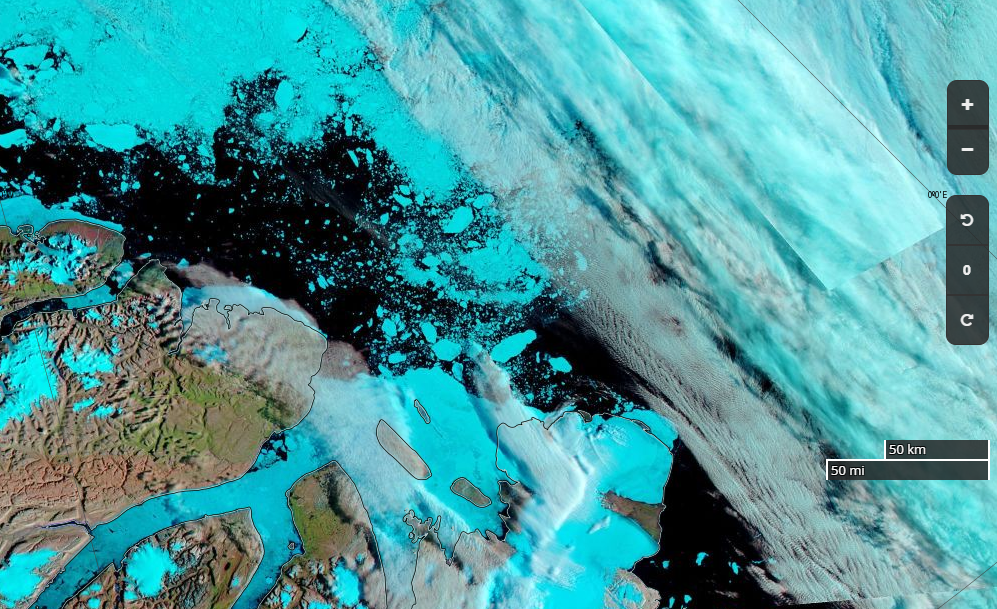
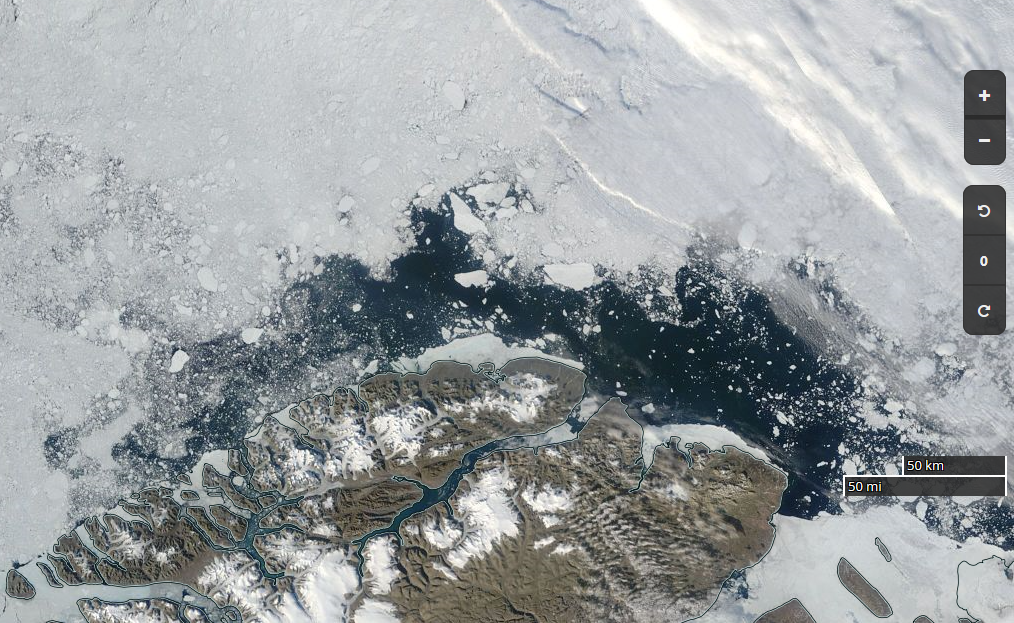
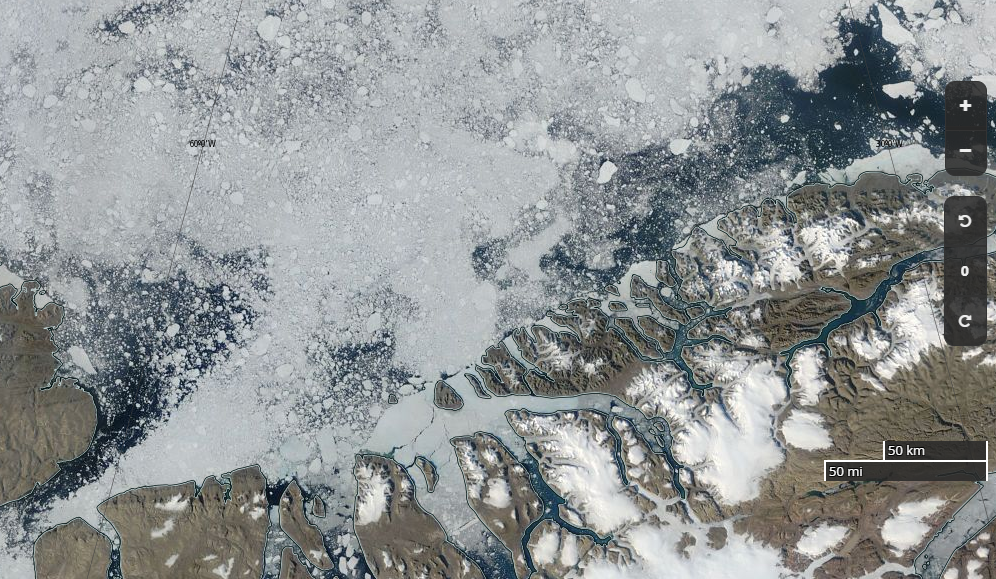
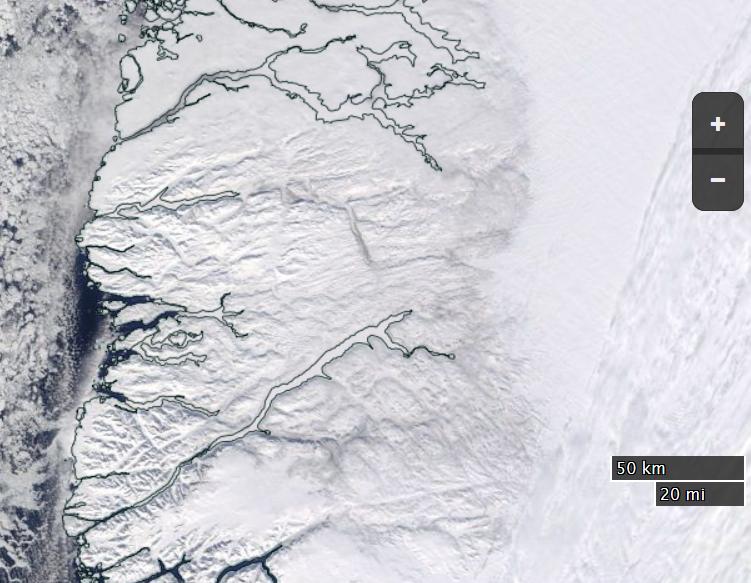
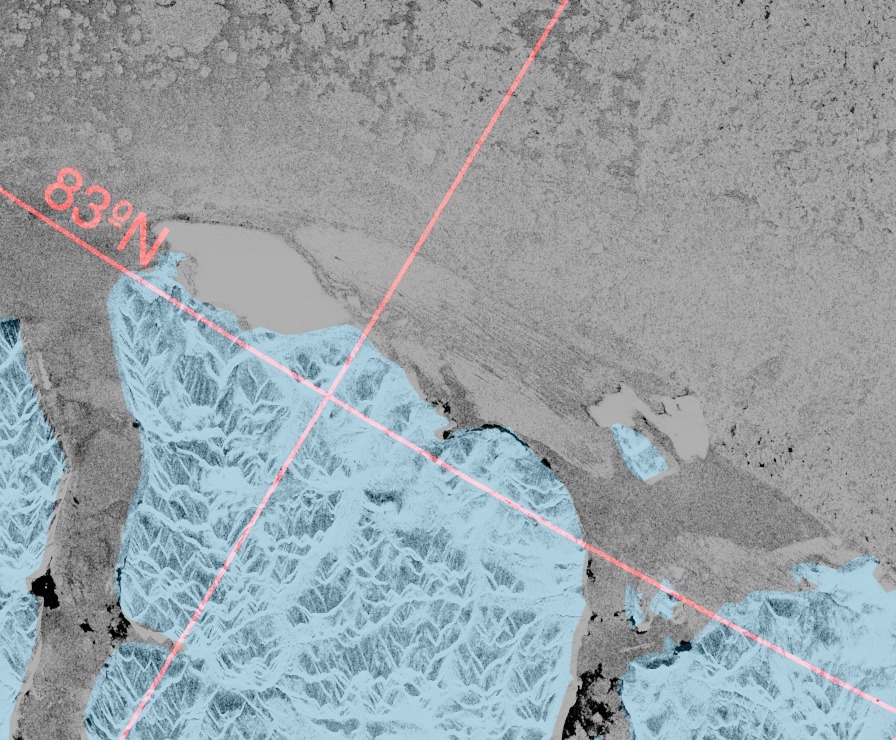
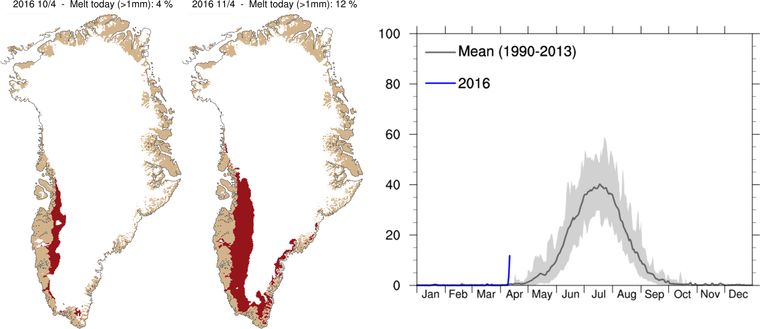
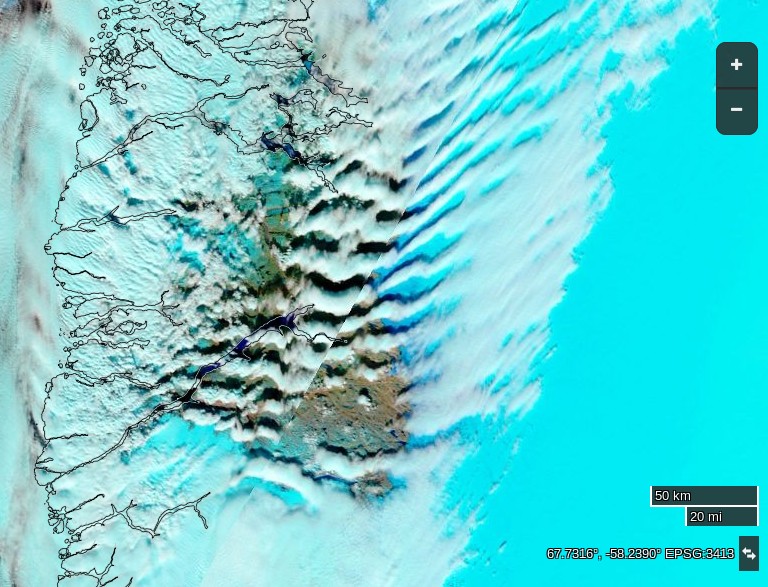
For our latest review of Steven E. Koonin’s new book, “Unsettled”, we’re moving from the ice covering the Arctic seas on to land. Greenland to be specific. Unlike Arctic sea ice the Greenland Ice Sheet does merit a mention in the book. In fact it’s one of the bullet points Steve leads with on page 2:
Here are three more [climate facts] that might surprise you, drawn directly from recent published research or the latest assessments of climate science published by the US government and the UN:
- Humans have had no detectable impact on hurricanes over the past century.
- Greenland’s ice sheet isn’t shrinking any more rapidly today than it was eighty years ago.
- The net economic impact of human-induced climate change will be minimal through at least the end of this century.
So what gives?
A very good question Steve, because if we stick with the Arctic land ice referred to in the middle bullet, Professor Koonin makes no reference at this juncture to any “recent published research or latest assessment of climate science” to justify his assertion.
Which is a bit of a shame since in the Climate Feedback critique of Professor Koonin’s statement which was mentioned in our introductory article, Twila Moon from the United States’ National Snow and Ice Data Center points out that:
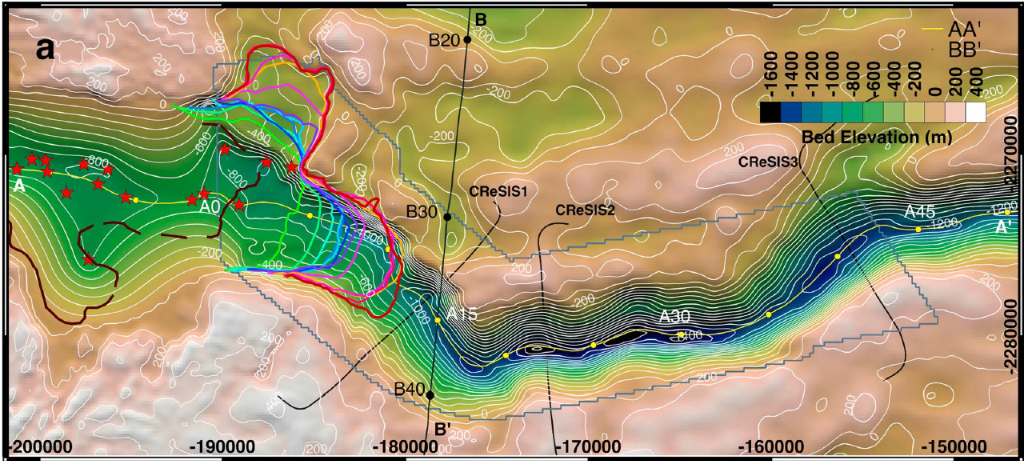
This statement is untrue. In fact, the Greenland Ice Sheet lost more mass during 2003-2010 than during all of 1900-2003 combined. This is evident in the following figure from Kjeldsen et al. (2015)
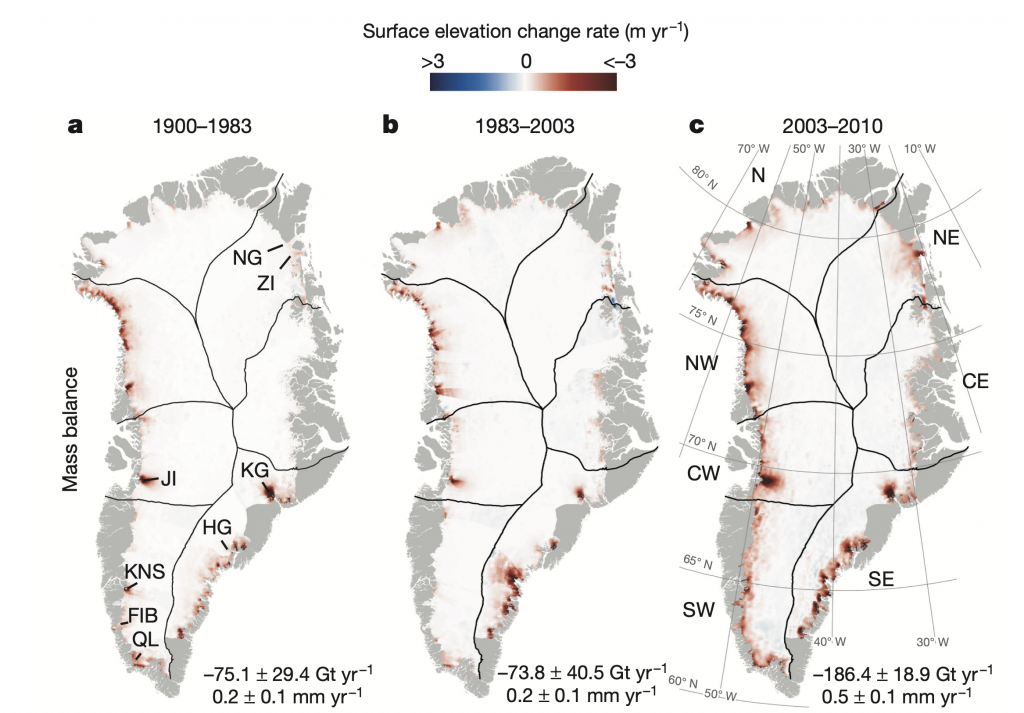
If we look in more detail at changes over 1972-2018, we can further see that the ice sheet was mostly in balance (gain about the same amount of snow/ice in winter as is lost in summer) during the 1970s and 1980s [Mouginot and Rignot et al. (2019)]. It was only in the mid-1990s that Greenland ice loss began to increase more substantially.
Over the last 20 years, ice loss has been rapid and large, creating measurable sea level rise, which we experience as increases in coastal erosion, flooding, problems with water and sewer systems at the coasts, and saltwater inundation of freshwater sources.
So how is it possible for Steve Koonin to have got his facts so wrong? For his attempt at justification we have to wait until chapter 8 of “Unsettled” on the subject of “Sea Level Scares”. On page 160 of my Kindle edition Steve writes:
So future global sea level rise is uncertain not only because of all of the model uncertainties in the global temperature rise discussed in Chapter 4, but also because the dynamics of the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets are quite uncertain. The IPCC summarizes the situation (SMB is the Surface Mass Balance, measuring the net change in ice due to atmospheric processes): . . .
“For periods prior to 1970, significant discrepancies between climate models and observations arise from the inability of climate models to reproduce some observed regional changes in glacier and GIS [Greenland Ice Sheet] SMB around the southern tip of Greenland. It is not clear whether this bias in climate models is due to the internal variability of the climate system or deficiencies in climate models. For this reason, there is still medium confidence in the ability of climate models to simulate past and future changes in glaciers mass loss and Greenland SMB.”
The reference for this quotation is given as “IPCC SROCC Section 4.2.2.2.6“, which on inspection is entitled “Budget of global mean sea level change”. The immediate question that springs to my mind is “Why didn’t Steve refer to SROCC Section 1.4.2?”. That section is entitled “Observed and Projected Changes in the Cryosphere”, and skipping over the Arctic sea ice section for the moment it states:
AR5 assessed that the annual mean loss from the Greenland ice sheet very likely substantially increased from 34 (-6–74) Gt yr–1 (billion tonnes yr–1) over the period 1992–2001, to 215 (157–274) Gt yr–1 over the period 2002–2011.
Or Steve might have quoted from Section 4.2.2.2.4 “Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets”, but for some reason he didn’t:
Frequent observations of ice sheet mass changes have only been available since the advent of space observations (see Section 3.3.1). In the pre-satellite era, mass balance was geodetically reconstructed only for the GIS (Kjeldsen et al., 2015)
op. cit., or as suggested there he could even have quoted from Section 3.3.1 “Ice Sheet Changes”, but once again he didn’t:
The GIS was close to balance in the early years of the 1990s (Hanna et al., 2013; Khan et al., 2015), the interior above 2000 m altitude gained mass from 1961 to 1990 (Colgan et al., 2015) and both coastal and ice sheet sites experienced an increasing precipitation trend from 1890 to 2012 and 1890 to 2000 respectively (Mernild et al., 2015), but since the early 1990s multiple observations and modelling studies show strong warming and an increase in runoff (very high confidence).
Personally I have very high confidence that Professor Koonin had great difficulty cherry picking a Greenland Ice Sheet quote from the IPCC that could be “spun” into supporting his case. Frankly his “southern tip of Greenland” effort smacks of desperation.
Unsettling, is it not?
Here’s a long thread on Twitter from Helen Fricker, explaining the genesis of the IPCC’s Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate. Essential reading for Steve Koonin, since he is apparently unaware of any of this!
Helen refers to her recent op-ed for The Hill which goes into slightly more detail:
The upcoming sixth IPCC report in 2022 will contain updated projections of future sea level rise based on tens of different simulations provided by research groups around the world. These groups all worked together in a community-led effort, involving ice sheet, ocean and atmosphere modeling and observational teams.
We have come a long way, but even after all this we are still playing “catch-up,” and there are still gaps in our understanding. We do know, however, that the ocean is warming and that both Antarctica and Greenland are vulnerable to this warming. The same goes for the atmosphere. We worry that the biggest portion of Antarctica, East Antarctica — which we still think of as a sleepy giant since it is so thick and vast, making it harder for warming ocean waters and increasing air temperatures to reach it — is starting to show signs of change. We also worry that there may be mechanisms, that we have not been able to witness in the modern record and hence that are not in the models, that may amplify the ice loss. Scientists are using paleo-reconstructions to figure out whether these may be important.
Still, we can say with confidence that sea level will continue to rise (faster) in the future and that our projections are conservative estimates. Indeed, satellite observations that measure the changing height (altimetry) and changing mass (gravimetry) of ice sheets are tracking the worst-case predictions from IPCC’s fifth report.
As we gather more data, both on and around the ice sheets using all available tools, including satellites, our observational record gets longer and our understanding improves. As our understanding improves, our models get better. Long-term measurements, sometimes acquired by launching new satellites (such as NASA’s ICESat-2 and other follow-on missions), coordinated modeling and international collaboration are key to delivering more accurate predictions, so that coastal communities can make informed decisions to protect infrastructure and citizens and manage resources.