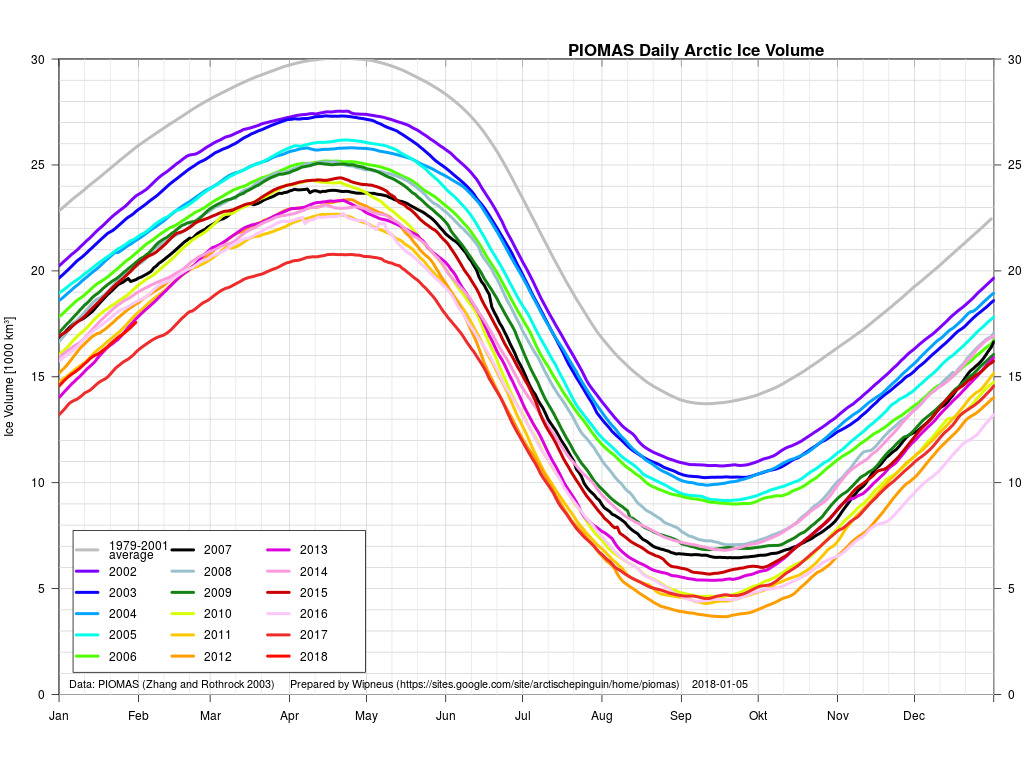
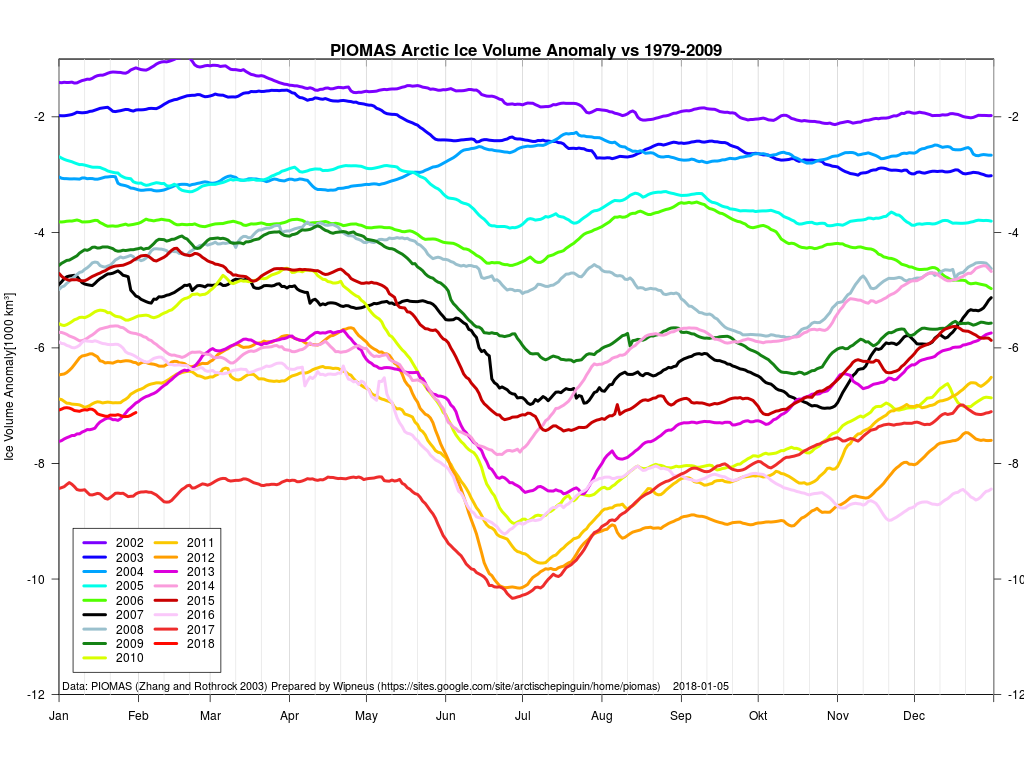
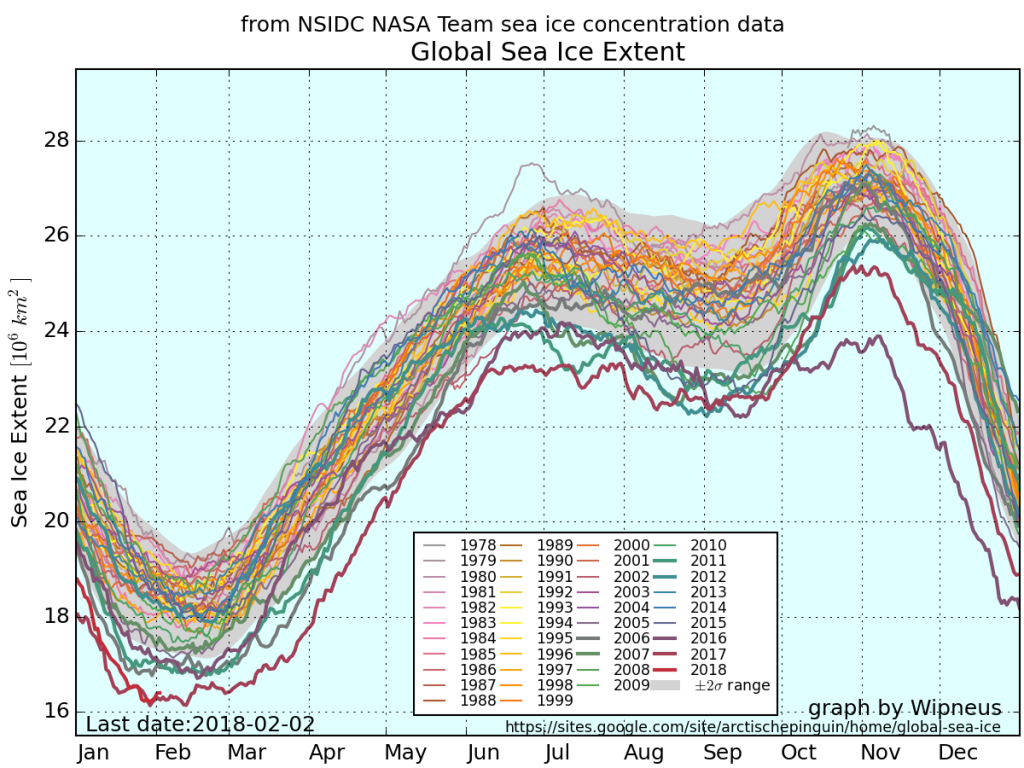
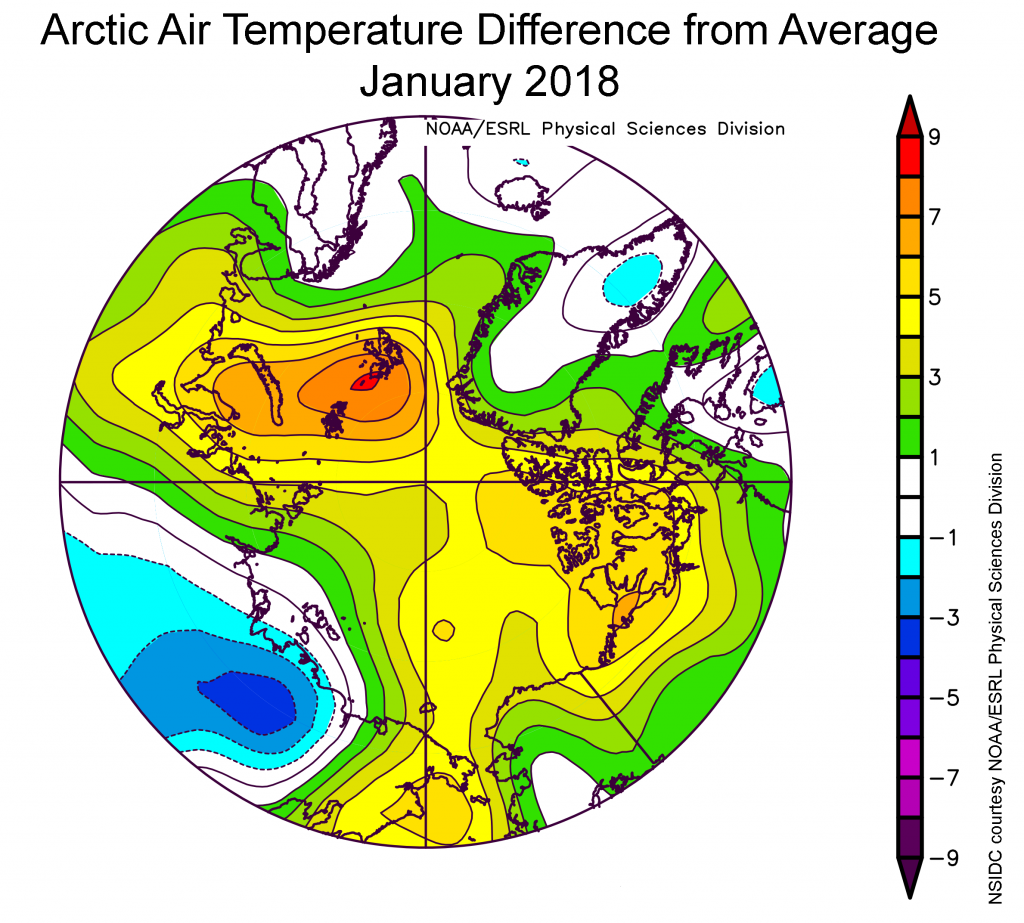
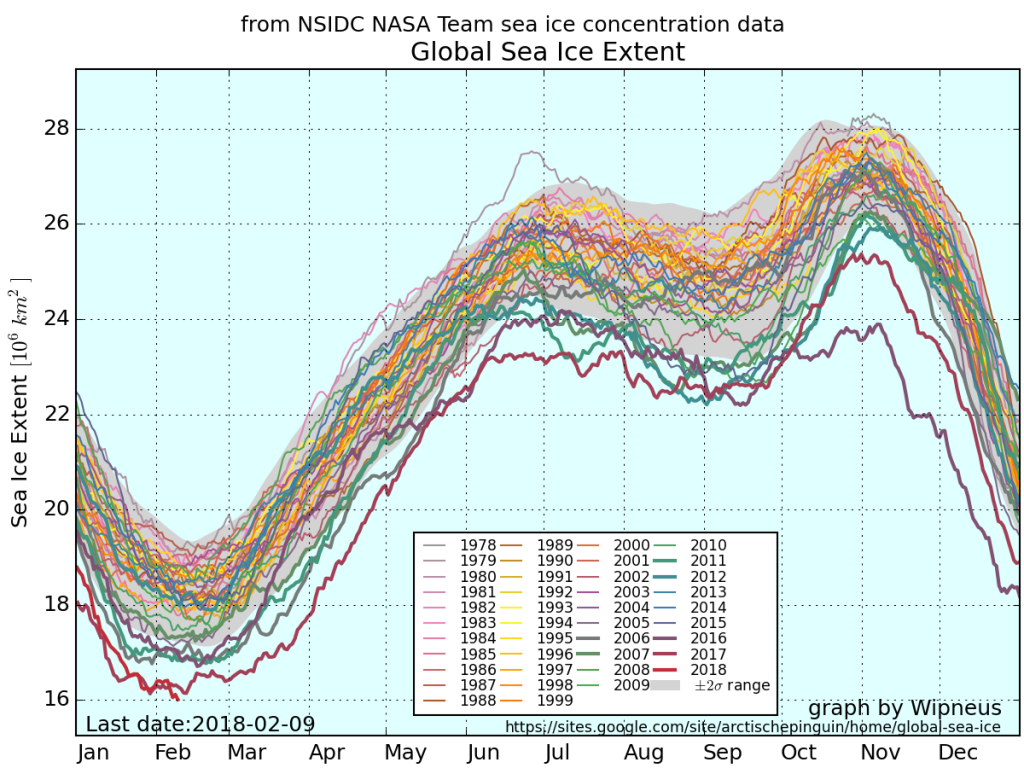
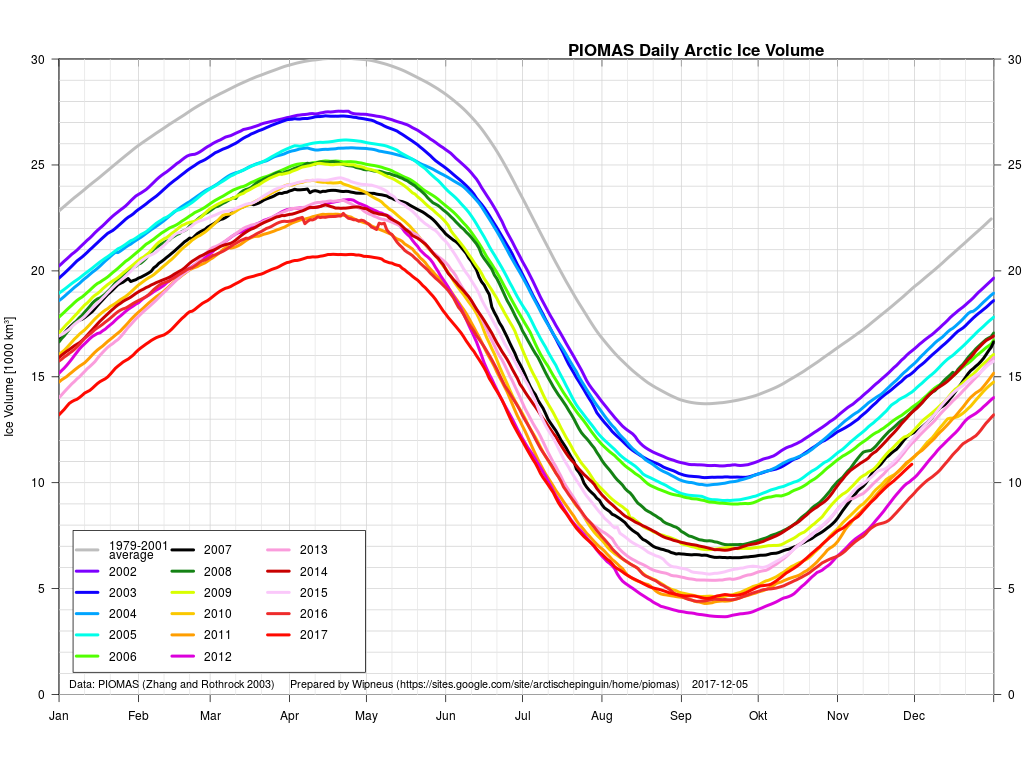
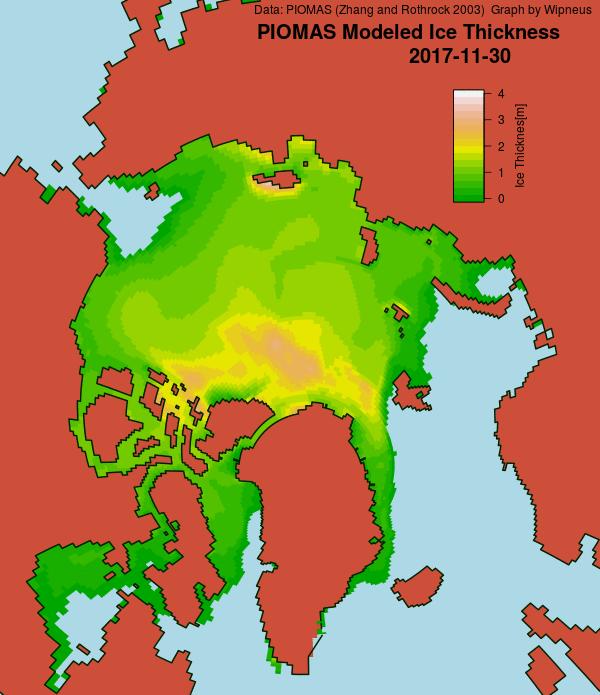
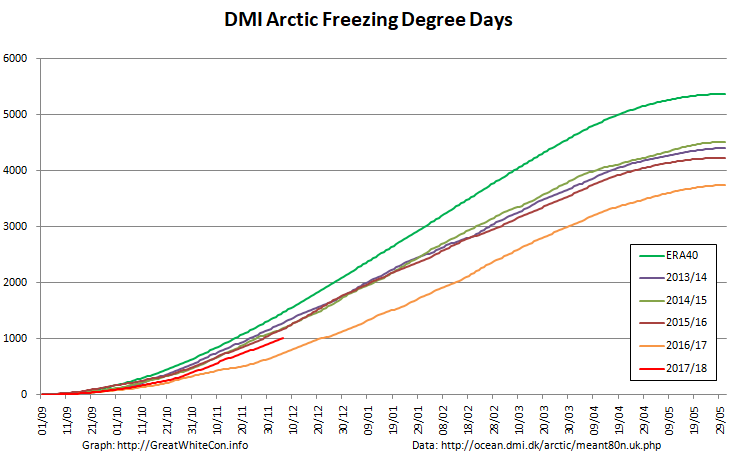
