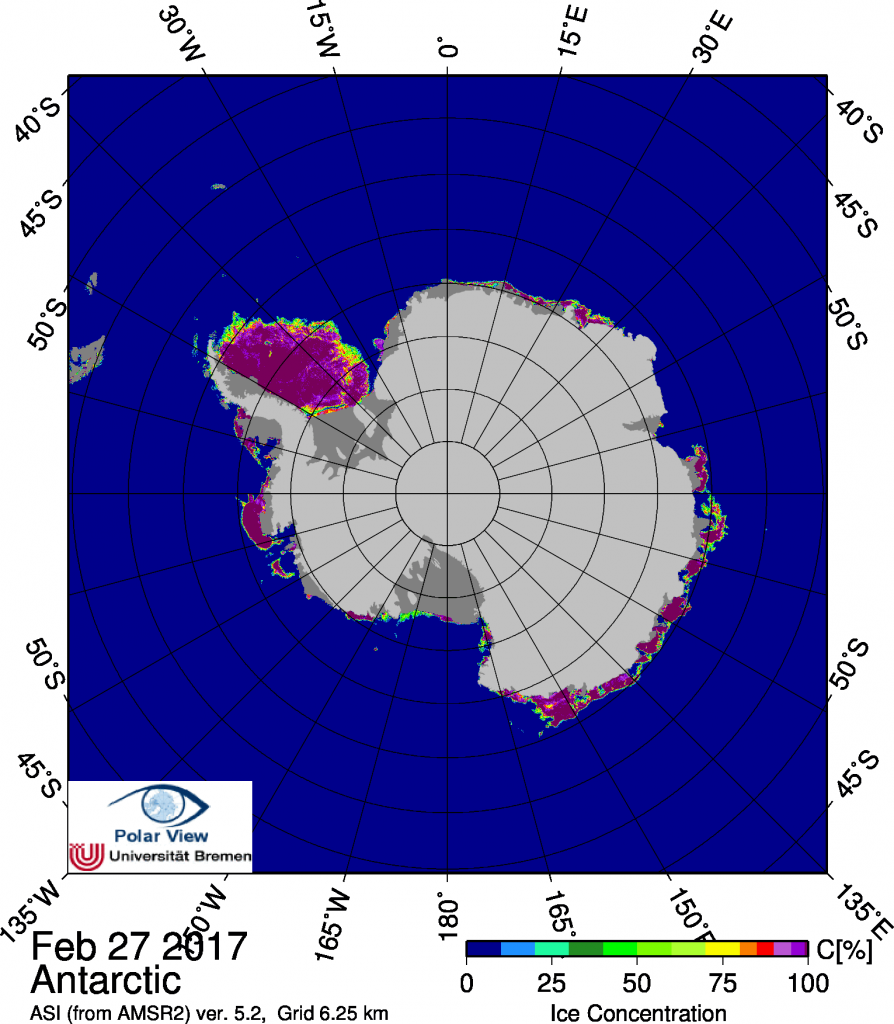
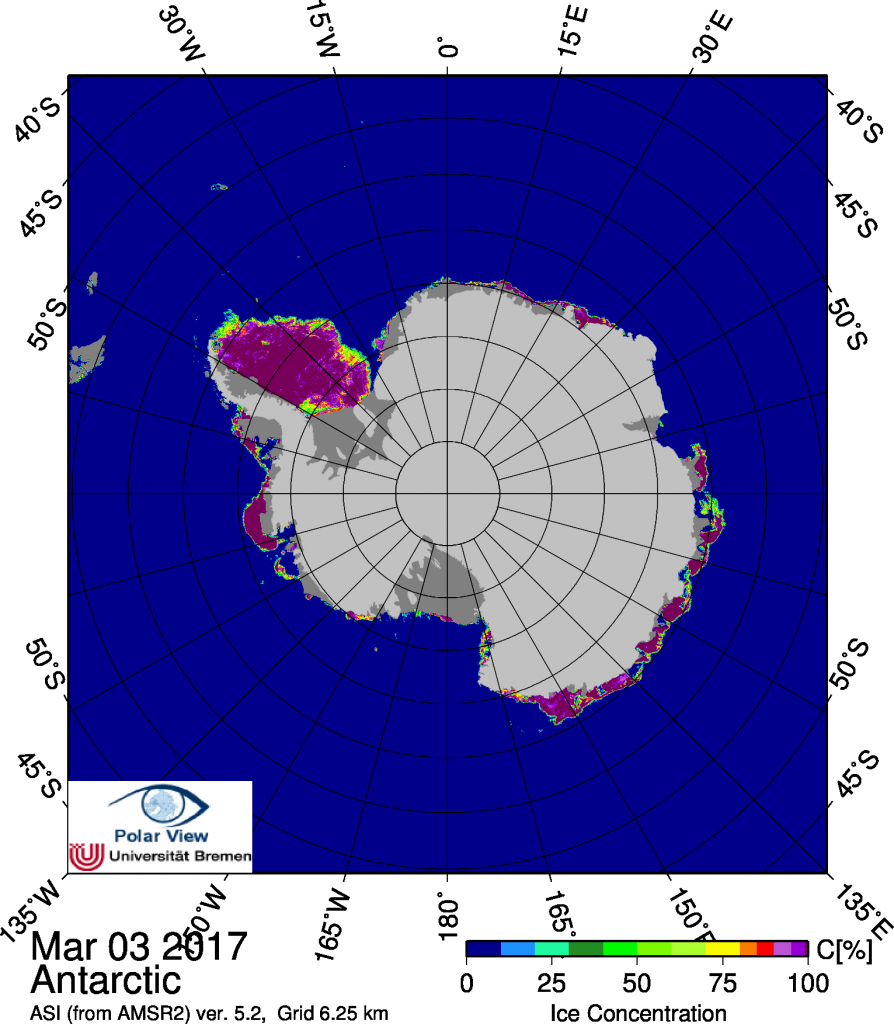
I should of course add “in the satellite era”, but the title is pretty unwieldy as it is!
I was up early (UTC) to check the latest JAXA data, and sure enough that confirmed a new record minimum Antarctic sea ice extent of 2.11 million km² was reached yesterday:
Having added a note to that effect the Arctic open thread, Lars Kaleschke from the Alfred Wegener Institute pointed out over on Mastodon that the AWI had published a press release about the event this morning:
Let’s take a closer look at what the AWI had to say:
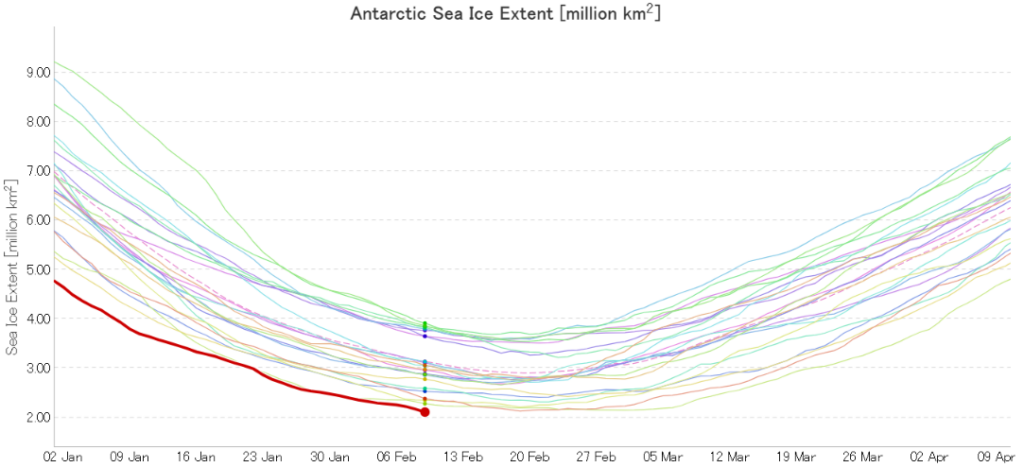
On 8 February 2023, at 2.20 million square kilometres, the Antarctic sea ice extent had already dropped below the previous record minimum from 2022 (2.27 million square kilometres on 24 February 2022). Since the sea ice melting in the Antarctic will most likely continue in the second half of the month, we can’t say yet when the record low will be reached or how much more sea ice will melt between now and then,” says Prof Christian Haas, Head of the Sea Ice Physics Section at the Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research (AWI), with regard to the current developments in the Antarctic. “The rapid decline in sea ice over the past six years is quite remarkable, since the ice cover hardly changed at all in the thirty-five years before. It is still unclear whether what we are seeing is the beginning of a rapid end to summer sea ice in the Antarctic, or if it is merely the beginning of a new phase characterised by low but still stable sea ice cover in the summer.”
Here’s how that news looks in the AWI’s official press release:
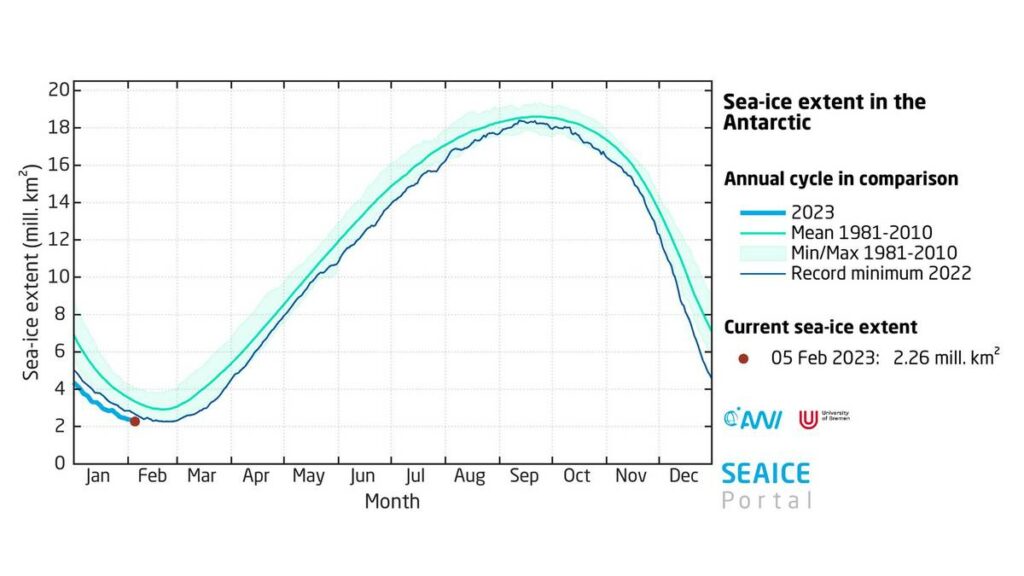
and here’s how it looks in Lars’ experimental AMSR2 graphic, with current minimum at 1.97 million km²:
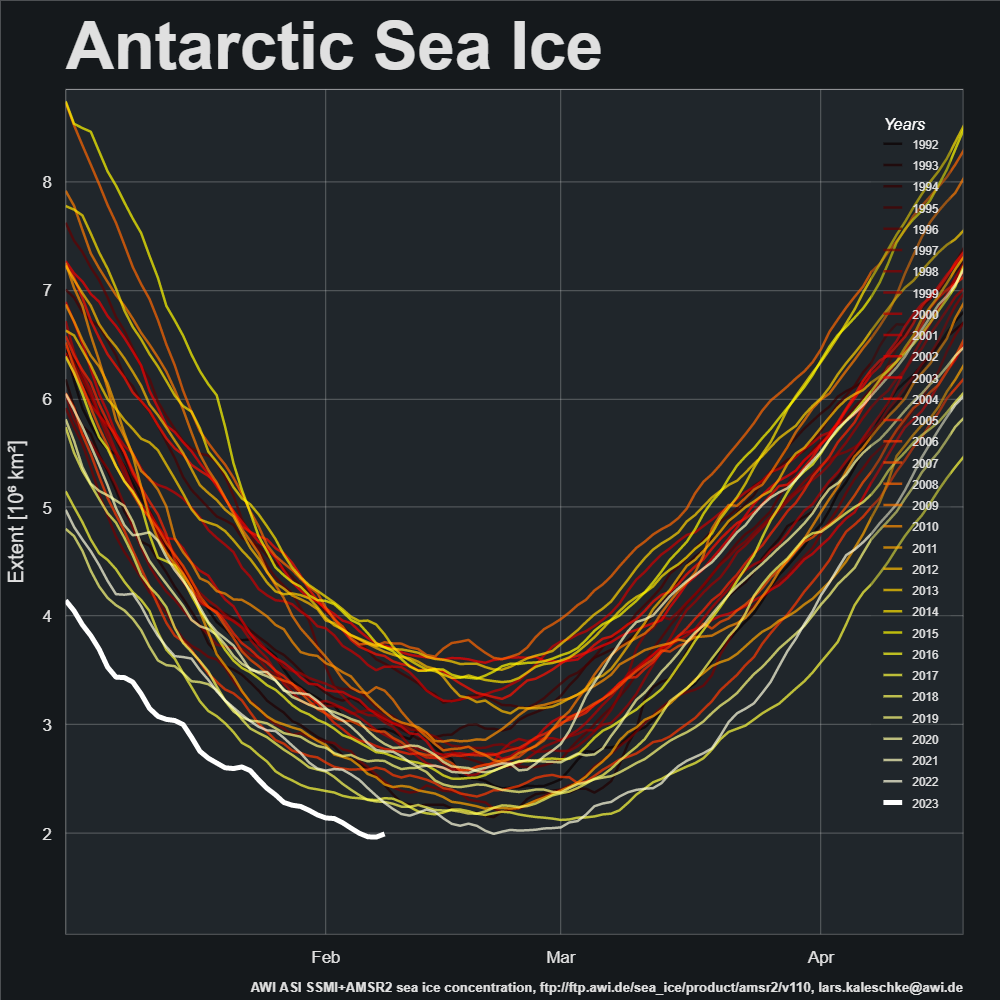
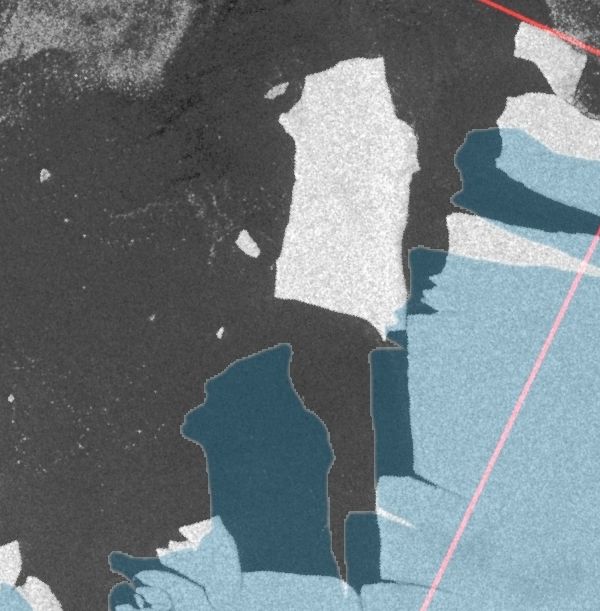
By way of prognostication here too is the current JAXA AMSR2 concentration map:
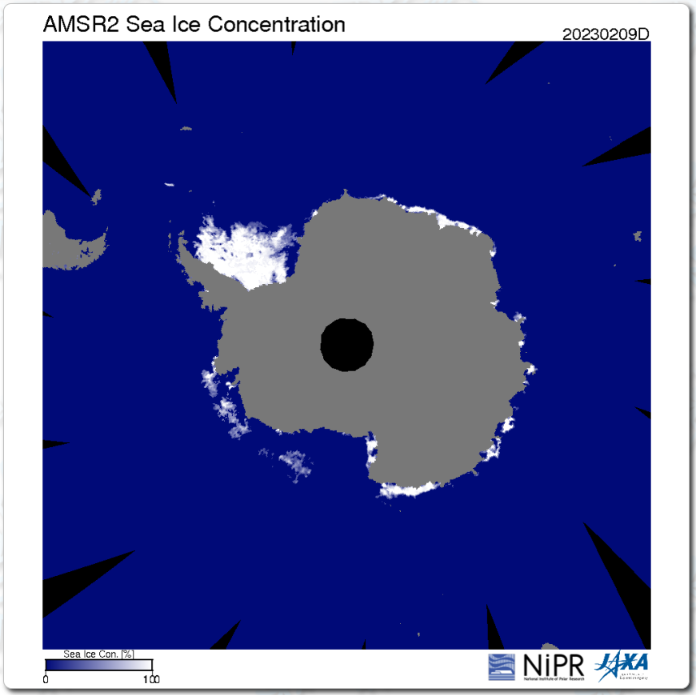
There are some low concentration areas which suggest further extent reductions still to come, despite the recent uptick in the high resolution graph.
Getting back to the AWI’s text:
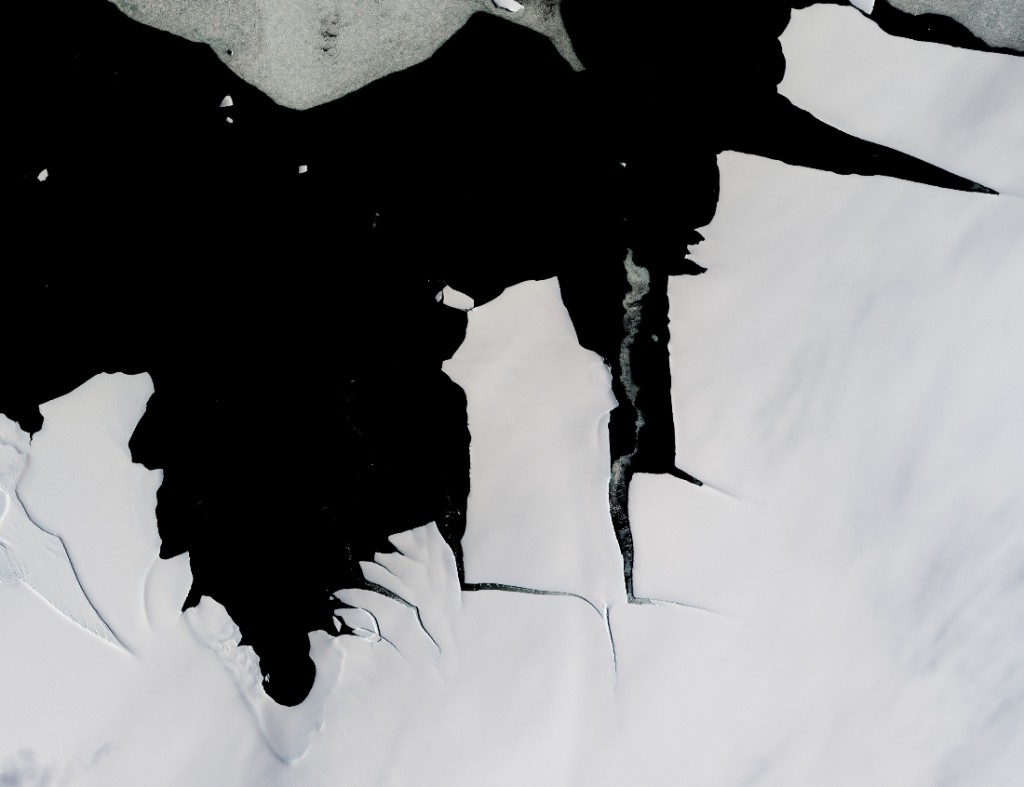
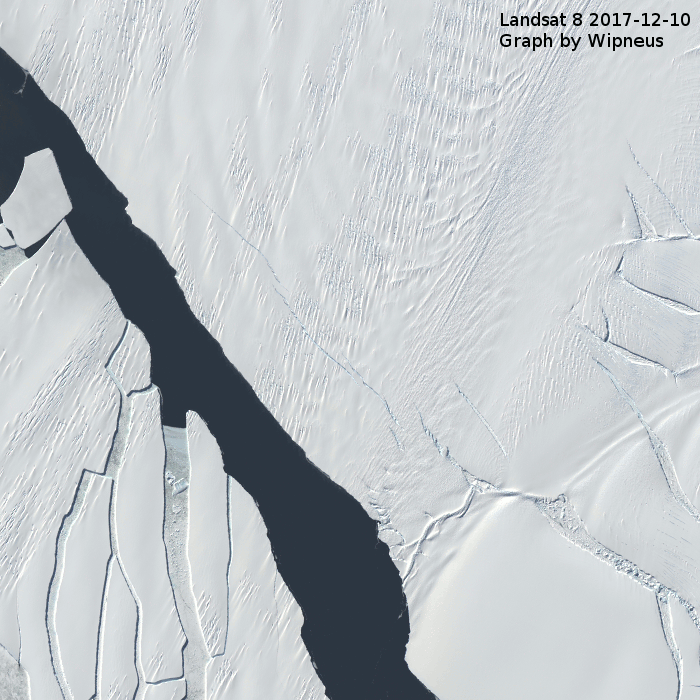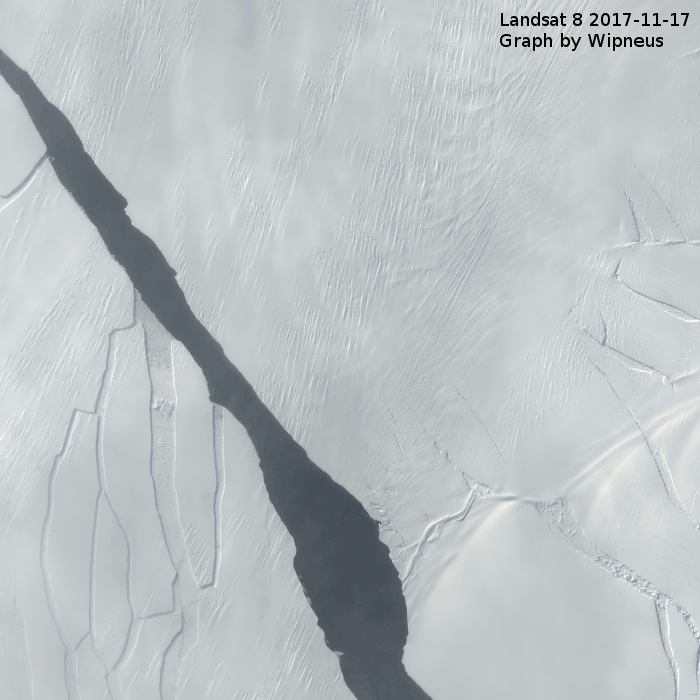
The melting has progressed since December 2022, especially in the Bellingshausen and Amundsen Seas in the West Antarctic; the former is virtually ice-free. That is also where the research vessel Polarstern currently is, exploring the evidence left behind of past glacials and interglacials. According to expedition leader and AWI geophysicist Prof Karsten Gohl, who is now in the region for the seventh time, having first come in 1994: “I have never seen such an extreme, ice-free situation here before. The continental shelf, an area the size of Germany, is now completely ice-free. Though these conditions are advantageous for our vessel-based fieldwork, it is still troubling to consider how quickly this change has taken place.”

Analyses of the current sea ice extent, conducted by the Sea Ice Portal team, show that, for the entire month of January 2023, the ice was at its lowest-ever extent recorded for the time of year since the beginning of record-keeping in 1979. The monthly mean value was 3.22 million square kilometres, ca. 478,000 square kilometres (an area roughly the size of Sweden) below the previous minimum from 2017. With regard to its long-term development, the Antarctic sea ice shows a declining trend of 2.6 percent per decade. This is the eighth consecutive year in which the mean sea-ice extent in January has been below the long-term trend.
But what has caused the current lack of Antipodean sea ice? The press release continues:
This intense melting could be due to unusually high air temperatures to the west and east of the Antarctic Peninsula, which were ca. 1.5 °C above the long-term average. In addition, the Southern Annular Mode (SAM) is in a strongly positive phase, which influences the prevailing wind circulation in the Antarctic. In a positive SAM phase (like today), a low-pressure anomaly forms over the Antarctic, while a high-pressure anomaly develops over the middle latitudes. This intensifies the westerly winds and causes them to contract toward the Antarctic. As a result, upwelling of circumpolar deep water on the continental shelf intensifies in the Antarctic, promoting sea-ice retreat. More importantly, it also intensifies the melting of ice shelves, an essential aspect for future global sea-level rise.
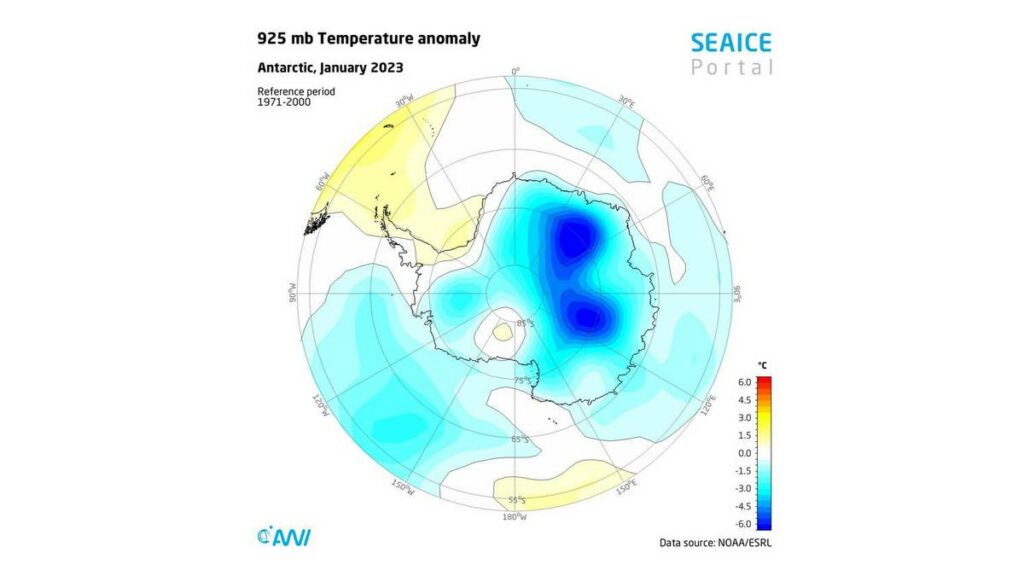
The press release concludes:
Historical records also reflect the tremendous changes. For example, in the Antarctic summer 125 years ago, the Belgian research vessel Belgica was trapped in the massive pack ice for more than a year – in exactly the same region where the Polarstern can now operate in completely ice-free waters. The photographs and diaries of the Belgica’s crew offer a unique chronicle of the ice conditions in the Bellingshausen Sea at the dawn of the industrial age, which climate researchers often use as a benchmark for comparison with today’s climate change.
Belgica became ice bound near Peter I island on February 28th 1898. On board was second officer Roald Amundsen. The leader of the expedition, Adrien de Gerlache, published a French language book about the voyage in 1902: “Quinze mois en Antarctique“.
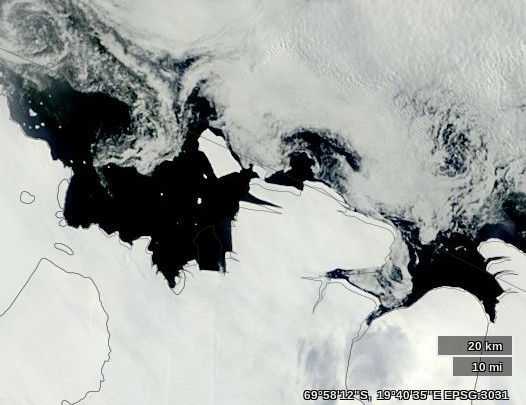
Finally, for the moment at least, here is the University of Bremen’s map of Polarstern’s current location and the sea ice concentration in the vicinity thereof:
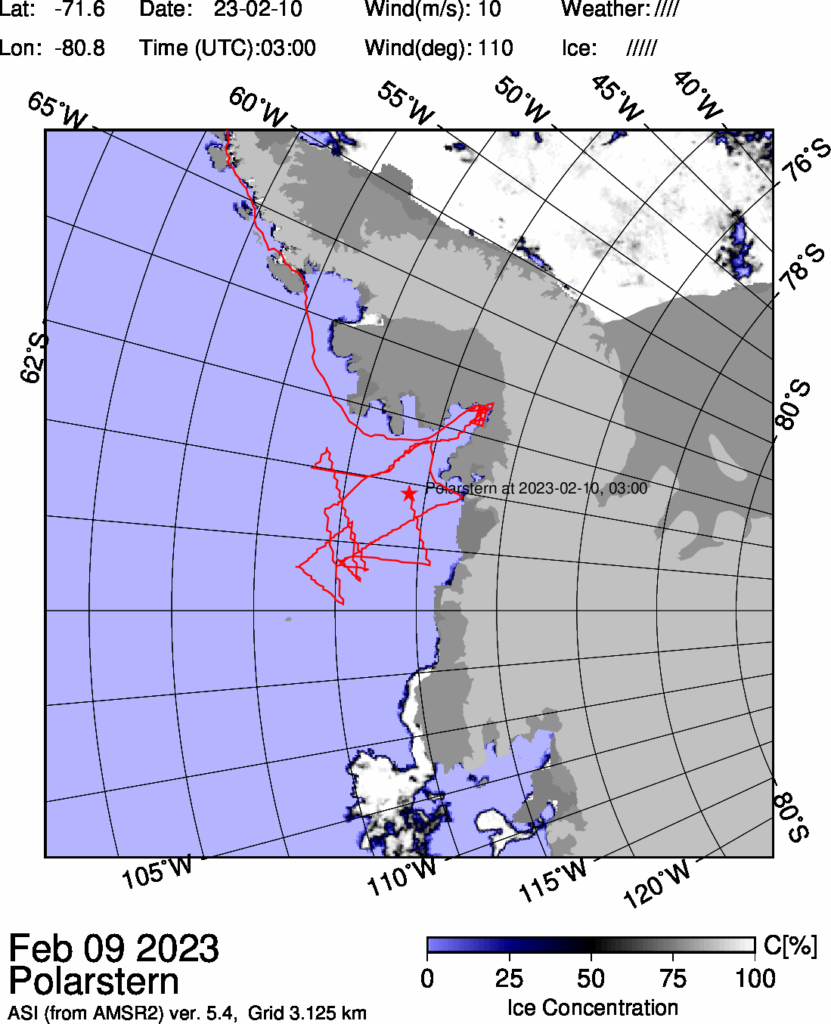
JAXA Antarctic sea ice extent is now down to 2.06 million km². Accompanied by a significant fall in Arctic extent, JAXA’s flavour of global sea ice extent has now also reached the lowest level ever recorded in the satellite era, at 15.51 million km² :
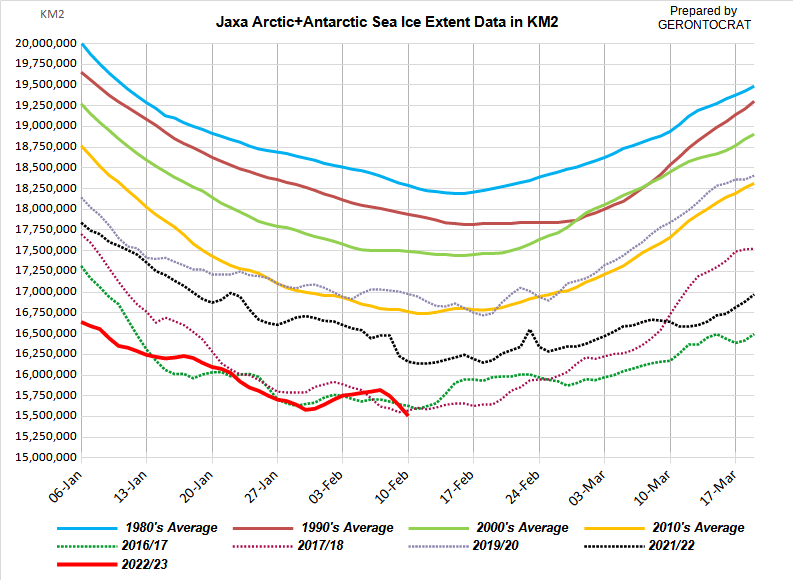
P.S. The NSIDC’s 5 day averaged extent hasn’t quite reached a record minimum yet:
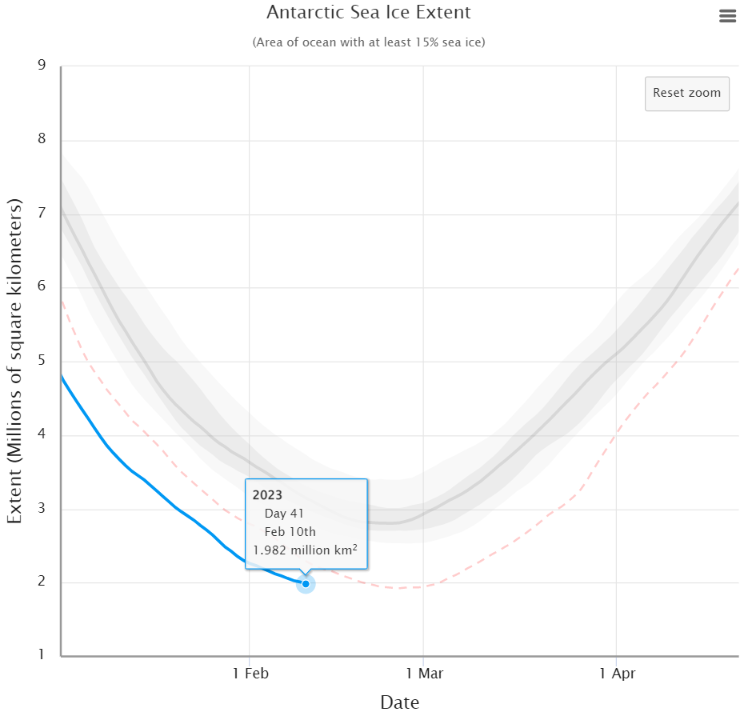
However their daily extent has reached a new satellite era record minimum:
The NSIDC’s 5 day average Antarctic sea ice extent metric has duly reached a new record low level of 1.91 million km² :
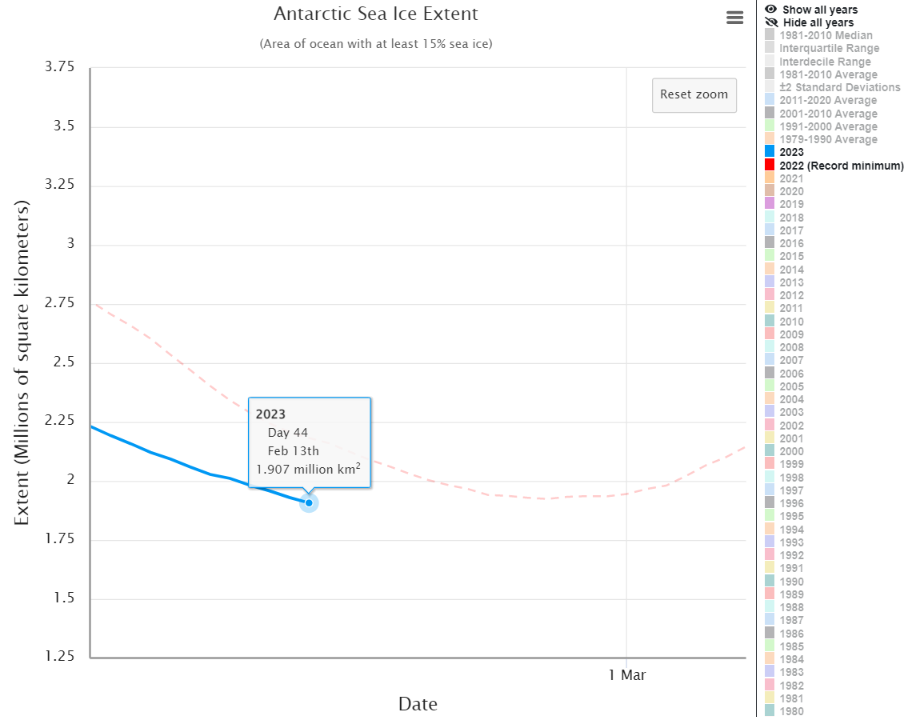
P.S. The NSIDC has now published its own article about the record minimum:
With a couple more weeks likely left in the melt season, the extent is expected to drop further before reaching its annual minimum. Much of the Antarctic coast is ice free, exposing the ice shelves that fringe the ice sheet to wave action and warmer conditions…
Extent has tracked well below last year’s melt season levels since mid-December. As noted in our previous post, a positive Southern Annular Mode has led to stronger-than-average westerly winds. Along with a strong Amundsen Sea Low, the weather conditions have brought warm air to the region on both sides of the Antarctic Peninsula. This has largely cleared out the ice cover in the Amundsen and Bellingshausen Seas, and reduced the sea ice extent in the northwestern Weddell Sea. Sea ice is patchy and nearly absent over a long stretch of the Pacific-facing coastline of Antarctica. Earlier studies have linked low sea ice cover with wave-induced stresses on the floating ice shelves that hem the continent, leading to break up of weaker areas.
Antarctic sea ice extent has been highly variable over the last several years. While 2022 and 2023 have had record low minimum extent, four out of the five highest minimums have occurred since 2008. Overall, the trend in Antarctic minimum extent over 1979 to 2023 is near zero. The current downward linear trend in the Antarctic minimum extent from 1979 to 2023 is 2,400 square kilometers per year, or 0.9 percent per decade, which is currently not statistically significant. Nevertheless, the sharp decline in sea ice extent since 2016 has fueled research on potential causes and whether sea ice loss in the Southern Hemisphere is developing a significant downward trend.
Watch this space!