The celebrated web site of our old friend Anthony Watts published an article yesterday entitled “The polar ice melt myth“. As a self styled expert on that particular topic I popped over there expectantly, only to discover that it is an actual fact a cut ‘n’ paste of an April 30th article by Dr. Jay Lehr at CFACT. Part of that article reads as follows:
Al Gore predicted in 2007 that by 2013 the Arctic Ocean would be completely ice free. In the summer of 2012 ice levels did reach all time lows in the Arctic. Emboldened by this report Australian Professor Chris Turney launched an expedition in December of 2013 to prove that the Antarctic Sea Ice was also undergoing catastrophic melting only to have his ship trapped in sea ice such that it could not even be rescued by modern ice-breakers.
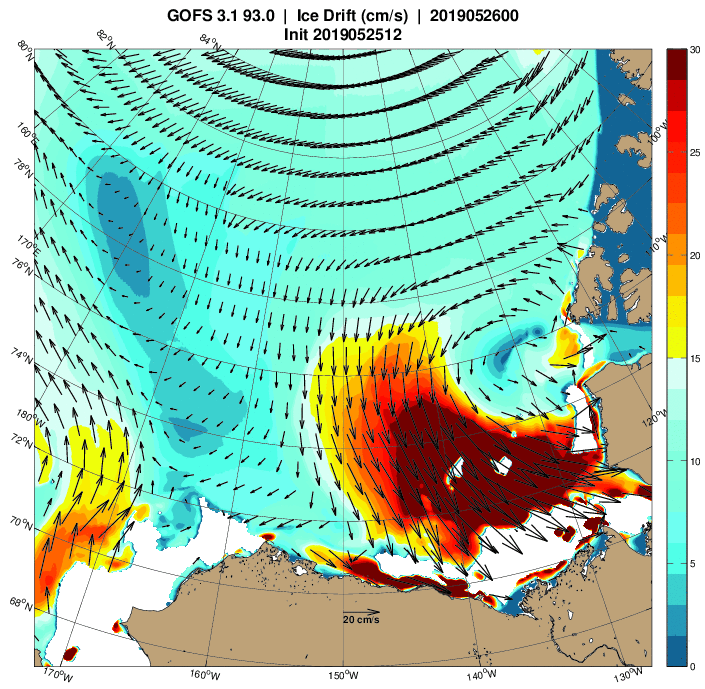
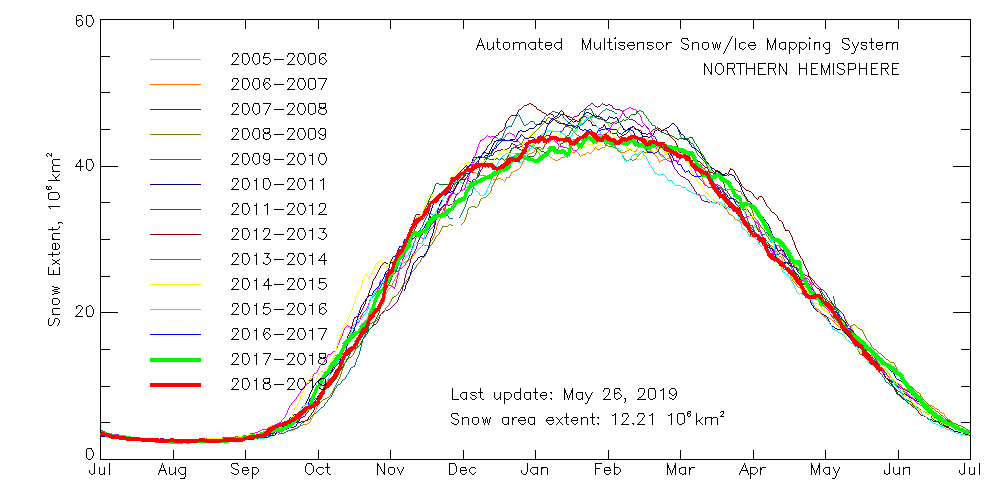
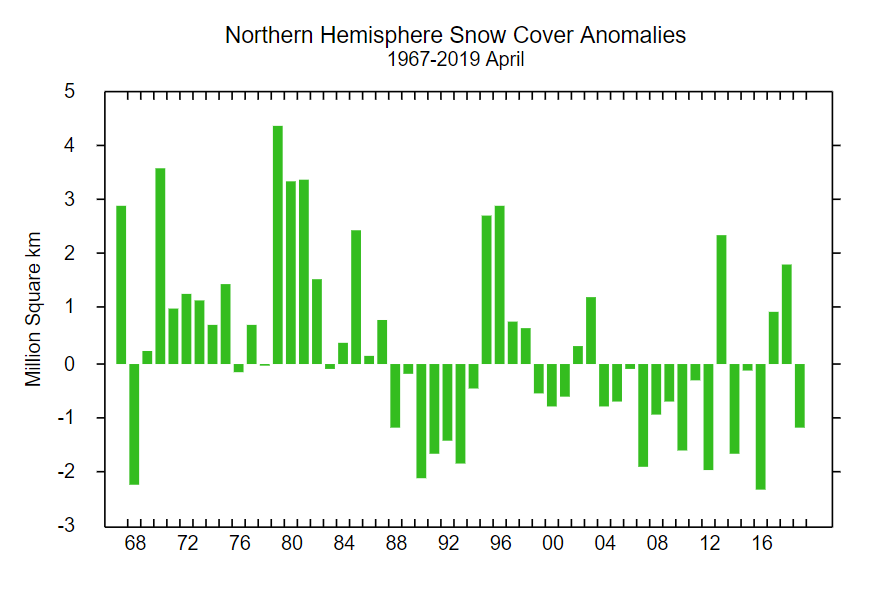
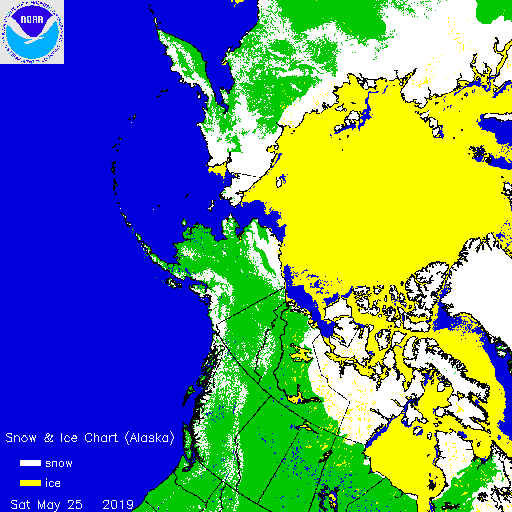
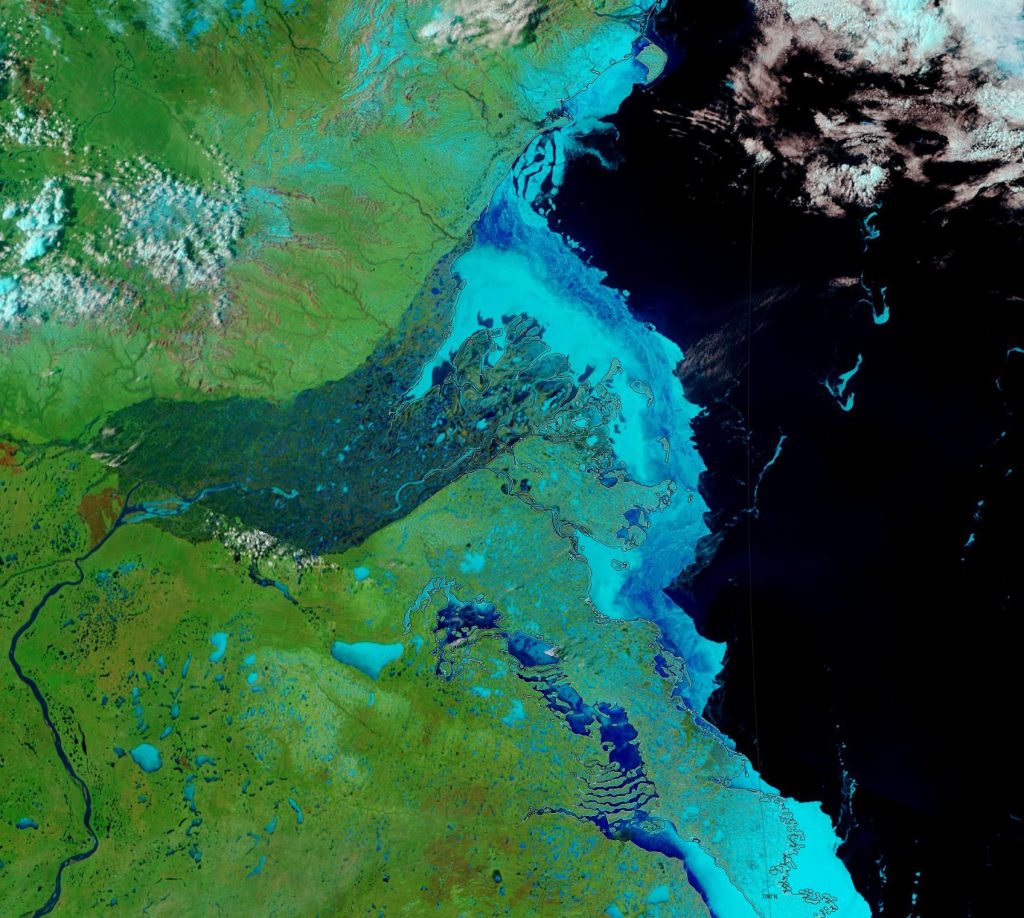
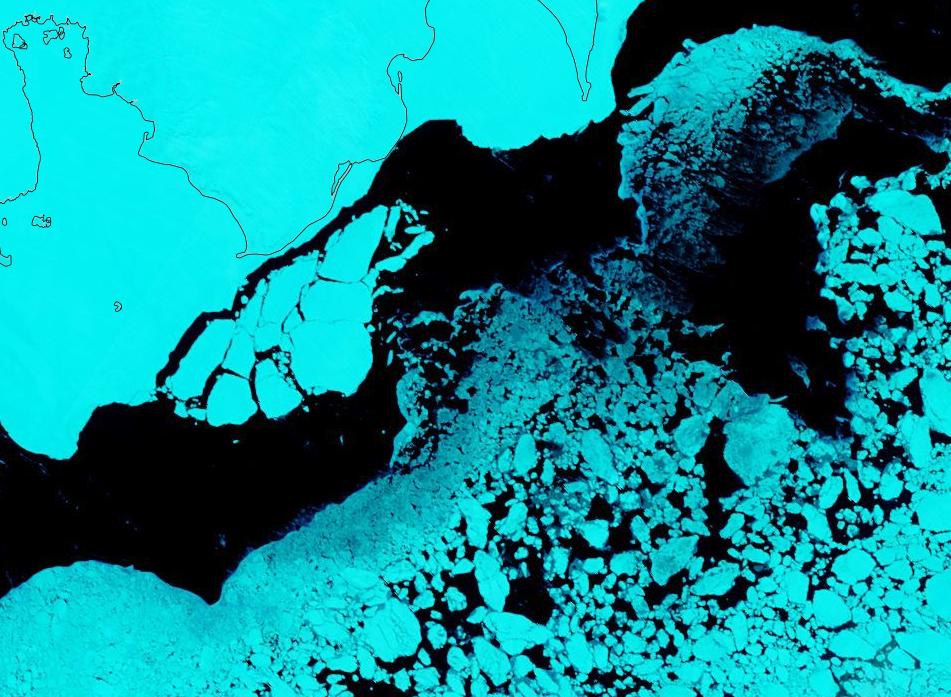
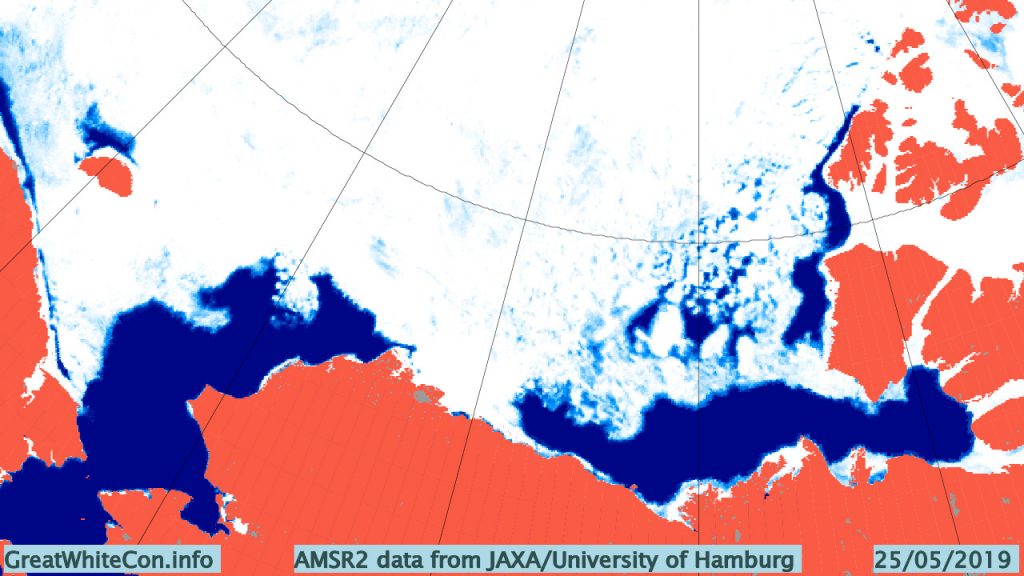
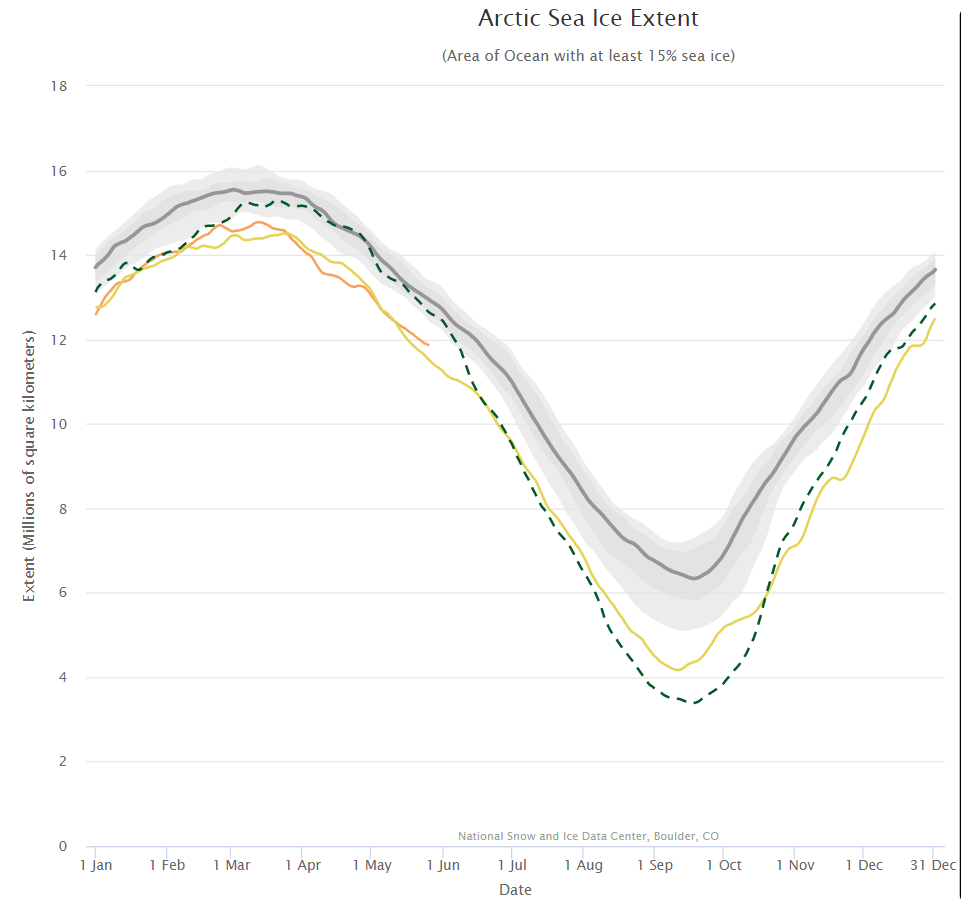
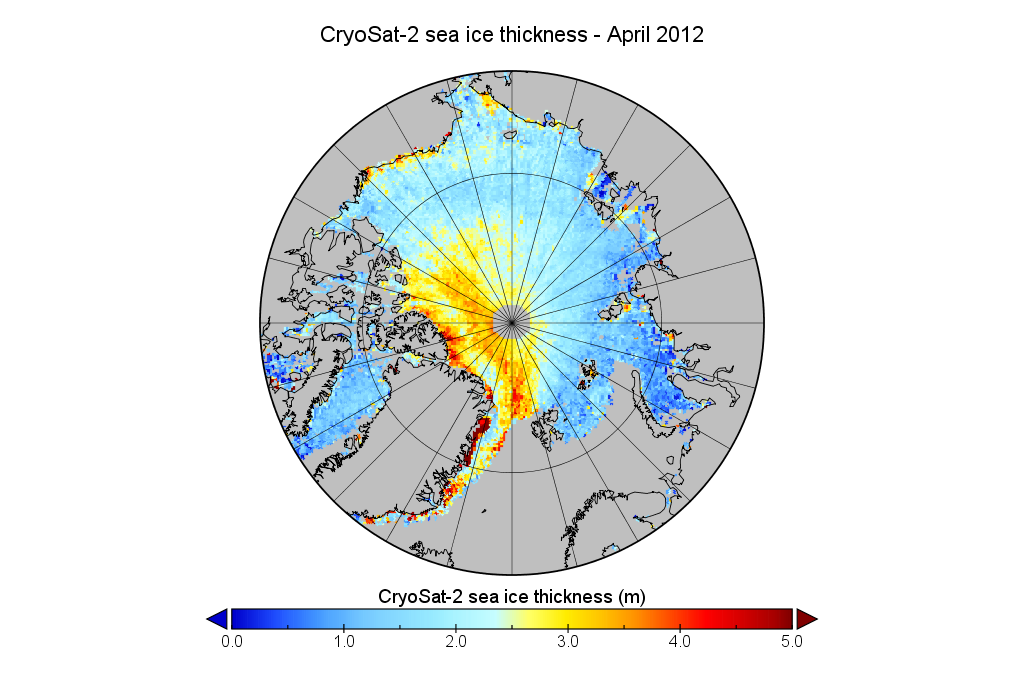
The Professor should have known that a more accurate estimate of sea ice can be had from satellite images taken every day at the Poles since 1981. These images show that between summer and winter, regardless of the degree of summer melting, the sea ice completely recovers to its original size the winter before for almost every year since the pictures were taken. The sea ice has been stubbornly resistant to Al Gore’s predictions. In fact the average annual coverage of sea ice has been essentially the same since satellite observations began in 1981. However that has not stopped global warming advocates and even government agencies from cherry picking the data to mislead the public.
I also like to think that I’m something of an expert on the way “skeptical” folks cherry pick the data to mislead the public. For example I once wrote a post about David Rose‘s Mail on Sunday article concerning Al Gore’s interpretation of Prof. Wieslaw Maslowski’s research into Arctic sea ice decline. Hence I felt compelled to comment on this most recent of misleadling WUWT articles about polar ice!
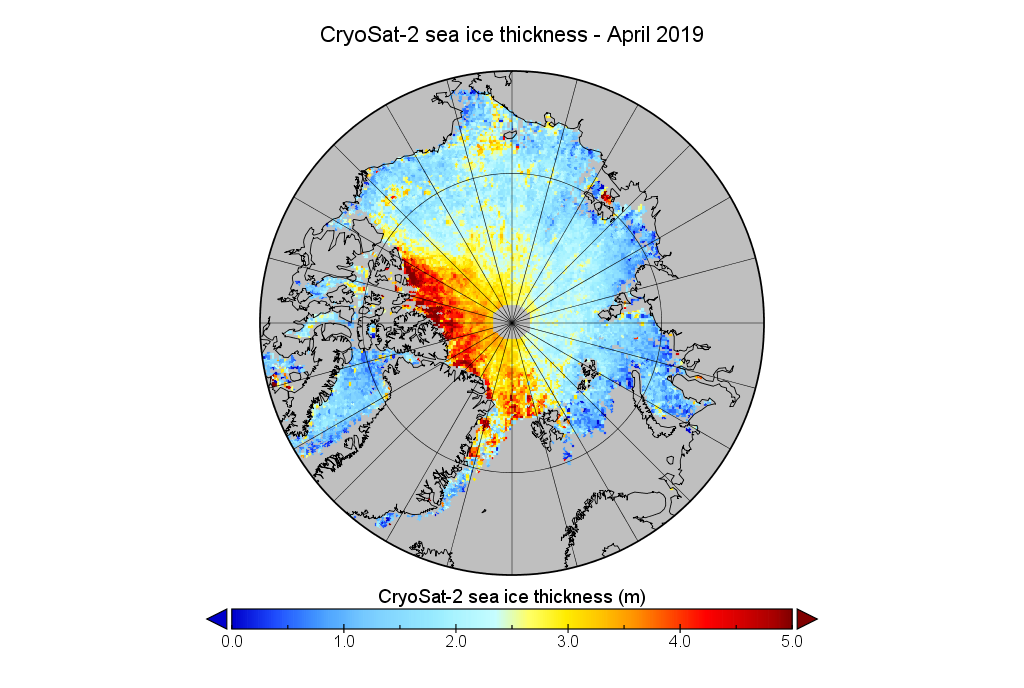
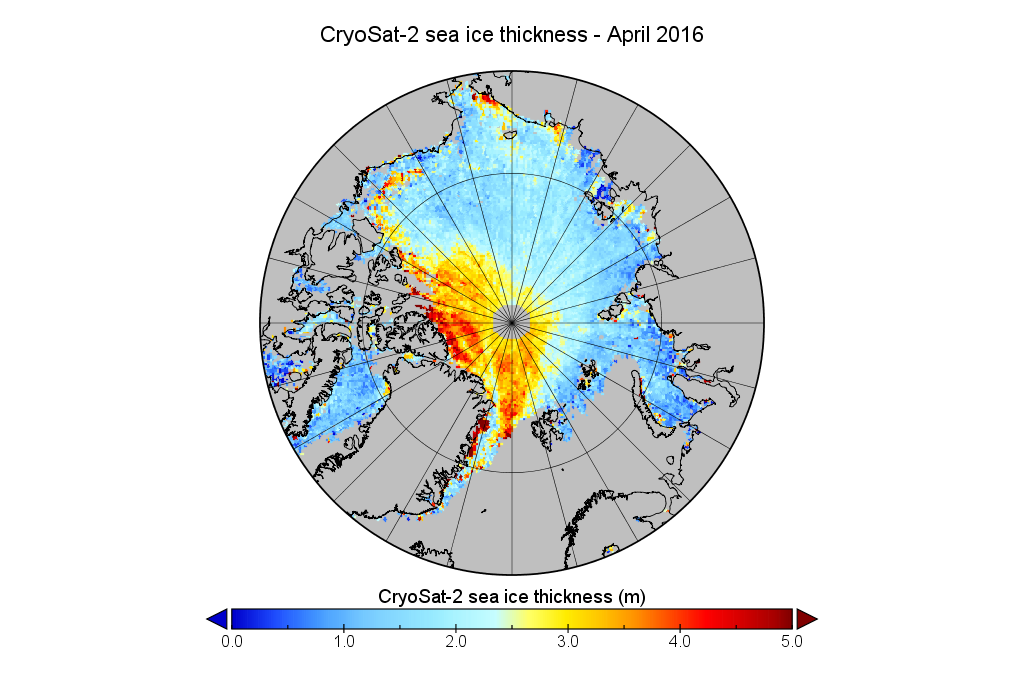
As luck would have it Guy McPherson recently interviewed Wieslaw about events back in 2007 and his more recent research on Arctic sea ice melt. Here is a video recording of their conversation:
I endeavoured to bring this most relevant piece of information to the attention of Anthony’s loyal readership last night (UTC) as follows:
This morning my pertinent comment is still “awaiting moderation”.
Q.E.D?