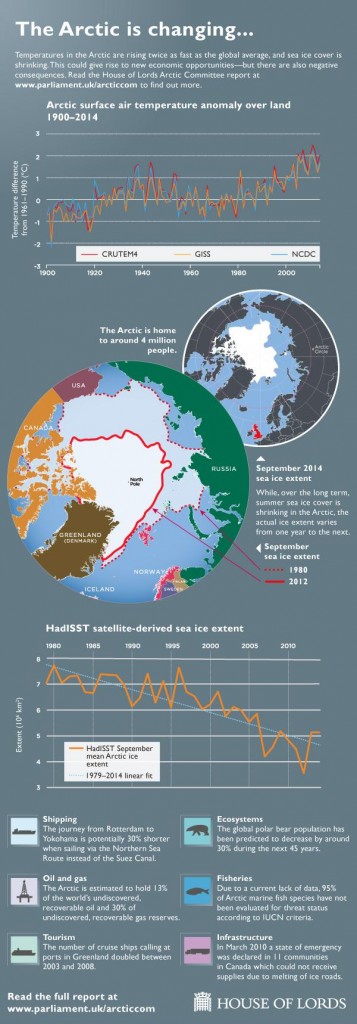
One eminent sea ice researcher certainly seems to think that time is indeed running out for the sea ice in the Arctic. First let’s take a look at the results of the first call for contributions of the 2015 melting season from the Sea Ice Prediction Network:
Note that in the bottom left hand corner of that graph there is a prediction of 0.98 million square kilometers labelled “Wadhams (SIPOG)”. The acronym refers to the Sea Ice and Polar Oceanography Group in the Department of Applied Mathematics and Theoretical Physics at the University of Cambridge, of which Prof. Peter Wadhams is the head. Before we get on to his explanation for what the SIPN refers to as “an extreme outlier” amongst all the other predictions, here’s a TEDx presentation given by Dr. David Barber, who is currently Associate Dean (Research) in the CHR Faculty of Environment, Earth and Resources at the University of Manitoba in Canada:
Here are what Dr. Barber refers to as the “seven surprising impacts” of declining Arctic sea ice:
-
Increasing coverage of young ice significantly changes atmospheric chemistry
-
More snow both preserves and destroys ice
-
Polar bear habitat can actually improve in some areas while deteriorating in others
-
Match-mismatch timing in the marine ecosystem increases vulnerability
-
Uncertainty as to whether the Arctic ocean will increase or decrease in overall productivity is a key unknown
-
Evidence that ice hazards are actually increasing while the world marshals to increase development of Arctic resources
-
Evidence that our recent cold winters are actually linked to our warming Arctic.
However those bullet points from David’s closing summary don’t actually mention the part of his presentation that most interested me. Listen carefully at 7:40 when he says that:
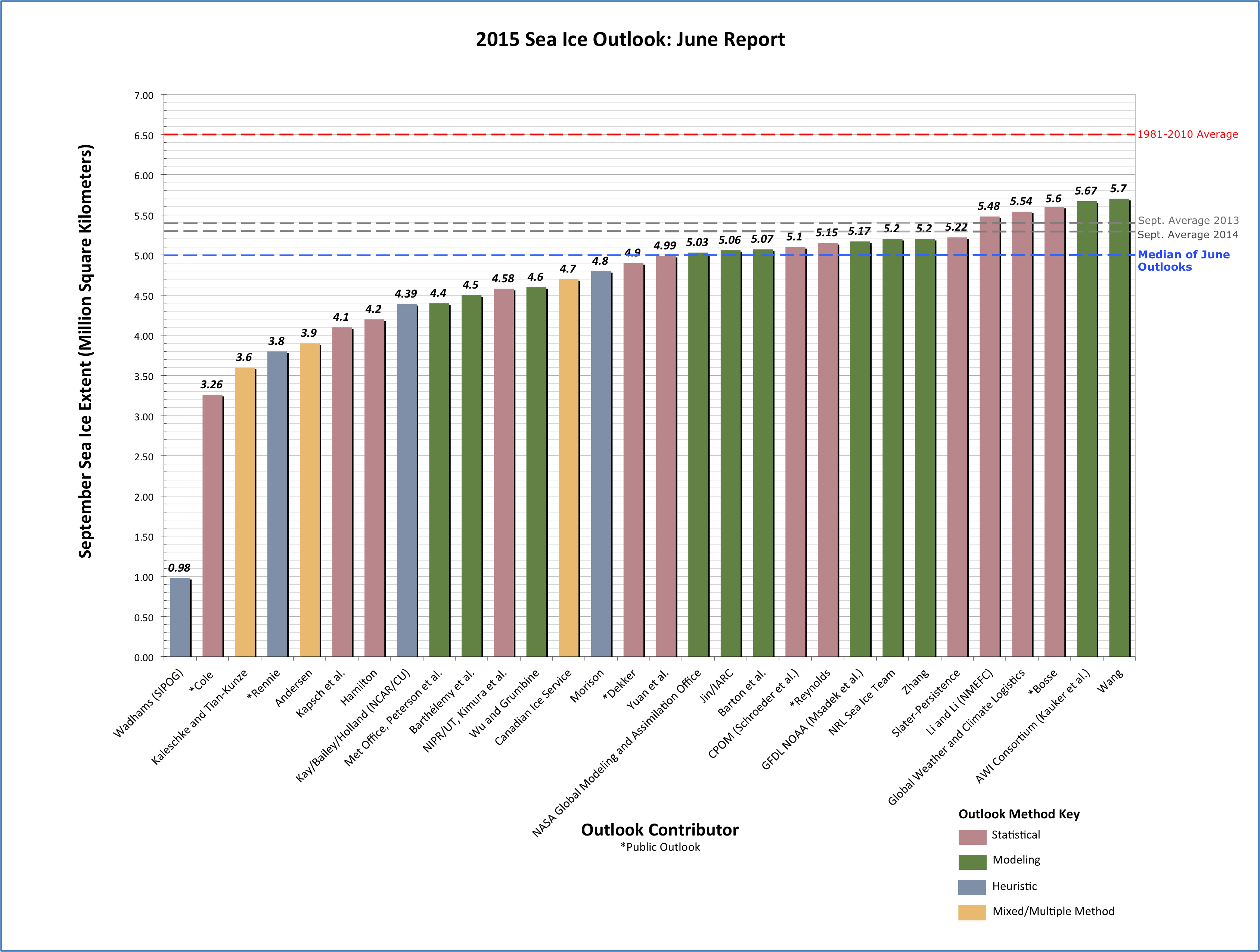
In 2009 we had our icebreaker down here and we went up this line that you see right here in this figure.
Here’s a version of the map Dr. Barber is referring that comes from a 2009 paper of his entitled “Perennial pack ice in the southern Beaufort Sea was not as it appeared in the summer of 2009“:
Here’s the relevant passage from the paper rather than the TEDx video:
We departed from station L1 heading north towards station L1.5, expecting to enter MY sea ice cover at about 71°20′N, 139°00′W based on remotely sensed information (Orange polygon in the figure). The Canadian Ice Service (CIS) ice chart (which relies extensively on Radarsat-1 data) for 4 September 2009 indicated the ship track would range from 7 to 9 tenths coverage and this ice would consist of partial concentrations of 5 tenths to 7 tenths old ice and from 2 to 3 tenths thick first year ice.
In situ observations of the sea ice conditions however showed that the ice we were traversing was not MY or thick FY, nor was it 7 to 9 tenths concentration, but rather it was a mixture of a few small MY ice floes (1 tenth coverage) interspersed in a cover dominated by small (10–100 m) rounded floes of heavily decayed first year sea ice (4 tenths). These floes were overlain by a thin layer of new ice (7 tenth) where freeboard was negative and thin ice growing between remnant pieces when the ice had a positive freeboard. Likewise, some new ice covered open water areas between floes.
This is the “rotten sea ice” David refers to in the video, about which he says:
It was so rotten in fact that the ship that we had does 13.5 knots in open water, and we were able to traverse that ice at 13 knots, yet the satellites all thought that this was very thick multi-year sea ice, because that’s what it had always traditionally been.
This information is obviously very interesting of course, but even more interesting (to me at least) is a subsequent paper by Dr. Barber about the same voyage of the Canadian Research Icebreaker Amundsen, published in 2012 and entitled “Fracture of summer perennial sea ice by ocean swell as a result of Arctic storms“. Here’s a pertinent extract:
We progressed through the heavily decayed ice region into a transitional region containing a mix of decayed old and FY sea ice floes, and finally into thick late summer MY pack ice. Using the onboard helicopter to survey the area, we identified a vast MY floe (10 km diameter), to which we intended to moor the ship, and conduct our typical science operations. The ice in this area was much thicker than the heavily decayed FY ice we that we had encountered the previous day to the west. Our helicopter EMI system recorded overall thicknesses of sea ice around station MYI (e.g., mean = 2.0 m, max = 10 m).
As ice teams initially prepared to deploy to the ice, we noticed the appearance of a swell from the ships helicopter deck. Laser data collected during the helicopter EMI survey at station MYI indicated a swell period of 13.5 s, and a wavelength ranging from 200–300 m. Laser data were collected while the helicopter hovered over a large MY ice floe. These data were augmented with three-dimensional dynamic ship positioning data, which revealed approximate ship heave amplitude of 0.4 m, also with a period of 13.5 s. The swell caused the vast MY ice floe nearest the Amundsen to ride up one side of the swell and fracture as it crested the wave peak, creating smaller ice floes of width approximately one half of the wavelength of the swell. In a matter of minutes from the initial onset of swell propagation, all large MY ice floes in the region were fractured in this manner, yielding a new distribution of smaller MY ice floes ranging from 100–150 m in diameter. A helicopter-borne video system recorded this event in still photographs along its flight track which were later combined to create a series of photo mosaics.
On 09 September 2009, we conducted a longitudinal helicopter EMI survey at 72.5 N, and determined the limit of the swell penetration into the pack ice at 72.526 N 134.51 W, a penetration of 350 km. Furthermore, the rotted FY ice margin was heavily fractured, with small floe sizes ranging from 20–50 m in diameter.
Moving on from Manitoba to Cambridge, Peter Wadhams has recently recorded an interview for The University of Earth, which describes itself as “an entertaining educational reality television series”. Here it is:
So what is “the reality” of the situation in the Arctic? Prof. Wadhams doesn’t explain his “extreme outlier” 2015 prediction in detail in the interview, but he does identify three potentially significant problems:
- The “minor thing, in a way” of several feet of global sea level rise this century due to melting of the Greenland ice sheet
- A sudden increase in the rate of “global warming” due to Arctic albedo feedback, which leads to
- The exposure of the methane hydrate bearing continental shelves off Siberia to increasing water temperatures as the sea ice above them melts. “It’s a massive risk, if you do a risk analysis”
Peter also highlights the same concerns as Barber et al. 2012, often referred to in the literature as “waves-in-ice“. I highly recommend watching both videos from cover to cover. However if you’re in a rush then at least skip to 28:30 minutes where he points out that on his cruise around the Arctic this coming September:
We’re looking at one particular thing, which may not be the most important thing, but the retreat of the sea ice in summer is going much faster than computer models predict, and we think that one factor there is the fact that as the sea ice retreats it opens up this huge area of open water in the Arctic Ocean which then becomes like an ocean, with lots of waves and storms and swell, and the waves themselves break the remaining ice up and cause it to retreat faster so that there’s a kind of collaborative effect there that the remaining ice is vanishing faster because of so much open water producing wave action.
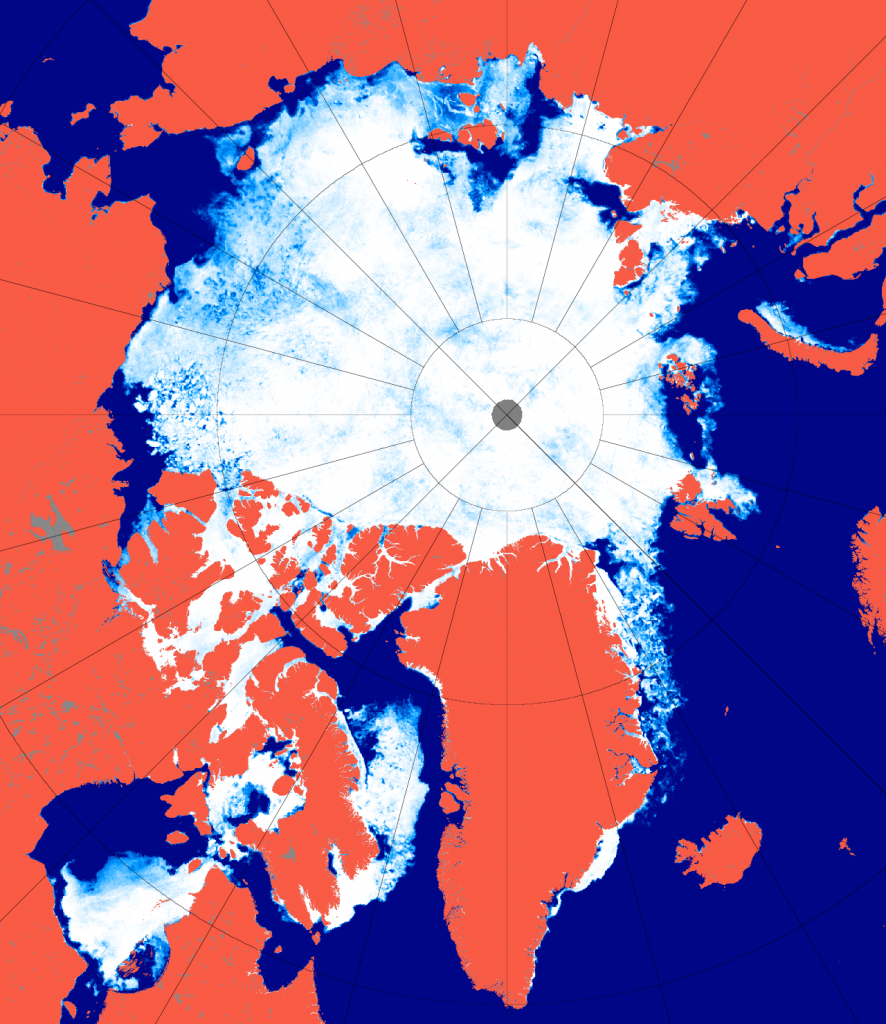
Getting back to the current situation in the 2015 melting season, here’s what the University of Hamburg’s AMSR2 sea ice concentration map currently reveals:
and here’s what the Slater Probabilistic Ice Extent methodology is predicting will happen over the next 50 days:
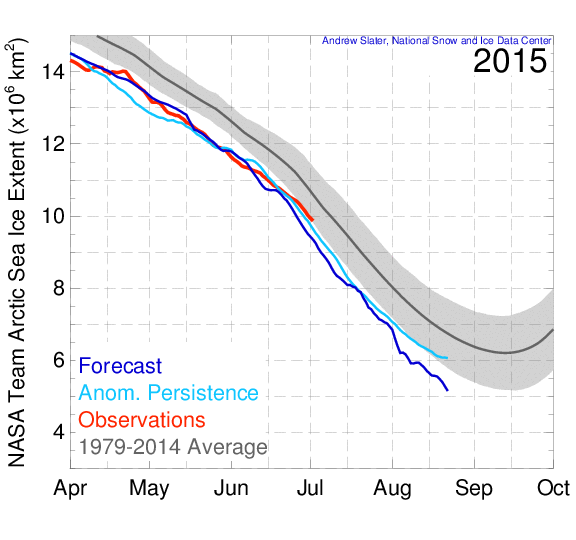
Both suggest to me that although the rate of decline in the area of Arctic sea ice is not currently abnormal for post 2007 years, it may well become so in another month or so, when the extent curve “normally” starts to flatten out. Possibly even sooner than that, because here is the current GFS 2 metre temperature map for the Arctic:
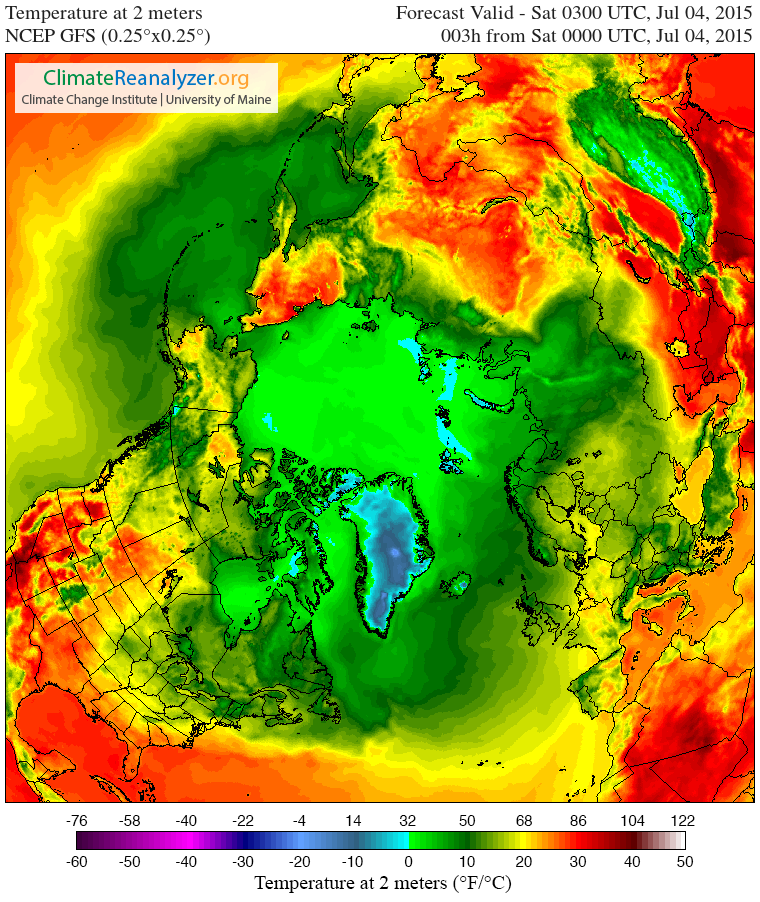
and temperatures, particularly on the Pacific side of the Arctic, are forecast to get warmer still over the next few days.
Watch this space and we’ll keep you posted, but in the meantime here’s a final thought from Peter Wadhams:
Our children have a future only if we take action now.
[Edit – July 6th 2015]
In a personal communication Prof. Wadhams informs me that:
This year I’m going out in September in the “Sikuliaq” (University of Alaska) to do some more specific wave-ice interaction experiments [in the Beaufort Sea Marginal Ice Zone], assuming there is any ice to experiment on.
[/Edit]