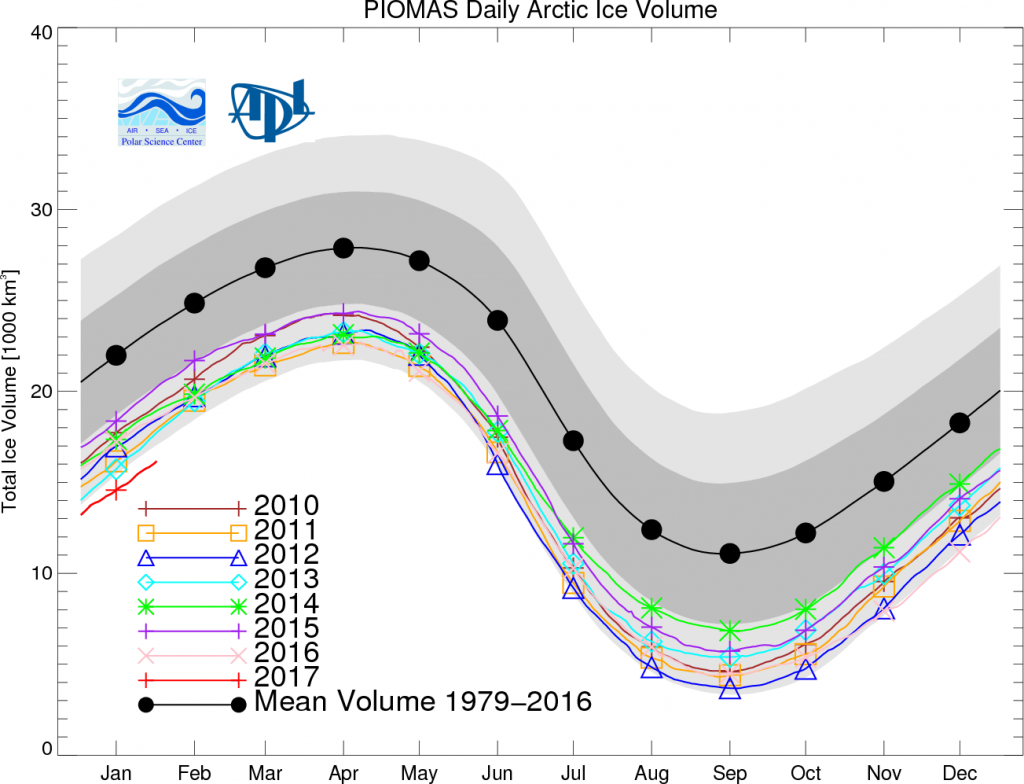
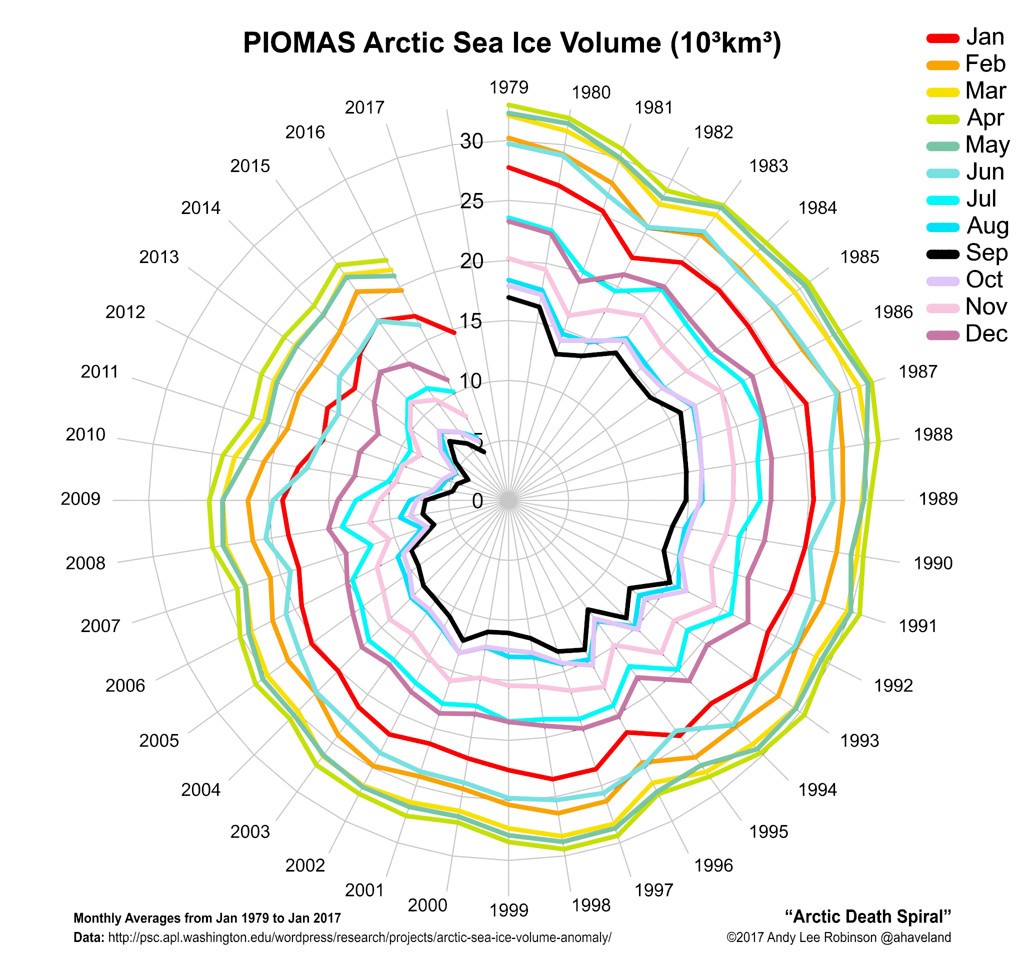
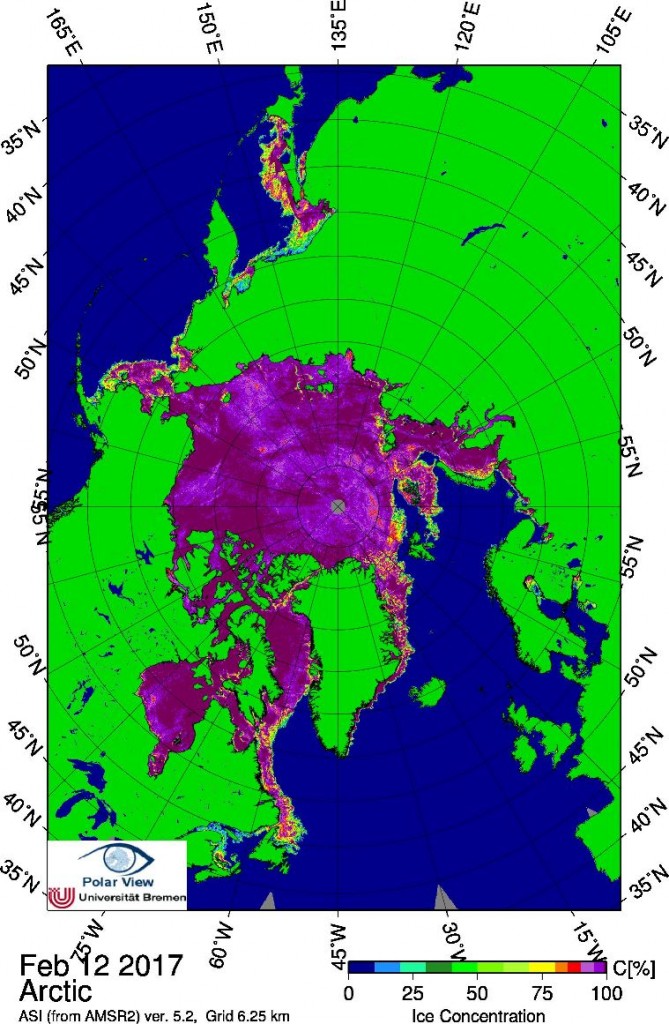
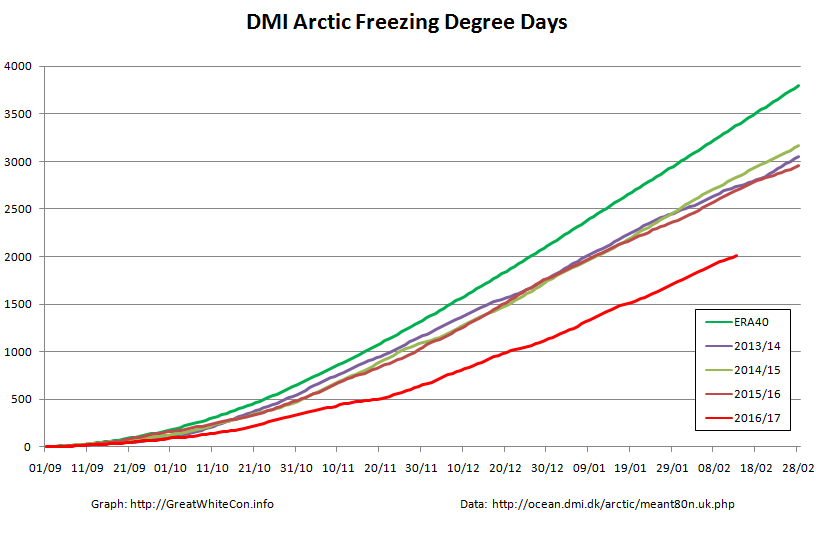
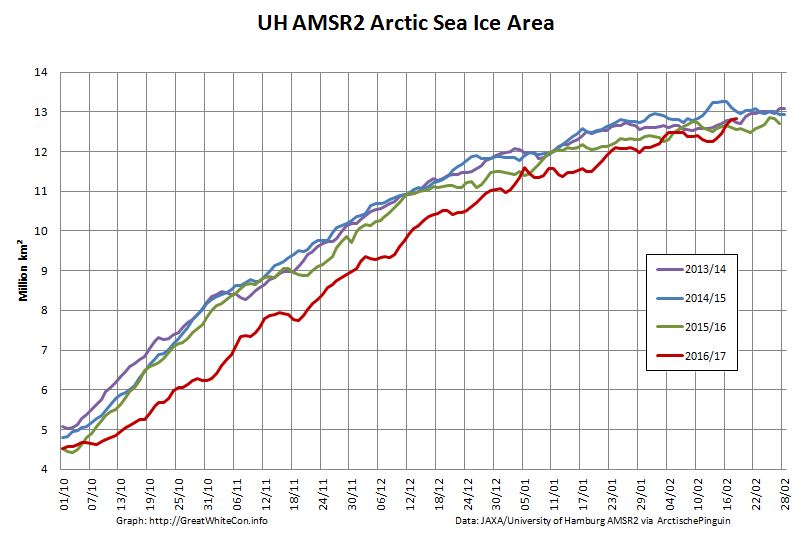
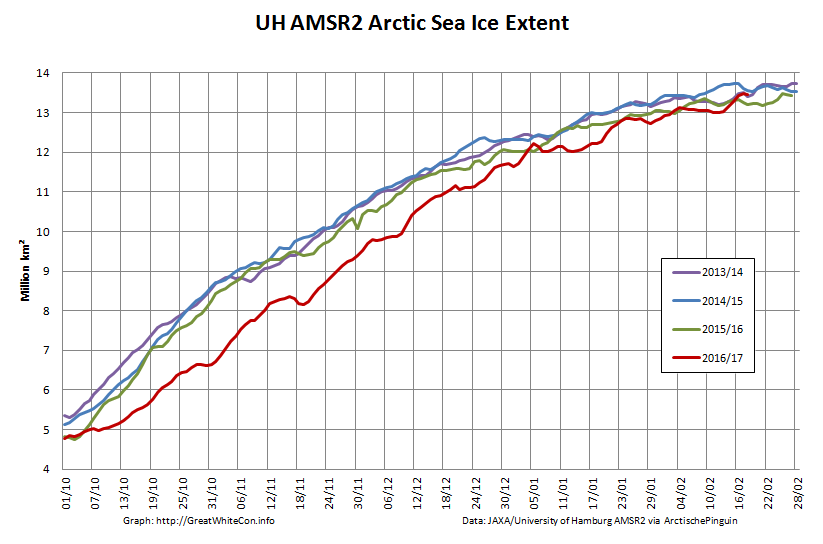
According to the latest edition of the National Snow and Ice Data Center’s “Arctic Sea Ice News”
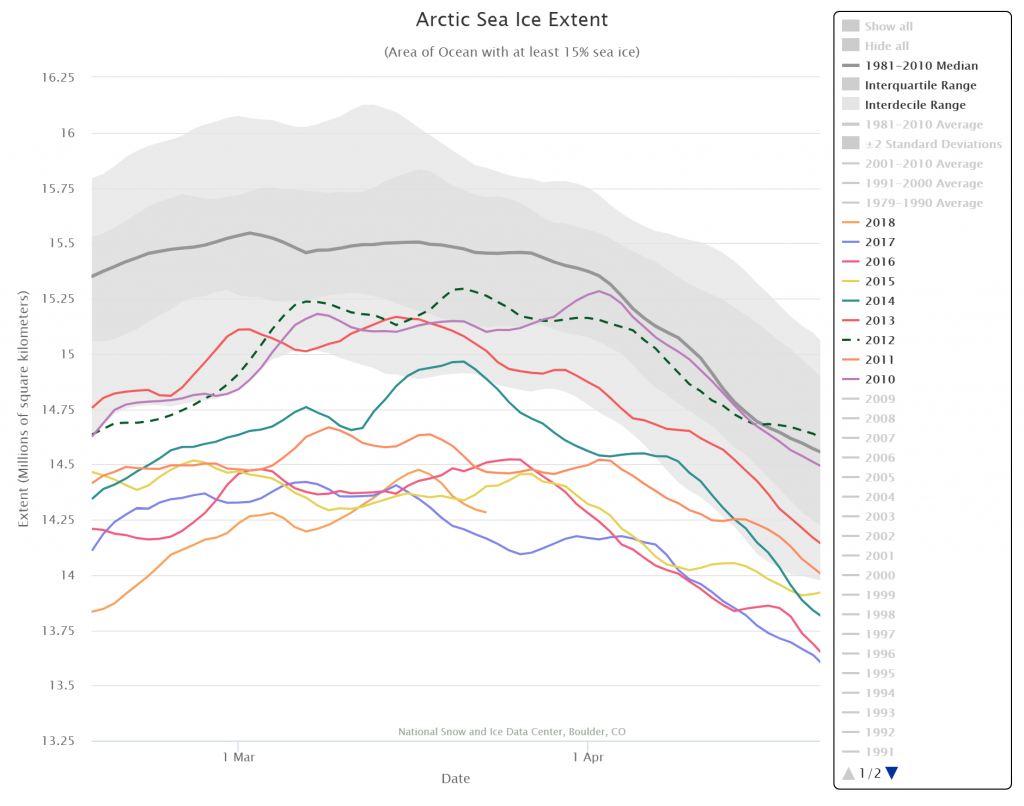
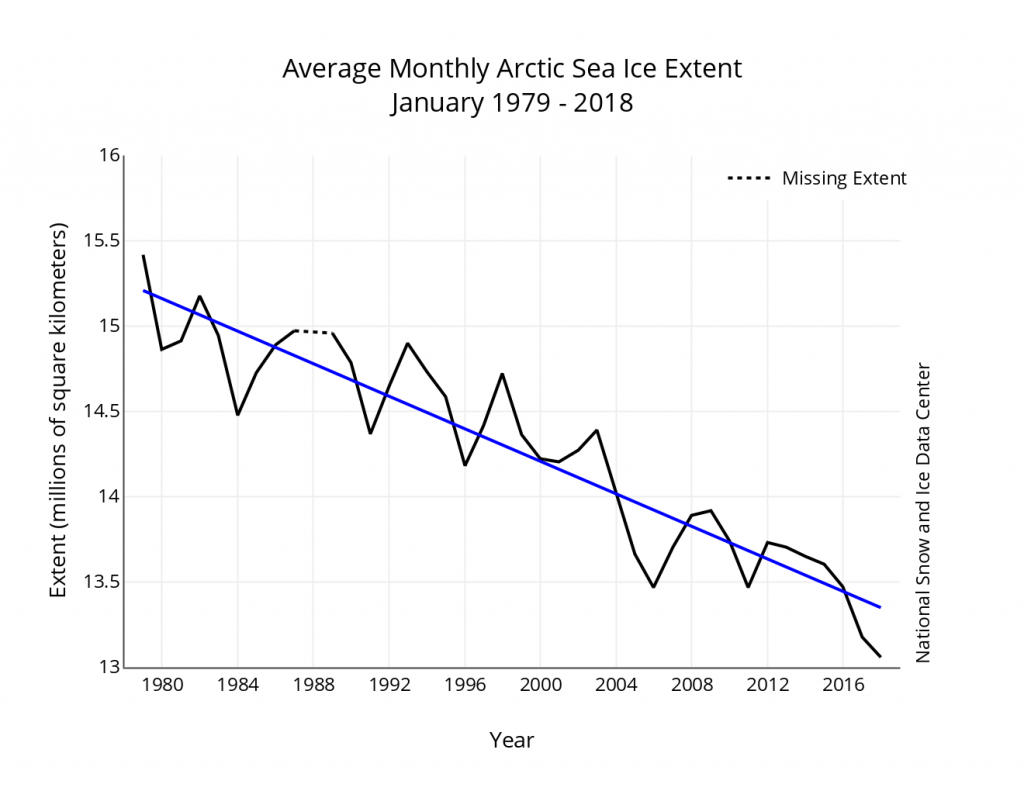
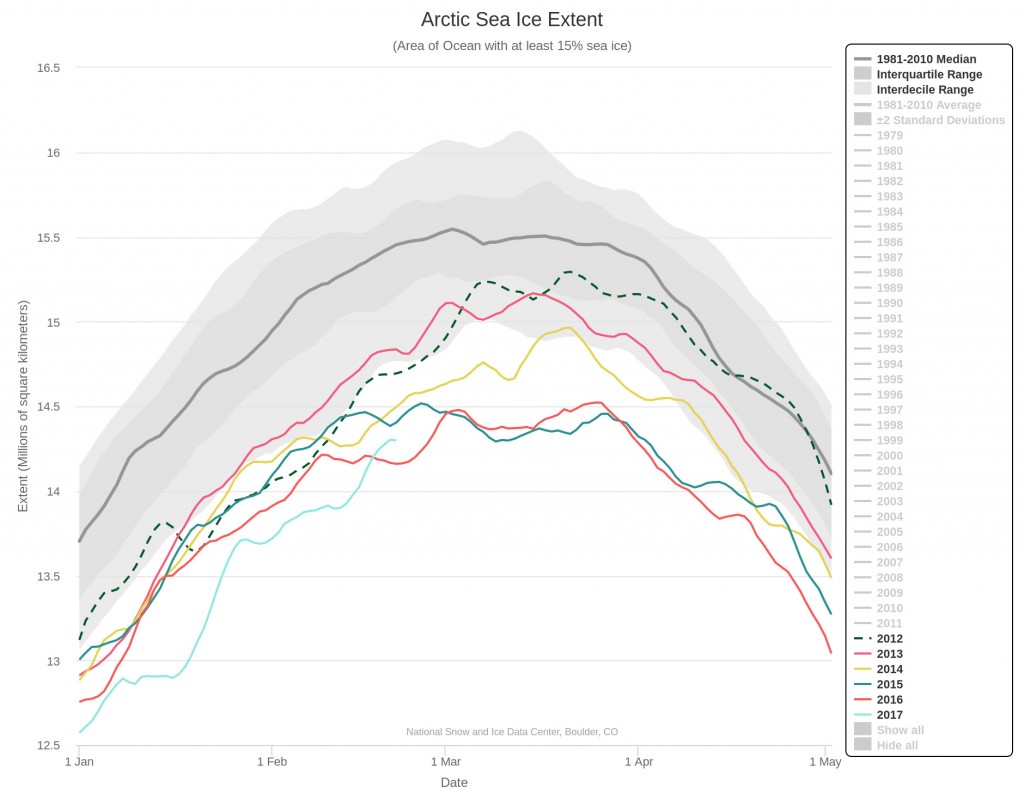
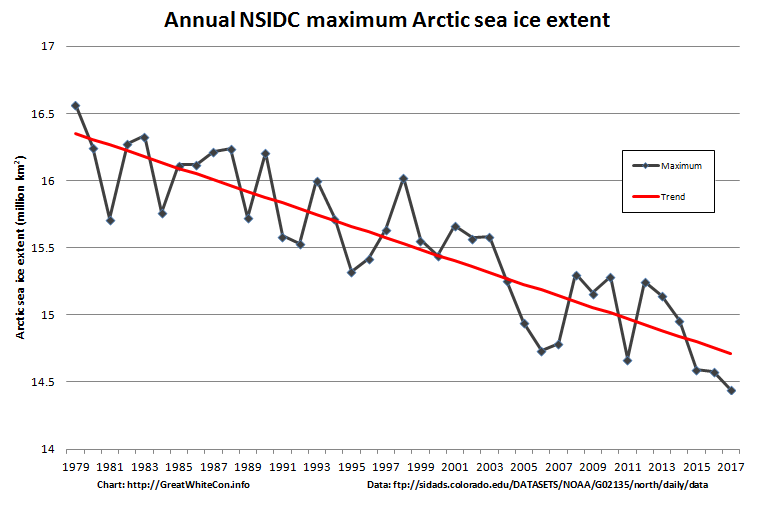
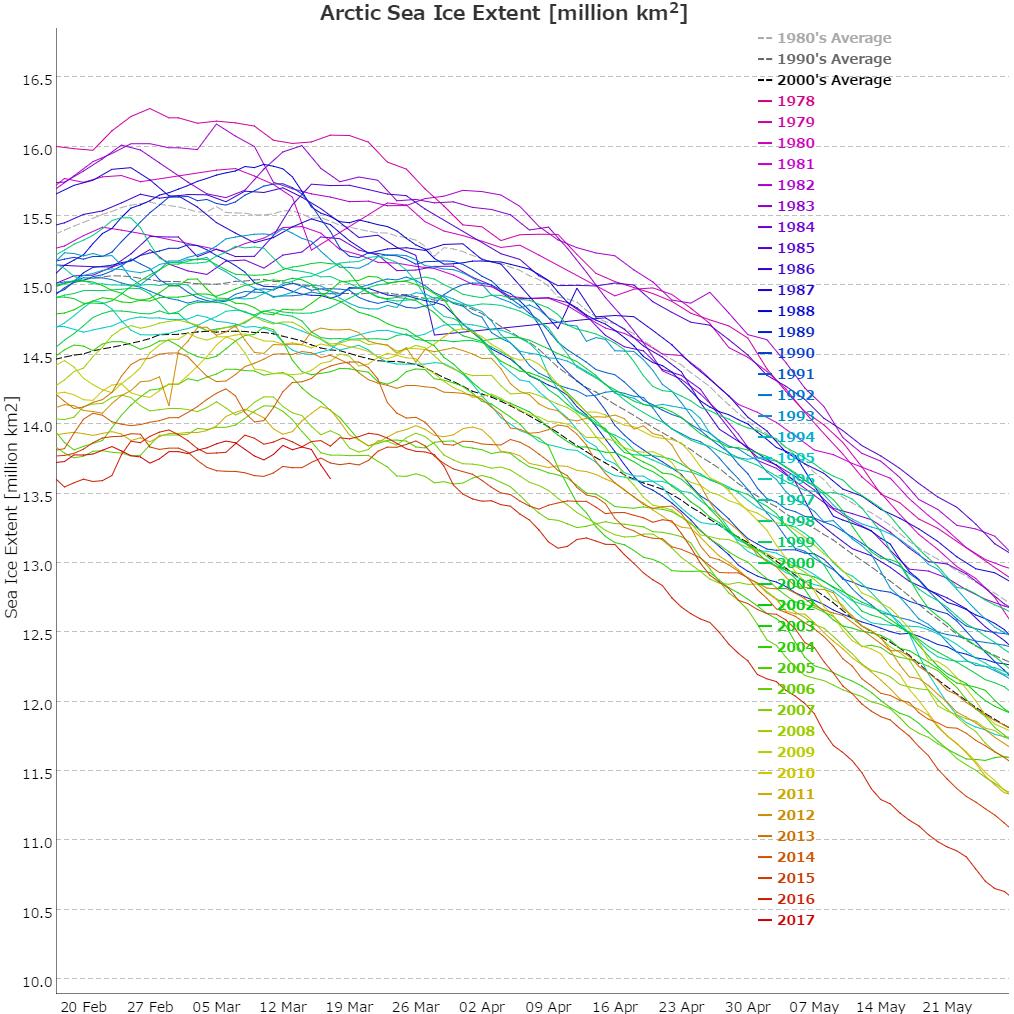
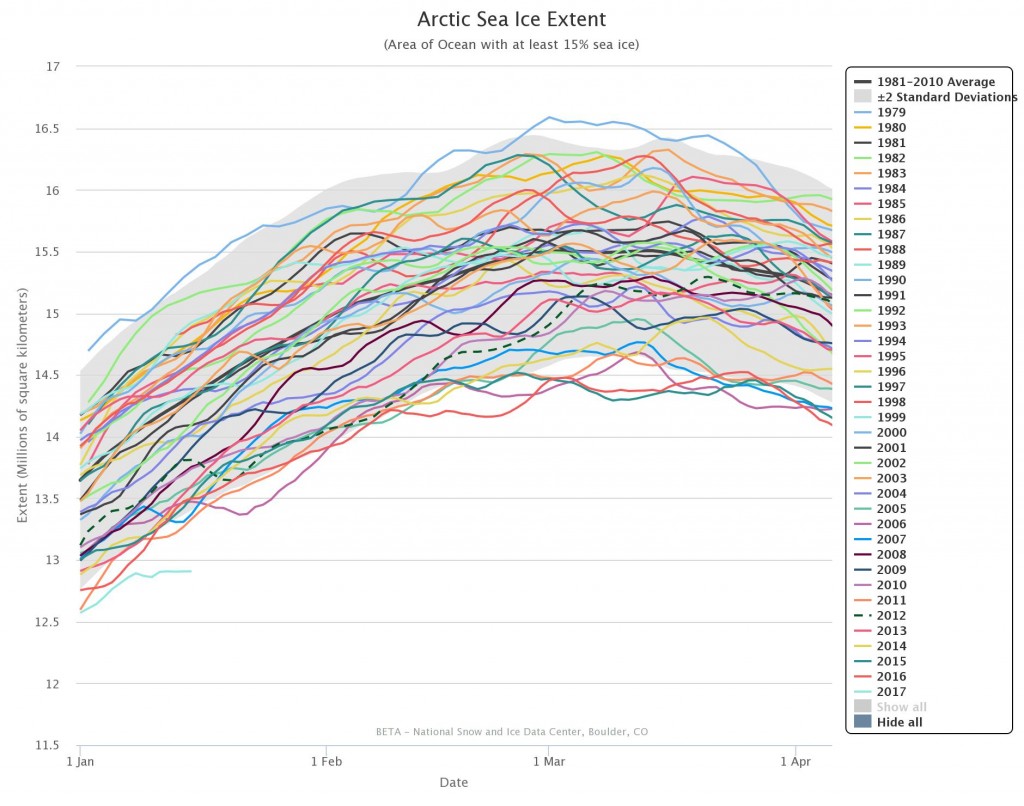
On March 17, 2018, Arctic sea ice likely reached its maximum extent for the year, at 14.48 million square kilometers (5.59 million square miles), the second lowest in the 39-year satellite record, falling just behind 2017. This year’s maximum extent is 1.16 million square kilometers (448,000 square miles) below the 1981 to 2010 average maximum of 15.64 million square kilometers (6.04 million square miles).
The four lowest seasonal maxima have all occurred during the last four years. The 2018 maximum is 60,000 square kilometers (23,200 square miles) above the record low maximum that occurred on March 7, 2017.
Here’s a close up view of recent maxima via the NSIDC’s Charctic interactive sea ice graph:
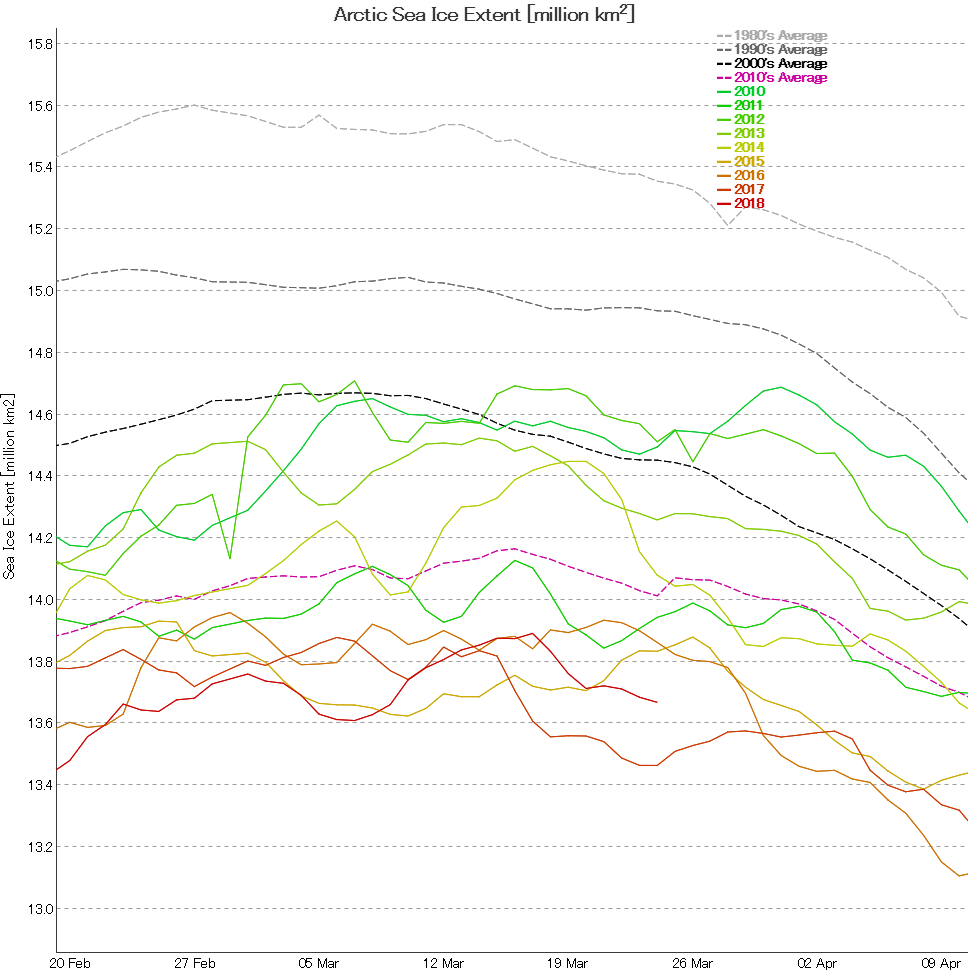
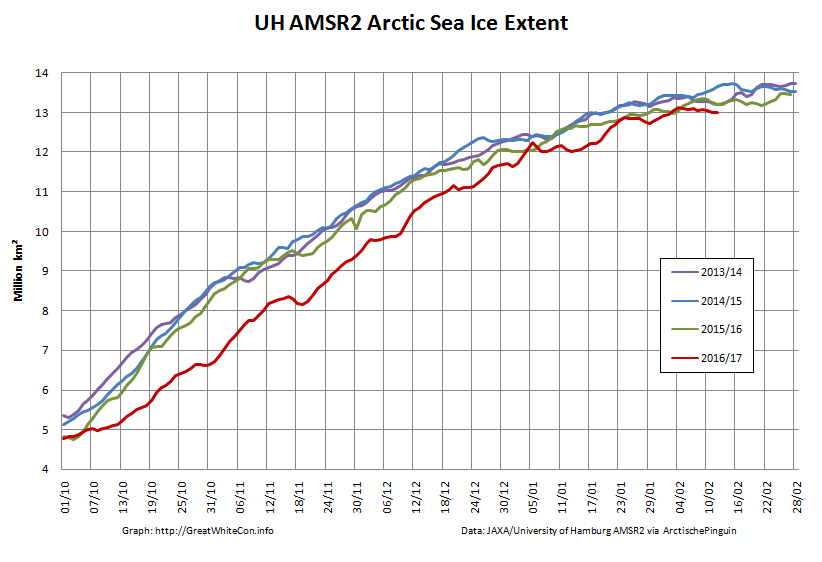
Next let’s take a look at extent data from the Japanese National Institute of Polar Research, colloquially referred to as “JAXA extent”
In this case the maximum was 13.89 million square kilometers, also on March 17th.
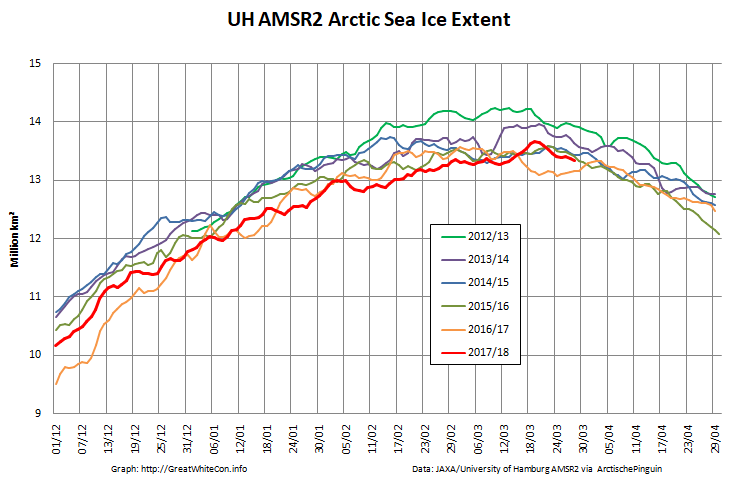
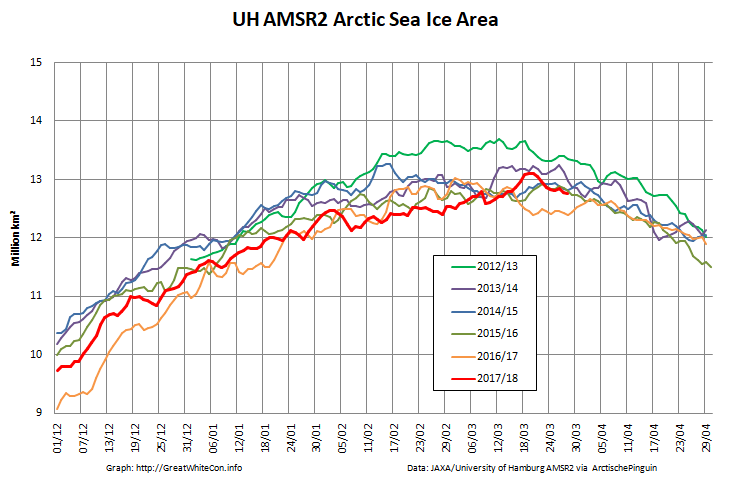
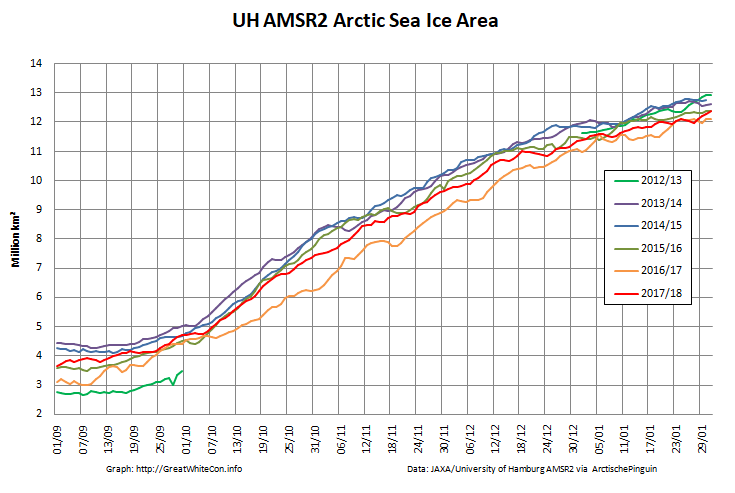
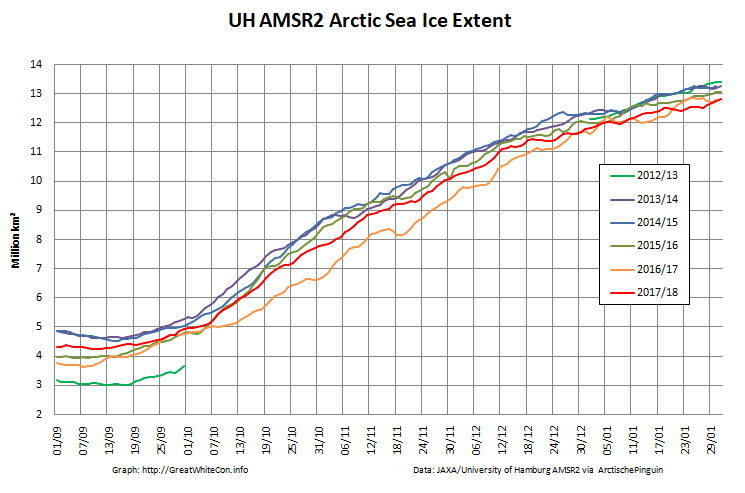
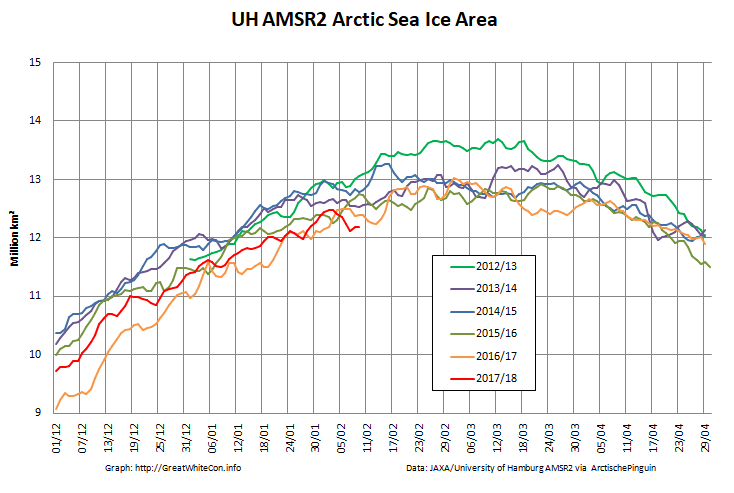
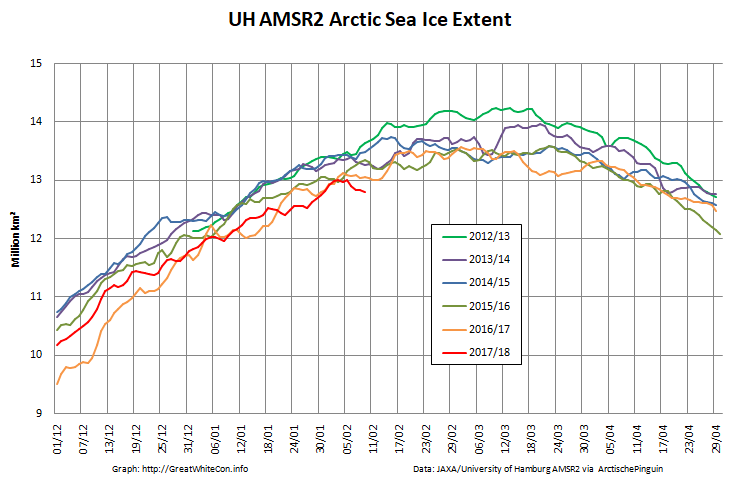
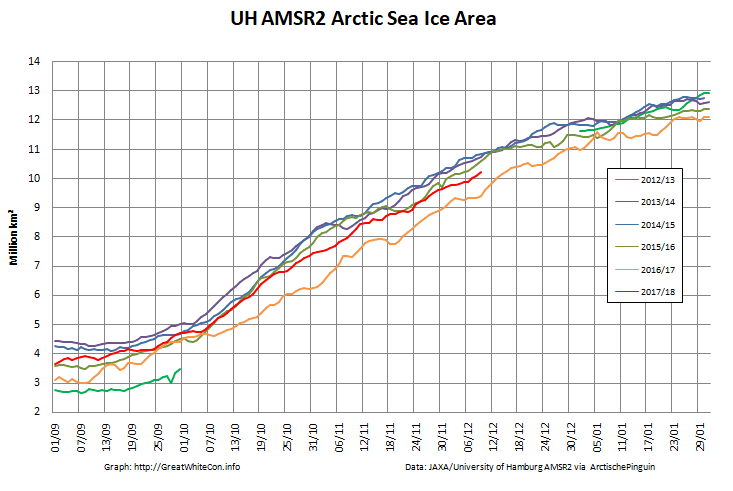
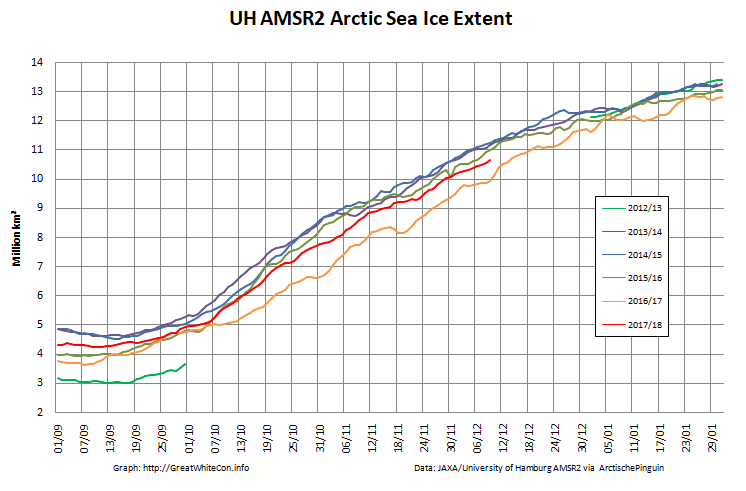
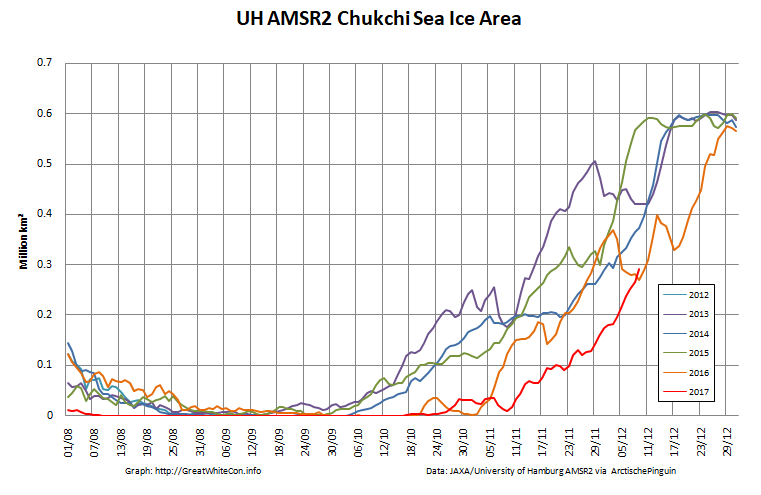
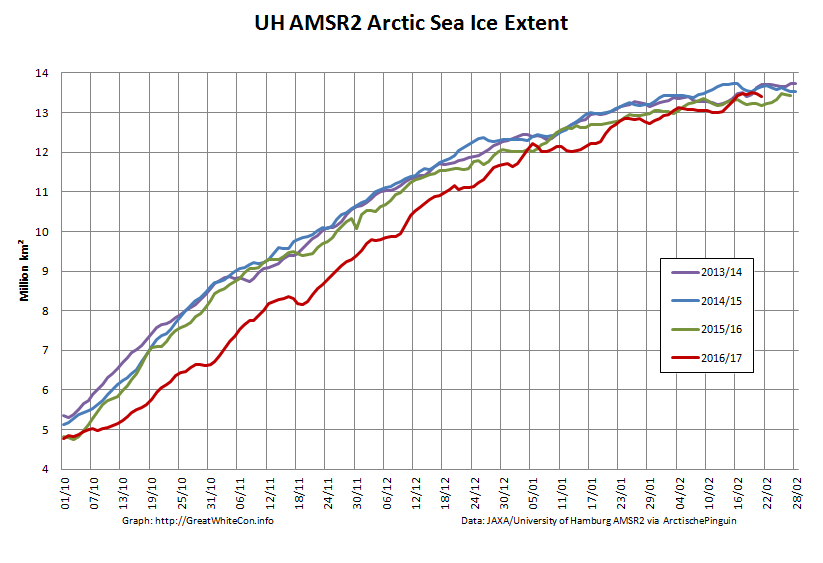
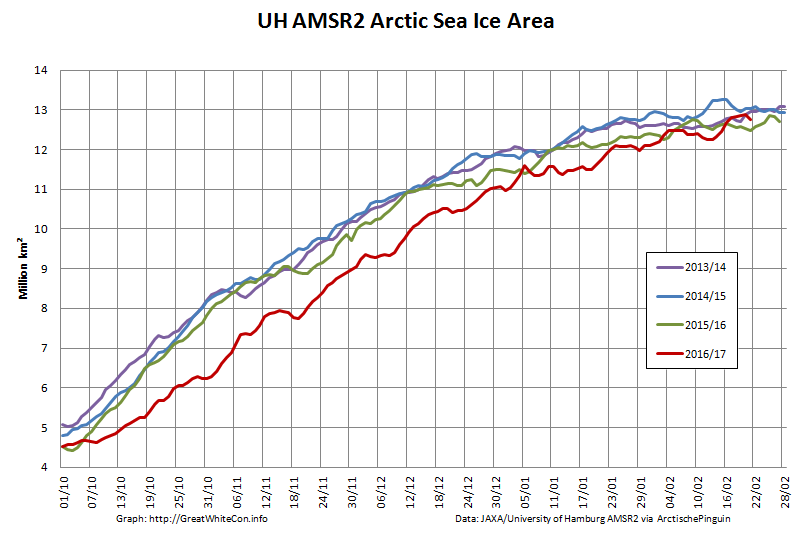
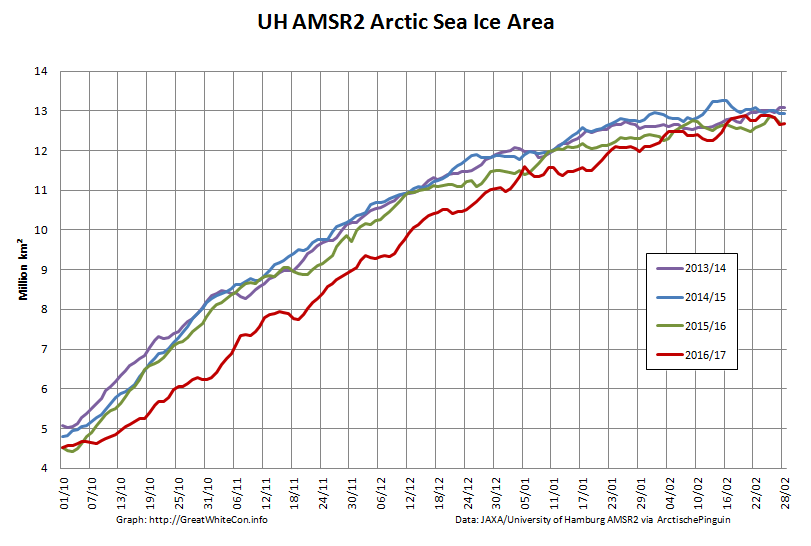
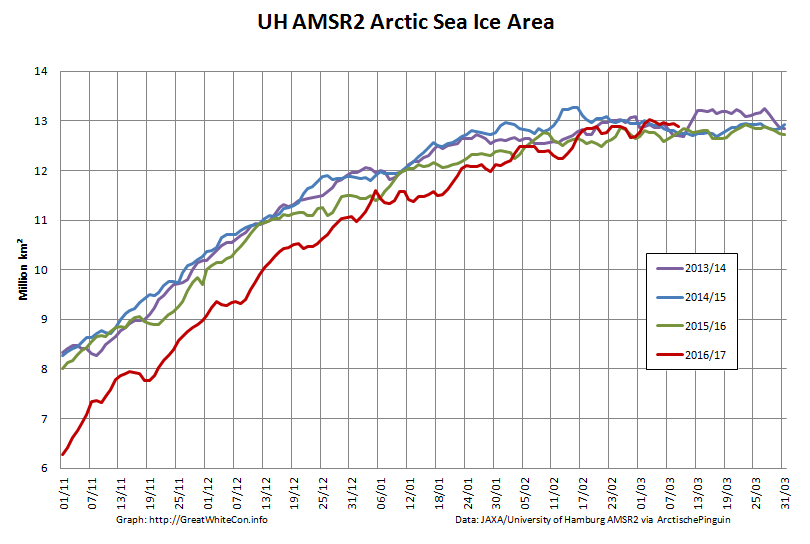
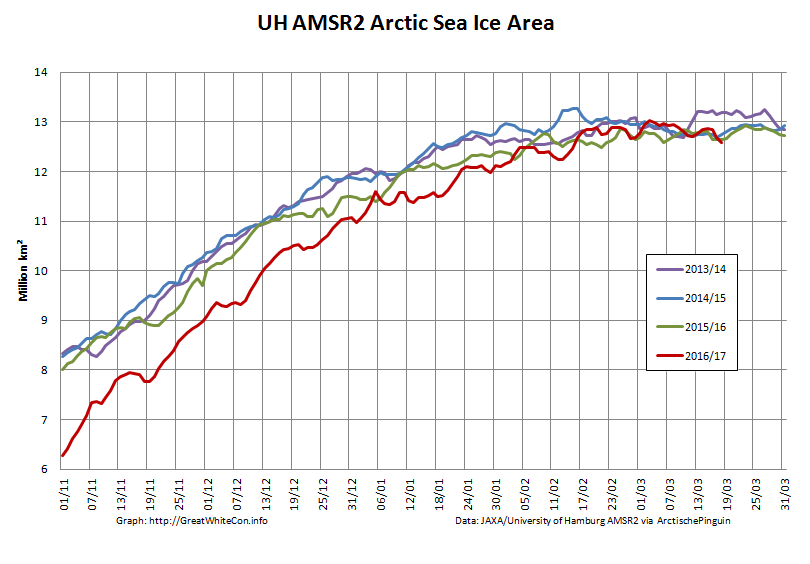
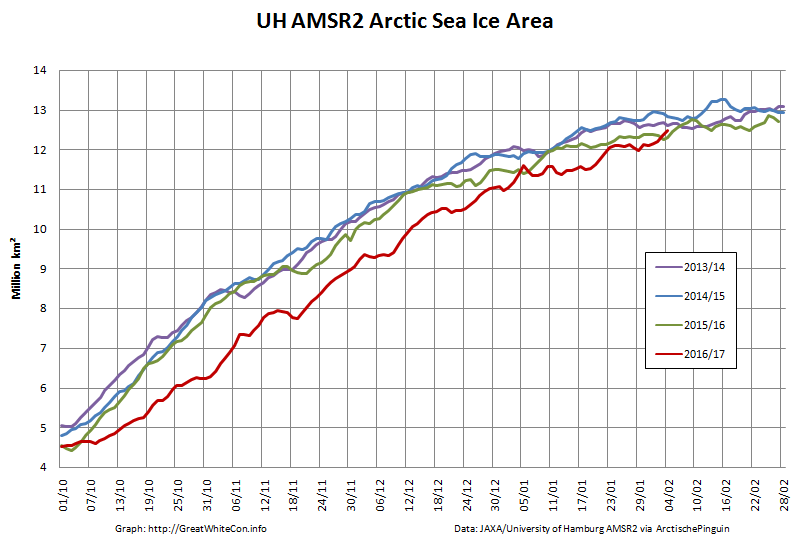
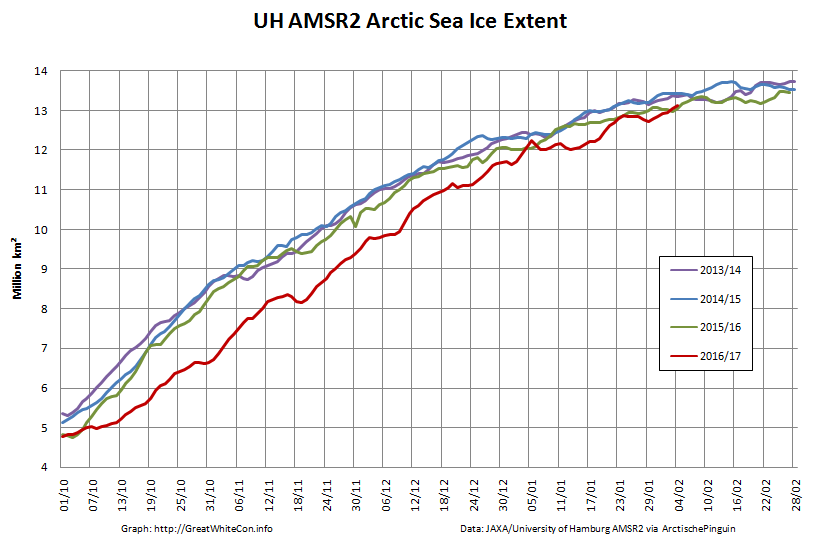
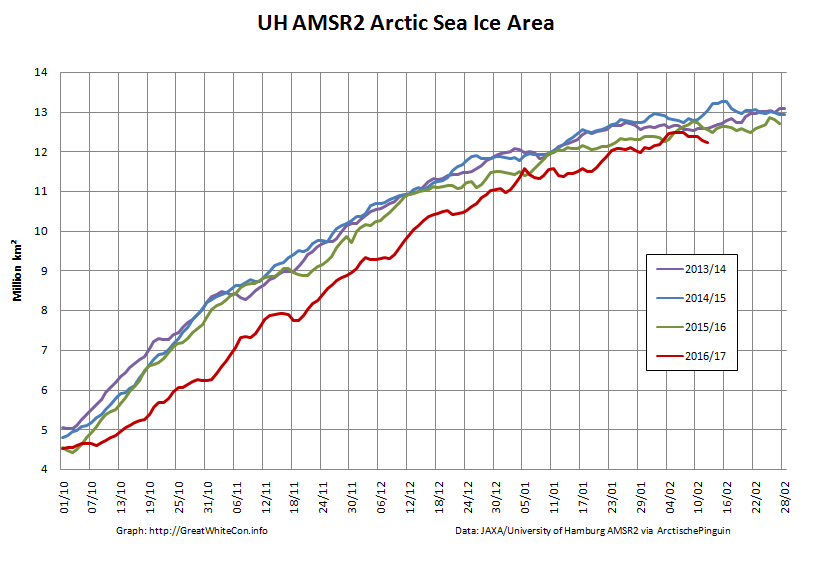
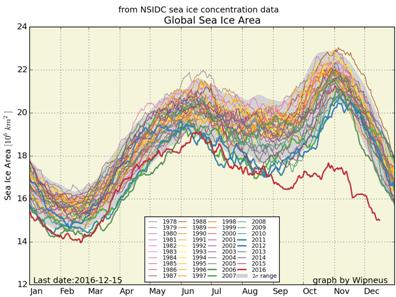
Here too are the extent and area graphs based on Wipneus’ processing of the University of Hamburg’s AMSR2 based concentration data:
They highlight the surge in Arctic sea ice area in the middle of March due to the sudden “cold snap”:
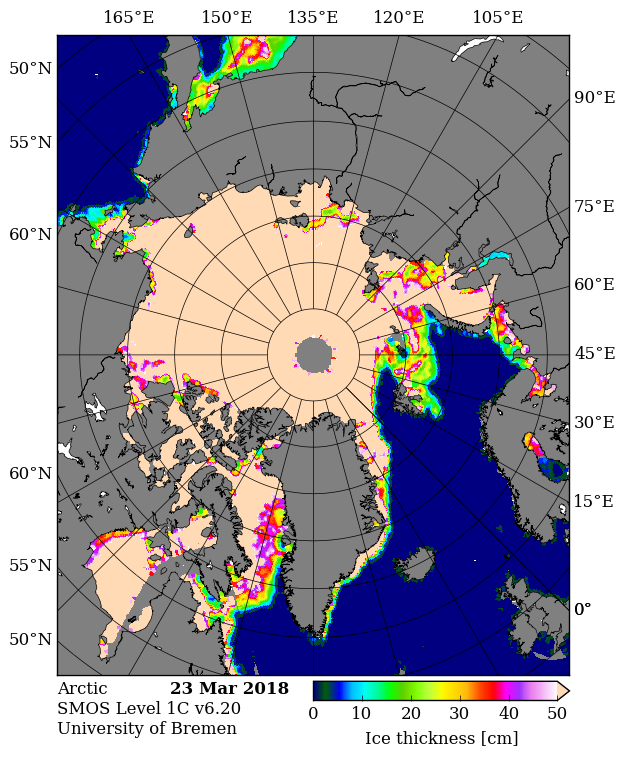
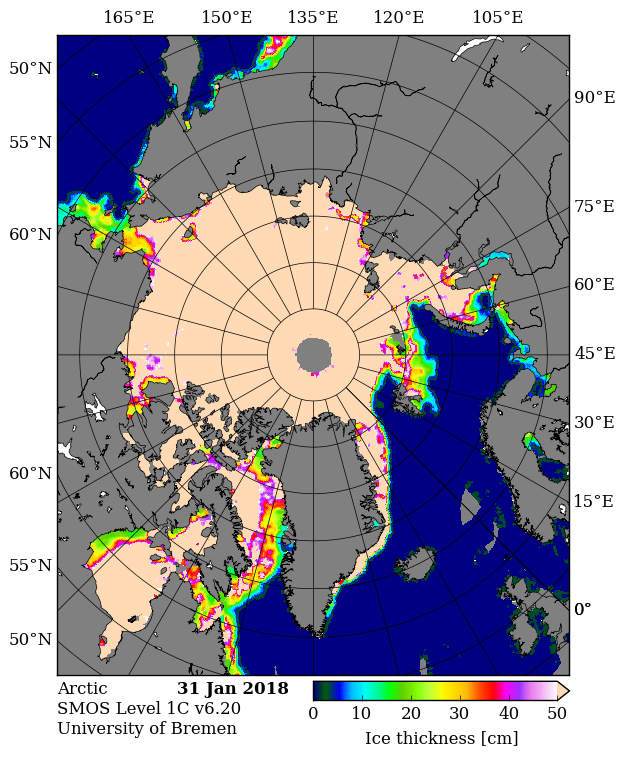
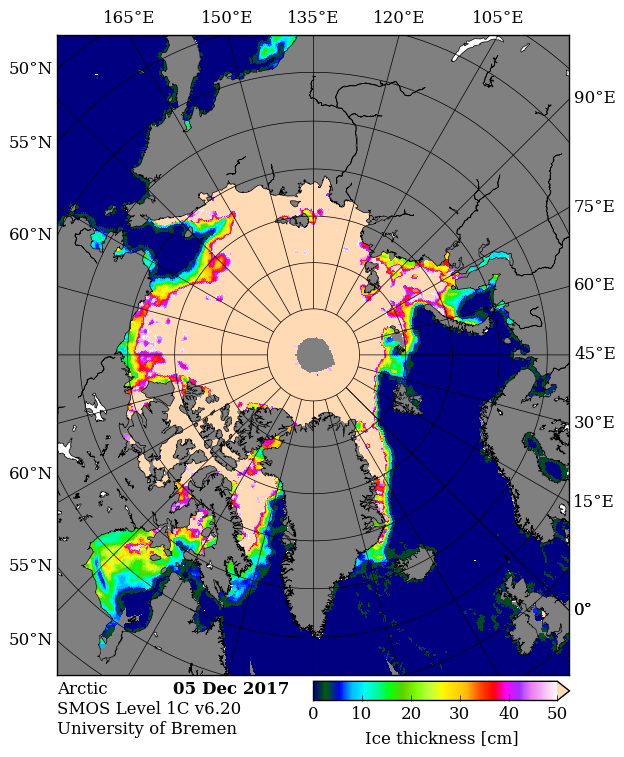
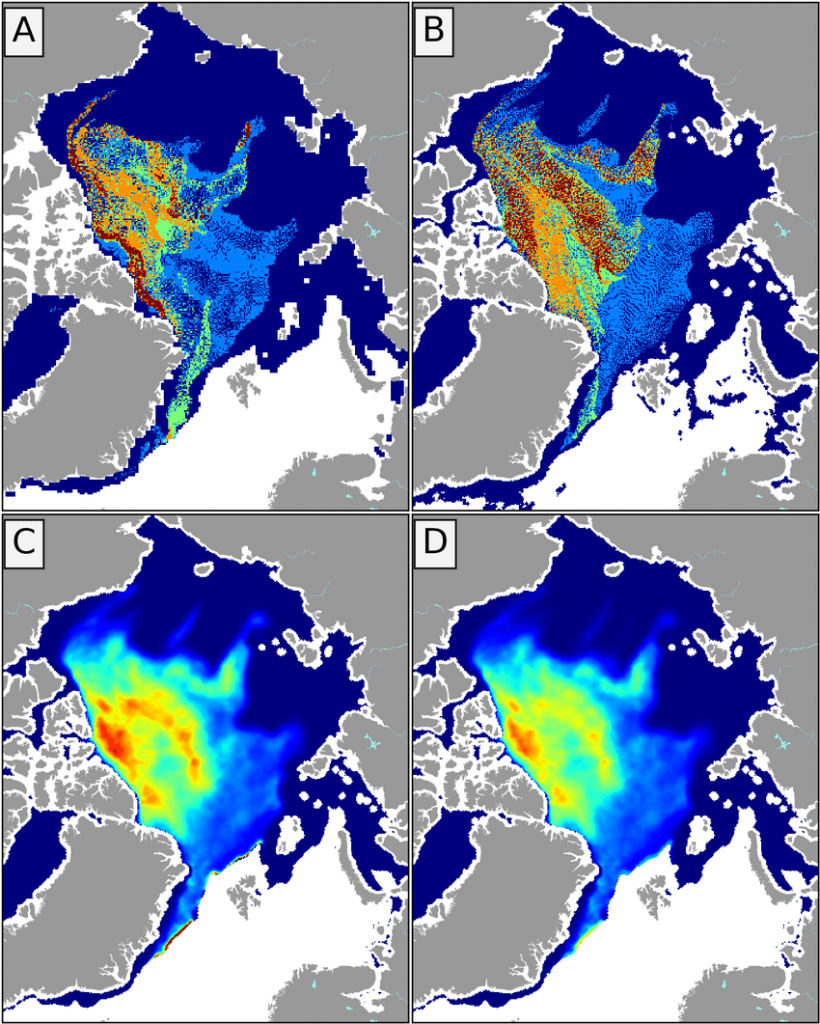
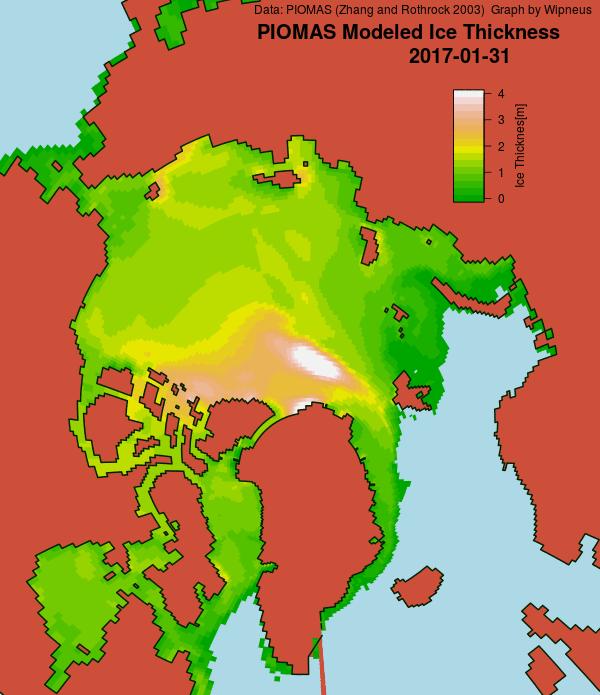
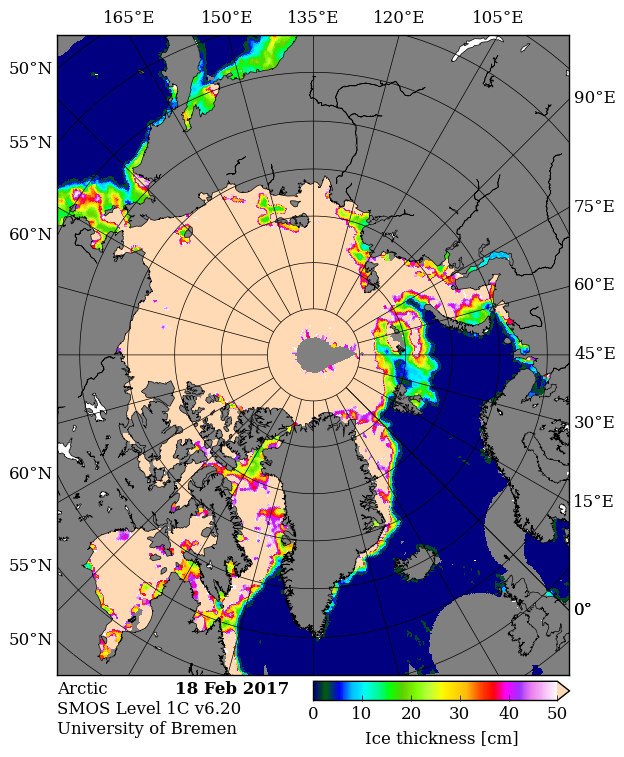
Looking at the third Arctic dimension, here’s the latest SMOS thickness map from the University of Bremen:
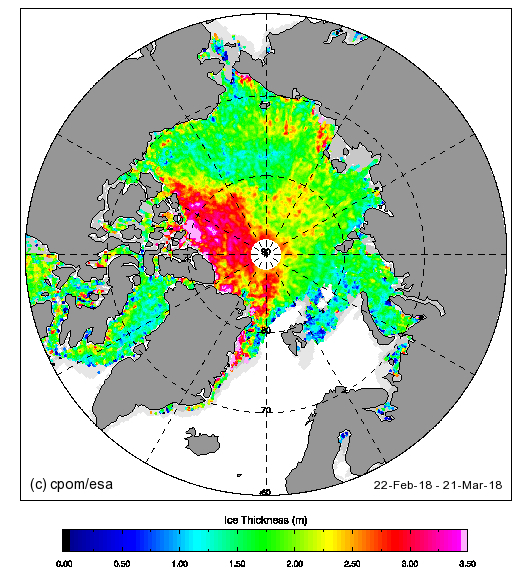
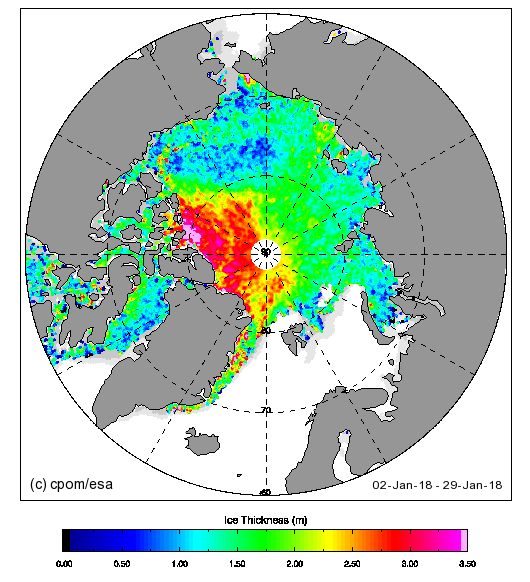
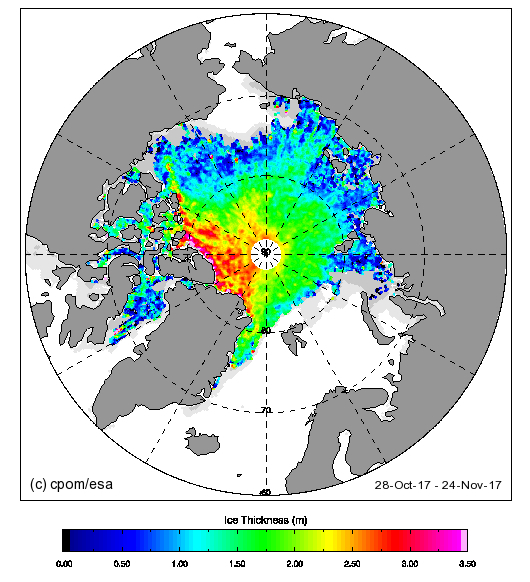
and here’s the latest CryoSat-2 thickness map:
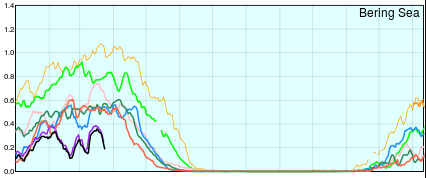
They reveal large areas of relatively thin sea ice in the Okhotsk and Barents Seas where the ice can now be expected to melt as quickly as it formed. There is also remarkably little sea ice in the Bering Sea for the time of year: