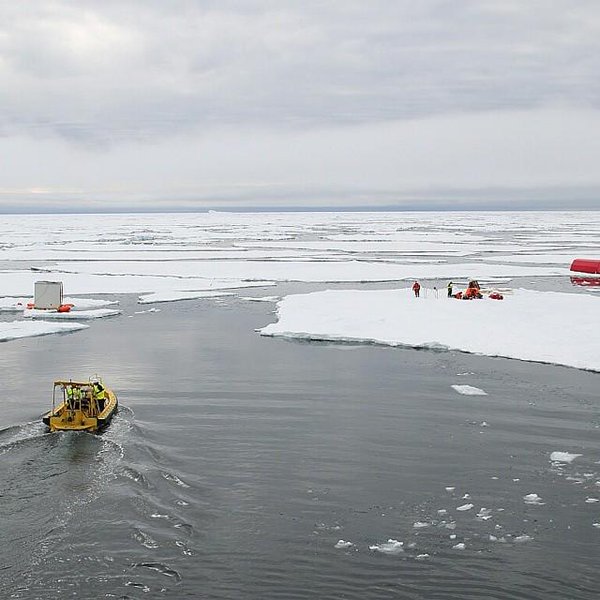
I just watched the live stream of the fall 2016 AGU press conference about the findings of the “First results from the Norwegian Young Sea ICE Expedition”.
Here’s the associated video of the expedition:
Here are the bullet points:
Initial results suggest that the thinner and younger ice is altogether different from older multiyear ice. It moves faster, breaks up easier, melts faster, and is more vulnerable to storms. This has important consequences for the Arctic as a whole, as our current knowledge is largely based on information from the “old Arctic.”
The Atmosphere
• For the first time, N-ICE2015 researchers directly observed large winter storms over sea ice and saw that they have significant effects on the young, thinner ice. The high winds create a lot of stress on the sea ice by pushing it around and breaking it up.
• One winter storm raised the air temperature from -40 F to +32 F in less than 48 hours, while the moisture in the air increased 10 times. All of these factors significantly warm the surface of the snow, even in mid-winter, and slow the growth of ice.The Sea Ice and Snow Cover
• Researchers on the drifting ice camps found more snow on top of the ice than expected. This insulated the ice from the atmosphere, slowing its growth in winter and surface melt in summer.
• The sea ice was sometimes flooded by seawater as the large snow load pushed the thinner ice below sea level.
• The thinner sea ice was more dynamic than researchers have seen before. This could mean more ridging but also more cracks and leads between ice floes.The Ocean
• Winter storms caused the sea ice to drift so fast that it increased mixing of the water beneath the ice. Deeper, warmer water was mixed up closer to the sea ice, causing it to melt from below despite winter air temperatures that were below freezing.
• Researchers saw summer storms stir up deep warm waters and melt as much as 25 cm of ice in a single day.The Ecosystem
• For the first time, N-ICE2015 researchers observed an algae bloom under snow-covered pack ice. Thinner and more dynamic Arctic sea ice allows more light transmission to the ocean, especially through cracks and leads. This triggers earlier phytoplankton blooms under the snow-covered ice.
• The phytoplankton species that dominated the under-ice bloom does not sink to the deep ocean. Such shifts in phytoplankton species composition, associated with early under-ice phytoplankton blooms, could thus have important implications for the strength of the biological carbon pump in the Arctic.
There was also mention of the “waves in ice” event that the R/V Lance experienced back in June 2015:
P.S. A recording of the N-ICE2015 press conference is now available:
Next up on the live stream is was the 2016 “Arctic Report Card“. Here’s the associated video:
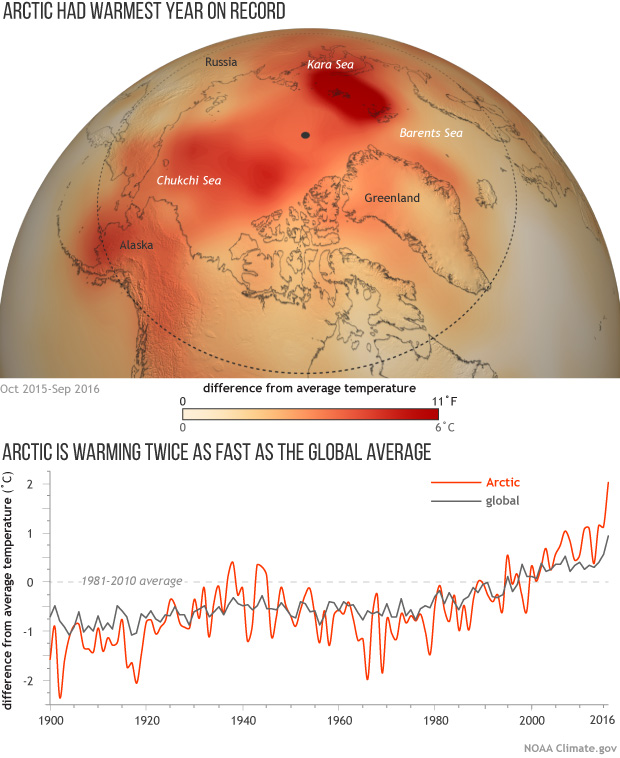
No doubt because of the recent controversy concerning the effects of the 2015/16 El Niño the first graphic that caught my eye was this one:
In the question and answer session the obvious question was asked. The answer was that while attribution is difficult the 2015/16 El Niño did have some effect on Arctic sea ice. However currently we’ve only seen “the first act of a 3 act play”. Act 2 will be the maximum extent in March.
In answer to another question, a focus of research over the next 10 years should be the interactions between mid latitudes and the Arctic.
P.S. A recording of the Arctic Report Card press conference is now available:
A variety of cryospheric posters are available via:
https://agu.confex.com/agu/fm16/meetingapp.cgi/Index/EPoster~1/Program/1175