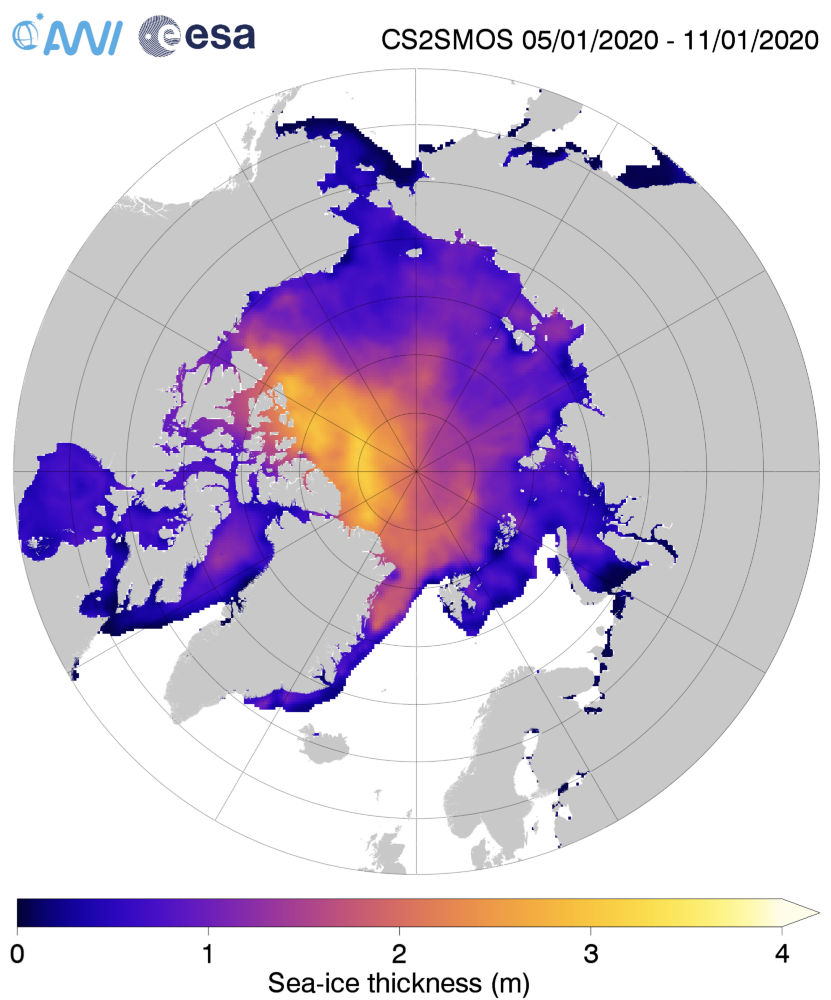
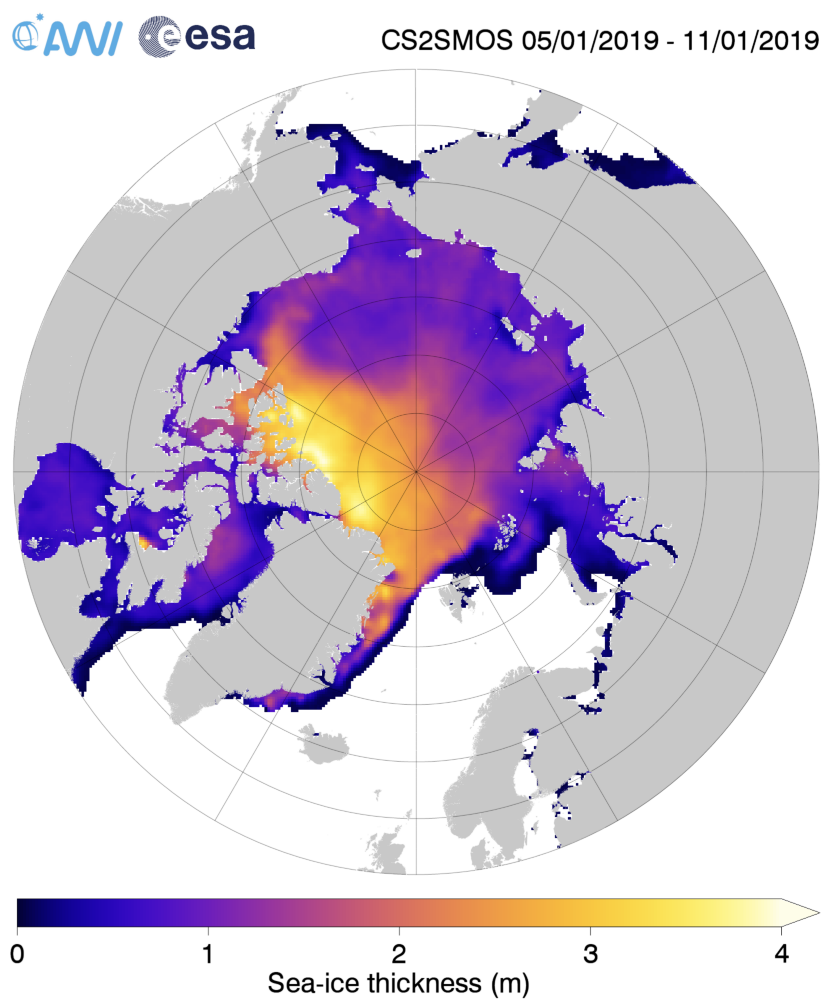
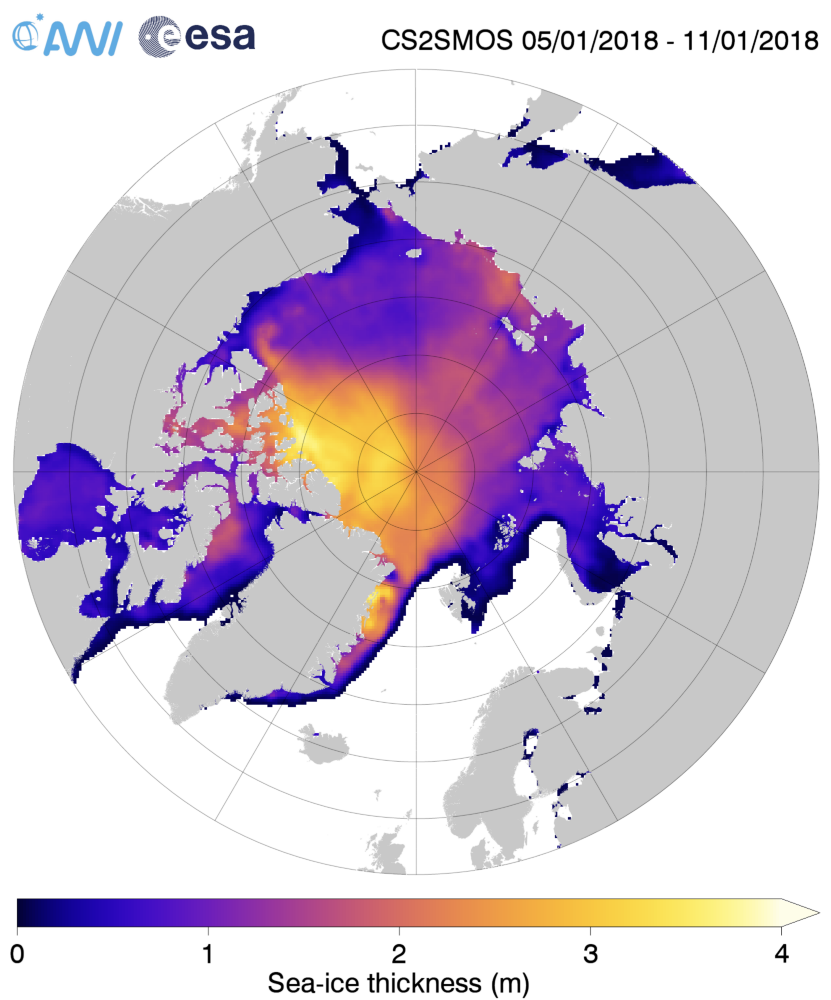
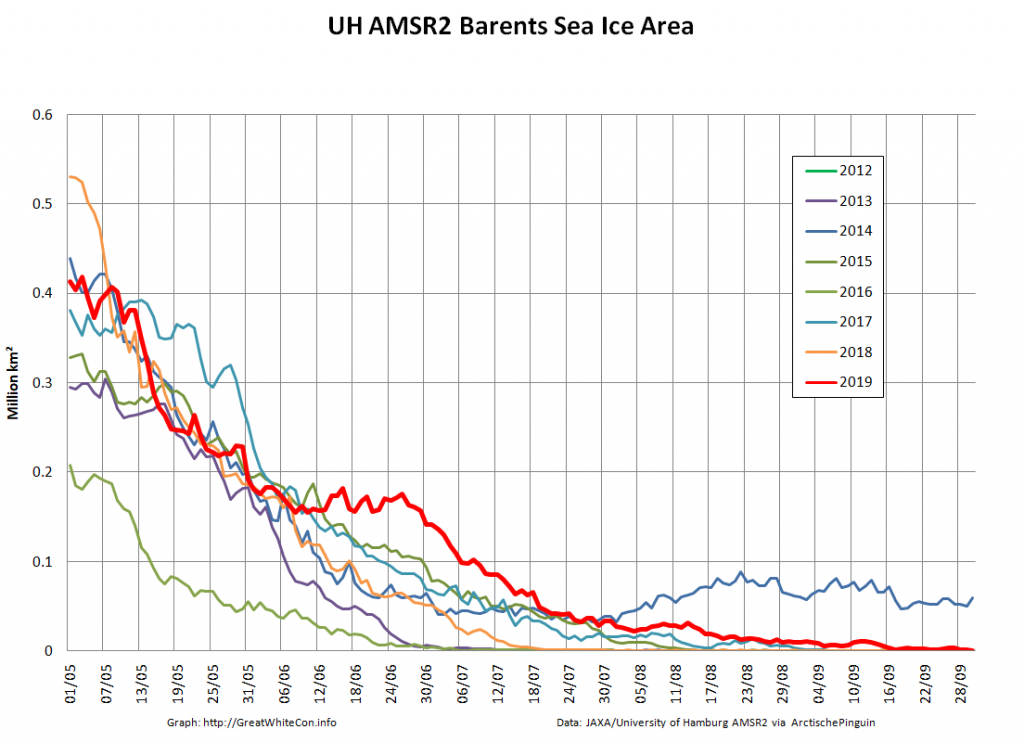
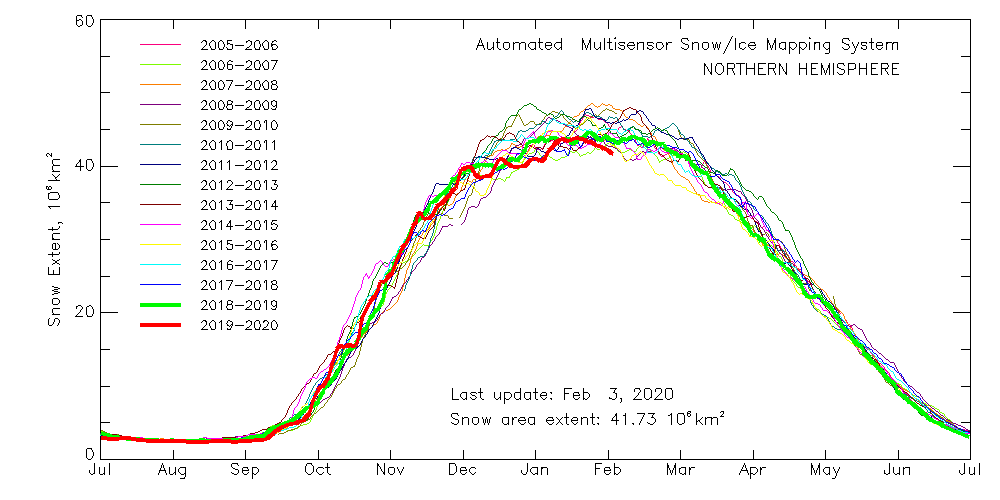
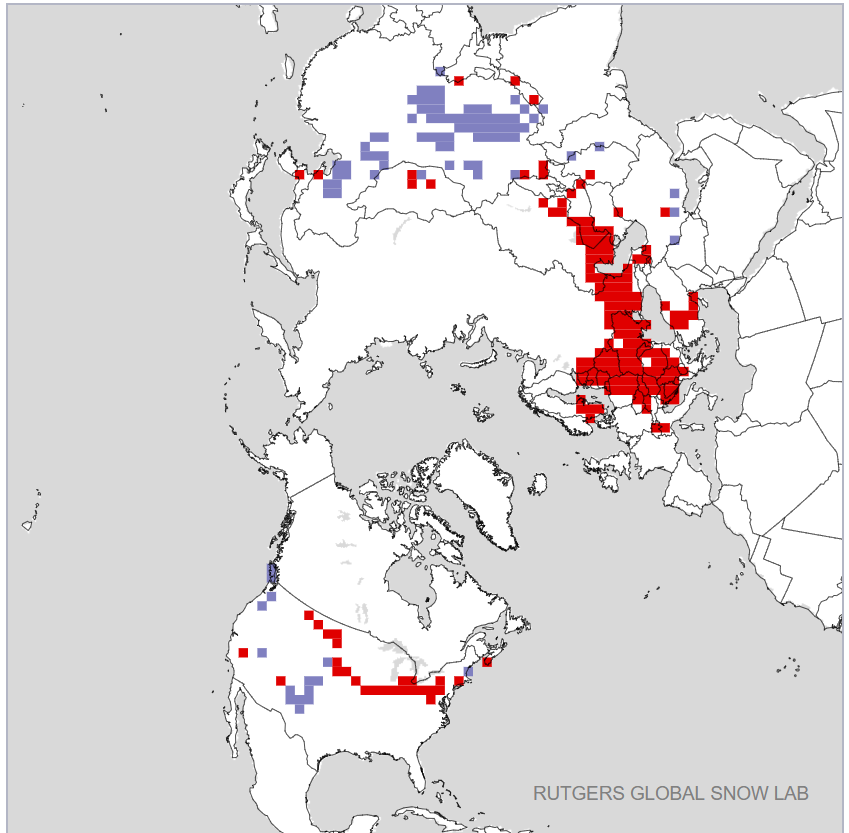
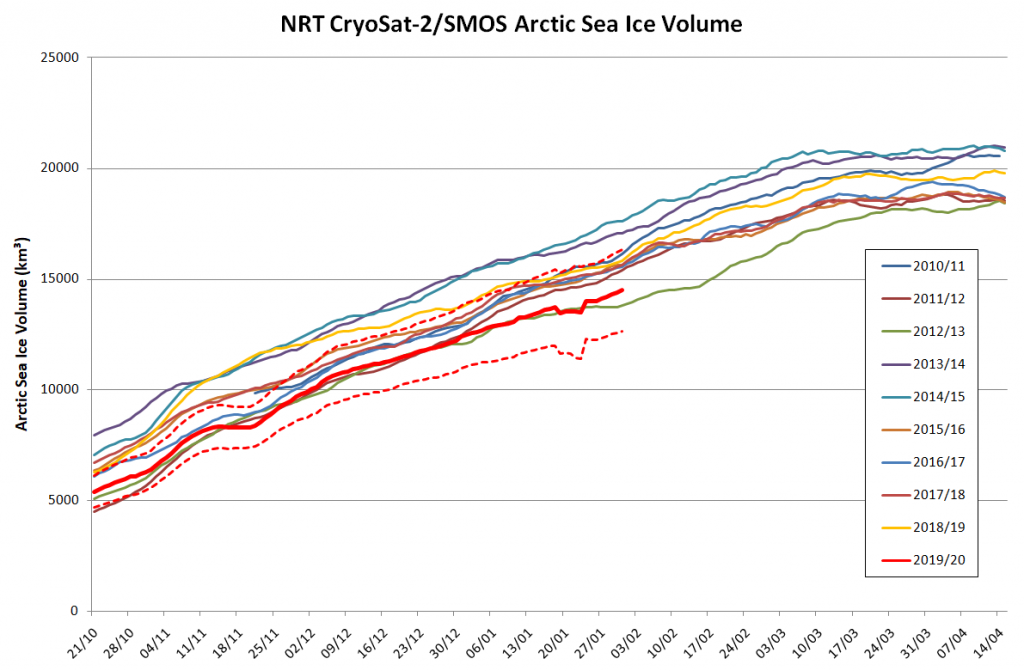
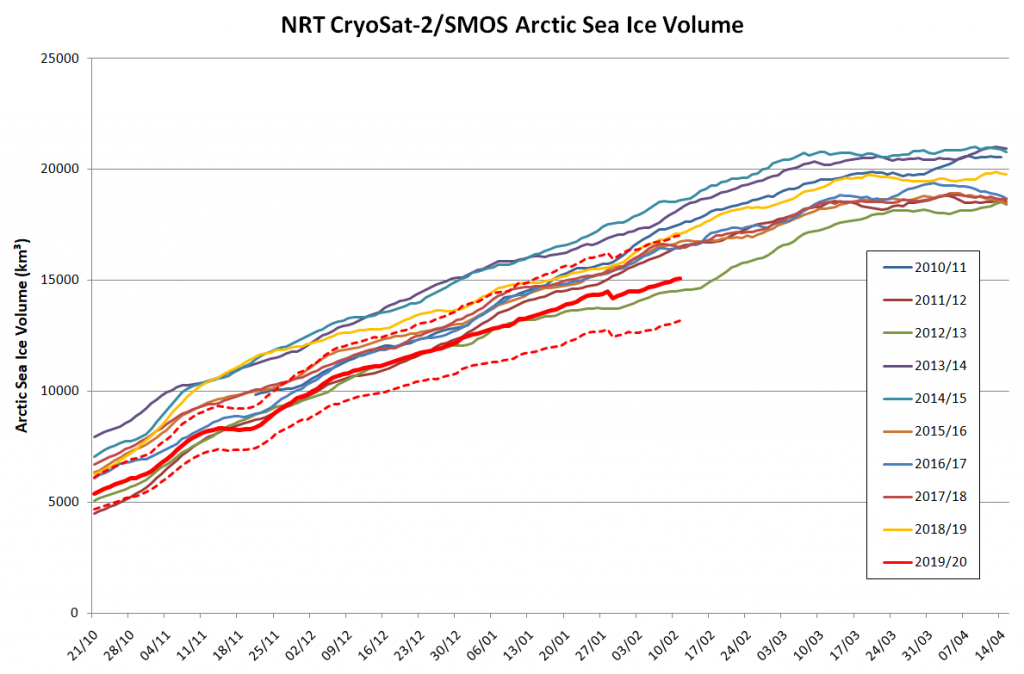
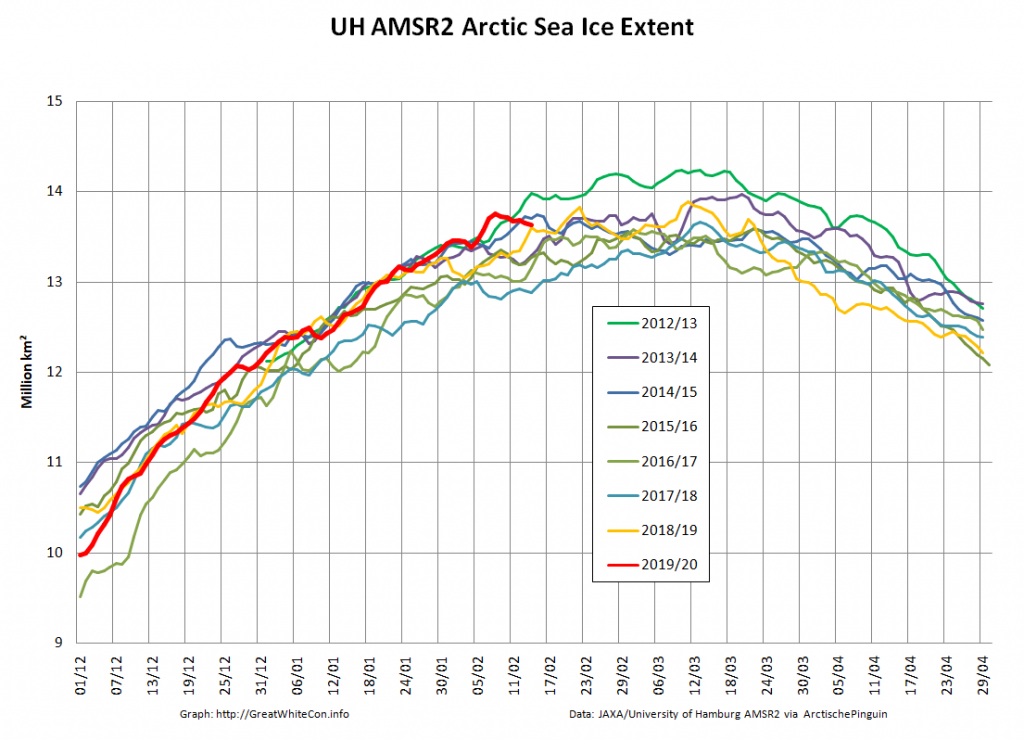
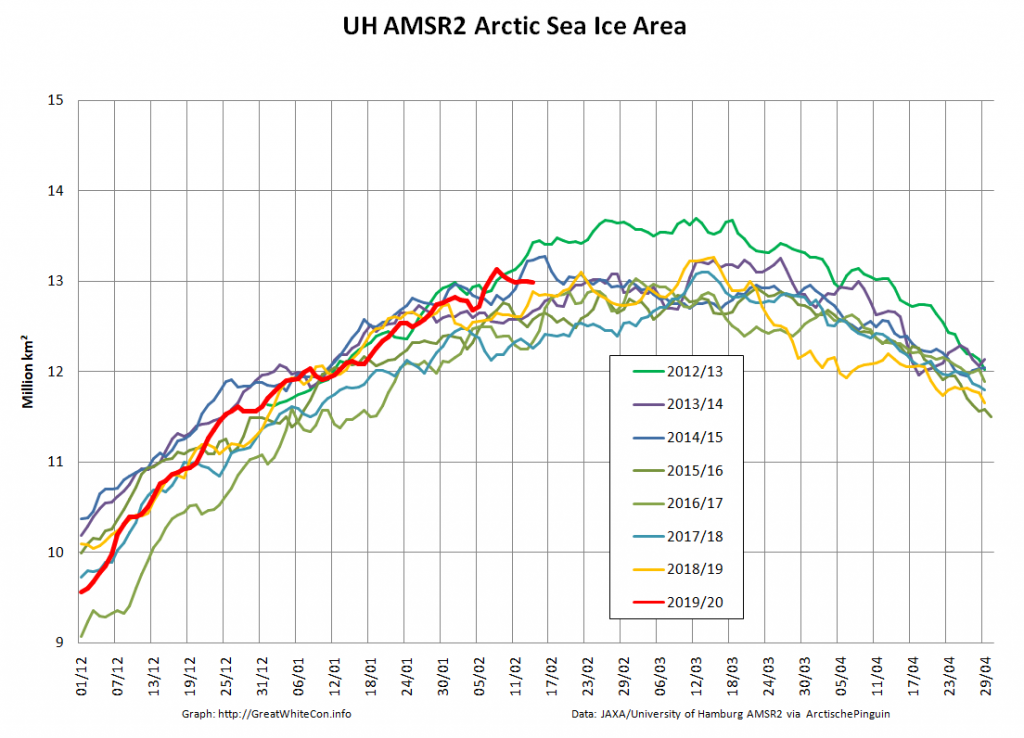
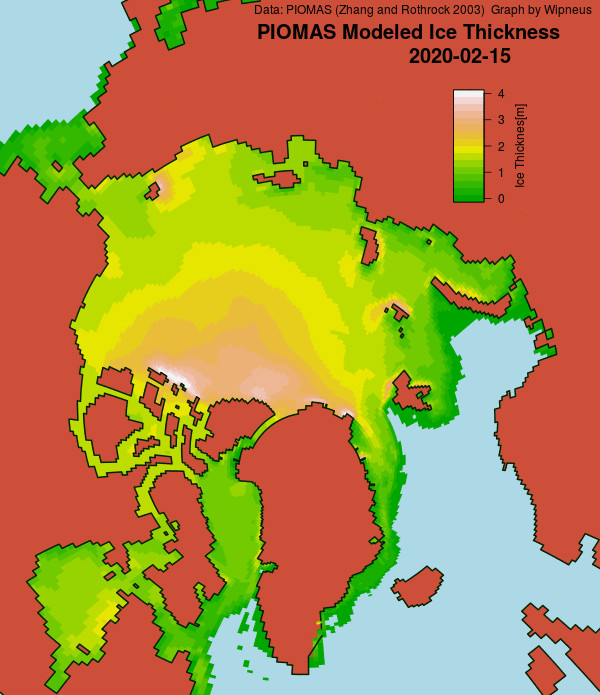
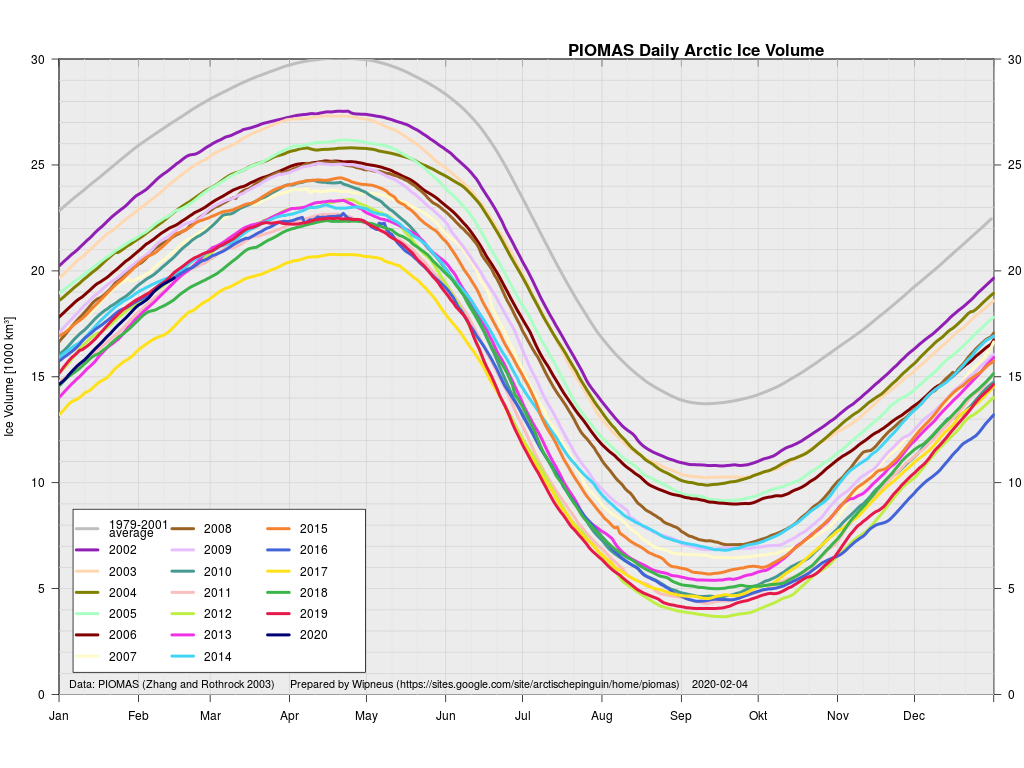
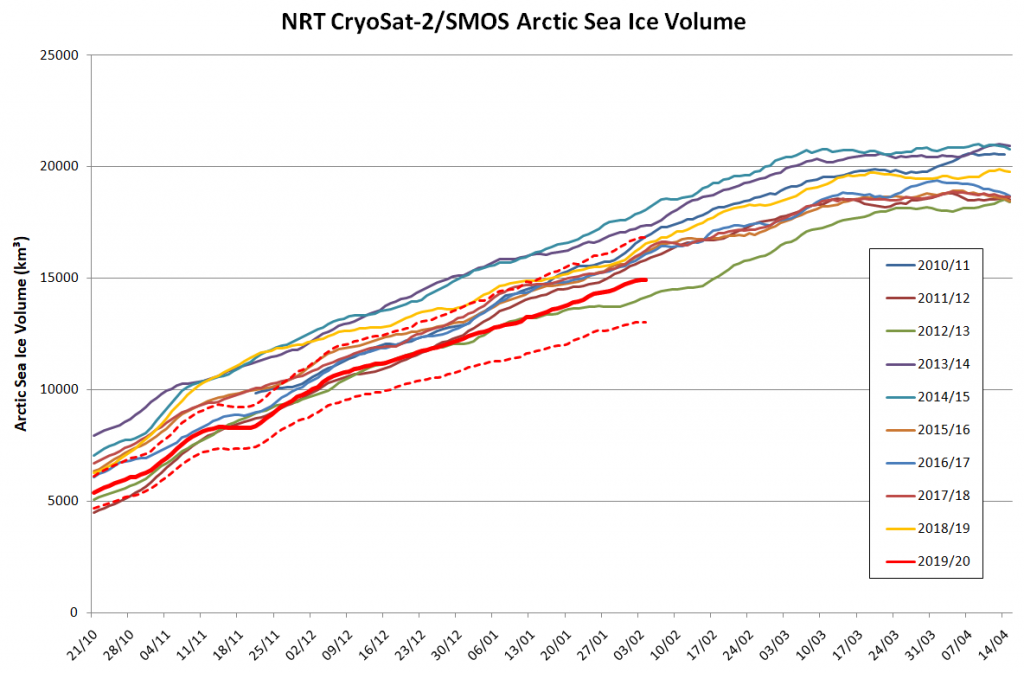
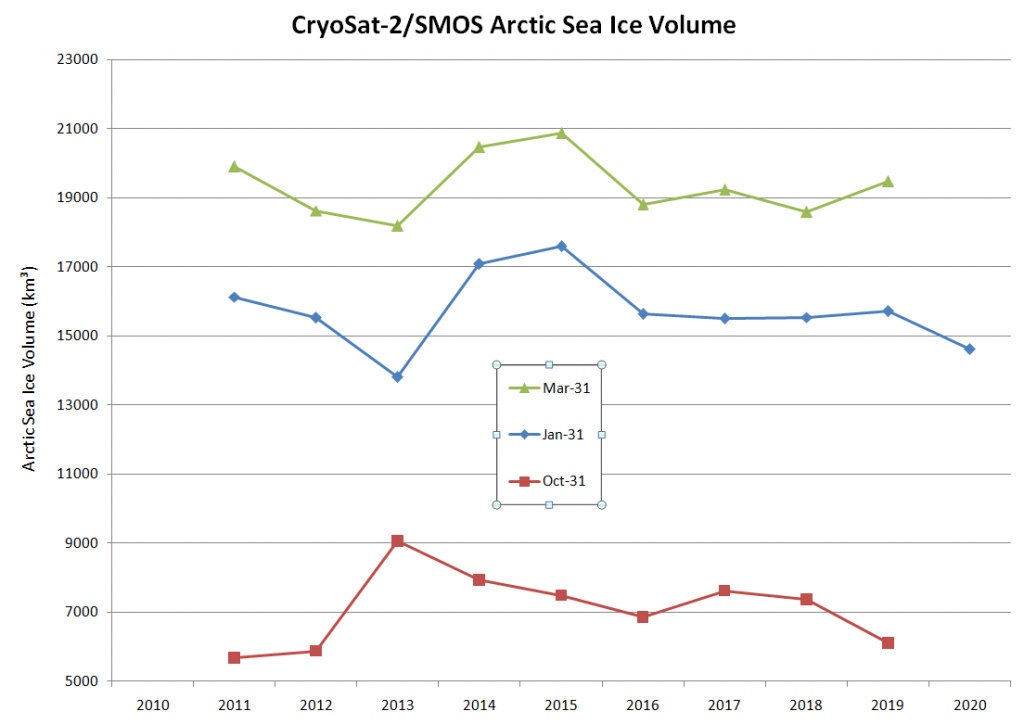
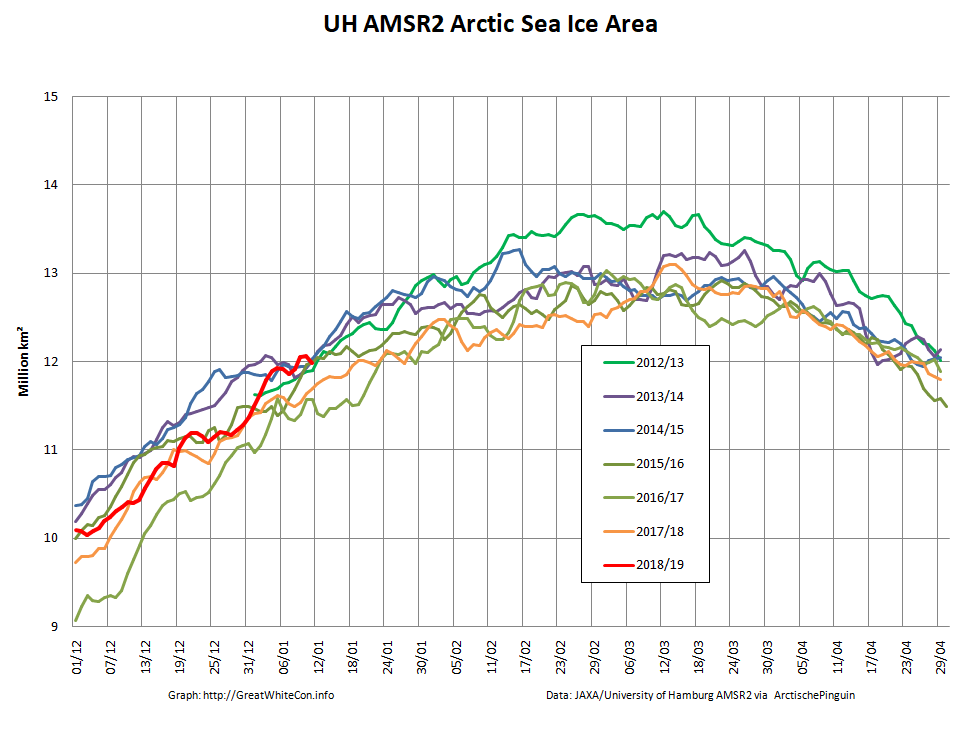
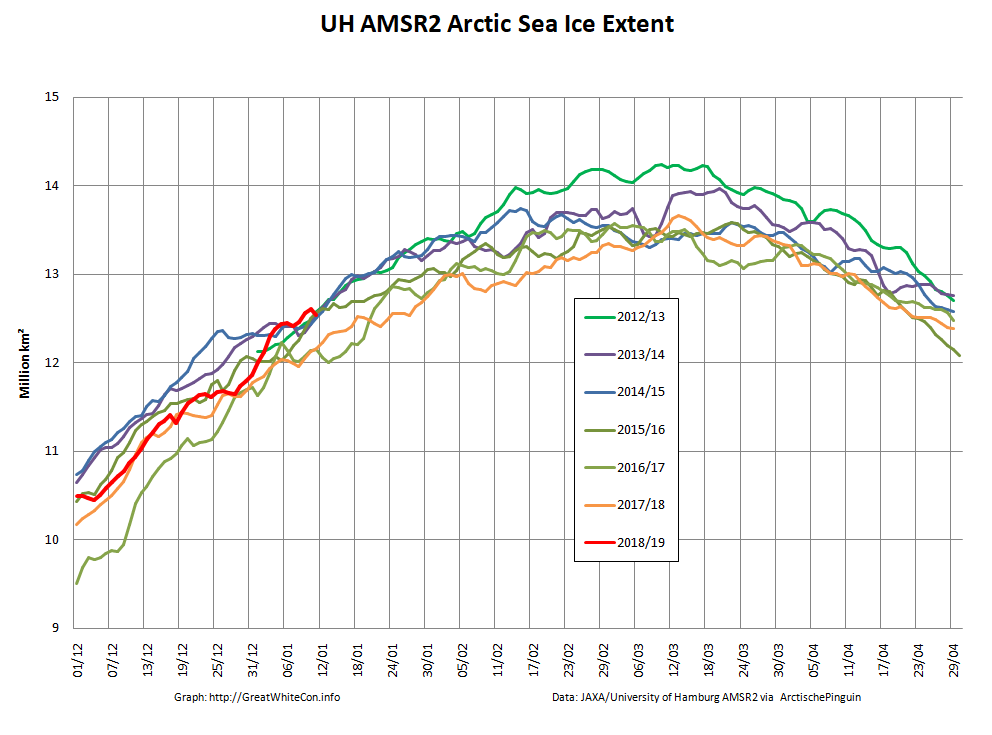
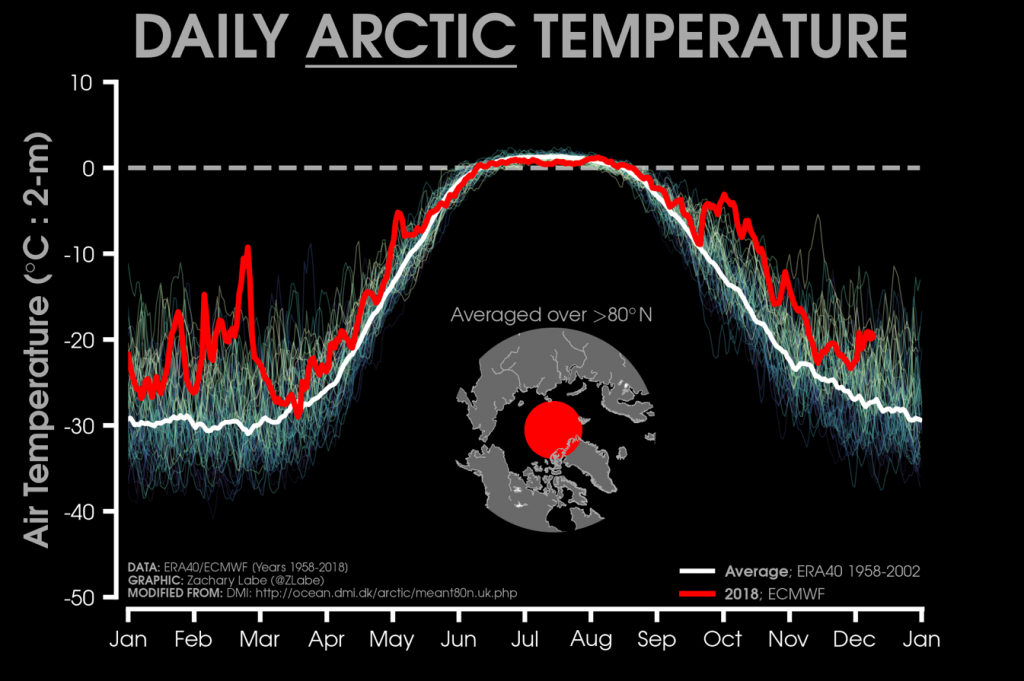
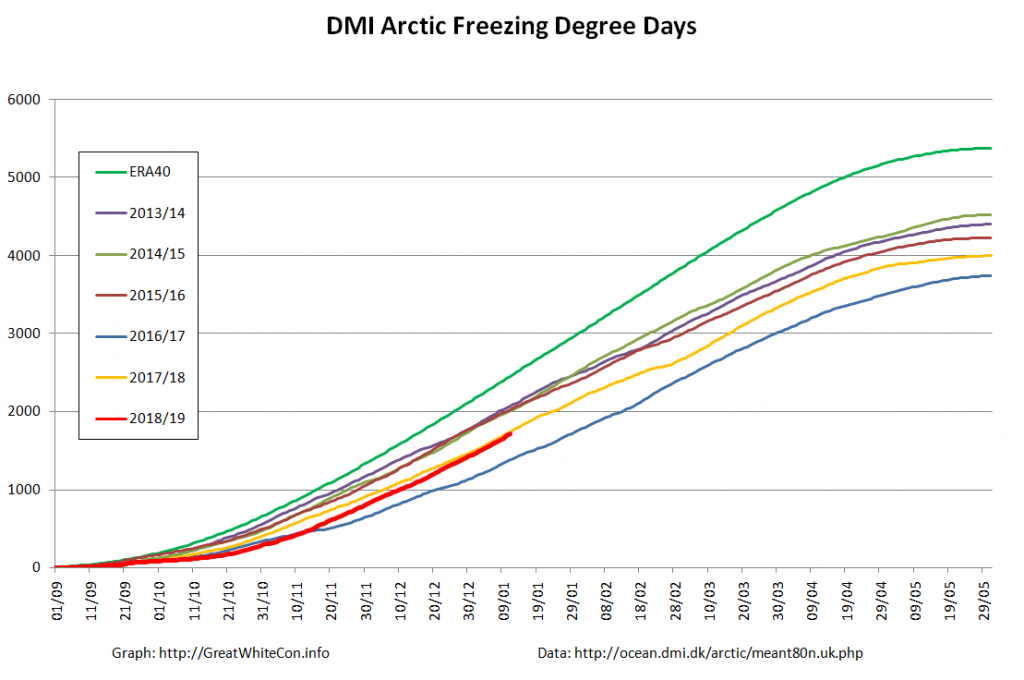
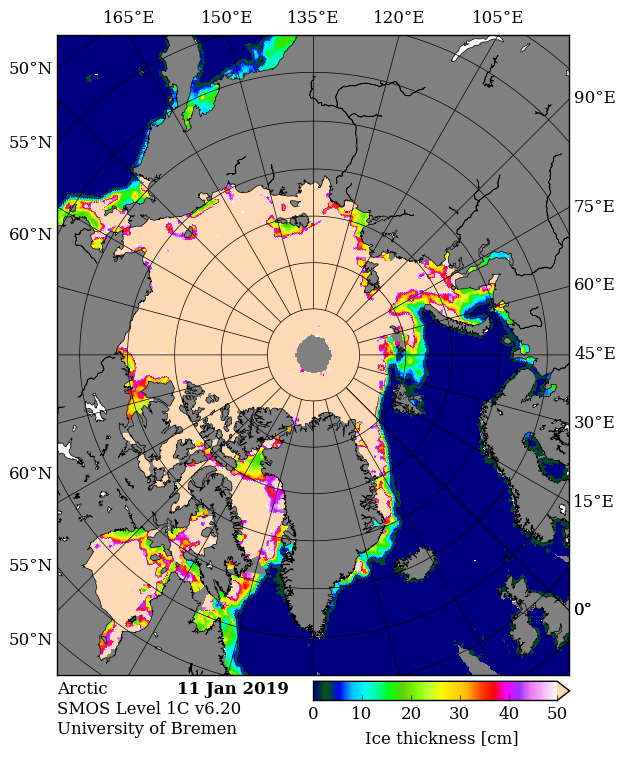
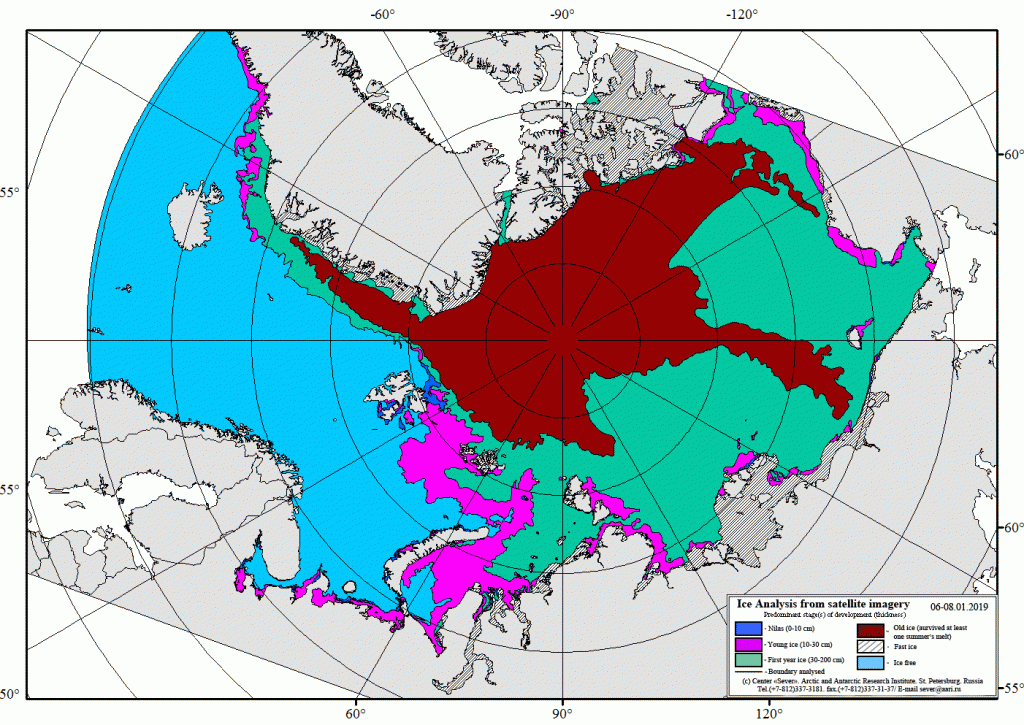
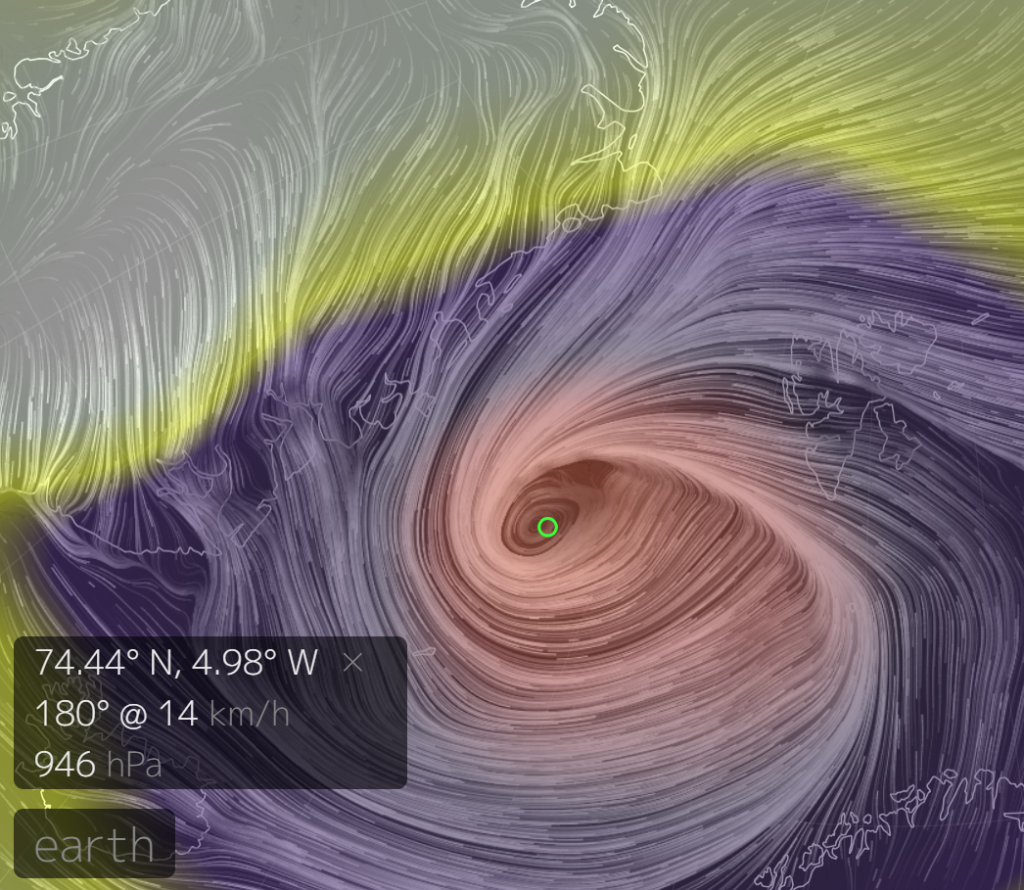
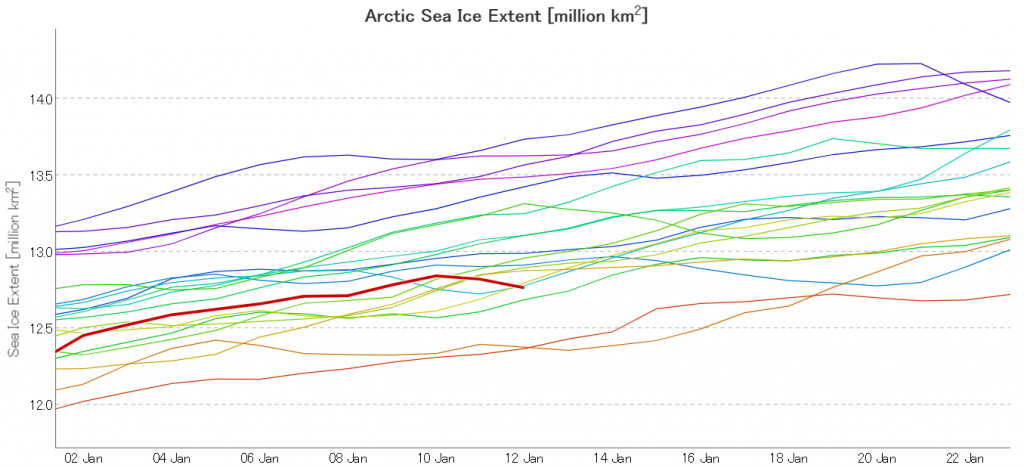
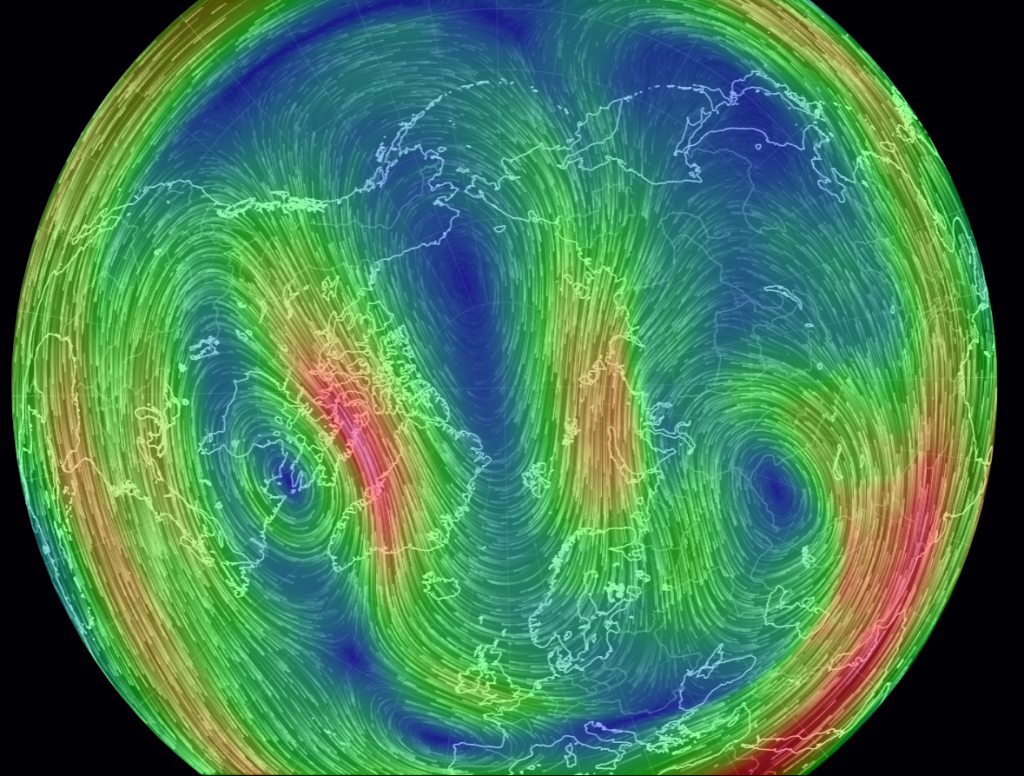
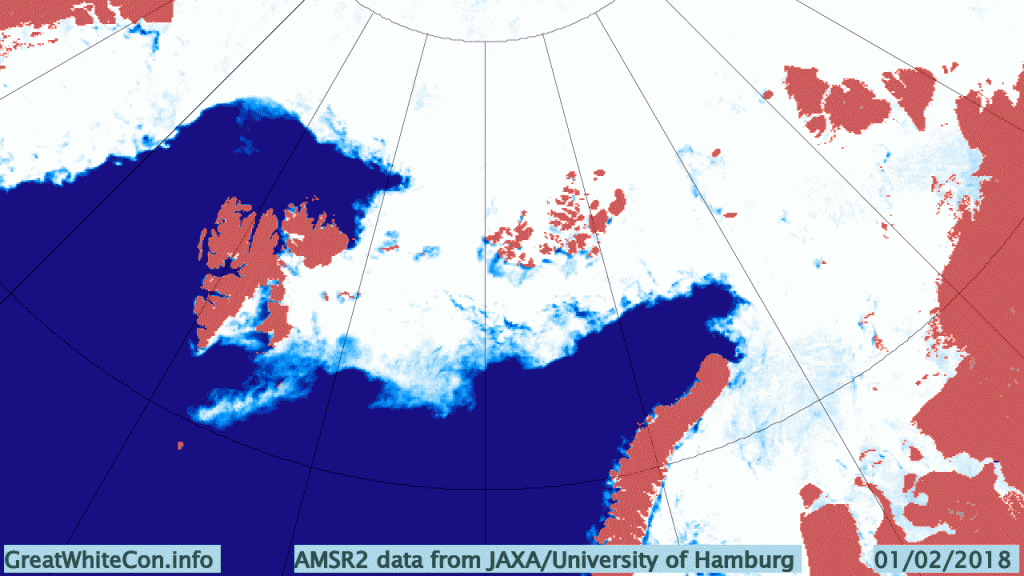
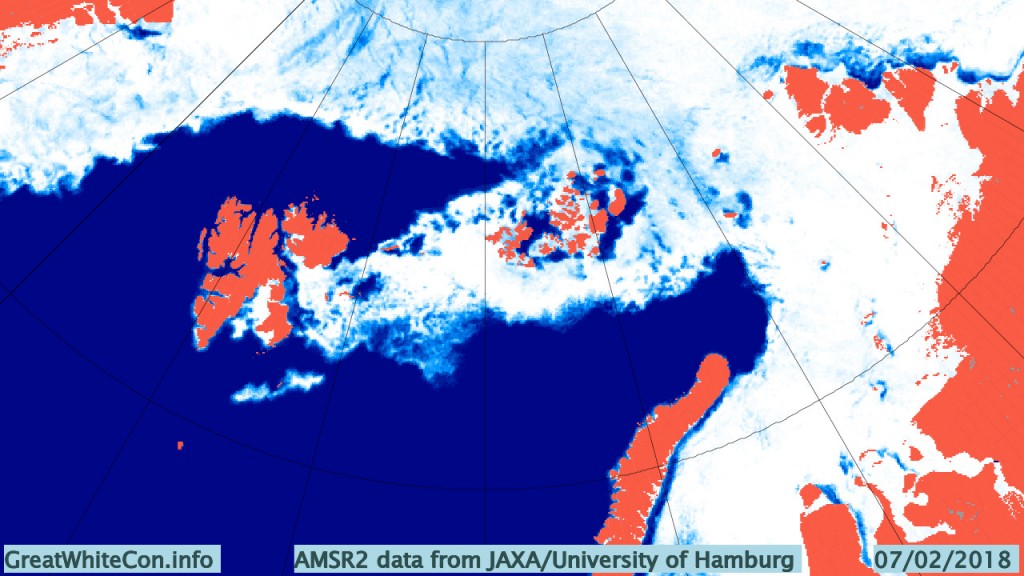
The Polar Amplification Model Intercomparison Project (PAMIP for short) is one of several Community Earth System Model (CESM for short) based climate modelling projects.
As the project’s web site points out:
Polar amplification, the phenomenon that external radiative forcing produces a larger change in surface temperature at high latitudes than the global average, is a key aspect of anthropogenic climate change but its causes and consequences are not fully understood.
PAMIP, co-led by Dr. Doug Smith, Dr. James Screen, and Dr. Clara Deser seeks to improve our understanding of this phenomenon through a coordinated set of numerical model experiments. As one of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) endorsed MIPs, PAMIP will address the following primary questions:
1. What are the relative roles of local sea ice and remote sea surface temperature changes in driving polar amplification?
2. How does the global climate system respond to changes in Arctic and Antarctic sea ice?
The following article provides an overview of the PAMIP including the protocols: https://www.geosci-model-dev.net/12/1139/2019/
The PAMIP project is thus part of the global climate modelling effort leading up to the long anticipated publication of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s next series of assessment reports, conveniently abbreviated as simply “AR6”. The project has been in the news recently. According to an article in Science magazine:
Every time severe winter weather strikes the United States or Europe, reporters are fond of saying that global warming may be to blame. The paradox goes like this: As Arctic sea ice melts and the polar atmosphere warms, the swirling winds that confine cold Arctic air weaken, letting it spill farther south. But this idea, popularized a decade ago, has long faced skepticism from many atmospheric scientists, who found the proposed linkage unconvincing and saw little evidence of it in simulations of the climate.
Now, the most comprehensive modeling investigation into this link has delivered the heaviest blow yet: Even after the massive sea ice loss expected by midcentury, the polar jet stream will only weaken by tiny amounts—at most only 10% of its natural swings. And in today’s world, the influence of ice loss on winter weather is negligible, says James Screen, a climate scientist at the University of Exeter and co-leader of the investigation, which presented its results last month at the annual meeting of the European Geosciences Union (EGU for short). “To say the loss of sea ice has an effect over a particular extreme event, or even over the last 20 years, is a stretch.”
The idea that Arctic sea ice loss could influence midlatitude winter weather first gained traction in 2012, in a paper by two climate scientists, Jennifer Francis, now at the Woodwell Climate Research Center, and Stephen Vavrus at the University of Wisconsin, Madison. It started with a simple observation: The Arctic is warming nearly three times faster than the rest of the world. At the time, sea ice loss was thought to be the primary accelerant for this amplification: As bright, reflective ice is replaced by dark, sunlight-absorbing water, the Arctic heats up, causing more ice loss, and more warming in turn.
The warming, Francis and Vavrus proposed, would inflate the height of the polar troposphere—the lowest layer of the atmosphere and home to its weather. That would decrease the pressure differences between polar and midlatitude air that drive the polar jet stream, which separates the air masses and keeps cold air collared around the pole. The jet would grow weaker and wavier, allowing cold air to intrude farther south. In their paper, Francis and Vavrus argued such a trend was visible in weather records and worsening with Arctic warming and ice loss.
The results of the project presented at the EGU haven’t been published in an academic journal yet, but according to Science once again:
In the years long PAMIP investigation researchers ran more than a dozen climate models 100 times each. One set of model runs simulated the Arctic atmosphere without pronounced sea ice loss, using ocean temperatures and sea ice extent from 2000. The other kept the ocean temperatures the same, but reduced the ice coverage to the extent expected decades from now, after 2°C of global warming, when the Arctic could be ice free in the summer. Keeping the oceans the same should highlight the influence—if any—of sea ice loss.
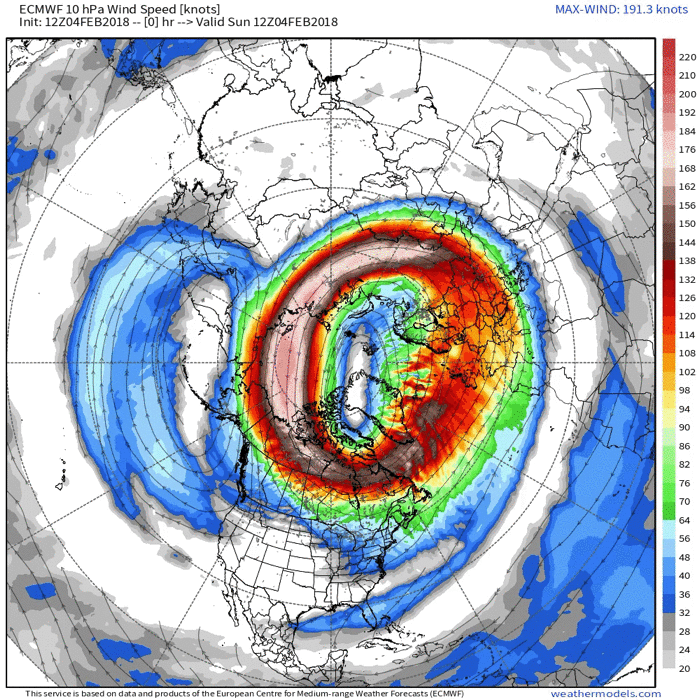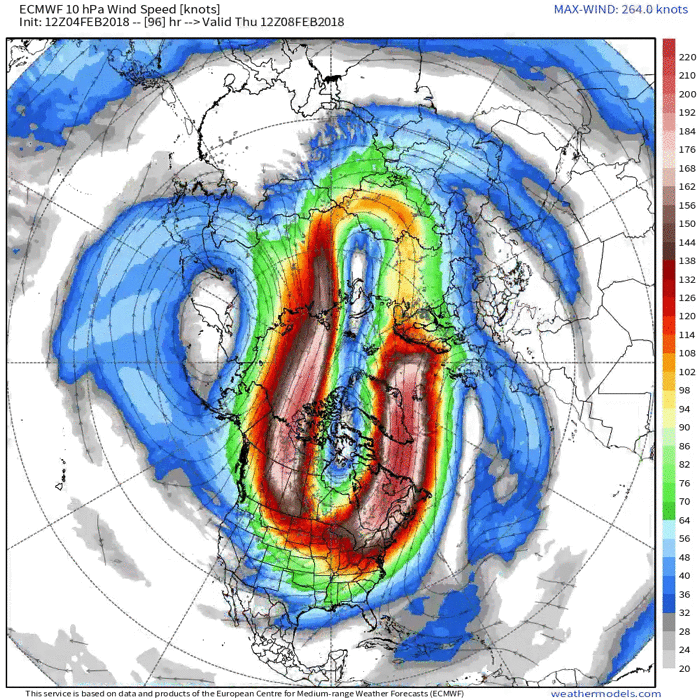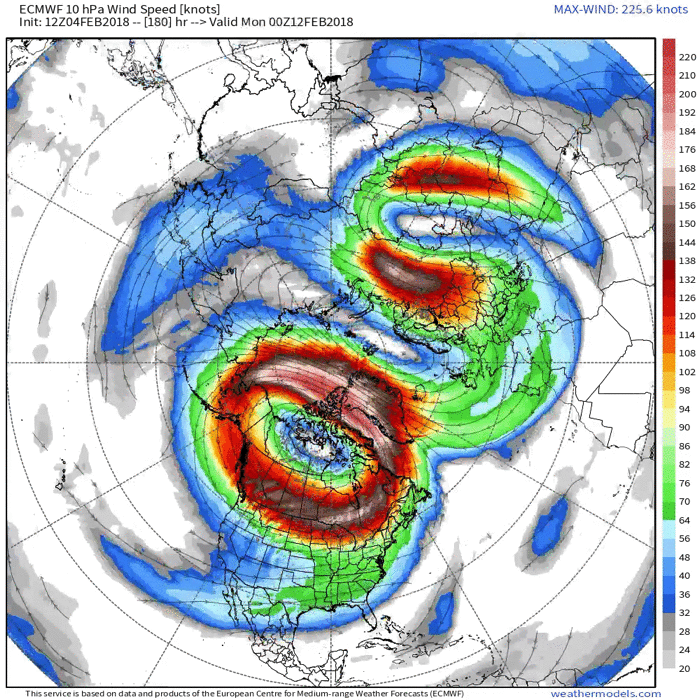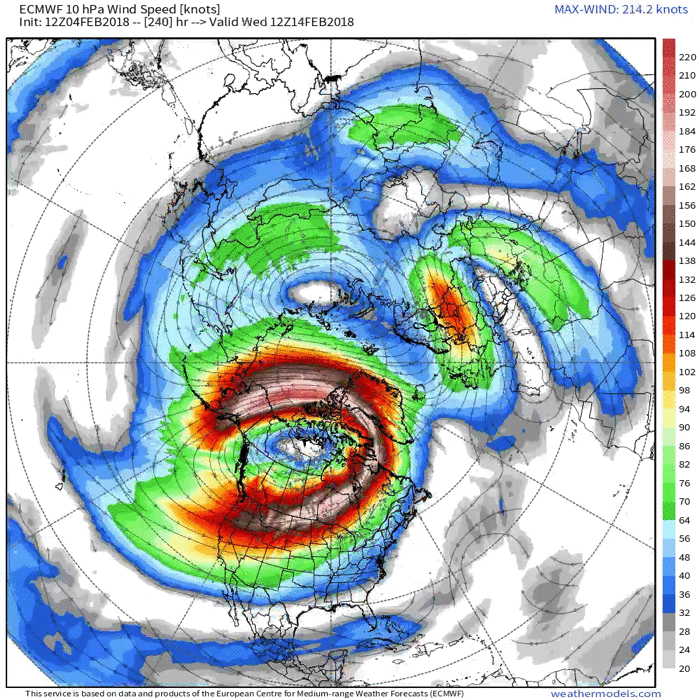
In addition to finding only a tiny effect of sea ice loss on the polar jet stream, the models also found no coherent sign of a second proposed effect of reduced sea ice: more frequent disruptions of the stratospheric polar vortex—a second set of swirling winds, much higher up. Such disruptions, which occur every 2 years on average, ultimately allow cold air lower in the atmosphere to spill southward, causing extreme winter storms, including the cold that gripped Texas this past winter.
However not everyone is convinced by the modelling results:
Judah Cohen, director of seasonal forecasting at Atmospheric and Environmental Research, has long argued that increased snow cover and diminished sea ice in Siberia favor weather patterns that propagate energy into the stratosphere, making the high-altitude disruptions more frequent. He notes that the models also forecast unrealistically warm winter weather in the midlatitudes, making other predictions suspect. “There’s clearly something missing.” And Francis says the PAMIP experiment may be too simplistic, now that “we know there’s a lot more to Arctic amplification than sea ice loss.”
Whilst we wait to discover precisely what was revealed to the EGU audience, here is a list of current PAMIP publications:
https://www.cesm.ucar.edu/projects/CMIP6/PAMIP/publications.html
In conclusion, for the moment at least, here’s an illustration of one of the issues PAMIP is endeavouring to address. The difference between the outputs of previous generation of CMIP5 global climate models and observations taken from Smith et al. (2019):
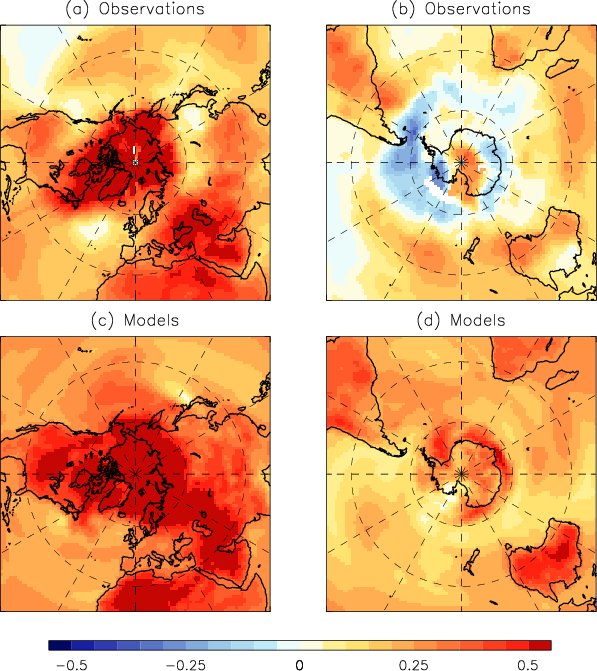
It will be extremely interesting to discover what the working group 1 section of the IPCC’s 6th Assessment Report ultimately has to say on the topic of Arctic amplification. The current AR6 timeline states that:
The Working Group I contribution is expected to be considered at the 54th Session of the IPCC which is scheduled to take place in the 14 days from 26 July 2021. The report will be released, subject to approval and acceptance by the Panel, on or around 9 August.