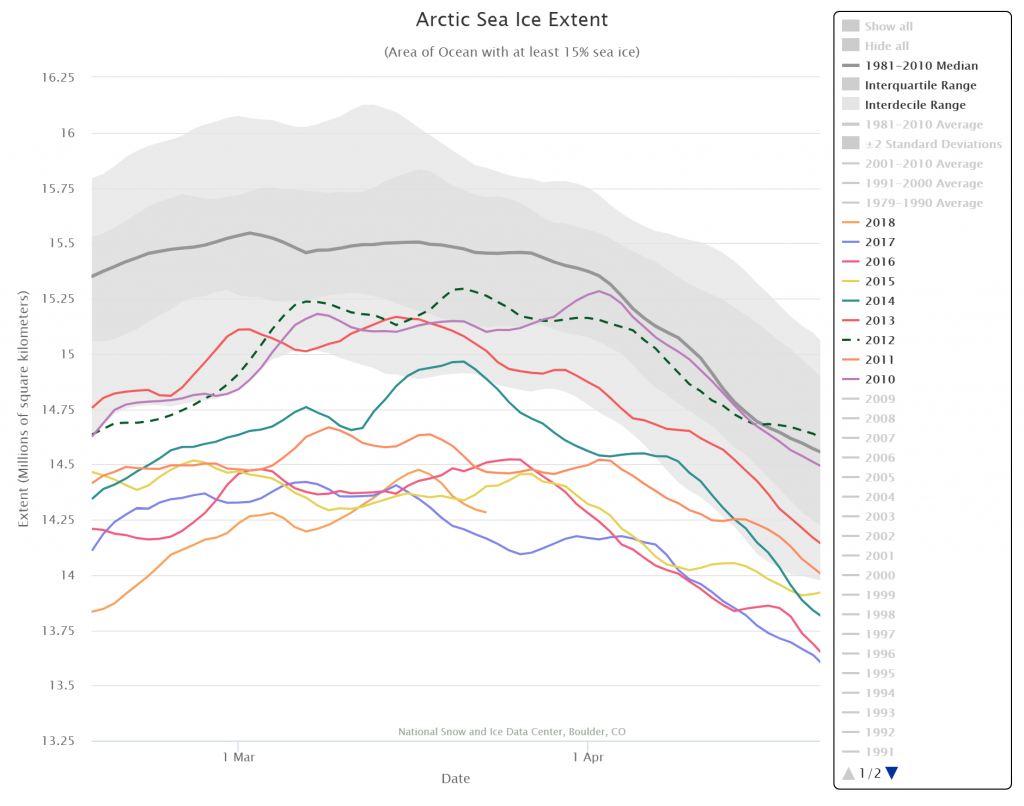
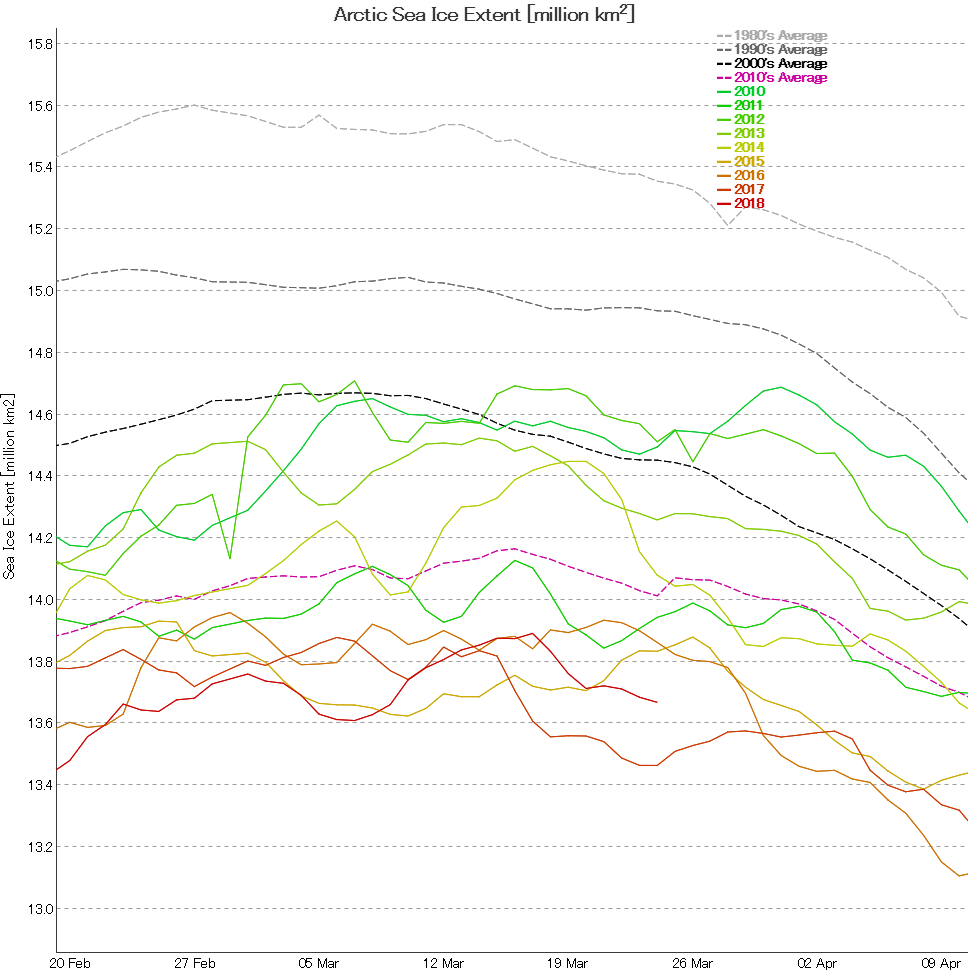
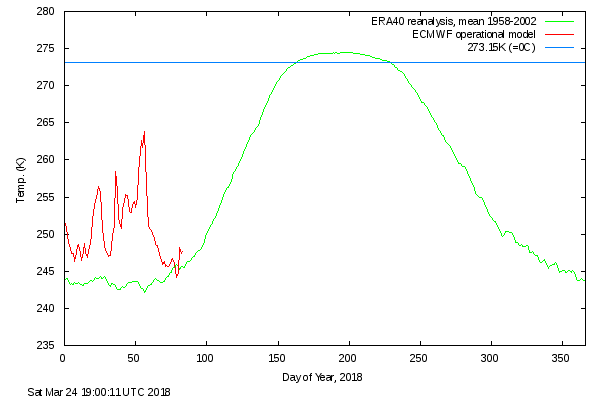
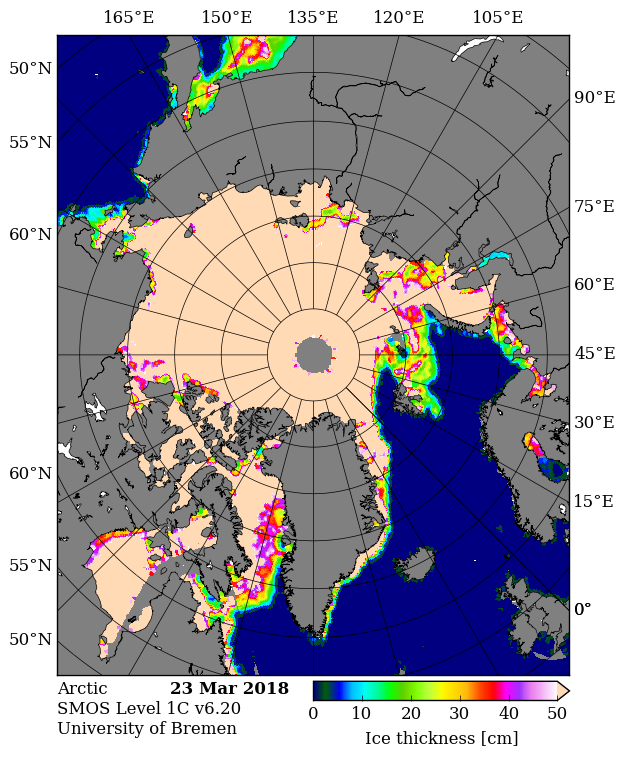
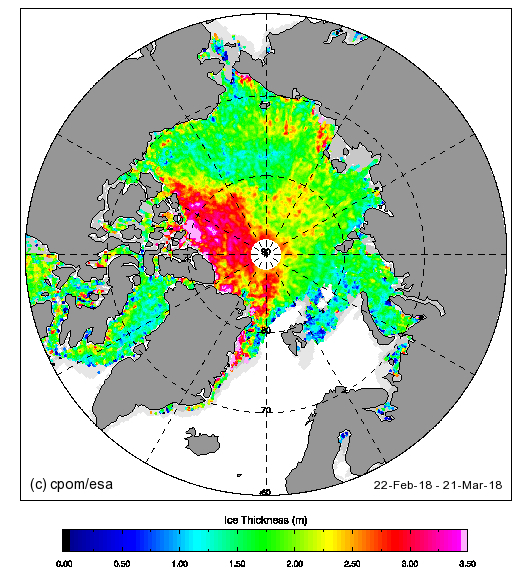
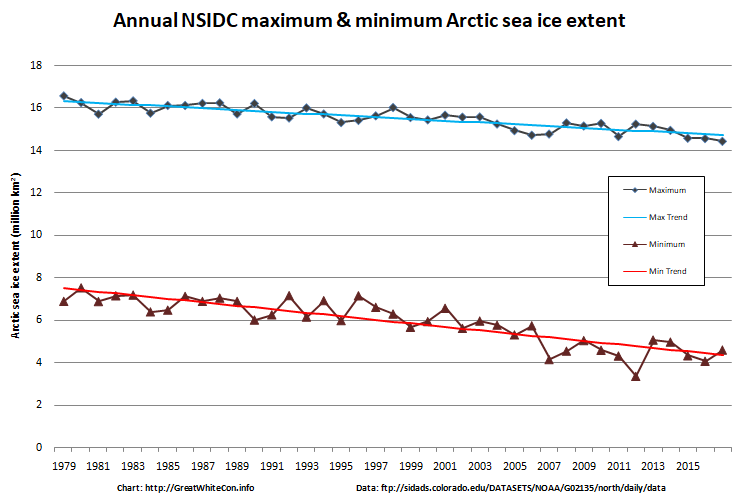
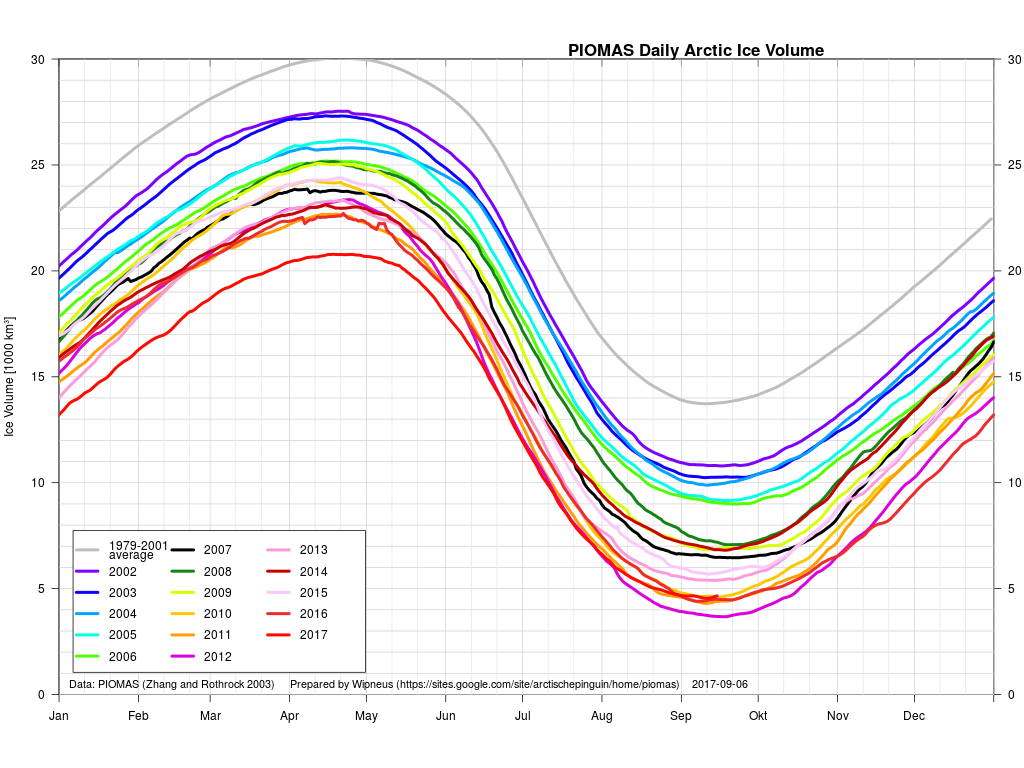
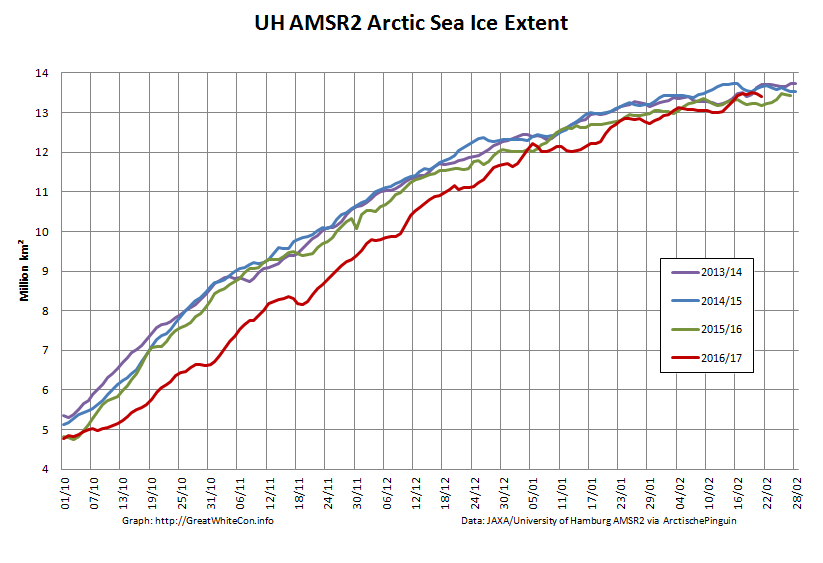
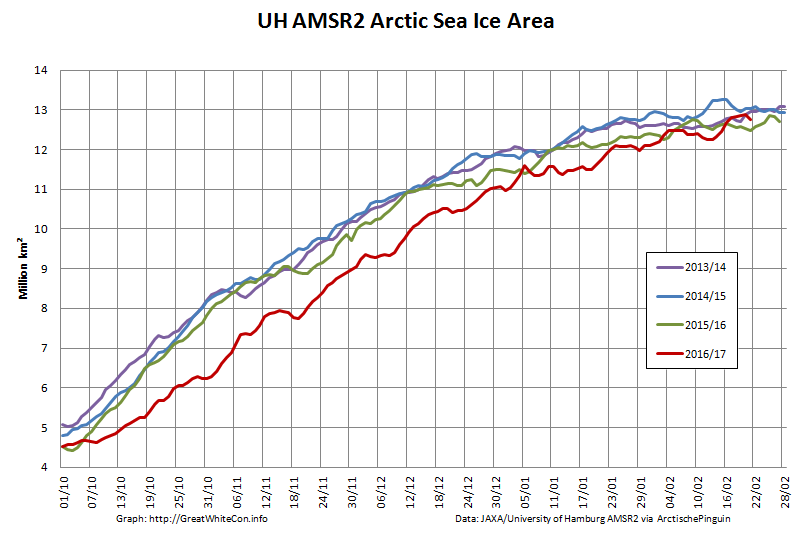
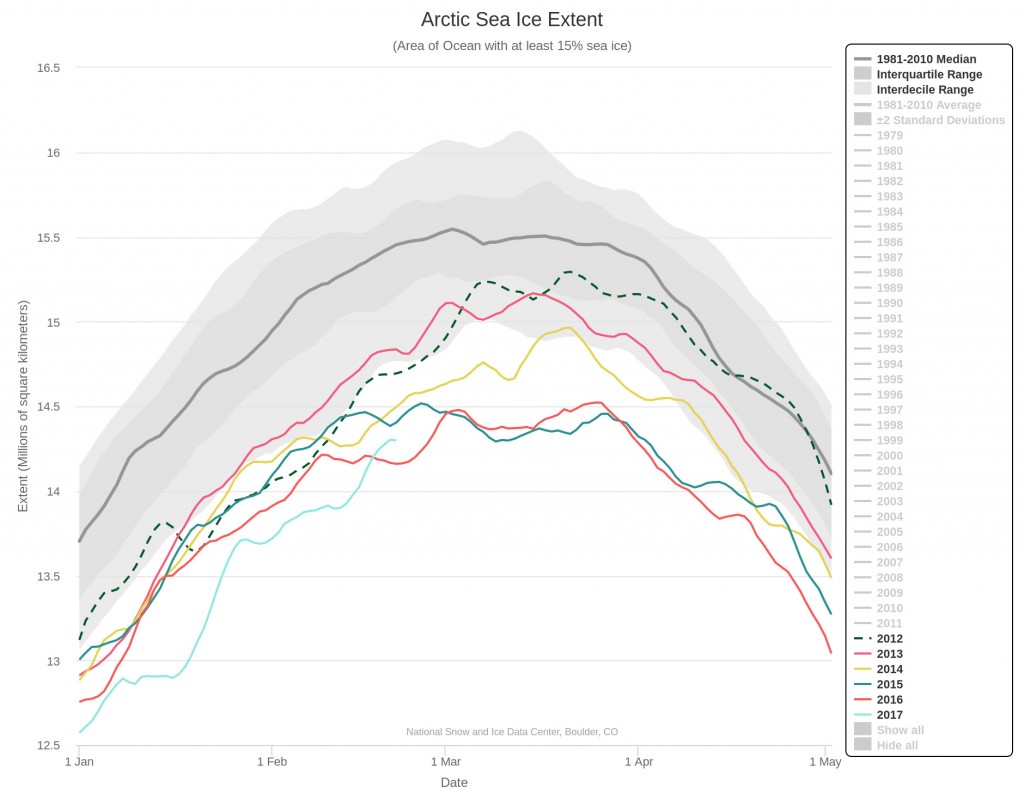
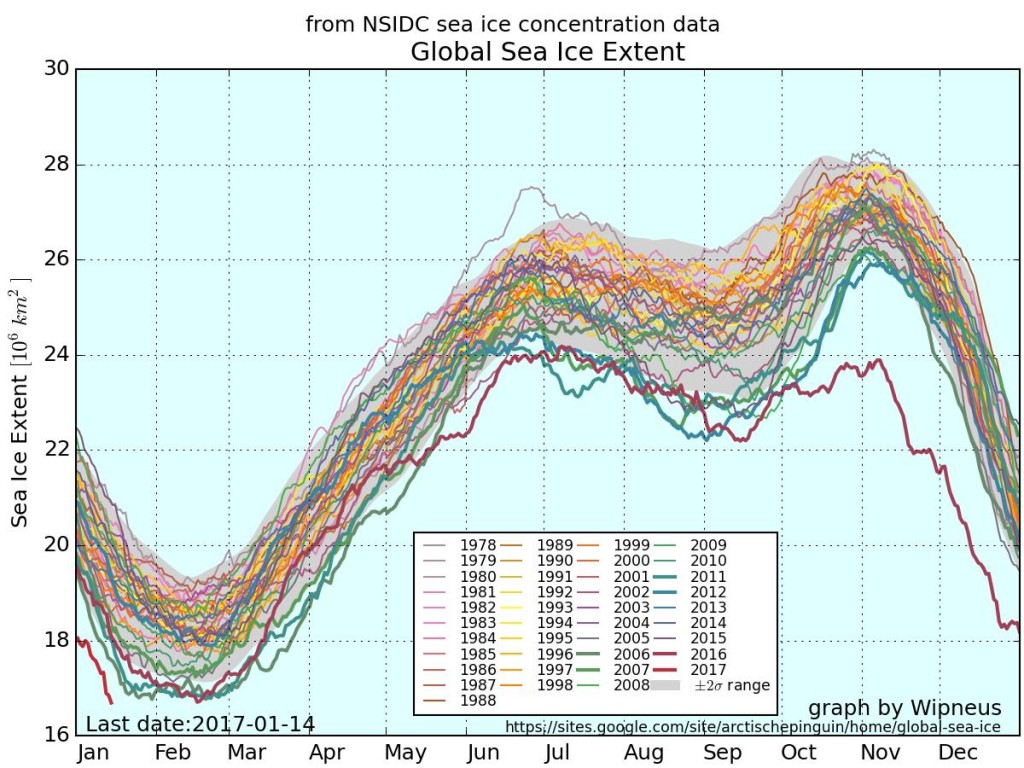
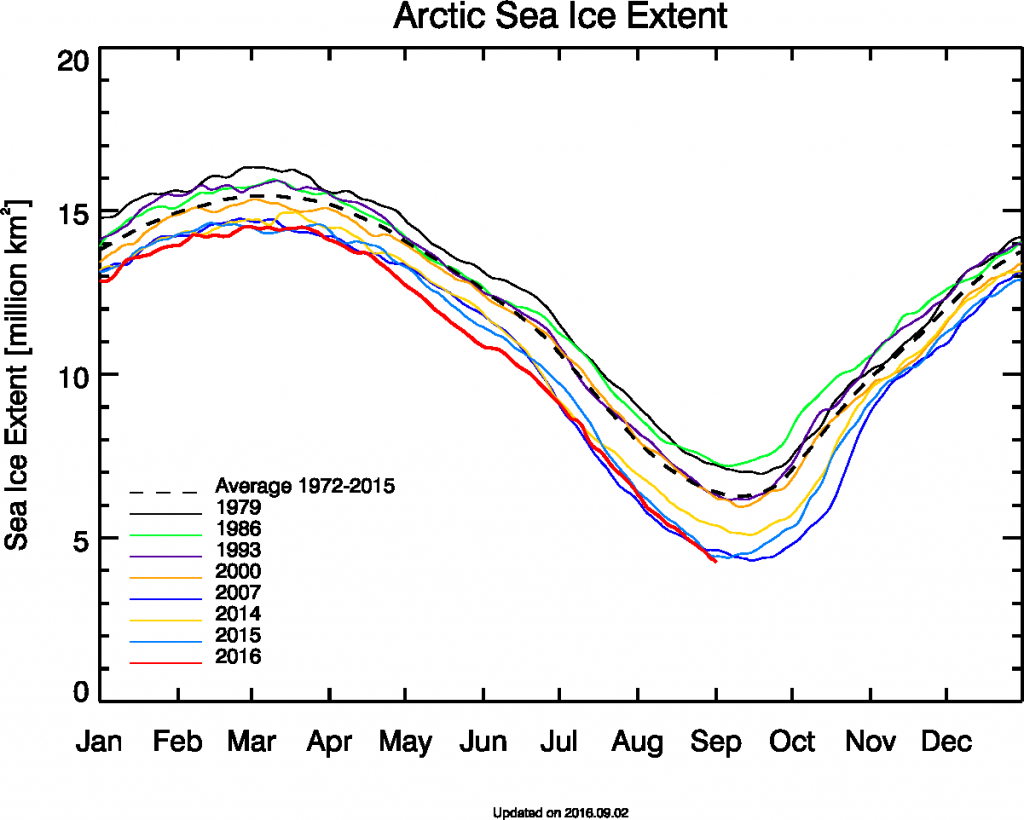
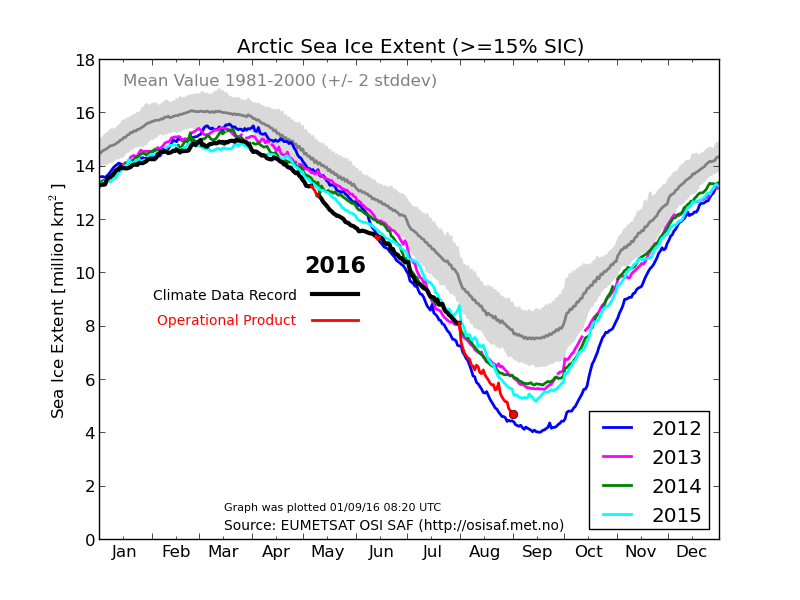
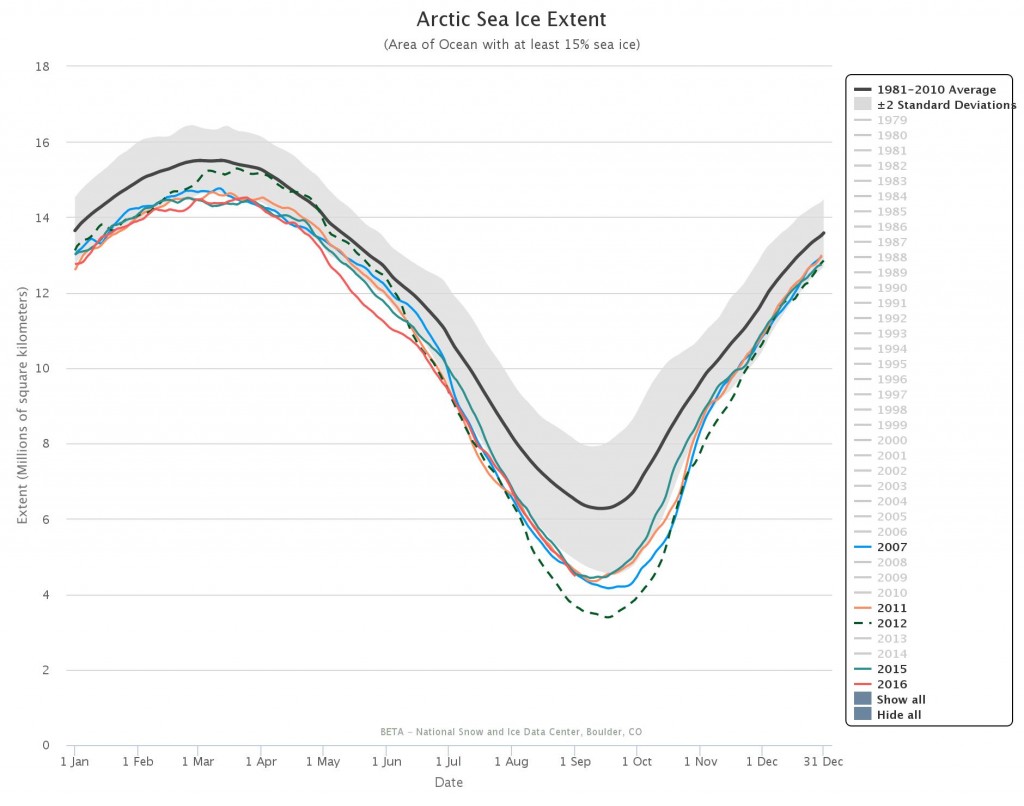
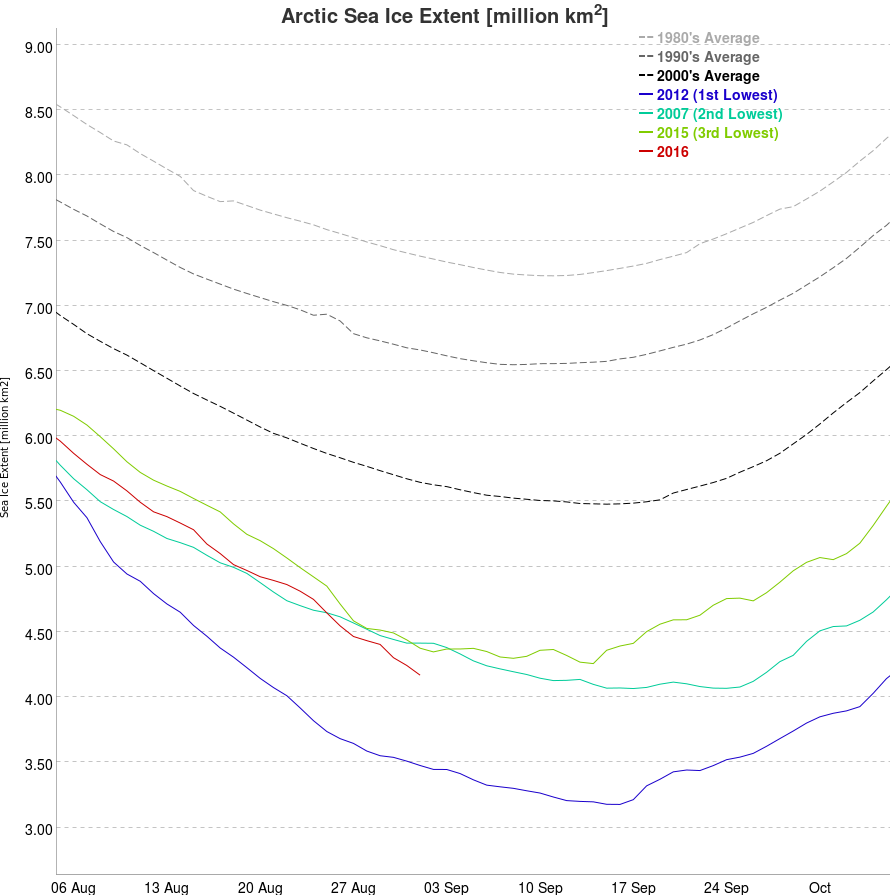
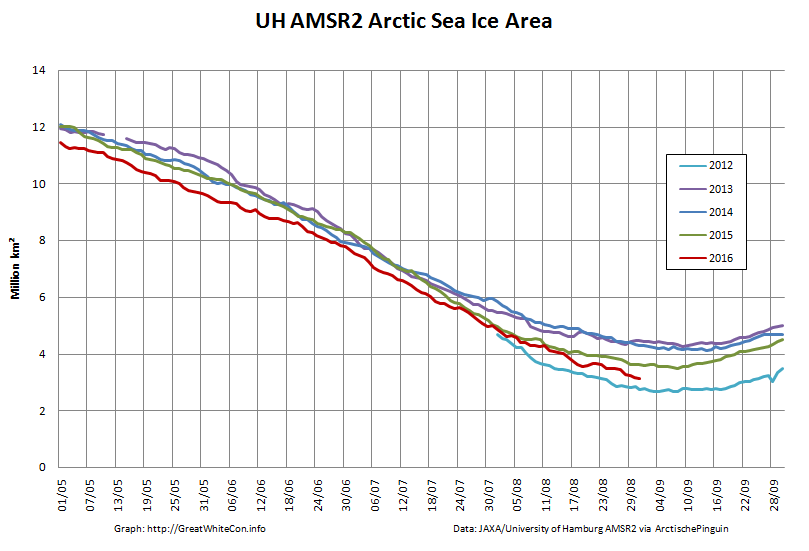
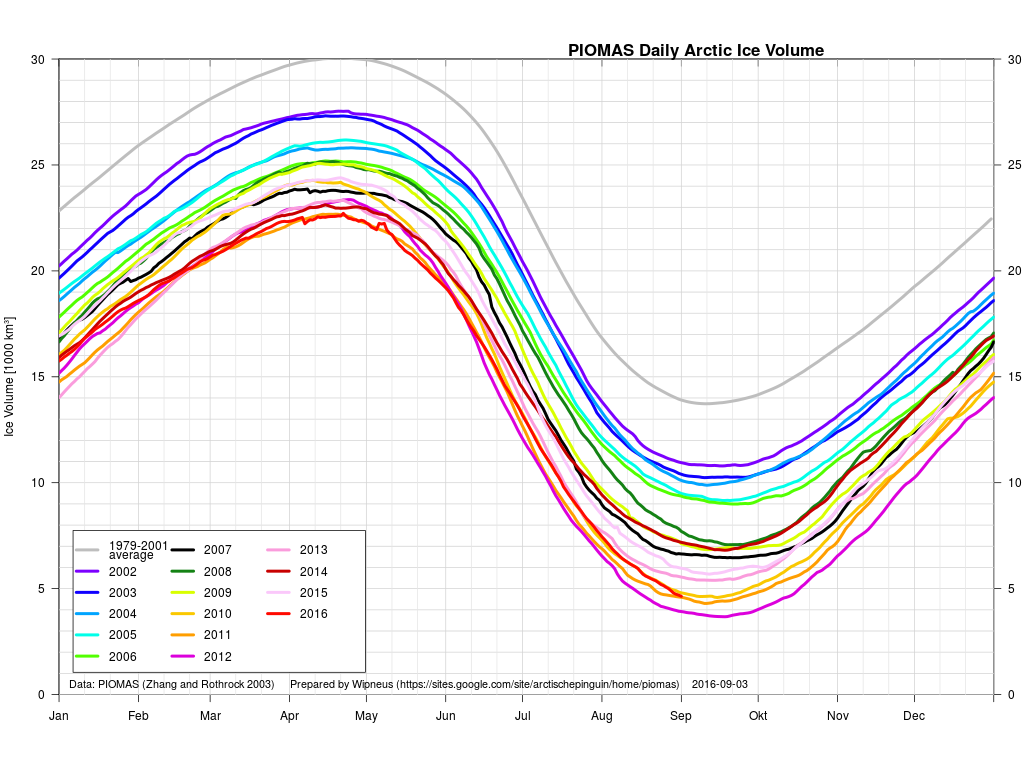
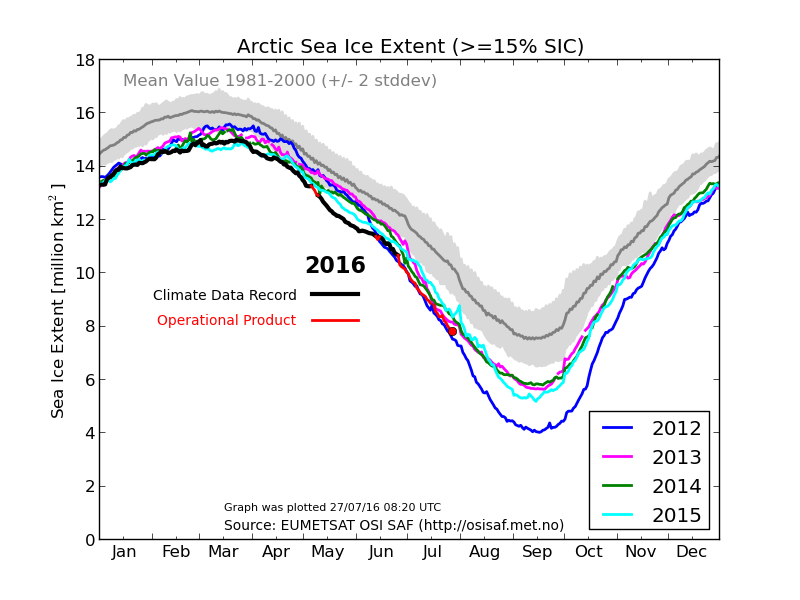
