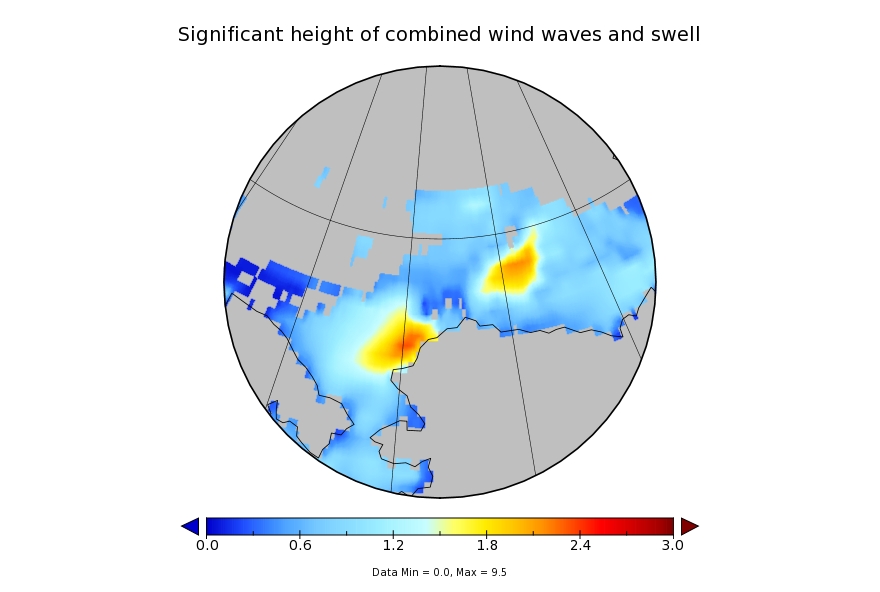
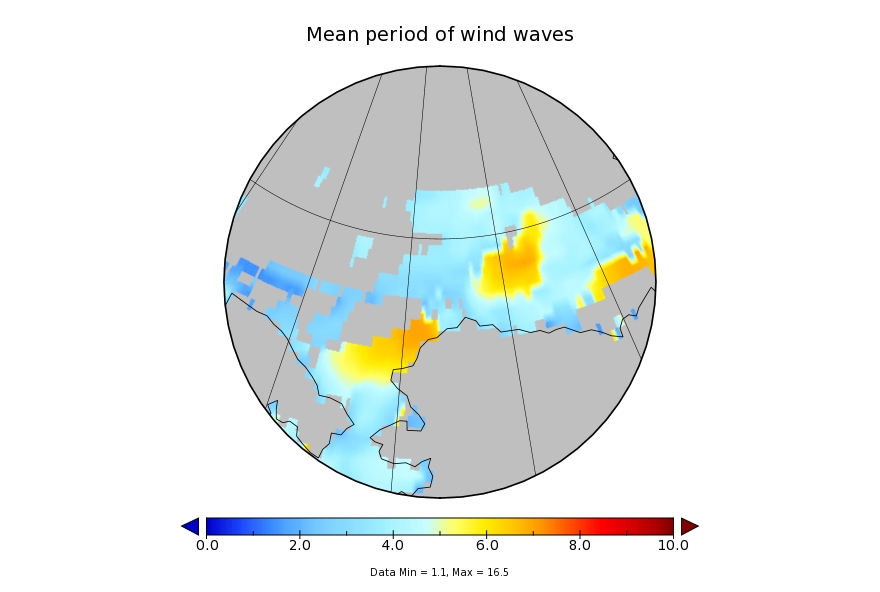
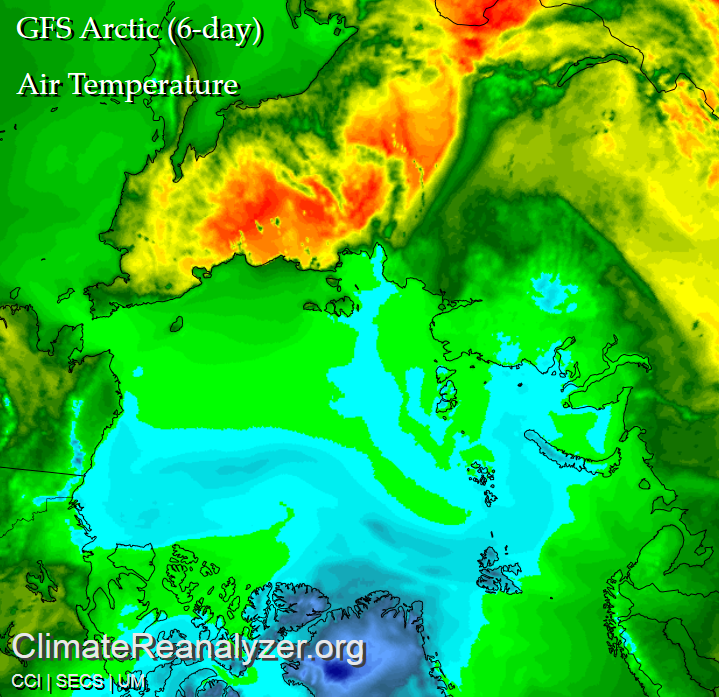
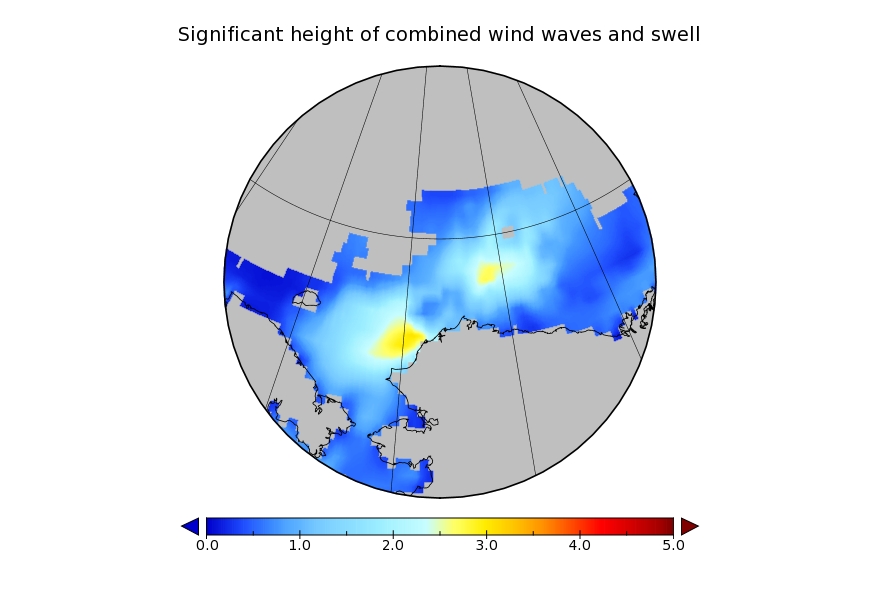
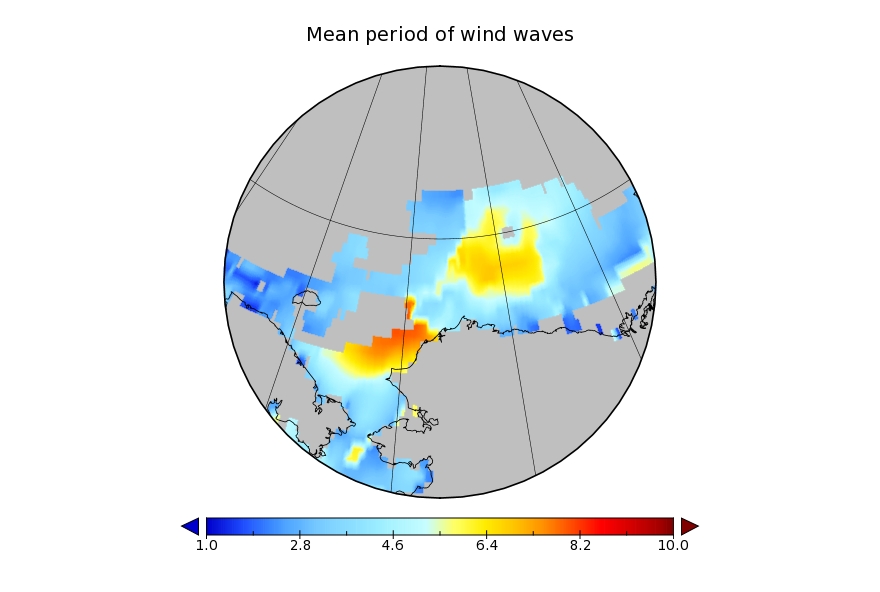
It looks like a storm is brewing in the Arctic. The long range weather forecasts for the Arctic have been remarkably unreliable recently, but this one is for a mere three days from now. WaveWatch III suggests there will be some significant waves in the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas this coming weekend, travelling in the direction of the ice edge:
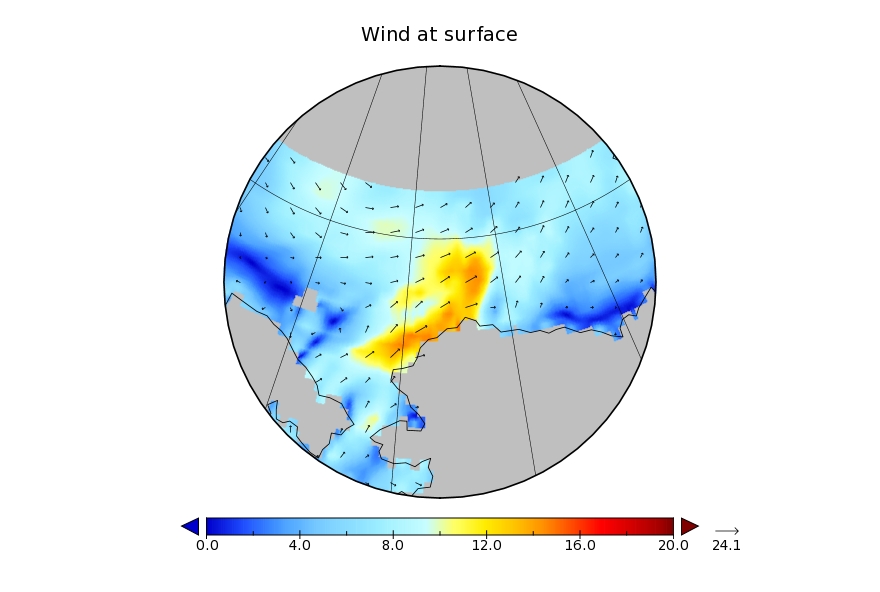
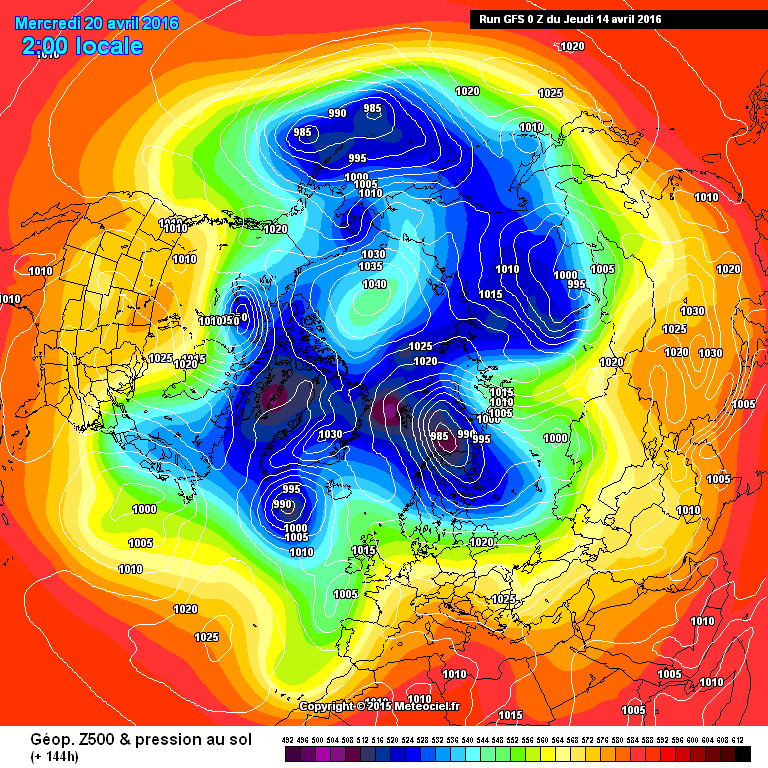
Sunday is only two days away now, and here is the current ECMWF prognosis:
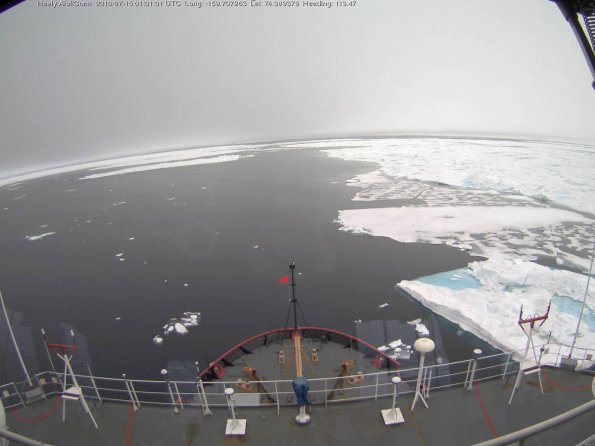
Here’s how “the surf” looks today, courtesy of United States Coast Guard Cutter Healy:

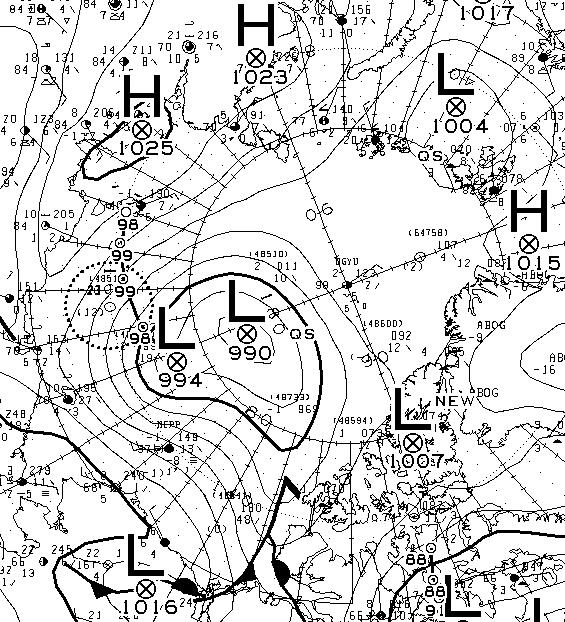
Another day has dawned, and the Environment Canada synoptic chart shows that the low pressure system currently over the Arctic has reached a central pressure of 990 hPa:
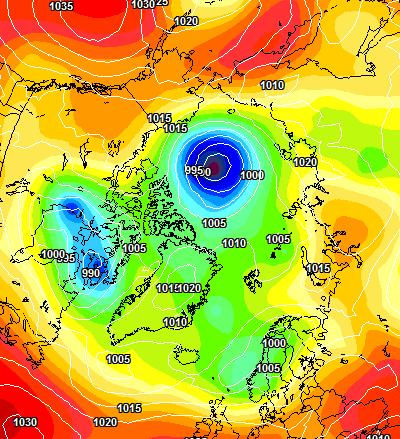
The latest ECMWF SLP forecast for tomorrow is firming up:
A modest swell is now visible from USCGC Healy’s “AloftCon” webcam:

whilst the WaveWatch III forecast for tomorrow has dropped off to a significant wave height of around 2 metres with an average period of 7 seconds:
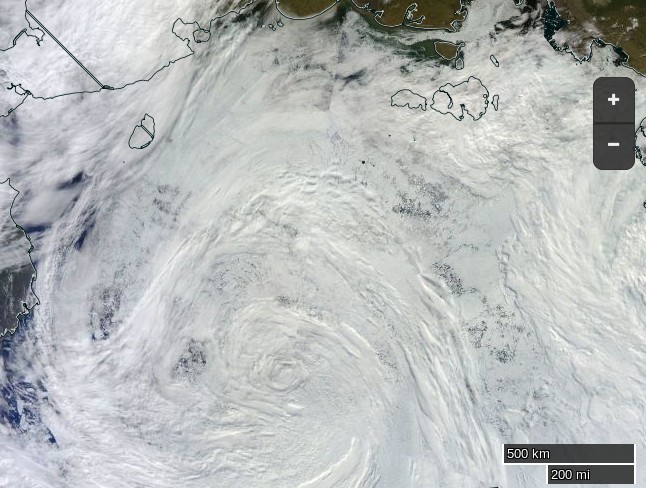
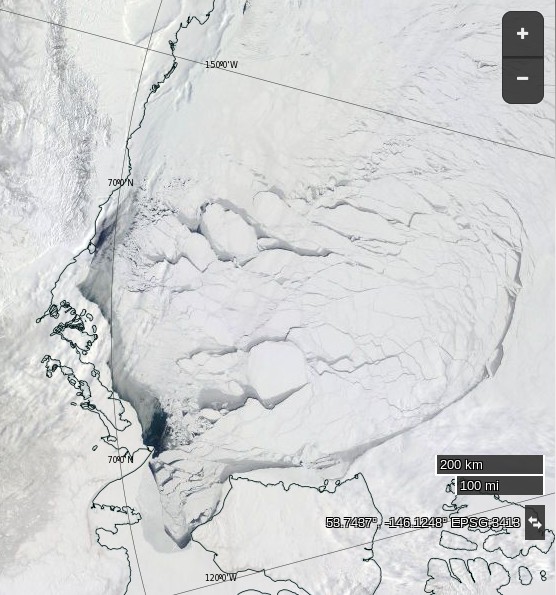
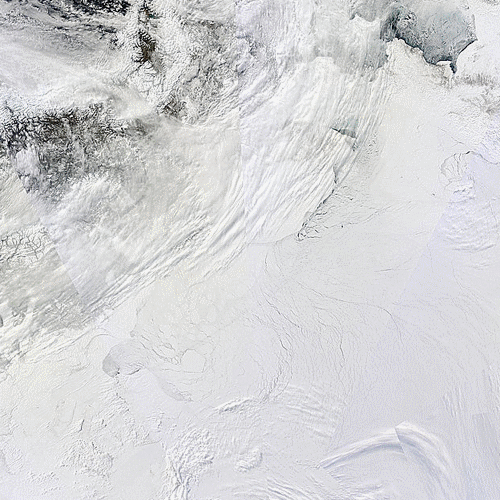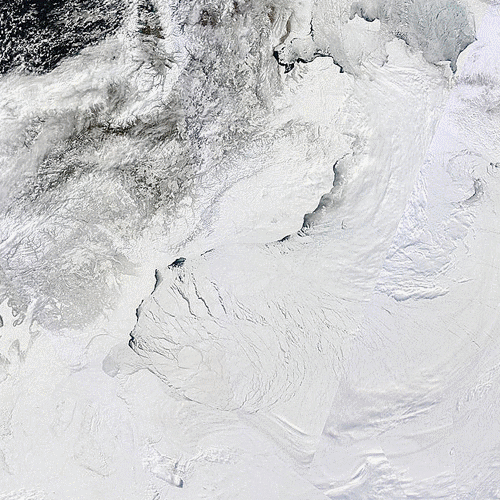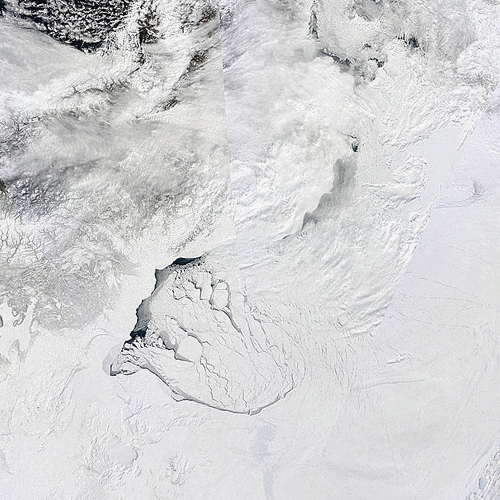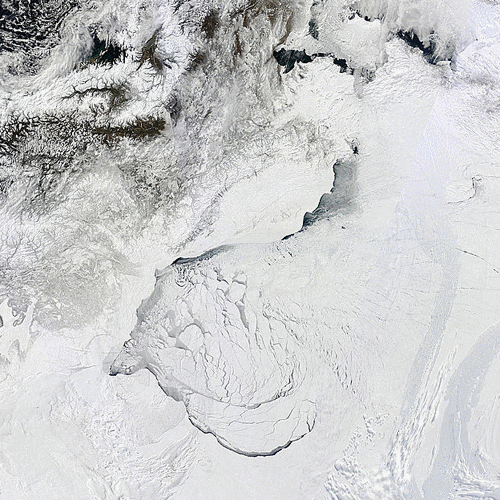
Meanwhile an image from the VIIRS instrument on the Suomi NPP satellite reveals the current storm in all its glory, together with confirmation that the “Big Block” multi-year ice floe north of Barrow has split asunder overnight:
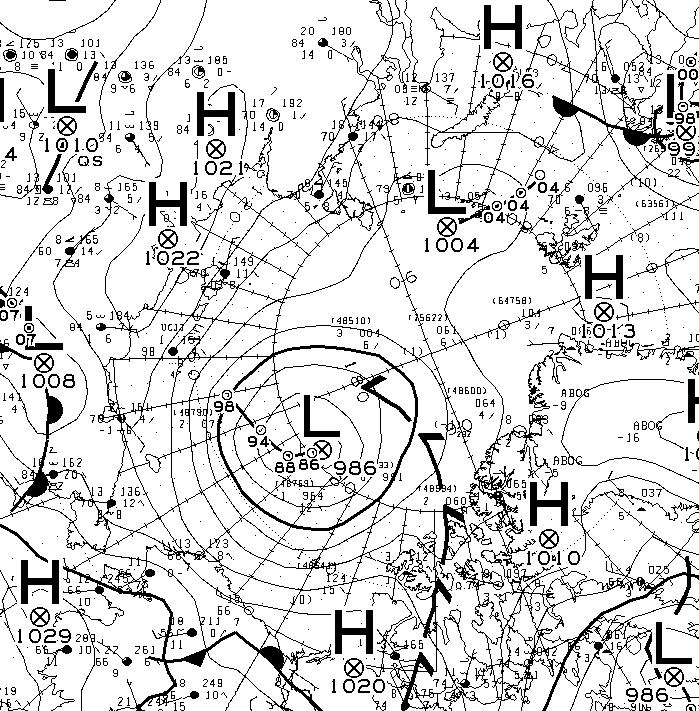
Sunday morning has now arrived. The storm in the Arctic looks to have bottomed out at 986 hPa central pressure. Here’s the Environment Canada synoptic chart for 00:00 this morning:
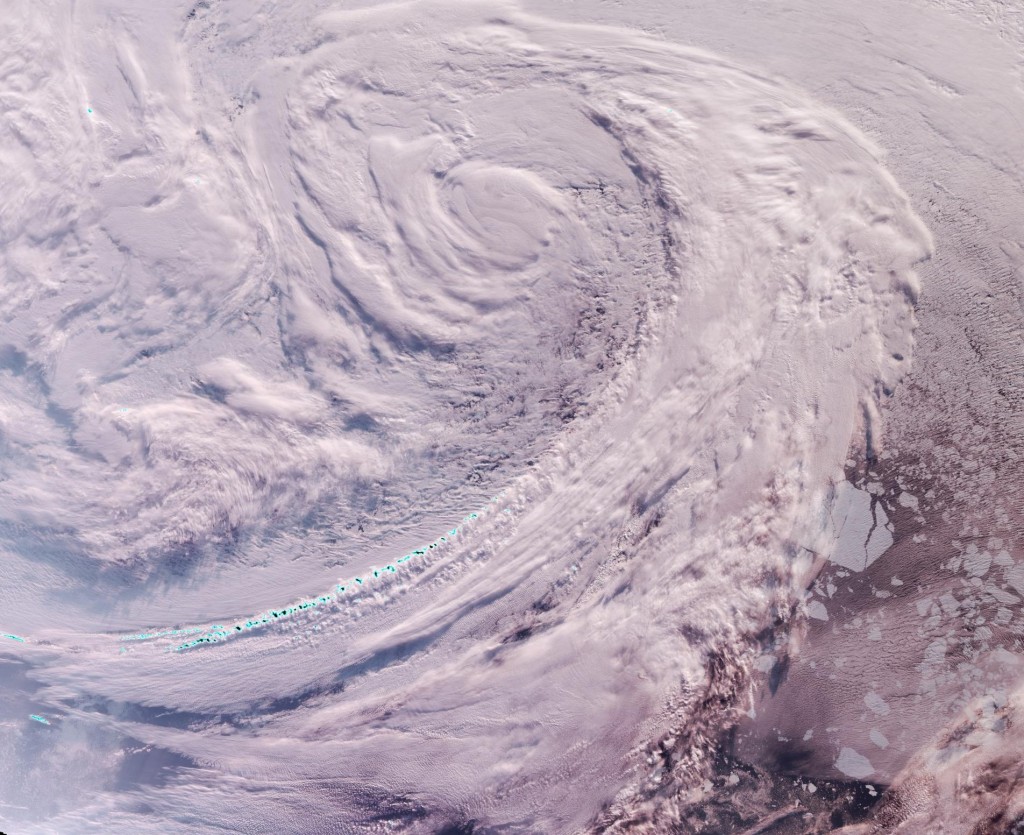
and here’s how the storm looks from the Terra satellite today:
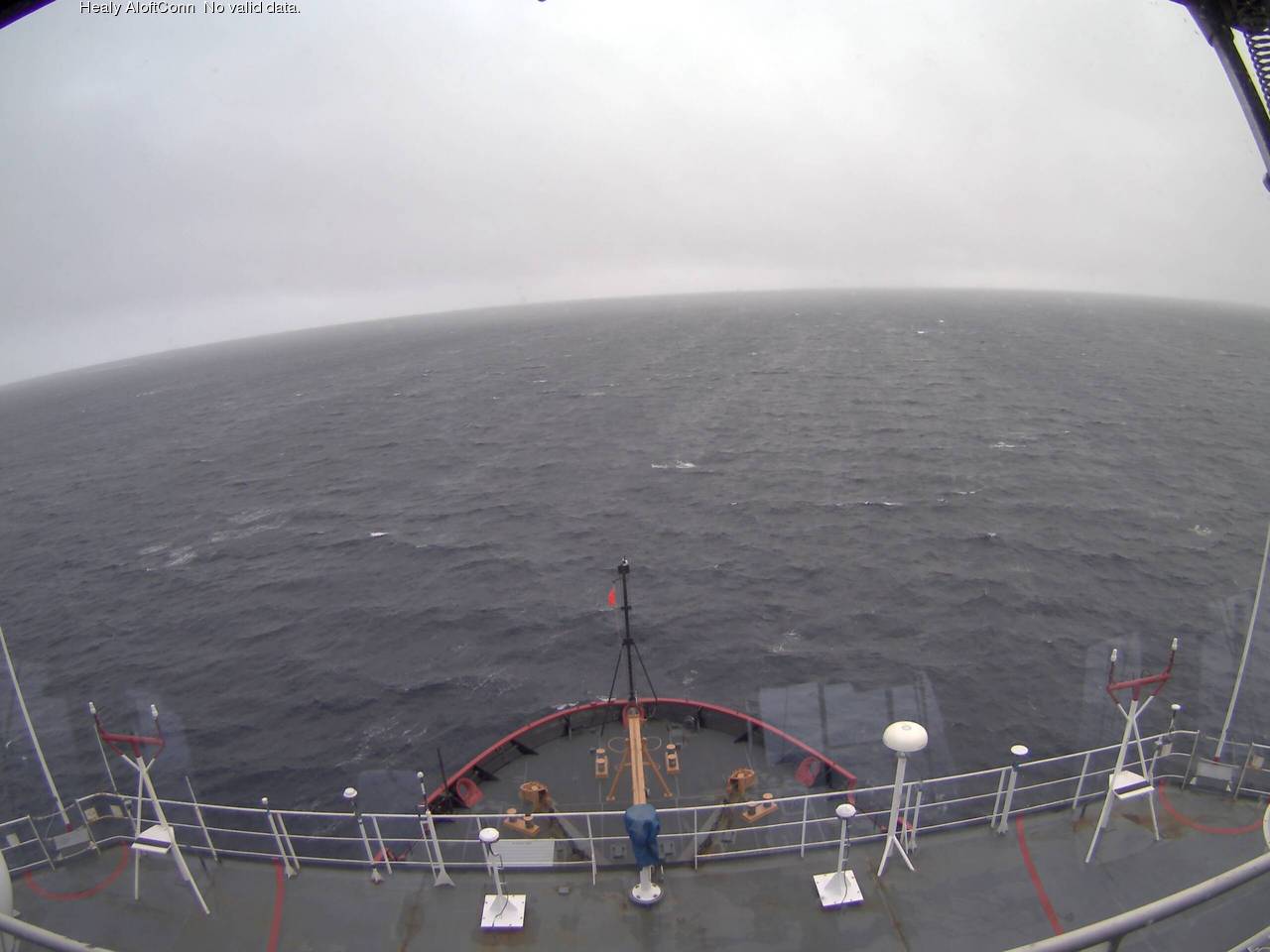
This is how the resultant swell looked from USCGC Healy at 06:00:

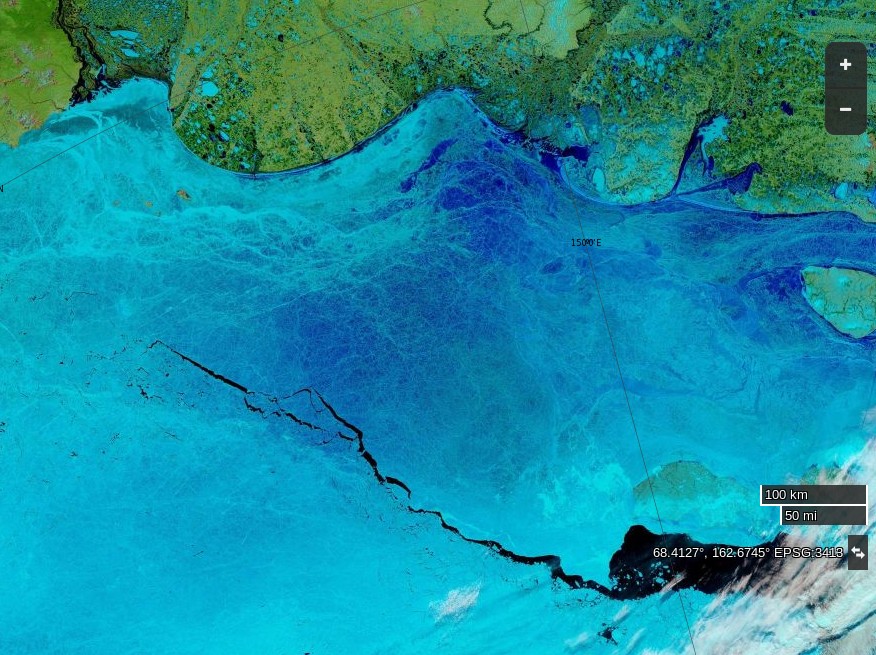
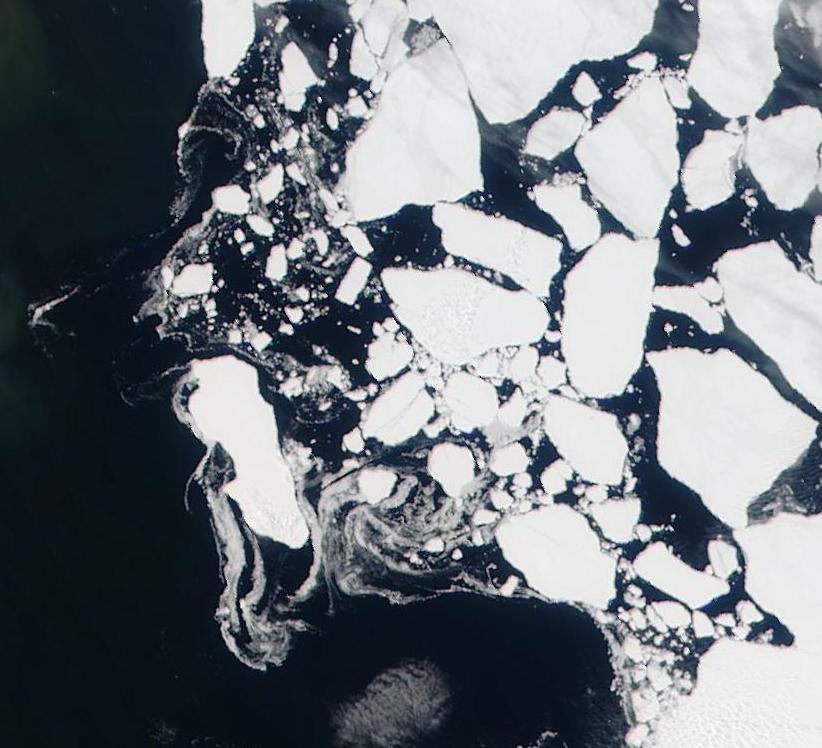
Here’s what the Beaufort and Chukchi Sea north of Barrow look like this morning through the clouds:
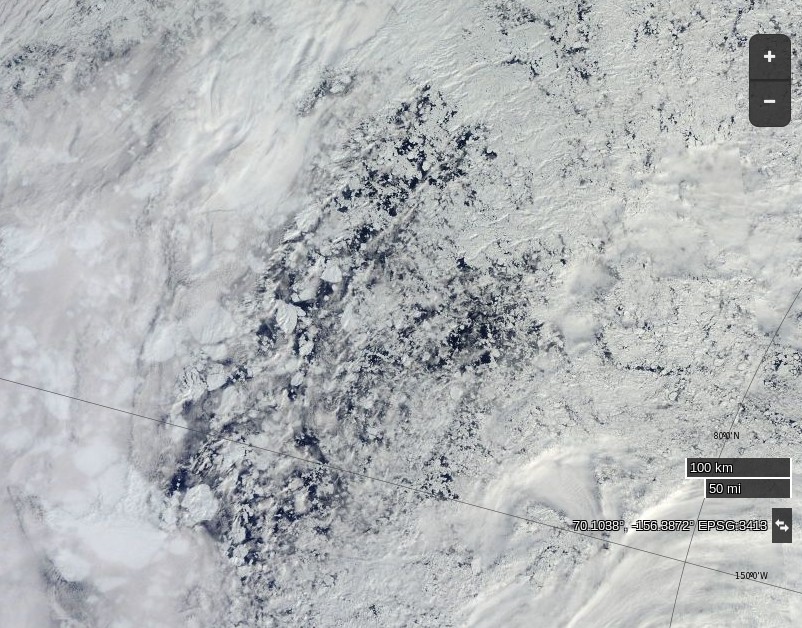

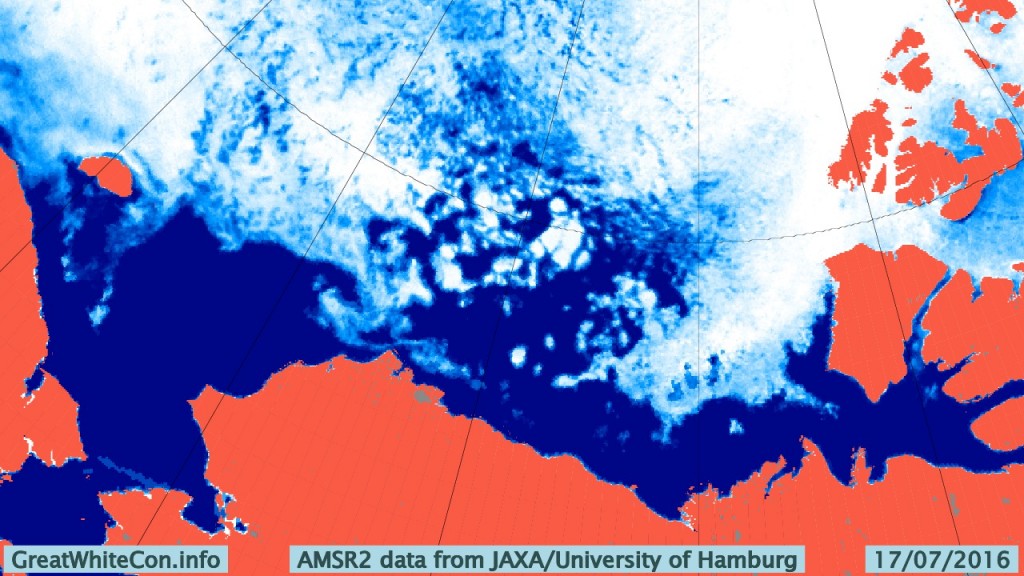
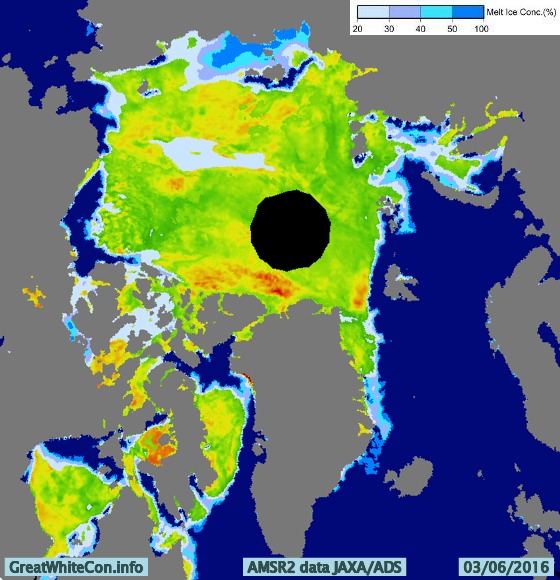
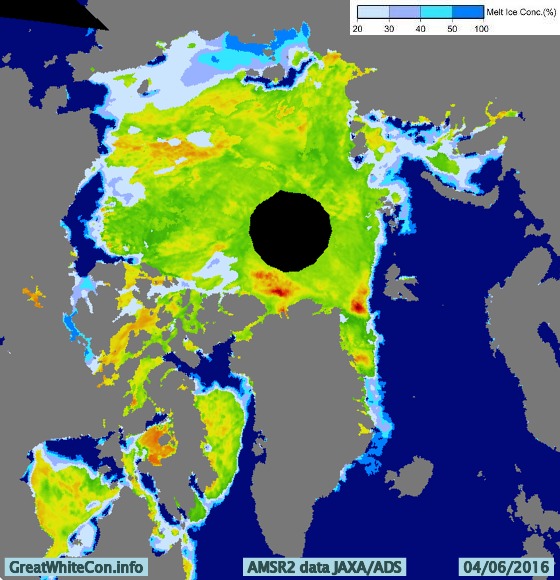
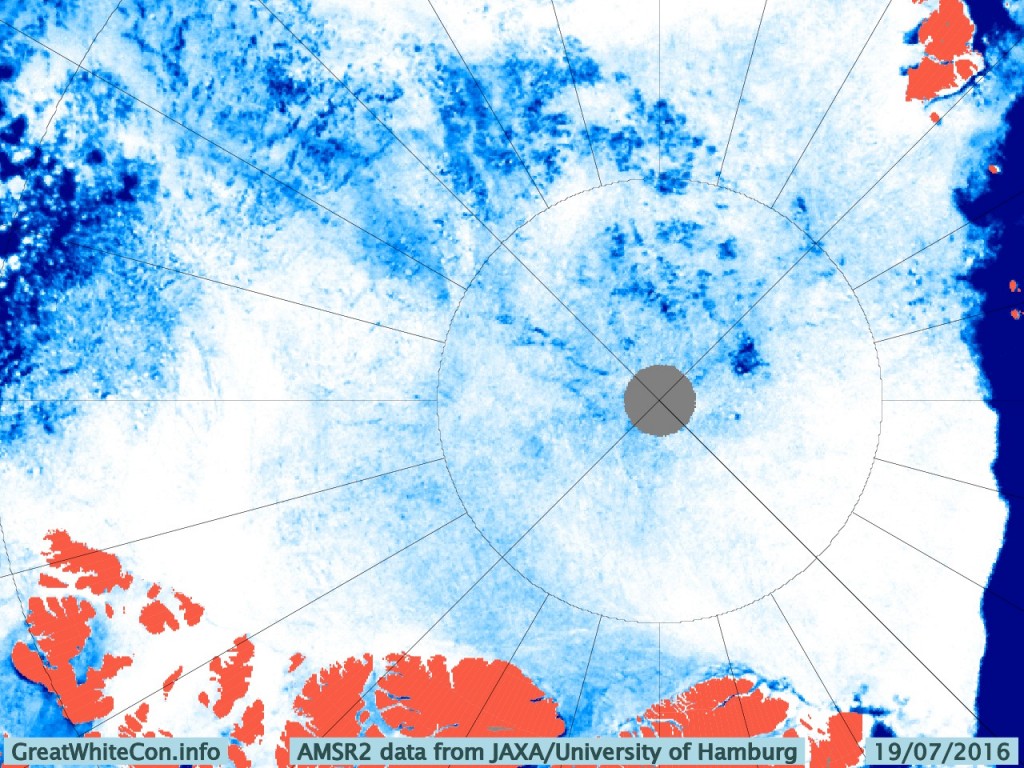
The remains of the now not so “Big Block” can just be made out in the bottom left. For a cloud free image here’s the latest AMSR2 passive microwave imagery of the area from the University of Hamburg:
The USCGC Healy and the remnants of the swell are in amongst the ice:
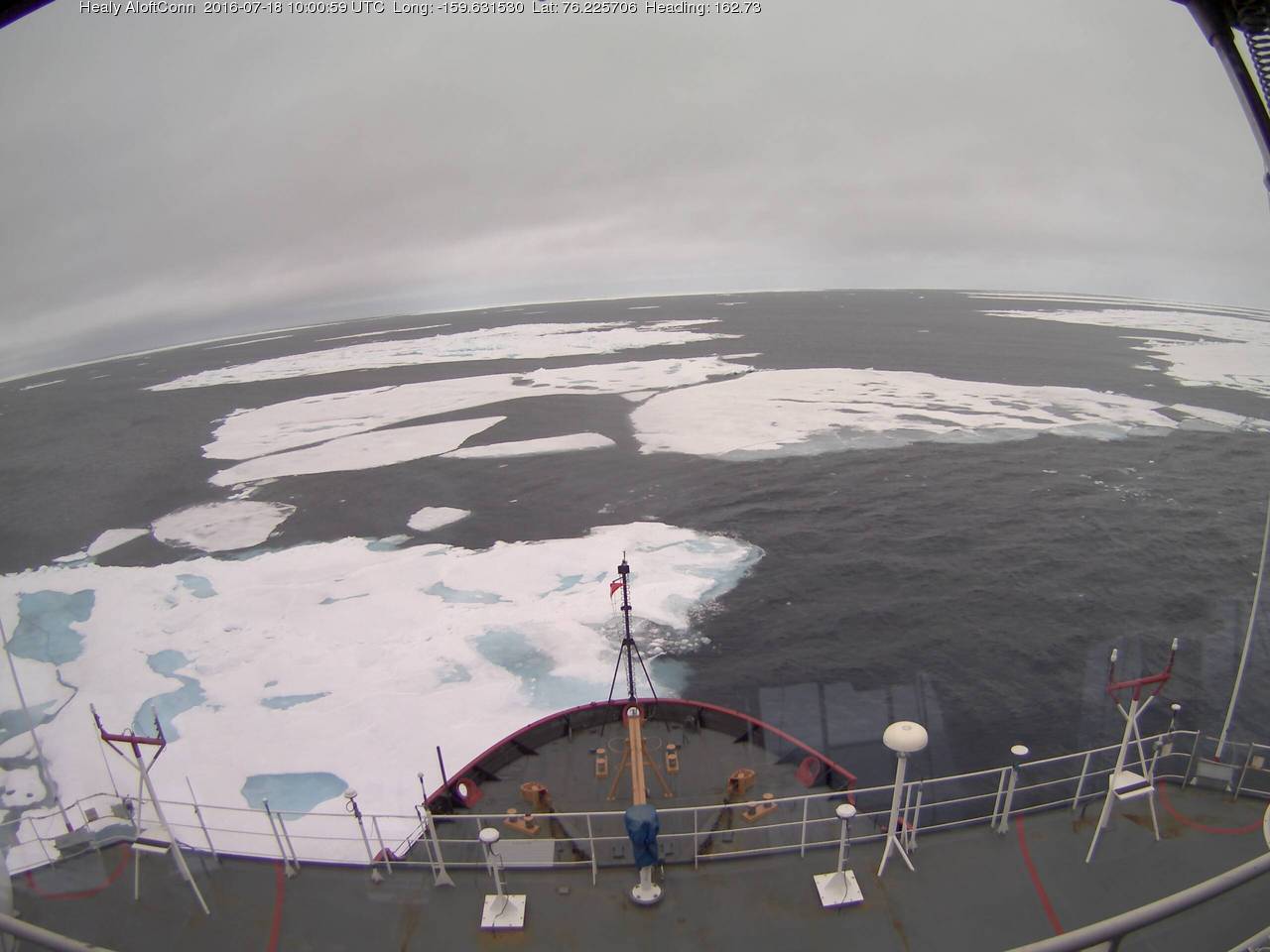

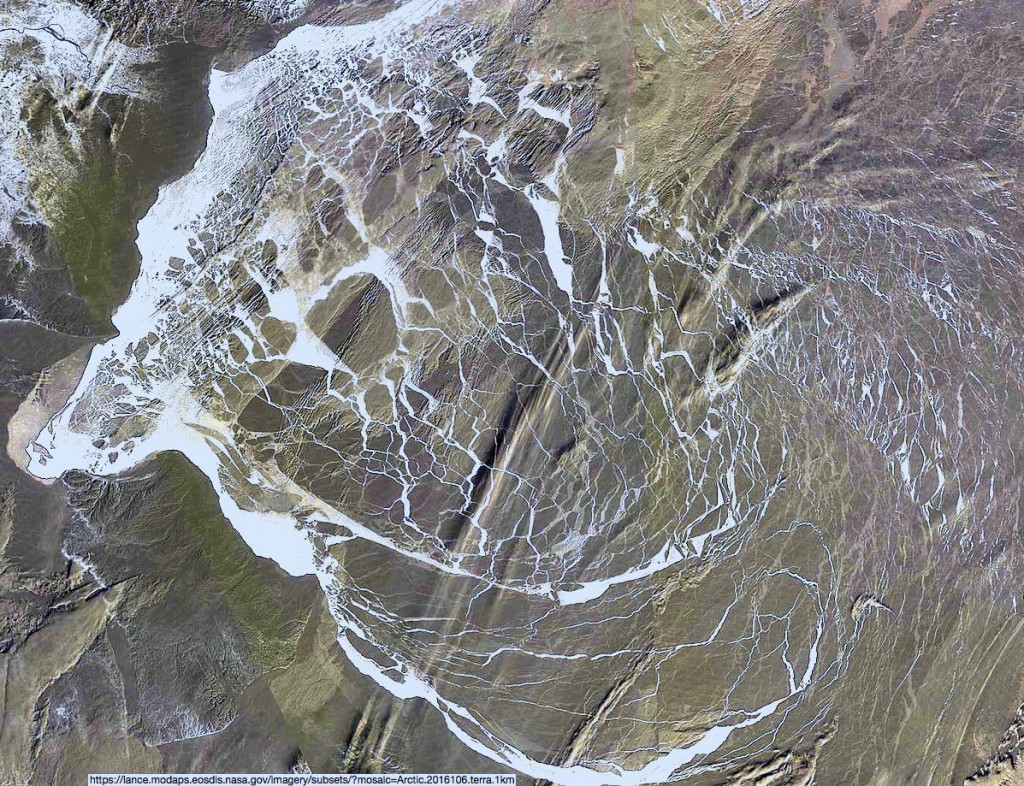
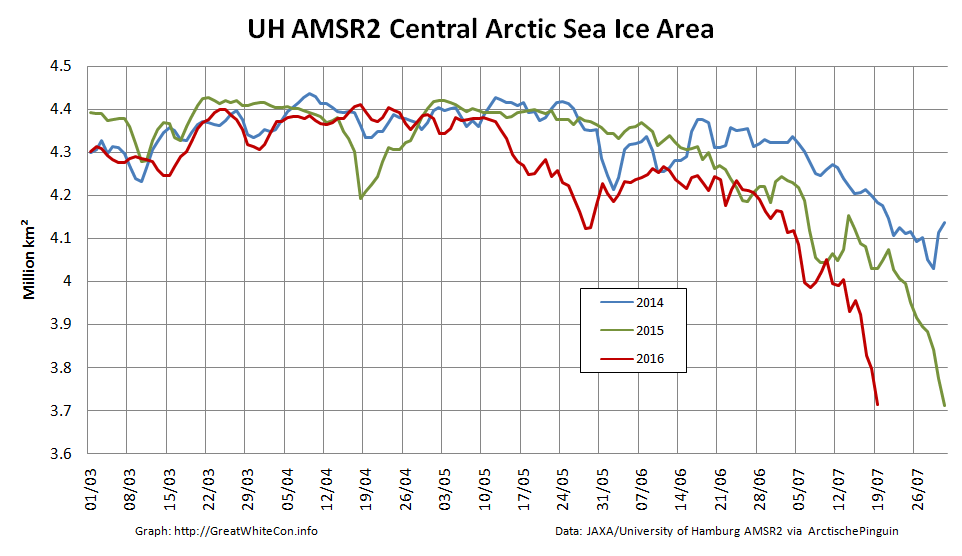
As the remnants of the storm head off across the Canadian Arctic Archipelago here is what it has left in its wake in the Central Arctic Basin:
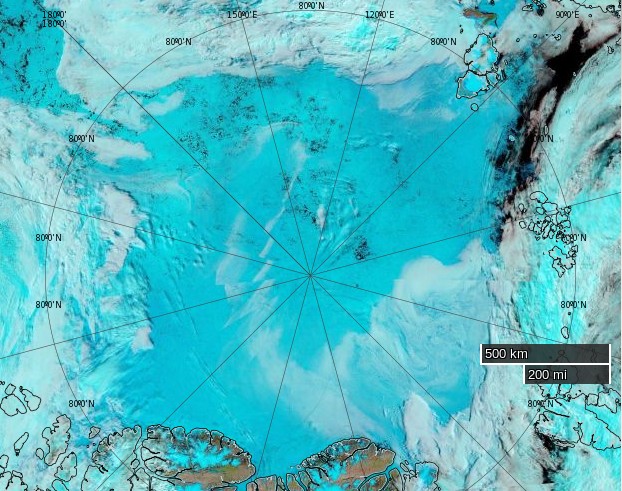

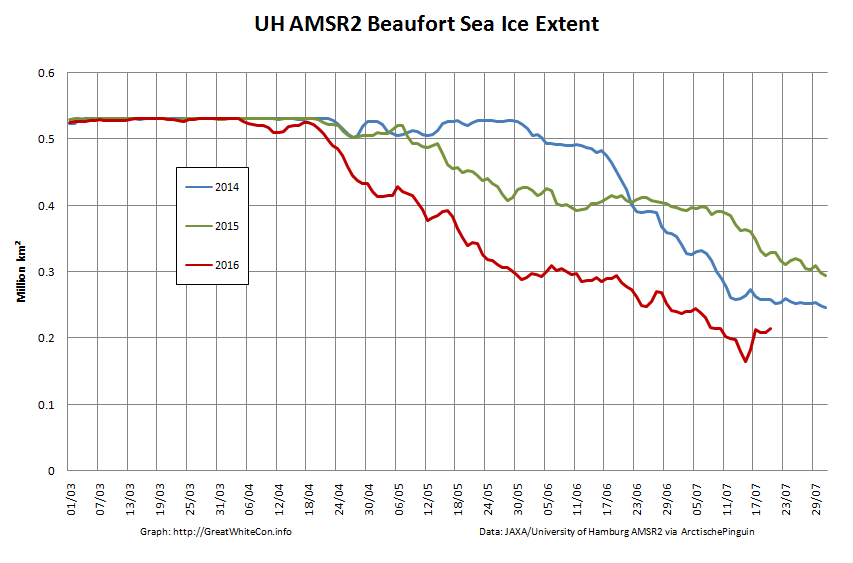
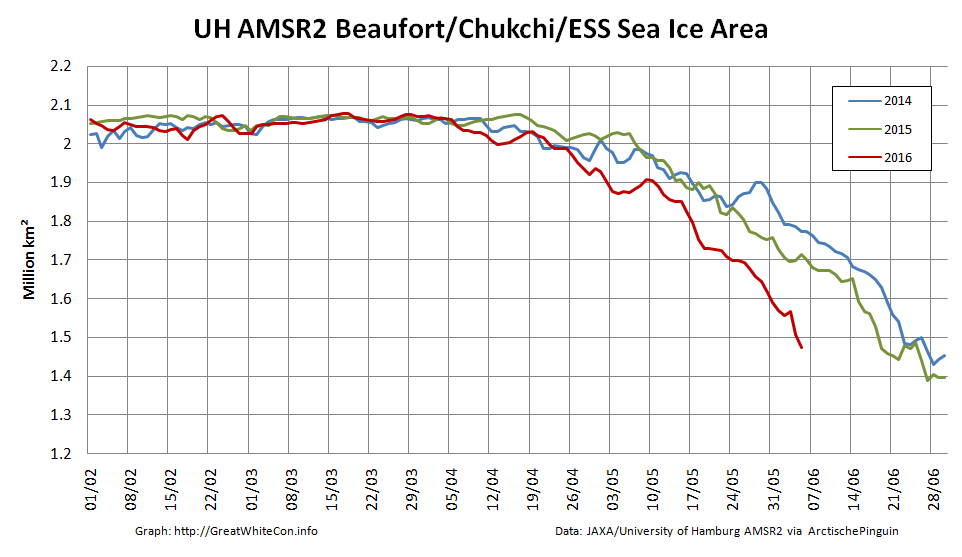
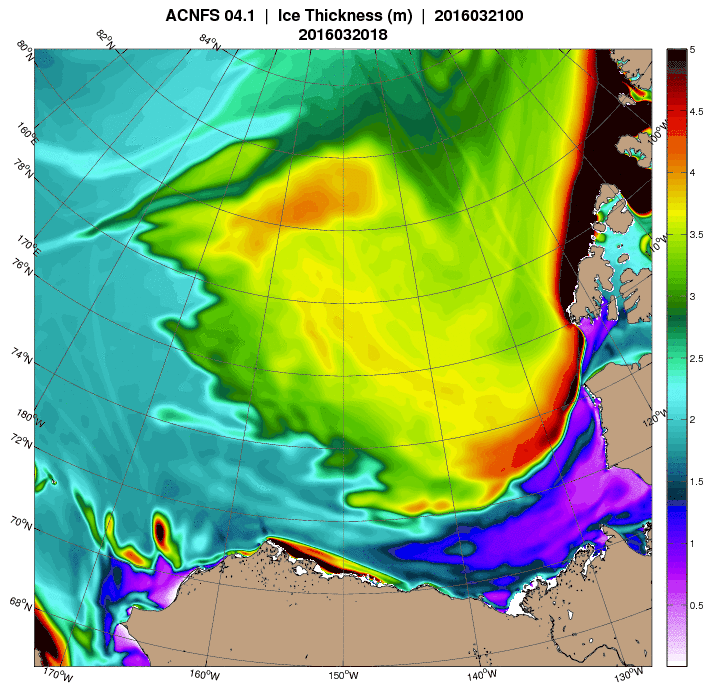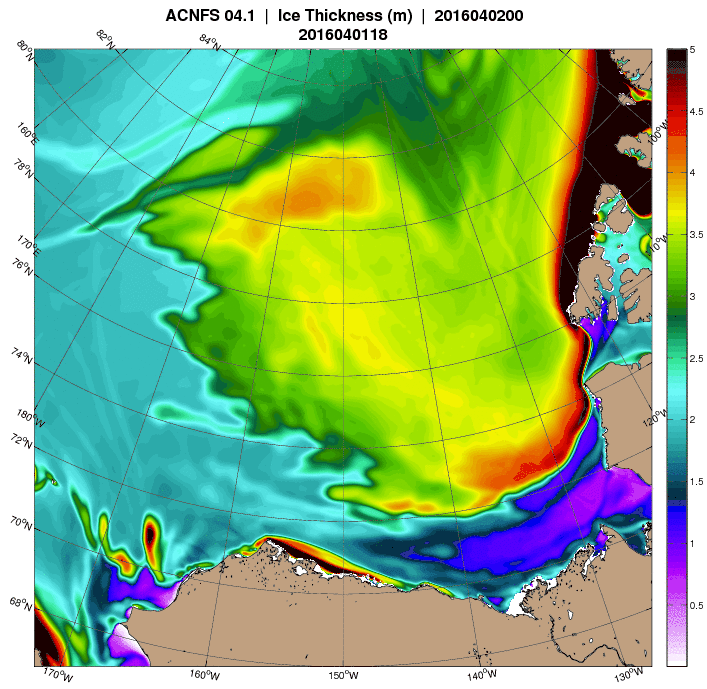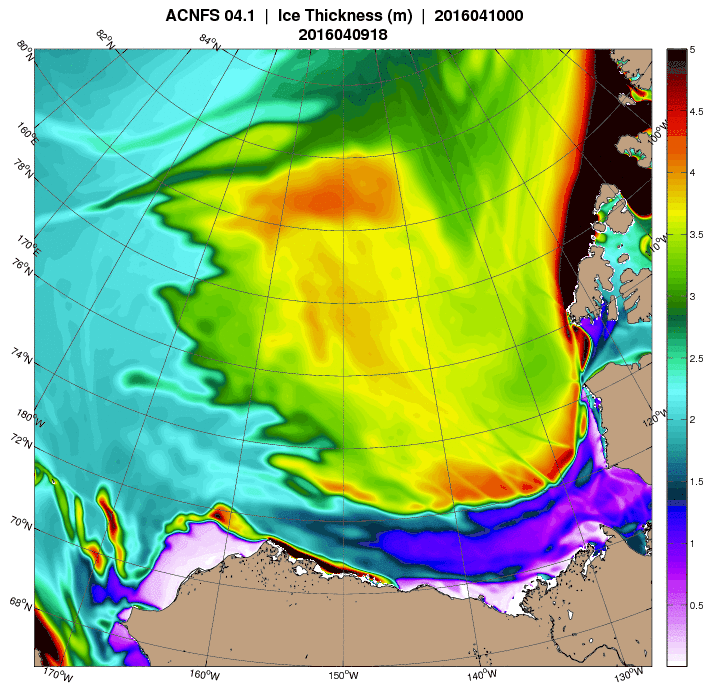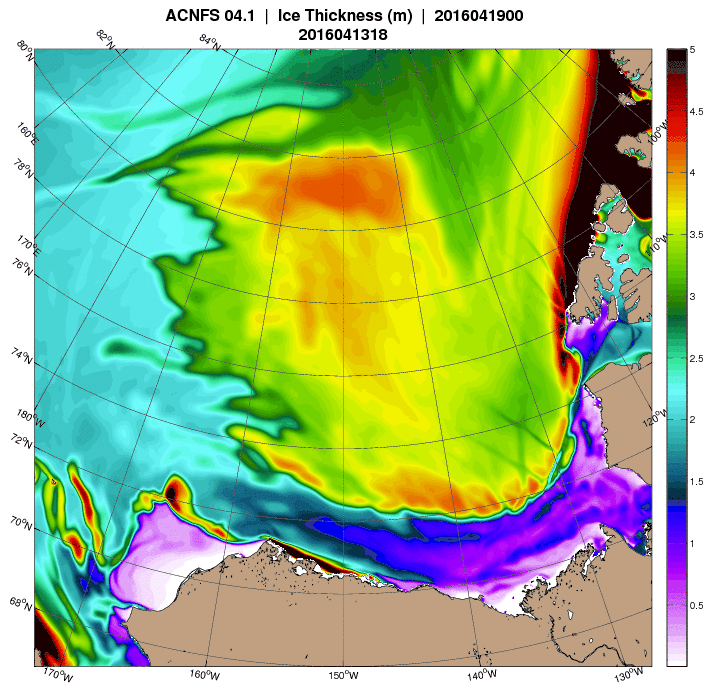
The storm has dispersed the remaining ice in the Beaufort Sea over the last few days:
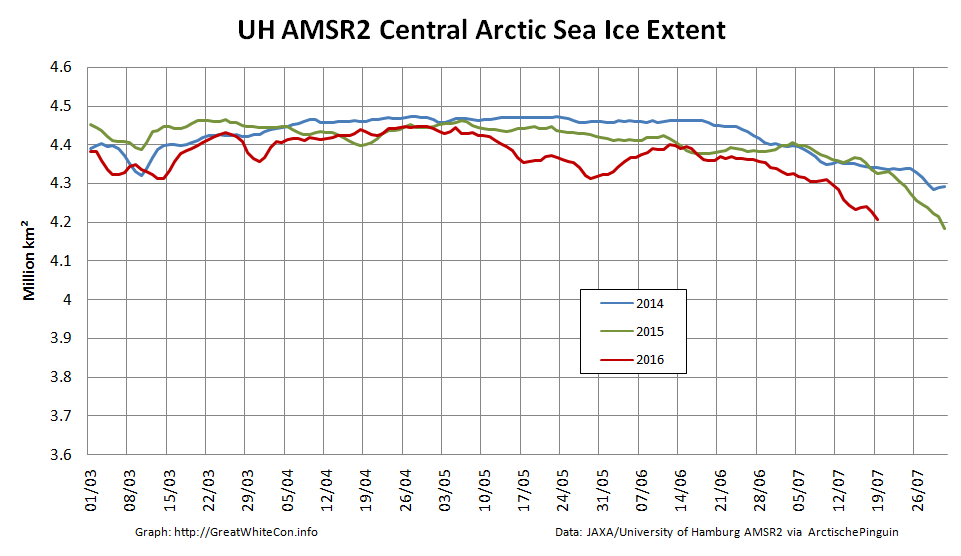
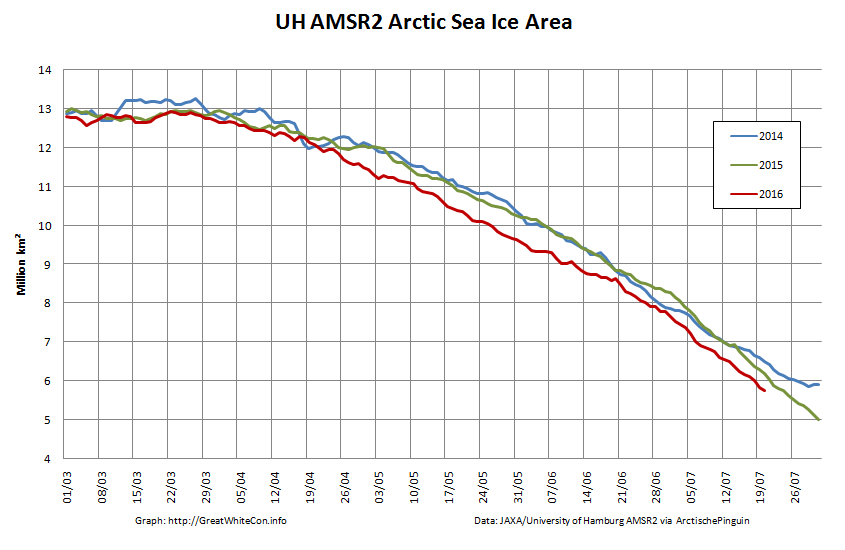
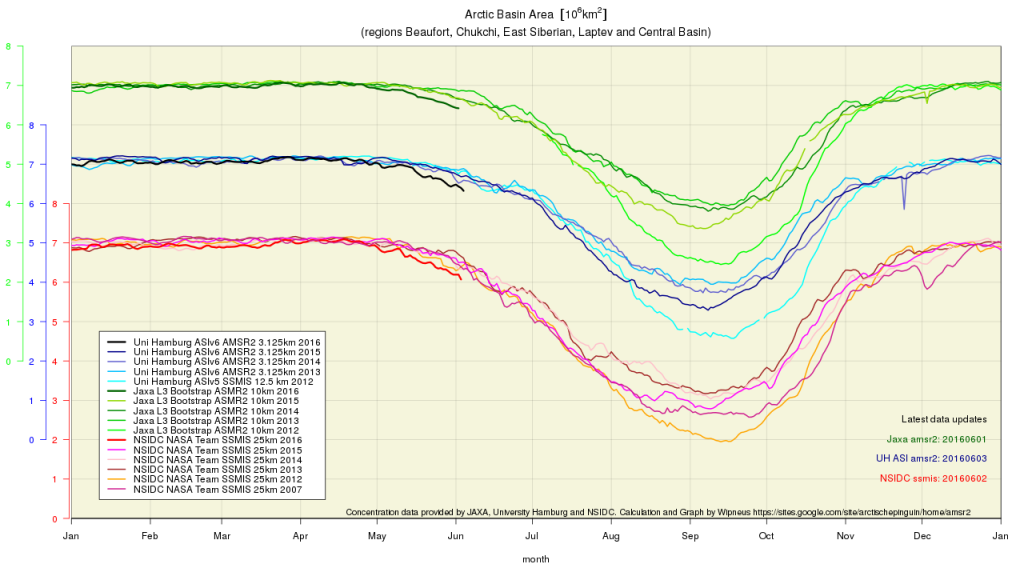
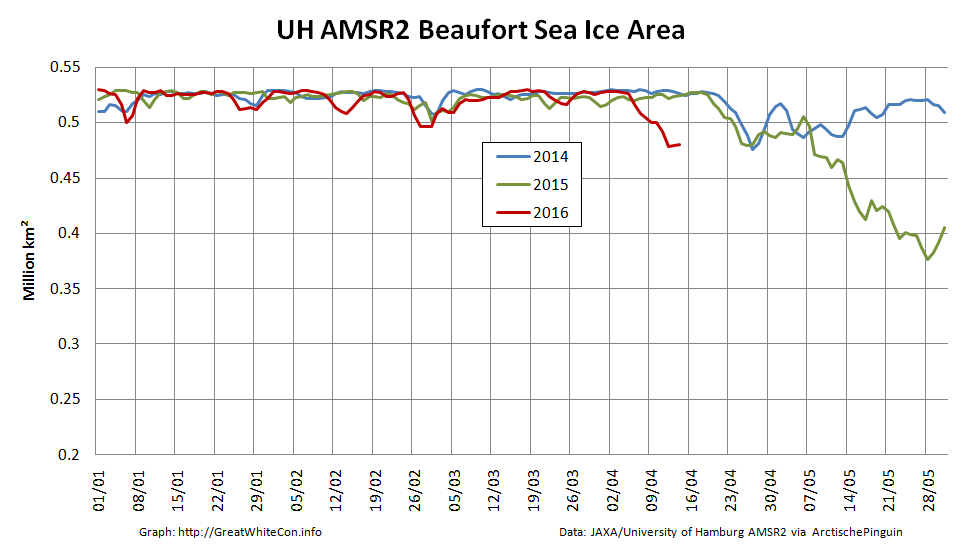
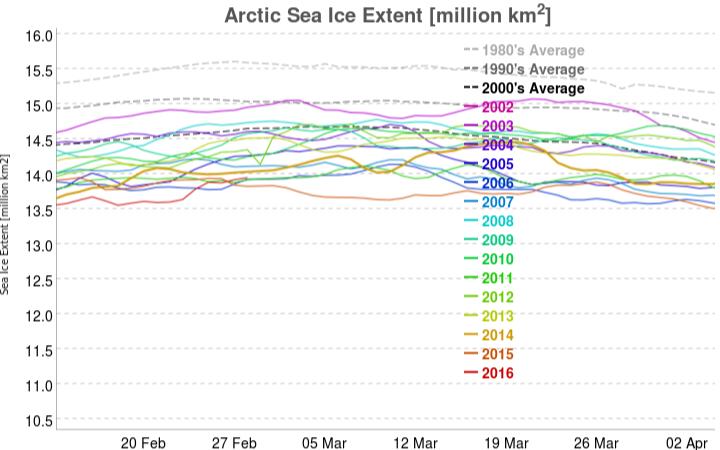
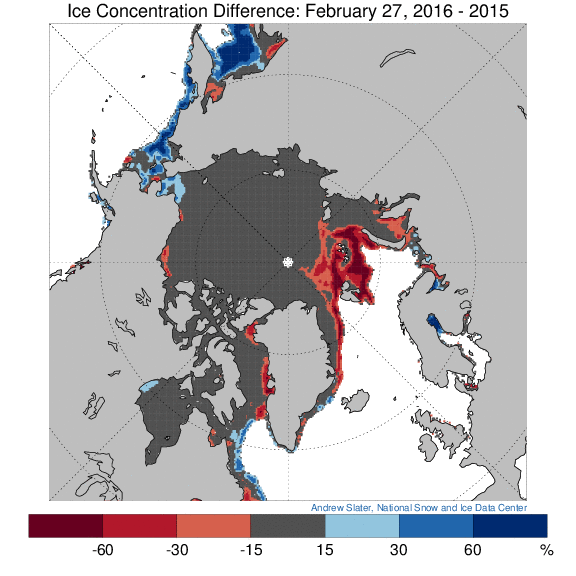
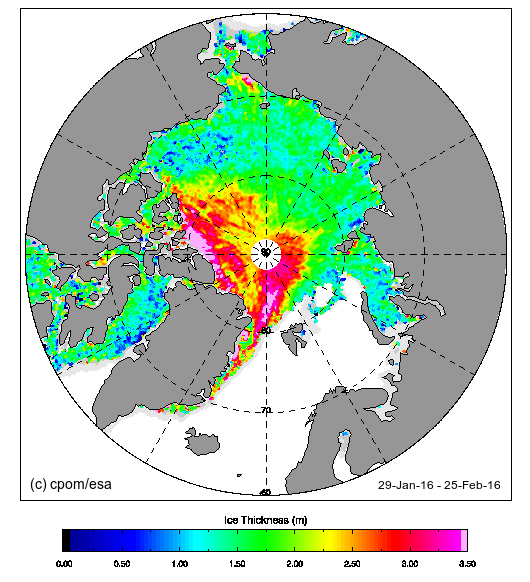
However across the Arctic as a whole sea ice area continues its downward trend: