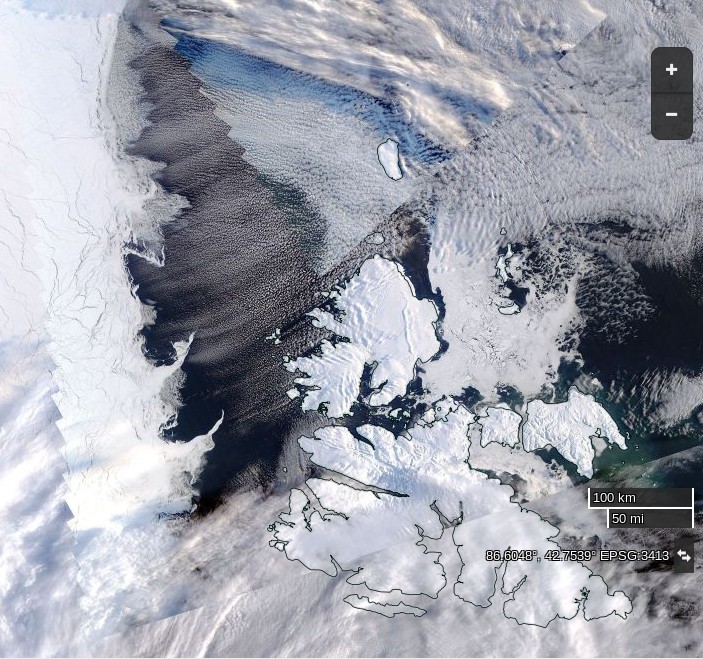
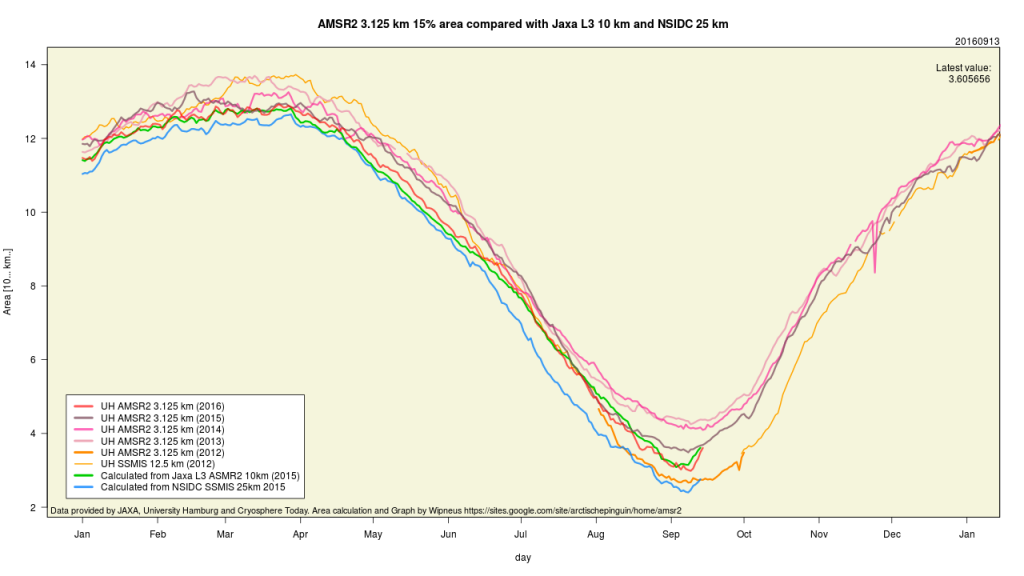
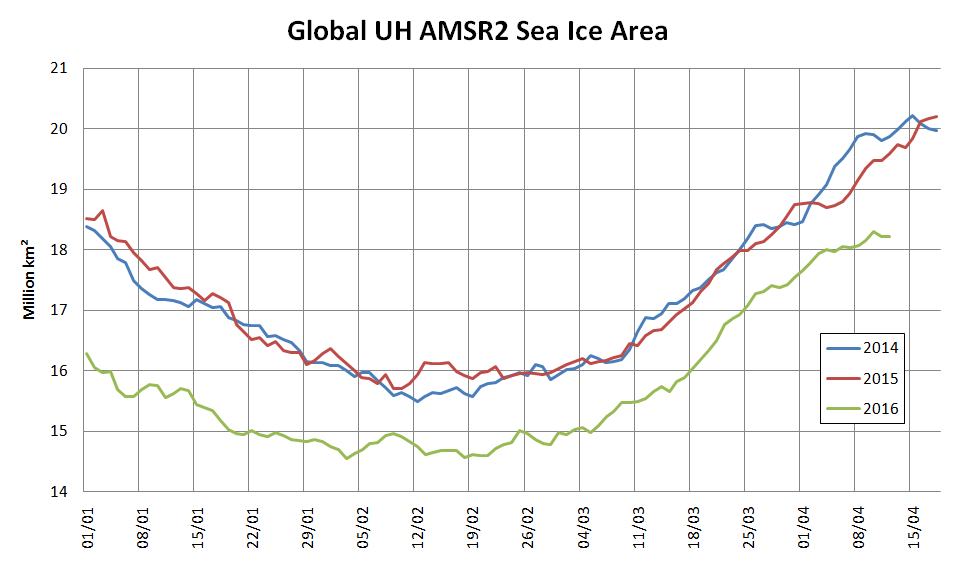
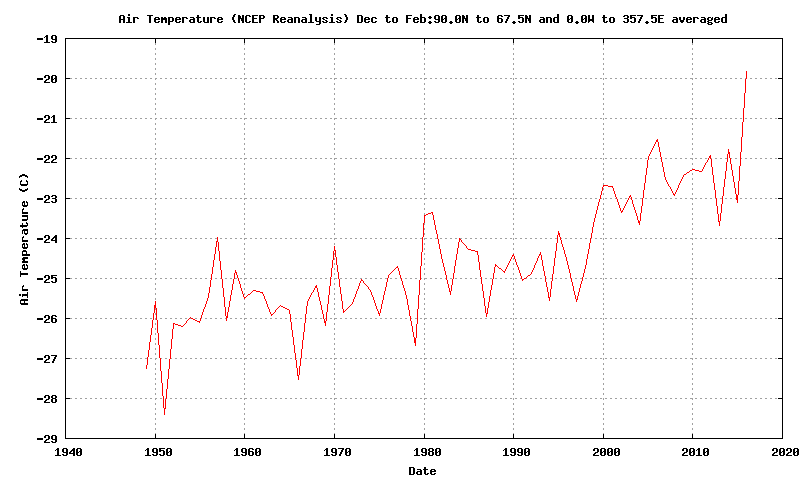
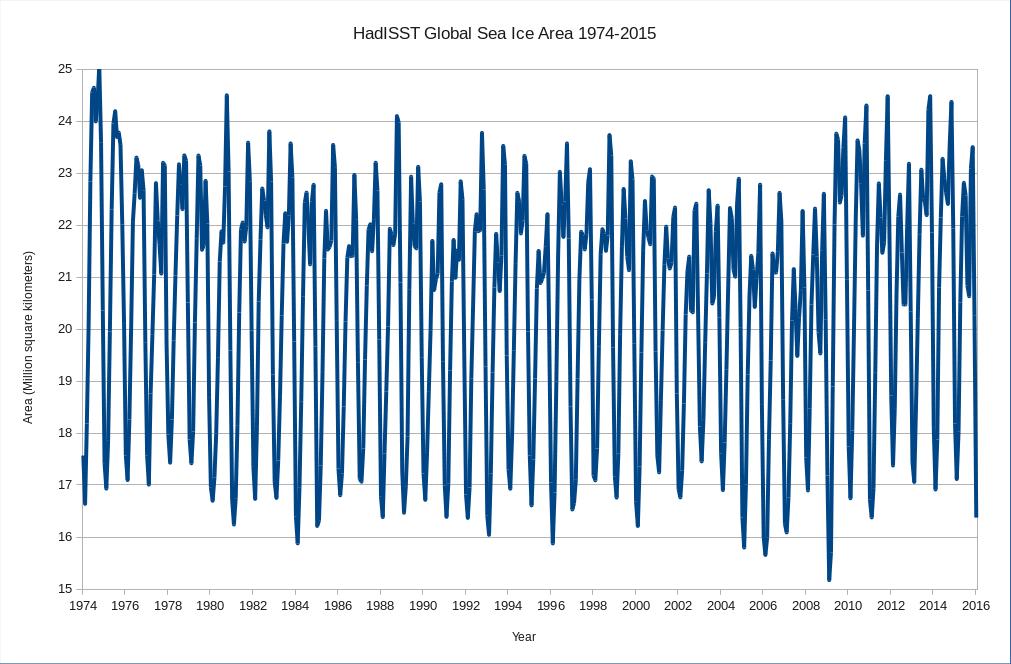
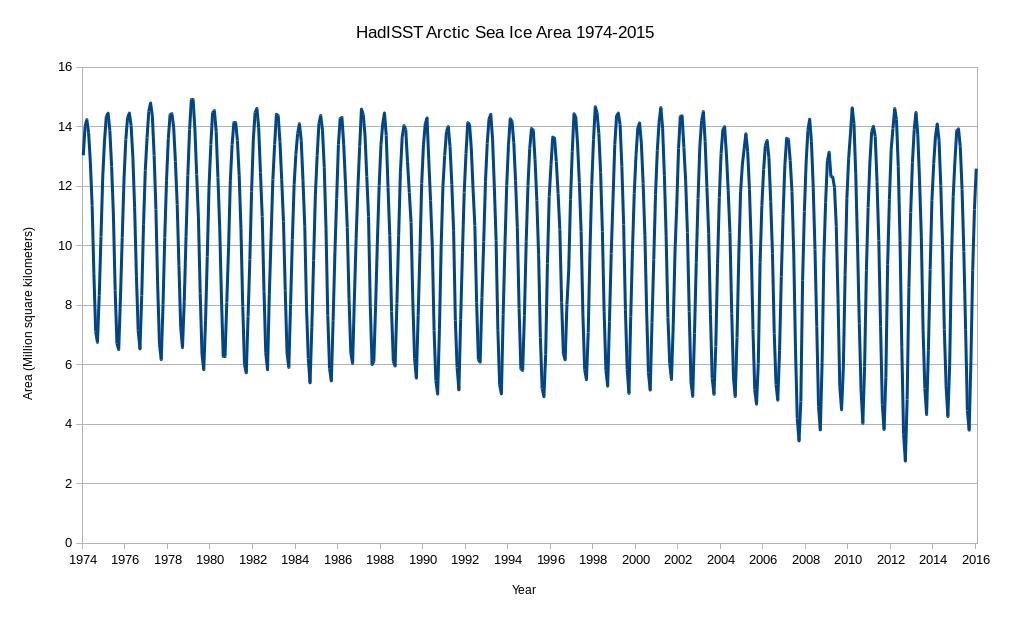
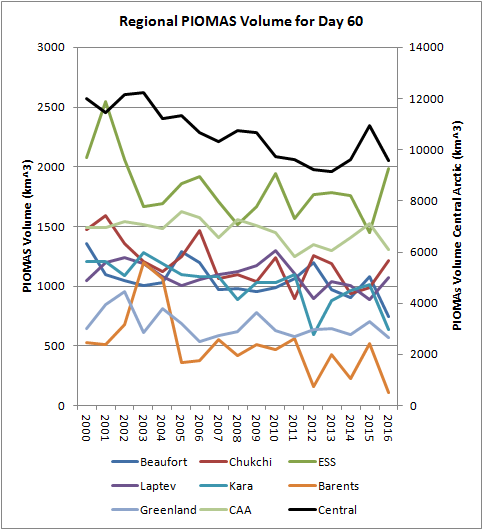
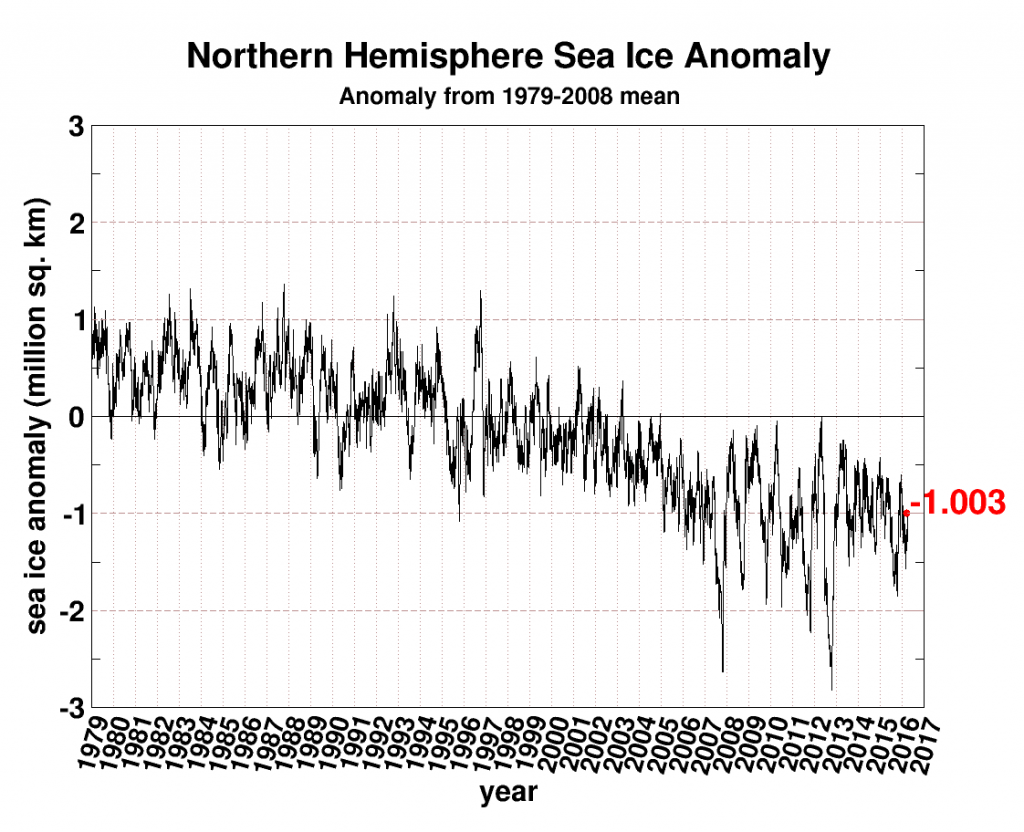
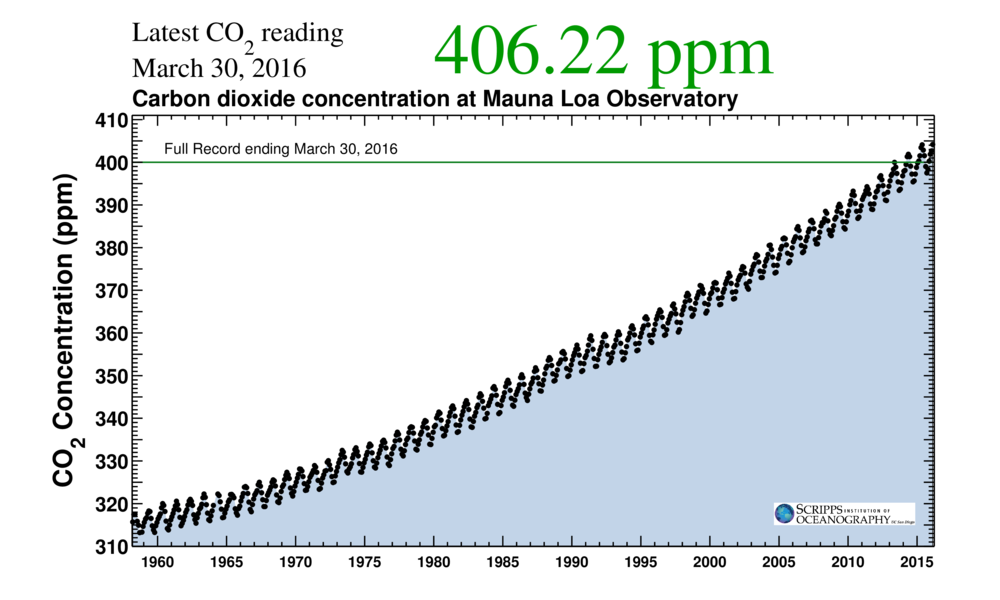
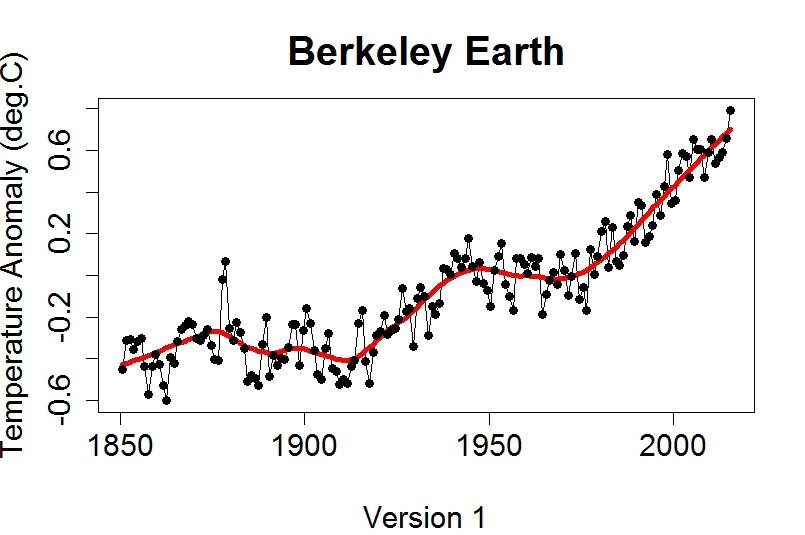
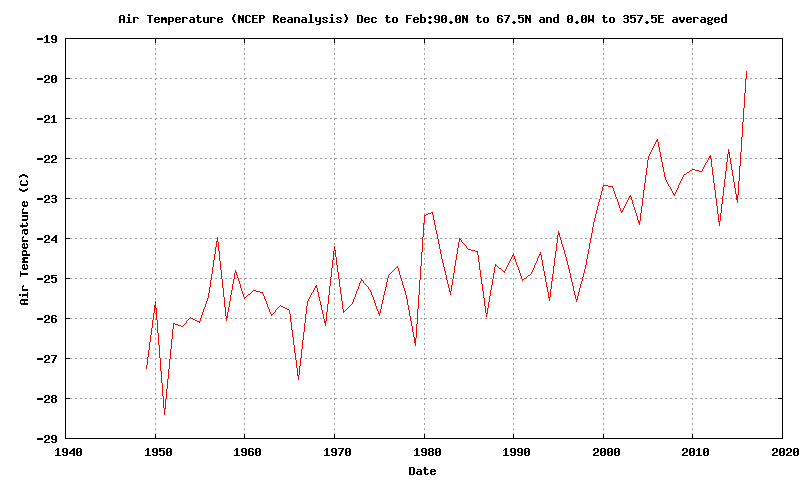
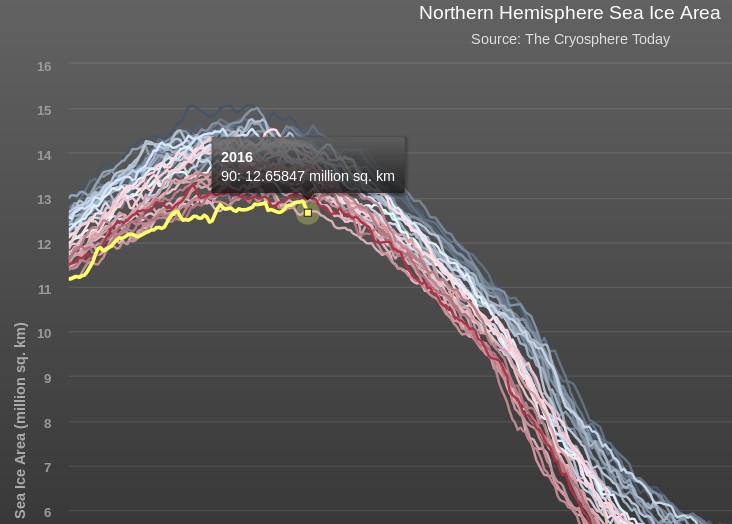
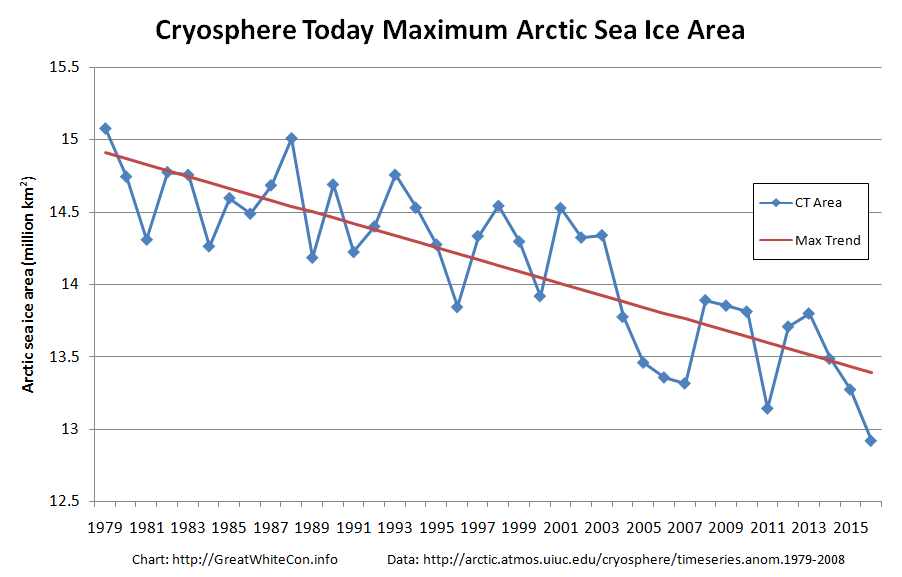
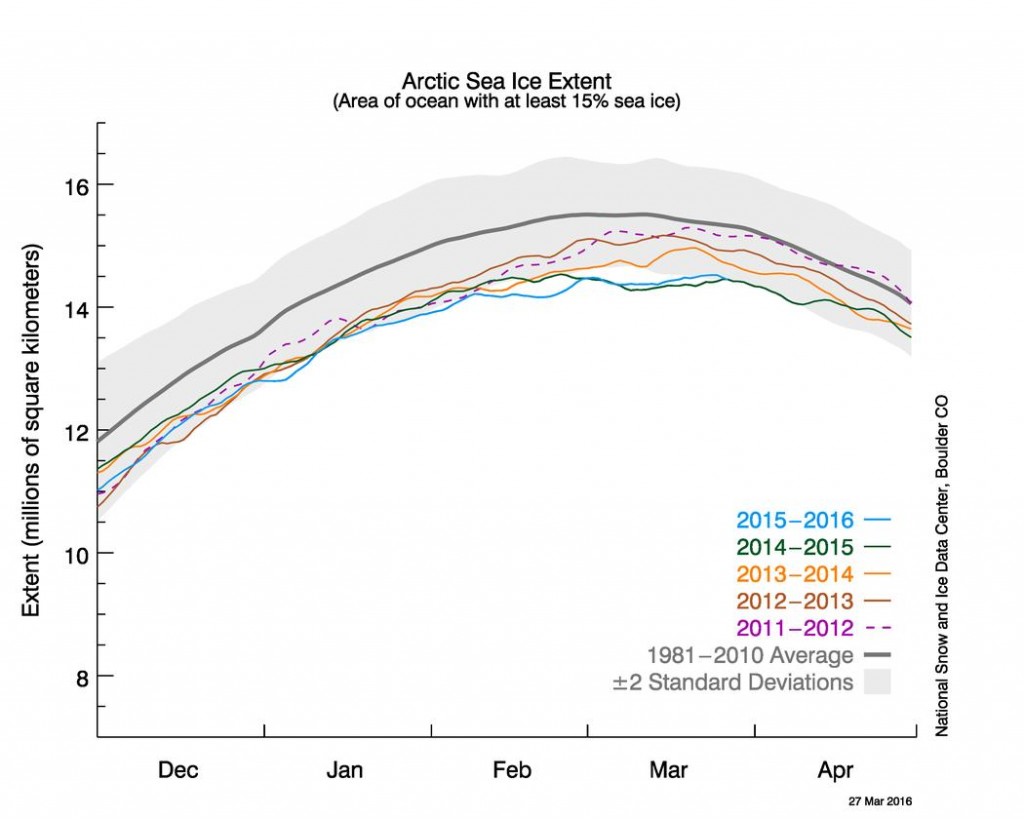
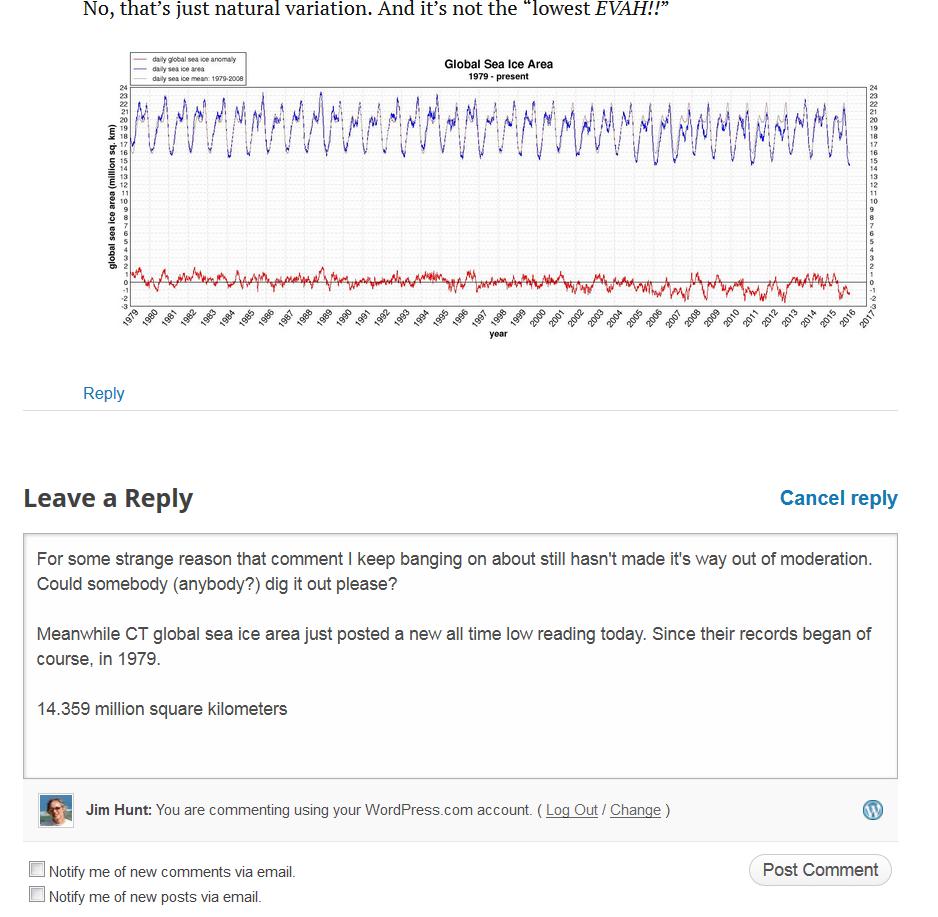
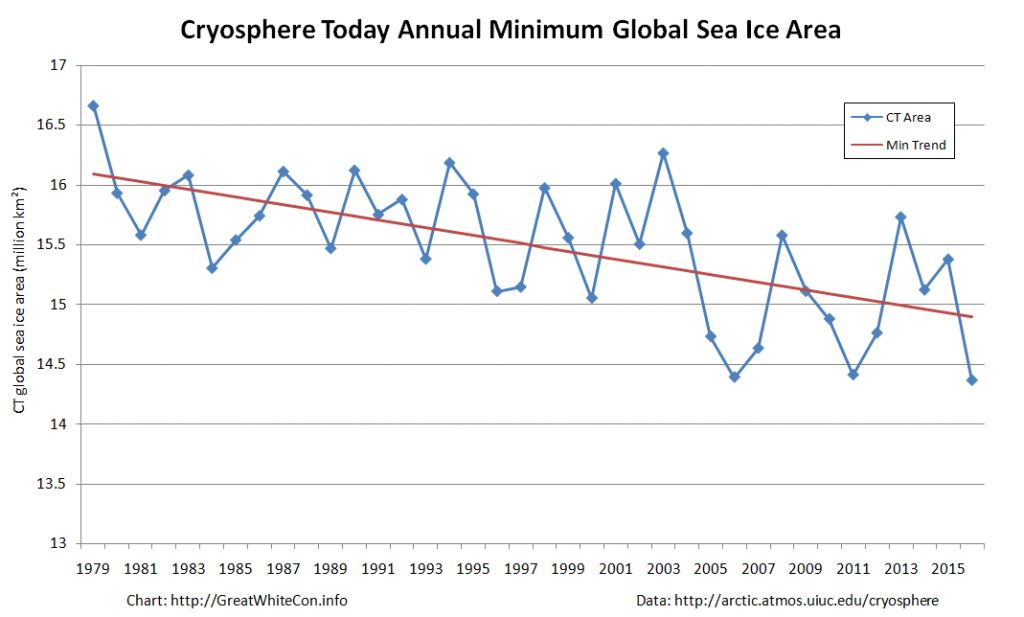
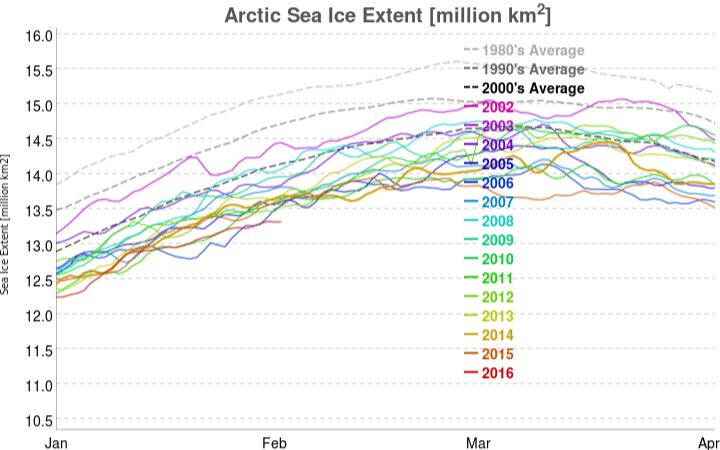
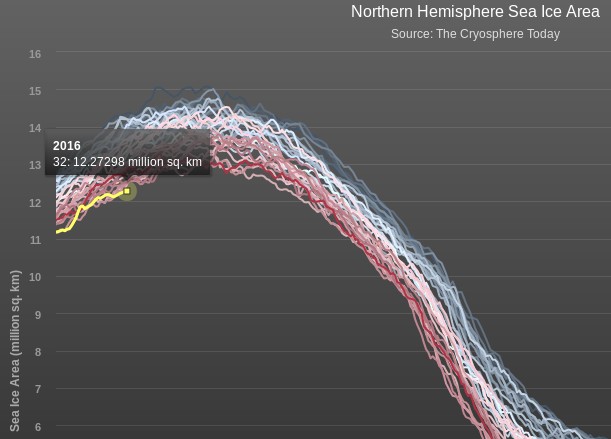
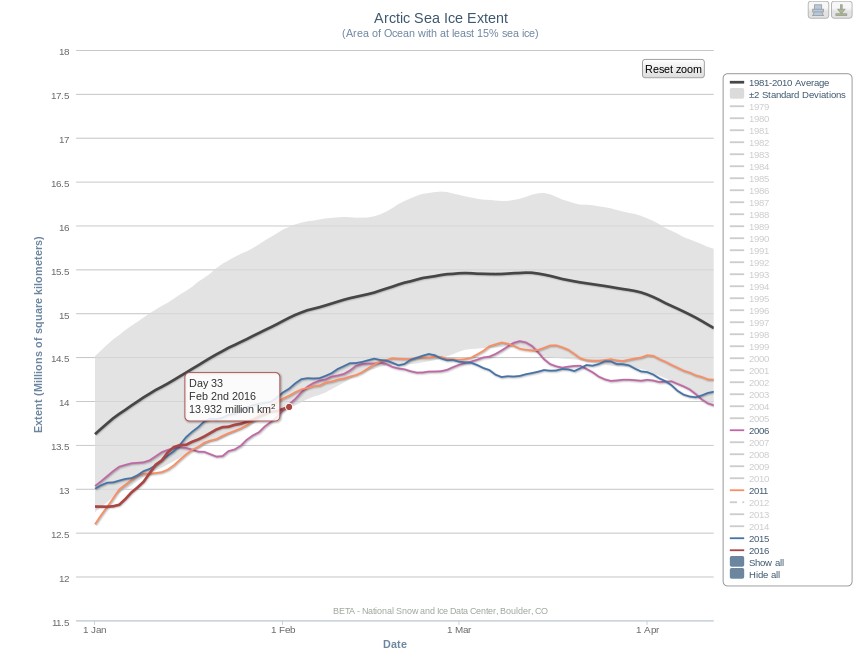
Today we bring a positive plethora of “Shock News!”. Starting with sea ice, yesterday Anthony Watts published an article on WUWT about the 2016 Arctic minimum extent. That’s not too surprising perhaps, but what’s shocking is that included one of Wipneus’ graphs of Arctic sea ice AREA that has been gracing our very own Arctic Sea Ice Graphs page since Anthony mocked us for not having such a thing. His take on this momentous event?
All of the data I’ve looked at agrees, Arctic sea ice is now on the upswing, and in a big way.
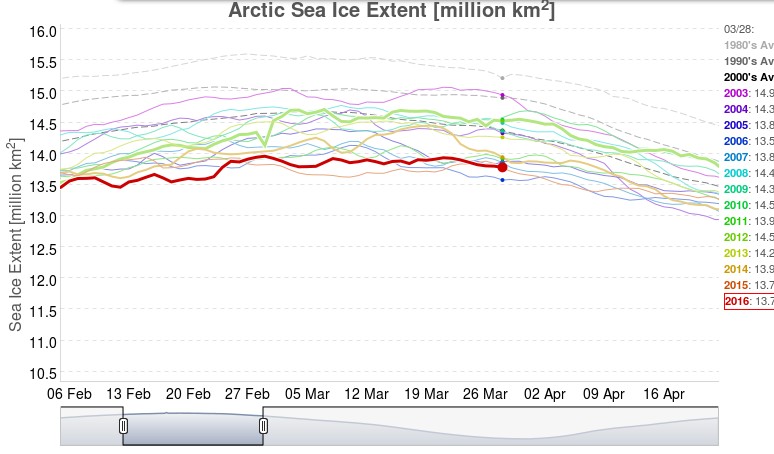
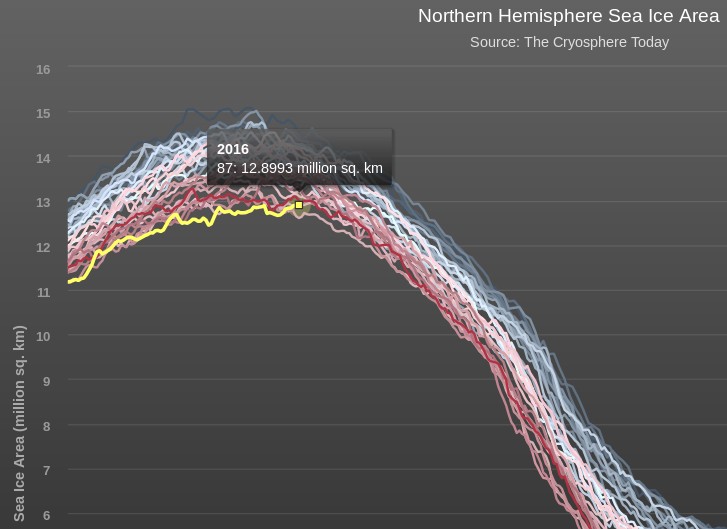
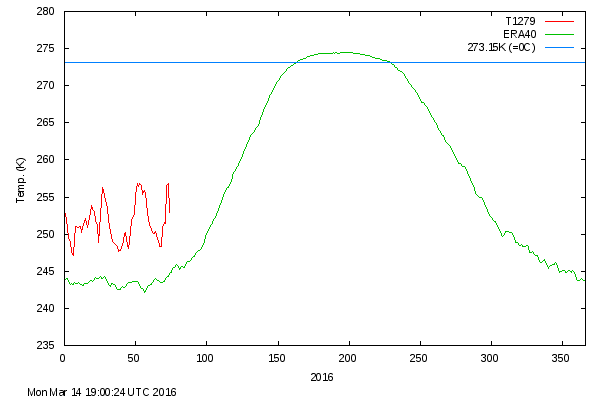
This graph from Wipneus shows the abruptness of the change.
Here it is, in all its glory:
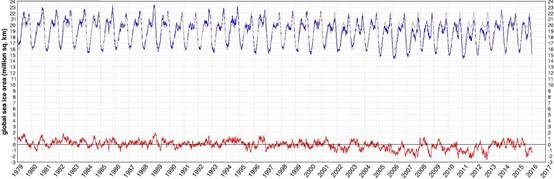
What’s not in the least surprising is that Anthony failed to provide a link to the source of the graph, and that our polite request for that to be corrected remains invisible took a long time to be approved over at Watts Up With That. Here it is, in all its ignominy:
As if that isn’t enough to cope with for one day, there was even bigger shock yesterday. Tony Heller stated:
which is accompanied by a screenshot from an Independent article which reads as follows:
One of Britain’s leading climate change sceptics – former Chancellor Nigel Lawson – has admitted that humans are causing global warming.
Speaking to the House of Lords’ Economic Affairs Committee, Lord Lawson said he did not “question for a moment” that carbon dioxide was a greenhouse gas.
And he accepted there was “huge agreement” among scientists that it was having “some effect” on the atmosphere.
But the former Conservative Cabinet minister argued it would be “crazy” for the UK to try to stop burning the fossil fuels that produce carbon dioxide, claiming countries like China were simply carrying on doing so.
Lord Lawson founded the Global Warming Policy Foundation in 2009 to oppose attempts to reduce the rise in temperatures and has emerged as one of Britain’s leading sceptics.
Here’s a recording of Nigel Lawson versus Adair Turner yesterday, testifying before the Economic Affairs Committee:
It seems as if the “97% consensus” on “anthropogenic global warming” is now at least 97.1%. I cannot help but wonder when Anthony Watts will reveal the news to his faithful followers? Meanwhile most of Tony’s many merry minions are unhappy bunnies this morning. 2015 “New Einstein” award winner Gail Combs complains:
The biggest problem is with that statement he just betrayed every skeptic and agreed that we are all tinfoil hat Den1ers.
It does not matter what else he added. That ‘sound bite’ is a HUGE WIN for the other side. Add the Ship of Fools ‘win’ and they will bash us into the ground.
I am sorry Tony, but it is a complete PR disaster especially right before the US elections.
As you well know this has never been about science. Our side plays by the Marquess of Queensberry Rules, their side are dirty street fighters using Alinsky’s Rules for Radicals and lie and cheat and browbeat at every turn. So their side wins EVERY D@MN TIME!
Mr. Heller comments:
I completely agree with [Nigel Lawson]. Do you consider me to be a “real skeptic” ?
Answers on a virtual postcard please, in the space provided below.