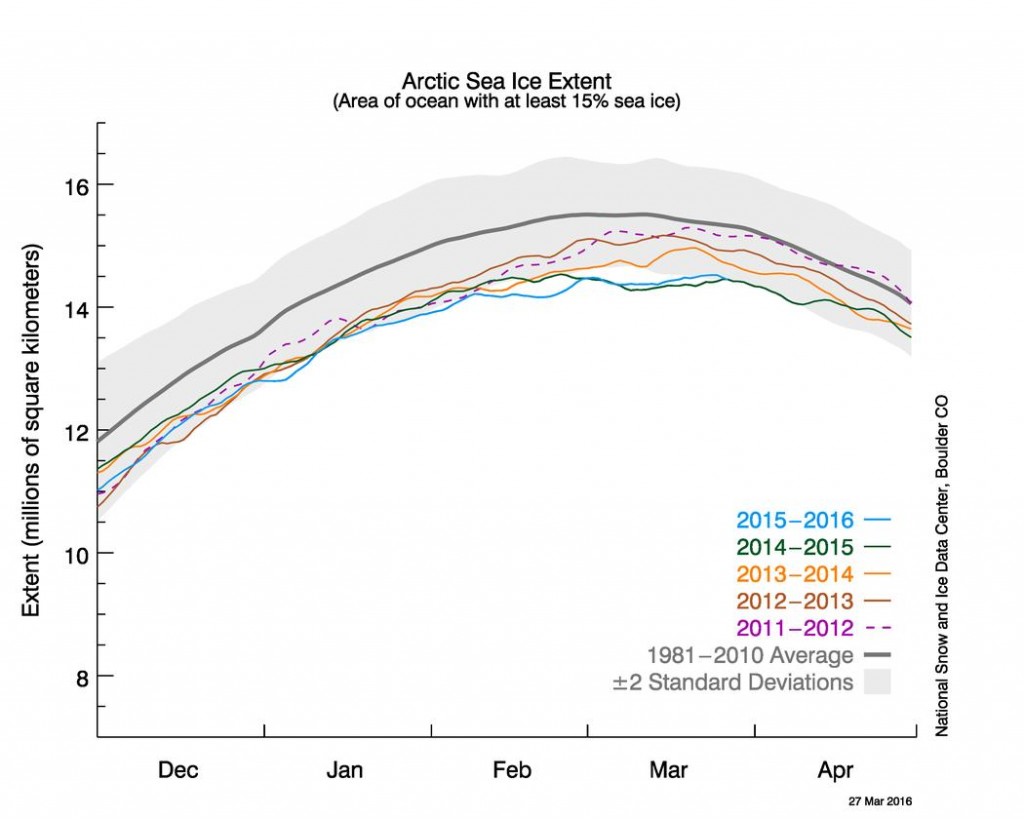
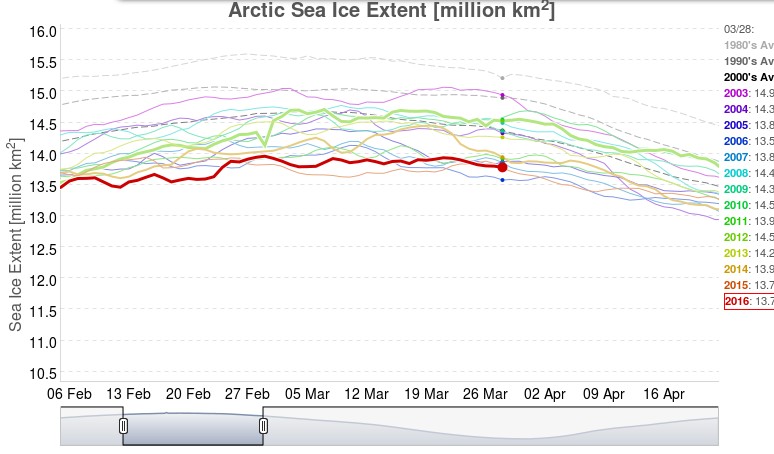
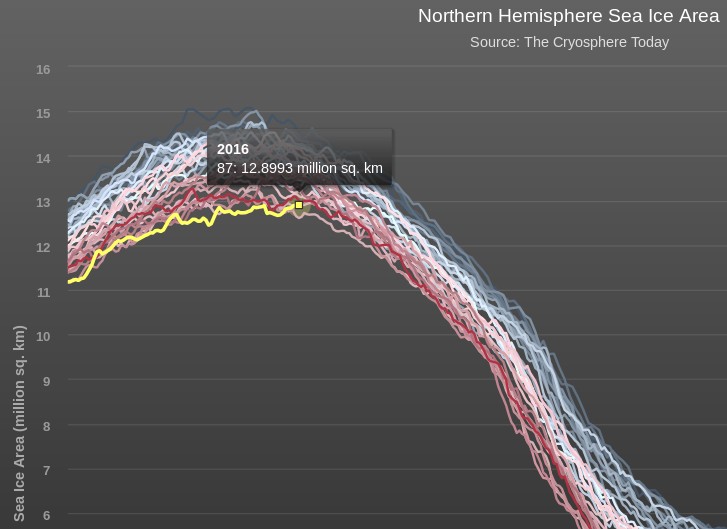
September is upon us once again, the month in which the assorted Arctic sea ice area and extent metrics (almost) always reach their respective annual minima. Now we are free to start speculating about what the assorted minima will be, and on what date.
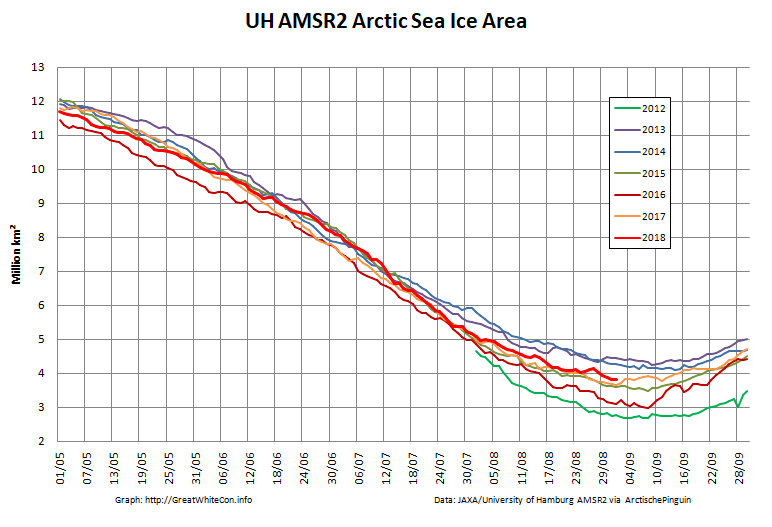
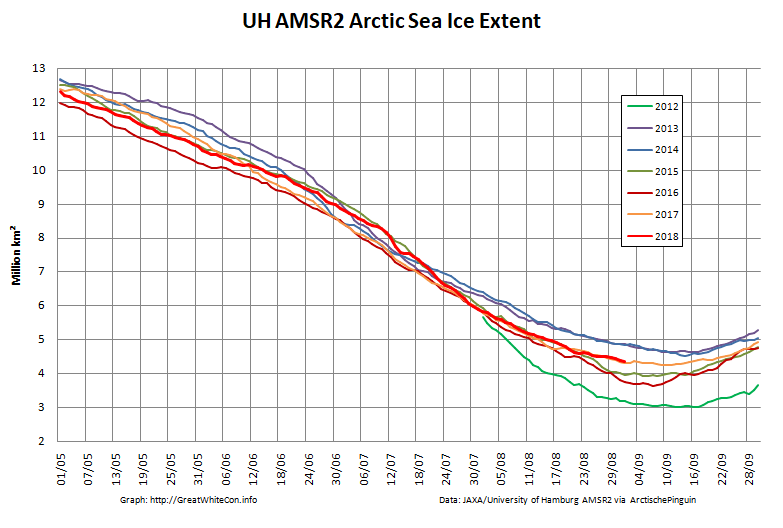
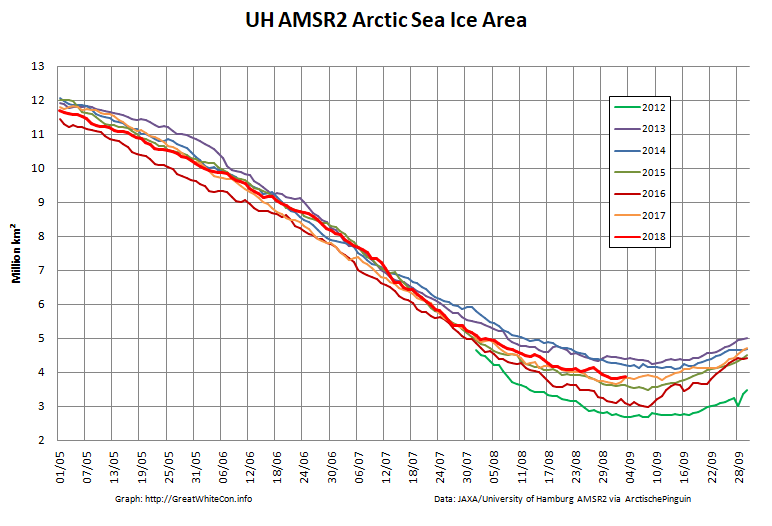
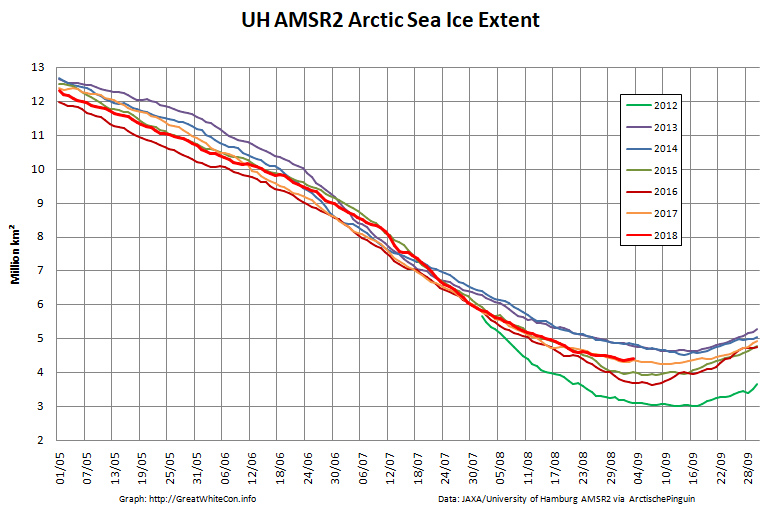
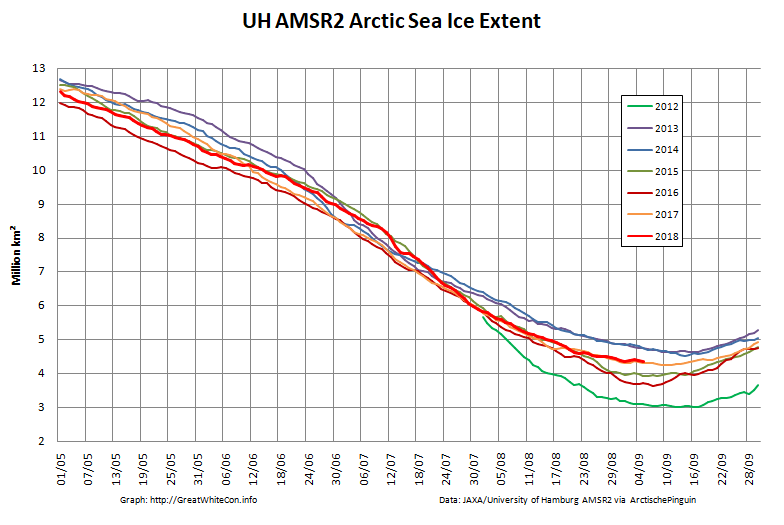
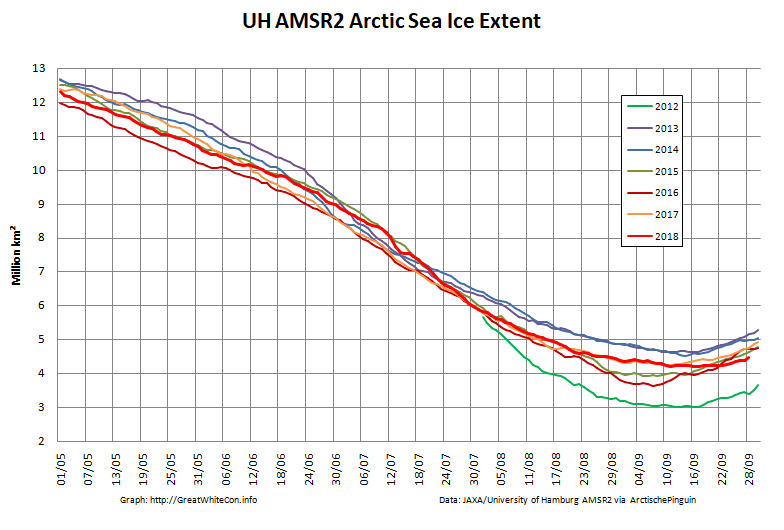
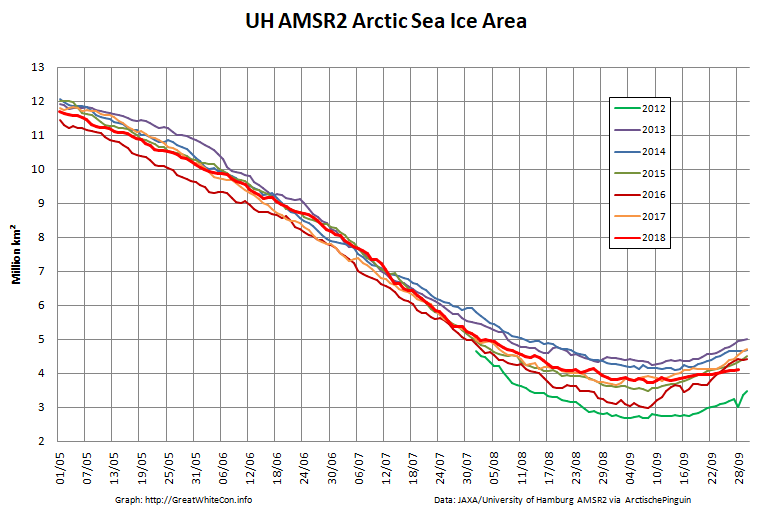
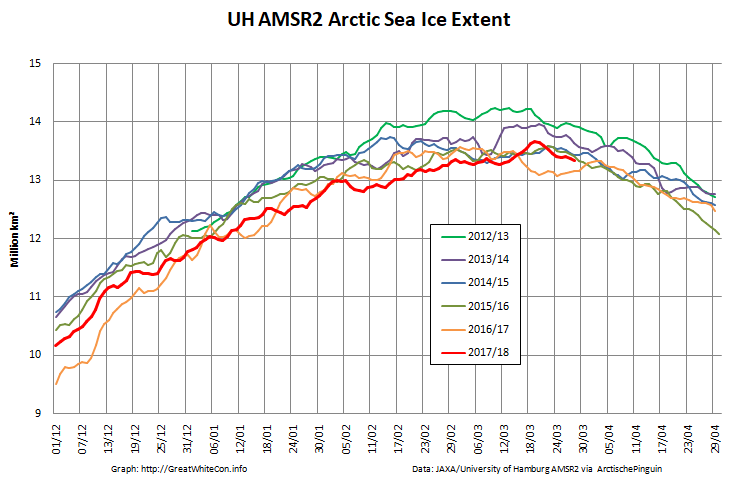
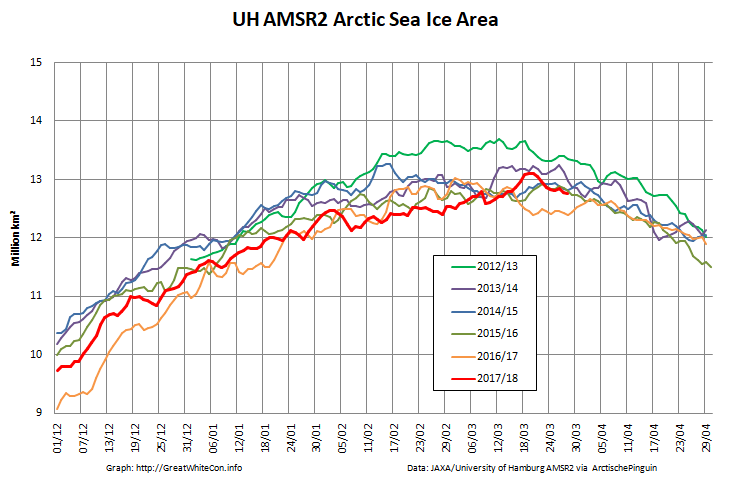
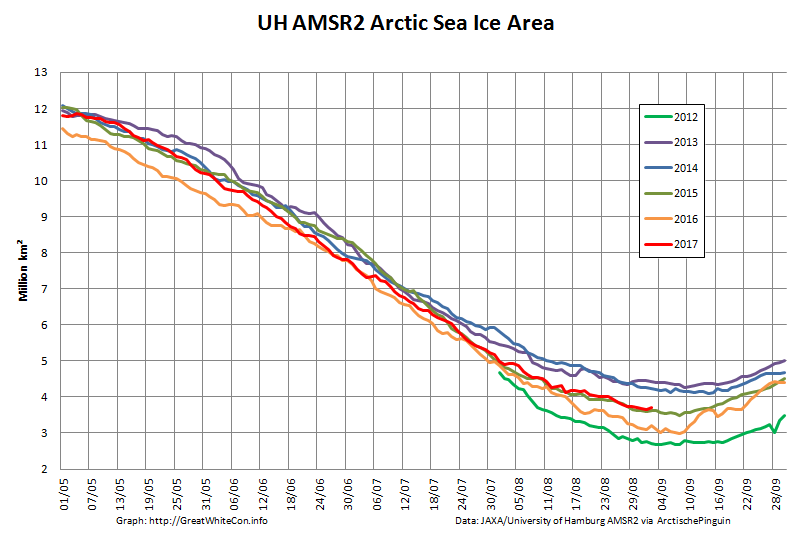
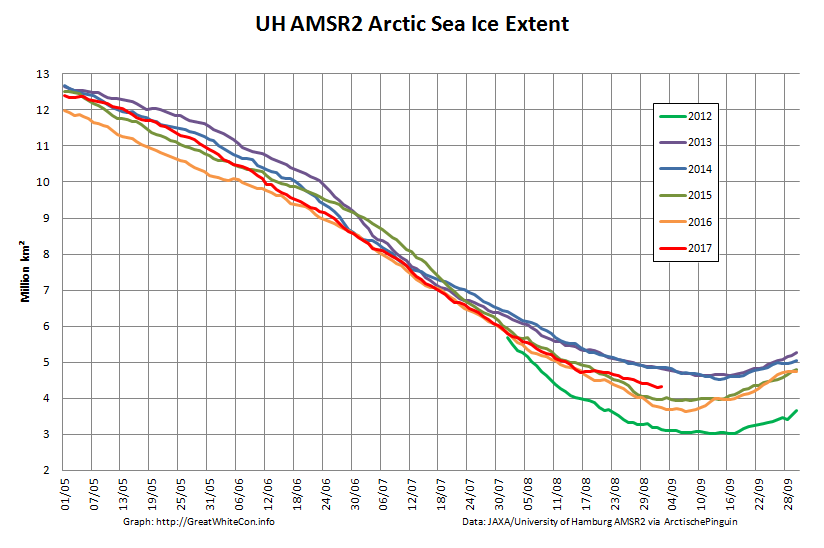
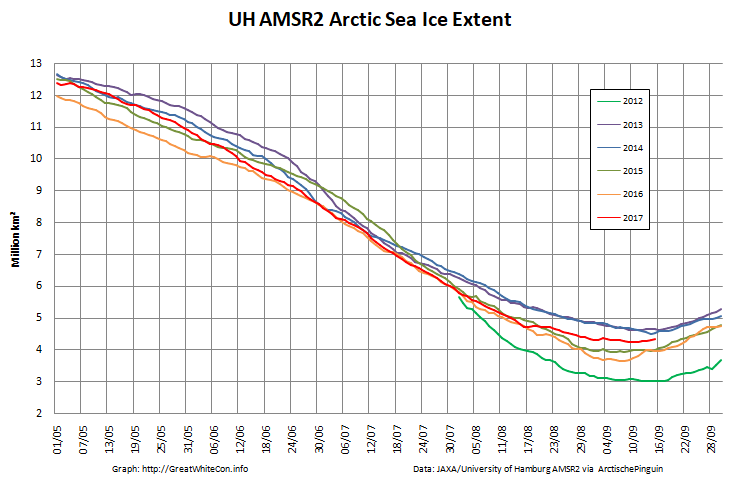
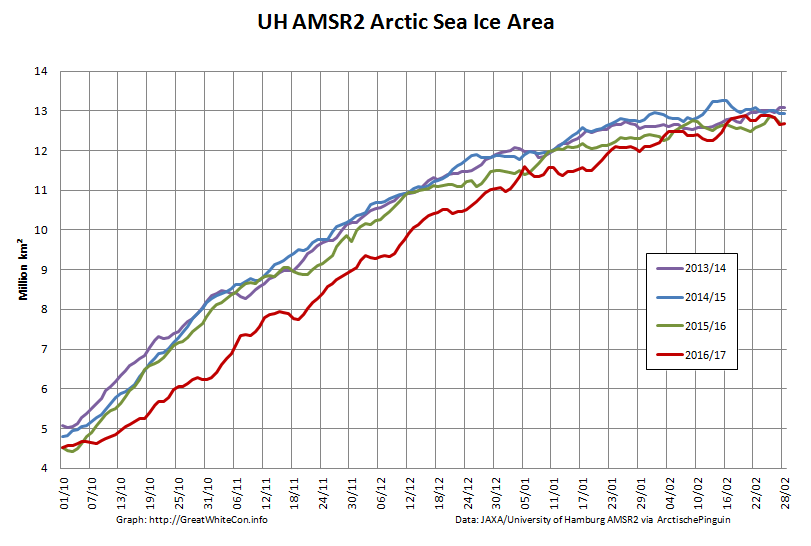
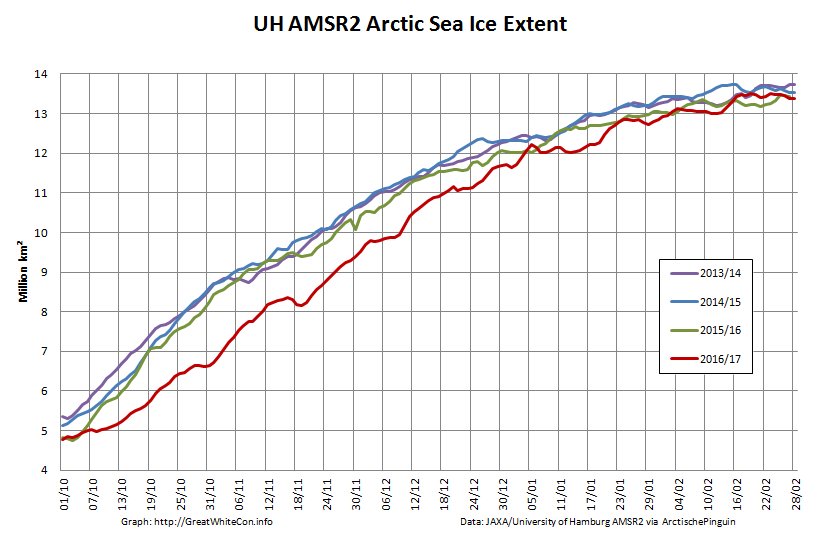
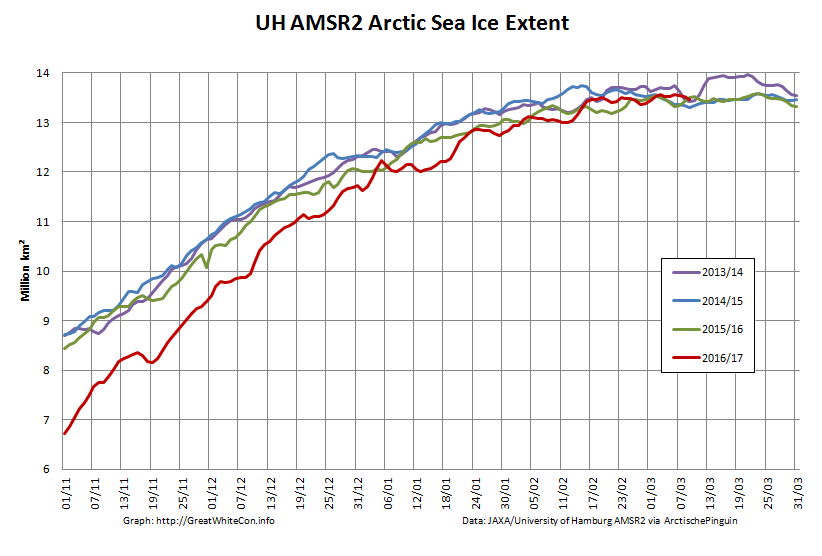
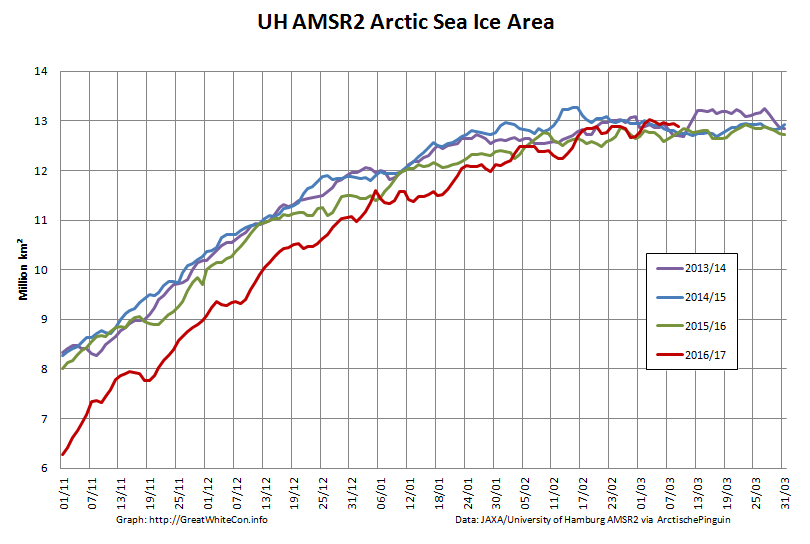
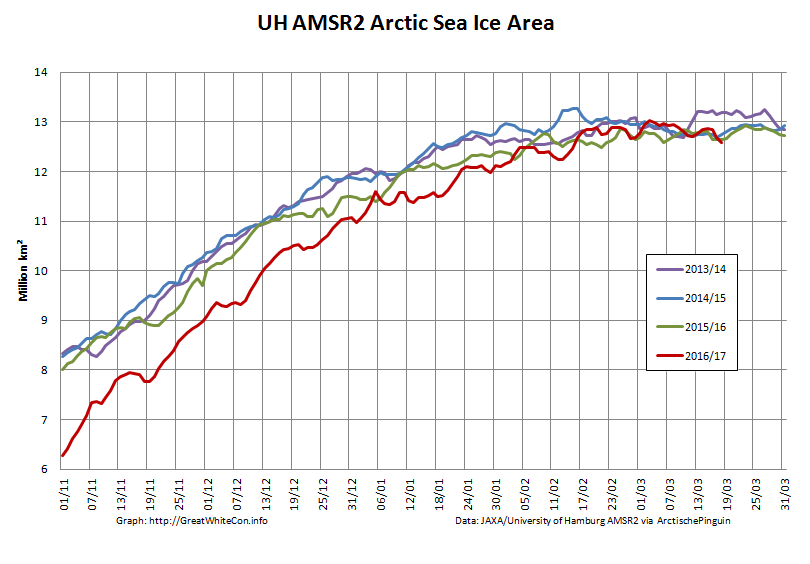
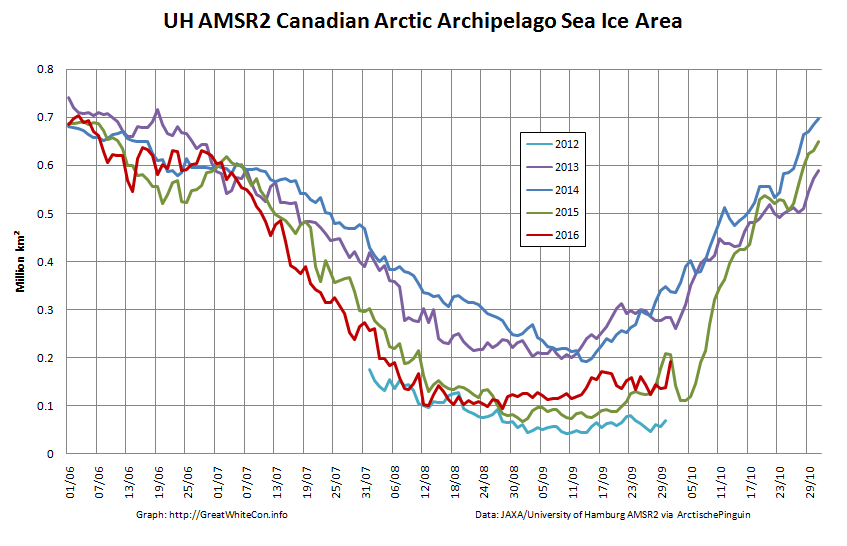
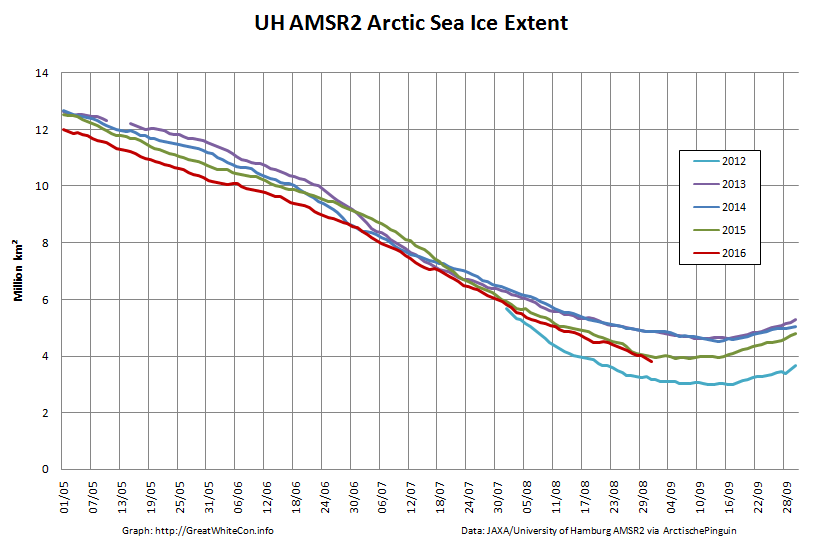
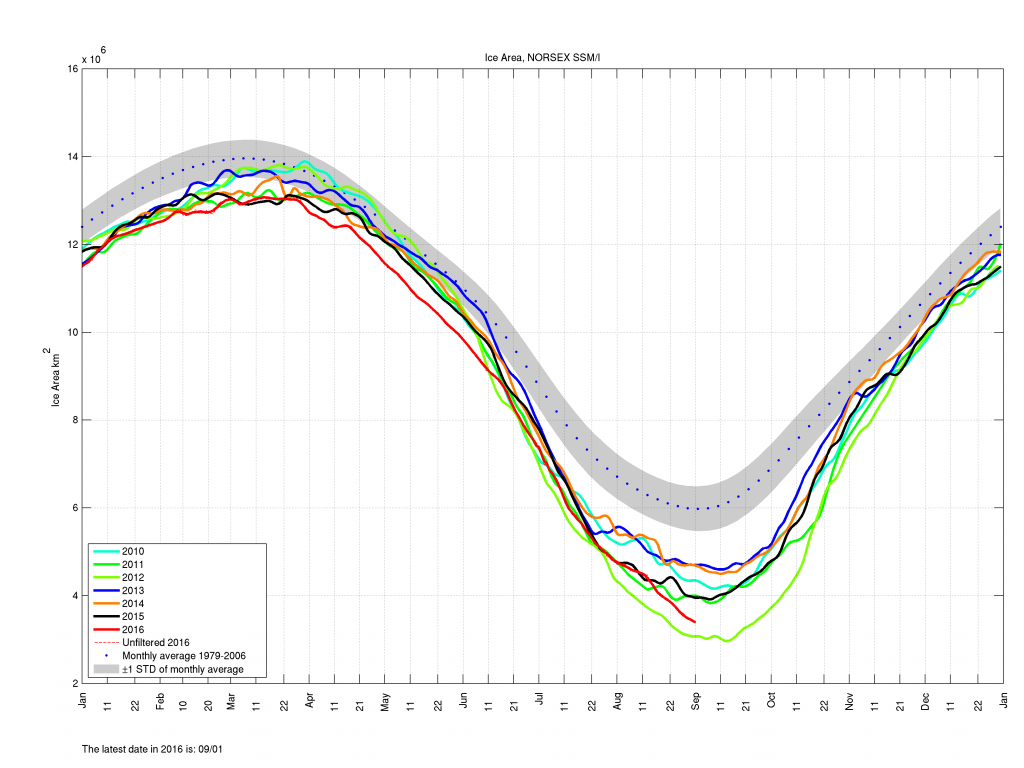
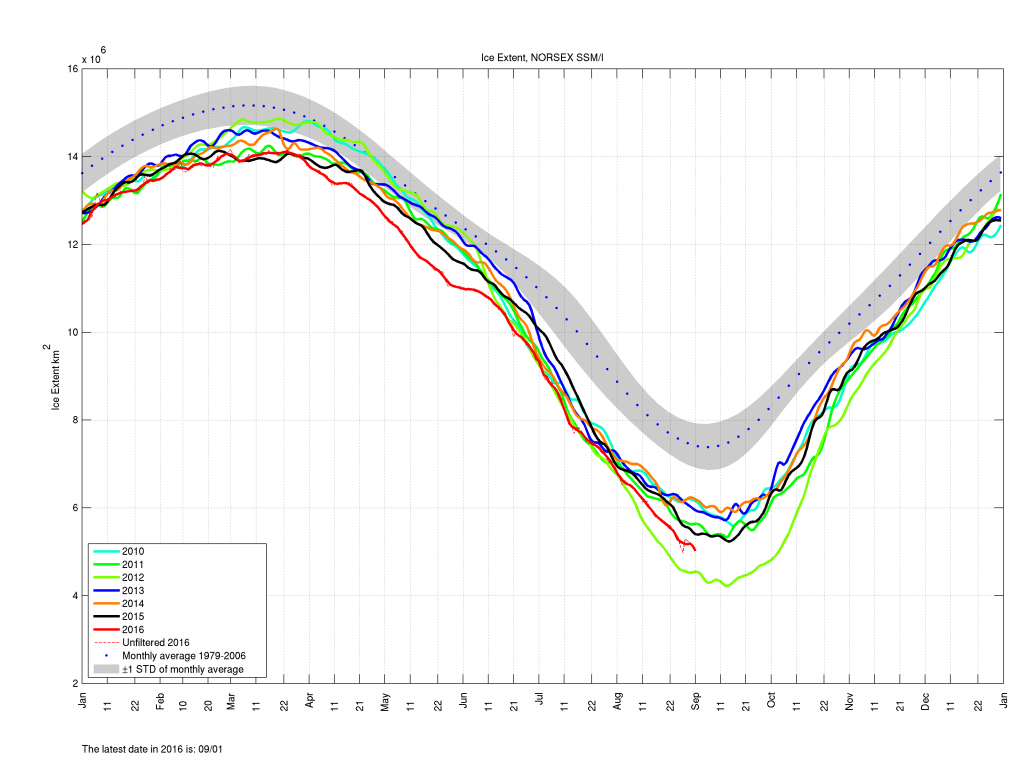
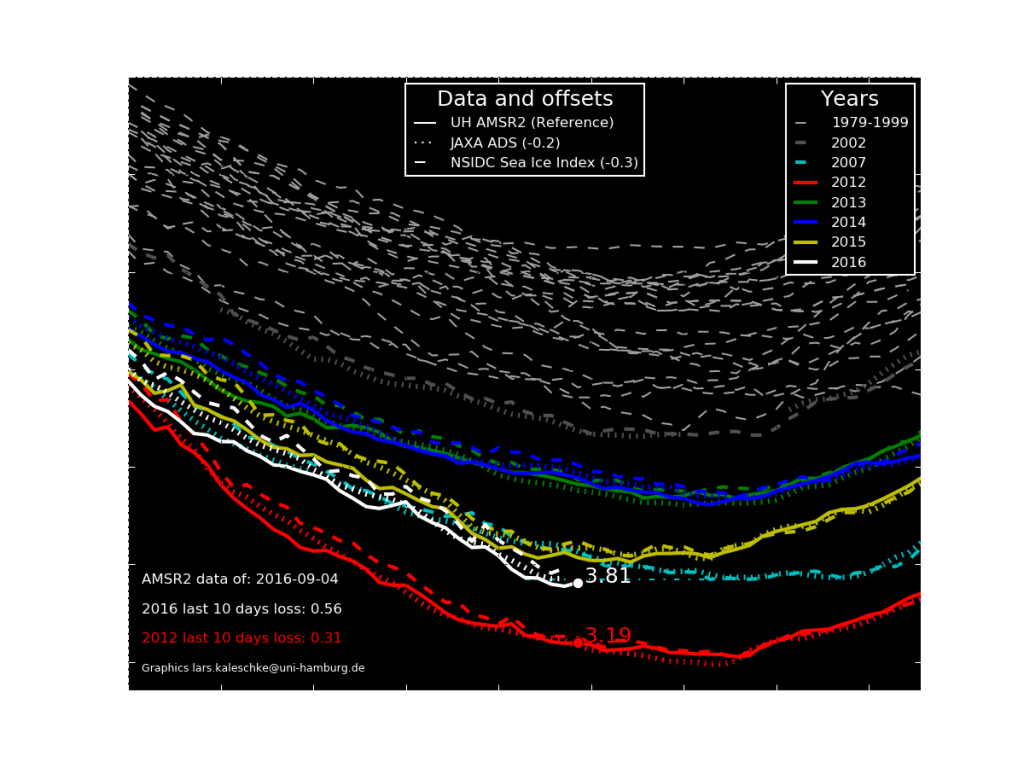
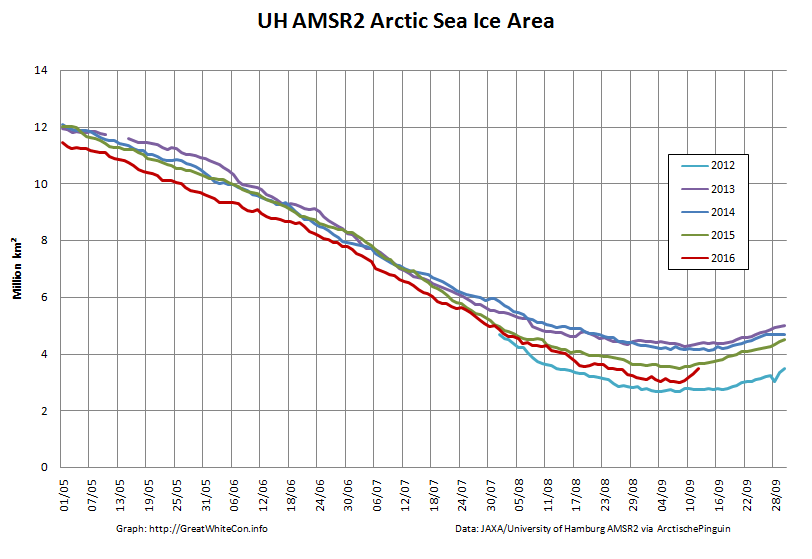
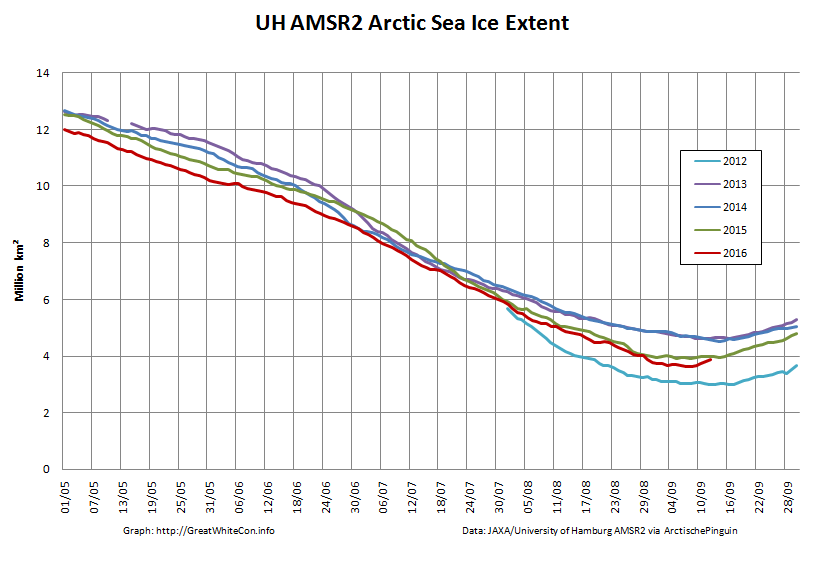
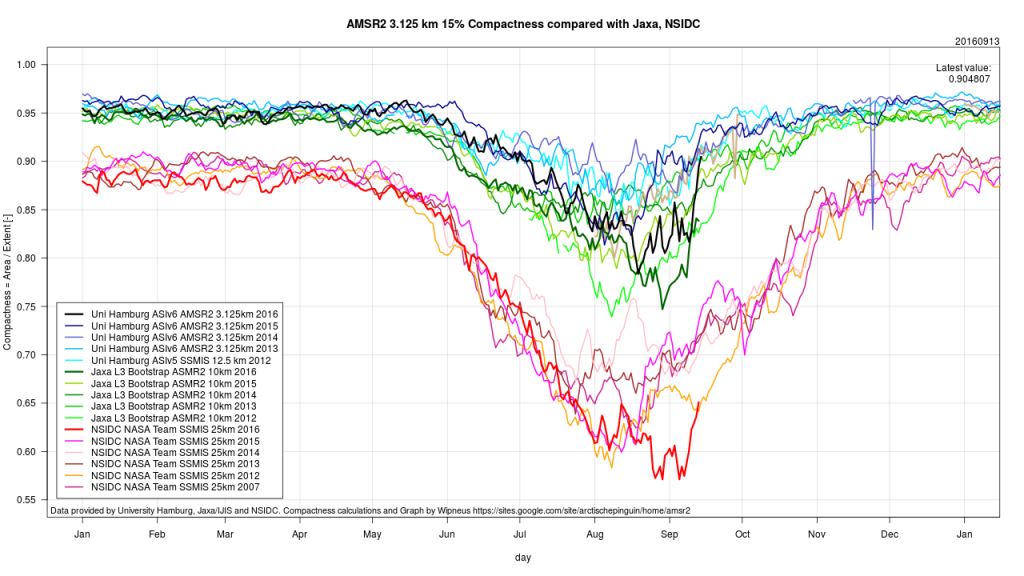
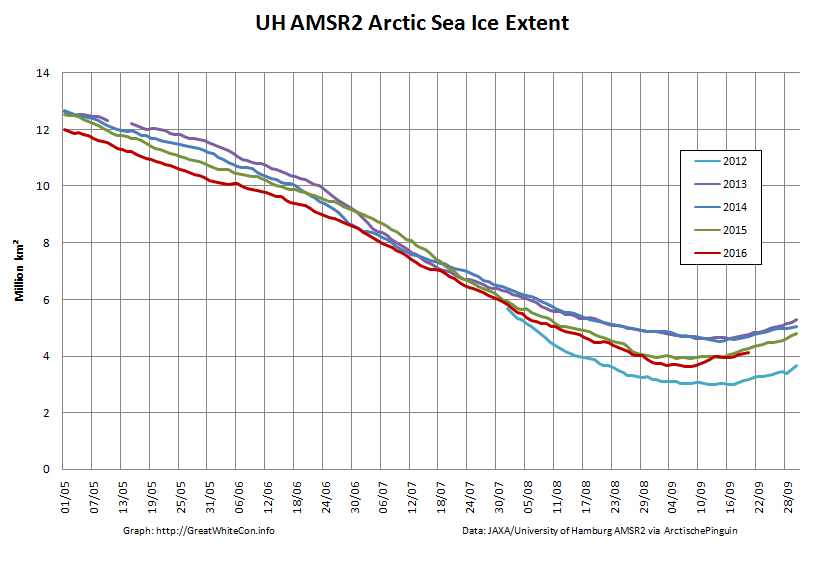
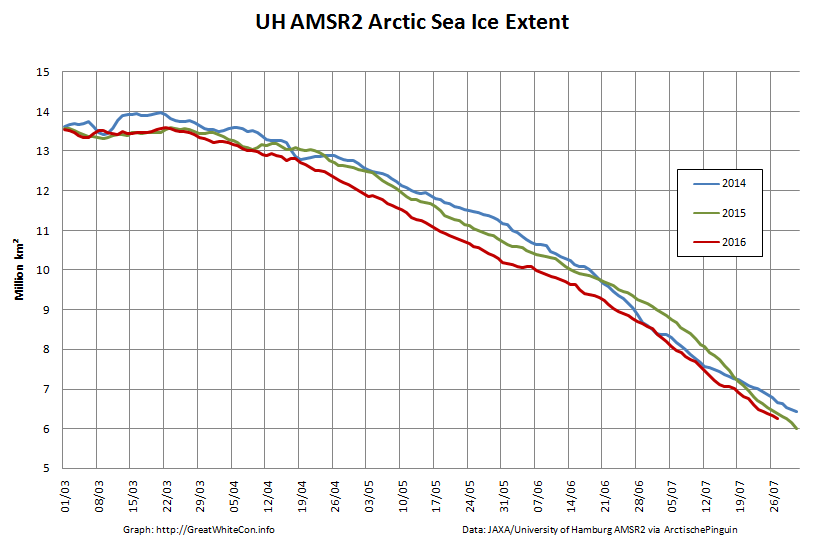
To begin with let’s take a look at our much beloved high resolution AMSR2 metrics derived by “Wipneus” from the University of Hamburg’s AMSR2 concentration data:
There’s currently some divergence between the area and extent graphs. Area is declining rapidly for the time of year, whilst extent seems to almost have come to a standstill!
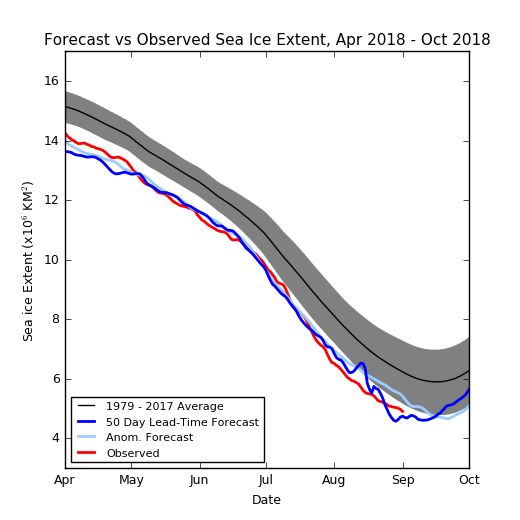
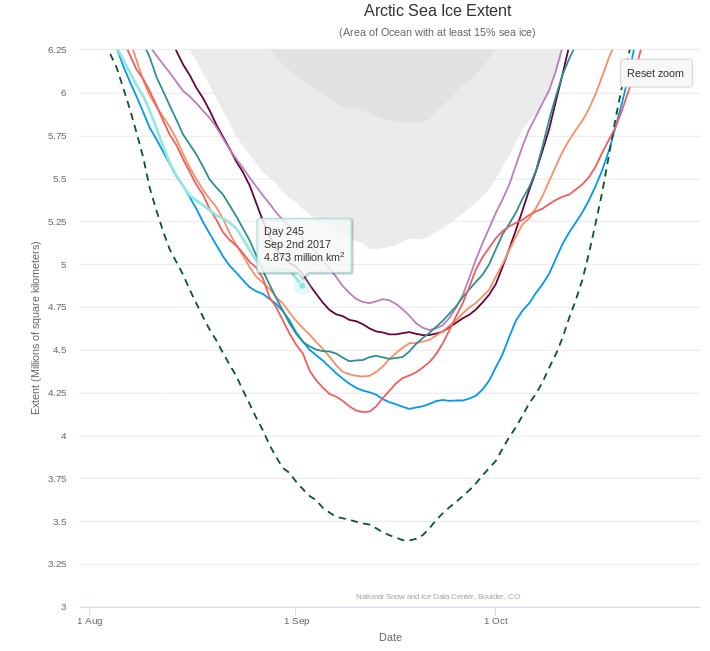
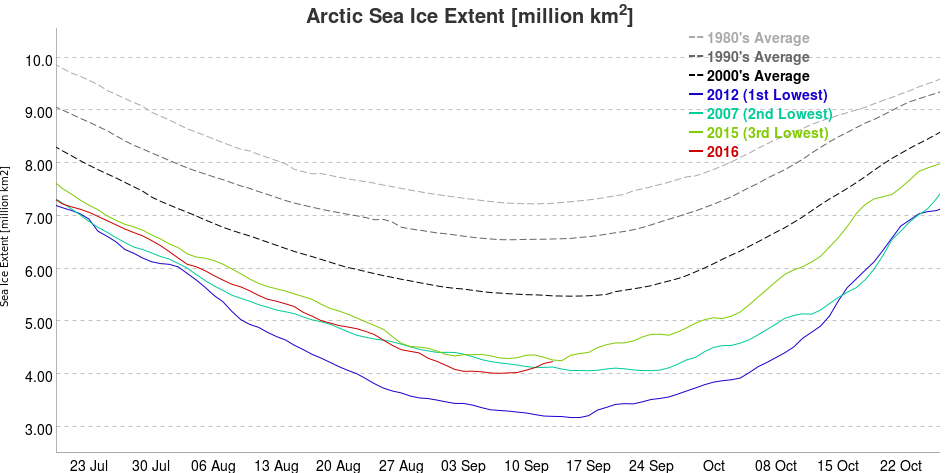
Next here’s the prediction of the late, great Andrew Slater’s Probabilistic Ice Extent algorithm:
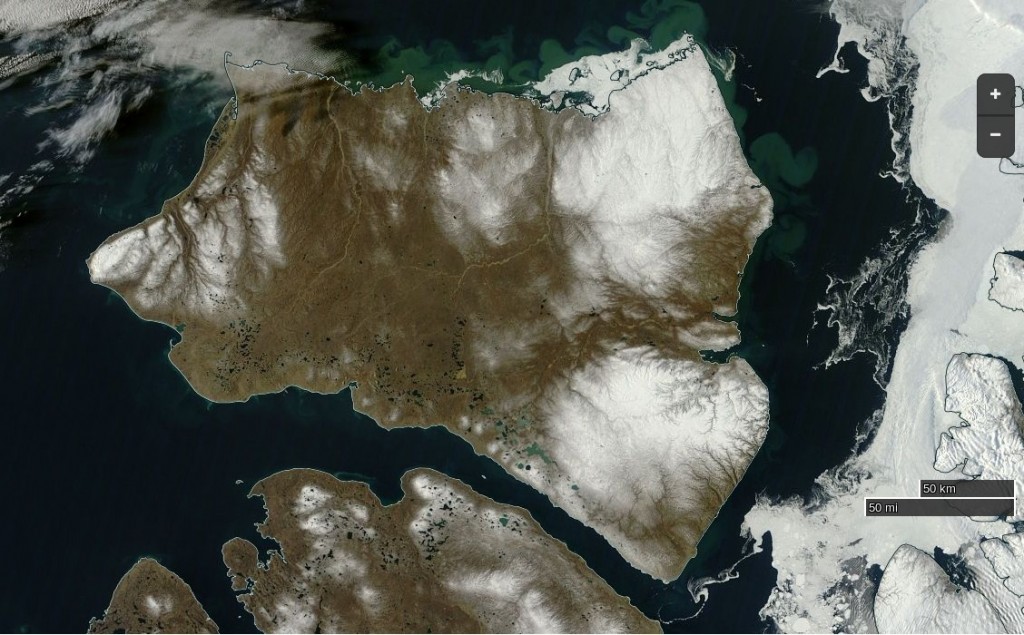
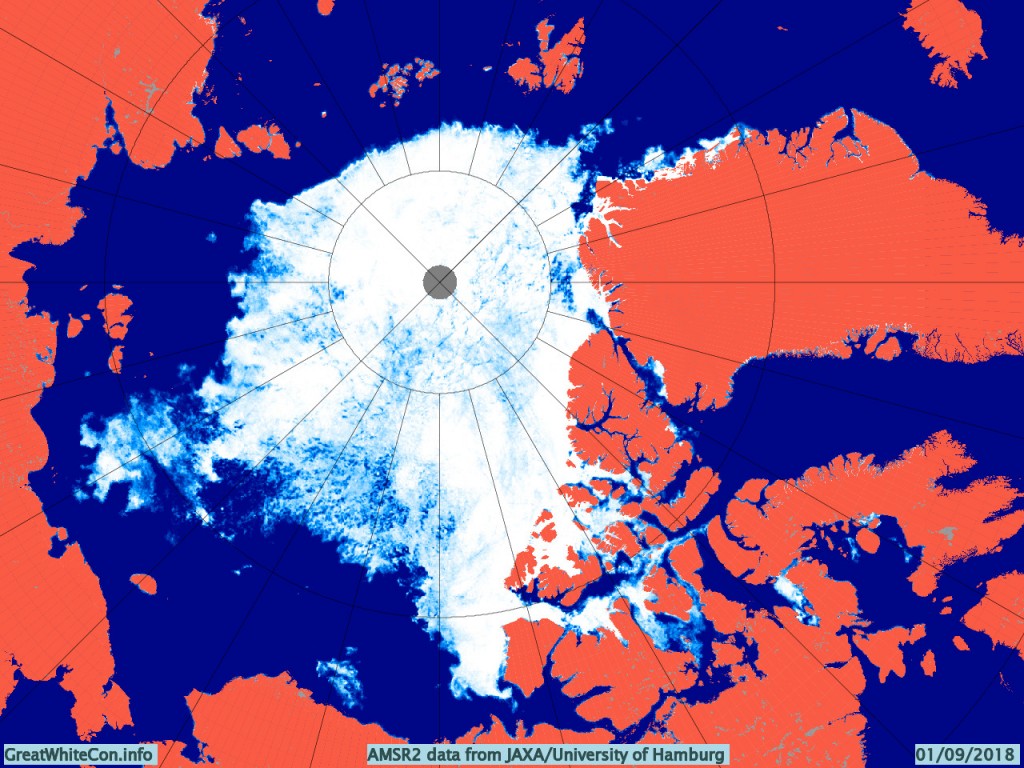
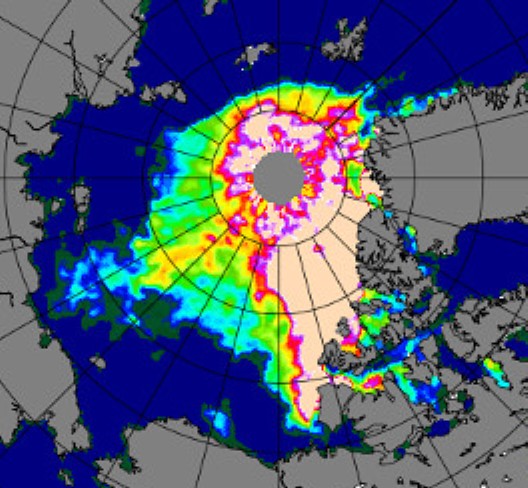
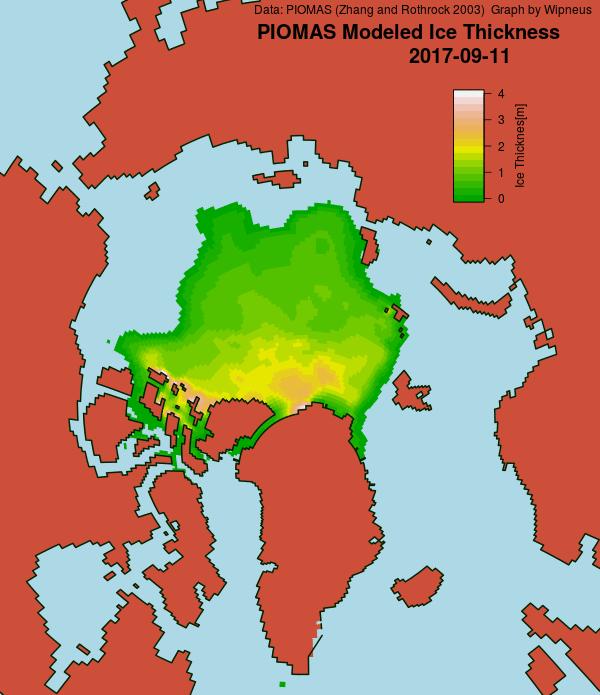
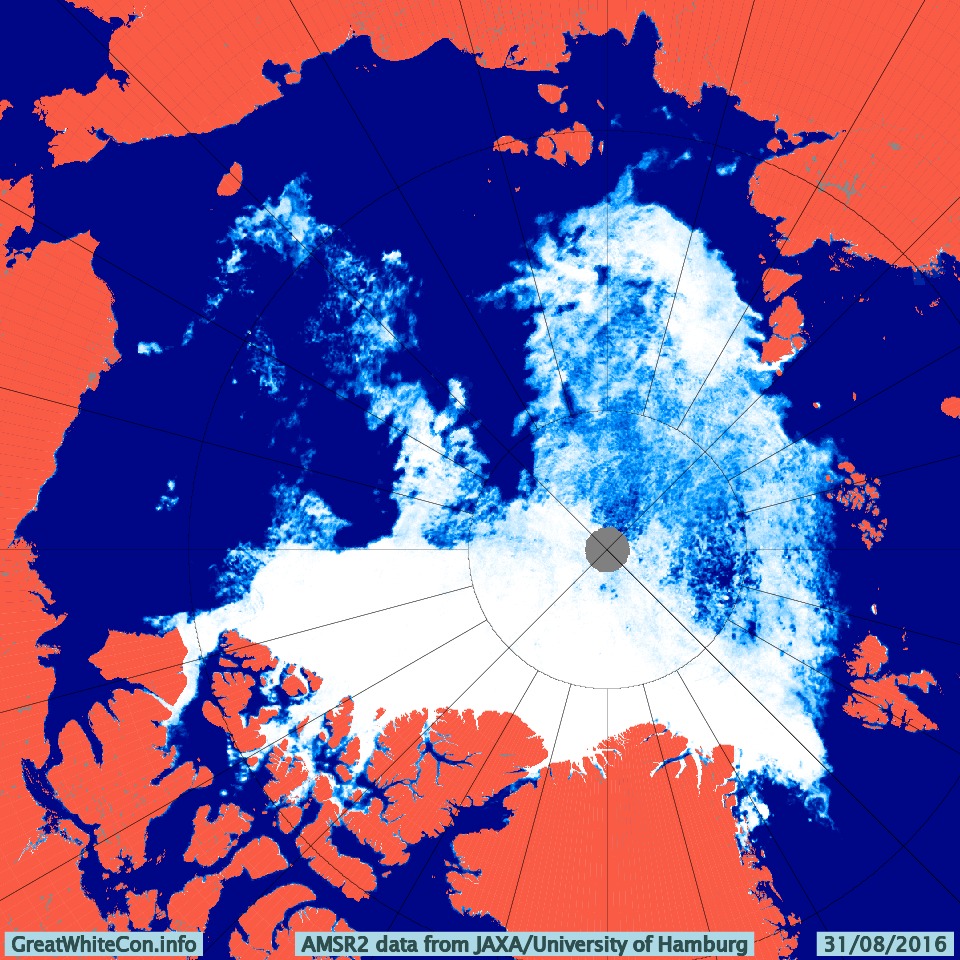
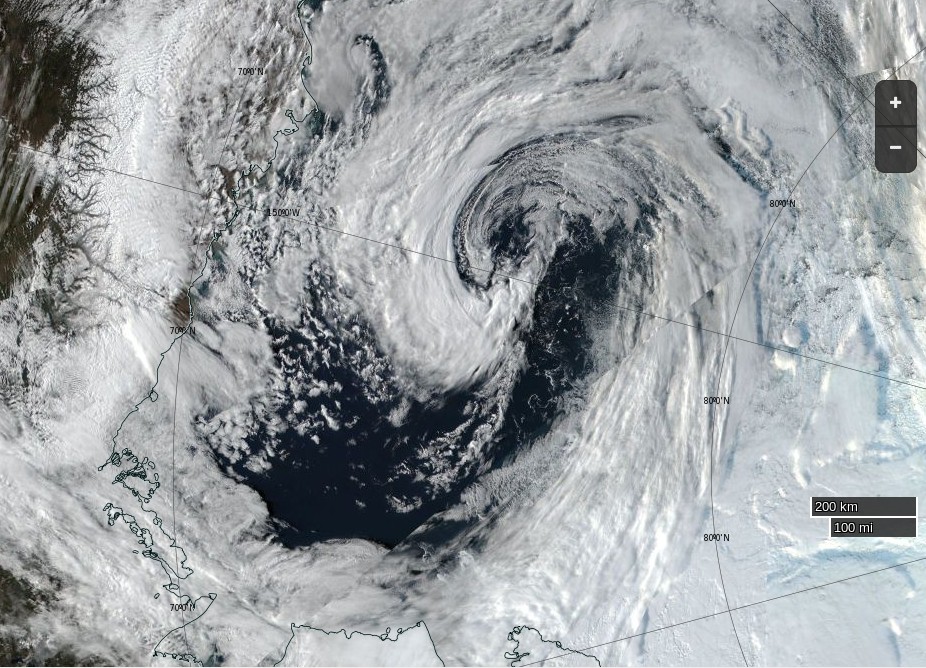
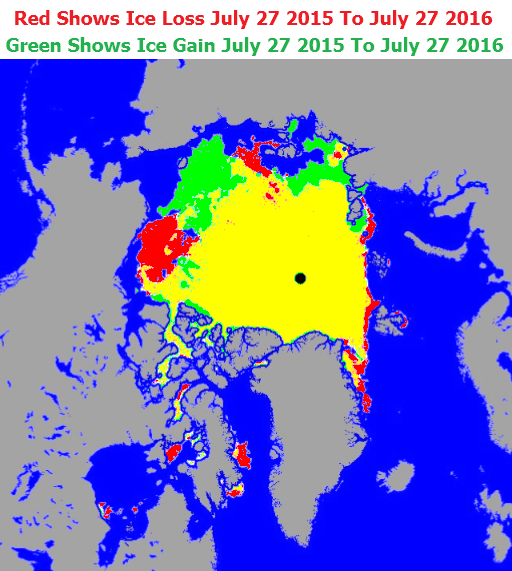
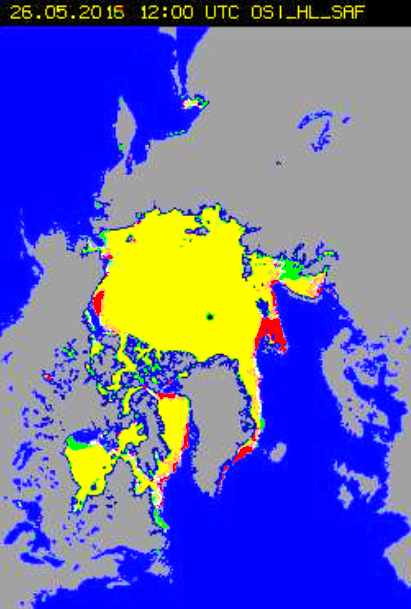
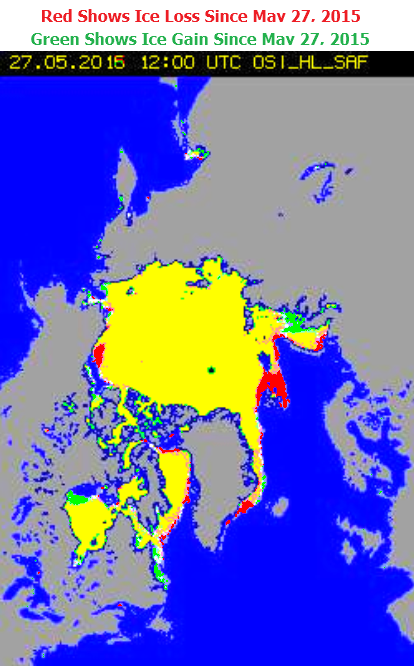
Before looking at some of the other metrics we’ll wait for the effect of the assorted storms currently circling the Arctic to play out. Here’s how the AMSR2 concentration map looks at the moment:
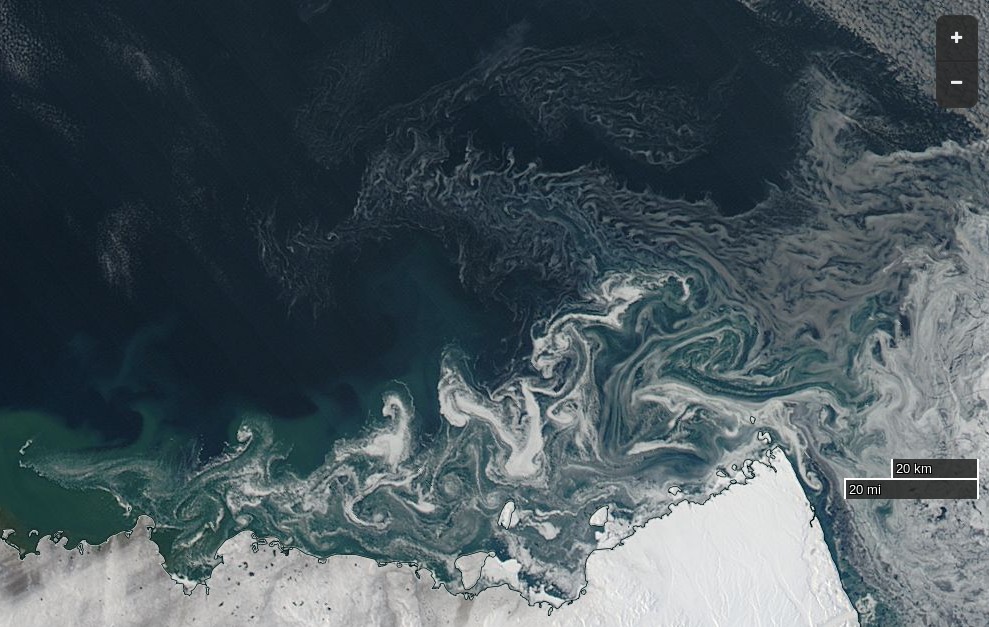
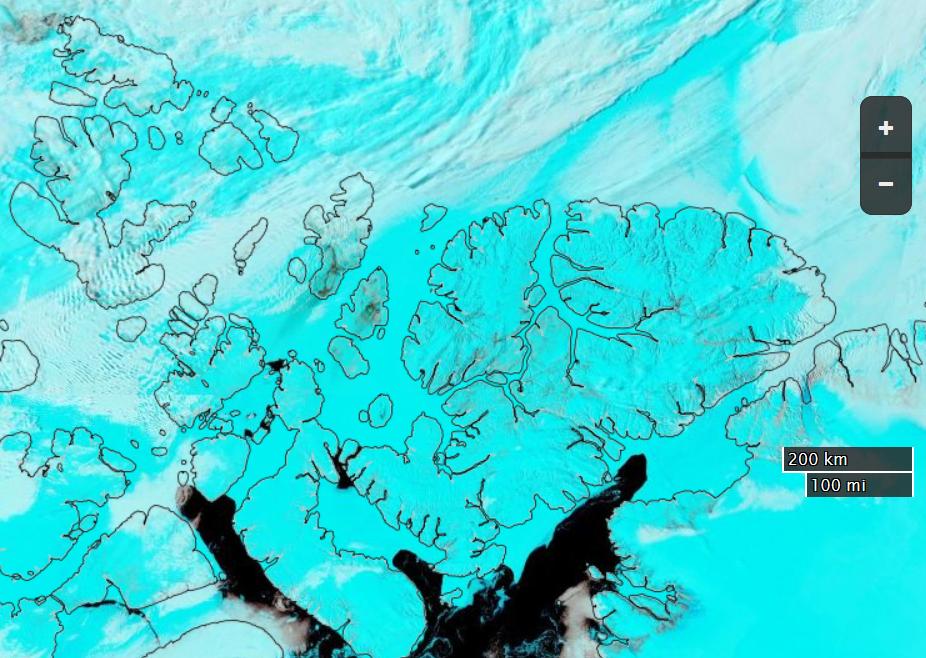
whilst here’s the University of Bremen’s summer SMOS sea ice “thinness” map:
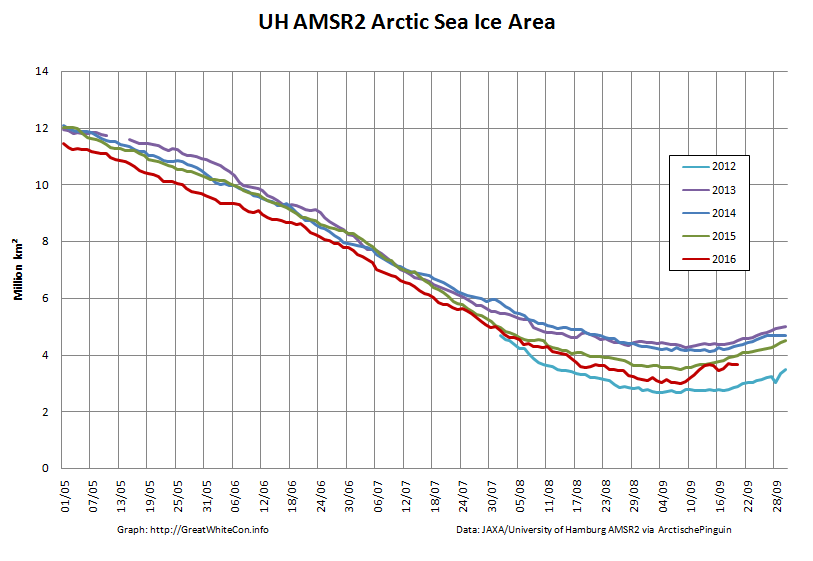
UH AMSR2 area and extent both increased yesterday, so we have a (very!) provisional minimum extent of 4.35 million square kilometres on September 1st.
Area and extent have both increased again:
Is the minimum already in, or will the storms still circulating around the Arctic Ocean reverse that trend over the next few days?
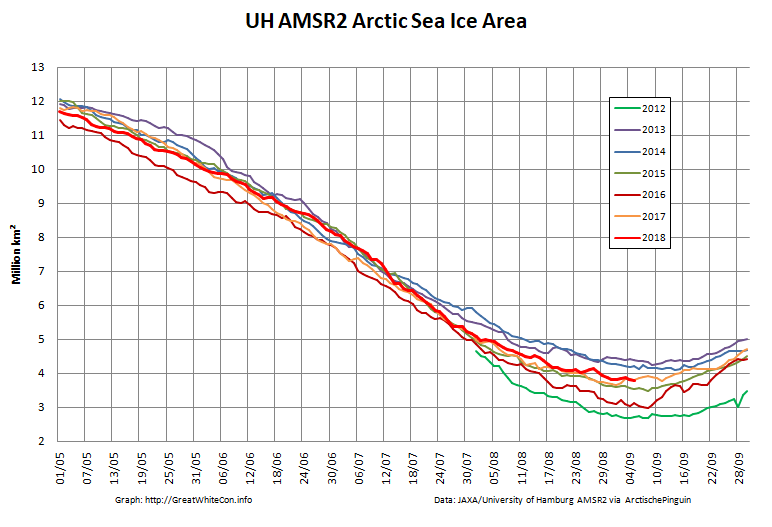
High resolution area and extent both posted marginal new lows for the year yesterday:
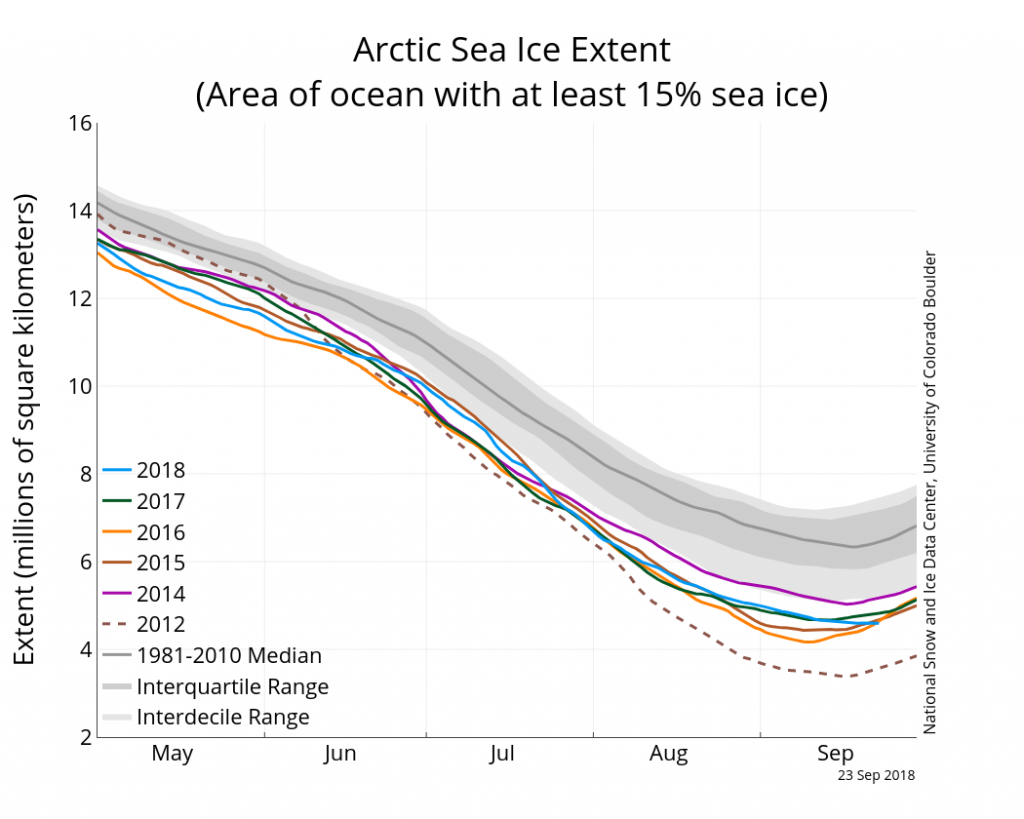
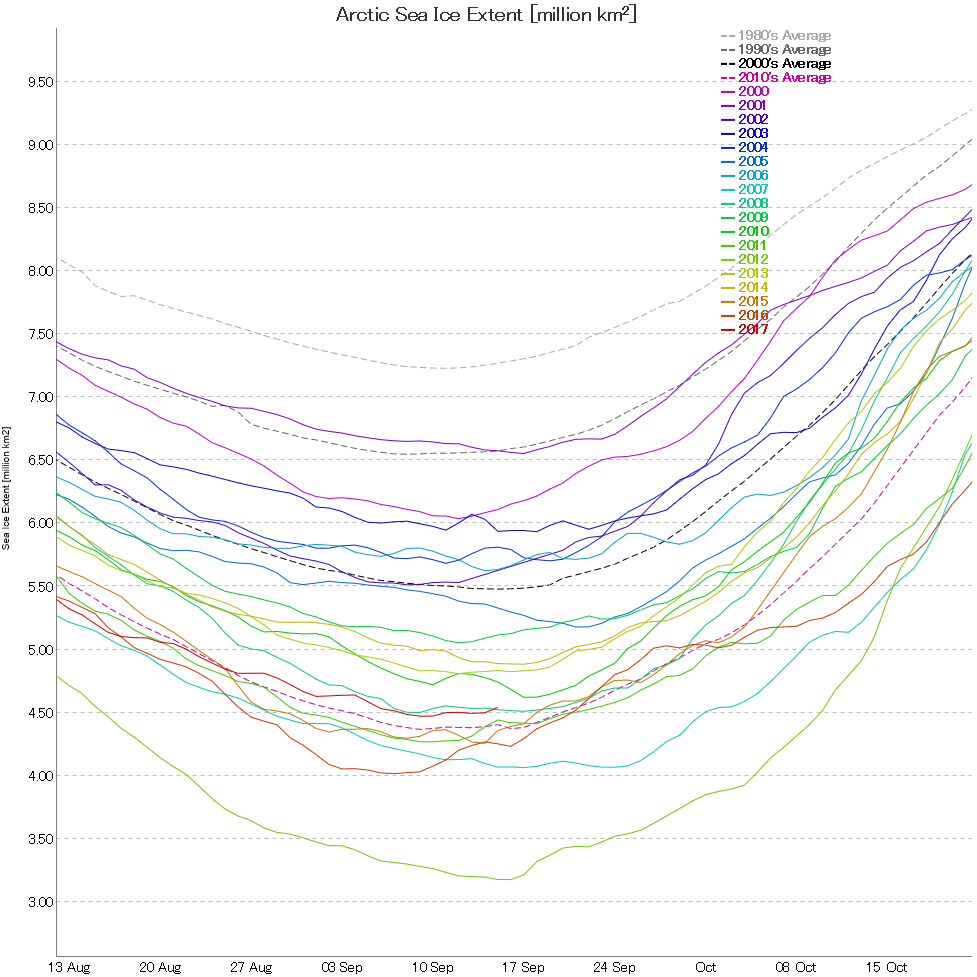
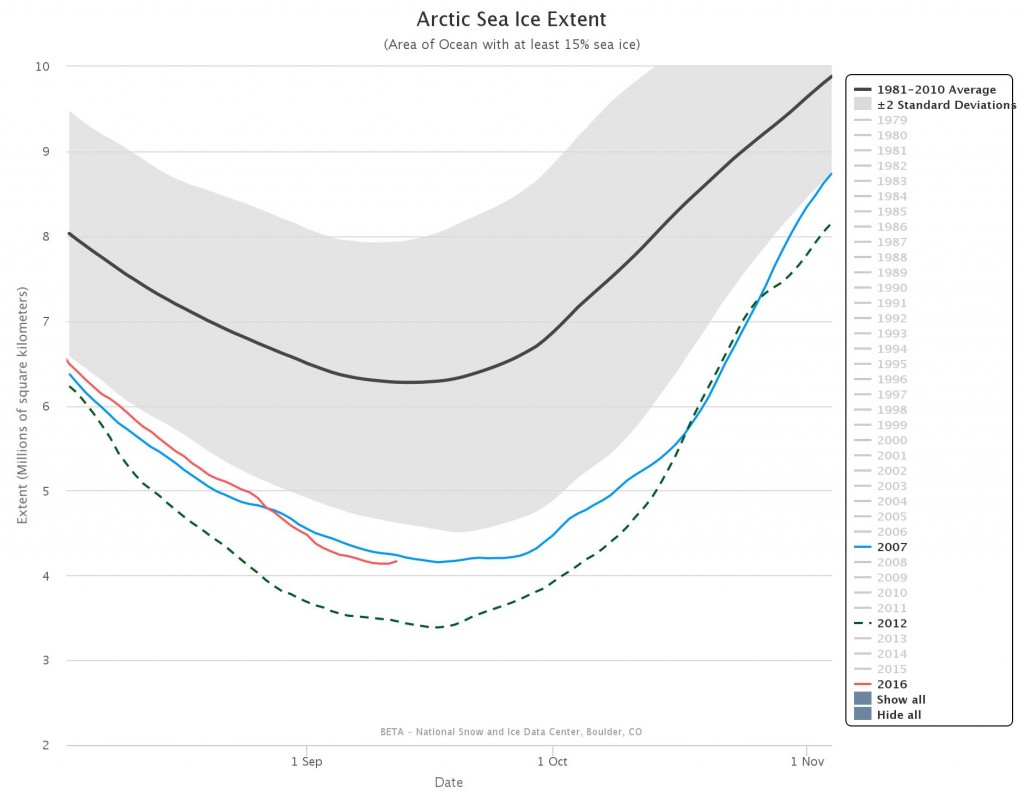
According to the latest edition of the NSIDC’s Arctic Sea Ice News:
On September 19 and 23, Arctic sea ice appeared to have reached its seasonal minimum extent for the year, at 4.59 million square kilometers (1.77 million square miles). This ties 2018 with 2008 and 2010 for the sixth lowest minimum extent in the nearly 40-year satellite record.
Please note that this is a preliminary announcement. Changing winds or late-season melt could still reduce the Arctic ice extent, as happened in 2005 and 2010. NSIDC scientists will release a full analysis of the Arctic melt season, and discuss the Antarctic winter sea ice growth, in early October.
The NSIDC numbers are based on a 5 day average, whereas the one day high resolution AMSR2 extent reached a minimum of 4.195 million square kilometers on September 17th:
The AMSR2 area minimum occurred significantly earlier. 3.737 million square kilometers on September 9th: