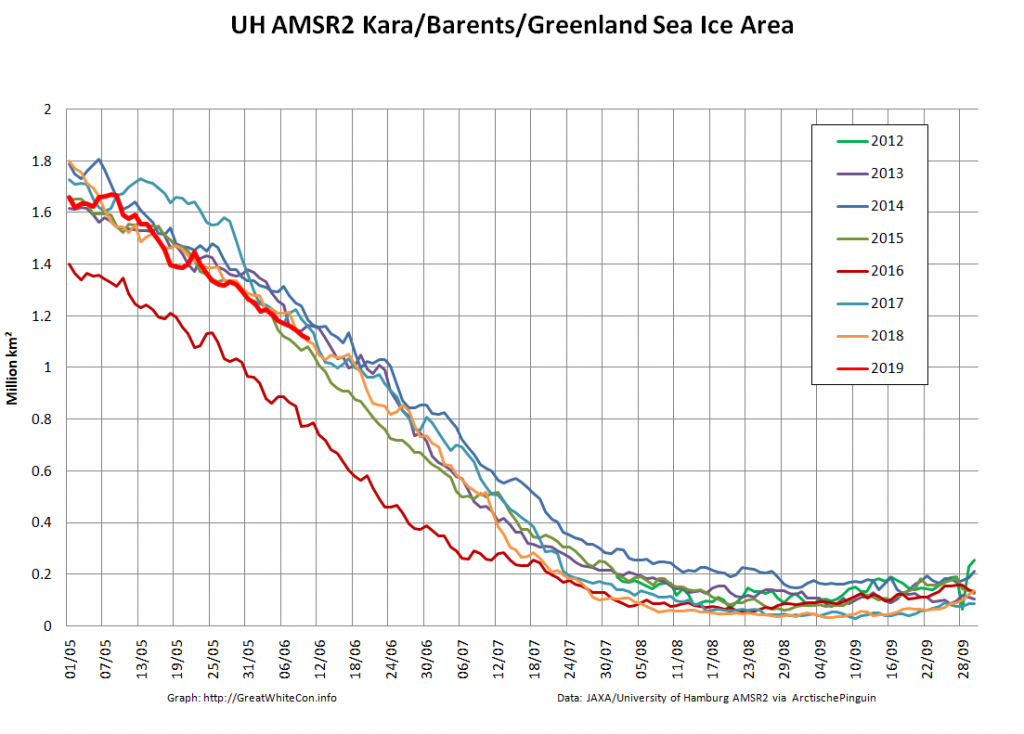
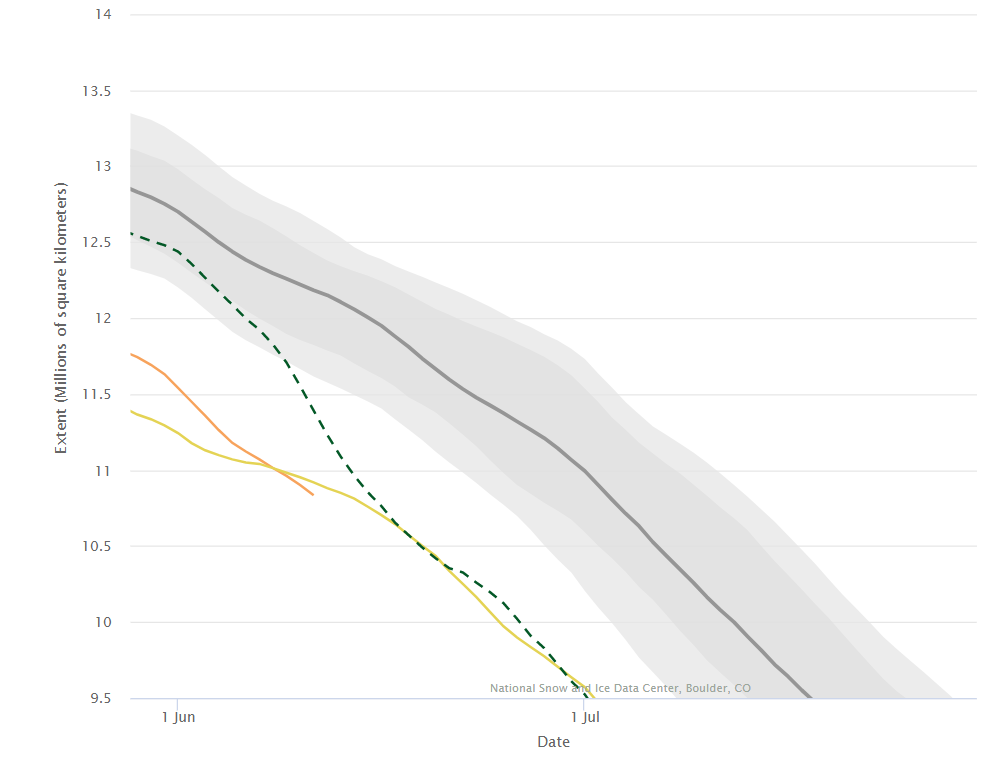
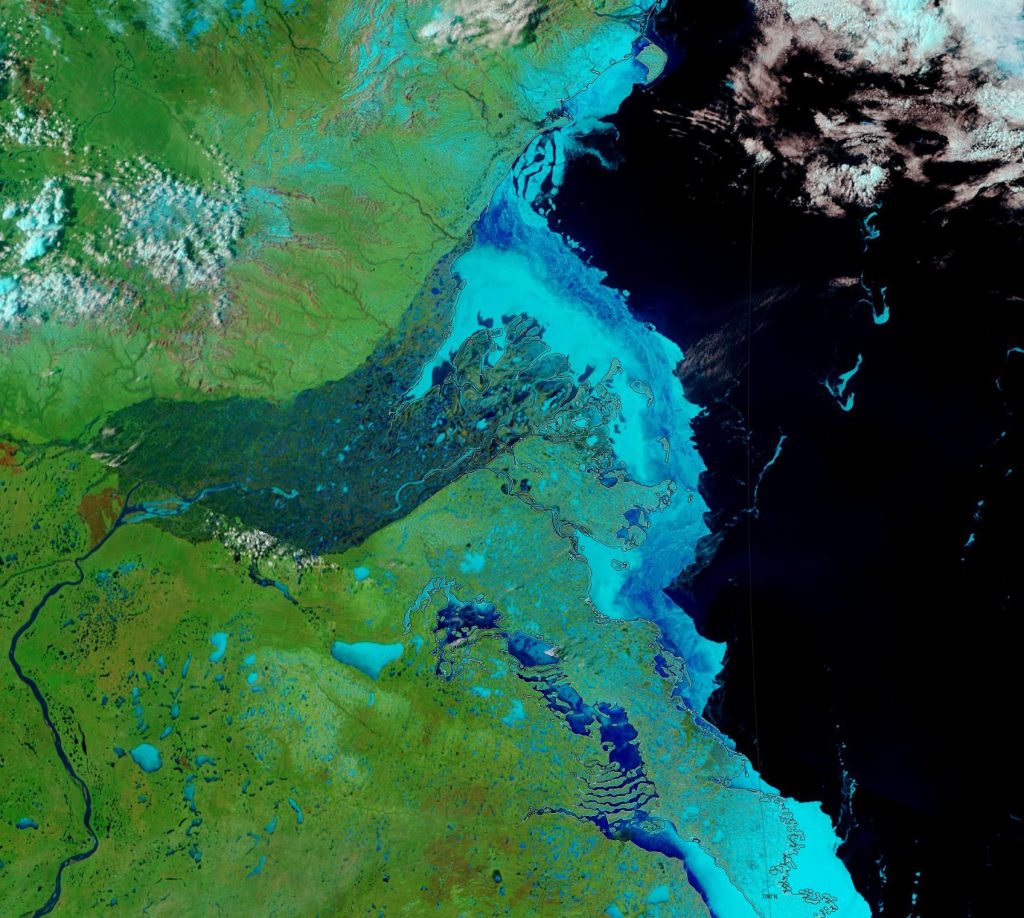
Not unexpectedly that meant that ice in the northern Barents Sea was slow to melt out in the summer of 2019:
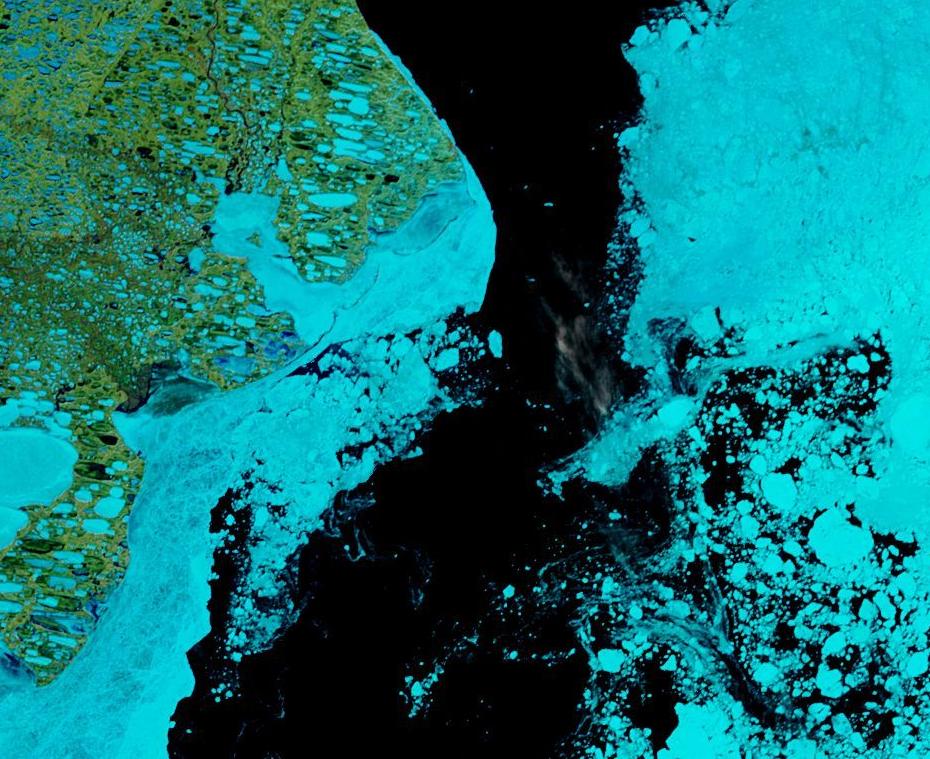
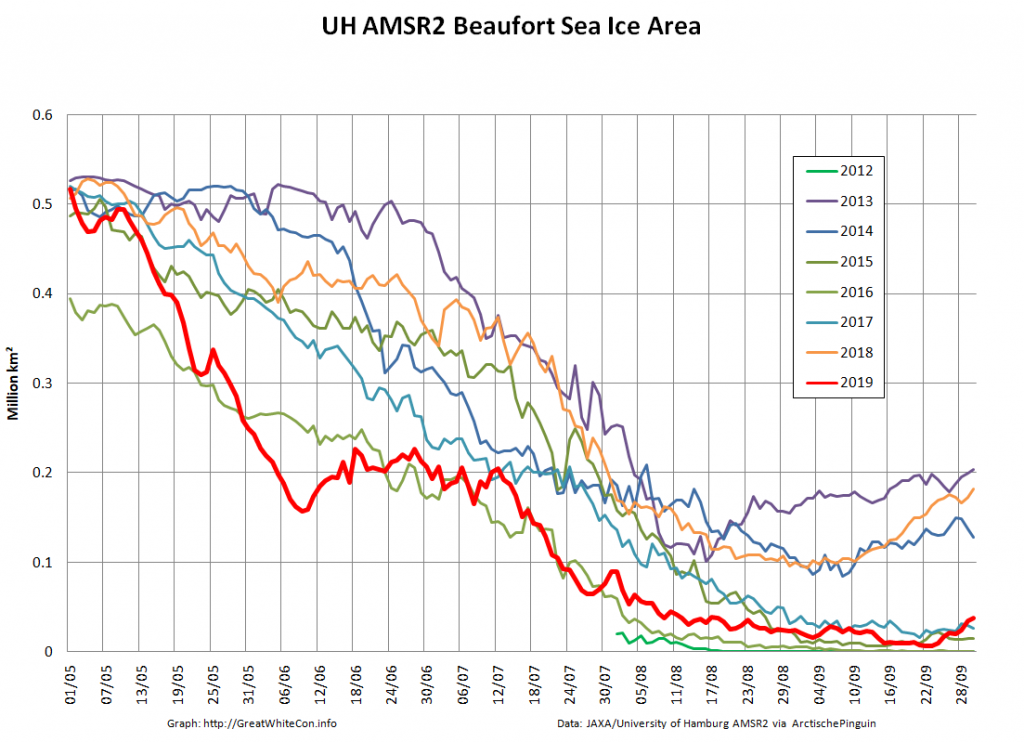
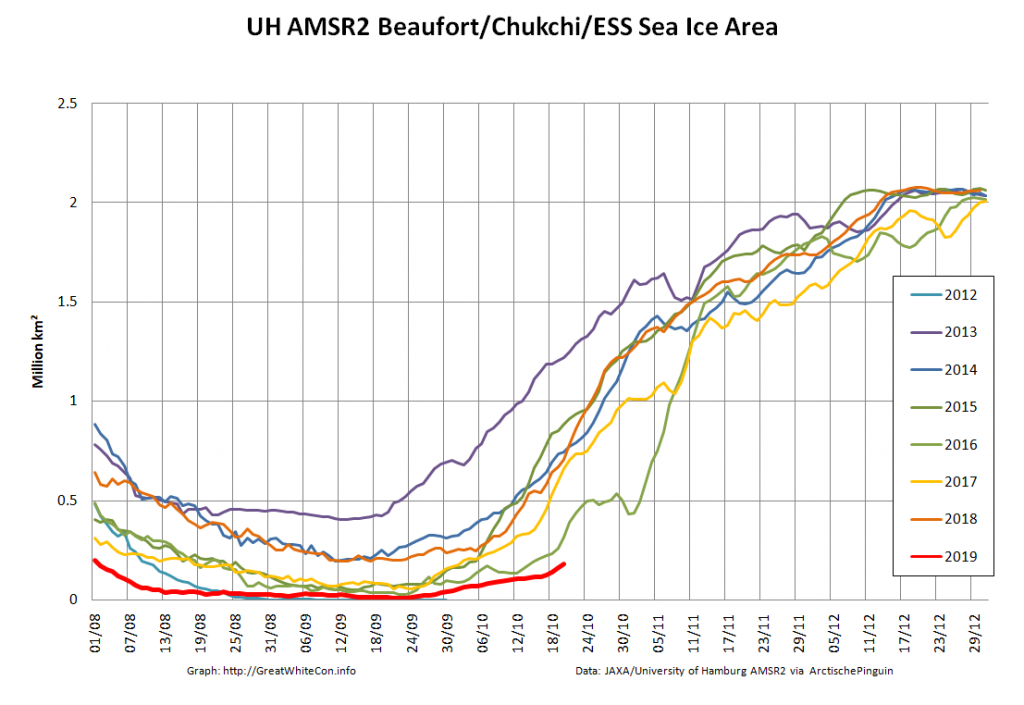
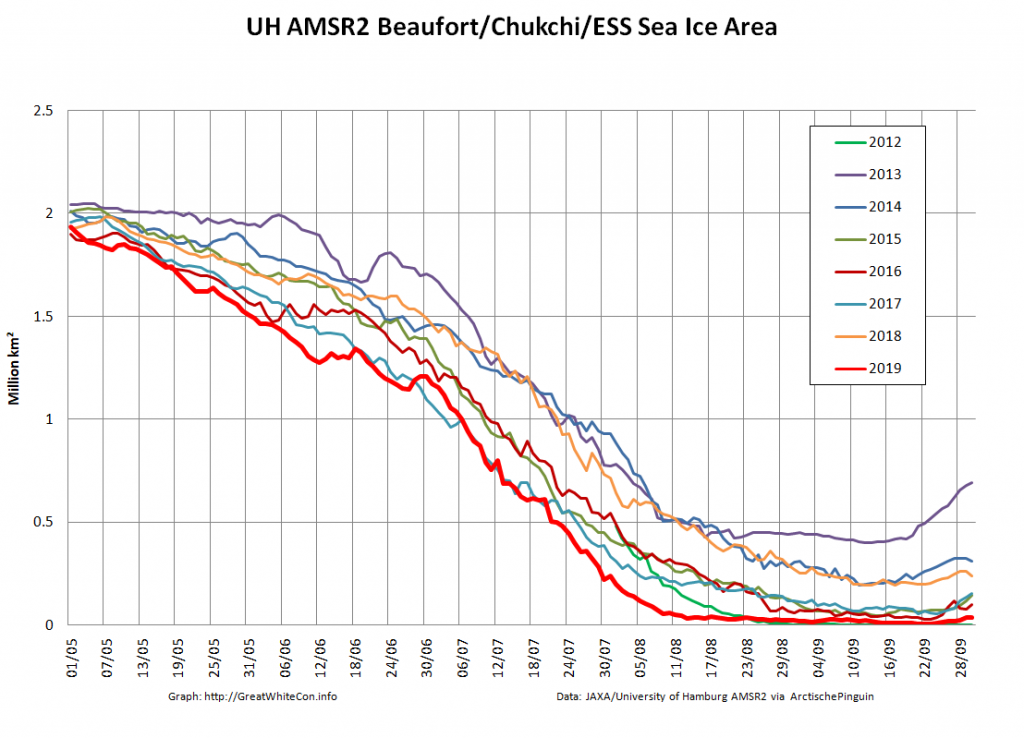
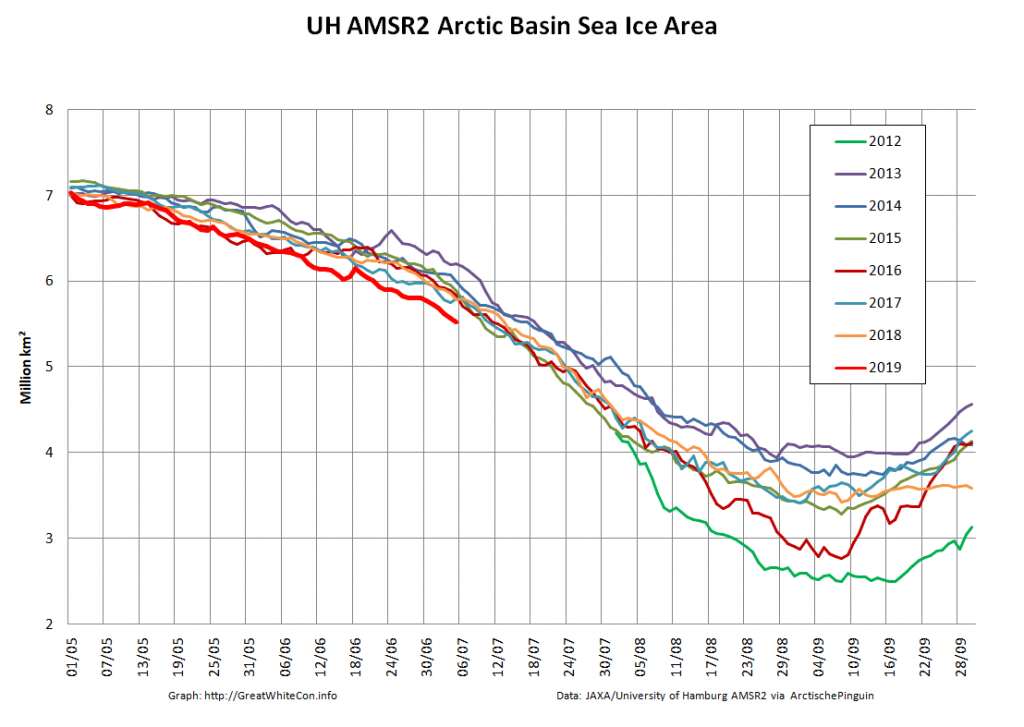
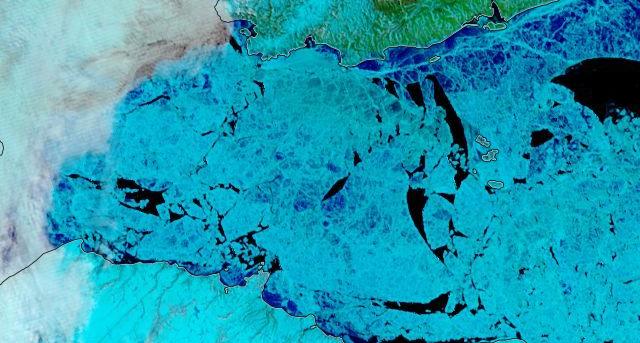
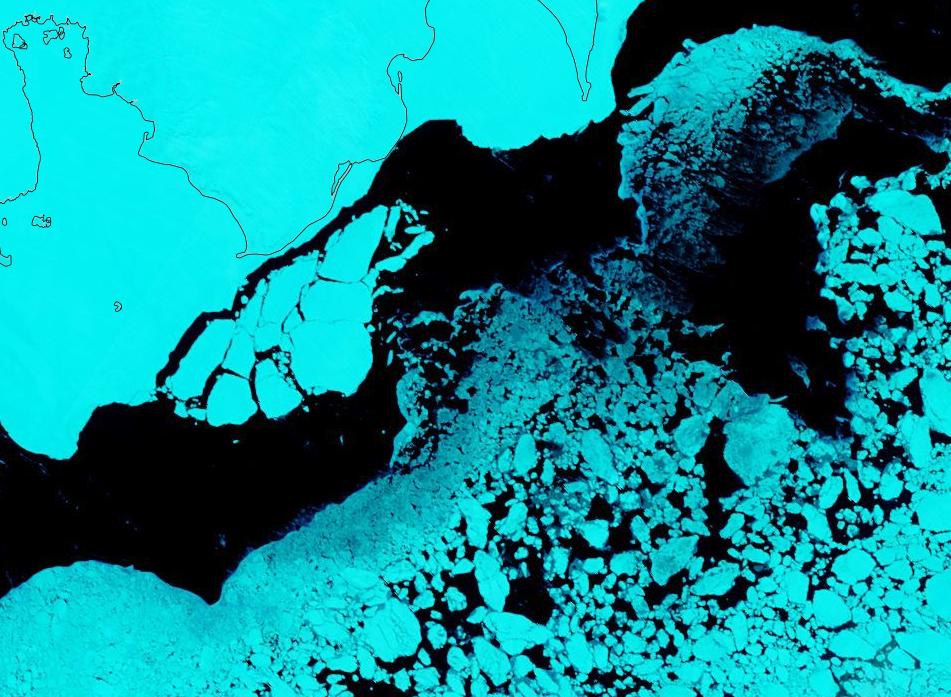
whilst after a fast start the melt in the Beaufort Sea also suffered a “brief hiatus” in June before ultimately melting out almost completely as well:
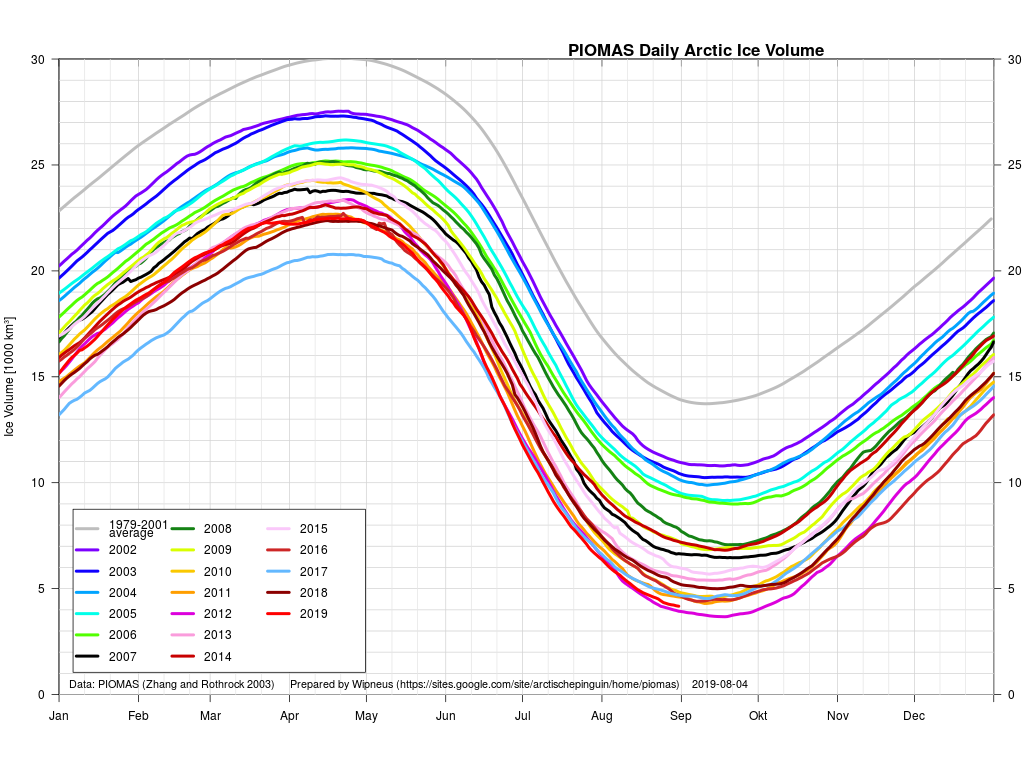
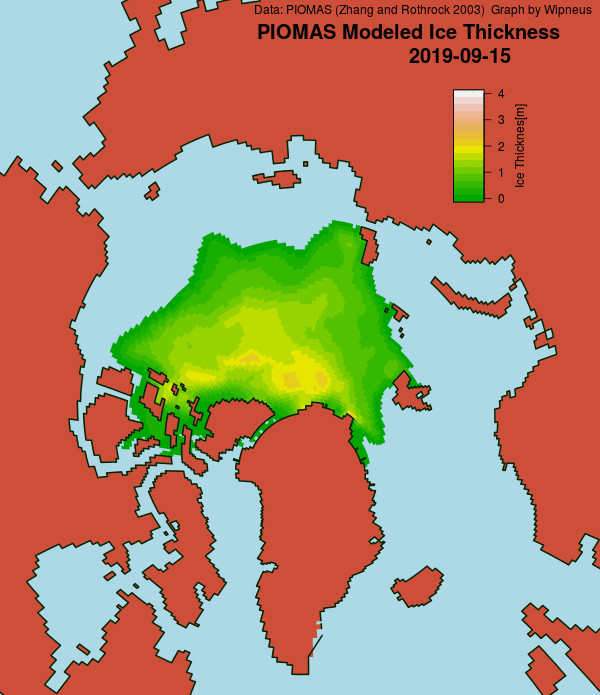
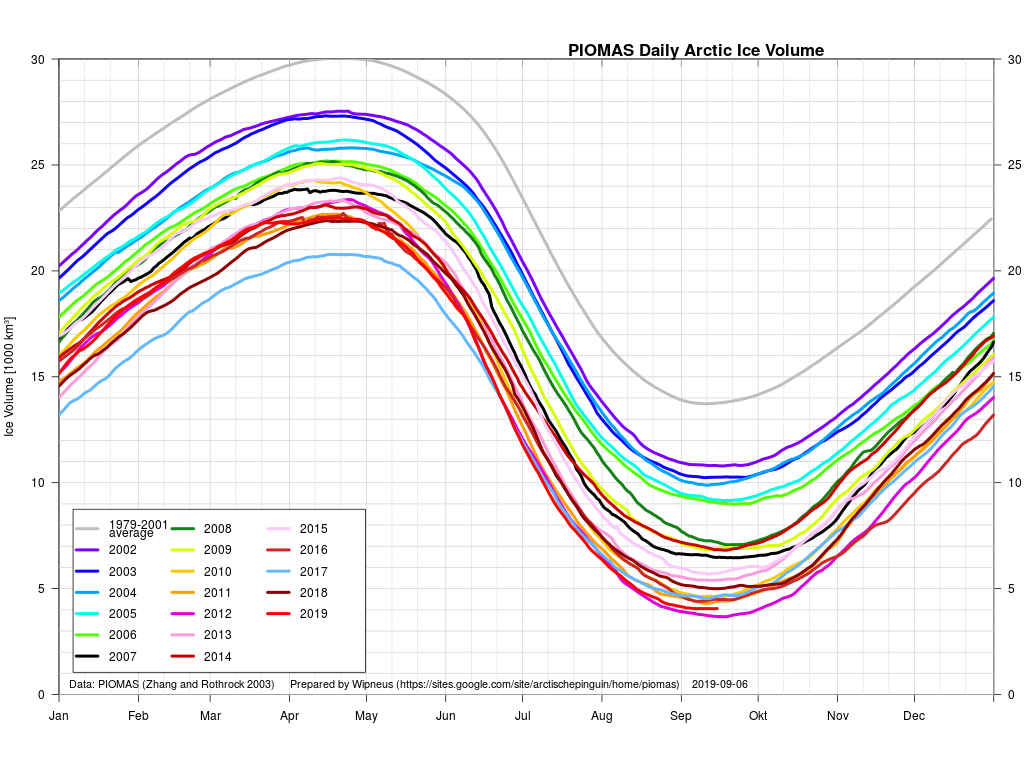
Perhaps a significant amount of the multi-year ice that survived the winter of 2018/19 has now simply melted away in warm water, to be replaced by much less robust first year ice in the area between the North Pole and the Siberian coast? It will be very interesting to see what the next PIOMAS update in early February reveals.
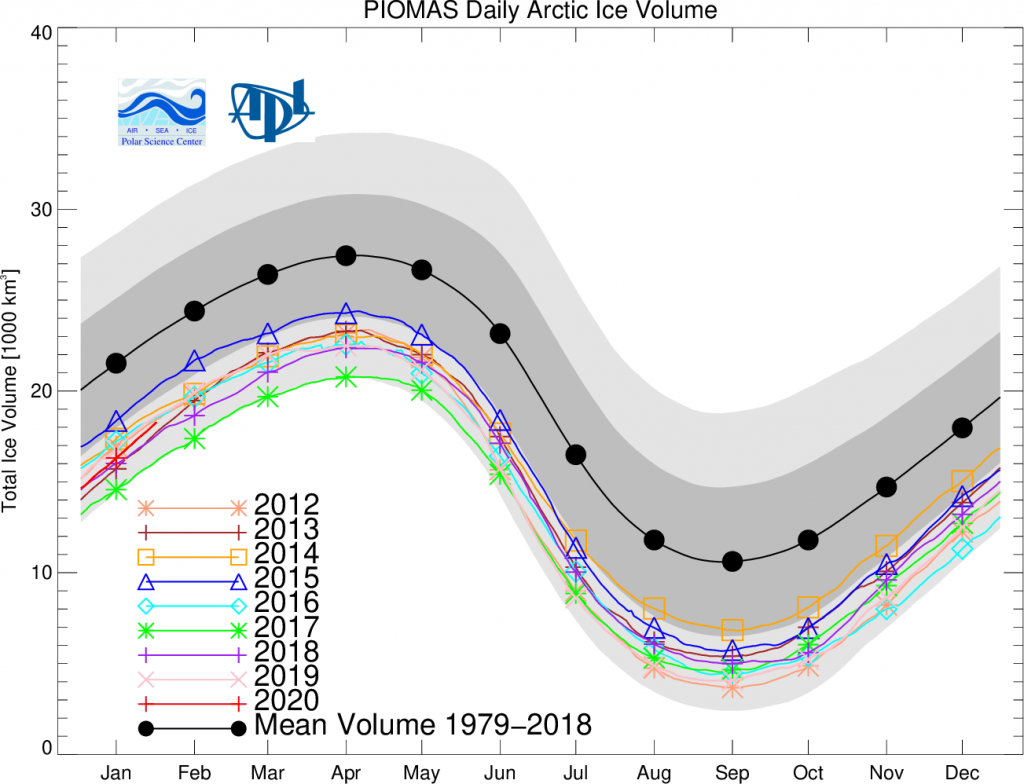
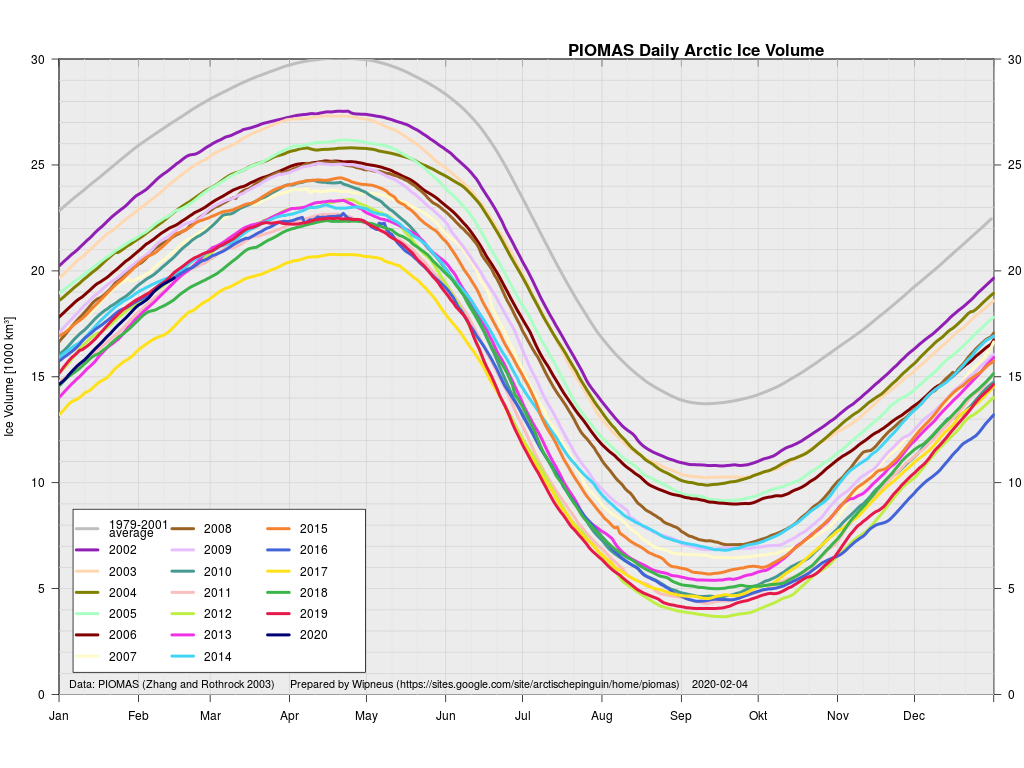
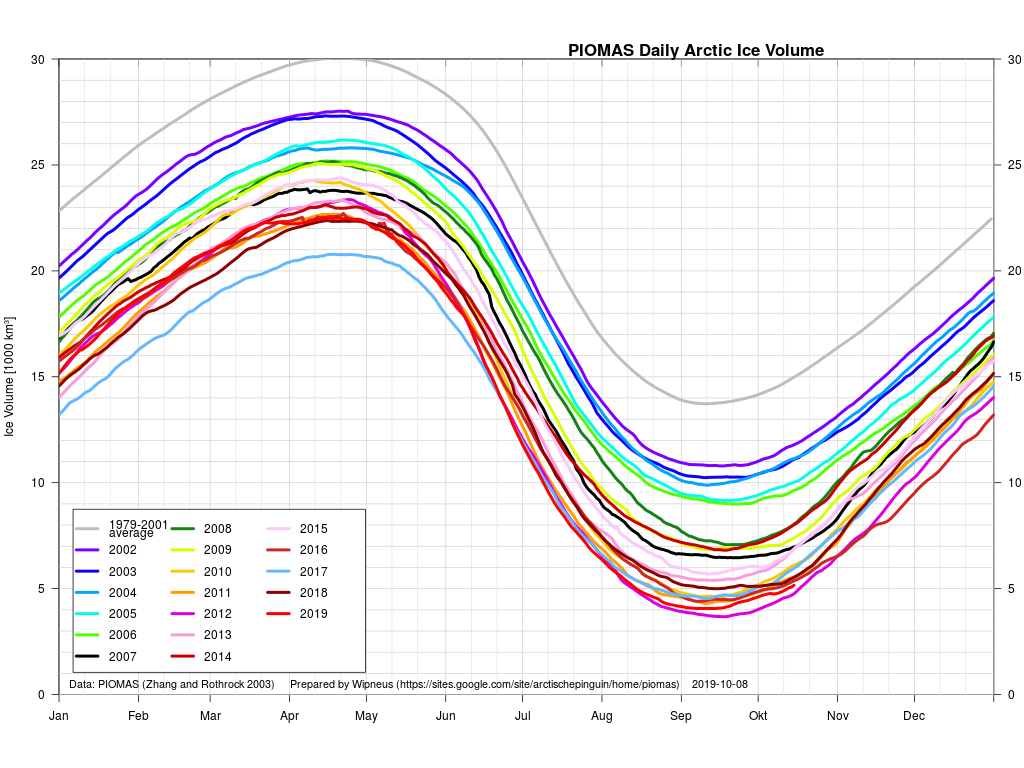
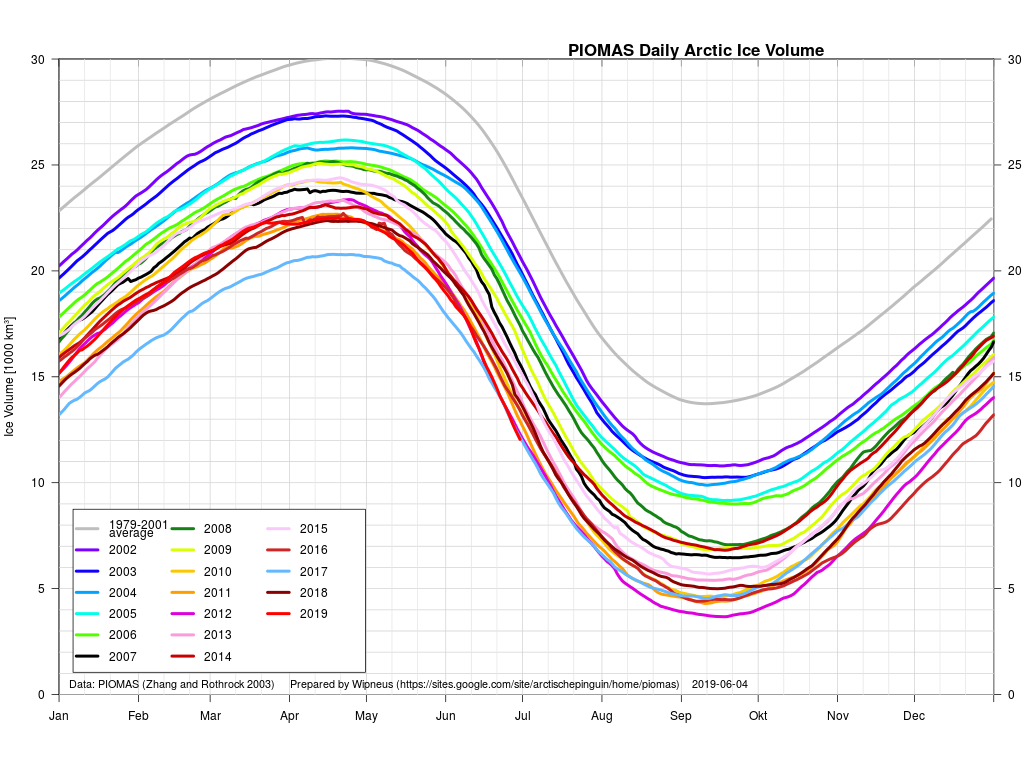
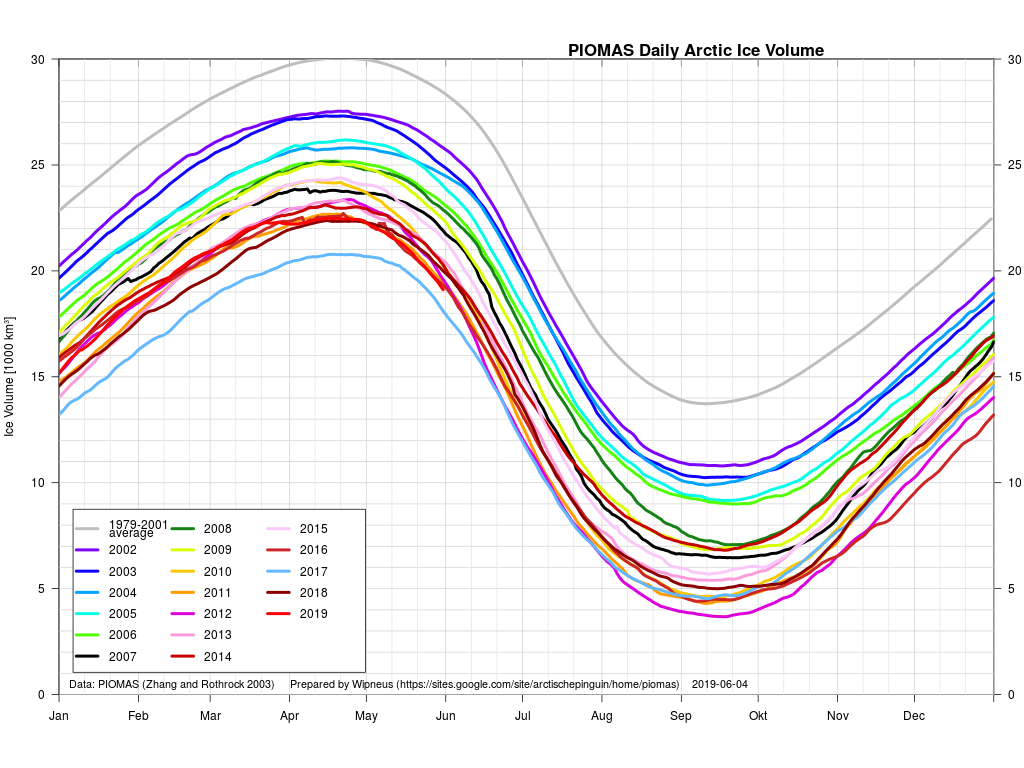
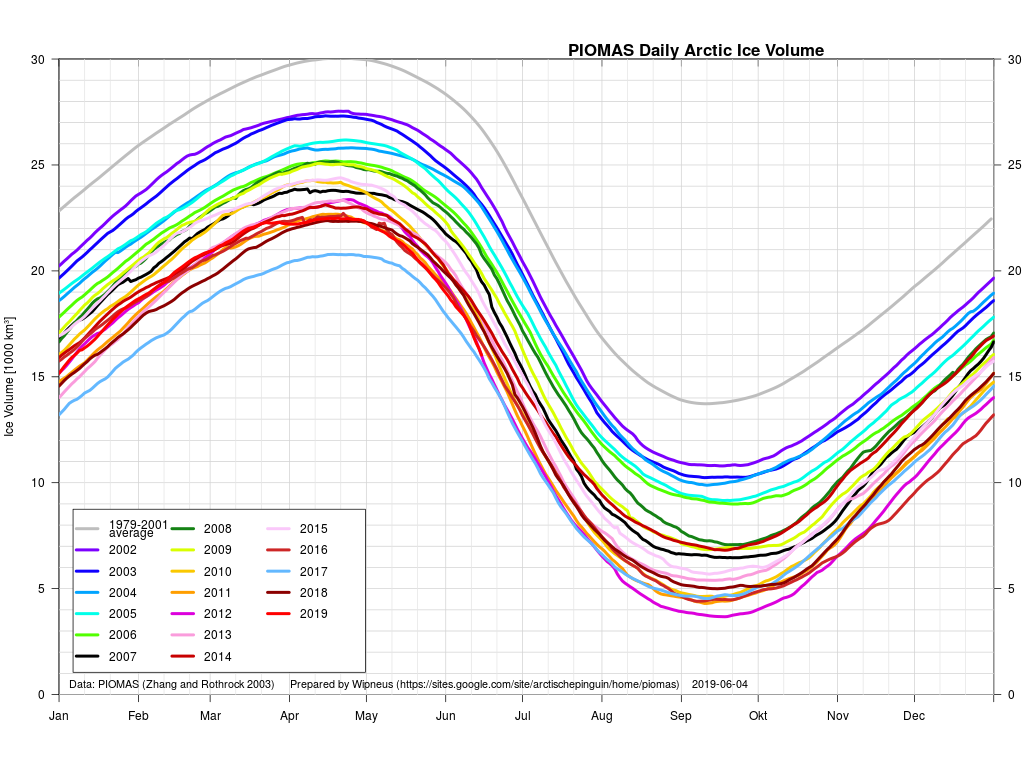
The next PIOMAS update referred to above has now arrived. Here’s the Polar Science Center’s graph:
Over on Climate Etc. angech is already exclaiming:
Strange it did go up a fair bit the old PIOMAS.
No publicity at the usual going down sites.
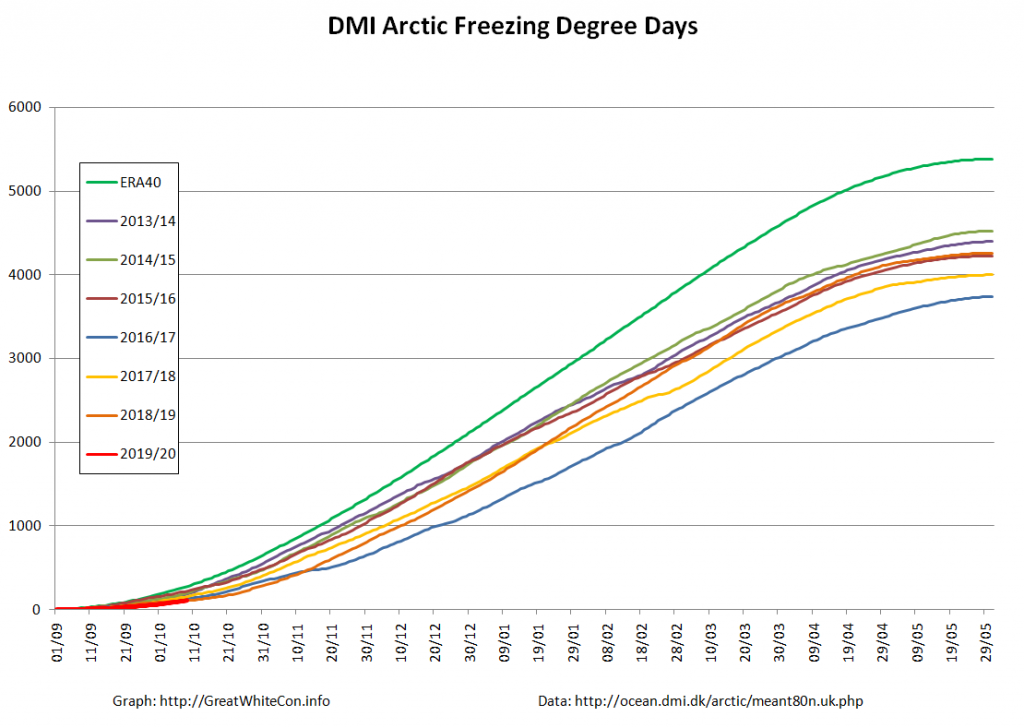
Actually it’s not at all strange, because thus far this winter the polar vortex has been remarkably well behaved. By and large cold air air has stayed in the Arctic. There hasn’t been much in the way of cold air intrusions into mid latitudes or warm air intrusions into the Arctic.
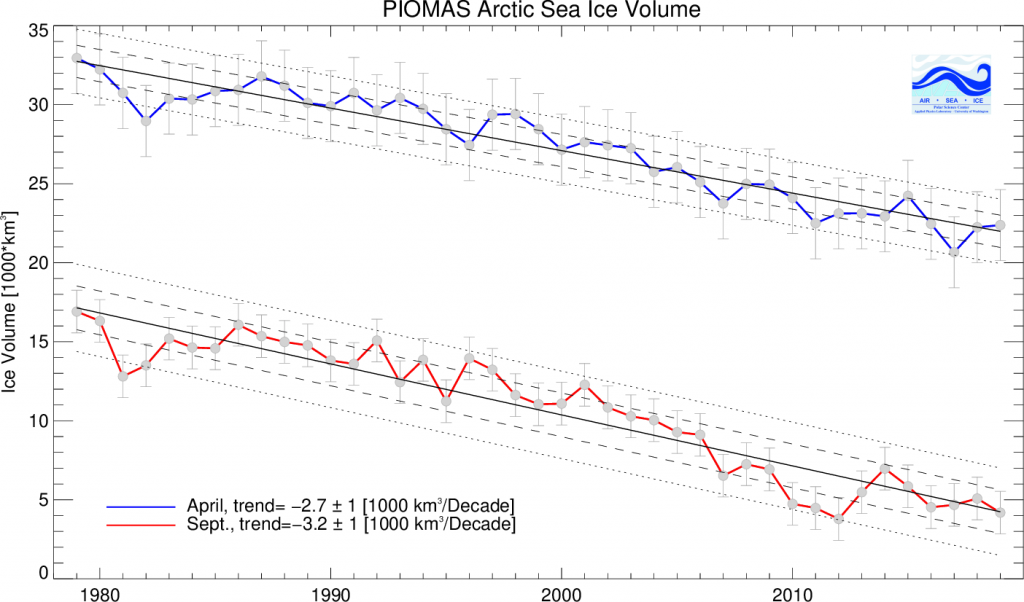
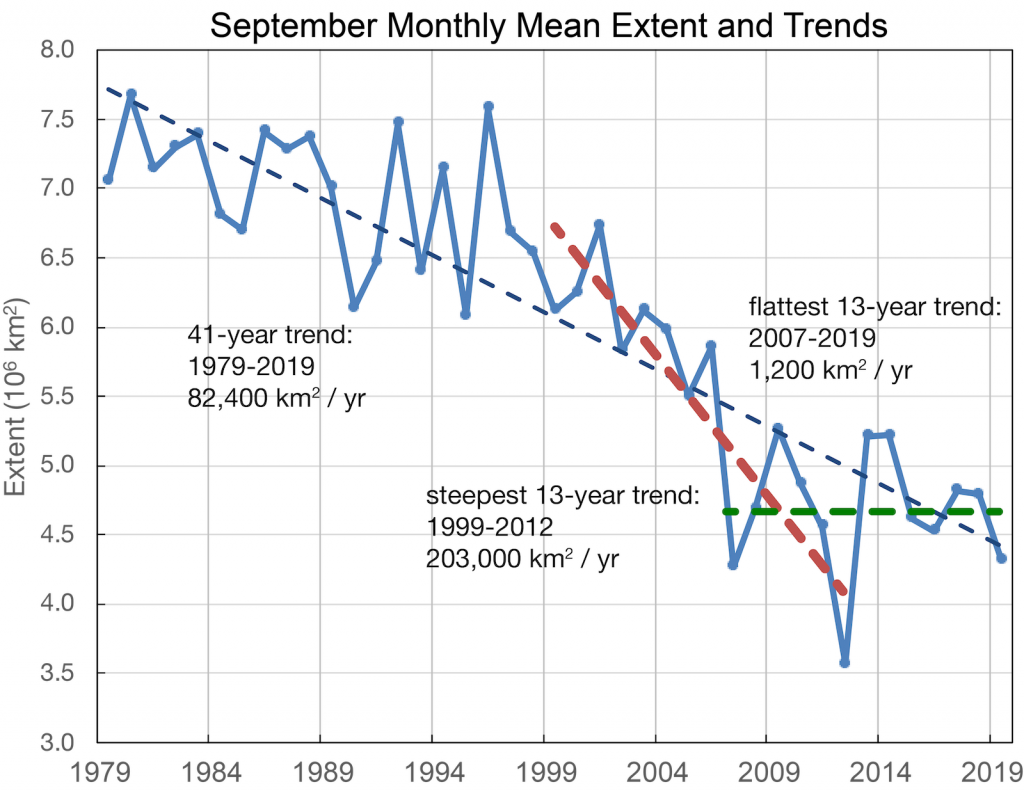
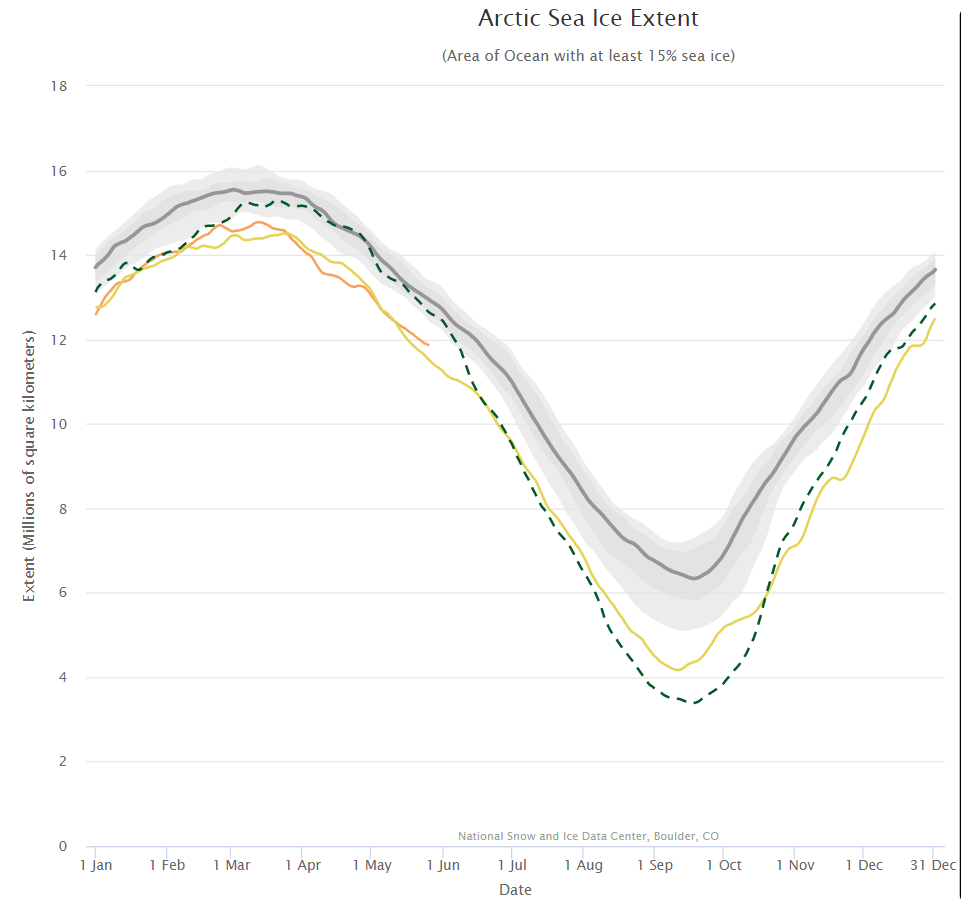
Hence it’s not at all surprising that the thickness of sea ice in the Arctic has been increasing slightly more quickly this winter than in other recent years. By way of some longer term context, here are the official Polar Science Center min/max trends:
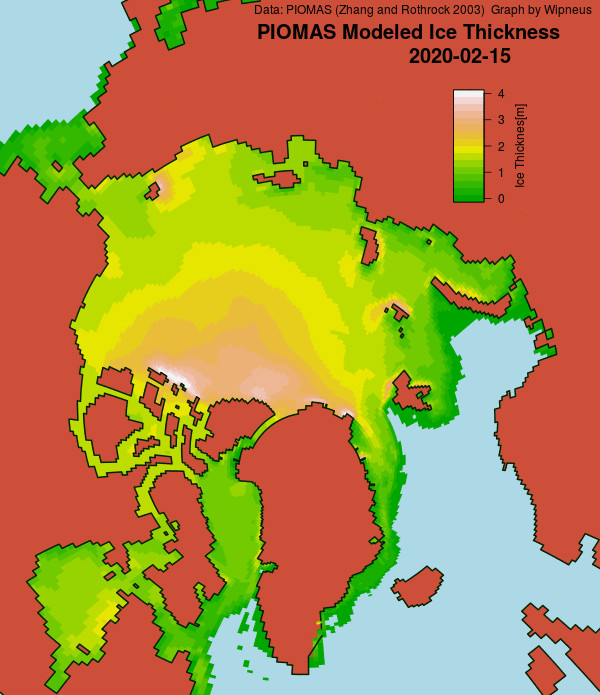
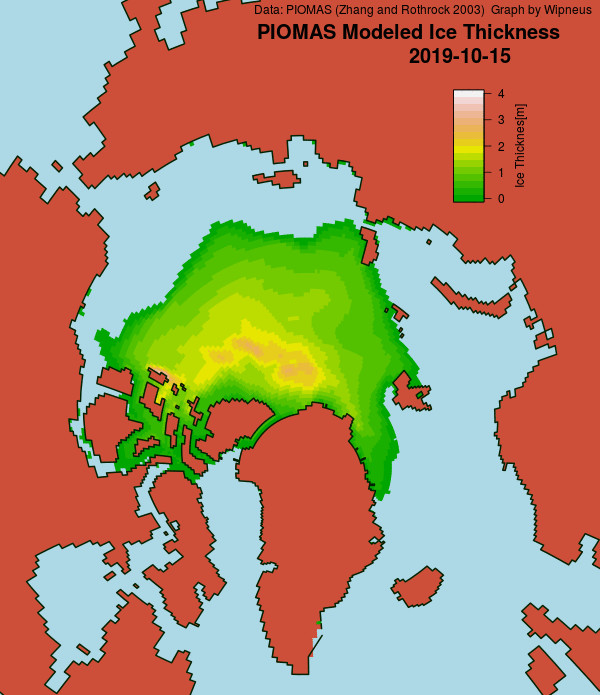
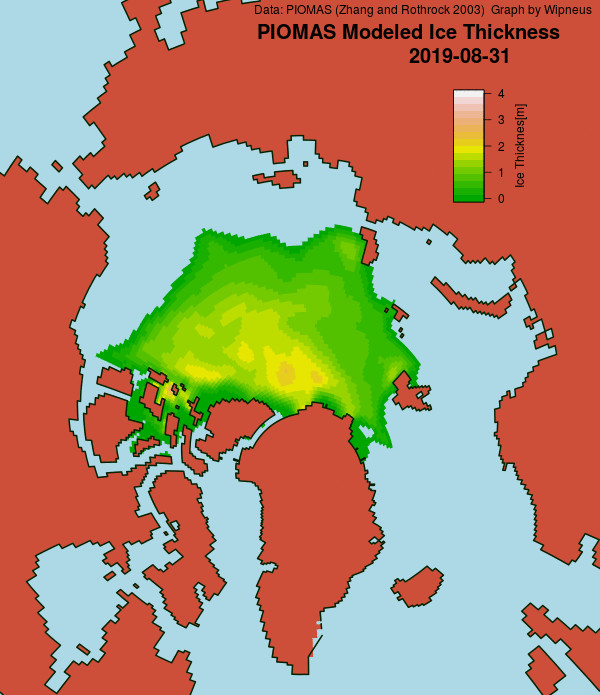
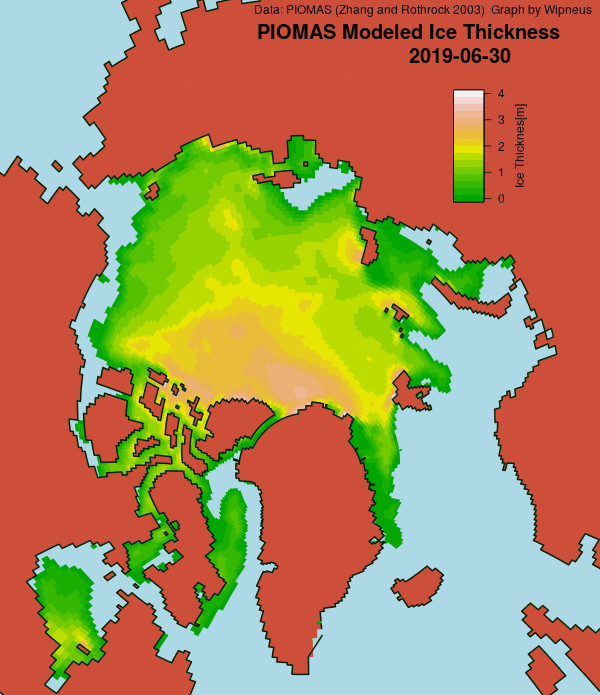
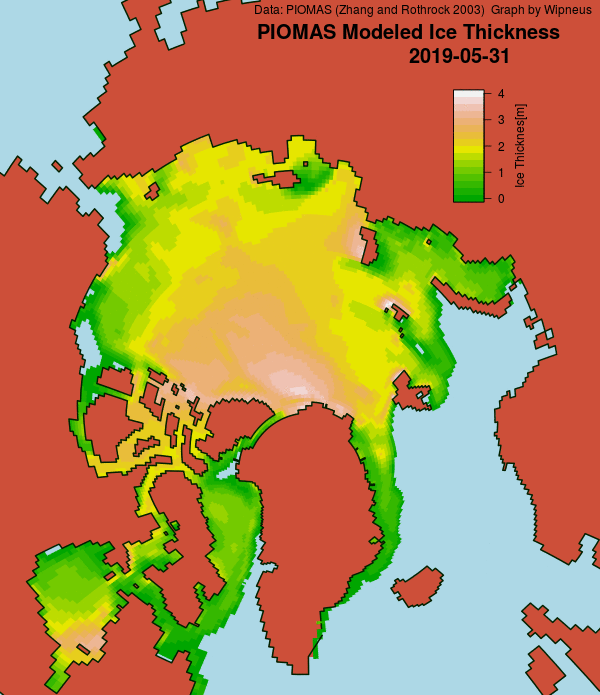
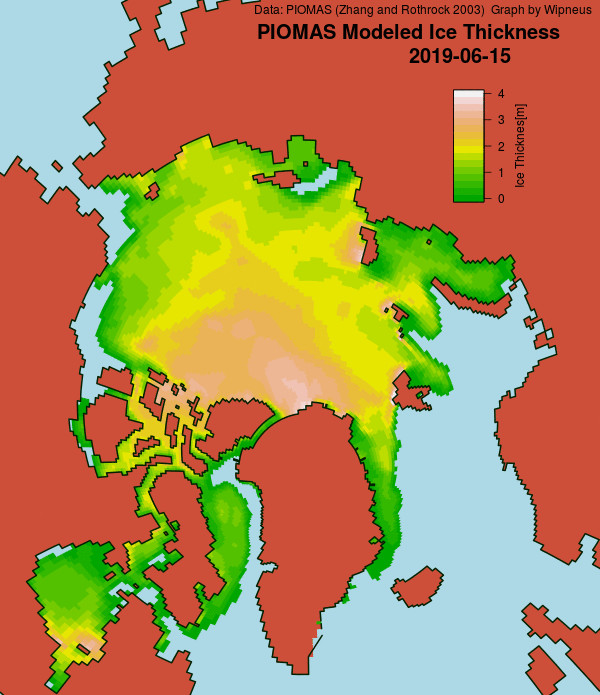
Wipneus has just released the January PIOMAS gridded thickness map. Here it is:
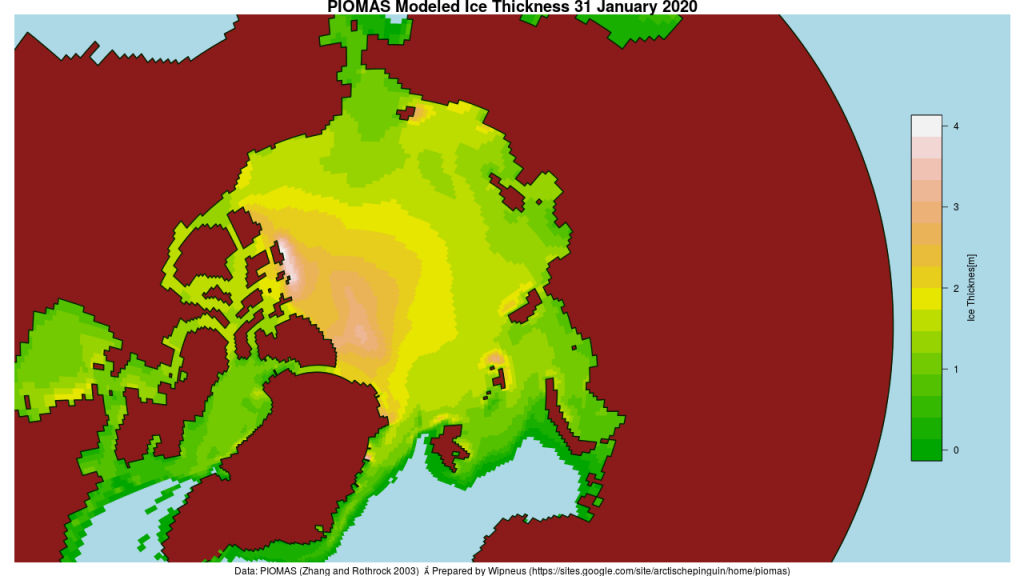
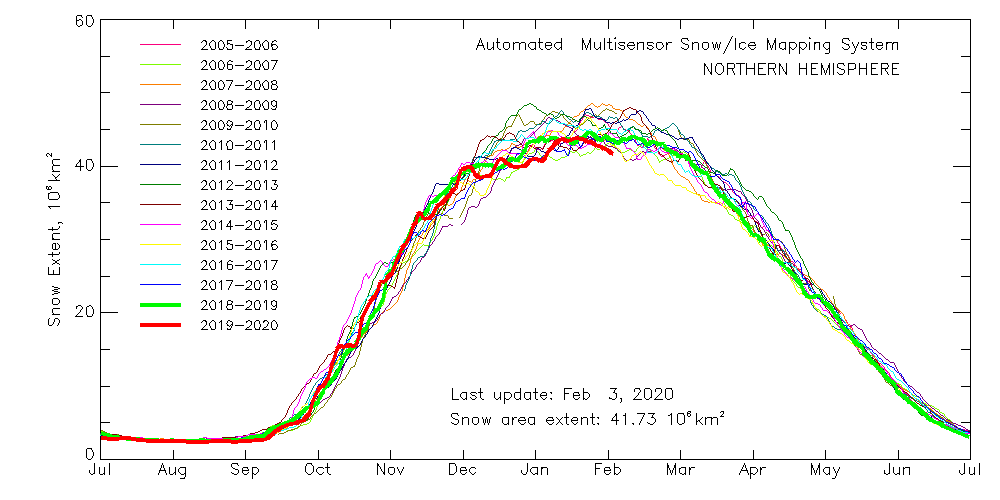
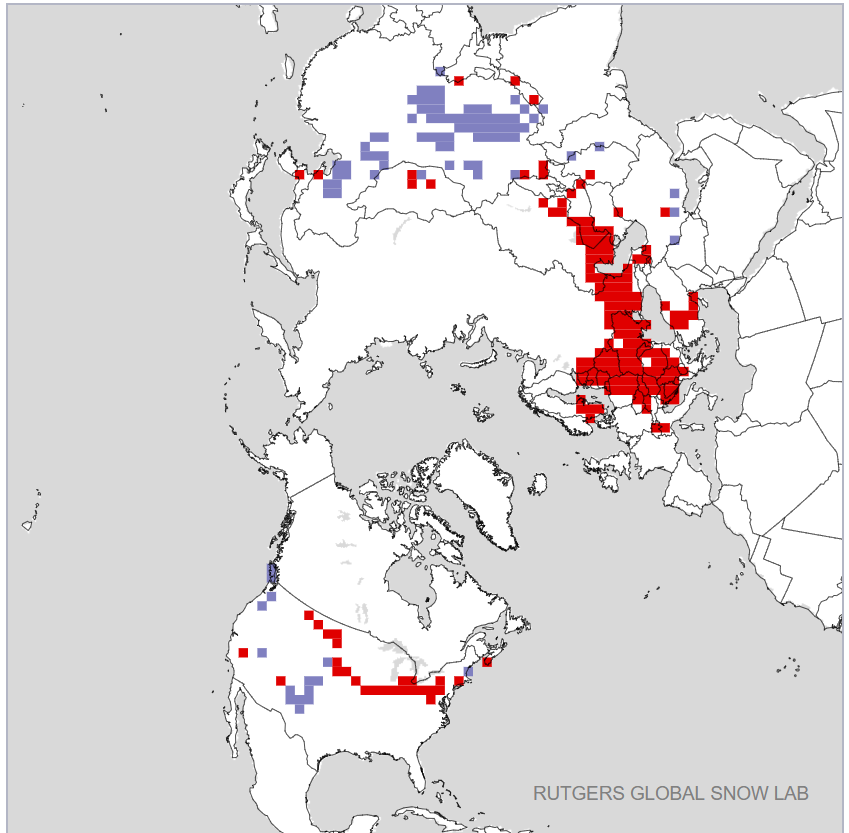
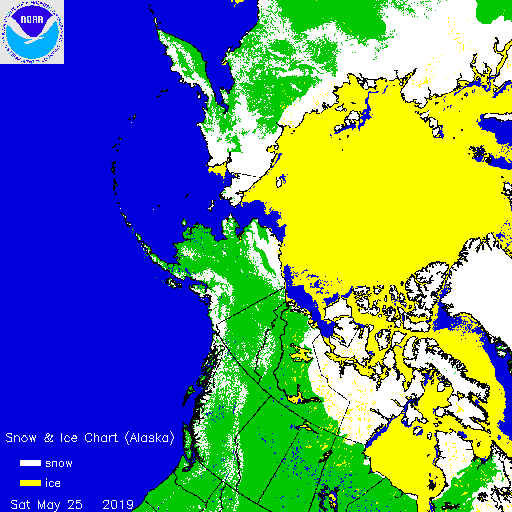
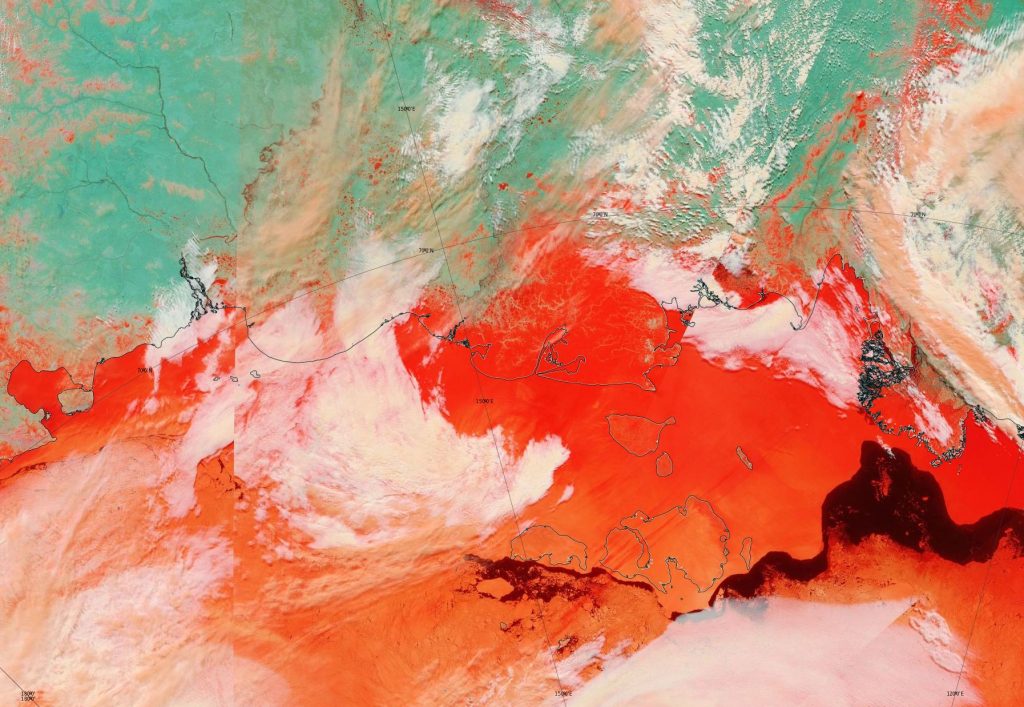
As is all too frequently the case, AdR and other commenters below get very excited about trivial increases in sea ice extent without considering snow extent. One side effect of the lack of cold air outbreaks into mid latitudes so far this winter currently looks like this:
The AWI and PIOMAS sea ice thickness maps above look somewhat different at first glance. That being the case, I’ve written a program to crunch the AWI numbers. Here’s the result:
The source code plus raw and processed data can be accessed via the Arctic Sea Ice Forum:
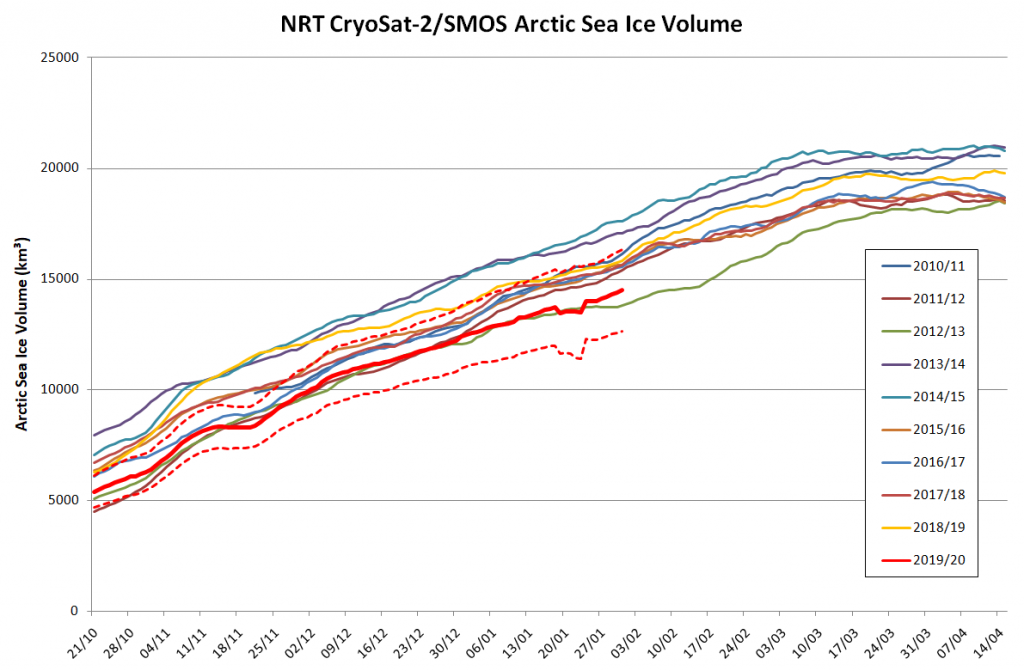
“CryoSat-2/SMOS Arctic Sea Ice Volume”
Further support for my “polar vortex” theory, from Judah Cohen no less!
I think this plot best sums up the #winter for the Northern Hemisphere –#PolarVortex strength bouncing around from near (daily) record strong to normal all winter long. One more near record strong (PV) for latter half of February. Pretty much the nail in the coffin on this winter pic.twitter.com/OiSZw07VOF
— Judah Cohen (@judah47) February 10, 2020
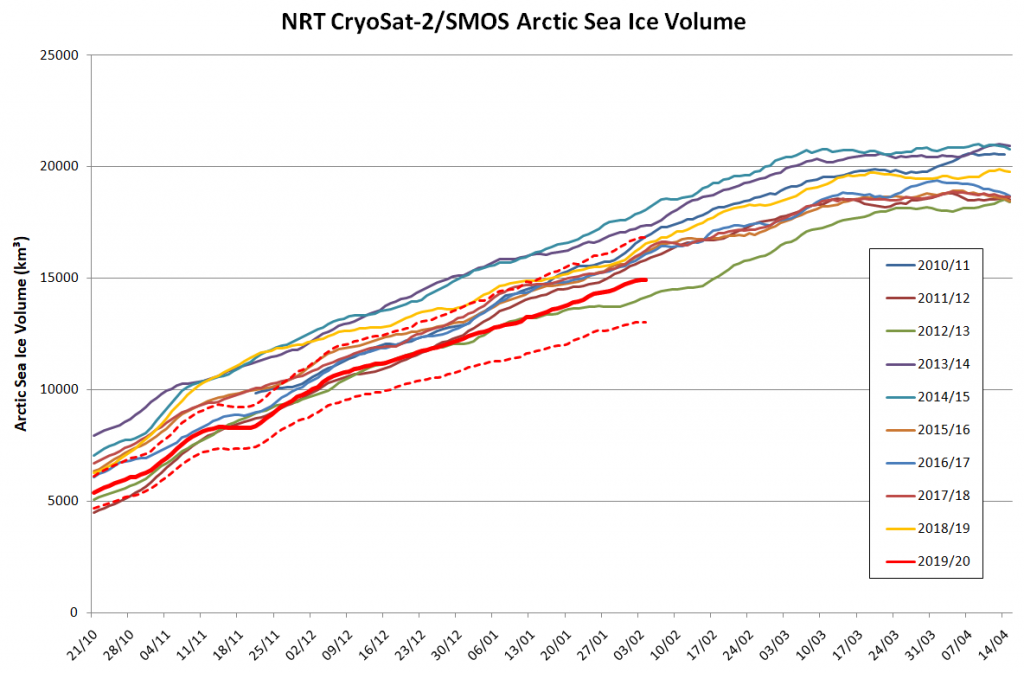
Here’s the latest update of our novel NRT volume metric:
Please note that there is a known problem with the NRT data from January 31st onwards.
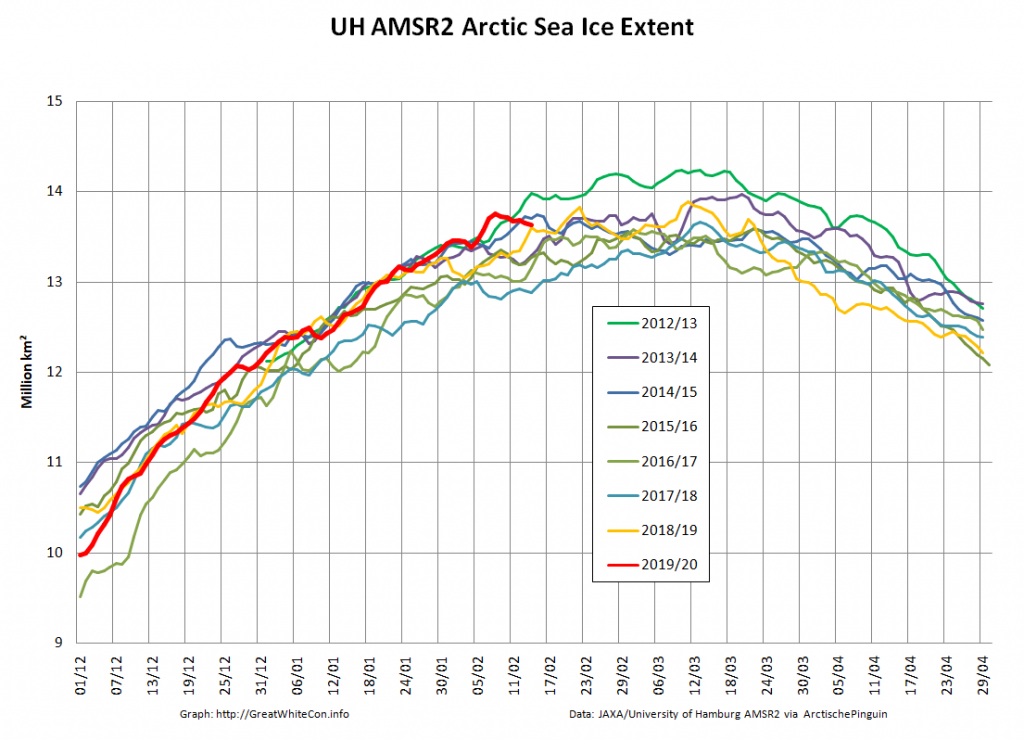
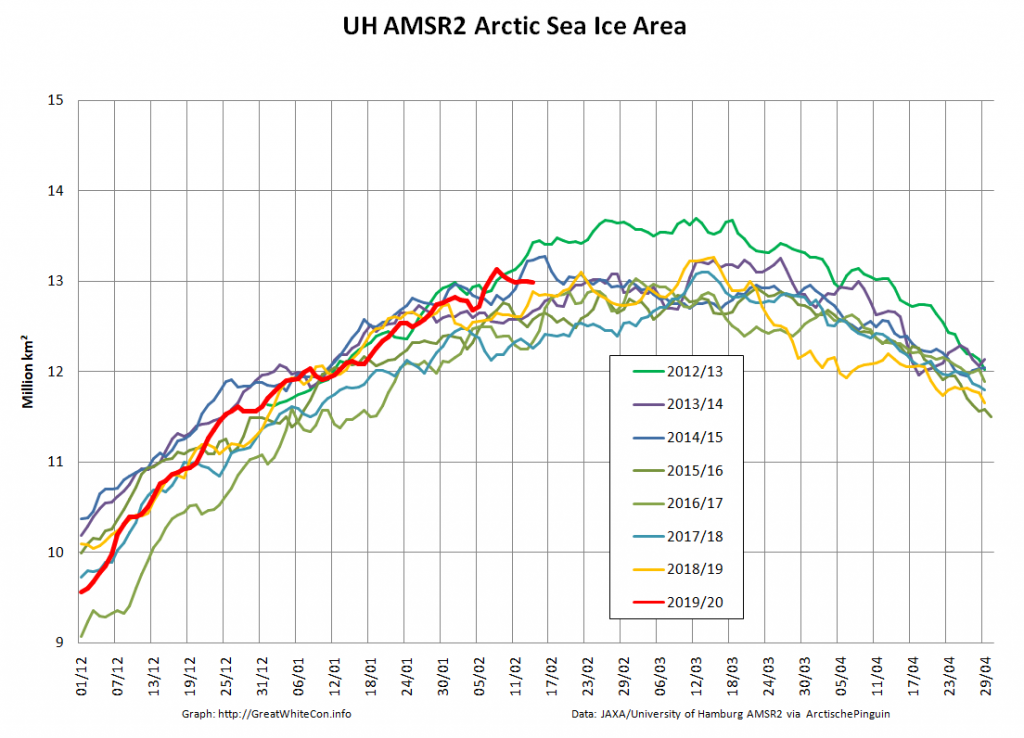
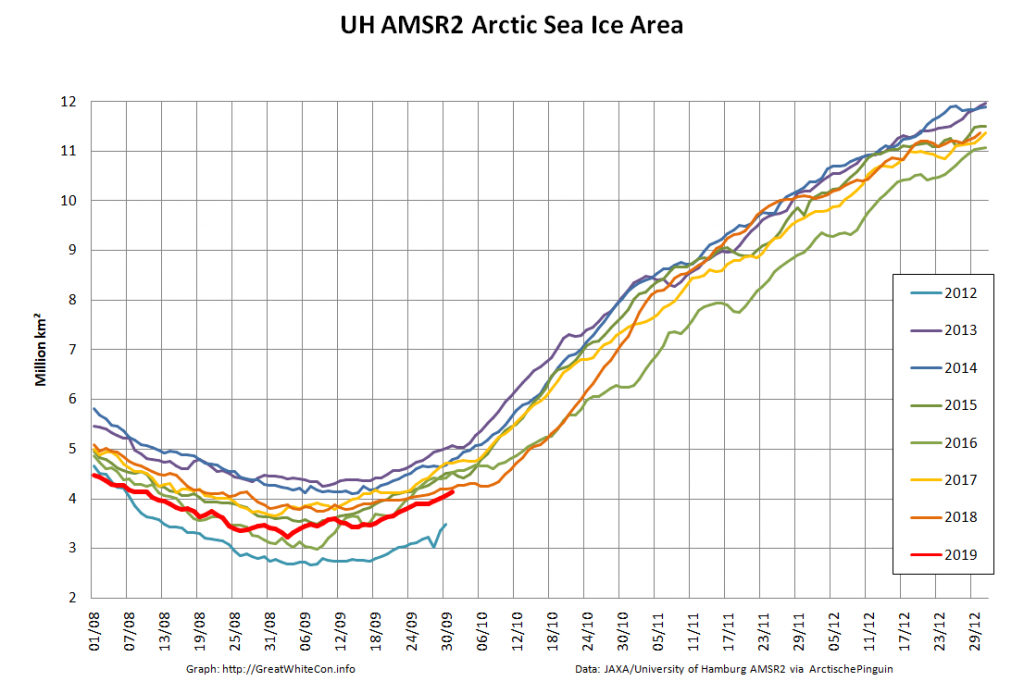
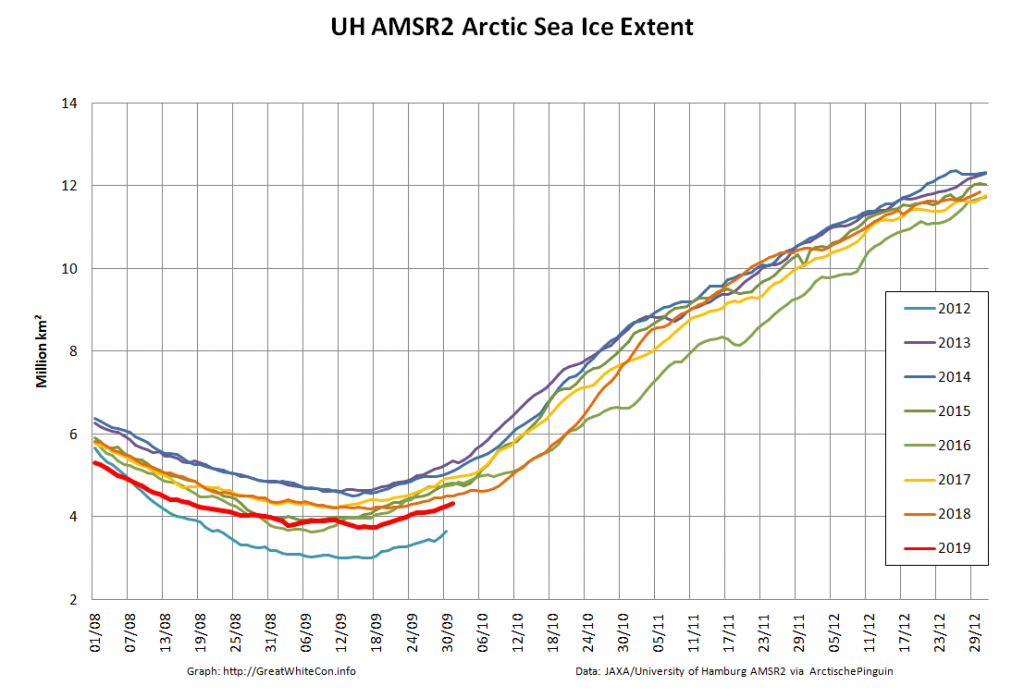
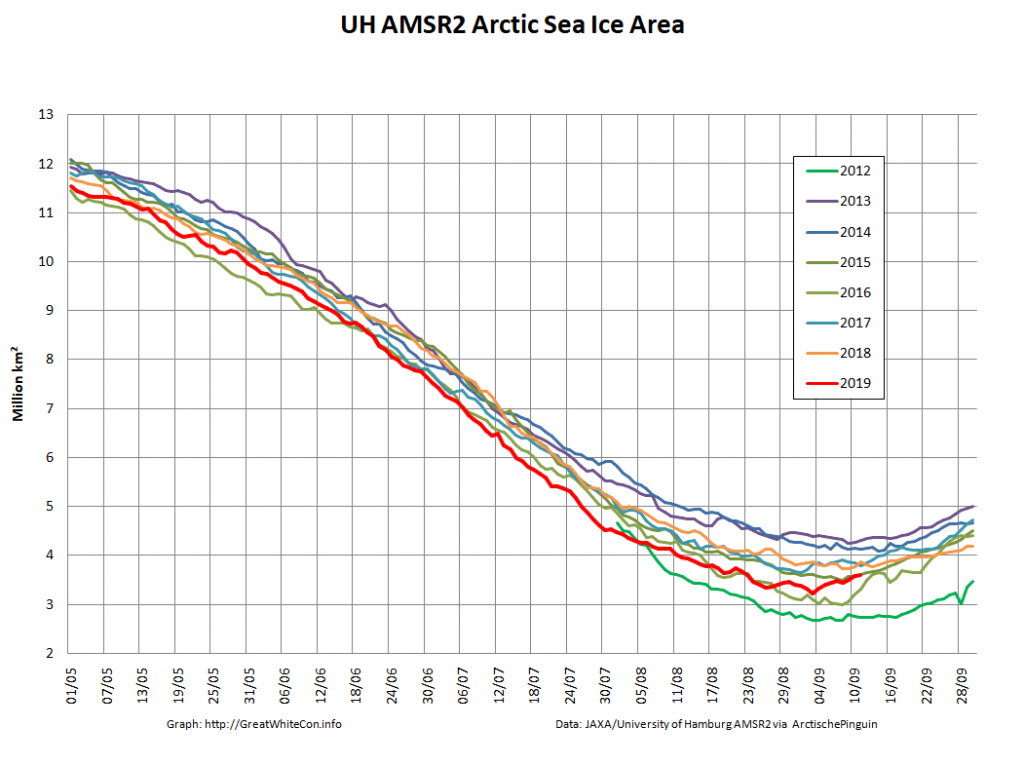
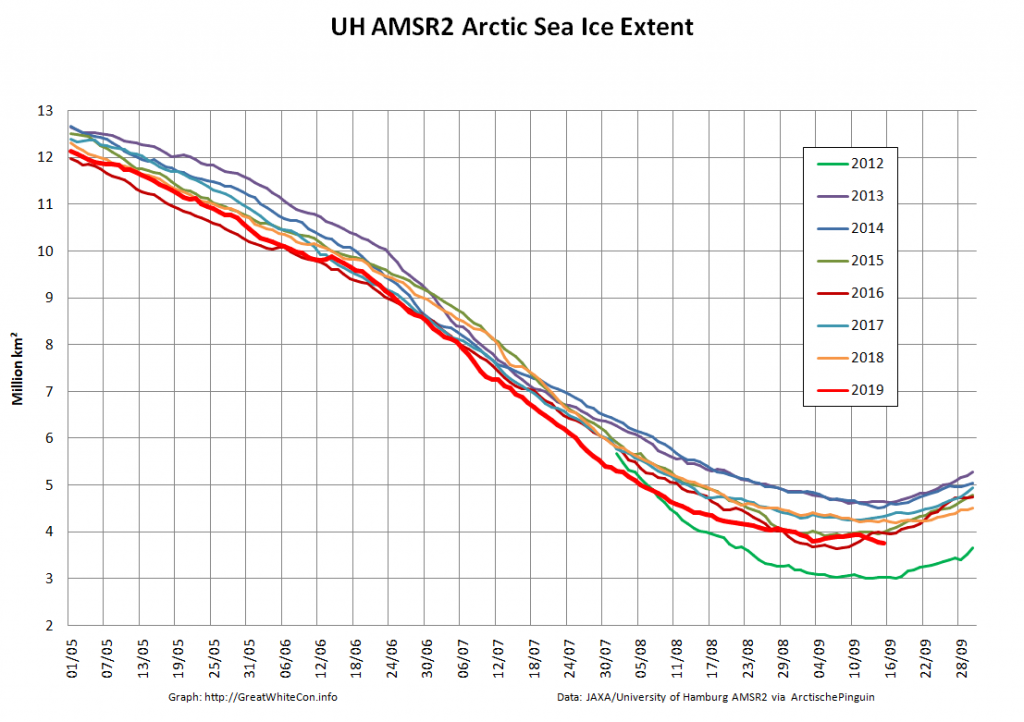
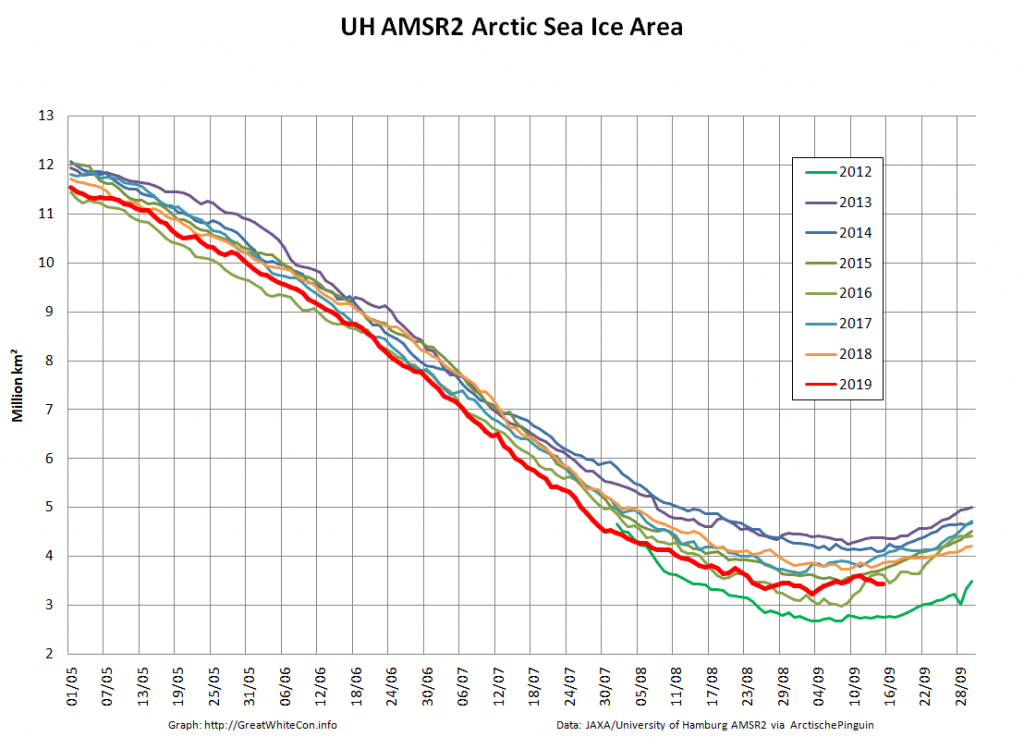
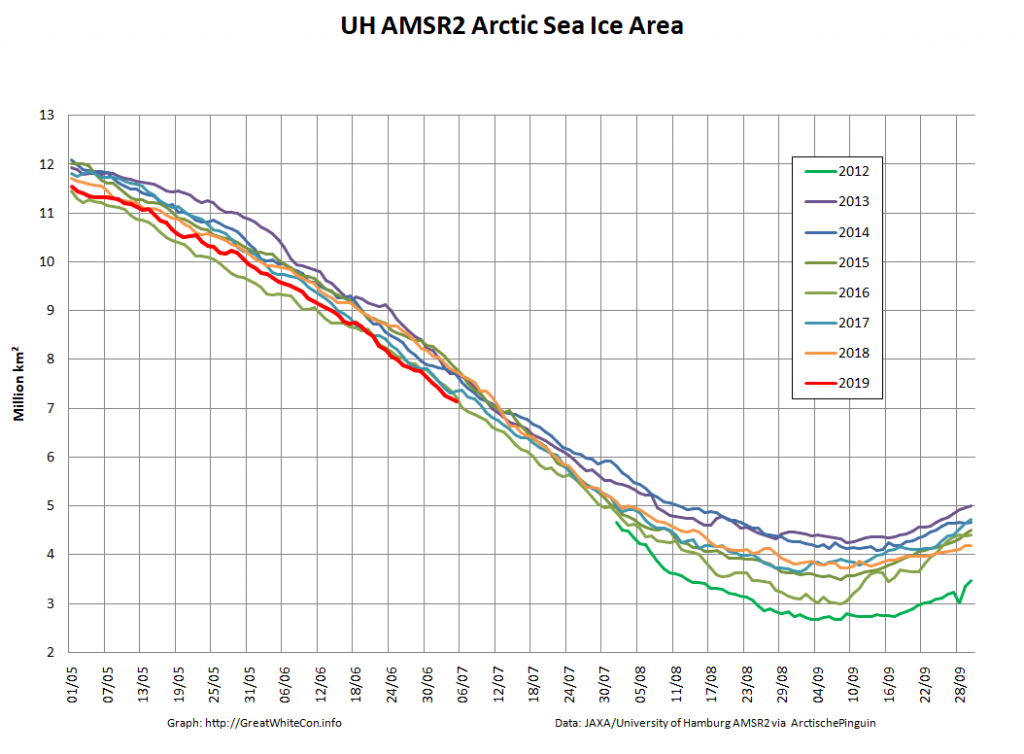
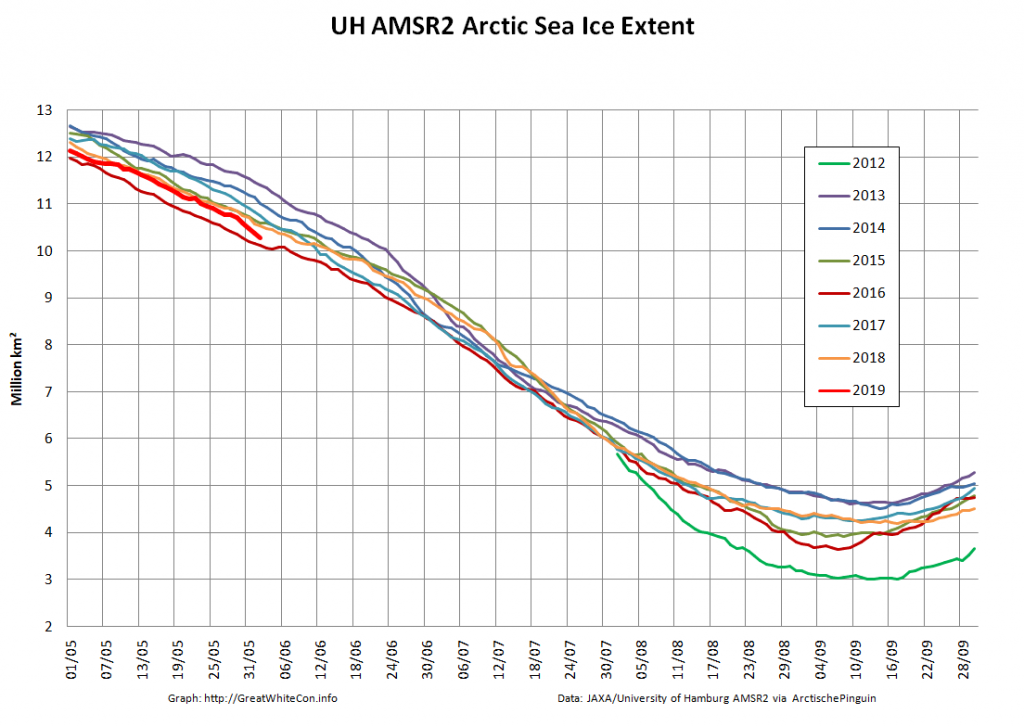
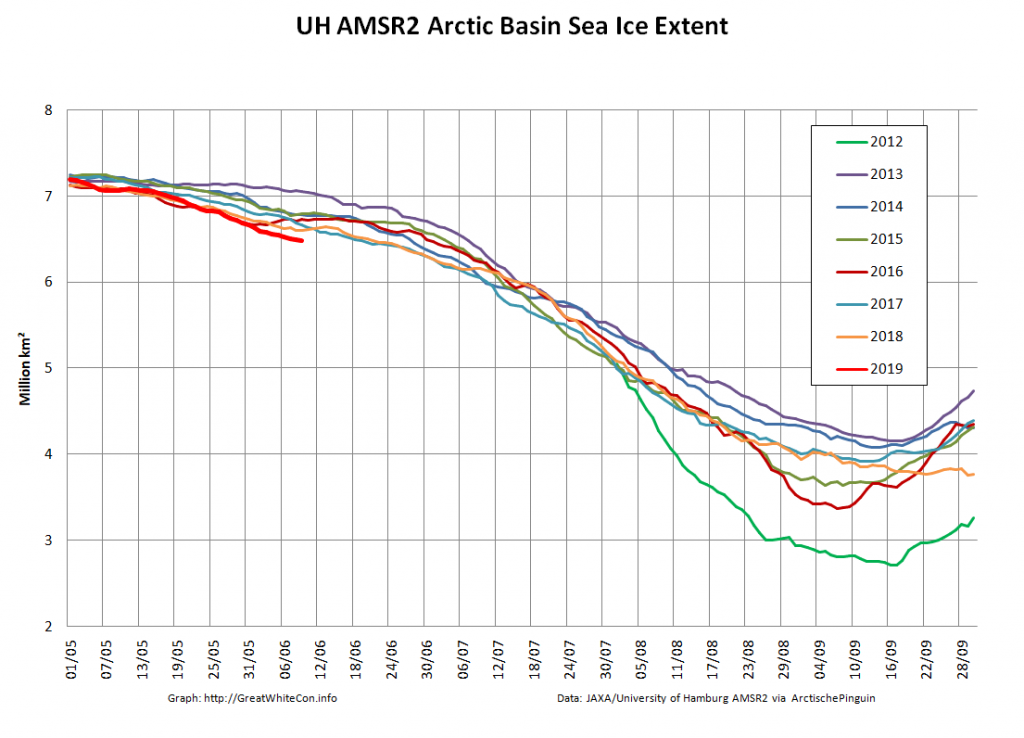
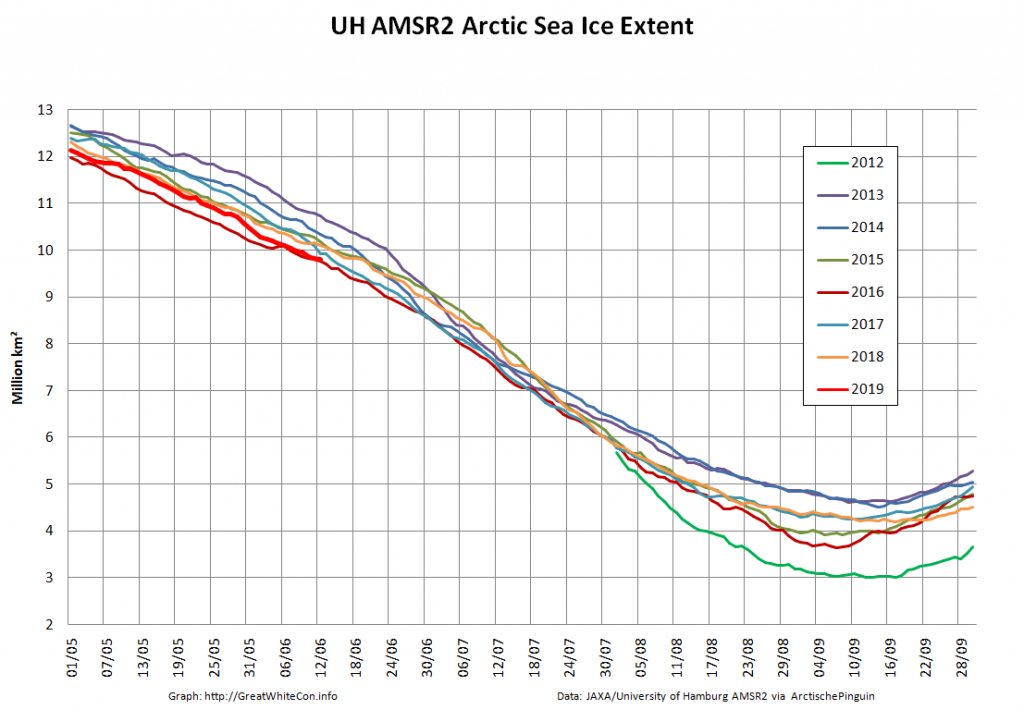
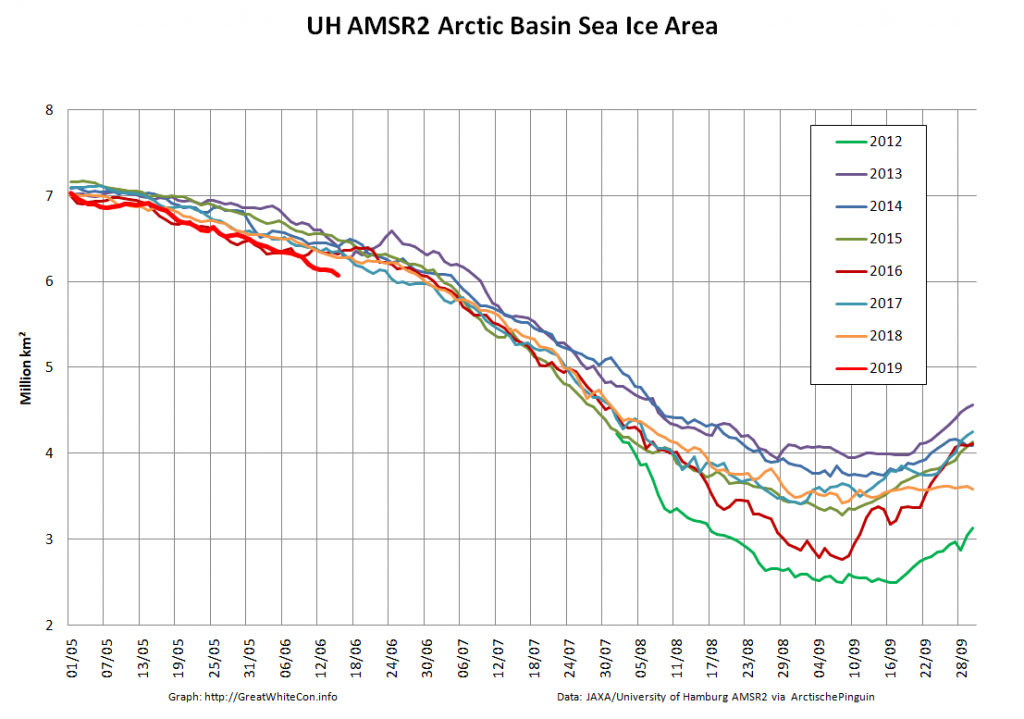
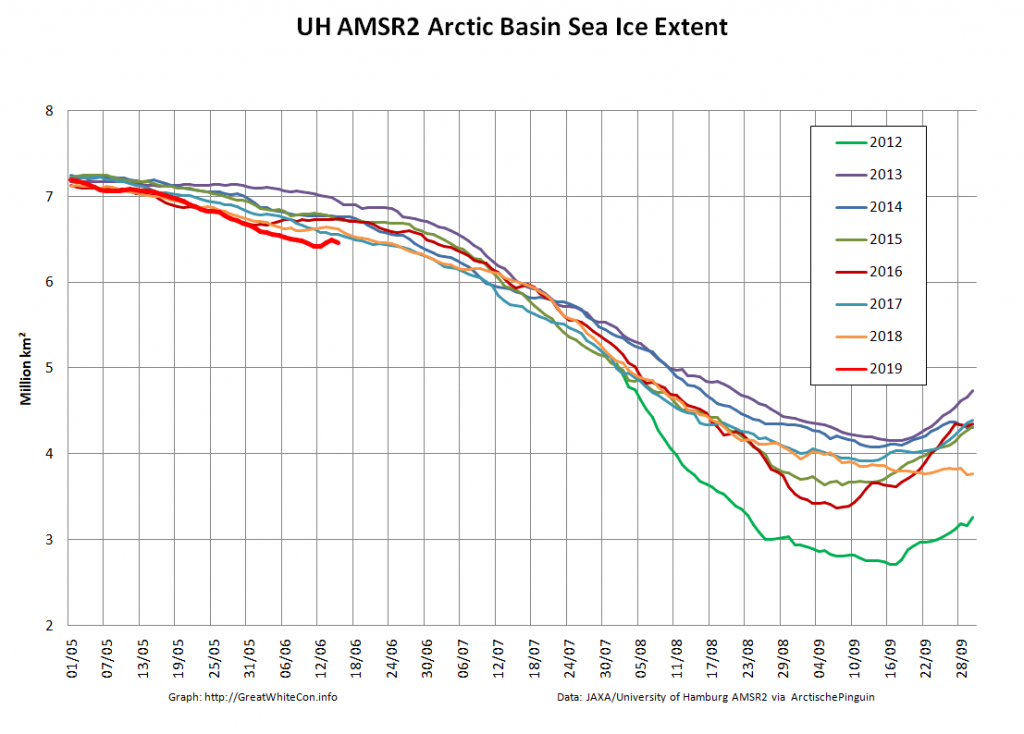
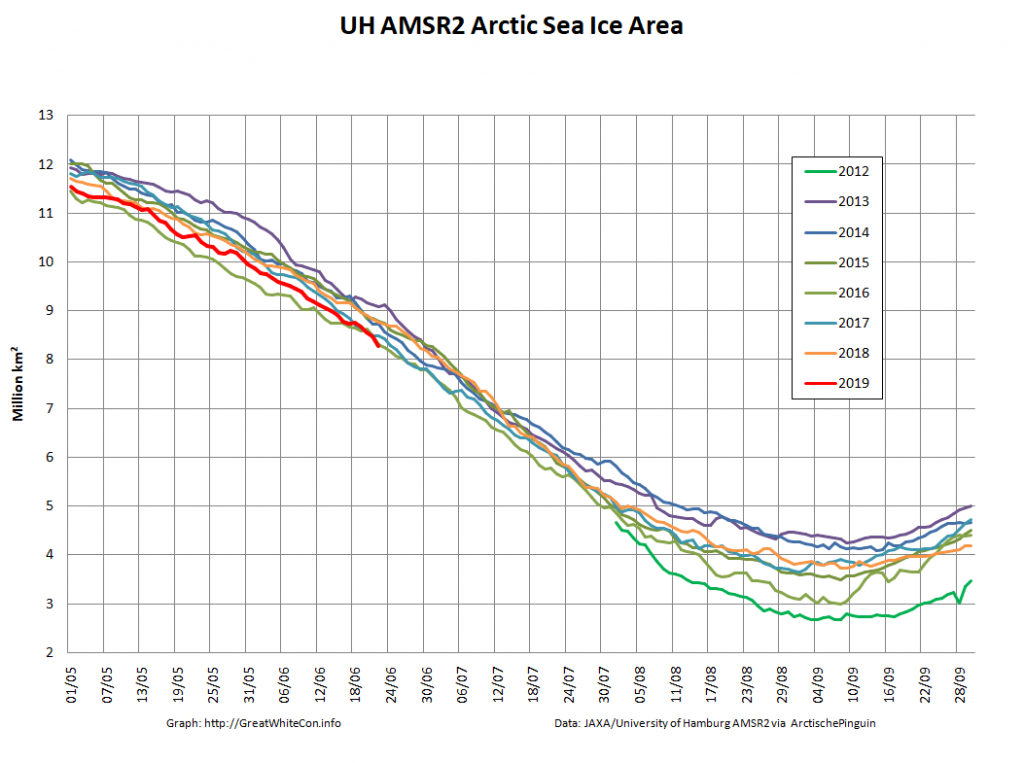
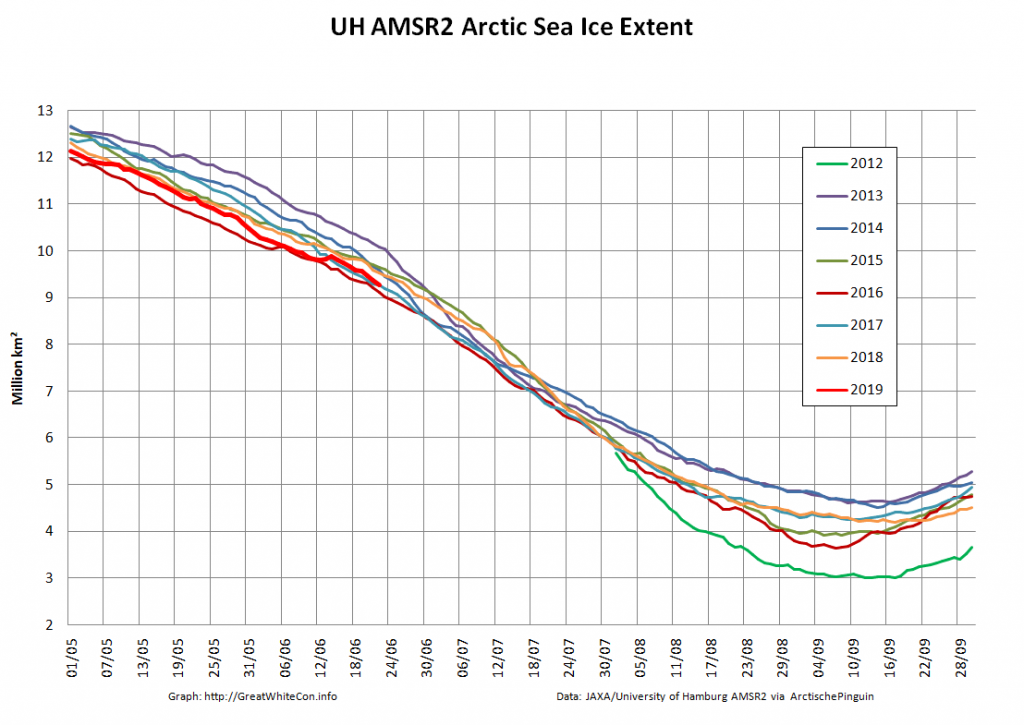
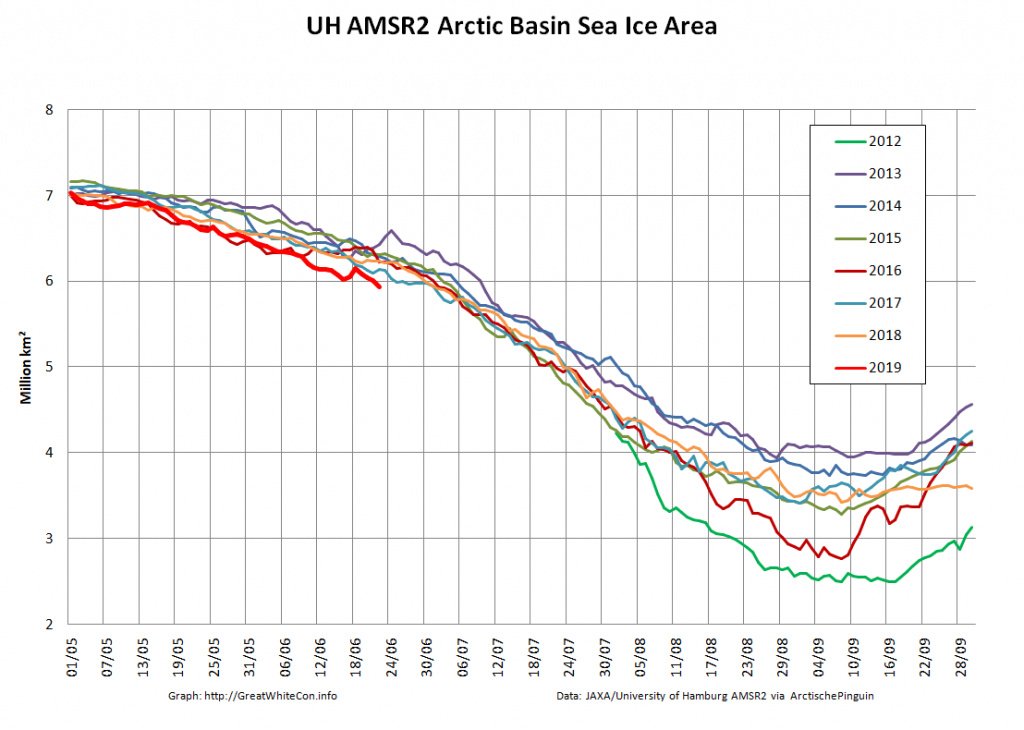
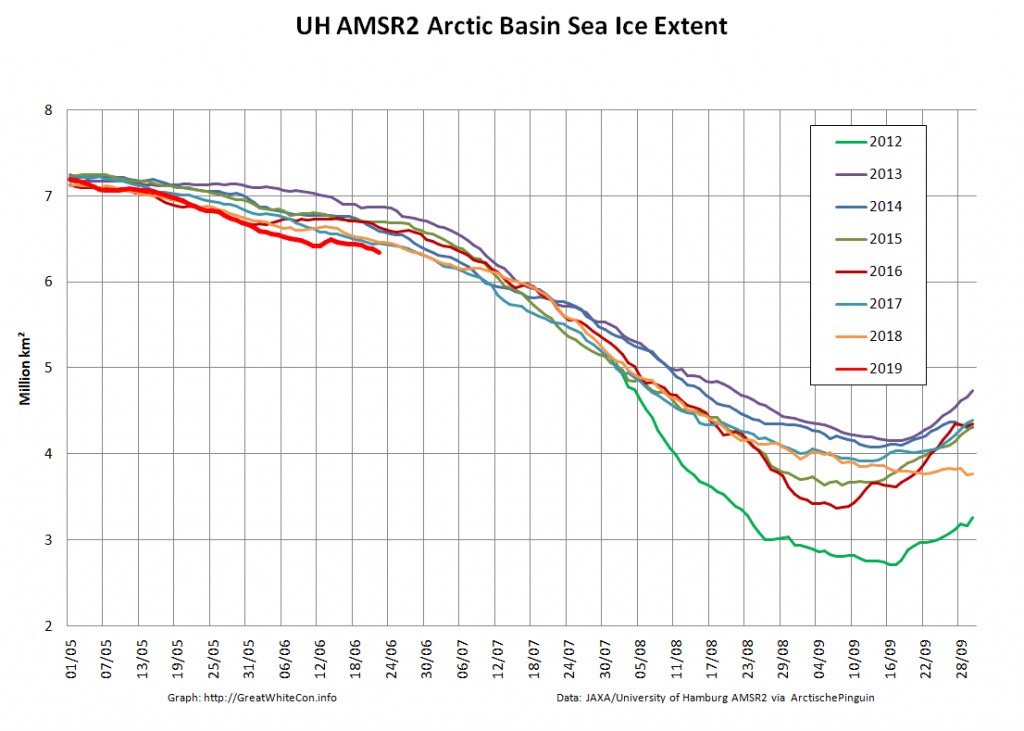
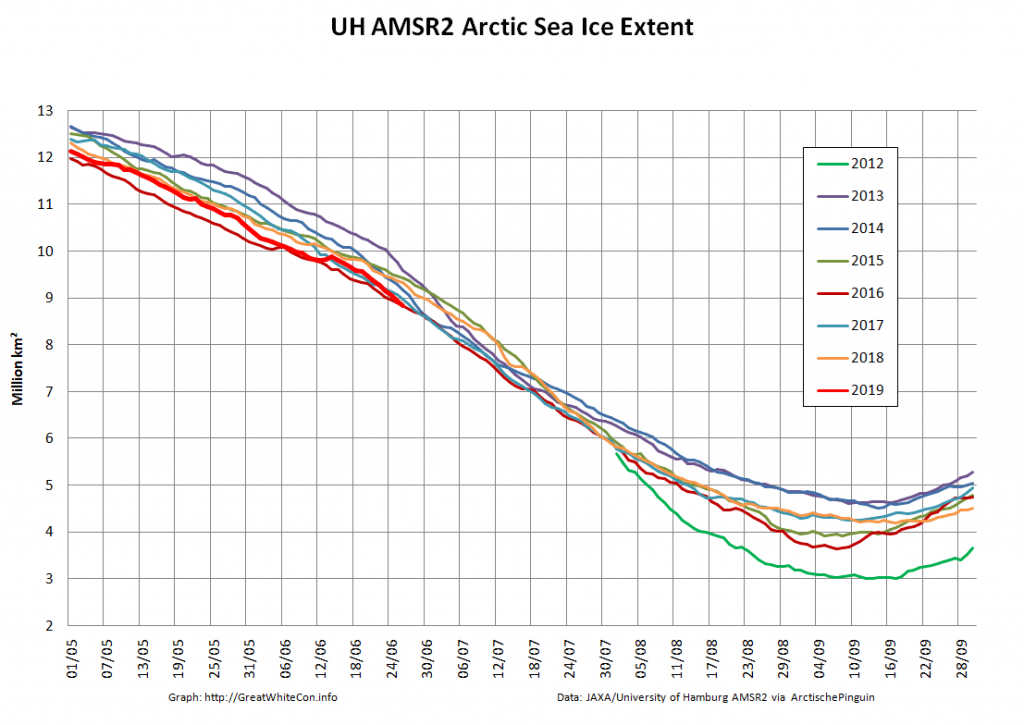
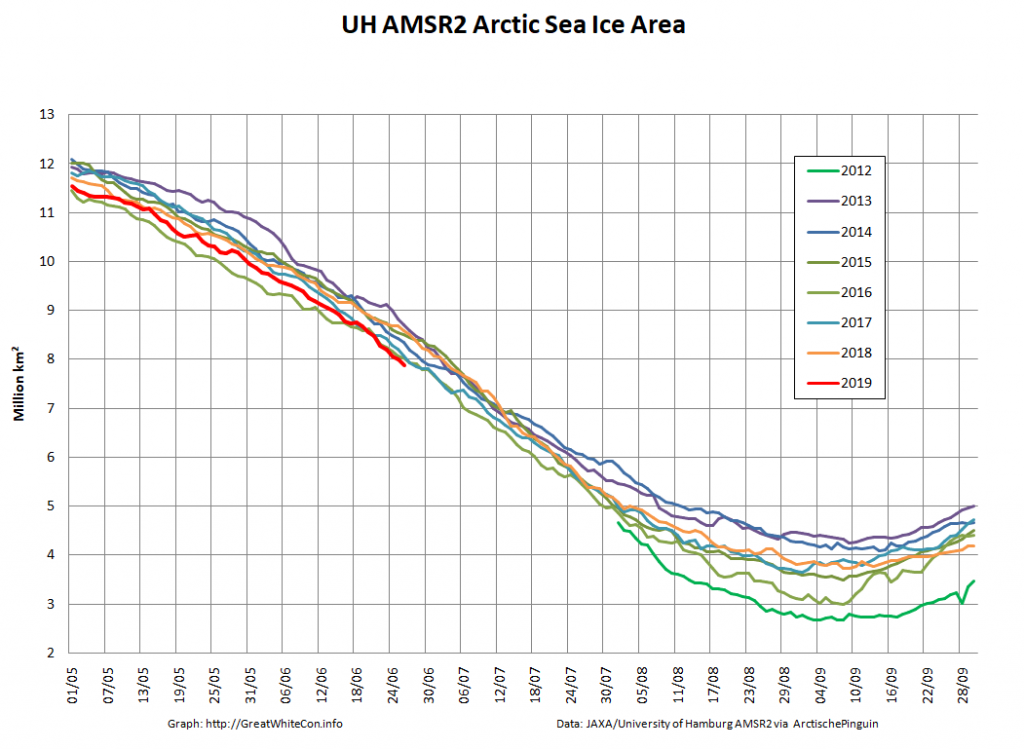
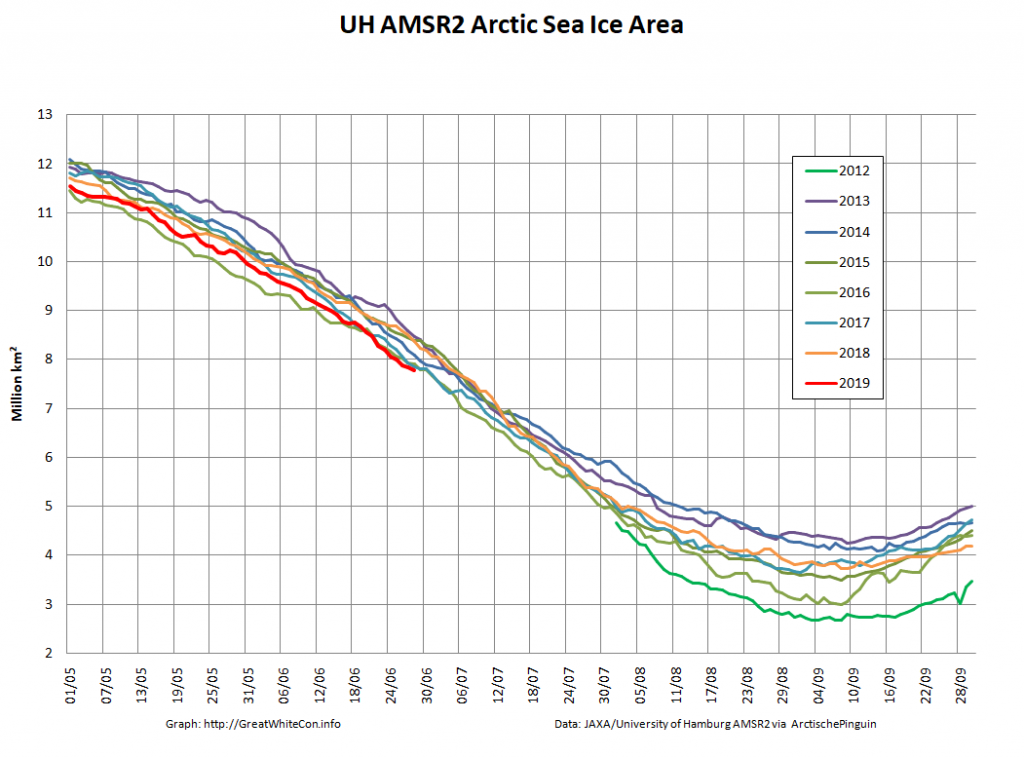
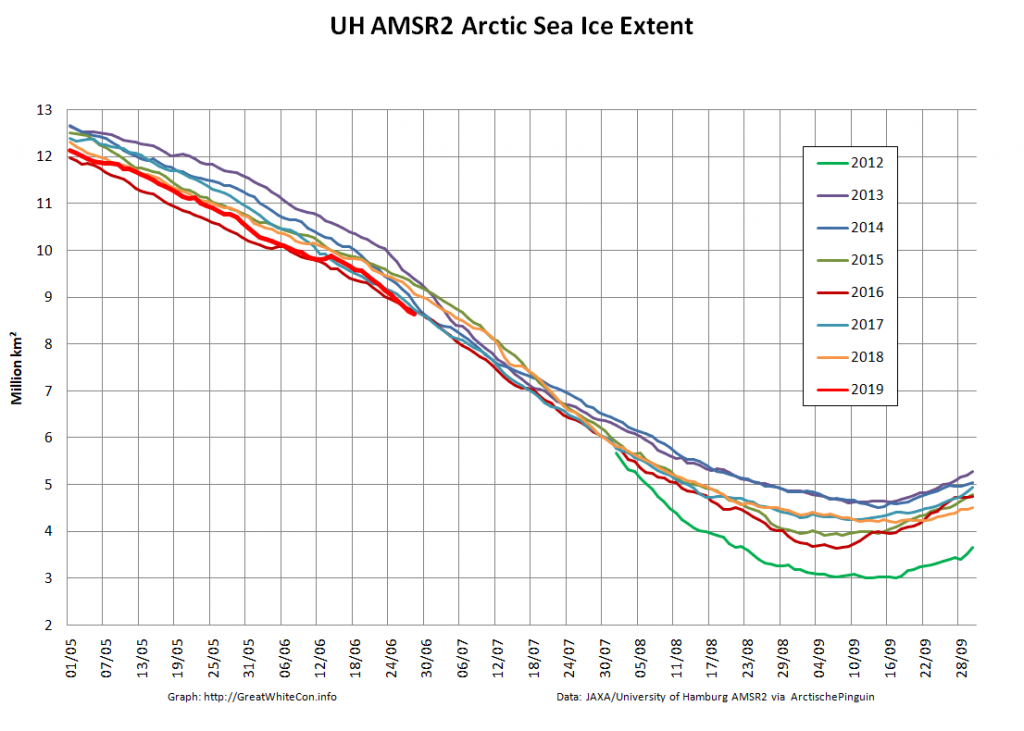
Here too are Wipneus’ latest high resolution AMSR2 area and extent graphs:
Wipneus has released his usual mid month PIOMAS update on the Arctic Sea Ice Forum:
I am forced to ponder once again why the CryoSat-2/SMOS thickness “measured” numbers just above seem to be more at variance with PIOMAS in 2020 than in previous years:
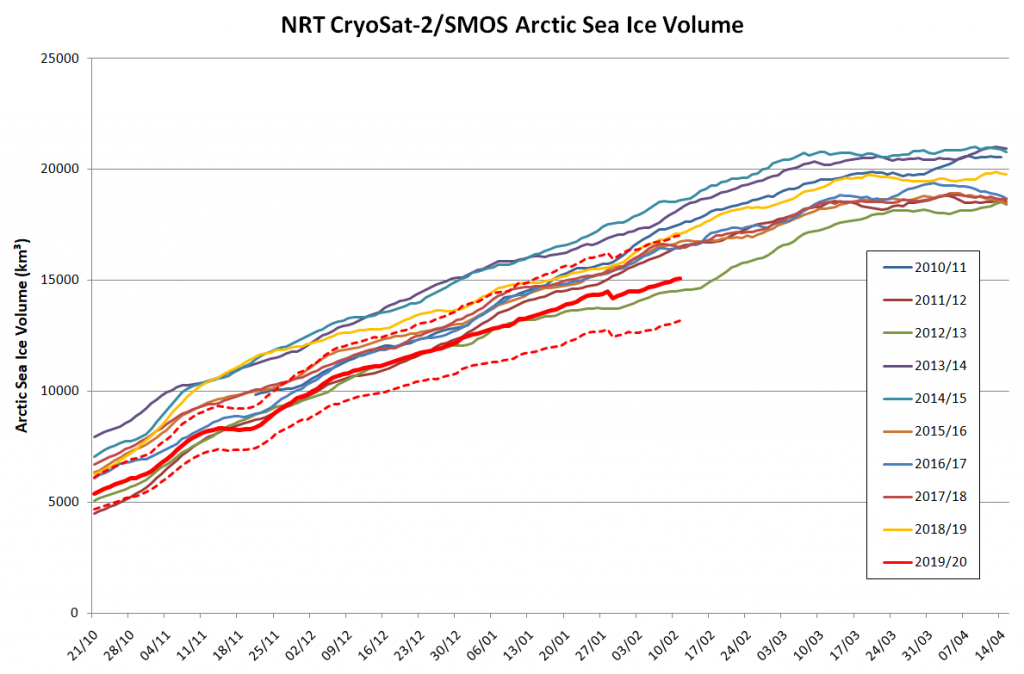
Here’s another weekly NRT volume update:
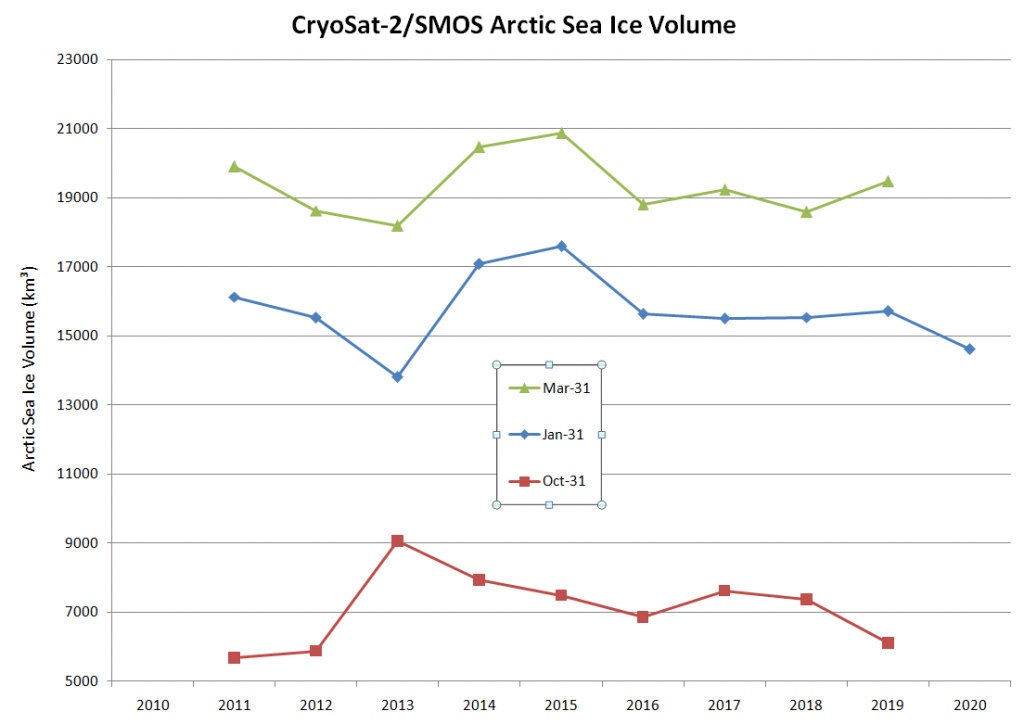
This time I’ve left off the NRT data from February 6th onwards, since the “issue” referred to above obviously hasn’t been solved yet. As an added bonus here’s a graph showing the trends (or lack thereof) on 3 dates during the October to April freezing season: