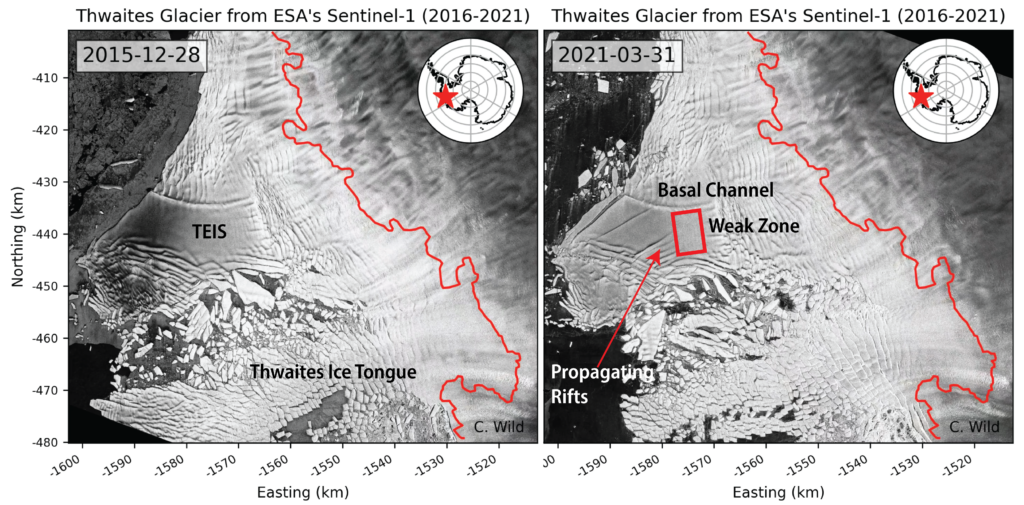
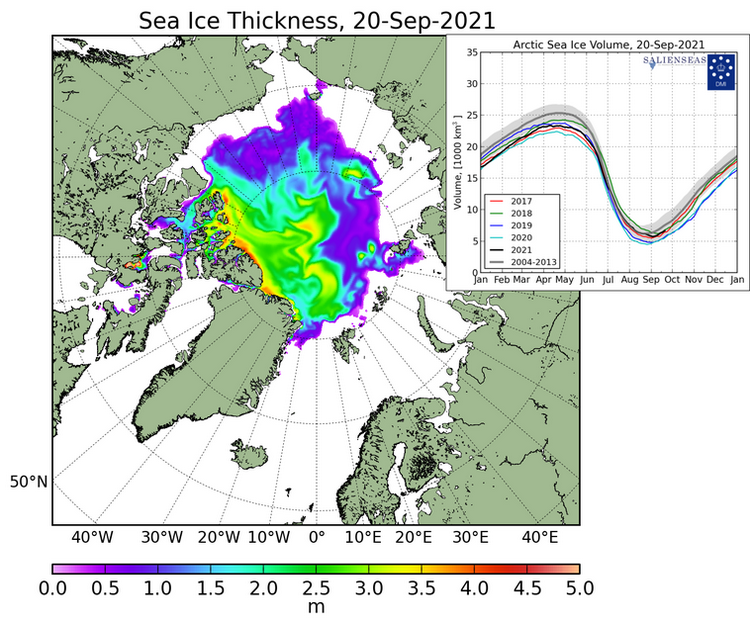
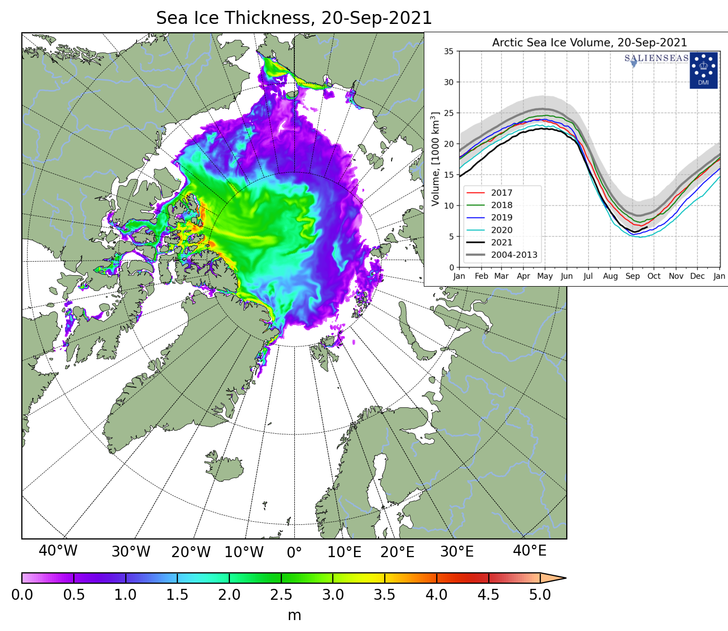
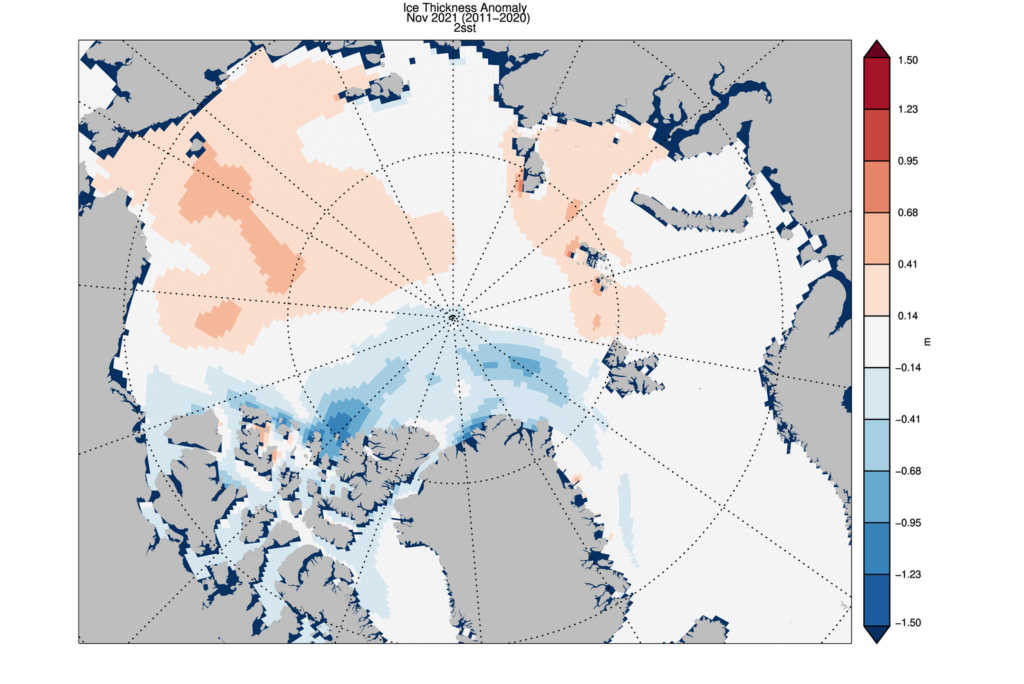
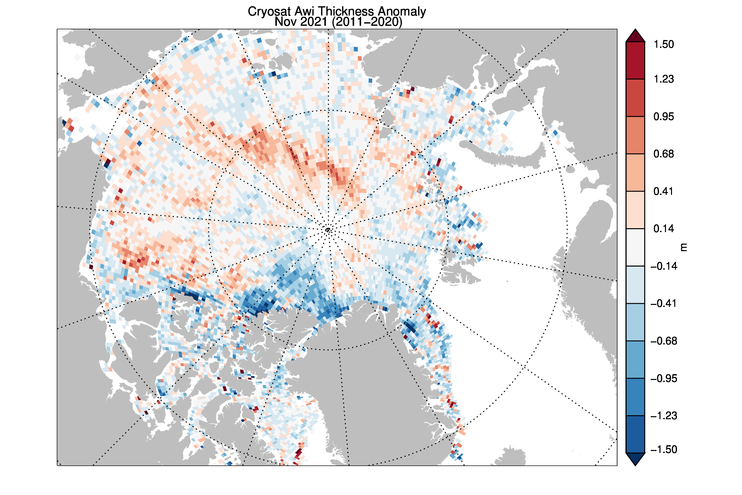
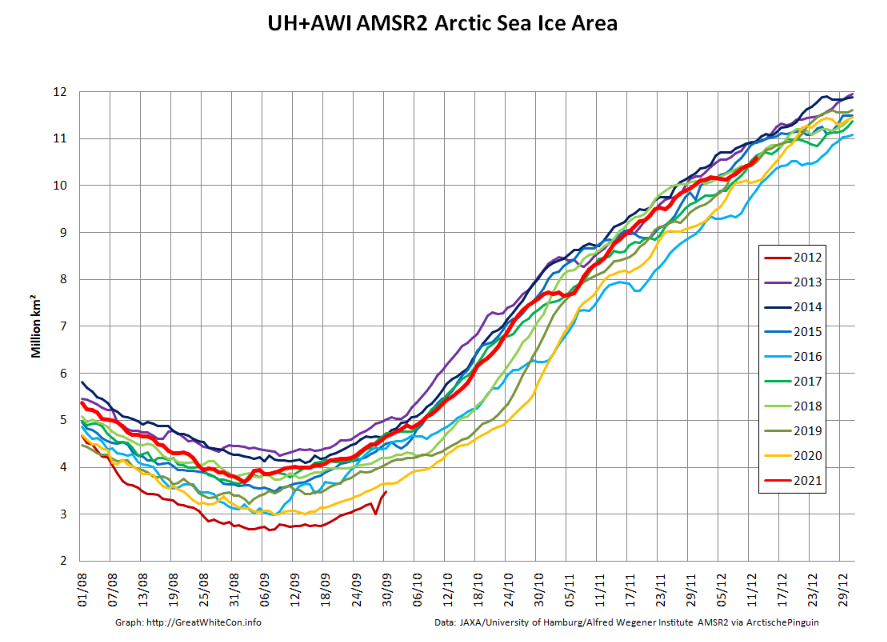
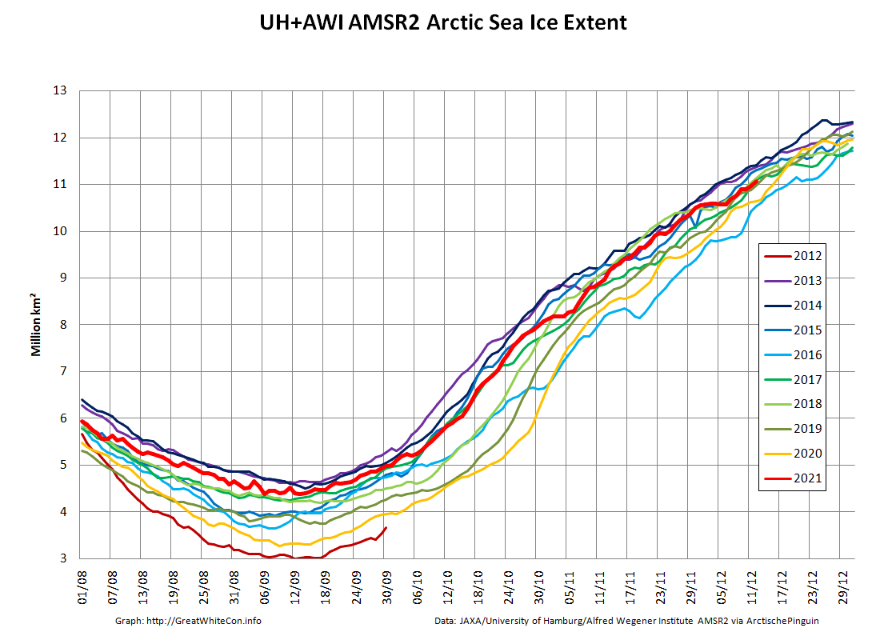
My apologies for the mixed metaphors in today’s title, but the news I bear is beyond bizarre.
In a press release earlier today The Global Warming Policy Foundation proudly announced that:
A new paper by an eminent meteorologist says that trends in polar sea-ice levels give little cause for alarm. The paper, by Professor J. Ray Bates has just been published by the Global Warming Policy Foundation.
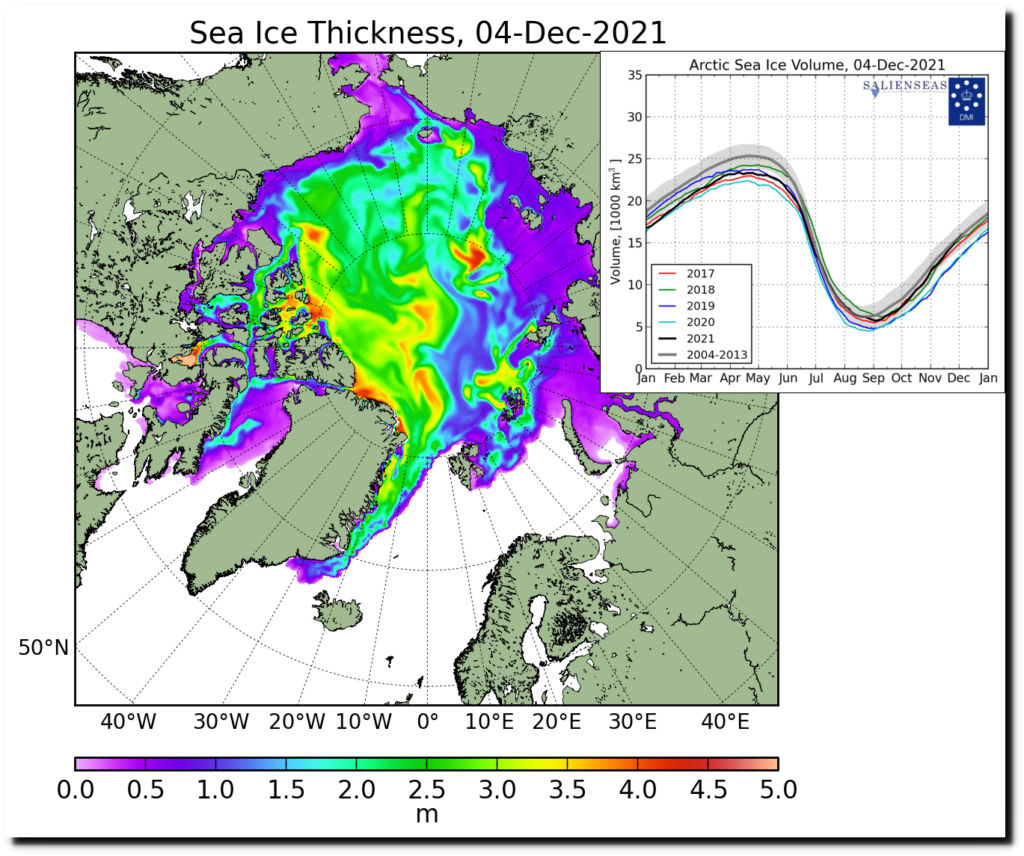
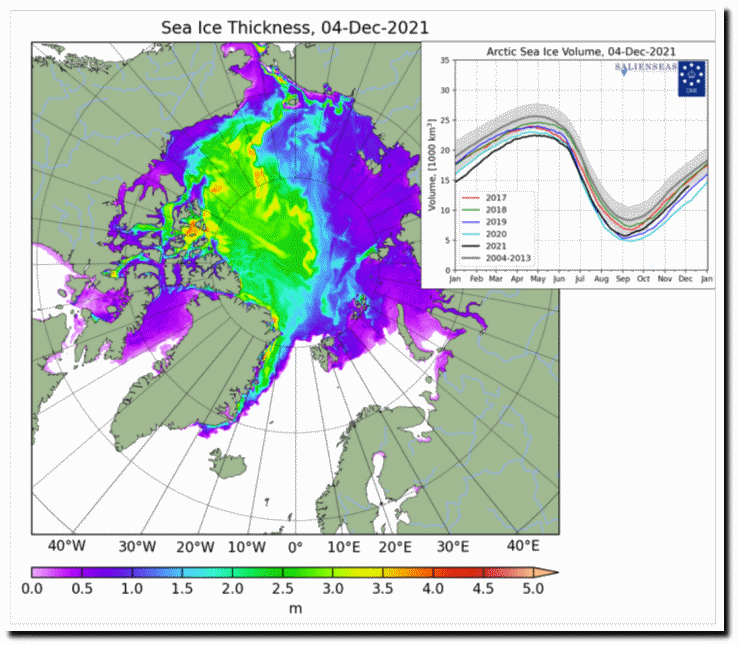
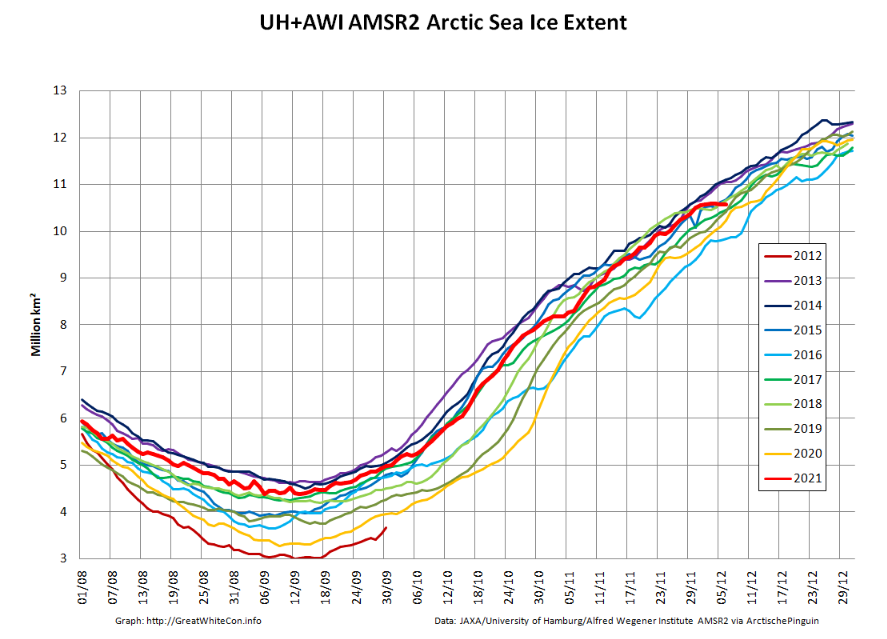
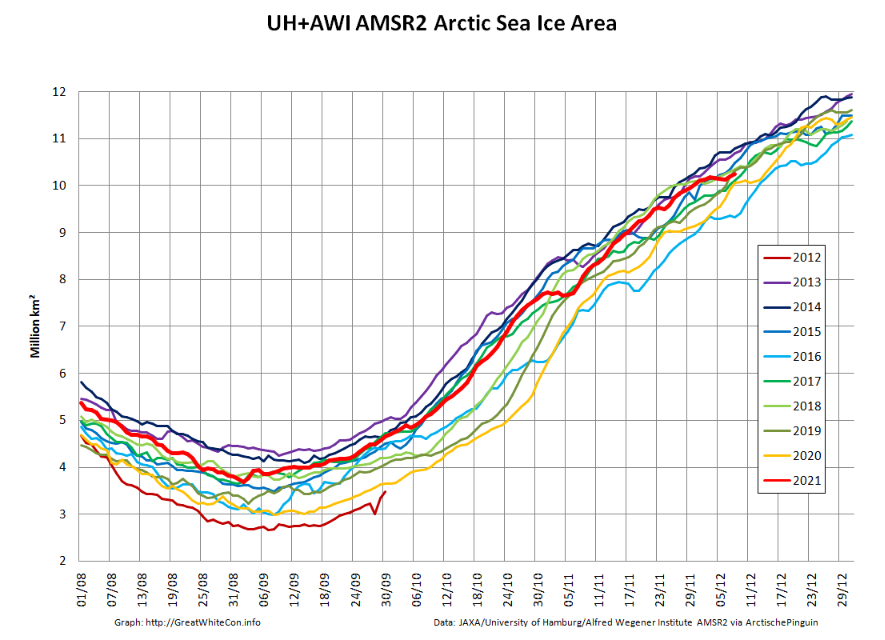
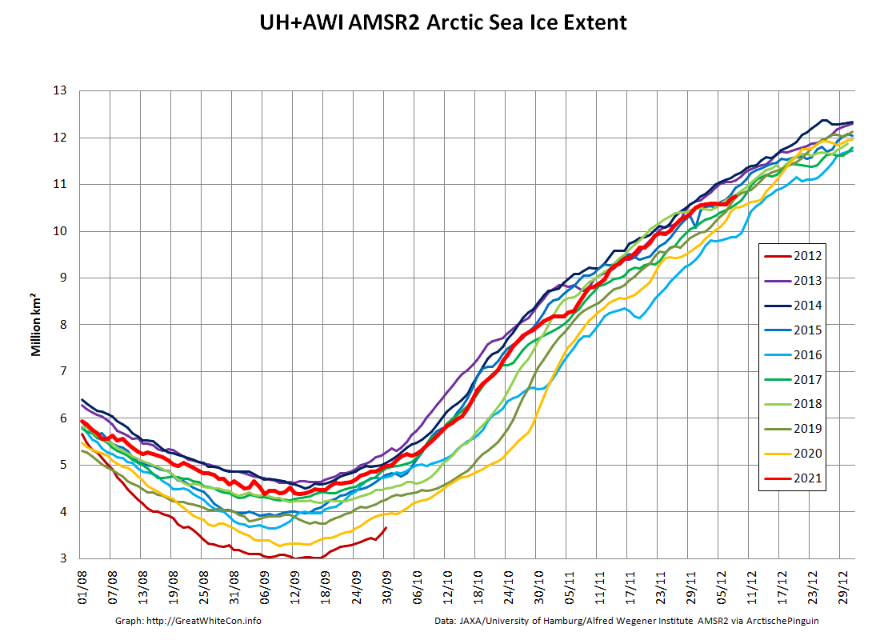
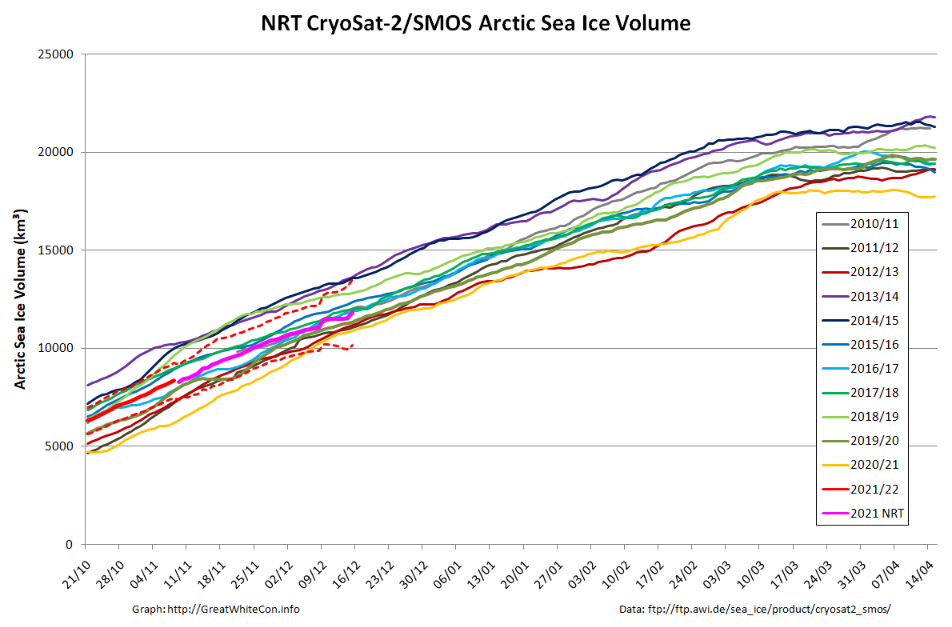
According to Professor Bates, climate model simulations indicate significantly decreasing sea ice levels in both hemispheres, with the greatest decreases occurring in September each year. However, the observed September trend in the Antarctic is actually slightly upwards, and while observed levels in the Arctic have fallen over the last 40 years, they have been quite stable since around 2007.
Professor Bates said:
“In 2007, Al Gore told us that Arctic sea ice levels were ‘falling off a cliff’. It’s clear now that he was completely wrong. In fact, the trends in sea-ice are an antidote to climate alarm.”
Professor Bates also says that little reliance should be placed on model simulations of future sea-ice decline:
“Climate models failed to predict the growth in Antarctic sea ice, and they missed the recent marked slowdown of sea-ice decline in the Arctic. It would be unwarranted to think they are going to get things right over the next 30 years.”
Professor Bates’ paper is published today, and can be downloaded here (pdf).
By all means download Ray’s “paper” from the link above and take a look at his introduction, which begins as follows:
The recent publication of the book Unsettled by Steven Koonin has led to the likelihood of increased scrutiny of the perception of a climate emergency,1 an idea which has become so widely established in recent years. Koonin, a former scientific advisor to the Obama administration, has demonstrated that what the public are being told by the media is not necessarily what the scientists are saying. He has also shown that what is being relayed in the national and UN climate assessments has often been written for the purpose of persuading rather than informing.
Unsettled clearly shows that important aspects of climate science, which the public have been persuaded to regard as beyond dispute are, in fact, quite unsettled.
Regular readers may recall that as soon as Steve’s book was published in machine readable format we established that it made no mention whatsoever of sea ice, whether of the Arctic or Antarctic variety.
Furthermore, when I attempted to debate that fact with Prof. Koonin he disappeared without trace before justifying that strange omission, beyond asserting that:
The topic is somewhat distant from ordinary folks’ perception.
It seems that Prof. Bates and the GWPF disagree with Prof. Koonin on this topic, since presumably their “paper” is addressed to ordinary folks? Ray even explicitly states that:
Although Unsettled covers a broad spectrum of climate topics, it does not treat in depth the issue of recent polar sea-ice trends, which are key indicators of changes in the global climate.
His “paper” goes on to assert in section 2 that:
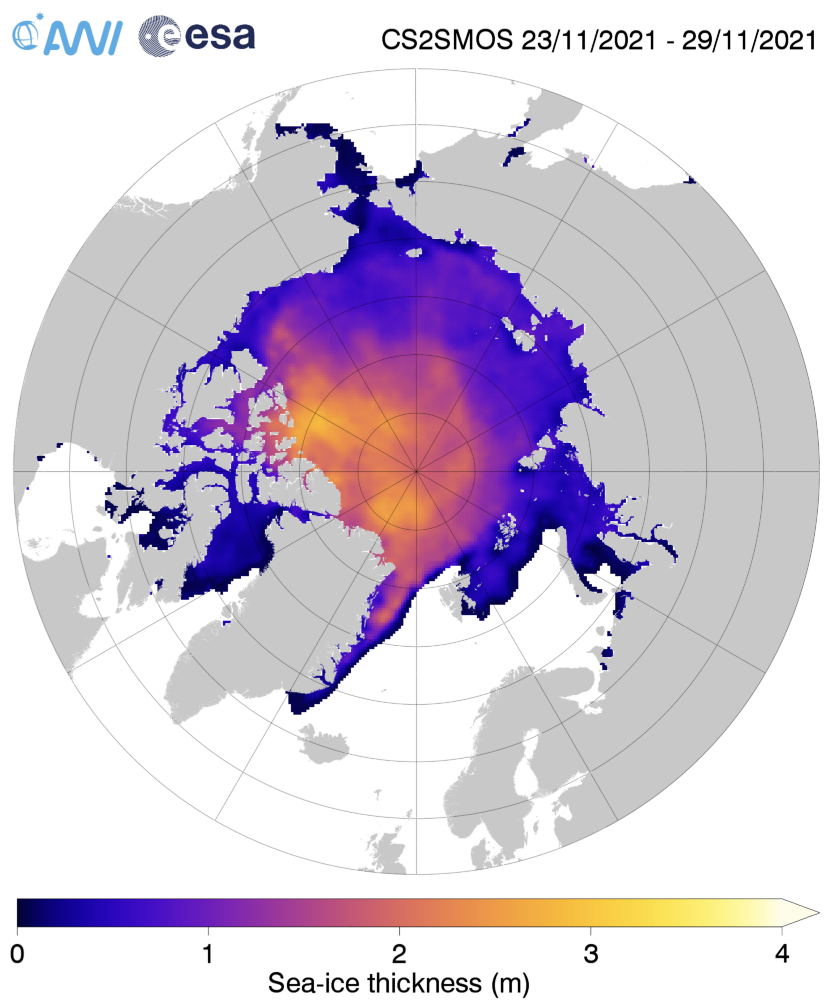
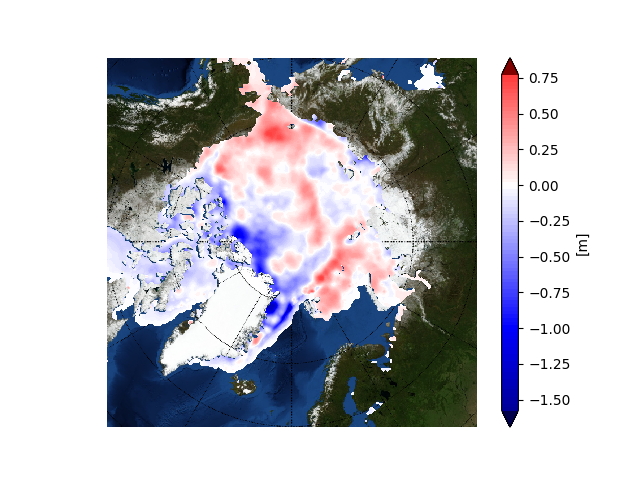
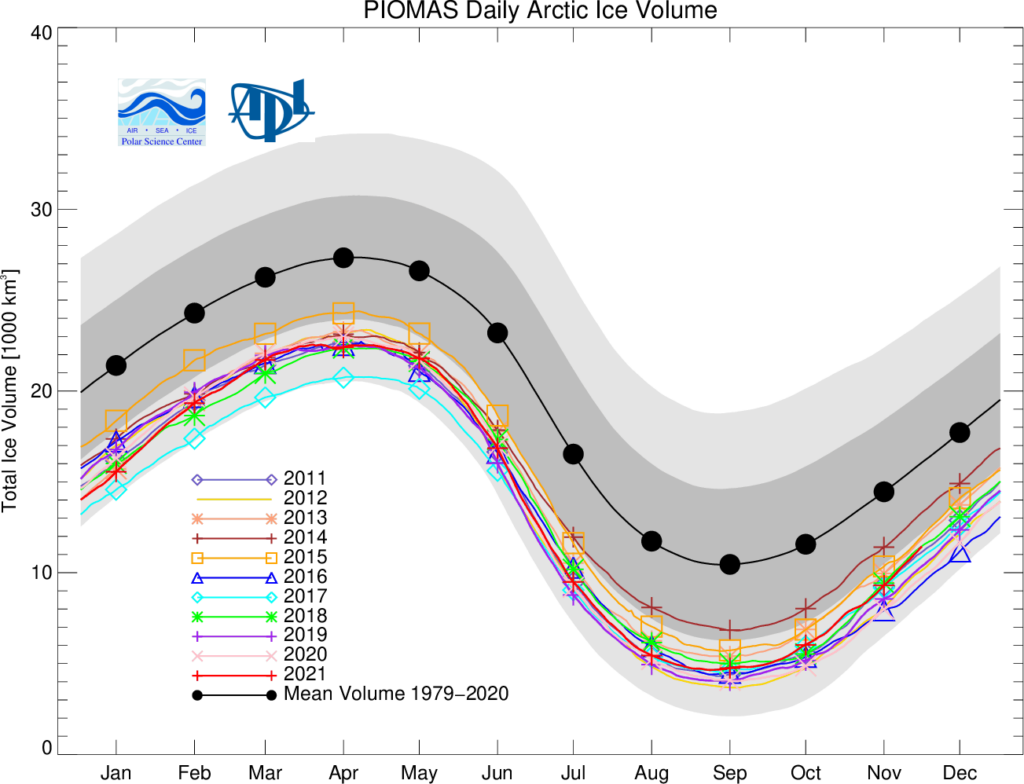
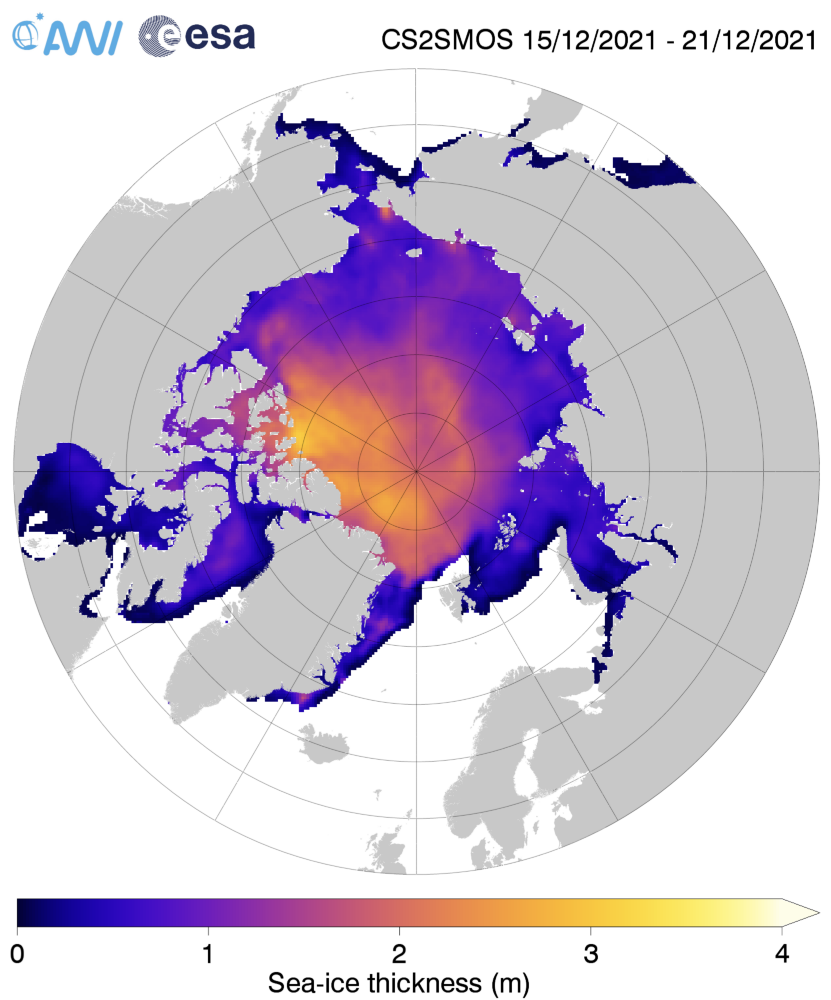
Since the introduction of passive-microwave satellite observations in the late 1970s, polar sea-ice extent has been among the most accurately observed climate indicators. Sea-ice volume, on the other hand, is much more difficult to measure.
So far so good I suppose, but then we are told:
In December 2007, former US vice-president Al Gore, in his Nobel Peace Prize acceptance speech in Oslo, referred to scientific studies warning that the Arctic sea ice was ‘falling off a cliff’. He highlighted forthcoming model results that projected largely ice-free Arctic summers in ‘as little as seven years’. He repeated this warning two years later at the 2009 COP15 climate meeting in Copenhagen.
Gore’s claim was based on a study by researchers from the US Naval Postgraduate School, who used a regional model of the sea ice–ocean system in the Arctic, constrained using observational data for the 12-year period 1996–2007, and concluded that the Arctic would be nearly ice-free in summer by 2016 (plus or minus three years).
Prof. Bates seems blithely unaware that we thoroughly debunked this nonsense many moons ago. What Prof. Wieslaw Maslowski, one of those pesky “researchers from the US Naval Postgraduate School”, actually said in December 2007 was:
If we project this trend ongoing for the last 10–15 years, we probably will reach zero in summer some time mid next decade.
At the risk of repeating myself it seems I must once again:
Reiterate for the benefit of those who seem unable to understand either English or Mathematics that a “projection” is not the same thing as a “prediction”.
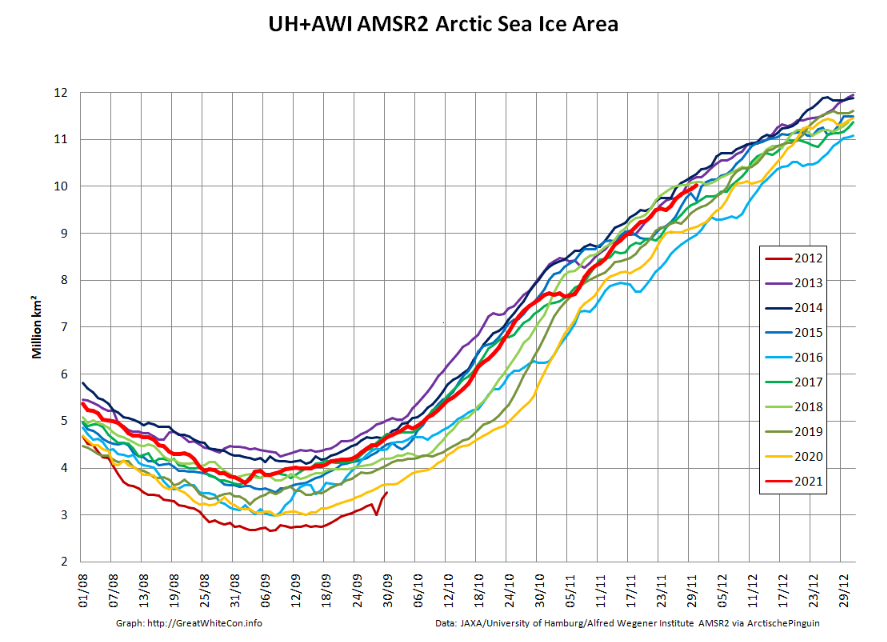
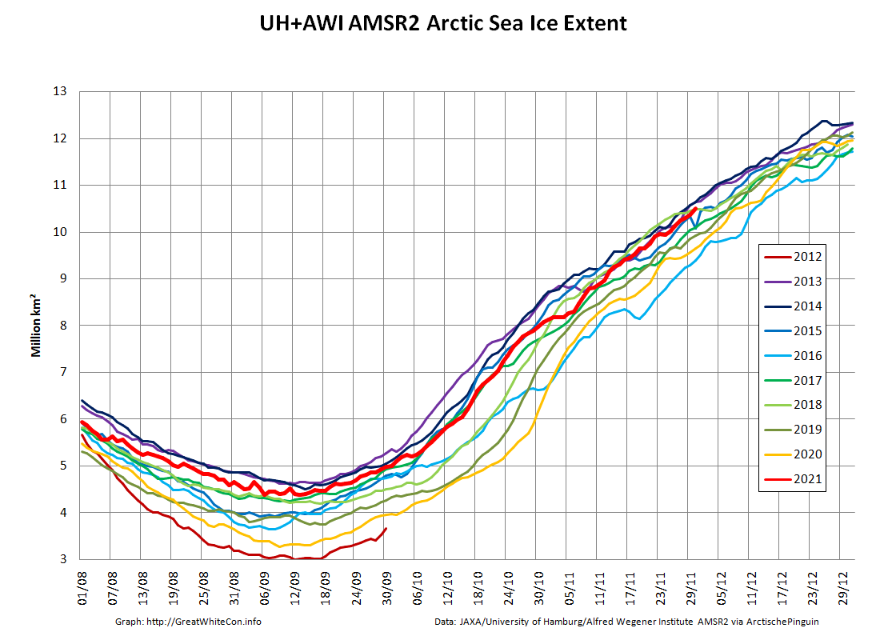
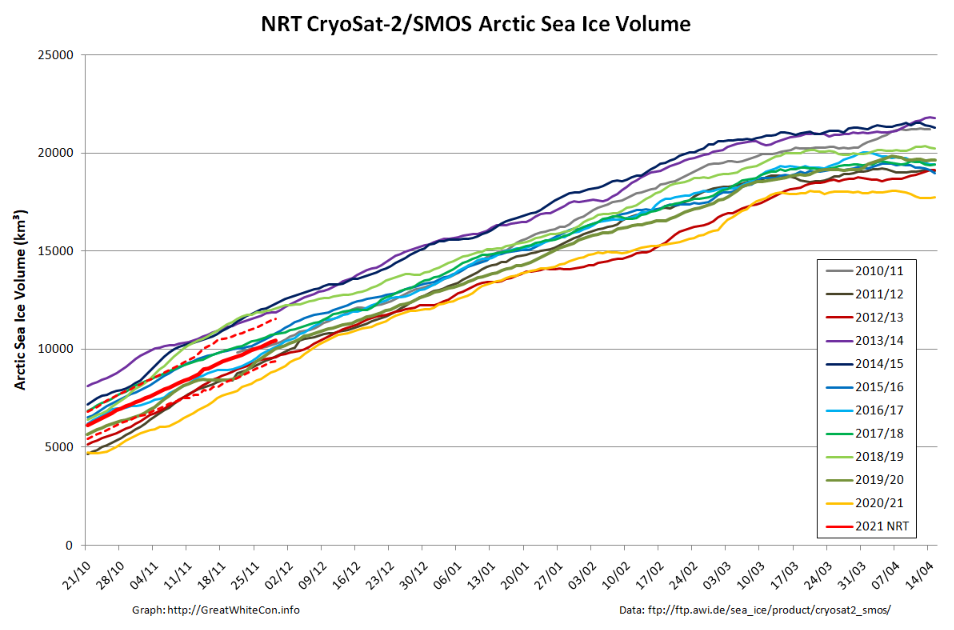
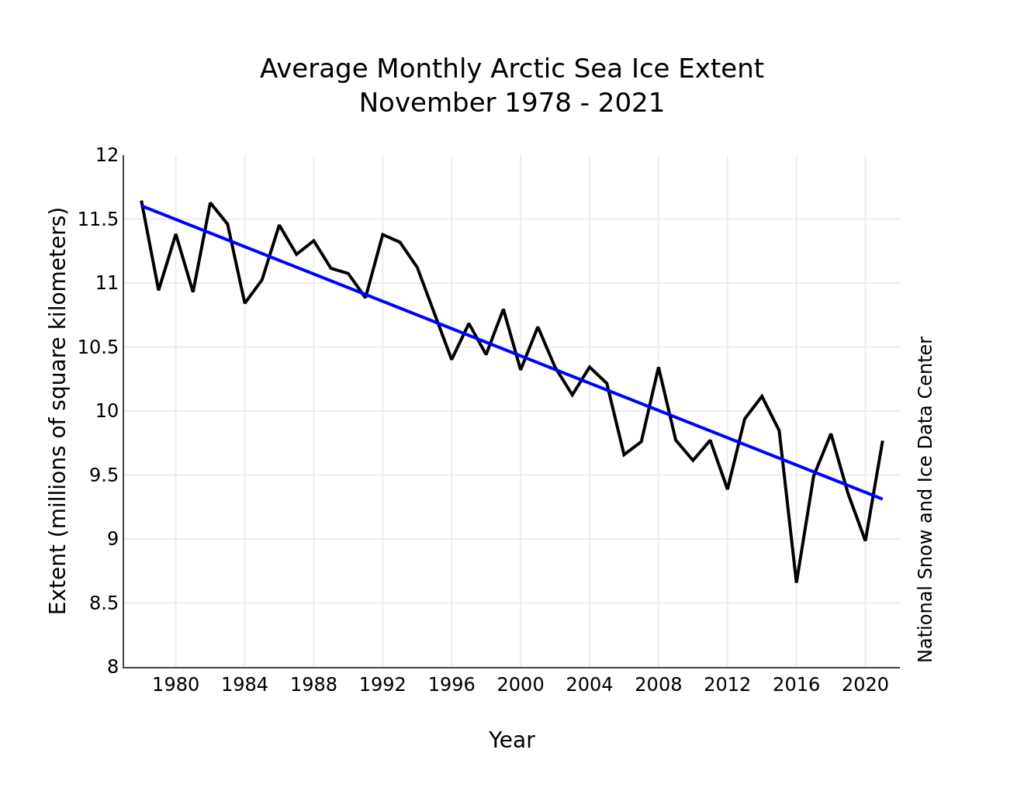
Ray then goes on to quibble with the NSIDC’s graph of September average Arctic sea ice extent:
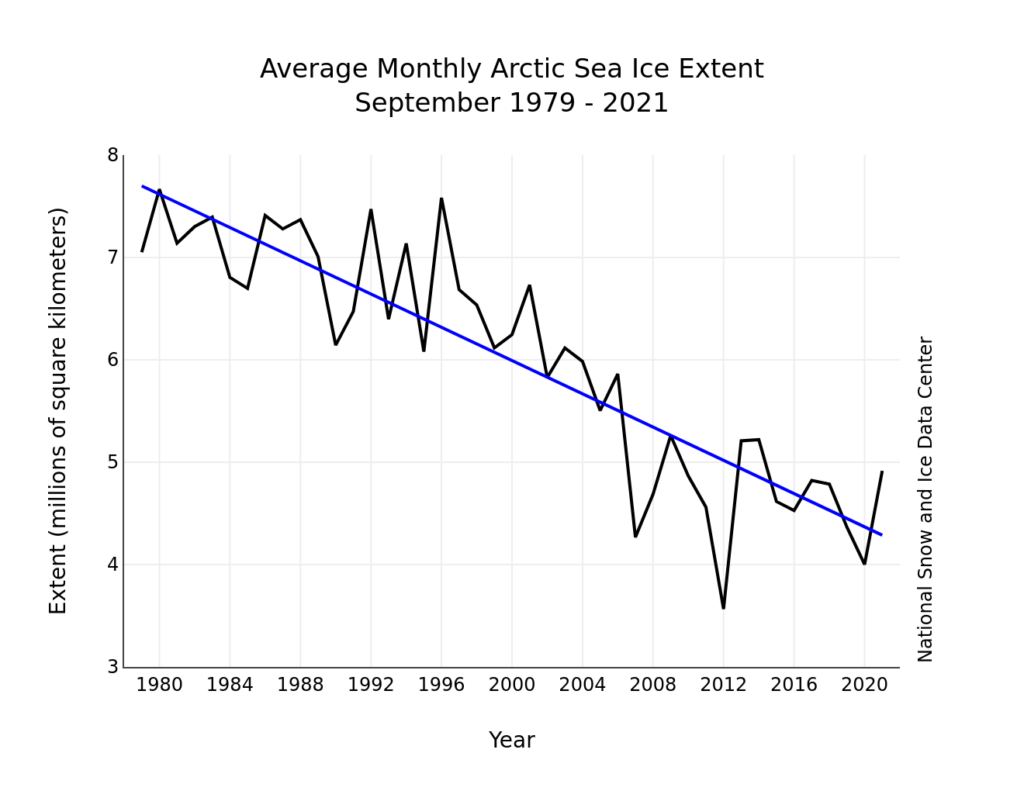
preferring instead a version of his own construction, which looks like this:
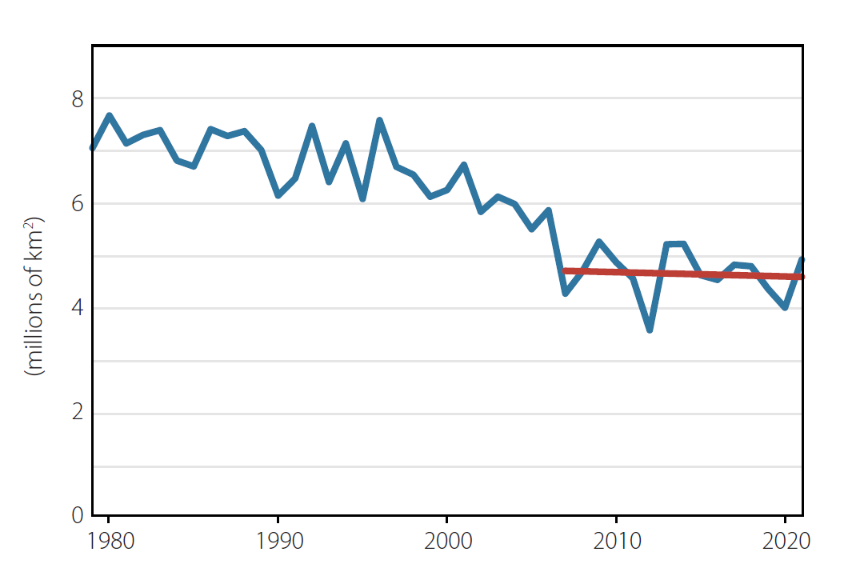
Ray then confidently asserts that:
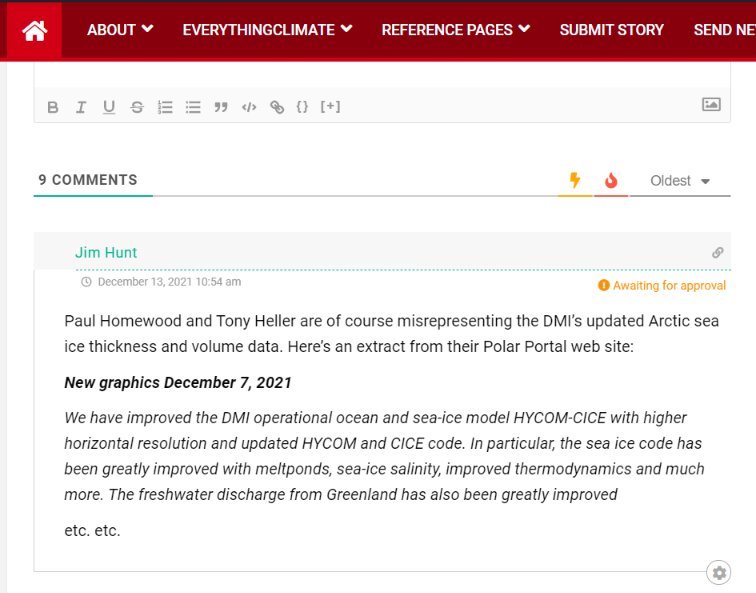
The current slowdown in the rate of sea-ice loss was not expected, and the reasons for it are uncertain.
Sadly Ray’s exhaustive list of references fails to mention this learned journal article from 2011 by authors from the University of Washington and Los Alamos National Laboratory, which not only anticipated such a “slow transition” but also offered reasons for it:
Given the strong thickness–growth feedback of sea ice (Bitz and Roe 2004), where in a warming climate we can expect the thicker MY ice to thin at a greater rate than the thinner FY ice, and the fact that the ratio of MY to FY ice entering into the MY ice category each year is decreasing, it is likely that the difference between FY and MY ice survival ratios will decrease in a warming climate. If this occurs, the Arctic sea ice system would move toward a regime of decreased memory and decreased sensitivity to climate forcing…
There is of course plenty more GWPF sea ice nonsense where that lot came from, but it’s already past my tea time (UTC) and so further debunking will have to wait a while. In the meantime here’s a wake up call for Professor J. Ray Bates:

Moving further down section 2 Ray assures us that:
Any objective discussion of the recent Arctic sea-ice decline also requires that some consideration be given to the evidence regarding past natural variability on a multi-decadal timescale. In the pre-satellite era, reliable data on sea-ice coverage was sparse.
So far so good again? Not really! Ray’s gets on to his go to reference, Connolly, Connolly and Soon (2017):
By combining the temperature and partial sea-ice records, statistical reconstructions of the total sea-ice extent going back to the early 1900s can be created. Some of these reconstructions indicate that between the 1900s and 1940s, Arctic sea-ice extent comparable to the present reduced levels may have occurred.
Ray doesn’t sound very certain, which is perhaps because the paper in question blithely states that:
Because Arctic sea ice trends are closely correlated to Arctic temperature trends, they are often discussed in the context of global temperature trends.
Maybe so, but to the best of my recollection Connolly et al. never attempt to “prove” the asserted correlation. Here’s an alternative assessment of “Arctic sea-ice extent between the 1900s and 1940s“:
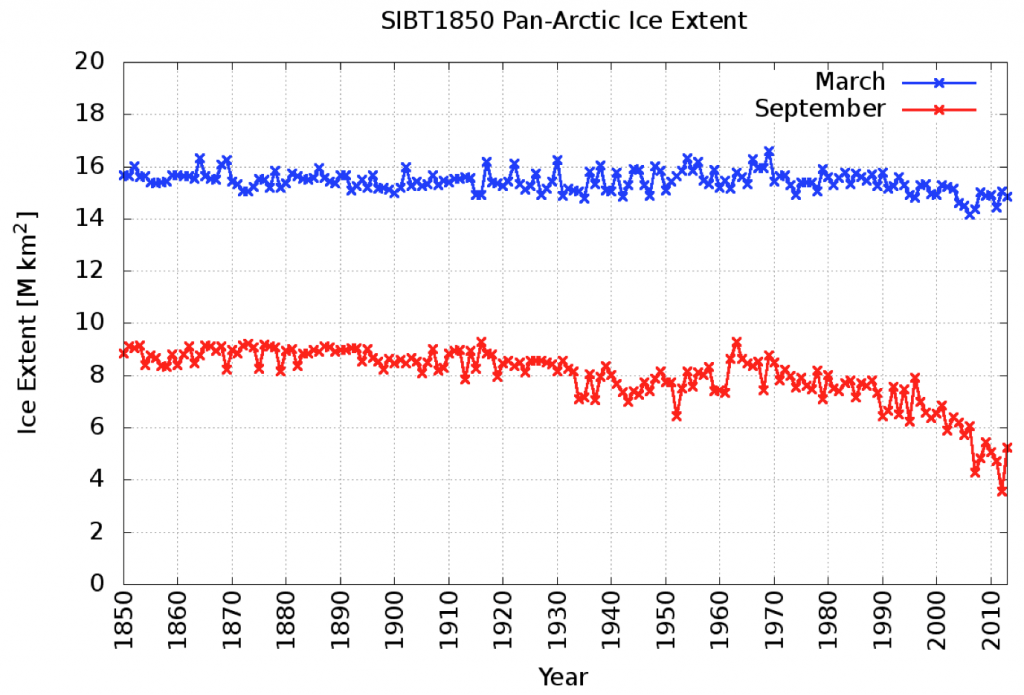
Watch this space!